Rubric Best Practices, Examples, and Templates
A rubric is a scoring tool that identifies the different criteria relevant to an assignment, assessment, or learning outcome and states the possible levels of achievement in a specific, clear, and objective way. Use rubrics to assess project-based student work including essays, group projects, creative endeavors, and oral presentations.
Rubrics can help instructors communicate expectations to students and assess student work fairly, consistently and efficiently. Rubrics can provide students with informative feedback on their strengths and weaknesses so that they can reflect on their performance and work on areas that need improvement.

How to Get Started
Best practices, moodle how-to guides.
- Workshop Recording (Spring 2024)
- Workshop Registration
Step 1: Analyze the assignment
The first step in the rubric creation process is to analyze the assignment or assessment for which you are creating a rubric. To do this, consider the following questions:
- What is the purpose of the assignment and your feedback? What do you want students to demonstrate through the completion of this assignment (i.e. what are the learning objectives measured by it)? Is it a summative assessment, or will students use the feedback to create an improved product?
- Does the assignment break down into different or smaller tasks? Are these tasks equally important as the main assignment?
- What would an “excellent” assignment look like? An “acceptable” assignment? One that still needs major work?
- How detailed do you want the feedback you give students to be? Do you want/need to give them a grade?
Step 2: Decide what kind of rubric you will use
Types of rubrics: holistic, analytic/descriptive, single-point
Holistic Rubric. A holistic rubric includes all the criteria (such as clarity, organization, mechanics, etc.) to be considered together and included in a single evaluation. With a holistic rubric, the rater or grader assigns a single score based on an overall judgment of the student’s work, using descriptions of each performance level to assign the score.
Advantages of holistic rubrics:
- Can p lace an emphasis on what learners can demonstrate rather than what they cannot
- Save grader time by minimizing the number of evaluations to be made for each student
- Can be used consistently across raters, provided they have all been trained
Disadvantages of holistic rubrics:
- Provide less specific feedback than analytic/descriptive rubrics
- Can be difficult to choose a score when a student’s work is at varying levels across the criteria
- Any weighting of c riteria cannot be indicated in the rubric
Analytic/Descriptive Rubric . An analytic or descriptive rubric often takes the form of a table with the criteria listed in the left column and with levels of performance listed across the top row. Each cell contains a description of what the specified criterion looks like at a given level of performance. Each of the criteria is scored individually.
Advantages of analytic rubrics:
- Provide detailed feedback on areas of strength or weakness
- Each criterion can be weighted to reflect its relative importance
Disadvantages of analytic rubrics:
- More time-consuming to create and use than a holistic rubric
- May not be used consistently across raters unless the cells are well defined
- May result in giving less personalized feedback
Single-Point Rubric . A single-point rubric is breaks down the components of an assignment into different criteria, but instead of describing different levels of performance, only the “proficient” level is described. Feedback space is provided for instructors to give individualized comments to help students improve and/or show where they excelled beyond the proficiency descriptors.
Advantages of single-point rubrics:
- Easier to create than an analytic/descriptive rubric
- Perhaps more likely that students will read the descriptors
- Areas of concern and excellence are open-ended
- May removes a focus on the grade/points
- May increase student creativity in project-based assignments
Disadvantage of analytic rubrics: Requires more work for instructors writing feedback
Step 3 (Optional): Look for templates and examples.
You might Google, “Rubric for persuasive essay at the college level” and see if there are any publicly available examples to start from. Ask your colleagues if they have used a rubric for a similar assignment. Some examples are also available at the end of this article. These rubrics can be a great starting point for you, but consider steps 3, 4, and 5 below to ensure that the rubric matches your assignment description, learning objectives and expectations.
Step 4: Define the assignment criteria
Make a list of the knowledge and skills are you measuring with the assignment/assessment Refer to your stated learning objectives, the assignment instructions, past examples of student work, etc. for help.
Helpful strategies for defining grading criteria:
- Collaborate with co-instructors, teaching assistants, and other colleagues
- Brainstorm and discuss with students
- Can they be observed and measured?
- Are they important and essential?
- Are they distinct from other criteria?
- Are they phrased in precise, unambiguous language?
- Revise the criteria as needed
- Consider whether some are more important than others, and how you will weight them.
Step 5: Design the rating scale
Most ratings scales include between 3 and 5 levels. Consider the following questions when designing your rating scale:
- Given what students are able to demonstrate in this assignment/assessment, what are the possible levels of achievement?
- How many levels would you like to include (more levels means more detailed descriptions)
- Will you use numbers and/or descriptive labels for each level of performance? (for example 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 and/or Exceeds expectations, Accomplished, Proficient, Developing, Beginning, etc.)
- Don’t use too many columns, and recognize that some criteria can have more columns that others . The rubric needs to be comprehensible and organized. Pick the right amount of columns so that the criteria flow logically and naturally across levels.
Step 6: Write descriptions for each level of the rating scale
Artificial Intelligence tools like Chat GPT have proven to be useful tools for creating a rubric. You will want to engineer your prompt that you provide the AI assistant to ensure you get what you want. For example, you might provide the assignment description, the criteria you feel are important, and the number of levels of performance you want in your prompt. Use the results as a starting point, and adjust the descriptions as needed.
Building a rubric from scratch
For a single-point rubric , describe what would be considered “proficient,” i.e. B-level work, and provide that description. You might also include suggestions for students outside of the actual rubric about how they might surpass proficient-level work.
For analytic and holistic rubrics , c reate statements of expected performance at each level of the rubric.
- Consider what descriptor is appropriate for each criteria, e.g., presence vs absence, complete vs incomplete, many vs none, major vs minor, consistent vs inconsistent, always vs never. If you have an indicator described in one level, it will need to be described in each level.
- You might start with the top/exemplary level. What does it look like when a student has achieved excellence for each/every criterion? Then, look at the “bottom” level. What does it look like when a student has not achieved the learning goals in any way? Then, complete the in-between levels.
- For an analytic rubric , do this for each particular criterion of the rubric so that every cell in the table is filled. These descriptions help students understand your expectations and their performance in regard to those expectations.
Well-written descriptions:
- Describe observable and measurable behavior
- Use parallel language across the scale
- Indicate the degree to which the standards are met
Step 7: Create your rubric
Create your rubric in a table or spreadsheet in Word, Google Docs, Sheets, etc., and then transfer it by typing it into Moodle. You can also use online tools to create the rubric, but you will still have to type the criteria, indicators, levels, etc., into Moodle. Rubric creators: Rubistar , iRubric
Step 8: Pilot-test your rubric
Prior to implementing your rubric on a live course, obtain feedback from:
- Teacher assistants
Try out your new rubric on a sample of student work. After you pilot-test your rubric, analyze the results to consider its effectiveness and revise accordingly.
- Limit the rubric to a single page for reading and grading ease
- Use parallel language . Use similar language and syntax/wording from column to column. Make sure that the rubric can be easily read from left to right or vice versa.
- Use student-friendly language . Make sure the language is learning-level appropriate. If you use academic language or concepts, you will need to teach those concepts.
- Share and discuss the rubric with your students . Students should understand that the rubric is there to help them learn, reflect, and self-assess. If students use a rubric, they will understand the expectations and their relevance to learning.
- Consider scalability and reusability of rubrics. Create rubric templates that you can alter as needed for multiple assignments.
- Maximize the descriptiveness of your language. Avoid words like “good” and “excellent.” For example, instead of saying, “uses excellent sources,” you might describe what makes a resource excellent so that students will know. You might also consider reducing the reliance on quantity, such as a number of allowable misspelled words. Focus instead, for example, on how distracting any spelling errors are.
Example of an analytic rubric for a final paper
| Above Average (4) | Sufficient (3) | Developing (2) | Needs improvement (1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Thesis supported by relevant information and ideas | The central purpose of the student work is clear and supporting ideas always are always well-focused. Details are relevant, enrich the work. | The central purpose of the student work is clear and ideas are almost always focused in a way that supports the thesis. Relevant details illustrate the author’s ideas. | The central purpose of the student work is identified. Ideas are mostly focused in a way that supports the thesis. | The purpose of the student work is not well-defined. A number of central ideas do not support the thesis. Thoughts appear disconnected. |
| (Sequencing of elements/ ideas) | Information and ideas are presented in a logical sequence which flows naturally and is engaging to the audience. | Information and ideas are presented in a logical sequence which is followed by the reader with little or no difficulty. | Information and ideas are presented in an order that the audience can mostly follow. | Information and ideas are poorly sequenced. The audience has difficulty following the thread of thought. |
| (Correctness of grammar and spelling) | Minimal to no distracting errors in grammar and spelling. | The readability of the work is only slightly interrupted by spelling and/or grammatical errors. | Grammatical and/or spelling errors distract from the work. | The readability of the work is seriously hampered by spelling and/or grammatical errors. |
Example of a holistic rubric for a final paper
| The audience is able to easily identify the central message of the work and is engaged by the paper’s clear focus and relevant details. Information is presented logically and naturally. There are minimal to no distracting errors in grammar and spelling. : The audience is easily able to identify the focus of the student work which is supported by relevant ideas and supporting details. Information is presented in a logical manner that is easily followed. The readability of the work is only slightly interrupted by errors. : The audience can identify the central purpose of the student work without little difficulty and supporting ideas are present and clear. The information is presented in an orderly fashion that can be followed with little difficulty. Grammatical and spelling errors distract from the work. : The audience cannot clearly or easily identify the central ideas or purpose of the student work. Information is presented in a disorganized fashion causing the audience to have difficulty following the author’s ideas. The readability of the work is seriously hampered by errors. |
Single-Point Rubric
| Advanced (evidence of exceeding standards) | Criteria described a proficient level | Concerns (things that need work) |
|---|---|---|
| Criteria #1: Description reflecting achievement of proficient level of performance | ||
| Criteria #2: Description reflecting achievement of proficient level of performance | ||
| Criteria #3: Description reflecting achievement of proficient level of performance | ||
| Criteria #4: Description reflecting achievement of proficient level of performance | ||
| 90-100 points | 80-90 points | <80 points |
More examples:
- Single Point Rubric Template ( variation )
- Analytic Rubric Template make a copy to edit
- A Rubric for Rubrics
- Bank of Online Discussion Rubrics in different formats
- Mathematical Presentations Descriptive Rubric
- Math Proof Assessment Rubric
- Kansas State Sample Rubrics
- Design Single Point Rubric
Technology Tools: Rubrics in Moodle
- Moodle Docs: Rubrics
- Moodle Docs: Grading Guide (use for single-point rubrics)
Tools with rubrics (other than Moodle)
- Google Assignments
- Turnitin Assignments: Rubric or Grading Form
Other resources
- DePaul University (n.d.). Rubrics .
- Gonzalez, J. (2014). Know your terms: Holistic, Analytic, and Single-Point Rubrics . Cult of Pedagogy.
- Goodrich, H. (1996). Understanding rubrics . Teaching for Authentic Student Performance, 54 (4), 14-17. Retrieved from
- Miller, A. (2012). Tame the beast: tips for designing and using rubrics.
- Ragupathi, K., Lee, A. (2020). Beyond Fairness and Consistency in Grading: The Role of Rubrics in Higher Education. In: Sanger, C., Gleason, N. (eds) Diversity and Inclusion in Global Higher Education. Palgrave Macmillan, Singapore.
Think you can get into a top-10 school? Take our chance-me calculator... if you dare. 🔥
Last updated August 6, 2024
Every piece we write is researched and vetted by a former admissions officer. Read about our mission to pull back the admissions curtain.
Blog > Common App > The Best College Application Essay Rubric
The Best College Application Essay Rubric
Admissions officer reviewed by Ben Bousquet, M.Ed Former Vanderbilt University
Written by Kylie Kistner, MA Former Willamette University Admissions
Key Takeaway
Are your eyes blurry from staring at your college essay for hours on end? It's time to pull out a rubric. Rubrics are scoring tools that can help you identify changes to make before you submit.
If you’re reading this post, you probably have a finished draft of your college essay. Congrats!
Now, you might be wondering: what do I do now?
It’s time to evaluate what you’ve written so you can get to editing.
But evaluating writing is difficult. Different people have different opinions about what a piece of writing should do or look like, so one person may love an essay that another person hates. Unlike disciplines with clearer, more objective solutions to problems (think math or chemistry), writing leaves a lot of room for interpretation.
Even in college admissions, what resonates with one admissions officer may be uninspired to a different one.
But if everyone has different opinions, then how do you know whether what you’ve written is good?
Enter: a rubric.
Rubrics are excellent tools to help you evaluate your writing. They’re those pesky tables that your English teachers have probably stapled to the back of your AP Lit essays.
While rubrics won’t eliminate differences of opinion, they can help you understand how your essay stacks up to a generally agreed-upon set of standardized college essay conventions.
In this post, we break down what a rubric is and how you can use one to score your essay. We also give you some tips for editing after you evaluate your essay.
What is a rubric?
Rubrics can have different layouts. But in general, they are tables that outline the specific criteria that a piece of writing should meet. They often measure factors like organization, theme, grammar, and more.
The table then ranks each of these categories on a numerical scale. A lower score means that the essay needs a lot of improvement in that particular category. A higher score means that the essay excels in that category.
Overall, the point of a rubric is to help you evaluate your own essay in a semi-objective way.
This is important because it gives you guidance about how to proceed with your editing process. Just like you should have a plan before you start drafting, you should also have a plan before you start editing.
Application deadlines will be here before you know it, so being strategic about your editing process will help you use your time efficiently. You’ll know where your essay is weakest, so you can focus most of your effort there. You’ll also know where your essay excels, so you can use those sections to build momentum for the rest of your essay.
Alright—let’s go through the rubric.
College Essay Rubric Breakdown
We developed this rubric to help our Essay Academy students assess their essays. If you’d like to join the ranks of Essay Academy members and get a fuller version of this rubric, check out the Essay Academy program .
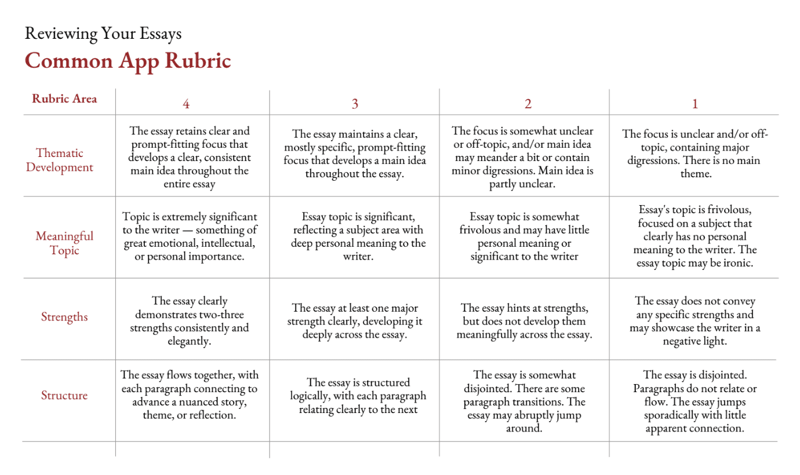
But this version is available free for download below. It’s designed specifically for the Common Application, and it lists five categories that all good college essays should excel at.
Thematic Development: What is your essay’s theme, and how well do you develop it?
Meaningful Topic: Is your topic meaningful, deeply personal, and vulnerable?
Strengths: Does your essay convey a core strength?
Structure: How well is your essay organized?
Grammar, Spelling, and Punctuation: Is your essay free of errors? Does it demonstrate skill in standard written English?
Attention to each of these categories is necessary to writing a successful college essay.
To help you evaluate how well your essay does in each category, the rubric lays out a ranking system, with 1 being the lowest and 4 being the highest.
Each column of the table shows a numerical rank and a description of what an essay that scores in that category will look like.
1: The essay does not meet the requirements of the category and needs significant improvements.
2: The essay makes an earnest attempt at meeting the requirements of the category, but it still needs improvement.
3: The essay meets the requirements of the category but does not exceed them.
4: The essay exceeds the requirements of the category. It is exemplary.
These measurements apply to each of the five categories.
An essay that deserves a “4” in “Thematic Development,” for example, will “retain clear and prompt-fitting focus that develops a clear, consistent main idea throughout the entire essay.”
Now that we’ve gotten the rubric basics down, let’s talk about how to score your essay.
How to Score Your Essay with a Rubric
For the rubric to be useful, you’ll need to score your essay in each category. That means that you’ll need to re-read your essay and honestly evaluate it.
First, a brief note on critical evaluation is in order. Throughout the writing process, there are times to be critical of yourself and times to be forgiving. Evaluating your essay is a time to be critical. That doesn’t mean tearing yourself down or being too harsh on yourself. It does mean being realistic with yourself and not sugarcoating your evaluation. It’s better for you to be critical now than for an admissions officer to be critical later. The consequences of you being critical will be a better final draft. The consequences of an admissions officer being critical could be a rejection.
This process is a little tedious, so we’ll go step by step.
Step 1: Before you being reading, explore the rubric thoroughly and understand what each of the categories asks you to do. You might also consider reading our guide to writing a college essay to get a more holistic view of what you’re aiming for.
Step 2: Start by thinking about the first four categories (thematic development, meaningful topic, strengths, and structure). These are the biggest categories that will have the most significant impact on the overall makeup of your essay.
Step 3: Re-read your essay with these criteria in mind, and circle your scores on the rubric. Don’t worry about fixing them quite yet.
Step 4: Then think through the final category (grammar, spelling, and punctuation).
Step 5: Re-read your essay again, paying particular attention to these sections. As you go, feel free to note any glaring errors, run-on sentences, or odd word choice you notice.
Step 6: Circle your grammar score on the rubric
You should now have five total scores, one in each category.
Step 7: Take the lowest scores, and that’s where you’ll start your revisions.
Using a Rubric to Edit Your College Essay
Once you’ve evaluated your college essay, it’s time to begin editing.
Make a list of which revisions you want to prioritize first based on your lowest scores. Look at the description for a “4” score in those categories. What do those descriptions list that your essay doesn’t have? Make note of each thing you need to improve.
Then get to editing. It’s a good idea to copy and paste your essay into a new document so you don’t lose any of your original work, just in case you want to recover anything.
Start with the larger issues first—those of theme, meaning, strength, and structure. You’ll want to prioritize the biggest revisions because those will likely affect all parts of your essay. Prioritizing these first will help you avoid doing work that you’ll later delete anyway.
Once you’re done with your revisions, re-score your essay using the rubric. You can even hand your essay and the rubric to a trusted adult to score. If you still have areas of improvement, revise again.
When you’re scoring 3-4 in every category, you’ll know you’re ready to submit.
( Psst—need more editing help? Let's work together .)
Liked that? Try this next.

The Incredible Power of a Cohesive College Application

How to Write a College Essay (Exercises + Examples)

12 Common App Essay Examples (Graded by Former Admissions Officers)

How to Write Supplemental Essays that Will Impress Admissions Officers
"the only actually useful chance calculator i’ve seen—plus a crash course on the application review process.".
Irena Smith, Former Stanford Admissions Officer
We built the best admissions chancer in the world . How is it the best? It draws from our experience in top-10 admissions offices to show you how selective admissions actually works.
- Utility Menu
GA4 Tracking Code
fa51e2b1dc8cca8f7467da564e77b5ea
- Make a Gift
- Join Our Email List
| Want to follow step-by-step instructions for building your own rubric? Visit the Bok Center's ! |
Whenever we give feedback, it inevitably reflects our priorities and expectations about the assignment. In other words, we're using a rubric to choose which elements (e.g., right/wrong answer, work shown, thesis analysis, style, etc.) receive more or less feedback and what counts as a "good thesis" or a "less good thesis." When we evaluate student work, that is, we always have a rubric. The question is how consciously we’re applying it, whether we’re transparent with students about what it is, whether it’s aligned with what students are learning in our course, and whether we’re applying it consistently. The more we’re doing all of the following, the more consistent and equitable our feedback and grading will be:
Being conscious of your rubric ideally means having one written out, with explicit criteria and concrete features that describe more/less successful versions of each criterion. If you don't have a rubric written out, you can use this assignment prompt decoder for TFs & TAs to determine which elements and criteria should be the focus of your rubric.
Being transparent with students about your rubric means sharing it with them ahead of time and making sure they understand it. This assignment prompt decoder for students is designed to facilitate this discussion between students and instructors.
Aligning your rubric with your course means articulating the relationship between “this” assignment and the ones that scaffold up and build from it, which ideally involves giving students the chance to practice different elements of the assignment and get formative feedback before they’re asked to submit material that will be graded. For more ideas and advice on how this looks, see the " Formative Assignments " page at Gen Ed Writes.
Applying your rubric consistently means using a stable vocabulary when making your comments and keeping your feedback focused on the criteria in your rubric.
How to Build a Rubric
Rubrics and assignment prompts are two sides of a coin. If you’ve already created a prompt, you should have all of the information you need to make a rubric. Of course, it doesn’t always work out that way, and that itself turns out to be an advantage of making rubrics: it’s a great way to test whether your prompt is in fact communicating to students everything they need to know about the assignment they’ll be doing.
So what do students need to know? In general, assignment prompts boil down to a small number of common elements :
- Evidence and Analysis
- Style and Conventions
- Specific Guidelines
- Advice on Process
If an assignment prompt is clearly addressing each of these elements, then students know what they’re doing, why they’re doing it, and when/how/for whom they’re doing it. From the standpoint of a rubric, we can see how these elements correspond to the criteria for feedback:
| 1. Purpose | ||
| 2. Genre | Does it have a clear thesis (if it’s an expository essay)? Does it have method and results sections (if it’s a lab report)? | |
| 3. Evidence and Analysis | Does it use the kinds/number of sources laid out in the prompt? Does it stick to, or move beyond, summary (depending on whether it’s more of an analysis or a reconstruction of someone else’s argument)? | |
| 4. Audience | Is it appropriately aimed at scholars, peers, general readers, ... ? | |
| 5. Style and Conventions | MLA or APA? Clarity and proofreading etc. | |
| 6. Specific Guidelines | Submitted on time, to the designated folder, in the designated format? | |
| 7. Advice on process |
All of these criteria can be weighed and given feedback, and they’re all things that students can be taught and given opportunities to practice. That makes them good criteria for a rubric, and that in turn is why they belong in every assignment prompt.
Which leaves “purpose” and “advice on process.” These elements are, in a sense, the heart and engine of any assignment, but their role in a rubric will differ from assignment to assignment. Here are a couple of ways to think about each.
On the one hand, “purpose” is the rationale for how the other elements are working in an assignment, and so feedback on them adds up to feedback on the skills students are learning vis-a-vis the overall purpose. In that sense, separately grading whether students have achieved an assignment’s “purpose” can be tricky.
On the other hand, metacognitive components such as journals or cover letters or artist statements are a great way for students to tie work on their assignment to the broader (often future-oriented) reasons why they’ve been doing the assignment. Making this kind of component a small part of the overall grade, e.g., 5% and/or part of “specific guidelines,” can allow it to be a nudge toward a meaningful self-reflection for students on what they’ve been learning and how it might build toward other assignments or experiences.
Advice on process
As with “purpose,” “advice on process” often amounts to helping students break down an assignment into the elements they’ll get feedback on. In that sense, feedback on those steps is often more informal or aimed at giving students practice with skills or components that will be parts of the bigger assignment.
For those reasons, though, the kind of feedback we give students on smaller steps has its own (even if ungraded) rubric. For example, if a prompt asks students to propose a research question as part of the bigger project, they might get feedback on whether it can be answered by evidence, or whether it has a feasible scope, or who the audience for its findings might be. All of those criteria, in turn, could—and ideally would—later be part of the rubric for the graded project itself. Or perhaps students are submitting earlier, smaller components of an assignment for separate grades; or are expected to submit separate components all together at the end as a portfolio, perhaps together with a cover letter or artist statement .
Using Rubrics Effectively
In the same way that rubrics can facilitate the design phase of assignment, they can also facilitate the teaching and feedback phases, including of course grading. Here are a few ways this can work in a course:
Discuss the rubric ahead of time with your teaching team. Getting on the same page about what students will be doing and how different parts of the assignment fit together is, in effect, laying out what needs to happen in class and in section, both in terms of what students need to learn and practice, and how the coming days or weeks should be sequenced.
Share the rubric with your students ahead of time. For the same reason it's ideal for course heads to discuss rubrics with their teaching team, it’s ideal for the teaching team to discuss the rubric with students. Not only does the rubric lay out the different skills students will learn during an assignment and which skills are more or less important for that assignment, it means that the formative feedback they get along the way is more legible as getting practice on elements of the “bigger assignment.” To be sure, this can’t always happen. Rubrics aren’t always up and running at the beginning of an assignment, and sometimes they emerge more inductively during the feedback and grading process, as instructors take stock of what students have actually submitted. In both cases, later is better than never—there’s no need to make the perfect the enemy of the good. Circulating a rubric at the time you return student work can still be a valuable tool to help students see the relationship between the learning objectives and goals of the assignment and the feedback and grade they’ve received.
Discuss the rubric with your teaching team during the grading process. If your assignment has a rubric, it’s important to make sure that everyone who will be grading is able to use the rubric consistently. Most rubrics aren’t exhaustive—see the note above on rubrics that are “too specific”—and a great way to see how different graders are handling “real-life” scenarios for an assignment is to have the entire team grade a few samples (including examples that seem more representative of an “A” or a “B”) and compare everyone’s approaches. We suggest scheduling a grade-norming session for your teaching staff.
- Designing Your Course
- In the Classroom
- When/Why/How: Some General Principles of Responding to Student Work
- Consistency and Equity in Grading
- Assessing Class Participation
- Assessing Non-Traditional Assignments
- Decreasing Student Anxiety about Grades
- Beyond “the Grade”: Alternative Approaches to Assessment
- Getting Feedback
- Equitable & Inclusive Teaching
- Artificial Intelligence
- Advising and Mentoring
- Teaching and Your Career
- Teaching Remotely
- Tools and Platforms
- The Science of Learning
- Bok Publications
- Other Resources Around Campus
Essay Rubric: Grading Students Correctly
- Icon Calendar 10 July 2024
- Icon Page 2897 words
- Icon Clock 14 min read
Lectures and tutors provide specific requirements for students to meet when writing essays. Basically, an essay rubric helps tutors to analyze an overall quality of compositions written by students. In this case, a rubric refers to a scoring guide used to evaluate performance based on a set of criteria and standards. As such, useful marking schemes make an analysis process simple for lecturers as they focus on specific concepts related to a writing process. Moreover, an assessment table lists and organizes all of the criteria into one convenient paper. In other instances, students use assessment tables to enhance their writing skills by examining various requirements. Then, different types of essay rubrics vary from one educational level to another. Essentially, Master’s and Ph.D. grading schemes focus on examining complex thesis statements and other writing mechanics. However, high school evaluation tables examine basic writing concepts. In turn, guidelines on a common format for writing a good essay rubric and corresponding examples provided in this article can help students to evaluate their papers before submitting them to their teachers.

General Aspects
An essay rubric refers to a way for teachers to assess students’ composition writing skills and abilities. Basically, an evaluation scheme provides specific criteria to grade assignments. Moreover, the three basic elements of an essay rubric are criteria, performance levels, and descriptors. In this case, teachers use assessment guidelines to save time when evaluating and grading various papers. Hence, learners must use an essay rubric effectively to achieve desired goals and grades, while its general example is:
What Is an Essay Rubric and Its Purpose
According to its definition, an essay rubric is a structured evaluation tool that educators use to grade students’ compositions in a fair and consistent manner. The main purpose of an essay rubric in writing is to ensure consistent and fair grading by clearly defining what constitutes excellent, good, average, and poor performance (DeVries, 2023). This tool specifies a key criteria for grading various aspects of a written text, including a clarity of a thesis statement, an overall quality of a main argument, an organization of ideas, a particular use of evidence, and a correctness of grammar and mechanics. Moreover, an assessment grading helps students to understand their strengths to be proud of and weaknesses to be pointed out and guides them in improving their writing skills (Taylor et al., 2024). For teachers, such an assessment simplifies a grading process, making it more efficient and less subjective by providing a clear standard to follow. By using an essay rubric, both teachers and students can engage in a transparent, structured, and constructive evaluation process, enhancing an overall educational experience (Stevens & Levi, 2023). In turn, the length of an essay rubric depends on academic levels, types of papers, and specific requirements, while general guidelines are:
High School
- Length: 1-2 pages
- Word Count: 300-600 words
- Length: 1-3 pages
- Word Count: 300-900 words
University (Undergraduate)
- Length: 2-4 pages
- Word Count: 600-1,200 words
Master’s
- Length: 2-5 pages
- Word Count: 600-1,500 words
- Length: 3-6 pages
- Word Count: 900-1,800 words

| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Thesis Statement | A well-defined thesis statement is crucial as it sets a particular direction and purpose of an essay, making it clear what a writer intends to argue or explain. |
| Introduction | An introduction captures a reader’s interest and provides a framework for what a paper will cover, setting up a stage for arguments or ideas that follow after an opening paragraph. |
| Content | High-quality content demonstrates thorough understanding and research on a specific topic, providing valuable and relevant information that supports a thesis. |
| Organization | Effective organization ensures author’s ideas are presented in a clear, well-structure, and logical order, enhancing readability and an overall flow of a central argument. |
| Evidence and Support | Providing strong evidence and detailed analysis is essential for backing up main arguments, adding credibility and depth to a final document. |
| Conclusion | A strong conclusion ties all the main numbers together, reflects on potential implications of arguments, and reinforces a thesis, leaving a lasting impression on a reader. |
| Grammar and Mechanics | Proper grammar, spelling, and punctuation are vital for clarity and professionalism, making a whole text easy to read and understand. |
| Style and Tone | Correctness in writing style and author’s tone appropriate to a paper’s purpose and audience enhances an overall effectiveness of a particular text and engages a reader. |
| Citations and References | Accurate and complete citations and references are crucial for giving credit to sources, avoiding plagiarism, and allowing readers to follow up on the research. |
Note: Some elements of an essay rubric can be added, deled, or combined with each other because different types of papers, their requirements, and instructors’ choices affect a final assessment. To format an essay rubric, people create a table with criteria listed in rows, performance levels in columns, and detailed descriptors in each cell explaining principal expectations for each level of performance (Steven & Levi, 2023). Besides, the five main criteria in a rubric are thesis statement, content, organization, evidence and support, and grammar and mechanics. In turn, a good essay rubric is clear, specific, aligned with learning objectives, and provides detailed, consistent descriptors for each performance level.
Steps How to Write an Essay Rubric
In writing, the key elements of an essay rubric are clear criteria, defined performance levels, and detailed descriptors for each evaluation.
- Identify a Specific Purpose and Goals: Determine main objectives of an essay’s assignment and consider what skills and knowledge you want students to demonstrate.
- List a Key Criteria: Identify essential components that need to be evaluated, such as thesis statement, introduction, content, organization, evidence and support, conclusion, grammar and mechanics, writing style and tone, and citations and references.
- Define Performance Levels: Decide on a particular scale you will use to measure performance (e.g., Excellent, Good, Fair, Poor) and ensure each level is distinct and clearly defined.
- Create Descriptors for Each Criterion: Write detailed descriptions for what constitutes each level of performance for every criterion and be specific about what is expected at each level to avoid misunderstanding.
- Assign Number Values: Determine a specific range for each criterion and performance level and allocate numbers in a way that reflects an actual importance of each criterion in an overall assessment.
- Review and Revise: Examine a complete rubric to ensure it is comprehensive and clear and adjust any descriptions or number values that seem unclear or disproportionate.
- Test a Working Essay Rubric: Apply a grading scheme to a few sample compositions to see if it effectively differentiates between different levels of performance and make adjustments as necessary.
- Involve Peers for Feedback: Share marking criteria with colleagues or peers for feedback and insights on clarity and fairness that you might have overlooked.
- Provide Examples: Include examples of complete papers or writing excerpts at each performance level and help students to understand what is expected for grading.
- Communicate With Students: Share a complete rubric with students before they begin an assignment and explain each criterion and performance level so they understand how their work will be evaluated and what they need to do to achieve highest marks.
Essay Rubric Example
Organization
Excellent/8 points: A submitted essay contains stiff topic sentences and a controlled organization.
Very Good/6 points: A paper contains a logical and appropriate organization. An author uses clear topic sentences.
Average/4 points: A composition contains a logical and appropriate organization. An author uses clear topic sentences.
Needs Improvement/2 points: A provided text has an inconsistent organization.
Unacceptable/0 (zero): A complete document shows an absence of a planned organization.
Grade: ___ .
Excellent/8 points: A submitted essay shows the absence of a planned organization.
Very Good/6 points: A paper contains precise and varied sentence structures and word choices.
Average/4 points: A composition follows a limited but mostly correct sentence structure. There are different sentence structures and word choices.
Needs Improvement/2 points: A provided text contains several awkward and unclear sentences. There are some problems with word choices.
Unacceptable/0 (zero): An author does not have apparent control over sentence structures and word choice.
Excellent/8 points: An essay’s content appears sophisticated and contains well-developed ideas.
Very Good/6 points: A paper’s content appears illustrative and balanced.
Average/4 points: A composition contains unbalanced content that requires more analysis.
Needs Improvement/2 points: A provided text contains a lot of research information without analysis or commentary.
Unacceptable/0 (zero): A complete document lacks relevant content and does not fit the thesis statement. Essay rubric rules are not followed.
Excellent/8 points: A submitted essay contains a clearly stated and focused thesis statement.
Very Good/6 points: A paper comprises a clearly stated argument. However, a particular focus would have been sharper.
Average/4 points: A thesis statement phrasing sounds simple and lacks complexity. An author does not word the thesis correctly.
Needs Improvement/2 points: A thesis statement requires a clear objective and does not fit the theme in a paper’s content.
Unacceptable/0 (zero): A thesis statement is not evident in an introduction paragraph.
Excellent/8 points: A submitted is clear and focused. An overall work holds a reader’s attention. Besides, relevant details and quotes enrich a thesis statement.
Very Good/6 points: A paper is mostly focused and contains a few useful details and quotes.
Average/4 points: An author begins a composition by defining an assigned topic. However, a particular development of ideas appears general.
Needs Improvement/2 points: An author fails to define an assigned topic well or focuses on several issues.
Unacceptable/0 (zero): A complete document lacks a clear sense of a purpose or thesis statement. Readers have to make suggestions based on sketchy or missing ideas to understand an intended meaning. Essay rubric requirements are missed.
Sentence Fluency
Excellent/8 points: A submitted essay has a natural flow, rhythm, and cadence. Its sentences are well-built and have a wide-ranging and robust structure that enhances reading.
Very Good/6 points: Presented ideas mostly flow and motivate a compelling reading.
Average/4 points: A composition hums along with a balanced beat but tends to be more businesslike than musical. Besides, a particular flow of ideas tends to become more mechanical than fluid.
Needs Improvement/2 points: A provided text appears irregular and hard to read.
Unacceptable/0 (zero): Readers have to go through a complete document several times to give this paper a fair interpretive reading.
Conventions
Excellent/8 points: An author demonstrates proper use of standard writing conventions, like spelling, punctuation, capitalization, grammar, usage, and paragraphing. A person also uses correct protocols in a way that improves an overall readability of an essay.
Very Good/6 points: An author demonstrates proper writing conventions and uses them correctly. One can read a paper with ease, and errors are rare. Few touch-ups can make a submitted composition ready for publishing.
Average/4 points: An author shows reasonable control over a short range of standard writing rules. A person also handles all the conventions and enhances readability. Writing errors in a presented composition tend to distract and impair legibility.
Needs Improvement/2 points: An author makes an effort to use various conventions, including spelling, punctuation, capitalization, grammar usage, and paragraphing. A provided text contains multiple errors.
Unacceptable/0 (zero): An author makes repetitive errors in spelling, punctuation, capitalization, grammar, usage, and paragraphing. Some mistakes distract readers and make it hard to understand discussed concepts. Essay rubric rules are not covered.
Presentation
Excellent/8 points: A particular form and presentation of a text enhance an overall readability of an essay and its flow of ideas.
Very Good/6 points: A chosen format has few mistakes and is easy to read.
Average/4 points: An author’s message is understandable in this format.
Needs Improvement/2 points: An author’s message is only comprehensible infrequently, and a provided text appears disorganized.
Unacceptable/0 (zero): Readers receive a distorted message due to difficulties connecting to a presentation of an entire text.
Final Grade: ___ .
Grading Scheme
- A+ = 60+ points
- F = less than 9
Differences in Education Levels
An overall quality of various types of texts changes at different education levels. In writing, an essay rubric works by providing a structured framework with specific criteria and performance levels to consistently evaluate and grade a finished paper. For instance, college students must write miscellaneous papers when compared to high school learners (Harrington et al., 2021). In this case, assessment criteria will change for these different education levels. For example, university and college compositions should have a debatable thesis statement with varying points of view (Mewburn et al., 2021). However, high school compositions should have simple phrases as thesis statements. Then, other requirements in a marking rubric will be more straightforward for high school students (DeVries, 2023). For Master’s and Ph.D. works, a writing criteria presented in a scoring evaluation should focus on examining a paper’s complexity. In turn, compositions for these two categories should have thesis statements that demonstrate a detailed analysis of defined topics that advance knowledge in a specific area of study.
Recommendations
When observing any essay rubric, people should remember to ensure clarity and specificity in each criterion and performance level. This clarity helps both an evaluator and a student to understand principal expectations and how a written document will be assessed (Ozfidan & Mitchell, 2022). Consistency in language and terminology across an essay rubric is crucial to avoid confusion and maintain fairness. Further on, it is essential to align a working scheme with learning objectives and goals of an essay’s assignment, ensuring all key components, such as thesis, content, organization, and grammar, are covered comprehensively (Stevens & Levi, 2023). Evaluators should also be aware of the weighting and scoring distribution, making sure they accurately reflect an actual importance of each criterion. Moreover, testing a rubric on sample essays before finalizing it can help to identify any mistakes or imbalances in scores. Essentially, providing concrete examples or descriptions for each performance level can guide students in understanding what is expected for each grade (Taylor et al., 2024). In turn, an essay rubric should be reviewed, revised, and updated after each educational year to remain relevant and aligned with current academic standards. Lastly, sharing and explaining grading assessment with students before they start their composition fosters transparency and helps them to put more of their efforts into meeting defined criteria, ultimately improving their writing and learning experience in general.
Common Mistakes
- Lack of Specificity: Descriptions for each criterion and performance level are too vague, leading to ambiguity and confusion for both graders and students.
- Overcomplicating a Rubric: Including too many criteria or overly complex descriptions that make a scoring assessment difficult to use effectively.
- Unbalanced Weighting: Assigning disproportionate number values to different criteria, which can mislead an overall assessment and not accurately reflect an actual importance of each component.
- Inconsistent Language: Using inconsistent terminology or descriptors across performance levels, which can confuse users and make a rubric less reliable.
- Not Aligning With Objectives: Failing to align a particular criteria and performance levels with specific goals and learning outcomes of an assignment.
- Omitting Key Components: Leaving out important criteria that are essential for evaluating a paper comprehensively, such as citations or a conclusion part.
- Lack of Examples: Not providing examples or concrete descriptions of what constitutes each performance level, making it harder for students to understand expectations.
- Ignoring Grammar and Mechanics: Overlooking an actual importance of grammar, spelling, and punctuation, which are crucial for clear and professional writing.
- Not Updating an Essay Rubric: Using outdated rubrics that do not reflect current educational standards or specific assignment needs.
- Insufficient Testing: Failing to test a grading scheme on some sample documents to ensure it effectively differentiates between levels of performance and provides fair assessments.
Essay rubrics help teachers, instructors, professors, and tutors to analyze an overall quality of compositions written by students. Basically, an assessment scheme makes an analysis process simple for lecturers, and it lists and organizes all of the criteria into one convenient paper. In other instances, students use such evaluation tools to improve their writing skills. However, they vary from one educational level to the other. Master’s and Ph.D. assessment schemes focus on examining complex thesis statements and other writing mechanics. However, high school grading criteria examine basic writing concepts. As such, the following are some of the tips that one must consider when preparing any rubric.
- Include all mechanics that relate to essay writing.
- Cover different requirements and their relevant grades.
- Follow clear and understandable statements.
DeVries, B. A. (2023). Literacy assessment and intervention for classroom teachers . Routledge.
Harrington, E. R., Lofgren, I. E., Gottschalk Druschke, C., Karraker, N. E., Reynolds, N., & McWilliams, S. R. (2021). Training graduate students in multiple genres of public and academic science writing: An assessment using an adaptable, interdisciplinary rubric. Frontiers in Environmental Science , 9 , 1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2021.715409
Mewburn, I., Firth, K., & Lehmann, S. (2021). Level up your essays: How to get better grades at university . NewSouth.
Ozfidan, B., & Mitchell, C. (2022). Assessment of students’ argumentative writing: A rubric development. Journal of Ethnic and Cultural Studies , 9 (2), 121–133. https://doi.org/10.29333/ejecs/1064
Stevens, D. D., & Levi, A. (2023). Introduction to rubrics: An assessment tool to save grading time, convey effective feedback, and promote student learning . Routledge, Taylor & Francis Group.
Taylor, B., Kisby, F., & Reedy, A. (2024). Rubrics in higher education: An exploration of undergraduate students’ understanding and perspectives. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education , 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2023.2299330
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles

How to Cite a Newspaper Article in APA 7 With Examples
- Icon Calendar 12 October 2020
- Icon Page 754 words

"Who Am I" Essay Examples & Student Guidelines
- Icon Calendar 10 October 2020
- Icon Page 5309 words
- help_outline help
iRubric: Short Essay Questions rubric
| Rubric Code: By Ready to use Public Rubric Subject: Type: Grade Levels: (none) |
| Criteria | |||||
| | |||||
| | |||||
| | |||||
- Arts and Design
- Communication
- Engineering
- Foreign Languages
- Physical Ed., Fitness
- Political Science
- Social Sciences
- Presentation
Center for Excellence in Teaching
Home > Resources > Academic essay rubric
Academic essay rubric
This is a grading rubric an instructor uses to assess students’ work on this type of assignment. It is a sample rubric that needs to be edited to reflect the specifics of a particular assignment.
Download this file
Download this file [63.33 KB]
Back to Resources Page
Academic Editing and Proofreading
- Tips to Self-Edit Your Dissertation
- Guide to Essay Editing: Methods, Tips, & Examples
- Journal Article Proofreading: Process, Cost, & Checklist
- The A–Z of Dissertation Editing: Standard Rates & Involved Steps
- Research Paper Editing | Guide to a Perfect Research Paper
- Dissertation Proofreading | Definition & Standard Rates
- Thesis Proofreading | Definition, Importance & Standard Pricing
- Research Paper Proofreading | Definition, Significance & Standard Rates
- Essay Proofreading | Options, Cost & Checklist
- Top 10 Paper Editing Services of 2024 (Costs & Features)
- Top 10 Essay Checkers in 2024 (Free & Paid)
- Top 10 AI Proofreaders to Perfect Your Writing in 2024
- Top 10 English Correctors to Perfect Your Text in 2024
- Top 10 Essay Editing Services of 2024
- 10 Advanced AI Text Editors to Transform Writing in 2024
- Personal Statement Editing Services: Craft a Winning Essay
- Top 10 Academic Proofreading Services & How They Help
College Essay Review: A Step-by-Step Guide (With Examples)
Academic research.
- Research Paper Outline: Free Templates & Examples to Guide You
- How to Write a Research Paper: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Write a Lab Report: Examples from Academic Editors
- Research Methodology Guide: Writing Tips, Types, & Examples
- The 10 Best Essential Resources for Academic Research
- 100+ Useful ChatGPT Prompts for Thesis Writing in 2024
- Best ChatGPT Prompts for Academic Writing (100+ Prompts!)
- Sampling Methods Guide: Types, Strategies, and Examples
- Independent vs. Dependent Variables | Meaning & Examples
Academic Writing & Publishing
- Difference Between Paper Editing and Peer Review
- What are the different types of peer review?
- How to Handle Journal Rejection: Essential Tips
- Editing and Proofreading Academic Papers: A Short Guide
- How to Carry Out Secondary Research
- The Results Section of a Dissertation
- Checklist: Is my Article Ready for Submitting to Journals?
- Types of Research Articles to Boost Your Research Profile
- 8 Types of Peer Review Processes You Should Know
- The Ethics of Academic Research
- How does LaTeX based proofreading work?
- How to Improve Your Scientific Writing: A Short Guide
- Chicago Title, Cover Page & Body | Paper Format Guidelines
- How to Write a Thesis Statement: Examples & Tips
- Chicago Style Citation: Quick Guide & Examples
- The A-Z Of Publishing Your Article in A Journal
- What is Journal Article Editing? 3 Reasons You Need It
- 5 Powerful Personal Statement Examples (Template Included)
- Complete Guide to MLA Format (9th Edition)
- How to Cite a Book in APA Style | Format & Examples
- How to Start a Research Paper | Step-by-step Guide
- APA Citations Made Easy with Our Concise Guide for 2024
- A Step-by-Step Guide to APA Formatting Style (7th Edition)
- Top 10 Online Dissertation Editing Services of 2024
- Academic Writing in 2024: 5 Key Dos & Don’ts + Examples
- What Are the Standard Book Sizes for Publishing Your Book?
- MLA Works Cited Page: Quick Tips & Examples
- 2024’s Top 10 Thesis Statement Generators (Free Included!)
- Top 10 Title Page Generators for Students in 2024
- What Is an Open Access Journal? 10 Myths Busted!
- Primary vs. Secondary Sources: Definition, Types & Examples
- How To Write a College Admissions Essay That Stands Out
- How to Write a Dissertation & Thesis Conclusion (+ Examples)
- APA Journal Citation: 7 Types, In-Text Rules, & Examples
- What Is Predatory Publishing and How to Avoid It!
- What Is Plagiarism? Meaning, Types & Examples
- How to Write a Strong Dissertation & Thesis Introduction
- How to Cite a Book in MLA Format (9th Edition)
- How to Cite a Website in MLA Format | 9th Edition Rules
- 10 Best AI Conclusion Generators (Features & Pricing)
- Top 10 Academic Editing Services of 2024 [with Pricing]
- 100+ Writing Prompts for College Students (10+ Categories!)
- How to Create the Perfect Thesis Title Page in 2024
- Additional Resources
- Preventing Plagiarism in Your Thesis: Tips & Best Practices
- Final Submission Checklist | Dissertation & Thesis
- 7 Useful MS Word Formatting Tips for Dissertation Writing
- How to Write a MEAL Paragraph: Writing Plan Explained in Detail
- Em Dash vs. En Dash vs. Hyphen: When to Use Which
- The 10 Best Citation Generators in 2024 | Free & Paid Plans!
- 2024’s Top 10 Self-Help Books for Better Living
- The 10 Best Free Character and Word Counters of 2024
- Know Everything About How to Make an Audiobook
- Mastering Metaphors: Definition, Types, and Examples
- Citation and Referencing
- Citing References: APA, MLA, and Chicago
- How to Cite Sources in the MLA Format
- MLA Citation Examples: Cite Essays, Websites, Movies & More
- Citations and References: What Are They and Why They Matter
- APA Headings & Subheadings | Formatting Guidelines & Examples
- Formatting an APA Reference Page | Template & Examples
- Research Paper Format: APA, MLA, & Chicago Style
- How to Create an MLA Title Page | Format, Steps, & Examples
- How to Create an MLA Header | Format Guidelines & Examples
- MLA Annotated Bibliography | Guidelines and Examples
- APA Website Citation (7th Edition) Guide | Format & Examples
- APA Citation Examples: The Bible, TED Talk, PPT & More
- APA Header Format: 5 Steps & Running Head Examples
- APA Title Page Format Simplified | Examples + Free Template
- How to Write an Abstract in MLA Format: Tips & Examples
- 10 Best Free Plagiarism Checkers of 2024 [100% Free Tools]
- 5 Reasons to Cite Your Sources Properly | Avoid Plagiarism!
- Dissertation Writing Guide
- Writing a Dissertation Proposal
- The Acknowledgments Section of a Dissertation
- The Table of Contents Page of a Dissertation
- The Introduction Chapter of a Dissertation
- The Literature Review of a Dissertation
- The Only Dissertation Toolkit You’ll Ever Need!
- 5 Thesis Writing Tips for Master Procrastinators
- How to Write a Dissertation | 5 Tips from Academic Editors
- The 5 Things to Look for in a Dissertation Editing Service
- Top 10 Dissertation Editing & Proofreading Services
- Why is it important to add references to your thesis?
- Thesis Editing | Definition, Scope & Standard Rates
- Expert Formatting Tips on MS Word for Dissertations
- A 7-Step Guide on How to Choose a Dissertation Topic
- 350 Best Dissertation Topic Ideas for All Streams in 2024
- A Guide on How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- Dissertation Defense: What to Expect and How to Prepare
- Creating a Dissertation Title Page (Examples & Templates)
- Essay Writing Guide
- Essential Research Tips for Essay Writing
- What Is a Mind Map? Free Mind Map Templates & Examples
- How to Write an Essay Outline: 5 Examples & Free Template
- How to Write an Essay Header: MLA and APA Essay Headers
- What Is an Essay? Structure, Parts, and Types
- How to Write an Essay in 8 Simple Steps (Examples Included)
- 8 Types of Essays | Quick Summary with Examples
- Expository Essays | Step-by-Step Manual with Examples
- Narrative Essay | Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- How to Write an Argumentative Essay (Examples Included)
- Guide to a Perfect Descriptive Essay [Examples & Outline Included]
- How to Start an Essay: 4 Introduction Paragraph Examples
- How to Write a Conclusion for an Essay (Examples Included!)
- How to Write an Impactful Personal Statement (Examples Included)
- Literary Analysis Essay: 5 Steps to a Perfect Assignment
- Compare and Contrast Essay | Quick Guide with Examples
- Top AI Essay Writers in 2024: 10 Must-Haves
- 100 Best College Essay Topics & How to Pick the Perfect One!
- College Essay Format: Tips, Examples, and Free Template
- Structure of an Essay: 5 Tips to Write an Outstanding Essay
- 10 Best AI Essay Outline Generators of 2024
- The Best Essay Graders of 2024 That You Can Use for Free!
- Top 10 Free Essay Writing Tools for Students in 2024
Still have questions? Leave a comment
Add Comment

Checklist: Dissertation Proposal
Enter your email id to get the downloadable right in your inbox!

Examples: Edited Papers
Need editing and proofreading services.
- Tags: Academic Editing , Academic Proofreading , Academic Writing , College Admission , Writing Tips
When you write an essay, do you read and reread it to ensure your content is impressive before finally submitting it for grading? What this means is that you prefer to review your college essays thoroughly before your teacher or instructor peruses them.
However, this task may become overwhelming at times. Don’t worry. We have a solution that will streamline essay reviewing for you.
In this article, we will discuss how to review your college essay step by step and ensure that you do not miss verifying the effectiveness of any aspect of your essay. So, let’s begin!
Need help with essay reviews? Explore our essay editing services. Learn more
How to review a college essay: A step-by-step guide
College essay reviews can be simple to execute if a defined process is followed. A structured process ensures that the output is superior in terms of relevance, information, and overall quality.
By evaluating your work in advance, you can identify and correct mistakes that could potentially harm your essay score. Editing and proofreading your essays will help polish them to a great extent, bringing them closer to perfection in that instance.
Here are the points you can follow to edit, proofread, and review your college essays:
1. Understand the essay prompts and requirements
The prompt that your college or teacher has asked you to work with must be carefully studied and understood. Take the key objectives and expectations into account before finalizing the essay outline. Also, ensure that you keep the essay writing and submission requirements in view.
2. Check the essay outline
Precisely interpreting the meaning of the topic is key to generating an essay outline. This outline should guide you in organizing your points logically, ensuring that the content flows smoothly and remains relevant throughout.
3. Evaluate the essay structure and flow
If the essay outline seems apt, checking whether the final structure upon adding content is effective goes a long way in making your essay interesting and informative. Assess whether the information is presented logically and whether the transitions between paragraphs are smooth. A well-structured essay keeps the reader engaged and makes your arguments more compelling.
4. Run content checks
Read the content to catch errors and verify the factual accuracy of your essay. Ensure that your arguments are logically sound and well-supported by evidence. This step is crucial in making your essay both informative and persuasive.
5. Check grammar, spelling, and punctuation
Incorrect grammar can make your content difficult to understand, and spelling mistakes are simply exhausting. Grammar and spelling play a key role in ensuring that readers remain focused on your message.
6. Revisit the tone and style
Examine the tone and writing style to ensure they are appropriate for the audience and purpose of your essay. Additionally, verify that the formatting style adheres to your university’s guidelines. Consistency in tone and style helps convey your ideas more effectively.
7. Ensure clarity and coherence
Analyze your essay to check whether your ideas are clearly expressed and logically connected. Each paragraph should build upon the previous one, making for a cohesive argument throughout. Avoid ambiguity and ensure that your essay communicates your message effectively.
8. Analyze the content for originality and depth
You can use free plagiarism checkers available online to check if your content gets flagged for plagiarism. This step helps you avoid any potential plagiarism issues before submission. Additionally, review your essay for depth, making sure that your analysis and arguments are insightful and contribute meaningfully to the topic.
Why reviewing a college essay is crucial?
A college essay that undergoes a detailed review has a higher chance of being graded better than one that has not been evaluated a second time. A thoroughly reviewed college essay directly impacts the quality of your submission.
Such an essay goes beyond just meeting your college or teacher’s essay writing requirements. It ensures your content is clear and coherent. It also increases the effectiveness of your essay and makes it sound more compelling.
Through reviews, you can identify and correct errors, refine your arguments, and enhance your essay’s overall structure and flow. This process helps you present ideas more effectively.
Moreover, you can assess whether your work is original. Unintentional plagiarism is a possibility, and reviewing college essays allows you to double-check whether your work offers fresh insights. An in-depth review converts a good essay into an exceptional one.
If you are worried about reviewing important essays, particularly college admissions essays , seeking college essay editing services might prove to be a good decision.
Common mistakes to avoid during essay review
While reviewing the content of a college essay, you might inadvertently overlook certain mistakes that can negatively impact your grade. That is why free online essay checkers and grammar checkers come in handy during a college essay review.
To simplify the college essay review process, we have outlined some common mistakes you should try (as far as possible) to avoid during college essay reviews:
- Undertaking speedy reviews: You must allow yourself adequate time to review your work. Taking a break from the essay content and returning with fresh eyes is important.
- Ignoring thesis or topic checks: Verify the clarity and strength of your topic sentence or thesis statement to ensure the content is relevant. A clear and specific statement or prompt gives the right direction to the rest of the content.
- Missing sentence structure checks: Complex, lengthy, or awkward sentence structures can confuse readers, introduce redundancies, and make your message unintelligible. To strengthen your arguments, sentence structure checks are unavoidable.
- Disregarding aspects other than grammar and spelling: Grammar and spelling must be taken care of, there is no doubt about it. However, ignoring the soundness of arguments or the coherence of the ideas in your essay can prove to be detrimental.
- Failing to fact-check: If you do not verify the accuracy of facts or statistics and corroborate them with the right sources, your teacher will end up doing it for you during essay grading. Inaccurate information can result in a low grade.
- Dismissing tone and style issues: Tone and writing style are important aspects of any writing endeavor. Check whether they match the essay’s purpose and audience. Inconsistent tone and/or style can impact your standing as a student.
- Leaving transitions unchecked: If you want the content to flow smoothly, checking transitions between paragraphs and sentences is crucial. They help maintain the flow. An unconnected or irrelevant thought or idea can make your essay difficult to follow.
- Brushing aside plagiarism checks: We cannot stress the importance of using plagiarism detection tools to ensure your content is original and properly cited. This is a non-negotiable step!
- Not seeking feedback: Conducting a review but not asking peers or mentors to read your work might lead to a biased assessment. Hence, you should seek feedback from others to identify if any areas need improvement.
Some examples of college essays
Here are some college essay examples for your reference. Note that these can be further reviewed and edited if needed.
Example 1: Reflect on a time when you challenged a belief or idea. What prompted you to act? Would you make the same decision again?
In my sophomore year, I was part of a debate team where we discussed the merits of mandatory volunteerism. I initially believed that forcing people to volunteer was counterproductive. However, after conducting research and hearing opposing views, I found myself questioning my stance.
During the debate, I decided to argue in favor of mandatory volunteerism, emphasizing the long-term benefits it could bring to society. This experience taught me the importance of being open to changing my perspective when presented with new evidence.
Example 2: Describe an extracurricular activity that has been meaningful to you.
As the president of the Robotics Club, I had the opportunity to lead a team of passionate students in designing and building robots for regional competitions. This experience has not only honed my technical skills but also taught me the value of teamwork, problem-solving, and perseverance.
One of our proudest achievements was winning the Innovation Award at the state championship, a moment that validated our countless hours of hard work. Being part of this club has solidified my desire to pursue a career in engineering.
Utilize tools and resources for college essay reviews
Before you begin writing a college essay, using essay outline generators can help create relevant points for your essay. Once your essay is ready, reviews are essential. Let us discuss this further.
Essay checkers and essay graders are useful tools for essay reviews. Similarly, grammar checkers and spell checkers are also important. Additionally, you can look for college essay editing and essay proofreading services for essays that can make or break your academic journey.
Here are some tools and resources for college essay reviews:
- Essay checkers: Using essay checkers like Grammarly, QuillBot, PaperRater, etc., can help you understand how effective your essay is and correct it before submission.
- Essay graders: Several free and paid essay graders are available today. You can look for a suitable essay grader and secure feedback for essay revision. Some popular ones include Perfect Essay Writer, Essay-Grader AI, My Essay Writer, etc.
- Grammar checkers: They help you correct grammar mistakes and fix sentences wherever required. Popular grammar checkers include Grammar Check, Reverso, etc.
- Spell checkers: Many grammar checkers have integrated spell checks in their tools. However, a separate spell check is always recommended. You can use tools like Grammarly, LanguageTool, etc.
- College essay editing services: Hiring college essay editing services like PaperTrue is advisable if your essay is the deciding factor in what happens next in your academics.
- College essay proofreading services: These services provide similar support in terms of correction and feedback as college essay editing services. PaperTrue, a renowned name in the editing industry, offers both essay editing and proofreading .
- Books and essay writing guides: Books are timeless! You can always rely on books and essay editing guides, both online and in print, to write a good essay and verify its relevance and effectiveness.
College essay reviews can only enhance your essay and polish it, making it an interesting read. It is an essential step that you should not ignore or avoid. By following a structured review process that also includes relying on tools and resources to get the best results, you will likely earn a high score.
Professional college essay editing services can further streamline the college essay review process and help you achieve your academic goals. A well-reviewed essay not only meets academic requirements but also showcases your ability to communicate skillfully.
For more articles on essays, grammar, and sentence structure, refer to the links below:
- 100 Best College Essay Topics & How to Pick the Perfect One!
- What Is a Subject of a Sentence? Meaning, Examples & Types
- What are the Parts of a Sentence? An Easy-to-Learn Guide
- Academic Writing in 2024: 5 Key Dos & Don’ts + Examples
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is it important to review a college essay before submission, how important is it to get feedback from peers or teachers on my essay, how can i evaluate the structure and flow of my college essay effectively, how do i ensure my essay meets the requirements of the prompt.
Found this article helpful?
Leave a Comment: Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Your vs. You’re: When to Use Your and You’re
Your organization needs a technical editor: here’s why, your guide to the best ebook readers in 2024, writing for the web: 7 expert tips for web content writing.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Get carefully curated resources about writing, editing, and publishing in the comfort of your inbox.
How to Copyright Your Book?
If you’ve thought about copyrighting your book, you’re on the right path.
© 2024 All rights reserved
- Terms of service
- Privacy policy
- Self Publishing Guide
- Pre-Publishing Steps
- Fiction Writing Tips
- Traditional Publishing
- Academic Writing and Publishing
- Partner with us
- Annual report
- Website content
- Marketing material
- Job Applicant
- Cover letter
- Resource Center
- Case studies

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This is a grading rubric an instructor uses to assess students' work on this type of. assignment. It is a sample rubric that needs to be edited to reflect the specifics of a. particular assignment. Students can self-assess using the rubric as a checklist before. submitting their assignment. This sample rubric can also be found under the ...
Short Essay Question Rubric* EXCELLENT MEETS EXPECTATIONS APPROACHES EXPECTATIONS NEEDS IMPROVEMENT Completeness Shows a thorough understanding of the question. Addresses all aspects of the question completely. Presents a general understanding of the question. Completely addresses most aspects of the question, or addresses all aspects incompletely.
Rubric Best Practices, Examples, and Templates. A rubric is a scoring tool that identifies the different criteria relevant to an assignment, assessment, or learning outcome and states the possible levels of achievement in a specific, clear, and objective way. Use rubrics to assess project-based student work including essays, group projects ...
The professor will use the writing rubric to grade your essay. Writing rubrics offer guidance and help you make sure you're ticking every box as you write. They don't always involve points. Sometimes, rubrics score papers on a scale from poor to excellent. Occasionally a rubric will specify which elements of a topic must be covered in a ...
Logical, compelling progression of ideas in essay;clear structure which enhances and showcases the central idea or theme and moves the reader through the text. Organization flows so smoothly the reader hardly thinks about it. Effective, mature, graceful transitions exist throughout the essay.
Engaging and full development of a clear thesis as appropriate to assignment purpose. Consistent evidence with originality and depth of ideas; ideas work together as a unified whole; main points are sufficiently supported (with evidence); support is valid and specific. Organization is sequential and appropriate to assignment; paragraphs are ...
2: The essay makes an earnest attempt at meeting the requirements of the category, but it still needs improvement. 3: The essay meets the requirements of the category but does not exceed them. 4: The essay exceeds the requirements of the category. It is exemplary. These measurements apply to each of the five categories.
Writing Rubric (Johnson Community College) 2 Subject A Scoring Guide (University of CA) 3 Scoring Guide for Writing (CA State University, Fresno) 4 ... 5 = Essay contains strong composition skills including a clear and thought-provoking thesis, although development, diction, and sentence style may suffer minor flaws. ...
Section 1. Evaluation of Thinking (continued) Directions: For each of the three criteria (content and focus; analysis and critical thinking; logic and flow) select 10, 8, 6, 4, or 2 from the five possible scores (representing strong, proficient, satisfactory, weak, or unacceptable, respectively). Section 2. Evaluation of Communicating Ideas.
electronic rubric for specific essay prompts) •Essay did not address or answer the given prompt • Reader didn't see any relatability to the prompt or the subject of the scholarship essay : Essay somewhat addressed or answered the given prompt • Reader saw some relatability to the prompt or the subject of the scholarship essay Essay mostly
AP English Language Scoring Rubric, Free-Response Question 1-3 | SG 1 Scoring Rubric for Question 1: Synthesis Essay 6 points Reporting Category Scoring Criteria Row A Thesis (0-1 points) 4.B 0 points For any of the following: • There is no defensible thesis. • The intended thesis only restates the prompt.
9-10 pts. -Essay maintains a clear, mostly specific, prompt-appropriate focus that develops a clear main idea throughout the essay. -Essay develops purpose with a clear angle. 8 pts. -Essay's focus is somewhat unclear or off-topic, and/or main idea may meander a bit or contain minor digressions.
Essay Rubric Directions: Your essay will be graded based on this rubric. Consequently, use this rubric as a guide when writing your essay and check it again before you submit your essay. Traits 4 3 2 1 Focus & Details There is one clear, well-focused topic. Main ideas are clear and are well supported by detailed and accurate information.
AP History Long Essay Question (LEQ) Rubric (6 points) Reporting Category. Scoring Criteria. Decision Rules. THESIS/CLAIM. (0-1 pt) 1 pt. Responds to the prompt with a historically defensible thesis/claim that establishes a line of reasoning. To earn this point, the thesis must make a claim that responds to the prompt, rather than merely ...
If an assignment prompt is clearly addressing each of these elements, then students know what they're doing, why they're doing it, and when/how/for whom they're doing it. From the standpoint of a rubric, we can see how these elements correspond to the criteria for feedback: 1. Purpose. 2. Genre.
An essay rubric refers to a way for teachers to assess students' composition writing skills and abilities. Basically, an evaluation scheme provides specific criteria to grade assignments. Moreover, the three basic elements of an essay rubric are criteria, performance levels, and descriptors. In this case, teachers use assessment guidelines to ...
AP English Literature Scoring Rubric, Free-Response Question 1-3 | SG 1 Scoring Rubric for Question 1: Poetry Analysis 6 points Reporting Category Scoring Criteria Row A Thesis (0-1 points) 7.B 0 points For any of the following: • There is no defensible thesis. • The intended thesis only restates the prompt.
Short Essay Questions. Use this rubric for grading student responses that are part of a test or quiz that include other types of questions as well. Can be customized for any subject. Rubric Code: N4AA82. By marquezh5.
Needs Work. Title, Introduction, Conclusion. Title includes both subject and a hint about the thesis or point of view; engaging introduction that prepares the reader accurately for the body paragraphs; thought-provoking or interesting conclusion that ties everything back together and takes the thesis further. Most but not all of the qualities ...
Essay Questions and Scoring Rubric Essay Questions 1. Describe the field of study in which you would like to pursue a doctoral degree and the research ... Many professionals with doctoral degrees enter careers to serve as college and university faculty, and most faculty serve a diverse student body. Describe your interest in a faculty career ...
Students can self-assess using the rubric as a checklist before. submitting their assignment. This sample rubric can also be found under the Turnitin tool in. Edit the assignment requirements column, performance level descriptions in each box, and. point values to align with a particular course assignment. Distribute the rubric to students.
The rubrics for the AP History Document-Based Question (DBQ) and Long Essay Question (LEQ) have been modified for the 2017-18 school year, using feedback received from AP teachers and Readers and in tandem with recently announced changes to the Course and Exam Description for each course.
AP History LEQ Rubric (6 points) Responds to the prompt with a historically defensible thesis/claim that establishes a line of reasoning. To earn this point, the thesis must make a claim that responds to the prompt, rather than merely restating or rephrasing the prompt. The thesis must consist of one or more sentences located in one place ...
Learn how to do a college essay review with a PaperTrue step-by-step guide. Get the best tips on structure, content, and grammar to ensure your essay stands out. MENU MENU. Services. ... 100 Best College Essay Topics & How to Pick the Perfect One! Top AI Essay Writers in 2024: 10 Must-Haves; What Is a Subject of a Sentence? Meaning, Examples ...