

I Gave Myself Three Months to Change My Personality
The results were mixed.

Listen to this article
Listen to more stories on audm
This article was featured in One Story to Read Today, a newsletter in which our editors recommend a single must-read from The Atlantic , Monday through Friday. Sign up for it here.
O ne morning last summer , I woke up and announced, to no one in particular: “I choose to be happy today!” Next I journaled about the things I was grateful for and tried to think more positively about my enemies and myself. When someone later criticized me on Twitter, I suppressed my rage and tried to sympathize with my hater. Then, to loosen up and expand my social skills, I headed to an improv class.

Explore the March 2022 Issue
Check out more from this issue and find your next story to read.
I was midway through an experiment—sample size: 1—to see whether I could change my personality. Because these activities were supposed to make me happier, I approached them with the desperate hope of a supplicant kneeling at a shrine.
Psychologists say that personality is made up of five traits : extroversion, or how sociable you are; conscientiousness, or how self-disciplined and organized you are; agreeableness, or how warm and empathetic you are; openness, or how receptive you are to new ideas and activities; and neuroticism, or how depressed or anxious you are. People tend to be happier and healthier when they score higher on the first four traits and lower on neuroticism. I’m pretty open and conscientious, but I’m low on extroversion, middling on agreeableness, and off the charts on neuroticism.
Researching the science of personality, I learned that it was possible to deliberately mold these five traits, to an extent, by adopting certain behaviors. I began wondering whether the tactics of personality change could work on me.
I’ve never really liked my personality, and other people don’t like it either. In grad school, a partner and I were assigned to write fake obituaries for each other by interviewing our families and friends. The nicest thing my partner could shake out of my loved ones was that I “really enjoy grocery shopping.” Recently, a friend named me maid of honor in her wedding; on the website for the event, she described me as “strongly opinionated and fiercely persistent.” Not wrong, but not what I want on my tombstone. I’ve always been bad at parties because the topics I bring up are too depressing, such as everything that’s wrong with my life, and everything that’s wrong with the world, and the futility of doing anything about either.
Neurotic people, twitchy and suspicious, can often “detect things that less sensitive people simply don’t register,” writes the personality psychologist Brian Little in Who Are You, Really? “This is not conducive to relaxed and easy living.” Rather than being motivated by rewards, neurotic people tend to fear risks and punishments; we ruminate on negative events more than emotionally stable people do. Many, like me, spend a lot of money on therapy and brain medications.
And while there’s nothing wrong with being an introvert, we tend to underestimate how much we’d enjoy behaving like extroverts. People have the most friends they will ever have at age 25 , and I am much older than that and never had very many friends to begin with. Besides, my editors wanted me to see if I could change my personality, and I’ll try anything once. (I’m open to experiences!) Maybe I, too, could become a friendly extrovert who doesn’t carry around emergency Xanax.
I gave myself three months.
The best-known expert on personality change is Brent Roberts, a psychologist at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. Our interview in June felt, to me, a bit like visiting an evidence-based spiritual guru—he had a Zoom background of the red rocks of Sedona and the answers to all my big questions. Roberts has published dozens of studies showing that personality can change in many ways over time, challenging the notion that our traits are “set like plaster,” as the psychologist William James put it in 1887. But other psychologists still sometimes tell Roberts that they simply don’t believe it. There is a “deep-seated desire on the part of many people to think of personality as unchanging,” he told me. “It simplifies your world in a way that’s quite nice.” Because then you don’t have to take responsibility for what you’re like.
Don’t get too excited: Personality typically remains fairly stable throughout your life, especially in relation to other people. If you were the most outgoing of your friends in college, you will probably still be the bubbliest among them in your 30s. But our temperaments tend to shift naturally over the years. We change a bit during adolescence and a lot during our early 20s, and continue to evolve into late adulthood. Generally, people grow less neurotic and more agreeable and conscientious with age, a trend sometimes referred to as the “maturity principle.”
Longitudinal research suggests that careless, sullen teenagers can transform into gregarious seniors who are sticklers for the rules. One study of people born in Scotland in the mid-1930s—which admittedly had some methodological issues—found no correlation between participants’ conscientiousness at ages 14 and 77. A later study by Rodica Damian, a psychologist at the University of Houston, and her colleagues assessed the personalities of a group of American high-school students in 1960 and again 50 years later. They found that 98 percent of the participants had changed at least one personality trait.
Even our career interests are more stable than our personalities, though our jobs can also change us: In one study, people with stressful jobs became more introverted and neurotic within five years.
With a little work, you can nudge your personality in a more positive direction. Several studies have found that people can meaningfully change their personalities, sometimes within a few weeks , by behaving like the sort of person they want to be. Students who put more effort into their homework became more conscientious. In a 2017 meta-analysis of 207 studies, Roberts and others found that a month of therapy could reduce neuroticism by about half the amount it would typically decline over a person’s life. Even a change as minor as taking up puzzles can have an effect: One study found that senior citizens who played brain games and completed crossword and sudoku puzzles became more open to experiences. Though most personality-change studies have tracked people for only a few months or a year afterward, the changes seem to stick for at least that long.
When researchers ask, people typically say they want the success-oriented traits: to become more extroverted, more conscientious, and less neurotic. Roberts was surprised that I wanted to become more agreeable. Lots of people think they’re too agreeable, he told me. They feel they’ve become doormats.
Toward the end of our conversation, I asked Roberts whether there’s anything he would change about his own personality. He admitted that he’s not always very detail-oriented (a.k.a. conscientious). He also regretted the anxiety (a.k.a. neuroticism) he experienced early in his career. Grad school was a “disconcerting experience,” he said: The son of a Marine and an artist, he felt that his classmates were all “brilliant and smart” and understood the world of academia better than he did.
I was struck by how similar his story sounded to my own. My parents are from the Soviet Union and barely understand my career in journalism. I went to crappy public schools and a little-known college. I’ve notched every minor career achievement through night sweats and meticulous emails and aching computer shoulders. Neuroticism had kept my inner fire burning, but now it was suffocating me with its smoke.
To begin my transformation, I called Nathan Hudson, a psychology professor at Southern Methodist University who created a tool to help people alter their personality. For a 2019 paper, Hudson and three other psychologists devised a list of “challenges” for students who wanted to change their traits. For, say, increased extroversion, a challenge would be to “introduce yourself to someone new.” Those who completed the challenges experienced changes in their personality over the course of the 15-week study, Hudson found. “Faking it until you make it seems to be a viable strategy for personality change,” he told me.
But before I could tinker with my personality, I needed to find out exactly what that personality consisted of. So I logged on to a website Hudson had created and took a personality test, answering dozens of questions about whether I liked poetry and parties, whether I acted “wild and crazy,” whether I worked hard. “I radiate joy” got a “strongly disagree.” I disagreed that “we should be tough on crime” and that I “try not to think about the needy.” I had to agree, but not strongly, that “I believe that I am better than others.”
I scored in the 23rd percentile on extroversion—“very low,” especially when it came to being friendly or cheerful. Meanwhile, I scored “very high” on conscientiousness and openness and “average” on agreeableness, my high level of sympathy for other people making up for my low level of trust in them. Finally, I came to the source of half my breakups, 90 percent of my therapy appointments, and most of my problems in general: neuroticism. I’m in the 94th percentile—“extremely high.”
I prescribed myself the same challenges that Hudson had given his students. To become more extroverted, I would meet new people. To decrease neuroticism, I would meditate often and make gratitude lists. To increase agreeableness, the challenges included sending supportive texts and cards, thinking more positively about people who frustrate me, and, regrettably, hugging. In addition to completing Hudson’s challenges, I decided to sign up for improv in hopes of increasing my extroversion and reducing my social anxiety. To cut down on how pissed off I am in general, and because I’m an overachiever, I also signed up for an anger-management class.
Read: Can personality be changed?
Hudson’s findings on the mutability of personality seem to endorse the ancient Buddhist idea of “no-self”—no core “you.” To believe otherwise, the sutras say, is a source of suffering. Similarly, Brian Little writes that people can have “multiple authenticities”—that you can sincerely be a different person in different situations. He proposes that people have the ability to temporarily act out of character by adopting “free traits,” often in the service of an important personal or professional project. If a shy introvert longs to schmooze the bosses at the office holiday party, they can grab a canapé and make the rounds. The more you do this, Little says, the easier it gets.
Staring at my test results, I told myself, This will be fun! After all, I had changed my personality before. In high school, I was shy, studious, and, for a while, deeply religious. In college, I was fun-loving and boy-crazy. Now I’m a basically hermetic “pressure addict,” as one former editor put it. It was time for yet another me to make her debut.
Ideally, in the end I would be happy, relaxed, personable. The screams of angry sources, the failure of my boyfriend to do the tiniest fucking thing—they would be nothing to me. I would finally understand what my therapist means when she says I should “just observe my thoughts and let them pass without judgment.” I made a list of the challenges and attached them to my nightstand, because I’m very conscientious.
Immediately I encountered a problem: I don’t like improv. It’s basically a Quaker meeting in which a bunch of office workers sit quietly in a circle until someone jumps up, points toward a corner of the room, and says, “I think I found my kangaroo!” My vibe is less “yes, and” and more “well, actually.” When I told my boyfriend what I was up to, he said, “You doing improv is like Larry David doing ice hockey.”
I was also scared out of my mind. I hate looking silly, and that’s all improv is. The first night, we met in someone’s townhouse in Washington, D.C., in a room that was, for no discernible reason, decorated with dozens of elephant sculptures. Right after the instructor said, “Let’s get started,” I began hoping that someone would grab one and knock me unconscious.
That didn’t happen, so instead I played a game called Zip Zap Zop, which involved making lots of eye contact while tossing around an imaginary ball of energy, with a software engineer, two lawyers, and a guy who works on Capitol Hill. Then we pretended to be traveling salespeople peddling sulfuric acid. If someone had walked in on us, they would have thought we were insane. And yet I didn’t hate it. I decided I could think of being funny and spontaneous as a kind of intellectual challenge. Still, when I got home, I unwound by drinking one of those single-serving wines meant for petite female alcoholics.
A few days later, I logged in to my first Zoom anger-management class. Christian Jarrett, a neuroscientist and the author of Be Who You Want , writes that spending quality time with people who are dissimilar to you increases agreeableness. And the people in my anger-management class did seem pretty different from me. Among other things, I was the only person who wasn’t court-ordered to be there.
We took turns sharing how anger has affected our lives. I said it makes my relationship worse—less like a romantic partnership and more like a toxic workplace. Other people worried that their anger was hurting their family. One guy shared that he didn’t understand why we were talking about our feelings when kids in China and Russia were learning to make weapons, which I deemed an interesting point, because you’re not allowed to criticize others in anger management.
The sessions—I went to six—mostly involved reading worksheets together, which was tedious, but I did learn a few things. Anger is driven by expectations. If you think you’re going to be in an anger-inducing situation, one instructor said, try drinking a cold can of Coke, which may stimulate your vagus nerve and calm you down. A few weeks in, I had a rough day, my boyfriend gave me some stupid suggestions, and I yelled at him. Then he said I’m just like my dad, which made me yell more. When I shared this in anger management, the instructors said I should be clearer about what I need from him when I’m in a bad mood—which is listening, not advice.
All the while, I had been working on my neuroticism, which involved making a lot of gratitude lists. Sometimes it came naturally. As I drove around my little town one morning, I thought about how grateful I was for my boyfriend, and how lonely I had been before I met him, even in other relationships. Is this gratitude? I wondered. Am I doing it?
What is personality, anyway, and where does it come from?
Contrary to conventional wisdom about bossy firstborns and peacemaking middles, birth order doesn’t influence personality . Nor do our parents shape us like lumps of clay. If they did, siblings would have similar dispositions, when they often have no more in common than strangers chosen off the street. Our friends do influence us, though, so one way to become more extroverted is to befriend some extroverts. Your life circumstances also have an effect: Getting rich can make you less agreeable, but so can growing up poor with high levels of lead exposure.
A common estimate is that about 30 to 50 percent of the differences between two people’s personalities are attributable to their genes. But just because something is genetic doesn’t mean it’s permanent. Those genes interact with one another in ways that can change how they behave, says Kathryn Paige Harden, a behavioral geneticist at the University of Texas. They also interact with your environment in ways that can change how you behave. For example: Happy people smile more, so people react more positively to them, which makes them even more agreeable. Open-minded adventure seekers are more likely to go to college, where they grow even more open-minded.
Harden told me about an experiment in which mice that were genetically similar and reared in the same conditions were moved into a big cage where they could play with one another. Over time, these very similar mice developed dramatically different personalities. Some became fearful, others sociable and dominant. Living in Mouseville, the mice carved out their own ways of being, and people do that too. “We can think of personality as a learning process,” Harden said. “We learn to be people who interact with our social environments in a certain way.”
This more fluid understanding of personality is a departure from earlier theories. A 1914 best seller called The Eugenic Marriage (which is exactly as offensive as it sounds) argued that it is not possible to change a child’s personality “one particle after conception takes place.” In the 1920s, the psychoanalyst Carl Jung posited that the world consists of different “types” of people—thinkers and feelers, introverts and extroverts. (Even Jung cautioned, though, that “there is no such thing as a pure extravert or a pure introvert. Such a man would be in the lunatic asylum.”) Jung’s rubric captured the attention of a mother-daughter duo, Katharine Briggs and Isabel Briggs Myers, neither of whom had any formal scientific training. As Merve Emre describes in The Personality Brokers , the pair seized on Jung’s ideas to develop that staple of Career Day, the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator. But the test is virtually meaningless . Most people aren’t ENTJs or ISFPs; they fall between categories.
Over the years, poor parenting has been a popular scapegoat for bad personalities. Alfred Adler, a prominent turn-of-the-20th-century psychologist, blamed mothers, writing that “wherever the mother-child relationship is unsatisfactory, we usually find certain social defects in the children.” A few scholars attributed the rise of Nazism to strict German parenting that produced hateful people who worshipped power and authority. But maybe any nation could have embraced a Hitler: It turns out that the average personalities of different countries are fairly similar. Still, the belief that parents are to blame persists, so much so that Roberts closes the course he teaches at the University of Illinois by asking students to forgive their moms and dads for whatever personality traits they believe were instilled or inherited.
Not until the 1950s did researchers acknowledge people’s versatility—that we can reveal new faces and bury others. “Everyone is always and everywhere, more or less consciously, playing a role,” the sociologist Robert Ezra Park wrote in 1950. “It is in these roles that we know each other; it is in these roles that we know ourselves.”
Around this time, a psychologist named George Kelly began prescribing specific “roles” for his patients to play. Awkward wallflowers might go socialize in nightclubs, for example. Kelly’s was a rhapsodic view of change; at one point he wrote that “all of us would be better off if we set out to be something other than what we are.” Judging by the reams of self-help literature published each year, this is one of the few philosophies all Americans can get behind.
About six weeks in, my adventures in extroversion were going better than I’d anticipated. Intent on talking to strangers at my friend’s wedding, I approached a group of women and told them the story of how my boyfriend and I had met—I moved into his former room in a group house—which they deemed the “story of the night.” On the winds of that success, I tried to talk to more strangers, but soon encountered the common wedding problem of Too Drunk to Talk to People Who Don’t Know Me.
For more advice on becoming an extrovert, I reached out to Jessica Pan, a writer in London and the author of the book Sorry I’m Late, I Didn’t Want to Come . Pan was an extreme introvert, someone who would walk into parties and immediately walk out again. At the start of the book, she resolved to become an extrovert. She ran up to strangers and asked them embarrassing questions. She did improv and stand-up comedy. She went to Budapest and made a friend. Folks, she networked.

In the process, Pan “flung open the doors” to her life, she writes. “Having the ability to morph, to change, to try on free traits, to expand or contract at will, offers me an incredible feeling of freedom and a source of hope.” Pan told me that she didn’t quite become a hard-core extrovert, but that she would now describe herself as a “gregarious introvert.” She still craves alone time, but she’s more willing to talk to strangers and give speeches. “I will be anxious, but I can do it,” she said.
I asked her for advice on making new friends, and she told me something a “friendship mentor” once told her: “Make the first move, and make the second move, too.” That means you sometimes have to ask a friend target out twice in a row—a strategy I had thought was gauche.
I practiced by trying to befriend some female journalists I admired but had been too intimidated to get to know. I messaged someone who seemed cool based on her writing, and we arranged a casual beers thing. But on the night we were supposed to get together, her power went out, trapping her car in her garage.
Instead, I caught up with an old friend by phone, and we had one of those conversations you can have only with someone you’ve known for years, about how the people who are the worst remain the worst, and how all of your issues remain intractable, but good on you for sticking with it. By the end of our talk, I was high on agreeable feelings. “Love you, bye!” I said as I hung up.
“LOL,” she texted. “Did you mean to say ‘I love you’?”
Who was this new Olga?
For my gratitude journaling, I purchased a notebook whose cover said, “Gimme those bright sunshiney vibes.” I soon noticed, though, that my gratitude lists were repetitive odes to creature comforts and entertainment: Netflix, yoga, TikTok, leggings, wine. After I cut my finger cooking, I expressed gratitude for the dictation software that let me write without using my hands, but then my finger healed. “Very hard to come up with new things to say,” I wrote one day.
I find expressing gratitude unnatural, because Russians believe doing so will provoke the evil eye; our God doesn’t like too much bragging. The writer Gretchen Rubin hit a similar wall when keeping a gratitude journal for her book The Happiness Project . “It had started to feel forced and affected,” she wrote, making her annoyed rather than grateful.
I was also supposed to be meditating, but I couldn’t. On almost every page, my journal reads, “Meditating sucks!” I tried a guided meditation that involved breathing with a heavy book on my stomach—I chose Nabokov’s Letters to Véra —only to find that it’s really hard to breathe with a heavy book on your stomach.
I tweeted about my meditation failures, and Dan Harris, a former Good Morning America weekend anchor, replied: “The fact that you’re noticing the thoughts/obsessions is proof that you are doing it correctly!” I picked up Harris’s book 10% Happier , which chronicles his journey from a high-strung reporter who had a panic attack on air to a high-strung reporter who meditates a lot. At one point, he was meditating for two hours a day.
When I called Harris, he said that it’s normal for meditation to feel like “training your mind to not be a pack of wild squirrels all the time.” Very few people actually clear their minds when they’re meditating. The point is to focus on your breath for however long you can—even if it’s just a second—before you get distracted. Then do it over and over again. Occasionally, when Harris meditates, he still “rehearses some grand, expletive-filled speech I’m gonna deliver to someone who’s wronged me.” But now he can return to his breath more quickly, or just laugh off the obsessing.
Harris suggested that I try loving-kindness meditation, in which you beam affectionate thoughts toward yourself and others. This, he said, “sets off what I call a gooey upward spiral where, as your inner weather gets balmier, your relationships get better.” In his book, Harris describes meditating on his 2-year-old niece. As he thought about her “little feet” and “sweet face with her mischievous eyes,” he started crying uncontrollably.
What a pussy , I thought.
I downloaded Harris’s meditation app and pulled up a loving-kindness session by the meditation teacher Sharon Salzberg. She had me repeat calming phrases like “May you be safe” and “May you live with ease.” Then she asked me to envision myself surrounded by a circle of people who love me, radiating kindness toward me. I pictured my family, my boyfriend, my friends, my former professors, emitting beneficence from their bellies like Care Bears. “You’re good; you’re okay,” I imagined them saying. Before I knew what was happening, I had broken into sobs.
After two brutal years, people may be wondering if surviving a pandemic has at least improved their personality, making them kinder and less likely to sweat the small stuff. “Post-traumatic growth,” or the idea that stressful events can make us better people, is the subject of one particularly cheery branch of psychology. Some big events do seem to transform personality: People grow more conscientious when they start a job they like, and they become less neurotic when they enter a romantic relationship. But in general, it’s not the event that changes your personality; it’s the way you experience it. And the evidence that people grow as a result of difficulty is mixed. Studies of post-traumatic growth are tainted by the fact that people like to say they got something out of their trauma.
It’s a nice thing to believe about yourself—that, pummeled by misfortune, you’ve emerged stronger than ever. But these studies are mostly finding that people prefer to look on the bright side.
Read: The opposite of toxic positivity
In more rigorous studies, evidence of a transformative effect fades. Damian, the University of Houston psychologist, gave hundreds of students at the university a personality test a few months after Hurricane Harvey hit, in November 2017, and repeated the test a year later. The hurricane was devastating: Many students had to leave their homes; others lacked food, water, or medical care for weeks. Damian found that her participants hadn’t grown, and they hadn’t shriveled. Overall they stayed the same. Other research shows that difficult times prompt us to fall back on tried-and-true behaviors and traits, not experiment with new ones.
Growth is also a strange thing to ask of the traumatized. It’s like turning to a wounded person and demanding, “Well, why didn’t you grow, you lazy son of a bitch?” Roberts said. Just surviving should be enough.
It may be impossible to know how the pandemic will change us on average, because there is no “average.” Some people have struggled to keep their jobs while caring for children; some have lost their jobs; some have lost loved ones. Others have sat at home and ordered takeout. The pandemic probably hasn’t changed you if the pandemic itself hasn’t felt like that much of a change.
I blew off anger management one week to go see Kesha in concert. I justified it because the concert was a group activity, plus she makes me happy. The next time the class gathered, we talked about forgiveness, which Child Weapons Guy was not big on. He said that rather than forgive his enemies, he wanted to invite them onto a bridge and light the bridge on fire. I thought he should get credit for being honest—who hasn’t wanted to light all their enemies on fire?—but the anger-management instructors started to look a little angry themselves.
In the next session, Child Weapons Guy seemed contrite, saying he realized that he uses his anger to deal with life, which was a bigger breakthrough than anyone expected. I was also praised, for an unusually tranquil trip home to see my parents, which my instructors said was an example of good “expectation management.”
Meanwhile, my social life was slowly blooming. A Twitter acquaintance invited me and a few other strangers to a whiskey tasting, and I said yes even though I don’t like whiskey or strangers. At the bar, I made some normal-person small talk before having two sips of alcohol and wheeling the conversation around to my personal topic of interest: whether I should have a baby. The woman who organized the tasting, a self-proclaimed extrovert, said people are always grateful to her for getting everyone to socialize. At first, no one wants to come, but people are always happy they did.
I thought perhaps whiskey could be my “thing,” and, to tick off another challenge from Hudson’s list, decided to go to a whiskey bar on my own one night and talk to strangers. I bravely steered my Toyota to a sad little mixed-use development and pulled up a stool at the bar. I asked the bartender how long it had taken him to memorize all the whiskeys on the menu. “Two months,” he said, and turned back to peeling oranges. I asked the woman sitting next to me how she liked her appetizer. “It’s good!” she said. This is awful! I thought. I texted my boyfriend to come meet me.
The larger threat on my horizon was the improv showcase—a free performance for friends and family and whoever happened to jog past Picnic Grove No. 1 in Rock Creek Park. The night before, I kept jolting awake from intense, improv-themed nightmares. I spent the day grimly watching old Upright Citizens Brigade shows on YouTube. “I’m nervous on your behalf,” my boyfriend said when he saw me clutching a throw pillow like a life preserver.
From the January/February 2014 issue: Surviving anxiety
To describe an improv show is to unnecessarily punish the reader, but it went fairly well. Along with crushing anxiety, my brain courses with an immigrant kid’s overwhelming desire to do whatever people want in exchange for their approval. I improvised like they were giving out good SAT scores at the end. On the drive home, my boyfriend said, “Now that I’ve seen you do it, I don’t really know why I thought it’s something you wouldn’t do.”
I didn’t know either. I vaguely remembered past boyfriends telling me that I’m insecure, that I’m not funny. But why had I been trying to prove them right? Surviving improv made me feel like I could survive anything, as bratty as that must sound to all my ancestors who survived the siege of Leningrad.
Finally, the day came to retest my personality and see how much I’d changed. I thought I felt hints of a mild metamorphosis. I was meditating regularly, and had had several enjoyable get-togethers with people I wanted to befriend. And because I was writing them down, I had to admit that positive things did, in fact, happen to me.
But I wanted hard data. This time, the test told me that my extroversion had increased, going from the 23rd percentile to the 33rd. My neuroticism decreased from “extremely high” to merely “very high,” dropping to the 77th percentile. And my agreeableness score … well, it dropped, from “about average” to “low.”
I told Brian Little how I’d done. He said I likely did experience a “modest shift” in extroversion and neuroticism, but also that I might have simply triggered positive feedback loops. I got out more, so I enjoyed more things, so I went to more things, and so forth.
Why didn’t I become more agreeable, though? I had spent months dwelling on the goodness of people, devoted hours to anger management, and even sent an e-card to my mom. Little speculated that maybe by behaving so differently, I had heightened my internal sense that people aren’t to be trusted. Or I might have subconsciously bucked against all the syrupy gratitude time. That I had tried so hard and made negative progress—“I think it’s a bit of a hoot,” he said.
Perhaps it’s a relief that I’m not a completely new person. Little says that engaging in “free trait” behavior—acting outside your nature—for too long can be harmful, because you can start to feel like you are suppressing your true self. You end up feeling burned out or cynical.
The key may not be in swinging permanently to the other side of the personality scale, but in balancing between extremes, or in adjusting your personality depending on the situation. “The thing that makes a personality trait maladaptive is not being high or low on something; it’s more like rigidity across situations,” Harden, the behavioral geneticist, told me.
“So it’s okay to be a little bitchy in your heart, as long as you can turn it off?” I asked her.
“People who say they’re never bitchy in their heart are lying,” she said.
Susan Cain, the author of Quiet and the world’s most famous introvert, seems reluctant to endorse the idea that introverts should try to be more outgoing. Over the phone, she wondered why I wanted to be more extroverted in the first place. Society often urges people to conform to the qualities extolled in performance reviews—punctual, chipper, gregarious. But there are upsides to being introspective, skeptical, and even a little neurotic. She said it’s possible that I didn’t change my underlying introversion, that I just acquired new skills. She thought I could probably maintain this new personality, so long as I kept doing the tasks that got me here.
Hudson cautioned that personality scores can bounce around a bit from moment to moment; to be certain of my results, I ideally would have taken the test a number of times. Still, I felt sure that some change had taken place. A few weeks later, I wrote an article that made people on Twitter really mad. This happens to me once or twice a year, and I usually suffer a minor internal apocalypse. I fight the people on Twitter while crying, call my editor while crying, and Google How to become an actuary while crying. This time, I was stressed and angry, but I just waited it out.
This kind of modest improvement, I realized, is the goal of so much self-help material. Hours a day of meditation made Harris only 10 percent happier. My therapist is always suggesting ways for me to “go from a 10 to a nine on anxiety.” Some antidepressants make people feel only slightly less depressed, yet they take the drugs for years. Perhaps the real weakness of the “change your personality” proposition is that it implies incremental change isn’t real change. But being slightly different is still being different—the same you but with better armor.
The late psychologist Carl Rogers once wrote, “When I accept myself just as I am, then I can change,” and this is roughly where I’ve landed. Maybe I’m just an anxious little introvert who makes an effort to be less so. I can learn to meditate; I can talk to strangers; I can be the mouse who frolics through Mouseville, even if I never become the alpha. I learned to play the role of a calm, extroverted softy, and in doing so I got to know myself.
This article appears in the March 2022 print edition with the headline “My Personality Transplant.” When you buy a book using a link on this page, we receive a commission. Thank you for supporting The Atlantic.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Your Health
- Treatments & Tests
- Health Inc.
- Public Health
Personality Can Change Over A Lifetime, And Usually For The Better
Christopher Soto

Why do people act the way they do? Many of us intuitively gravitate toward explaining human behavior in terms of personality traits: characteristic patterns of thinking, feeling and behaving that tend to be stable over time and consistent across situations.
This intuition has been a topic of fierce scientific debate since the 1960s, with some psychologists arguing that situations — not traits — are the most important causes of behavior. Some have even argued that personality traits are figments of our imagination that don't exist at all.
But in the past two decades, a large and still-growing body of research has established that personality traits are very much real , and that how people describe someone's personality accurately predicts that person's actual behavior .
The effects of personality traits on behavior are easiest to see when people are observed repeatedly across a variety of situations. On any one occasion, a person's behavior is influenced by both their personality and the situation, as well as other factors such as their current thoughts, feelings and goals. But when someone is observed in many different situations, the influence of personality on behavior is hard to miss. For example, you probably know some people who consistently (but not always) show up on time, and others who consistently run late.
We've also gained a clear sense of which personality traits are most generally useful for understanding behavior. The world's languages include many thousands of words for describing personality, but most of these can be organized in terms of the "Big Five" trait dimensions : extraversion (characterized by adjectives like outgoing, assertive and energetic vs. quiet and reserved); agreeableness (compassionate, respectful and trusting vs. uncaring and argumentative); conscientiousness (orderly, hard-working and responsible vs. disorganized and distractible); negative emotionality (prone to worry, sadness and mood swings vs. calm and emotionally resilient); and open-mindedness (intellectually curious, artistic and imaginative vs. disinterested in art, beauty and abstract ideas).
The Personality Myth
We like to think of our own personalities, and those of our family and friends, as predictable, constant over time. But what if they aren't? Explore that question in the latest episode of the NPR podcast and show Invisibilia .
And while personality traits are relatively stable over time , they can and often do gradually change across the life span. What's more, those changes are usually for the better . Many studies , including some of my own, show that most adults become more agreeable, conscientious and emotionally resilient as they age. But these changes tend to unfold across years or decades, rather than days or weeks. Sudden, dramatic changes in personality are rare.
Due to their effects on behavior and continuity over time, personality traits help shape the course of people's lives. When measured using scientifically constructed and validated personality tests, like one that Oliver John and I recently developed, the Big Five traits predict a long list of consequential life outcomes: performance in school and at work, relationships with family, friends, and romantic partners, life satisfaction and emotional well-being, physical health and longevity, and many more. Of course, none of these outcomes are entirely determined by personality; all of them are also influenced by people's life circumstances. But personality traits clearly influence people's lives in important ways and help explain why two people in similar circumstances often end up with different outcomes.
Consider one of life's most important and potentially difficult decisions: who (if anyone!) to choose as your mate. The research evidence indicates that personality should play a role in this decision. Studies following couples over time have consistently found that choosing a spouse who is kind, responsible and emotionally resilient will substantially improve your chances of maintaining a stable and satisfying marriage. In fact, personality traits are some of the most powerful predictors of long-term relationship quality.
This is not to say that we've already figured out everything there is to know about personality traits.

Shots - Health News
Invisibilia: is your personality fixed, or can you change who you are.
For example, we know that personality change can happen, that it usually happens gradually, and that it's usually for the better. But we don't fully understand the causes of personality change just yet.
Research by Brent Roberts, Joshua Jackson, Wiebke Bleidorn and others highlights the importance of social roles . When we invest in a role that calls for particular kinds of behavior, such as a job that calls for being hard-working and responsible, then over time those behaviors tend to become integrated into our personality.
A 2015 study by Nathan Hudson and Chris Fraley indicates that some people may even be able to intentionally change their own personality through sustained personal effort and careful goal-setting. A study of mine published last year, and another by Jule Specht, suggest that positive personality changes accelerate when people are leading meaningful and satisfying lives.
So although we now know a lot more about personality than we did even a few years ago, we certainly don't know everything. The nature, development and consequences of personality traits remain hot topics of research, and we're learning new things all the time. Stay tuned.
Christopher Soto is an associate professor of psychology at Colby College and a member of the executive board of the Association for Research in Personality . Follow him on Twitter @cjsotomatic.
- personality
- behavioral psychology
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Review Article
- Published: 15 March 2024
The process and mechanisms of personality change
- Joshua J. Jackson ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9490-8890 1 &
- Amanda J. Wright ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8873-9405 2
Nature Reviews Psychology volume 3 , pages 305–318 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
1090 Accesses
1 Citations
208 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Human behaviour
- Personality
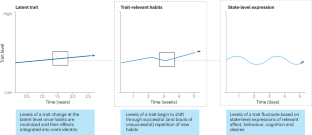
Although personality is relatively stable across the lifespan, there is also ample evidence that it is malleable. This potential for change is important because many individuals want to change aspects of their personality and because personality influences important life outcomes. In this Review, we examine the mechanisms responsible for intentional and naturally occurring changes in personality. We discuss four mechanisms — preconditions, triggers, reinforcers and integrators — that are theorized to produce effective change, as well as the forces that promote stability, thereby thwarting enduring changes. Although these mechanisms are common across theories of personality development, the empirical evidence is mixed and inconclusive. Personality change is most likely to occur gradually over long timescales but abrupt, transformative changes are possible when change is deliberately attempted or as a result of biologically mediated mechanisms. When change does occur, it is often modest in scale. Ultimately, it is difficult to cultivate a completely different personality, but small changes are possible.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
55,14 € per year
only 4,60 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Disentangling the personality pathways to well-being

Individual and generational value change in an adult population, a 12-year longitudinal panel study
Personality beyond taxonomy
Hudson, N. W. & Roberts, B. W. Goals to change personality traits: concurrent links between personality traits, daily behavior, and goals to change oneself. J. Res. Personal. 53 , 68–83 (2014).
Google Scholar
Beck, E. D. & Jackson, J. J. A mega-analysis of personality prediction: robustness and boundary conditions. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 122 , 523–553 (2022).
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Soto, C. J. How replicable are links between personality traits and consequential life outcomes? The life outcomes of personality replication project. Psychol. Sci. 30 , 711–727 (2019).
PubMed Google Scholar
Bleidorn, W. et al. Personality stability and change: a meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Psychol. Bull. 148 , 588–619 (2022).
Wright, A. J. & Jackson, J. J. Are some people more consistent? Examining the stability and underlying processes of personality profile consistency. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 124 , 1314–1337 (2023).
Bleidorn, W. et al. The policy relevance of personality traits. Am. Psychol. 74 , 1056–1067 (2019). This paper highlights the importance of intervening on personality traits.
Bleidorn, W., Hopwood, C. J. & Lucas, R. E. Life events and personality trait change. J. Pers. 86 , 83–96 (2018).
Bühler, J. L. et al. Life events and personality change: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Personal. https://doi.org/10.1177/08902070231190219 (2023).
Allemand, M. & Flückiger, C. Personality change through digital-coaching interventions. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 31 , 41–48 (2022). This paper provides an overview of a successful digital coaching intervention.
Allemand, M. & Flückiger, C. Changing personality traits: some considerations from psychotherapy process–outcome research for intervention efforts on intentional personality change. J. Psychother. Integr. 27 , 476–494 (2017). This broad theoretical overview on how to intervene to change personality borrows from ideas developed in psychotherapy.
Geukes, K., Zalk, M. & Back, M. D. Understanding personality development: an integrative state process model. Int. J. Behav. Dev. 42 , 43–51 (2018). This paper presents an innovative theoretical model on how personality develops.
Hennecke, M., Bleidorn, W., Denissen, J. J. A. & Wood, D. A three-part framework for self-regulated personality development across adulthood. Eur. J. Personal. 28 , 289–299 (2014). This article presents a theoretical model of how personality develops through the lens of self-regulation.
Wrzus, C. & Roberts, B. W. Processes of personality development in adulthood: the TESSERA framework. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Rev. 21 , 253–277 (2017). This article provides a detailed process view of the many potential intervening processes that result in personality change.
Baumert, A. et al. Integrating personality structure, personality process, and personality development. Eur. J. Personal. 31 , 503–528 (2017).
Roberts, B. W. & Jackson, J. J. Sociogenomic personality psychology. J. Pers. 76 , 1523–1544 (2008).
Roberts, B. W. A revised sociogenomic model of personality traits. J. Pers. 86 , 23–35 (2018).
Magidson, J. F., Roberts, B. W., Collado-Rodriguez, A. & Lejuez, C. W. Theory-driven intervention for changing personality: expectancy value theory, behavioral activation, and conscientiousness. Dev. Psychol. 50 , 1442 (2014). This article presents a therapy-informed theoretical account of the personality change process.
Roberts, B. W. & Caspi, A. in Understanding Human Development (eds Staudinger, U. M. & Lindenberger, U.) 183–214 (Springer, 2003). This chapter reviews the types of process that result in change and consistency in passive longitudinal studies.
Roberts, B. W. & Nickel, L. B. in Handbook of Personality Theory and Research (eds John, O. & Robins, R. W.) 259–283 (Guilford, 2021).
Specht, J. et al. What drives adult personality development? A comparison of theoretical perspectives and empirical evidence. Eur. J. Personal. 28 , 216–230 (2014). This article provides an overview of the predominant theoretical models of personality development.
Scarr, S. & McCartney, K. How people make their own environments: a theory of genotype → environment effects. Child. Dev. 54 , 424–435 (1983).
Briley, D. A. & Tucker-Drob, E. M. Genetic and environmental continuity in personality development: a meta-analysis. Psychol. Bull. 140 , 1303–1331 (2014).
Roberts, B. W. & Yoon, H. J. Personality psychology. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 73 , 489–516 (2022).
Wilt, J. & Revelle, W. Affect, behaviour, cognition and desire in the Big Five: an analysis of item content and structure. Eur. J. Personal. 29 , 478–497 (2015).
Stieger, M. et al. Becoming more conscientious or more open to experience? Effects of a two‐week smartphone‐based intervention for personality change. Eur. J. Personal. 34 , 345–366 (2020).
Rosenberg, E. L. Levels of analysis and the organization of affect. Rev. Gen. Psychol. 2 , 247–270 (1998).
Roberts, B. W. & Pomerantz, E. M. On traits, situations, and their integration: a developmental perspective. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Rev. 8 , 402–416 (2004). This article presents one of the most successful personality interventions.
Hooker, K. & McAdams, D. P. Personality reconsidered: a new agenda for aging research. J. Gerontol. B 58 , 296–304 (2003).
Terracciano, A., Stephan, Y., Luchetti, M. & Sutin, A. R. Cognitive impairment, dementia, and personality stability among older adults. Assessment 25 , 336–347 (2018).
Caselli, R. J. et al. Personality changes during the transition from cognitive health to mild cognitive impairment. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 66 , 671–678 (2018).
Robins Wahlin, T.-B. & Byrne, G. J. Personality changes in Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiat. 26 , 1019–1029 (2011).
Tang, T. Z. et al. Personality change during depression treatment: a placebo-controlled trial. Arch. Gen. Psychiat. 66 , 1322–1330 (2009).
Quilty, L. C., Meusel, L.-A. C. & Bagby, R. M. Neuroticism as a mediator of treatment response to SSRIs in major depressive disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 111 , 67–73 (2008).
Max, J. E. et al. Predictors of personality change due to traumatic brain injury in children and adolescents in the first six months after injury. J. Am. Acad. Child. Adolesc. Psychiat. 44 , 434–442 (2005).
Chapman, B. P., Hampson, S. & Clarkin, J. Personality-informed interventions for healthy aging: conclusions from a national institute on aging workgroup. Dev. Psychol. 50 , 1426–1441 (2014).
Wood, W. & Rünger, D. Psychology of habit. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 67 , 289–314 (2016).
Weiss, B., Miller, J. D., Carter, N. T. & Keith Campbell, W. Examining changes in personality following shamanic ceremonial use of ayahuasca. Sci. Rep. 11 , 6653 (2021).
Owens, M. et al. Habitual behavior as a mediator between food-related behavioral activation and change in symptoms of depression in the MooDFOOD trial. Clin. Psychol. Sci. 9 , 649–665 (2021).
Martell, C. R., Addis, M. E. & Jacobson, N. S. Depression in Context: Strategies for Guided Action (W W Norton & Co, 2001).
Watkins, E. R. & Nolen-Hoeksema, S. A habit–goal framework of depressive rumination. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 123 , 24–34 (2014).
Lally, P. & Gardner, B. Promoting habit formation. Health Psychol. Rev. 7 , 137–158 (2013).
Denissen, J. J. A., van Aken, M. A. G., Penke, L. & Wood, D. Self‐regulation underlies temperament and personality: an integrative developmental framework. Child. Dev. Perspect. 7 , 255–260 (2013).
Lally, P., van Jaarsveld, C. H. M., Potts, H. W. W. & Wardle, J. How are habits formed: modelling habit formation in the real world. Eur. J. Soc. Psychol. 40 , 998–1009 (2010).
Danner, U. N., Aarts, H. & de Vries, N. K. Habit vs. intention in the prediction of future behaviour: the role of frequency, context stability and mental accessibility of past behaviour. Br. J. Soc. Psychol. 47 , 245–265 (2008).
Wood, W. & Neal, D. T. A new look at habits and the habit–goal interface. Psychol. Rev. 114 , 843–863 (2007).
Fleeson, W. Toward a structure- and process-integrated view of personality: traits as density distributions of states. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 80 , 1011–1027 (2001).
Eid, M. & Diener, E. Global judgments of subjective well-being: situational variability and long-term stability. Soc. Indic. Res. 65 , 245–277 (2004).
Geukes, K., Nestler, S., Hutteman, R., Küfner, A. C. P. & Back, M. D. Trait personality and state variability: predicting individual differences in within- and cross-context fluctuations in affect, self-evaluations, and behavior in everyday life. J. Res. Personal. 69 , 124–138 (2017).
Reitz, A. K. Self‐esteem development and life events: a review and integrative process framework. Soc. Personal. Psychol. Compass 16 , 12709 (2022).
Stieger, M. et al. Changing personality traits with the help of a digital personality change intervention. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 118 , (2021).
Hampson, S. E. Personality processes: mechanisms by which personality traits ‘get outside the skin’. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 63 , 315–339 (2012).
Specht, J., Egloff, B. & Schmukle, S. C. Examining mechanisms of personality maturation: the impact of life satisfaction on the development of the big five personality traits. Soc. Psychol. Personal. Sci. 4 , 181–189 (2013).
Hudson, N. W. Does successfully changing personality traits via intervention require that participants be autonomously motivated to change? J. Res. Personal. 95 , 104160 (2021).
Borghuis, J. et al. Longitudinal associations between trait neuroticism and negative daily experiences in adolescence. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 118 , 348–363 (2020).
van Zalk, M. H. W., Nestler, S., Geukes, K., Hutteman, R. & Back, M. D. The codevelopment of extraversion and friendships: bonding and behavioral interaction mechanisms in friendship networks. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 118 , 1269–1290 (2020).
Quintus, M., Egloff, B. & Wrzus, C. Daily life processes predict long-term development in explicit and implicit representations of Big Five traits: testing predictions from the TESSERA (Triggering situations, Expectancies, States and State Expressions, and ReActions) framework. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 120 , 1049–1073 (2021).
Wrzus, C., Luong, G., Wagner, G. G. & Riediger, M. Longitudinal coupling of momentary stress reactivity and trait neuroticism: specificity of states, traits, and age period. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 121 , 691–706 (2021).
Hudson, N. W., Briley, D. A., Chopik, W. J. & Derringer, J. You have to follow through: attaining behavioral change goals predicts volitional personality change. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 117 , 839–857 (2019).
Roberts, B. W. & Wood, D. in Handbook of Personality Development (eds Mroczek, D. K. & Little, T. D.) 11–39 (Pyschology Press, 2006).
Lehnart, J., Neyer, F. J. & Eccles, J. Long-term effects of social investment: the case of partnering in young adulthood. J. Pers. 78 , 639–670 (2010).
Helson, R., Kwan, V. S. Y., John, O. P. & Jones, C. The growing evidence for personality change in adulthood: findings from research with personality inventories. J. Res. Personal. 36 , 287–306 (2002).
Caspi, A. & Roberts, B. W. in Handbook of Personality: Theory and Research 2nd edn (eds John, O. P. & Robins, R. W.) 300–326 (Guilford Press, 1999).
Sarbin, T. R. The dangerous individual: an outcome of social identity transformations. Br. J. Criminol. 7 , 285–295 (1967).
Roberts, B. W., Wood, D. & Smith, J. L. Evaluating five factor theory and social investment perspectives on personality trait development. J. Res. Personal. 39 , 166–184 (2005).
Bollich-Ziegler, K. L., Beck, E. D., Hill, P. L. & Jackson, J. J. Do correctional facilities correct our youth?: effects of incarceration and court-ordered community service on personality development. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 121 , 894–913 (2021).
Lücke, A. J., Quintus, M., Egloff, B. & Wrzus, C. You can’t always get what you want: the role of change goal importance, goal feasibility and momentary experiences for volitional personality development. Eur. J. Personal. 35 , 690–709 (2021).
Gallagher, P., Fleeson, W. & Hoyle, R. A self-regulatory mechanism for personality trait stability: contra-trait effort. Soc. Psychol. Personal. Sci. 2 , 333–342 (2011).
Verplanken, B. & Orbell, S. Attitudes, habits, and behavior change. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 73 , 327–352 (2022).
Hudson, N. W., Fraley, R. C., Briley, D. A. & Chopik, W. J. Your personality does not care whether you believe it can change: beliefs about whether personality can change do not predict trait change among emerging adults. Eur. J. Personal. 35 , 340–357 (2021).
Macnamara, B. N. & Burgoyne, A. P. Do growth mindset interventions impact students’ academic achievement? A systematic review and meta-analysis with recommendations for best practices. Psychol. Bull. 149 , 133–173 (2023).
Quoidbach, J., Gilbert, D. T. & Wilson, T. D. The end of history illusion. Science 339 , 96–98 (2013).
Williams, P. G., Smith, T. W., Gunn, H. E. & Uchino, B. N. in The Handbook of Stress Science: Biology, Psychology, and Health 231–245 (Springer, 2011).
Bolger, N., DeLongis, A., Kessler, R. C. & Schilling, E. A. Effects of daily stress on negative mood. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 57 , 808–818 (1989).
Mroczek, D. K. & Almeida, D. M. The effect of daily stress, personality, and age on daily negative affect. J. Pers. 72 , 355–378 (2004).
Cattran, C. J., Oddy, M., Wood, R. L. & Moir, J. F. Post-injury personality in the prediction of outcome following severe acquired brain injury. Brain Inj. 25 , 1035–1046 (2011).
James, B. D. & Bennett, D. A. Causes and patterns of dementia: an update in the era of redefining Alzheimer’s disease. Annu. Rev. Public. Health 40 , 65–84 (2019).
Denissen, J. J. A., Luhmann, M., Chung, J. M. & Bleidorn, W. Transactions between life events and personality traits across the adult lifespan. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 116 , 612–633 (2019).
Specht, J., Egloff, B. & Schmukle, S. C. Stability and change of personality across the life course: the impact of age and major life events on mean-level and rank-order stability of the Big Five. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 101 , 862–882 (2011).
Hudson, N. W. & Roberts, B. W. Social investment in work reliably predicts change in conscientiousness and agreeableness: a direct replication and extension of Hudson, Roberts, and Lodi-Smith (2012). J. Res. Personal. 60 , 12–23 (2016).
Hutteman, R., Hennecke, M., Orth, U., Reitz, A. K. & Specht, J. Developmental tasks as a framework to study personality development in adulthood and old age. Eur. J. Personal. 28 , 267–278 (2014).
Roberts, B. W. et al. A systematic review of personality trait change through intervention. Psychol. Bull. 143 , 117–141 (2017).
West, P. & Sweeting, H. Fifteen, female and stressed: changing patterns of psychological distress over time. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiat. 44 , 399–411 (2003).
Koval, P. et al. Emotion regulation in everyday life: mapping global self-reports to daily processes. Emotion 23 , 357–374 (2023).
Brockman, R., Ciarrochi, J., Parker, P. & Kashdan, T. Emotion regulation strategies in daily life: mindfulness, cognitive reappraisal and emotion suppression. Cogn. Behav. Ther. 46 , 91–113 (2017).
Rauthmann, J. F., Sherman, R. A. & Funder, D. C. Principles of situation research: towards a better understanding of psychological situations. Eur. J. Personal. 29 , 363–381 (2015).
Kuper, N. et al. Individual differences in contingencies between situation characteristics and personality states. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 123 , 1166–1198 (2022).
Mischel, W. Toward an integrative science of the person. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 55 , 1–22 (2004).
Beck, E. D. & Jackson, J. J. Personalized prediction of behaviors and experiences: an idiographic person–situation test. Psychol. Sci. 33 , 1767–1782 (2022).
Barlow, D. H. et al. The unified protocol for transdiagnostic treatment of emotional disorders compared with diagnosis-specific protocols for anxiety disorders: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiat. 74 , 875–884 (2017).
Sauer-Zavala, S. et al. Countering emotional behaviors in the treatment of borderline personality disorder. Personal. Disord. Theory Res. Treat. 11 , 328–338 (2020).
Aarts, H. & Dijksterhuis, A. Habits as knowledge structures: automaticity in goal-directed behavior. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 78 , 53–63 (2000).
Neal, D. T., Wood, W., Labrecque, J. S. & Lally, P. How do habits guide behavior? Perceived and actual triggers of habits in daily life. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 48 , 492–498 (2012).
Fehr, E. & Fischbacher, U. Social norms and human cooperation. Trends Cogn. Sci. 8 , 185–190 (2004).
Bicchieri, C. The Grammar of Society: The Nature and Dynamics of Social Norms xvi, 260 (Cambridge Univ. Press, 2006).
Fehr, E. & Schurtenberger, I. Normative foundations of human cooperation. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2 , 458–468 (2018).
Morris, M. W., Hong, Y., Chiu, C. & Liu, Z. Normology: integrating insights about social norms to understand cultural dynamics. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 129 , 1–13 (2015).
Cialdini, R. B. & Trost, M. R. Social influence: social norms, conformity and compliance. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 55 , 591–621 (1998).
Dempsey, R. C., McAlaney, J. & Bewick, B. M. A critical appraisal of the social norms approach as an interventional strategy for health-related behavior and attitude change. Front. Psychol. 9 , 2180 (2018).
Hoff, K. A., Einarsdóttir, S., Chu, C., Briley, D. A. & Rounds, J. Personality changes predict early career outcomes: discovery and replication in 12-year longitudinal studies. Psychol. Sci. 32 , 64–79 (2021).
Sutin, A. R., Costa, P. T., Miech, R. & Eaton, W. W. Personality and career success: concurrent and longitudinal relations. Eur. J. Personal. 23 , 71–84 (2009).
Bleidorn, W. & Hopwood, C. J. A motivational framework of personality development in late adulthood. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 55 , 101731 (2024). This theoretical account of personality development focuses on motivational aspects to explain normative ageing.
Raison, C. L., Capuron, L. & Miller, A. H. Cytokines sing the blues: inflammation and the pathogenesis of depression. Trends Immunol. 27 , 24–31 (2006).
Miller, G. E., Rohleder, N. & Cole, S. W. Chronic interpersonal stress predicts activation of pro- and anti-inflammatory signaling pathways 6 months later. Psychosom. Med. 71 , 57–62 (2009).
McEvoy, J. W. et al. Relationship of cigarette smoking with inflammation and subclinical vascular disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 35 , 1002–1010 (2015).
Deary, I. J. et al. Age-associated cognitive decline. Br. Med. Bull. 92 , 135–152 (2009).
Salthouse, T. A. When does age-related cognitive decline begin? Neurobiol. Aging 30 , 507–514 (2009).
Boyle, P. A. et al. Much of late life cognitive decline is not due to common neurodegenerative pathologies. Ann. Neurol. 74 , 478–489 (2013).
Balsis, S., Carpenter, B. D. & Storandt, M. Personality change precedes clinical diagnosis of dementia of the Alzheimer type. J. Gerontol. B 60 , P98–P101 (2005).
Terracciano, A., Stephan, Y., Luchetti, M., Albanese, E. & Sutin, A. R. Personality traits and risk of cognitive impairment and dementia. J. Psychiat. Res. 89 , 22–27 (2017).
Sala, G. et al. Near and far transfer in cognitive training: a second-order meta-analysis. Collabra Psychol . 5 , https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/9efqd (2019).
Olaru, G. et al. Personality change through a digital-coaching intervention: using measurement invariance testing to distinguish between trait domain, facet, and nuance change. Eur. J. Personal. 38 , https://doi.org/10.1177/08902070221145088 (2022).
Moreau, D. How malleable are cognitive abilities? A critical perspective on popular brief interventions. Am. Psychol. 77 , 409–423 (2022).
Boyd, E. M. & Fales, A. W. Reflective learning: key to learning from experience. J. Humanist. Psychol. 23 , 99–117 (1983).
Stedmon, J. & Dallos, R. Reflective Practice in Psychotherapy and Counselling (McGraw-Hill Education, 2009).
Keefe, J. R. et al. Reflective functioning and its potential to moderate the efficacy of manualized psychodynamic therapies versus other treatments for borderline personality disorder. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 91 , 50–56 (2023).
Lenhausen, M. R., Bleidorn, W. & Hopwood, C. J. Effects of reference group instructions on big five trait scores. Assessment 31 , https://doi.org/10.1177/10731911231175850 (2023).
Oltmanns, J. R., Jackson, J. J. & Oltmanns, T. F. Personality change: longitudinal self–other agreement and convergence with retrospective reports. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 118 , 1065–1079 (2020).
Credé, M., Bashshur, M. & Niehorster, S. Reference group effects in the measurement of personality and attitudes. J. Pers. Assess. 92 , 390–399 (2010).
Wrzus, C., Quintus, M. & Egloff, B. Age and context effects in personality development: a multimethod perspective. Psychol. Aging 38 , 1–16 (2023).
Jackson, J. J., Connolly, J. J., Garrison, S. M., Leveille, M. M. & Connolly, S. L. Your friends know how long you will live: a 75-year study of peer-rated personality traits. Psychol. Sci. 26 , 335–340 (2015).
Wright, A. J. et al. Prospective self- and informant-personality associations with inflammation, health behaviors, and health indicators. Health Psychol. 41 , 121–133 (2022).
Smith, T. W. et al. Associations of self-reports versus spouse ratings of negative affectivity, dominance, and affiliation with coronary artery disease: where should we look and who should we ask when studying personality and health? Health Psychol. 27 , 676–684 (2008).
Lenhausen, M., van Scheppingen, M. A. & Bleidorn, W. Self–other agreement in personality development in romantic couples. Eur. J. Personal. 35 , 797–813 (2021).
Rothman, A. J., Sheeran, P. & Wood, W. Reflective and automatic processes in the initiation and maintenance of dietary change. Ann. Behav. Med. 38 , s4–s17 (2009).
Caspi, A. & Roberts, B. W. Personality development across the life course: the argument for change and continuity. Psychol. Inq. 12 , 49–66 (2001).
Seger, C. A. Implicit learning. Psychol. Bull. 115 , 163–196 (1994).
Reber, P. J. The neural basis of implicit learning and memory: a review of neuropsychological and neuroimaging research. Neuropsychologia 51 , 2026–2042 (2013).
Back, M. D. & Nestler, S. in Reflective and Impulsive Determinants of Human Behavior 137–154 (Routledge/Taylor & Francis Group, 2017).
Hofmann, W., Friese, M. & Roefs, A. Three ways to resist temptation: the independent contributions of executive attention, inhibitory control, and affect regulation to the impulse control of eating behavior. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 45 , 431–435 (2009).
Gassmann, D. & Grawe, K. General change mechanisms: the relation between problem activation and resource activation in successful and unsuccessful therapeutic interactions. Clin. Psychol. Psychother. 13 , 1–11 (2006).
Anusic, I. & Schimmack, U. Stability and change of personality traits, self-esteem, and well-being: introducing the meta-analytic stability and change model of retest correlations. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 110 , 766–781 (2016).
Terracciano, A., McCrae, R. R. & Costa, P. T. Jr Intra-individual change in personality stability and age. J. Res. Personal. 44 , 31–37 (2010).
Jackson, J. J., Beck, E. D. & Mike, A. in Handbook of Personality: Theory and Research 4th edn, 793–805 (The Guilford Press, 2021). This article provides an overview of interventions that attempt to change constructs related to personality.
Headey, B. Life goals matter to happiness: a revision of set-point theory. Soc. Indic. Res. 86 , 213–231 (2007).
Clark, A. E., Diener, E., Georgellis, Y. & Lucas, R. E. Lags and leads in life satisfaction: a test of the baseline hypothesis. Econ. J. 118 , F222–F243 (2008).
Schwaba, T. & Bleidorn, W. Personality trait development across the transition to retirement. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 116 , 651–665 (2019).
Wright, A. J. & Jackson, J. J. The associations between life events and person-centered personality consistency. J. Pers. 92 , 162–179 (2024).
Asselmann, E. & Specht, J. Testing the social investment principle around childbirth: little evidence for personality maturation before and after becoming a parent. Eur. J. Personal. 35 , 85–102 (2020).
Denissen, J. J. A., Ulferts, H., Lüdtke, O., Muck, P. M. & Gerstorf, D. Longitudinal transactions between personality and occupational roles: a large and heterogeneous study of job beginners, stayers, and changers. Dev. Psychol. 50 , 1931–1942 (2014).
Roberts, B. W., Wood, D. & Caspi, A. in Handbook of Personality: Theory and Research 3rd edn, 375–398 (The Guilford Press, 2008).
Roberts, B. W. Personality development and organizational behavior. Res. Organ. Behav. 27 , 1–40 (2006).
Schneider, B., Smith, D. B., Taylor, S. & Fleenor, J. Personality and organizations: a test of the homogeneity of personality hypothesis. J. Appl. Psychol. 83 , 462–470 (1998).
Caspi, A., Roberts, B. W. & Shiner, R. L. Personality development: stability and change. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 56 , 453–484 (2005).
Mühlig-Versen, A., Bowen, C. E. & Staudinger, U. M. Personality plasticity in later adulthood: contextual and personal resources are needed to increase openness to new experiences. Psychol. Aging 27 , 855–866 (2012).
Baumeister, R. F., Vohs, K. D. & Tice, D. M. The strength model of self-control. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 16 , 351–355 (2007).
Buyalskaya, A. et al. What can machine learning teach us about habit formation? Evidence from exercise and hygiene. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 120 , e2216115120 (2023).
Jackson, J. J., Hill, P. L., Payne, B. R., Roberts, B. W. & Stine-Morrow, E. A. Can an old dog learn (and want to experience) new tricks? Cognitive training increases openness to experience in older adults. Psychol. Aging 27 , 286–292 (2012).
Beck, E. D. & Jackson, J. J. Idiographic personality coherence: a quasi experimental longitudinal ESM study. Eur. J. Personal. 36 , 391–412 (2022).
Caspi, A. & Moffitt, T. E. When do individual differences matter? A paradoxical theory of personality coherence. Psychol. Inq. 4 , 247–271 (1993).
Vygotsky, L. S. Mind in Society: Development of Higher Psychological Processes (Harvard Univ. Press, 1978).
Foa, E. B. & McLean, C. P. The efficacy of exposure therapy for anxiety-related disorders and its underlying mechanisms: the case of OCD and PTSD. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 12 , 1–28 (2016).
Swann Jr, W. B., Rentfrow, P. J. & Guinn, J. S. in Handbook of Self and Identity, 367–383 (The Guilford Press, 2003).
Headey, B. & Wearing, A. Personality, life events, and subjective well-being: toward a dynamic equilibrium model. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 57 , 731–739 (1989).
Roberts, B. W., Caspi, A. & Moffitt, T. E. Work experiences and personality development in young adulthood. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 84 , 582–593 (2003).
Scollon, C. N. & Diener, E. Love, work, and changes in extraversion and neuroticism over time. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 91 , 1152–1165 (2006).
Lüdtke, O., Roberts, B. W., Trautwein, U. & Nagy, G. A random walk down university avenue: life paths, life events, and personality trait change at the transition to university life. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 101 , 620–637 (2011).
Asselmann, E. & Specht, J. Till death do us part: transactions between losing one’s spouse and the Big Five personality traits. J. Pers. 88 , 659–675 (2020).
Boyce, C. J., Wood, A. M., Daly, M. & Sedikides, C. Personality change following unemployment. J. Appl. Psychol. 100 , 991–1011 (2015).
van Scheppingen, M. A. et al. Personality trait development during the transition to parenthood. Soc. Psychol. Personal. Sci. 7 , 452–462 (2016).
Gnambs, T. & Stiglbauer, B. No personality change following unemployment: a registered replication of Boyce, Wood, Daly, and Sedikides (2015). J. Res. Personal. 81 , 195–206 (2019).
Kammeyer-Mueller, J. D., Judge, T. A. & Piccolo, R. F. Self-esteem and extrinsic career success: test of a dynamic model. Appl. Psychol. Int. Rev. 57 , 204–224 (2008).
Asselmann, E. & Specht, J. Personality maturation and personality relaxation: differences of the Big Five personality traits in the years around the beginning and ending of working life. J. Pers. 89 , 1126–1142 (2021).
Lenhausen, M. R., Hopwood, C. J. & Bleidorn, W. Nature and impact of reference group effects in personality assessment data. J. Pers. Assess. 105 , 581–589 (2023).
Vaidya, J. G., Gray, E. K., Haig, J. R., Mroczek, D. K. & Watson, D. Differential stability and individual growth trajectories of big five and affective traits during young adulthood. J. Pers. 76 , 267–304 (2008).
Haehner, P. et al. Perception of major life events and personality trait change. Eur. J. Personal. 37 , 524–542 (2022).
Beck, E. D. & Jackson, J. J. Detecting idiographic personality change. J. Pers. Assess. 104 , 467–483 (2022).
Jackson, J. J. & Beck, E. D. Personality development beyond the mean: do life events shape personality variability, structure, and ipsative continuity? J. Gerontol. B 76 , 20–30 (2021).
Haehner, P., Pfeifer, L. S., Fassbender, I. & Luhmann, M. Are changes in the perception of major life events associated with changes in subjective well-being? J. Res. Personal. 102 , 104321 (2023).
Goodwin, R., Polek, E. & Bardi, A. The temporal reciprocity of values and beliefs: a longitudinal study within a major life transition. Eur. J. Personal. 26 , 360–370 (2012).
Zimmermann, J. & Neyer, F. J. Do we become a different person when hitting the road? Personality development of sojourners. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 105 , 515–530 (2013).
Jackson, J. J., Thoemmes, F., Jonkmann, K., Lüdtke, O. & Trautwein, U. Military training and personality trait development: does the military make the man, or does the man make the military? Psychol. Sci. 23 , 270–277 (2012).
Nissen, A. T., Bleidorn, W., Ericson, S. & Hopwood, C. J. Selection and socialization effects of studying abroad. J. Pers. 90 , 1021–1038 (2022).
van Agteren, J. et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of psychological interventions to improve mental wellbeing. Nat. Hum. Behav. 5 , 631–652 (2021).
Weiss, L. A., Westerhof, G. J. & Bohlmeijer, E. T. Can we increase psychological well-being? The effects of interventions on psychological well-being: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS ONE 11 , e0158092 (2016).
Jensen, S. E. et al. Cognitive–behavioral stress management and psychological well-being in HIV+ racial/ethnic-minority women with human papillomavirus. Health Psychol. 32 , 227–230 (2013).
Howells, A., Ivtzan, I. & Eiroa-Orosa, F. J. Putting the ‘app’ in happiness: a randomised controlled trial of a smartphone-based mindfulness intervention to enhance wellbeing. J. Happiness Stud. 17 , 163–185 (2016).
Dwyer, R. J. & Dunn, E. W. Wealth redistribution promotes happiness. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 119 , 2211123119 (2022).
White, C. A., Uttl, B. & Holder, M. D. Meta-analyses of positive psychology interventions: the effects are much smaller than previously reported. PLoS ONE 14 , 0216588 (2019).
Friese, M., Frankenbach, J., Job, V. & Loschelder, D. D. Does self-control training improve self-control? A meta-analysis. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. J. Assoc. Psychol. Sci. 12 , 1077–1099 (2017).
Sander, J., Schmiedek, F., Brose, A., Wagner, G. G. & Specht, J. Long-term effects of an extensive cognitive training on personality development. J. Pers. 85 , 454–463 (2017).
Hyun, M.-S., Chung, H.-I. C., De Gagne, J. C. & Kang, H. S. The effects of cognitive-behavioral therapy on depression, anger, and self-control for Korean soldiers. J. Psychosoc. Nurs. Ment. Health Serv. 52 , 22–28 (2014).
Stieger, M., Allemand, M. & Lachman, M. E. Effects of a digital self-control intervention to increase physical activity in middle-aged adults. J. Health Psychol. 28 , 984–996 (2023).
Cerino, E. S., Hooker, K., Goodrich, E. & Dodge, H. H. Personality moderates intervention effects on cognitive function: a 6-week conversation-based intervention. Gerontologist 60 , 958–967 (2020).
LeBouthillier, D. M. & Asmundson, G. J. G. The efficacy of aerobic exercise and resistance training as transdiagnostic interventions for anxiety-related disorders and constructs: a randomized controlled trial. J. Anxiety Disord. 52 , 43–52 (2017).
Barrett, E. L., Newton, N. C., Teesson, M., Slade, T. & Conrod, P. J. Adapting the personality‐targeted preventure program to prevent substance use and associated harms among high‐risk Australian adolescents. Early Interv. Psychiat. 9 , 308–315 (2015).
Fishbein, J. N., Haslbeck, J. & Arch, J. J. Network intervention analysis of anxiety-related outcomes and processes of acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT) for anxious cancer survivors. Behav. Res. Ther . 162 , (2023).
Bateman, A. & Fonagy, P. A randomized controlled trial of a mentalization-based intervention (MBT-FACTS) for families of people with borderline personality disorder. Personal. Disord. Theory Res. Treat. 10 , 70–79 (2019).
Sauer-Zavala, S., Wilner, J. G. & Barlow, D. H. Addressing neuroticism in psychological treatment. Personal. Disord. Theory Res. Treat. 8 , 191–198 (2017).
McMurran, M., Charlesworth, P., Duggan, C. & McCarthy, L. Controlling angry aggression: a pilot group intervention with personality disordered offenders. Behav. Cogn. Psychother. 29 , 473–483 (2001).
Wells-Parker, E., Dill, P., Williams, M. & Stoduto, G. Are depressed drinking/driving offenders more receptive to brief intervention? Addict. Behav. 31 , 339–350 (2006).
Fisher, B. M. The mediating role of self-concept and personality dimensions on factors influencing the rehabilitative treatment of violent male youthful offenders. (ProQuest Information & Learning, 2002).
Bailey, D. H., Duncan, G. J., Cunha, F., Foorman, B. R. & Yeager, D. S. Persistence and fade-out of educational-intervention effects: mechanisms and potential solutions. Psychol. Sci. Public. Interest. 21 , 55–97 (2020).
Hudson, N. W. & Fraley, R. C. Volitional personality trait change: can people choose to change their personality traits? J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 109 , 490–507 (2015).
Allemand, M. & Martin, M. On correlated change in personality. Eur. Psychol. 21 , 237–253 (2016).
Luhmann, M., Fassbender, I., Alcock, M. & Haehner, P. A dimensional taxonomy of perceived characteristics of major life events. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 121 , 633–668 (2021).
Boyatzis, R. E. & Akrivou, K. The ideal self as the driver of intentional change. J. Manag. Dev. 25 , 624–642 (2006).
Dweck, C. S. Can personality be changed? The role of beliefs in personality and change. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 17 , 391–394 (2008).
Baumeister, R. F. in Can Personality Change? (eds Heatherton, T. F. & Weinberger, J. L.) 281–297 (American Psychological Association, 1994).
Hudson, N. W. & Fraley, R. C. in Personality Development Across the Lifespan (ed. Specht, J.) 555–571 (Academic Press, 2017).
Roberts, B. W., O’Donnell, M. & Robins, R. W. Goal and personality trait development in emerging adulthood. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 87 , 541–550 (2004).
Winter, D. G., John, O. P., Stewart, A. J., Klohnen, E. C. & Duncan, L. E. Traits and motives: toward an integration of two traditions in personality research. Psychol. Rev. 105 , 230–250 (1998).
Barrick, M. R. & Mount, M. K. The big five personality dimensions and job performance: a meta-analysis. Pers. Psychol. 44 , 1–26 (1991).
Burke, P. J. Identity change. Soc. Psychol. Q. 69 , 81–96 (2006).
Funder, D. C. in Handbook of Personality: Theory and Research (eds John, O. P., Robins, R. W. & Pervin, L. A.) 568–580 (The Guilford Press, 2008).
Kandler, C. & Zapko-Willmes, A. in Personality Development Across the Lifespan (ed. Specht, J.) 101–115 (Academic Press, 2017).
Lodi-Smith, J. & Roberts, B. W. Social investment and personality: a meta-analysis of the relationship of personality traits to investment in work, family, religion, and volunteerism. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Rev. 11 , 68–86 (2007).
McAdams, D. P. & Pals, J. L. A new big five: fundamental principles for an integrative science of personality. Am. Psychol. 61 , 204–217 (2006).
Kandler, C. Nature and nurture in personality development: the case of neuroticism and extraversion. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 21 , 290–296 (2012).
McCrae, R. R. & Costa, P. T. in Handbook of Personality: Theory and Research (eds John, O. P. et al.) 150–181 (The Guilford Press, 2008).
Bleidorn, W. et al. Personality maturation around the world: a cross-cultural examination of social-investment theory. Psychol. Sci. 24 , 2530–2540 (2013).
Ardichvili, A., Cardozo, R. & Ray, S. A theory of entrepreneurial opportunity identification and development. J. Bus. Ventur. 18 , 105–123 (2003).
Kazdin, A. E. Behavior Modification in Applied Settings 7th edn (Waveland Press, 2012).
King, L. A. The hard road to the good life: the happy, mature person. J. Humanist Psychol. 41 , 51–72 (2001).
Ozbay, F. et al. Social support and resilience to stress. Psychiat. Edgmont 4 , 35–40 (2007).
Kandler, C. et al. Sources of cumulative continuity in personality: a longitudinal multiple-rater twin study. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 98 , 995–1008 (2010).
Bem, D. J. in Advances in Experimental Social Psychology Vol. 6 (ed. Berkowitz, L.) 1–62 (Academic Press, 1972).
Staudinger, U. M. Life reflection: a social–cognitive analysis of life review. Rev. Gen. Psychol. 5 , 148–160 (2001).
Appenzeller, Z. Dialectical behavior therapy and schema therapy for borderline personality disorder: mechanisms of change and assimilative integration. PhD thesis (ProQuest Information & Learning, 2022).
Back, M. D., Schmukle, S. C. & Egloff, B. Predicting actual behavior from the explicit and implicit self-concept of personality. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 97 , 533–548 (2009).
Brandtstädter, J. Personal self-regulation of development: cross-sequential analyses of development-related control beliefs and emotions. Dev. Psychol. 25 , 96–108 (1989).
Krampen, G. Toward an action‐theoretical model of personality. Eur. J. Personal. 2 , 39–55 (1988).
Hogan, R. & Roberts, B. W. A socioanalytic model of maturity. J. Career Assess. 12 , 207–217 (2004).
Arkowitz, H. Toward an integrative perspective on resistance to change. J. Clin. Psychol. 58 , 219–227 (2002).
Fleeson, W., Malanos, A. B. & Achille, N. M. An intraindividual process approach to the relationship between extraversion and positive affect: is acting extraverted as ‘good’ as being extraverted? J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 83 , 1409–1422 (2002).
Swann, W. B., Stein-Seroussi, A. & Giesler, R. B. Why people self-verify. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 62 , 392–401 (1992).
Wood, D. & Wortman, J. Trait means and desirabilities as artifactual and real sources of differential stability of personality traits. J. Personality 80 , 665–701 (2012).
Zelenski, J. M. et al. Personality and affective forecasting: trait introverts underpredict the hedonic benefits of acting extraverted. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 104 , 1092–1108 (2013).
Bradley, G. W. Self-serving biases in the attribution process: a reexamination of the fact or fiction question. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 36 , 56–71 (1978).
Levenson, H. Differentiating among internality, powerful others, and chance. In Research with the Locus of Control Construct (ed. Lefcourt, H. M.) (Academic Press, 1981).
Miller, D. T. Ego involvement and attributions for success and failure. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 34 , 901–906 (1976).
Gunty, A. L. et al. Moderators of the relation between perceived and actual posttraumatic growth. Psychol. Trauma Theory Res. Pract. Policy 3 , 61–66 (2011).
Robins, R. W., Noftle, E. E., Trzesniewski, K. H. & Roberts, B. W. Do people know how their personality has changed? Correlates of perceived and actual personality change in young adulthood. J. Pers. 73 , 489–522 (2005).
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Psychological and Brain Sciences, Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis, MO, USA
Joshua J. Jackson
Department of Psychology, University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
Amanda J. Wright
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
The authors contributed equally to all aspects of the article.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Joshua J. Jackson .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information.
Nature Reviews Psychology thanks Jaap Denissen, Ted Schwaba and Cornelia Wrzus for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Jackson, J.J., Wright, A.J. The process and mechanisms of personality change. Nat Rev Psychol 3 , 305–318 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44159-024-00295-z
Download citation
Accepted : 20 February 2024
Published : 15 March 2024
Issue Date : May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s44159-024-00295-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Can you change your personality?

It has long been believed that people can’t change their personalities, which are largely stable and inherited. But a review of recent research in personality science points to the possibility that personality traits can change through persistent intervention and major life events.
Personality traits, identified as neuroticism, extraversion, openness to experience, agreeableness and conscientiousness, can predict a wide range of important outcomes such as health, happiness and income. Because of this, these traits might represent an important target for policy interventions designed to improve human welfare.
The research, published in the December issue of American Psychologist, is the product of the Personality Change Consortium, an international group of researchers committed to advancing understanding of personality change. The consortium was initiated by Wiebke Bleidorn and Christopher Hopwood, University of California, Davis, professors of psychology who are also co-authors of the latest paper, “The Policy Relevance of Personality Traits.” The paper has 13 other co-authors.
Policy change could be more effective
“In this paper, we present the case that traits can serve both as relatively stable predictors of success and actionable targets for policy changes and interventions,” Bleidorn said.
“Parents, teachers, employers and others have been trying to change personality forever because of their implicit awareness that it is good to make people better people,” Hopwood added.
But now, he said, strong evidence suggests that personality traits are broad enough to account for a wide range of socially important behaviors at levels that surpass known predictors, and that they can change, especially if you catch people at the right age and exert sustained effort. However, these traits also remain relatively stable; thus while they can change, they are not easy to change.
Resources are often invested in costly interventions that are unlikely to work because they are not informed by evidence about personality traits. “For that reason, it would be helpful for public policymakers to think more explicitly about what it takes to change personality to improve personal and public welfare, the costs and benefits of such interventions, and the resources needed to achieve the best outcomes by both being informed by evidence about personality traits and investing more sustained resources and attention toward better understanding personality change,” researchers said.
Why focus on personality traits?
Research has found that a relatively small number of personality traits can account for most of the ways in which people differ from one another. Thus, they are related to a wide range of important life outcomes. These traits are also relatively stable, but changeable with effort and good timing. This combination — broad and enduring, yet changeable — makes them particularly promising targets for large-scale interventions. Both neuroticism and conscientiousness, for example, may represent good intervention targets in young adulthood. And certain interventions — especially those that require persistence and long-term commitment — may be more effective among conscientious, emotionally stable people. It is also important to consider motivational factors, as success is more likely if people are motivated and think change is feasible, researchers said.
Bleidorn and Hopwood said examples of important questions that could be more informed by personality science include: What is the long-term impact of social media and video games? How do we get children to be kinder and work harder at school? How do we help people acculturate to new environments? And, what is the best way to help people age with grace and dignity?
Keep reading

The time traveler: Eddie Cole on affirmative action and…
With affirmative action under attack, historian Eddie Cole ponders the past — his own, and the country’s — as American higher education barrels toward an uncertain future.

State funds development of first-of-its-kind police…
California allocated $6.87 million in its 2023-24 budget to UC Berkeley to develop the Police Records Access Project, a first-of-its-kind, state-wide database of police misconduct and use-of-force…
Greater Good Science Center • Magazine • In Action • In Education
Can Your Personality Change Over Your Lifetime?
When I was 16 years old, I was a pretty outgoing teen with lots of friends and a busy social calendar. I took my academics seriously and was diligent about doing homework. But I also tended to worry a lot and could cry at the drop of a hat.
Now here I am more than 50 years later, and, in many ways, I seem much the same: extraverted and conscientious, but a bit neurotic. Does that mean that my personality hasn’t changed over the last half-century?
Not necessarily. Many of us tend to think of personality as being fixed and unchangeable—the part of you that is inherently who you are. But according to a recent study , while our early personalities may provide a baseline, they are surprisingly malleable as we age.

In this study, researchers had access to unusual survey data. American adolescents had filled out questionnaires about their personalities in the 1960s and then had done so again fifty years later, reporting on personal qualities associated with the “ Big Five ” personality traits:
- Extraversion: How outgoing, social, cheerful, or full of energy and enthusiasm you are in social settings.
- Agreeableness: How warm, friendly, helpful, generous, and tactful you are.
- Emotional stability (or its opposite, neuroticism): How calm, content, and unflappable—versus anxious, angry, jealous, lonely, or insecure—you are.
- Conscientiousness: How organized, efficient, and committed you are to finishing projects or reaching your goals.
- Openness to experience: How curious, adventuresome, and receptive you are to new ideas, emotions, and experiences.
Some of the findings were quite provocative. Most notably, people’s personality traits did not always stay the same over the five decades, with many people showing quite dramatic changes.
“Some of the changes we saw in personality traits over the 50 years were very, very large,” says the lead author of the study, Rodica Damian of the University of Houston. “For emotional stability, conscientiousness, and agreeableness, the changes were one[s] which would be clearly visible to others.”
On the other hand, that didn’t mean that people didn’t stay true to their personality traits over time at all . Coauthor Brent Roberts of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign says that much of our personality does seem to stay the same—just not as much as we might expect. For example, an extraverted teenager like me would have a 63 percent chance of still identifying as an extravert in their 60s, he says.
Why does this matter? Thinking of personality as fixed could lead us to feel like we can never grow, or to dismiss people with certain qualities we don’t like, concerned that change isn’t possible when that’s not the case.
Still, we don’t simply change our personalities in random ways, explain the researchers. What seems to be more consistent over time is the relationship among all of our personality traits. This means that if someone tended to be really conscientious but a bit disagreeable or neurotic early on, they might keep that relative personality profile as they aged, even if some of their traits shifted a bit.
Additionally, the researchers found that adolescents as a group tended to move in a positive direction for particular traits—like emotional stability, conscientiousness, and agreeableness—after 50 years, suggesting a growth in social maturity.
“These attributes of social maturity are good things to acquire, if you want to get along with your spouse and coworkers and stay healthy,” Roberts says.
This finding fits well with some of Roberts’s prior research showing that people experience smaller, incremental personality changes over shorter periods of time. And it helps confirms his theory that personality change is cumulative over our lifespan, likely happens in response to our life experiences, and often leans in a positive, helpful direction.
So, apparently, our personalities are a mix of stable and unstable. Roberts advises parents and teachers to keep that in mind when they try to influence their children to be more responsible or mature. Change, when it happens, occurs gradually rather than all at once, he says, which means we need patience with kids who are growing into themselves.
More on Personality
Explore whether different treatments can change your personality .
Discover how different personalities relate to happiness .
Learn how personality affects the happiness we get from our purchases .
Find out how personality might influence the way you respond to forgiveness .
“If you go into the enterprise of shaping your child’s personality, be humble in your approach…and much more forgiving,” he says.
Even the elderly, whom we might expect to be more rigid and set in their ways, can change. Therapists who work with older clients with neurotic tendencies or troubled relationships should not feel discouraged or give up, says Damian, given what research shows is possible.
Damian also argues that this research could inform people in long-term relationships. Rather than expecting someone to be the same person they were decades ago, partners would be better served by learning to value what remains constant in someone’s personality while simultaneously embracing personality shifts as they occur.
“If you married someone because they’re a fine person, they’re probably still going to be a fine person later on; so that’s reassuring,” she says. “But at the same time, it’s important to keep an eye on them to see how they’re changing, so you don’t get blindsided by the changes and grow apart.”
So, am I changing myself? I hope so—at least on some level. I like the idea of letting go of some of my neuroticism, while becoming more agreeable and conscientious as I enter my older years.
Who knows? Maybe I am the teen I used to be…only a bit more mature.
About the Author

Jill Suttie
Jill Suttie, Psy.D. , is Greater Good ’s former book review editor and now serves as a staff writer and contributing editor for the magazine. She received her doctorate of psychology from the University of San Francisco in 1998 and was a psychologist in private practice before coming to Greater Good .
You May Also Enjoy

Why Is It So Hard to Make Positive Changes?

Can People Change?

Nine Things You Don’t Know about Yourself

Six Ways to Help People Change

How to Trick Your Brain for Happiness

What We Can Learn from Sensation Seekers
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Personality Theories in Psychology
Such theories help us understand how personality forms and influences behavior
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Adah Chung is a fact checker, writer, researcher, and occupational therapist.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Adah-Chung-1000-df54540455394e3ab797f6fce238d785.jpg)
Verywell / Bailey Mariner
- Theories of Personality
- Characteristics
- Research Methods
- Terminology
- Famous Psychologists
Personality theories seek to explain how personality forms, changes, and impacts behavior. Five key personality theories focus on biological, behavioral, psychodynamic, humanistic, and trait approaches. While these theories offer different explanations for personality, each offers important insights that help us better understand ourselves.
Understanding some of the basics about personality is essential to understanding personality theories in psychology. What exactly is personality? Where does it come from? Does it change as we grow older? These sorts of questions have long fascinated psychologists and inspired many different theories of personality.
At a Glance
Some of the best-known personality theories focus on how personality forms and influences behavior. Some focus on early childhood experiences, while others focus on the traits that make up personality. In other cases, personality theories are centered on how experiences and individual needs shape and influence personality. Keep reading to learn more about some of the major theories and how they have shaped our understanding of personality.
5 Major Personality Theories
Personality psychology is the focus of some of the best-known psychology theories by a number of famous thinkers including Sigmund Freud and Erik Erikson. Some of these theories attempt to tackle a specific area of personality while others attempt to explain personality much more broadly.
Five of the main theories of personality are biological theories, behavioral theories, psychodynamic theories, humanist theories, and trait theories.
Biological Personality Theories
Biological approaches suggest that genetics are primarily responsible for personality. In the classic nature versus nurture debate , the biological theories of personality side with nature.
Research on heritability suggests that there is a link between genetics and personality traits. Twin studies are often used to investigate which traits might be linked to genetics versus those that might be linked to environmental variables. For example, researchers might look at differences and similarities in the personalities of twins raised together versus those who are raised apart.
One of the best-known biological theorists was Hans Eysenck , who linked aspects of personality to biological processes.
Eysenck argued that personality is influenced by the stress hormone cortisol . According to his theory, introverts have high cortical arousal and avoid stimulation, while extroverts have low cortical arousal and crave stimulation.
Behavioral Personality Theories
Behavioral theorists include B. F. Skinner and John B. Watson . Behavioral personality theories suggest that personality is a result of interaction between the individual and the environment. Behavioral theorists study observable and measurable behaviors, rejecting theories that take internal thoughts, moods, and feelings play a part as these cannot be measured.
According to behavioral theorists, conditioning (predictable behavioral responses) occurs through interactions with our environment which ultimately shapes our personalities.
Psychodynamic Personality Theories
Psychodynamic theories of personality are heavily influenced by the work of Sigmund Freud and emphasize the influence of the unconscious mind and childhood experiences on personality. Psychodynamic theories include Sigmund Freud's psychosexual stage theory and Erik Erikson's stages of psychosocial development.
Freud believed the three components of personality were the id, ego, and superego . The id is responsible for needs and urges, while the superego regulates ideals and morals. The ego, in turn, moderates the demands of the id, superego, and reality.
Freud suggested that children progress through a series of stages in which the id's energy is focused on different erogenous zones.
Erikson also believed that personality progressed through a series of stages, with certain conflicts arising at each stage. Success in any stage depends on successfully overcoming these conflicts.
Humanist Personality Theories
Humanist theories emphasize the importance of free will and individual experience in personality development. Humanist theorists include Carl Rogers and Abraham Maslow.
Humanist theorists promote the concept of self-actualization , which is the innate need for personal growth and how personal growth motivates behavior. According to this approach, people are inherently good and have a natural tendency to want to make themselves and the world better.
Trait Personality Theories
The trait theory approach is one of the most prominent areas in personality psychology. According to these theories, personality is made up of a number of broad traits.
A trait is a relatively stable characteristic that causes an individual to behave in certain ways. It is essentially the psychological "blueprint" that informs behavioral patterns.
Some of the best-known trait theories include Eysenck's three-dimension theory and the five-factor theory of personality.
Eysenck utilized personality questionnaires to collect data from participants and then employed a statistical technique known as factor analysis to analyze the results. Eysenck concluded that there were three major dimensions of personality: extroversion, neuroticism, and psychoticism.
Eysenck believed that these dimensions then combine in different ways to form an individual's unique personality. Later, Eysenck added the third dimension known as psychoticism, which related to things such as aggression, empathy , and sociability.
Later, researchers suggested that a person's personality has five broad dimensions, often referred to as the Big 5 theory of personality .
The Big 5 theory suggests that all personalities can be characterized by five major personality dimensions: openness, conscientiousness, extroversion, agreeableness, and neuroticism, collectively referred to by the acronym OCEAN.
Defining Personality
While personality is something that we talk about all the time ("He has such a great personality!" or "Her personality is perfect for this job!"), you might be surprised to learn that psychologists do not necessarily agree on a single definition of what exactly constitutes personality.
Personality is broadly described as the characteristic patterns of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that make a person unique. In plain English, it is what makes you you.
Researchers have found while some external factors can influence how certain traits are expressed, personality originates within the individual. While a few aspects of personality may change as we grow older, personality also tends to remain fairly consistent throughout life.
Because personality plays such an important role in human behavior, an entire branch of psychology is devoted to studying this fascinating topic. Personality psychologists are interested in the unique characteristics of individuals and similarities among groups of people.
Characteristics of Personality
To understand the psychology of personality, it is important to learn some of the key characteristics of how personality works.
- Personality is organized and consistent. We tend to express certain aspects of our personality in different situations, and our responses are generally stable.
- Although personality is generally stable, it can be influenced by the environment. For example, while your personality might make you shy in social situations, an emergency might lead you to take on a more outspoken and take-charge approach.
- Personality causes behaviors to happen. You react to the people and objects in your environment based on your personality. From your personal preferences to your career choice, every aspect of your life is affected by your personality.
Investigating Personality Theories
Now that you know a bit more about the basics of personality, it's time to take a closer look at how scientists actually study human personality. There are different techniques that are used in the study of personality. Each technique has its own strengths and weaknesses.
Experimental Methods
Experimental methods are those in which the researcher controls and manipulates the variables of interest and takes measures of the results. This is the most scientific form of research, but experimental research can be difficult when studying aspects of personality such as motivations , emotions , and drives.
These ideas are internal, abstract, and can be difficult to measure. The experimental method allows researchers to look at cause-and-effect relationships between different variables of interest.
Case Studies
Case studies and self-report methods involve the in-depth analysis of an individual as well as information provided by the individual. Case studies rely heavily on the interpretations of the observer, while self-report methods depend on the memory of the individual of interest.
Because of this, these methods tend to be highly subjective and it is difficult to generalize the findings to a larger population.
Clinical Research
Clinical research relies upon information gathered from clinical patients over the course of treatment. Many personality theories are based on this type of research, but because the research subjects are unique and exhibit abnormal behavior, this research tends to be highly subjective and difficult to generalize.
Key Terms to Know About Personality Theories
In addition to understanding some of the major theories of personality psychology, it is important to know more about some of the key terms and concepts that are central to these theories.
Classical Conditioning
Classical conditioning is a behavioral training technique that begins with a naturally occurring stimulus eliciting an automatic response. Then, a previously neutral stimulus is paired with the naturally occurring stimulus.
Eventually, the previously neutral stimulus comes to evoke the response without the presence of the naturally occurring stimulus. The two elements are then known as the conditioned stimulus and the conditioned response .
Operant Conditioning
Operant conditioning is a behavior training technique in which reinforcements or punishments are used to influence behavior. An association is made between a behavior and a consequence for that behavior.
Unconscious
In Freud’s psychoanalytic theory of personality, the unconscious mind is a reservoir of feelings, thoughts, urges, and memories that are outside of our conscious awareness. Most of the contents of the unconscious are unacceptable or unpleasant, such as feelings of pain, anxiety, or conflict.
According to Freud, the unconscious mind continues to influence our behavior and experiences, even though we are unaware of these underlying influences.
According to Freud’s psychoanalytic theory of personality, the id is the personality component made up of unconscious psychic energy that works to satisfy basic urges, needs, and desires. The id operates based on the pleasure principle , which demands immediate gratification of needs.
According to Freud, the ego is the largely unconscious part of the personality that mediates the demands of the id, the superego, and reality. The ego prevents us from acting on our basic urges (created by the id) but also works to achieve a balance with our moral and idealistic standards (created by the superego).
The superego is the component of personality composed of our internalized ideals that we have acquired from our parents and from society. The superego works to suppress the urges of the id and tries to make the ego behave morally, rather than realistically.

Thinkers Behind Personality Theories
Some of the most famous figures in the history of psychology left a lasting mark on the field of personality. Learning more about the lives, theories, and contributions to the psychology of these eminent psychologists can help one better understand the different personality theories.
Sigmund Freud
Sigmund Freud (1856-1939) was the founder of psychoanalytic theory. His theories emphasized the importance of the unconscious mind, childhood experiences, dreams , and symbolism. His theory of psychosexual development suggested that children progress through a series of stages during which libidinal energy is focused on different regions of the body.
His ideas are known as grand theories because they seek to explain virtually every aspect of human behavior.
Although many of Freud's ideas are considered outdated by modern psychologists, he had a major influence on the course of psychology, and some concepts, such as the usefulness of talk therapy and the importance of the unconscious, are enduring.
Erik Erikson
Erik Erikson (1902-1994) was an ego psychologist trained by Anna Freud . His theory of psychosocial stages describes how personality develops throughout the lifespan. Like Freud, some aspects of Erikson's theory are considered outdated by contemporary researchers, but his eight-stage theory of development remains popular and influential.
B. F. Skinner
B. F. Skinner (1904-1990) was a behaviorist best known for his research on operant conditioning and the discovery of schedules of reinforcement . Schedules of reinforcement influence how quickly a behavior is acquired and the strength of response.
The schedules described by Skinner are fixed-ratio schedules, fixed-variable schedules, variable-ratio schedules, and variable-interval schedules .
Sandra Bem (1944-2014) had an important influence in psychology and on our understanding of sex roles, gender, and sexuality. She developed her gender schema theory to explain how society and culture transmit ideas about sex and gender. Gender schemas, Bem suggested, were formed by things such as parenting, school, mass media, and other cultural influences.
Abraham Maslow
Abraham Maslow (1908-1970) was a humanist psychologist who developed the well-known hierarchy of needs . The hierarchy includes physiological needs, safety and security needs, love and affection needs, self-esteem needs, and self-actualizing needs.
Carl Rogers
Carl Rogers (1902-1987) was a humanist psychologist who believed that all people have an actualizing tendency —a drive to fulfill the individual potential that motivates behavior. Rogers called healthy individuals fully functioning , describing them as those who are open to experience , live in the moment, trust their own judgment, feel free, and are creative.
Personality makes us who we are, so it is no wonder why it has been the source of such fascination in both science and in daily life. The various theories of personality that have been proposed by different psychologists have helped us gain a deeper and richer understanding of what makes each person unique.
By learning more about these theories, you can better understand how researchers have come to know the psychology of personality as well as consider questions that future research might explore.
Vukasović T, Bratko D. Heritability of personality: A meta-analysis of behavior genetic studies . Psychol Bull . 2015;141(4):769-785. doi:10.1037/bul0000017
Soliemanifar O, Soleymanifar A, Afrisham R. Relationship between personality and biological reactivity to stress: A review . Psychiatry Investig . 2018;15(12):1100-1114. doi:10.30773/pi.2018.10.14.2
Bishop SK, Dixon MR, Moore JW, Lundy MP. Behavioral perspectives on personality . In: Zeigler-Hill V, Shackelford T, eds. Encyclopedia of Personality and Individual Differences . Cham: Springer; 2016. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-28099-8
Bornstein RF. Psychodynamic models of personality . In: Millon T, Lerner MJ, eds. Handbook of psychology: Personality and social psychology, Vol. 5. New Jersey : John Wiley & Sons Inc; 2003.
Bland AM, DeRobertis EM. Humanistic perspective . In: Zeigler-Hill V, Shackelford TK, eds. Encyclopedia of Personality and Individual Differences . Springer International Publishing; 2020:2061-2079. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-24612-3_1484
Al-Alawi M, Al-Sinawi H, Al-Husseini S, et al. Influence of Eysenckian personality traits in choice of specialization by young Omani doctors . Oman Med J . 2017;32(4):291-296. doi:10.5001/omj.2017.57
Novikova IA. Big five (The five‐factor model and the five‐factor theory) . In: Keith KD, ed. The Encyclopedia of Cross‐Cultural Psychology . Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley and Sons; 2013. doi:10.1002/9781118339893.wbeccp054
Wright AJ, Jackson JJ. Do changes in personality predict life outcomes ? J Pers Soc Psychol . 2023;125(6):1495-1518. doi:10.1037/pspp0000472
Chopik WJ, Kitayama S. Personality change across the life span: Insights from a cross-cultural, longitudinal study . J Pers . 2018;86(3):508-521. doi:10.1111/jopy.12332
Boag S. Ego, drives, and the dynamics of internal objects . Front Psychol . 2014;5:666. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00666
Roediger HL 3rd. Varieties of fame in psychology . Perspect Psychol Sci . 2016;11(6):882-887. doi:10.1177/1745691616662457
Carducci BJ. The Psychology of Personality: Viewpoints, Research, and Applications . New York: Wiley Blackwell; 2009.
John OP, Robins RW, Pervin LA. Handbook of Personality: Theory and Research . 3rd ed. New York: The Guilford Press; 2008.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- HHS Author Manuscripts

The Power of Personality
Brent w. roberts.
University of Illinois
Nathan R. Kuncel
University of Minnesota
Rebecca Shiner
Colgate University
Avshalom Caspi
Institute of Psychiatry at Kings College, London, United Kingdom
Duke University
Lewis R. Goldberg
Oregon Research Institute
The ability of personality traits to predict important life outcomes has traditionally been questioned because of the putative small effects of personality. In this article, we compare the predictive validity of personality traits with that of socioeconomic status (SES) and cognitive ability to test the relative contribution of personality traits to predictions of three critical outcomes: mortality, divorce, and occupational attainment. Only evidence from prospective longitudinal studies was considered. In addition, an attempt was made to limit the review to studies that controlled for important background factors. Results showed that the magnitude of the effects of personality traits on mortality, divorce, and occupational attainment was indistinguishable from the effects of SES and cognitive ability on these outcomes. These results demonstrate the influence of personality traits on important life outcomes, highlight the need to more routinely incorporate measures of personality into quality of life surveys, and encourage further research about the developmental origins of personality traits and the processes by which these traits influence diverse life outcomes.
Starting in the 1980s, personality psychology began a profound renaissance and has now become an extraordinarily diverse and intellectually stimulating field ( Pervin & John, 1999 ). However, just because a field of inquiry is vibrant does not mean it is practical or useful—one would need to show that personality traits predict important life outcomes, such as health and longevity, marital success, and educational and occupational attainment. In fact, two recent reviews have shown that different personality traits are associated with outcomes in each of these domains ( Caspi, Roberts, & Shiner, 2005 ; Ozer & Benet-Martinez, 2006 ). But simply showing that personality traits are related to health, love, and attainment is not a stringent test of the utility of personality traits. These associations could be the result of “third” variables, such as socioeconomic status (SES), that account for the patterns but have not been controlled for in the studies reviewed. In addition, many of the studies reviewed were cross-sectional and therefore lacked the methodological rigor to show the predictive validity of personality traits. A more stringent test of the importance of personality traits can be found in prospective longitudinal studies that show the incremental validity of personality traits over and above other factors.
The analyses reported in this article test whether personality traits are important, practical predictors of significant life outcomes. We focus on three domains: longevity/mortality, divorce, and occupational attainment in work. Within each domain, we evaluate empirical evidence using the gold standard of prospective longitudinal studies—that is, those studies that can provide data about whether personality traits predict life outcomes above and beyond well-known factors such as SES and cognitive abilities. To guide the interpretation drawn from the results of these prospective longitudinal studies, we provide benchmark relations of SES and cognitive ability with outcomes from these three domains. The review proceeds in three sections. First, we address some misperceptions about personality traits that are, in part, responsible for the idea that personality does not predict important life outcomes. Second, we present a review of the evidence for the predictive validity of personality traits. Third, we conclude with a discussion of the implications of our findings and recommendations for future work in this area.
THE “PERSONALITY COEFFICIENT”: AN UNFORTUNATE LEGACY OF THE PERSON-SITUATION DEBATE
Before we embark on our review, it is necessary to lay to rest a myth perpetrated by the 1960s manifestation of the person–situation debate; this myth is often at the root of the perspective that personality traits do not predict outcomes well, if at all. Specifically, in his highly influential book, Walter Mischel (1968) argued that personality traits had limited utility in predicting behavior because their correlational upper limit appeared to be about .30. Subsequently, this .30 value became derided as the “personality coefficient.” Two conclusions were inferred from this argument. First, personality traits have little predictive validity. Second, if personality traits do not predict much, then other factors, such as the situation, must be responsible for the vast amounts of variance that are left unaccounted for. The idea that personality traits are the validity weaklings of the predictive panoply has been reiterated in unmitigated form to this day (e.g., Bandura, 1999 ; Lewis, 2001 ; Paul, 2004 ; Ross & Nisbett, 1991 ). In fact, this position is so widely accepted that personality psychologists often apologize for correlations in the range of .20 to .30 (e.g., Bornstein, 1999 ).
Should personality psychologists be apologetic for their modest validity coefficients? Apparently not, according to Meyer and his colleagues ( Meyer et al., 2001 ), who did psychological science a service by tabling the effect sizes for a wide variety of psychological investigations and placing them side-by-side with comparable effect sizes from medicine and everyday life. These investigators made several important points. First, the modal effect size on a correlational scale for psychology as a whole is between .10 and .40, including that seen in experimental investigations (see also Hemphill, 2003 ). It appears that the .30 barrier applies to most phenomena in psychology and not just to those in the realm of personality psychology. Second, the very largest effects for any variables in psychology are in the .50 to .60 range, and these are quite rare (e.g., the effect of increasing age on declining speed of information processing in adults). Third, effect sizes for assessment measures and therapeutic interventions in psychology are similar to those found in medicine. It is sobering to see that the effect sizes for many medical interventions—like consuming aspirin to treat heart disease or using chemotherapy to treat breast cancer—translate into correlations of .02 or .03. Taken together, the data presented by Meyer and colleagues make clear that our standards for effect sizes need to be established in light of what is typical for psychology and for other fields concerned with human functioning.
In the decades since Mischel’s (1968) critique, researchers have also directly addressed the claim that situations have a stronger influence on behavior than they do on personality traits. Social psychological research on the effects of situations typically involves experimental manipulation of the situation, and the results are analyzed to establish whether the situational manipulation has yielded a statistically significant difference in the outcome. When the effects of situations are converted into the same metric as that used in personality research (typically the correlation coefficient, which conveys both the direction and the size of an effect), the effects of personality traits are generally as strong as the effects of situations ( Funder & Ozer, 1983 ; Sarason, Smith, & Diener, 1975 ). Overall, it is the moderate position that is correct: Both the person and the situation are necessary for explaining human behavior, given that both have comparable relations with important outcomes.
As research on the relative magnitude of effects has documented, personality psychologists should not apologize for correlations between .10 and .30, given that the effect sizes found in personality psychology are no different than those found in other fields of inquiry. In addition, the importance of a predictor lies not only in the magnitude of its association with the outcome, but also in the nature of the outcome being predicted. A large association between two self-report measures of extraversion and positive affect may be theoretically interesting but may not offer much solace to the researcher searching for proof that extraversion is an important predictor for outcomes that society values. In contrast, a modest correlation between a personality trait and mortality or some other medical outcome, such as Alzheimer’s disease, would be quite important. Moreover, when attempting to predict these critical life outcomes, even relatively small effects can be important because of their pragmatic effects and because of their cumulative effects across a person’s life ( Abelson, 1985 ; Funder, 2004 ; Rosenthal, 1990 ). In terms of practicality, the −.03 association between taking aspirin and reducing heart attacks provides an excellent example. In one study, this surprisingly small association resulted in 85 fewer heart attacks among the patients of 10,845 physicians ( Rosenthal, 2000 ). Because of its practical significance, this type of association should not be ignored because of the small effect size. In terms of cumulative effects, a seemingly small effect that moves a person away from pursuing his or her education early in life can have monumental consequences for that person’s health and well-being later in life ( Hardarson et al., 2001 ). In other words, psychological processes with a statistically small or moderate effect can have important effects on individuals’ lives depending on the outcomes with which they are associated and depending on whether those effects get cumulated across a person’s life.
PERSONALITY EFFECTS ON MORTALITY, DIVORCE, AND OCCUPATIONAL ATTAINMENT
Selection of predictors, outcomes, and studies for this review.
To provide the most stringent test of the predictive validity of personality traits, we chose to focus on three objective outcomes: mortality, divorce, and occupational attainment. Although we could have chosen many different outcomes to examine, we selected these three because they are socially valued; they are measured in similar ways across studies; and they have been assessed as outcomes in studies of SES, cognitive ability, and personality traits. Mortality needs little justification as an outcome, as most individuals value a long life. Divorce and marital stability are important outcomes for several reasons. Divorce is a significant source of depression and distress for many individuals and can have negative consequences for children, whereas a happy marriage is one of the most important predictors of life satisfaction ( Myers, 2000 ). Divorce is also linked to disproportionate drops in economic status, especially for women ( Kuh & Maclean, 1990 ), and it can undermine men’s health (e.g., Lund, Holstein, & Osler, 2004 ). An intact marriage can also preserve cognitive function into old age for both men and women, particularly for those married to a high-ability spouse ( Schaie, 1994 ).
Educational and occupational attainment are also highly prized ( Roisman, Masten, Coatsworth, & Tellegen, 2004 ). Research on subjective well-being has shown that occupational attainment and its important correlate, income, are not as critical for happiness as many assume them to be ( Myers, 2000 ). Nonetheless, educational and occupational attainment are associated with greater access to many resources that can improve the quality of life (e.g., medical care, education) and with greater “social capital” (i.e., greater access to various resources through connections with others; Bradley & Corwyn, 2002 ; Conger & Donnellan, 2007 ). The greater income resulting from high educational and occupational attainment may also enable individuals to maintain strong life satisfaction when faced with difficult life circumstances ( Johnson & Krueger, 2006 ).
To better interpret the significance of the relations between personality traits and these outcomes, we have provided comparative information concerning the effect of SES and cognitive ability on each of these outcomes. We chose to use SES as a comparison because it is widely accepted to be one of the most important contributors to a more successful life, including better health and higher occupational attainment (e.g., Adler et al., 1994 ; Gallo & Mathews, 2003 ; Galobardes, Lynch, & Smith, 2004 ; Sapolsky, 2005 ). In addition, we chose cognitive ability as a comparison variable because, like SES, it is a widely accepted predictor of longevity and occupational success ( Deary, Batty, & Gottfredson, 2005 ; Schmidt & Hunter, 1998 ). In this article, we compare the effect sizes of personality traits with these two predictors in order to understand the relative contribution of personality to a long, stable, and successful life. We also required that the studies in this review make some attempt to control for background variables. For example, in the case of mortality, we looked for prospective longitudinal studies that controlled for previous medical conditions, gender, age, and other relevant variables.
We are not assuming that personality traits are direct causes of the outcomes under study. Rather, we were exclusively interested in whether personality traits predict mortality, divorce, and occupational attainment and in their modal effect sizes. If found to be robust, these patterns of statistical association then invite the question of why and how personality traits might cause these outcomes, and we have provided several examples in each section of potential mechanisms and causal steps involved in the process.
The Measurement of Effect Sizes in Prospective Longitudinal Studies
Before turning to the specific findings for personality, SES, and cognitive ability, we must first address the measurement of effect sizes in the studies reviewed here. Most of the studies that we reviewed used some form of regression analysis for either continuous or categorical outcomes. In studies with continuous outcomes, findings were typically reported as standardized regression weights (beta coefficients). In studies of categorical outcomes, the most common effect size indicators are odds ratios, relative risk ratios, or hazard ratios. Because many psychologists may be less familiar with these ratio statistics, a brief discussion of them is in order. In the context of individual differences, ratio statistics quantify the likelihood of an event (e.g., divorce, mortality) for a higher scoring group versus the likelihood of the same event for a lower scoring group (e.g., persons high in negative affect versus those low in negative affect). An odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of the event for one group over the odds of the same event for the second group. The risk ratio compares the probabilities of the event occurring for the two groups. The hazard ratio assesses the probability of an event occurring for a group over a specific window of time. For these statistics, a value of 1.0 equals no difference in odds or probabilities. Values above 1.0 indicate increased likelihood (odds or probabilities) for the experimental (or numerator) group, with the reverse being true for values below 1.0 (down to a lower limit of zero). Because of this asymmetry, the log of these statistics is often taken.
The primary advantage of ratio statistics in general, and the risk ratio in particular, is their ease of interpretation in applied settings. It is easier to understand that death is three times as likely to occur for one group than for another than it is to make sense out of a point-biserial correlation. However, there are also some disadvantages that should be understood. First, ratio statistics can make effects that are actually very small in absolute magnitude appear to be large when in fact they are very rare events. For example, although it is technically correct that one is three times as likely (risk ratio = 3.0) to win the lottery when buying three tickets instead of one ticket, the improved chances of winning are trivial in an absolute sense.
Second, there is no accepted practice for how to divide continuous predictor variables when computing odds, risk, and hazard ratios. Some predictors are naturally dichotomous (e.g., gender), but many are continuous (e.g., cognitive ability, SES). Researchers often divide continuous variables into some arbitrary set of categories in order to use the odds, rate, or hazard metrics. For example, instead of reporting an association between SES and mortality using a point-biserial correlation, a researcher may use proportional hazards models using some arbitrary categorization of SES, such as quartile estimates (e.g., lowest versus highest quartiles). This permits the researcher to draw conclusions such as “individuals from the highest category of SES are four times as likely to live longer than are groups lowest in SES.” Although more intuitively appealing, the odds statements derived from categorizing continuous variables makes it difficult to deduce the true effect size of a relation, especially across studies. Researchers with very large samples may have the luxury of carving a continuous variable into very fine-grained categories (e.g., 10 categories of SES), which may lead to seemingly huge hazard ratios. In contrast, researchers with smaller samples may only dichotomize or trichotomize the same variables, thus resulting in smaller hazard ratios and what appear to be smaller effects for identical predictors. Finally, many researchers may not categorize their continuous variables at all, which can result in hazard ratios very close to 1.0 that are nonetheless still statistically significant. These procedures for analyzing odds, rate, and hazard ratios produce a haphazard array of results from which it is almost impossible to discern a meaningful average effect size. 1
One of the primary tasks of this review is to transform the results from different studies into a common metric so that a fair comparison could be made across the predictors and outcomes. For this purpose, we chose the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient. We used a variety of techniques to arrive at an accurate estimate of the effect size from each study. When transforming relative risk ratios into the correlation metric, we used several methods to arrive at the most appropriate estimate of the effect size. For example, the correlation coefficient can be estimated from reported significance levels ( p values) and from test statistics such as the t test or chi-square, as well as from other effect size indicators such as d scores ( Rosenthal, 1991 ). Also, the correlation coefficient can be estimated directly from relative risk ratios and hazard ratios using the generic inverse variance approach ( The Cochrane Collaboration, 2005 ). In this procedure, the relative risk ratio and confidence intervals (CIs) are first transformed into z scores, and the z scores are then transformed into the correlation metric.
For most studies, the effect size correlation was estimated from information on relative risk ratios and p values. For the latter, we used the r equivalent effect size indicator ( Rosenthal & Rubin, 2003 ), which is computed from the sample size and p value associated with specific effects. All of these techniques transform the effect size information to a common correlational metric, making the results of the studies comparable across different analytical methods. After compiling effect sizes, meta-analytic techniques were used to estimate population effect sizes in both the risk ratio and correlation metric ( Hedges & Olkin, 1985 ). Specifically, a random-effects model with no moderators was used to estimate population effect sizes for both the rate ratio and correlation metrics. 2 When appropriate, we first averaged multiple nonindependent effects from studies that reported more than one relevant effect size.
The Predictive Validity of Personality Traits for Mortality
Before considering the role of personality traits in health and longevity, we reviewed a selection of studies linking SES and cognitive ability to these same outcomes. This information provides a point of reference to understand the relative contribution of personality. Table 1 presents the findings from 33 studies examining the prospective relations of low SES and low cognitive ability with mortality. 3 SES was measured using measures or composites of typical SES variables including income, education, and occupational status. Total IQ scores were commonly used in analyses of cognitive ability. Most studies demonstrated that being born into a low-SES household or achieving low SES in adulthood resulted in a higher risk of mortality (e.g., Deary & Der, 2005 ; Hart et al., 2003 ; Osler et al., 2002 ; Steenland, Henley, & Thun, 2002 ). The relative risk ratios and hazard ratios ranged from a low of 0.57 to a high of 1.30 and averaged 1.24 (CIs = 1.19 and 1.29). When translated into the correlation metric, the effect sizes for low SES ranged from −.02 to .08 and averaged .02 (CIs = .017 and .026).
SES and IQ Effects on Mortality/Longevity
Note. Confidence intervals are given in parentheses. SES = socioeconomic status; HR = hazard ratio; RR = relative risk ratio; OR = odds ratio; r rr = Correlation estimated from the rate ratio; r hr = correlation estimated from the hazard ratio; r or = correlation estimated from the odds ratio; r F = correlation estimated from F test; r e = r equivalent —correlation estimated from the reported p value and sample size; BMI = body mass index; FEV = forced expiratory volume; ADLs = activities of daily living; MMSE = Mini Mental State Examination; CPS = Cancer Prevention Study; RIFLE = risk factors and life expectancy.
Through the use of the relative risk metric, we determined that the effect of low IQ on mortality was similar to that of SES, ranging from a modest 0.74 to 2.42 and averaging 1.19 (CIs = 1.10 and 1.30). When translated into the correlation metric, however, the effect of low IQ on mortality was equivalent to a correlation of .06 (CIs = .03 and .09), which was three times larger than the effect of SES on mortality. The discrepancy between the relative risk and correlation metrics most likely resulted because some studies reported the relative risks in terms of continuous measures of IQ, which resulted in smaller relative risk ratios (e.g., St. John, Montgomery, Kristjansson, & McDowell, 2002 ). Merging relative risk ratios from these studies with those that carve the continuous variables into subgroups appears to underestimate the effect of IQ on mortality, at least in terms of the relative risk metric. The most telling comparison of IQ and SES comes from the five studies that include both variables in the prediction of mortality. Consistent with the aggregate results, IQ was a stronger predictor of mortality in each case (i.e., Deary & Der, 2005 ; Ganguli, Dodge, & Mulsant, 2002 ; Hart et al., 2003 ; Osler et al., 2002 ; Wilson, Bienia, Mendes de Leon, Evans, & Bennet, 2003 ).
Table 2 lists 34 studies that link personality traits to mortality/longevity. 4 In most of these studies, multiple factors such as SES, cognitive ability, gender, and disease severity were controlled for. We organized our review roughly around the Big Five taxonomy of personality traits (e.g., Conscientiousness, Extraversion, Neuroticism, Agreeableness, and Openness to Experience; Goldberg, 1993b ). For example, research drawn from the Terman Longitudinal Study showed that children who were more conscientious tended to live longer ( Friedman et al., 1993 ). This effect held even after controlling for gender and parental divorce, two known contributors to shorter lifespans. Moreover, a number of other factors, such as SES and childhood health difficulties, were unrelated to longevity in this study. The protective effect of Conscientiousness has now been replicated across several studies and more heterogeneous samples. Conscientiousness was found to be a rather strong protective factor in an elderly sample participating in a Medicare training program ( Weiss & Costa, 2005 ), even when controlling for education level, cardiovascular disease, and smoking, among other factors. Similarly, Conscientiousness predicted decreased rates of mortality in a sample of individuals suffering from chronic renal insufficiency, even after controlling for age, diabetic status, and hemoglobin count ( Christensen et al., 2002 ).
Personality Traits and Mortality
Note. Confidence intervals are given in parentheses. HR = hazard ratio; RR = relative risk ratio; OR = odds ratio; r rr = correlation estimated from the rate ratio; r hr = correlation estimated from the hazard ratio; r or = correlation estimated from the odds ratio; r B = correlation estimated from a beta weight and standard error; r e = r equivalent (correlation estimated from the reported p value and sample size); FEV = forced expiratory volume; CHD = coronary heart disease; SES =socioeconomic status; BMI =body-ass index; ADLs =activities of daily living; MMSE =Mini Mental State Examination.
Similarly, several studies have shown that dispositions reflecting Positive Emotionality or Extraversion were associated with longevity. For example, nuns who scored higher on an index of Positive Emotionality in young adulthood tended to live longer, even when controlling for age, education, and linguistic ability (an aspect of cognitive ability; Danner, Snowden, & Friesen, 2001 ). Similarly, Optimism was related to higher rates of survival following head and neck cancer ( Allison, Guichard, Fung, & Gilain, 2003 ). In contrast, several studies reported that Neuroticism and Pessimism were associated with increases in one’s risk for premature mortality ( Abas, Hotopf, & Prince, 2002 ; Denollet et al., 1996 ; Schulz, Bookwala, Knapp, Scheier, & Williamson, 1996 ; Wilson, Mendes de Leon, Bienias, Evans, & Bennett, 2004 ). It should be noted, however, that two studies reported a protective effect of high Neuroticism ( Korten et al., 1999 ; Weiss & Costa, 2005 ).
The domain of Agreeableness showed a less clear association to mortality, with some studies showing a protective effect of high Agreeableness ( Wilson et al., 2004 ) and others showing that high Agreeableness contributed to mortality ( Friedman et al., 1993 ). With respect to the domain of Openness to Experience, two studies showed that Openness or facets of Openness, such as creativity, had little or no relation to mortality ( Osler et al., 2002 ; Wilson et al., 2004 ).
Because aggregating all personality traits into one overall effect size washes out important distinctions among different trait domains, we examined the effect of specific trait domains by aggregating studies within four categories: Conscientiousness, Positive Emotion/Extraversion, Neuroticism/Negative Emotion, and Hostility/Disagreeableness. 5 Our Conscientiousness domain included four studies that linked Conscientiousness to mortality. Because only two of these studies reported the information necessary to compute an average relative risk ratio, we only examined the correlation metric. When translated into a correlation metric, the average effect size for Conscientiousness was −.09 (CIs = −.12 and −.05), indicating a protective effect. Our Extraversion/Positive Emotion domain included six studies that examined the effect of extraversion, positive emotion, and optimism. The average relative risk ratio for the low Extraversion/Positive Emotion was 1.04 (CIs = 1.00 and 1.10) with a corresponding correlation effect size for high Extraversion/Positive Emotion being −.07 (−.11, −.03), with the latter showing a statistically significant protective effect of Extraversion/Positive Emotion. Our Negative Emotionality domain included twelve studies that examined the effect of neuroticism, pessimism, mental instability, and sense of coherence. The average relative risk ratio for the Negative Emotionality domain was 1.15 (CIs = 1.04 and 1.26), and the corresponding correlation effect size was .05 (CIs = .02 and .08). Thus, Neuroticism was associated with a diminished life span. Nineteen studies reported relations between Hostility/Disagreeableness and all-cause mortality, with notable heterogeneity in the effects across studies. The risk ratio population estimate showed an effect equivalent to, if not larger than, the remaining personality domains (risk ratio = 1.14; CIs = 1.06 and 1.23). With the correlation metric, this effect translated into a small but statistically significant effect of .04 (CIs = .02 and .06), indicating that hostility was positively associated with mortality. Thus, the specific personality traits of Conscientiousness, Positive Emotionality/Extraversion, Neuroticism, and Hostility/Disagreeableness were stronger predictors of mortality than was SES when effects were translated into a correlation metric. The effect of personality traits on mortality appears to be equivalent to IQ, although the additive effect of multiple trait domains on mortality may well exceed that of IQ.
Why would personality traits predict mortality? Personality traits may affect health and ultimately longevity through at least three distinct processes ( Contrada, Cather, & O’Leary, 1999 ; Pressman & Cohen, 2005 ; Rozanski, Blumenthal, & Kaplan, 1999 ; T.W. Smith, 2006 ). First, personality differences may be related to pathogenesis or mechanisms that promote disease. This has been evaluated most directly in studies relating various facets of Hostility/Disagreeableness to greater reactivity in response to stressful experiences (T.W. Smith & Gallo, 2001 ) and in studies relating low Extraversion to neuroendocrine and immune functioning ( Miller, Cohen, Rabin, Skoner, & Doyle, 1999 ) and greater susceptibility to colds ( Cohen, Doyle, Turner, Alper, & Skoner, 2003a , 2003b ). Second, personality traits may be related to physical-health outcomes because they are associated with health-promoting or health-damaging behaviors. For example, individuals high in Extraversion may foster social relationships, social support, and social integration, all of which are positively associated with health outcomes ( Berkman, Glass, Brissette, & Seeman, 2000 ). In contrast, individuals low in Conscientiousness may engage in a variety of health-risk behaviors such as smoking, unhealthy eating habits, lack of exercise, unprotected sexual intercourse, and dangerous driving habits ( Bogg & Roberts, 2004 ). Third, personality differences may be related to reactions to illness. This includes a wide class of behaviors, such as the ways individuals cope with illness (e.g., Scheier & Carver, 1993 ), reduce stress, and adhere to prescribed treatments ( Kenford et al., 2002 ).
These processes linking personality traits to physical health are not mutually exclusive. Moreover, different personality traits may affect physical health via different processes. For example, facets of Disagreeableness may be most directly linked to disease processes, facets of low Conscientiousness may be implicated in health-damaging behaviors, and facets of Neuroticism may contribute to ill-health by shaping reactions to illness. In addition, it is likely that the impact of personality differences on health varies across the life course. For example, Neuroticism may have a protective effect on mortality in young adulthood, as individuals who are more neurotic tend to avoid accidents in adolescence and young adulthood ( Lee, Wadsworth, & Hotopf, 2006 ). It is apparent from the extant research that personality traits influence outcomes at all stages of the health process, but much more work remains to be done to specify the processes that account for these effects.
The Predictive Validity of Personality Traits for Divorce
Next, we considered the role that SES, cognitive ability, and personality traits play in divorce. Because there were fewer studies examining these issues, we included prospective studies of SES, IQ, and personality that did not control for many background variables.
In terms of SES and IQ, we found 11 studies that showed a wide range of associations with divorce and marriage (see Table 3 ). 6 For example, the SES of the couple in one study was unsystematically related to divorce ( Tzeng & Mare, 1995 ). In contrast, Kurdek (1993) reported relatively large, protective effects for education and income for both men and women. Because not all these studies reported relative risk ratios, we computed an aggregate using the correlation metric and found the relation between SES and divorce was −.05 (CIs = −.08 and − .02), which indicates a significant protective effect of SES on divorce across these studies. Contradictory patterns were found for the two studies that predicted divorce and marital patterns from measures of cognitive ability. Taylor et al. (2005) reported that IQ was positively related to the possibility of male participants ever marrying but was negatively related to the possibility of female participants ever marrying. Data drawn from the Mills Longitudinal study ( Helson, 2006 ) showed conflicting patterns of associations between verbal and mathematical aptitude and divorce. Because there were only two studies, we did not examine the average effects of IQ on divorce.
SES and IQ Effects on Divorce
Note. Confidence intervals are given in parentheses. SES = socioeconomic status; HR = hazard ratio; RR = relative risk ratio; OR = odds ratio; r z = correlation estimated from the z score and sample size; r or = correlation estimated from the odds ratio; r F = correlation estimated from F test; r B = correlation estimated from the reported unstandardized beta weight and standard error; r e = r equivalent (correlation estimated from the reported p value and sample size); WAIS = Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale; NLSY = National Longitudinal Study of Youth; NLSYM = National Longitudinal Study of Young Men; NLSYW = National Longitudinal Study of Young Women.
Table 4 shows the data from thirteen prospective studies testing whether personality traits predicted divorce. Traits associated with the domain of Neuroticism, such as being anxious and overly sensitive, increased the probability of experiencing divorce ( Kelly & Conley, 1987 ; Tucker, Kressin, Spiro, & Ruscio, 1998 ). In contrast, those individuals who were more conscientious and agreeable tended to remain longer in their marriages and avoided divorce ( Kelly & Conley, 1987 ; Kinnunen & Pulkkenin, 2003 ; Roberts & Bogg, 2004 ). Although these studies did not control for as many factors as the health studies, the time spans over which the studies were carried out were impressive (e.g., 45 years). We aggregated effects across these studies for the trait domains of Neuroticism, Agreeableness, and Conscientiousness with the correlation metric, as too few studies reported relative risk outcomes to warrant aggregating. When so aggregated, the effect of Neuroticism on divorce was .17 (CIs = .12 and .22), the effect of Agreeableness was − .18 (CIs = −.27 and −.09), and the effect of Conscientiousness on divorce was −.13 (CIs = −.17 and −.09). Thus, the predictive effects of these three personality traits on divorce were greater than those found for SES.
Personality Traits and Marital Outcomes
Note. Confidence intervals are given in parentheses. HR = hazard ratio; RR = relative risk ratio; OR = odds ratio; r d = Correlation estimated from the d score; r or = correlation estimated from the odds ratio; r F = correlation estimated from F test; r e = r equivalent (correlation estimated from the reported p value and sample size); MMPI = Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory; IHS = Institute of Human Development.
Why would personality traits lead to divorce or conversely marital stability? The most likely reason is because personality traits help shape the quality of long-term relationships. For example, Neuroticism is one of the strongest and most consistent personality predictors of relationship dissatisfaction, conflict, abuse, and ultimately dissolution ( Karney & Bradbury, 1995 ). Sophisticated studies that include dyads (not just individuals) and multiple methods (not just self reports) increasingly demonstrate that the links between personality traits and relationship processes are more than simply an artifact of shared method variance in the assessment of these two domains ( Donnellan, Conger, & Bryant, 2004 ; Robins, Caspi, & Moffitt, 2000 ; Watson, Hubbard, & Wiese, 2000 ). One study that followed a sample of young adults across their multiple relationships in early adulthood discovered that the influence of Negative Emotionality on relationship quality showed cross-relationship generalization; that is, it predicted the same kinds of experiences across relationships with different partners ( Robins, Caspi, & Moffitt, 2002 ).
An important goal for future research will be to uncover the proximal relationship-specific processes that mediate personality effects on relationship outcomes ( Reiss, Capobianco, & Tsai, 2002 ). Three processes merit attention. First, personality traits influence people’s exposure to relationship events. For example, people high in Neuroticism may be more likely to be exposed to daily conflicts in their relationships ( Bolger & Zuckerman, 1995 ; Suls & Martin, 2005 ). Second, personality traits shape people’s reactions to the behavior of their partners. For example, disagreeable individuals may escalate negative affect during conflict (e.g., Gottman, Coan, Carrere, & Swanson, 1998 ). Similarly, agreeable people may be better able to regulate emotions during interpersonal conflicts ( Jensen-Campbell & Graziano, 2001 ). Cognitive processes also factor in creating trait-correlated experiences ( Snyder & Stukas, 1999 ). For example, highly neurotic individuals may overreact to minor criticism from their partner, believe they are no longer loved when their partner does not call, or assume infidelity on the basis of mere flirtation. Third, personality traits evoke behaviors from partners that contribute to relationship quality. For example, people high in Neuroticism and low in Agreeableness may be more likely to express behaviors identified as detrimental to relationships such as criticism, contempt, defensiveness, and stonewalling ( Gottman, 1994 ).
The Predictive Validity of Personality Traits for Educational and Occupational Attainment
The role of personality traits in occupational attainment has been studied sporadically in longitudinal studies over the last few decades. In contrast, the roles of SES and IQ have been studied exhaustively by sociologists in their programmatic research on the antecedents to status attainment. In their seminal work, Blau and Duncan (1967) conceptualized a model of status attainment as a function of the SES of an individual’s father. Researchers at the University of Wisconsin added what they considered social-psychological factors ( Sewell, Haller, & Portes, 1969 ). In this Wisconsin model, attainment is a function of parental SES, cognitive abilities, academic performance, occupational and educational aspirations, and the role of significant others ( Haller & Portes, 1973 ). Each factor in the model has been found to be positively related to occupational attainment ( Hauser, Tsai, & Sewell, 1983 ). The key question here is to what extent SES and IQ predict educational and occupational attainment holding constant the remaining factors.
A great deal of research has validated the structure and content of the Wisconsin model ( Sewell & Hauser, 1980 ; Sewell & Hauser, 1992 ), and rather than compiling these studies, which are highly similar in structure and findings, we provide representative findings from a study that includes three replications of the model ( Jencks, Crouse, & Mueser, 1983 ). As can be seen in Table 5 , childhood socioeconomic indicators, such as father’s occupational status and mother’s education, are related to outcomes, such as grades, educational attainment, and eventual occupational attainment, even after controlling for the remaining variables in the Wisconsin model. The average beta weight of SES and education was .09. 7 Parental income had a stronger effect, with an average beta weight of .14 across these three studies. Cognitive abilities were even more powerful predictors of occupational attainment, with an average beta weight of .27.
SES, IQ, and Status Attainment
Note. SES = socioeconomic status.
Do personality traits contribute to the prediction of occupational attainment even when intelligence and socioeconomic background are taken into account? As there are far fewer studies linking personality traits directly to indices of occupational attainment, such as prestige and income, we also included prospective studies examining the impact of personality traits on related outcomes such as long-term unemployment and occupational stability. The studies listed in Table 6 attest to the fact that personality traits predict all of these work-related outcomes. For example, adolescent ratings of Neuroticism, Extraversion, Agreeableness, and Conscientiousness predicted occupational status 46 years later, even after controlling for childhood IQ ( Judge, Higgins, Thoresen, & Barrick, 1999 ). The weighted-average beta weight across the studies in Table 6 was .23 (CIs = .14 and .32), indicating that the modal effect size of personality traits was comparable with the effect of childhood SES and IQ on similar outcomes. 8
Personality Traits and Occupational Attainment
Note. SES = socioeconomic status; IHD = Institute of Human Development.
Why are personality traits related to achievement in educational and occupational domains? The personality processes involved may vary across different stages of development, and at least five candidate processes deserve research scrutiny ( Roberts, 2006 ). First, the personality-to-achievement associations may reflect “attraction” effects or “active niche-picking,” whereby people choose educational and work experiences whose qualities are concordant with their own personalities. For example, people who are more conscientious may prefer conventional jobs, such as accounting and farming ( Gottfredson, Jones, & Holland, 1993 ). People who are more extraverted may prefer jobs that are described as social or enterprising, such as teaching or business management ( Ackerman & Heggestad, 1997 ). Moreover, extraverted individuals are more likely to assume leadership roles in multiple settings ( Judge, Bono, Ilies, & Gerhardt, 2002 ). In fact, all of the Big Five personality traits have substantial relations with better performance when the personality predictor is appropriately aligned with work criteria ( Hogan & Holland, 2003 ). This indicates that if people find jobs that fit with their dispositions they will experience greater levels of job performance, which should lead to greater success, tenure, and satisfaction across the life course ( Judge et al., 1999 ).
Second, personality-to-achievement associations may reflect “recruitment effects,” whereby people are selected into achievement situations and are given preferential treatment on the basis of their personality characteristics. These recruitment effects begin to appear early in development. For example, children’s personality traits begin to influence their emerging relationships with teachers at a young age ( Birch & Ladd, 1998 ). In adulthood, job applicants who are more extraverted, conscientious, and less neurotic are liked better by interviewers and are more often recommended for the job ( Cook, Vance, & Spector, 2000 ).
Third, personality traits may affect work outcomes because people take an active role in shaping their work environment ( Roberts, 2006 ). For example, leaders have tremendous power to shape the nature of the organization by hiring, firing, and promoting individuals. Cross-sectional studies of groups have shown that leaders’ conscientiousness and cognitive ability affect decision making and treatment of subordinates ( LePine, Hollenbeck, Ilgen, & Hedlund, 1997 ). Individuals who are not leaders or supervisors may shape their work to better fit themselves through job crafting ( Wrzesniewski & Dutton, 2001 ) or job sculpting ( Bell & Staw, 1989 ). They can change their day-to-day work environments through changing the tasks they do, organizing their work differently, or changing the nature of the relationships they maintain with others ( Wrzesniewski & Dutton, 2001 ). Presumably these changes in their work environments lead to an increase in the fit between personality and work. In turn, increased fit with one’s environment is associated with elevated performance ( Harms, Roberts, & Winter, 2006 ).
Fourth, some personality-to-achievement associations emerge as consequences of “attrition” or “deselection pressures,” whereby people leave achievement settings (e.g., schools or jobs) that do not fit with their personality or are released from these settings because of their trait-correlated behaviors ( Cairns & Cairns, 1994 ). For example, longitudinal evidence from different countries shows that children who exhibit a combination of poor self-control and high irritability or antagonism are at heightened risk of unemployment ( Caspi, Wright, Moffitt, & Silva, 1998 ; Kokko, Bergman, & Pulkkinen, 2003 ; Kokko & Pulkkinen, 2000 ).
Fifth, personality-to-achievement associations may emerge as a result of direct effects of personality on performance. Personality traits may promote certain kinds of task effectiveness; there is some evidence that this occurs in part via the processing of information. For example, higher positive emotions facilitate the efficient processing of complex information and are associated with creative problem solving ( Ashby, Isen, & Turken, 1999 ). In addition to these effects on task effectiveness, personality may directly affect other aspects of work performance, such as interpersonal interactions ( Hurtz & Donovan, 2000 ). Personality traits may also directly influence performance motivation; for example, Conscientiousness consistently predicts stronger goal setting and self-efficacy, whereas Neuroticism predicts these motivations negatively ( Erez & Judge, 2001 ; Judge & Ilies, 2002 ).
GENERAL DISCUSSION
It is abundantly clear from this review that specific personality traits predict important life outcomes, such as mortality, divorce, and success in work. Depending on the sample, trait, and outcome, people with specific personality characteristics are more likely to experience important life outcomes even after controlling for other factors. Moreover, when compared with the effects reported for SES and cognitive abilities, the predictive validities of personality traits do not appear to be markedly different in magnitude. In fact, as can be seen in Figures 1 – 3 , in many cases, the evidence supports the conclusion that personality traits predict these outcomes better than SES does. Despite these impressive findings, a few limitations and qualifications must be kept in mind when interpreting these data.

Average effects (in the correlation metric) of low socioeconomic status (SES), low IQ, low Conscientiousness (C), low Extraversion/Positive Emotion(E/PE), Neuroticism (N), and low Agreeableness (A) on mortality. Error bars represent standard error.

Average effects (in the standardized beta weight metric) of high socioeconomic status (SES), high parental income, high IQ, and high personality trait scores on occupational outcomes.
The requirement that we only examine the incremental validity of personality measures after controlling for SES and cognitive abilities, though clearly the most stringent test of the relevance of personality traits, is also arbitrarily tough. In fact, controlling for variables that are assumed to be nuisance factors can obscure important relations ( Meehl, 1971 ). For example, SES, cognitive abilities, and personality traits may determine life outcomes through indirect rather than direct pathways. Consider cognitive abilities. These are only modest predictors of occupational attainment when “all other factors are controlled,” but they play a much more important, indirect role through their effect on educational attainment. Students with higher cognitive abilities tend to obtain better grades and go on to achieve more in the educational sphere across a range of disciplines ( Kuncel, Crede, & Thomas, 2007 ; Kuncel, Hezlett, & Ones, 2001 , 2004 ); in turn, educational attainment is the best predictor of occupational attainment. This observation about cumulative indirect effects applies equally well to SES and personality traits.
Furthermore, the effect sizes associated with SES, cognitive abilities, and personality traits were all uniformly small-to-medium in size. This finding is entirely consistent with those from other reviews showing that most psychological constructs have effect sizes in the range between .10 and .40 on a correlational scale ( Meyer et al., 2001 ). Our hope is that reviews like this one can help adjust the norms researchers hold for what the modal effect size is in psychology and related fields. Studies are often disparaged for having small effects as if it is not the norm. Moreover, small effect sizes are often criticized without any understanding of their practical significance. Practical significance can only be determined if we ground our research by both predicting consequential outcomes, such as mortality, and by translating the results into a metric that is clearly understandable, such as years lost or number of deaths. Correlations and ratio statistics do not provide this type of information. On the other hand, some researchers have translated their results into metrics that most individuals can grasp. As we noted in the introduction, Rosenthal (1990) showed that taking aspirin prevented approximately 85 heart attacks in the patients of 10,845 physicians despite the meager −.03 correlation between this practice and the outcome of having a heart attack. Several other studies in our review provided similar benchmarks. Hardarson et al., (2001) showed that 148 fewer people died in their high education group (out of 869) than in their low education group, despite the effect size being equal to a correlation of −.05. Danner et al. (2001) showed that the association between positive emotion and longevity was associated with a gain of almost 7 years of additional life, despite having an average effect size of around .20. Of course, our ability to draw these types of conclusions necessitates grounding our research in more practical outcomes and their respective metrics.
There is one salient difference between many of the studies of SES and cognitive abilities and the studies focusing on personality traits. The typical sample in studies of the long-term effect of personality traits was a sample of convenience or was distinctly unrepresentative. In contrast, many of the studies of SES and cognitive ability included nationally representative and/or remarkably large samples (e.g., 500,000 participants). Therefore, the results for SES and cognitive abilities are generalizable, whereas it is more difficult to generalize findings from personality research. Perhaps the situation will improve if future demographers include personality measures in large surveys of the general population.
Recommendations
One of the challenges of incorporating personality measures in large studies is the cost–benefit trade off involved with including a thorough assessment of personality traits in a reasonably short period of time. Because most personality inventories include many items, researchers may be pressed either to eliminate them from their studies or to use highly abbreviated measures of personality traits. The latter practice has become even more common now that most personality researchers have concluded that personality traits can be represented within five to seven broad domains ( Goldberg, 1993b ; Saucier, 2003 ). The temptation is to include a brief five-factor instrument under the assumption that this will provide good coverage of the entire range of personality traits. However, the use of short, broad bandwidth measures can lead to substantial decreases in predictive validity ( Goldberg, 1993a ), because short measures of the Big Five lack the breadth and depth of longer personality inventories. In contrast, research has shown that the predictive validity of personality measures increases when one uses a well-elaborated measure with many lower order facets ( Ashton, 1998 ; Mershon & Gorsuch, 1988 ; Paunonen, 1998 ; Paunonen & Ashton, 2001 ).
However, research participants do not have unlimited time, and researchers may need advice on the selection of optimal measures of personality traits. One solution is to pay attention to previous research and focus on those traits that have been found to be related to the specific outcomes under study instead of using an omnibus personality inventory. For example, given the clear and consistent finding that the personality trait of Conscientiousness is related to health behaviors and mortality (e.g., Bogg & Roberts, 2004 ; Friedman, 2000 ), it would seem prudent to measure this trait well if one wanted to control for this factor or include it in any study of health and mortality. Moreover, it appears that specific facets of this domain, such as self-control and conventionality, are more relevant to health than are other facets such as orderliness ( Bogg & Roberts, 2004 ). If researchers are truly interested in assessing personality traits well, then they should invest the time necessary for the task. This entails moving away from expedient surveys to more in-depth assessments. Finally, if one truly wants to assess personality traits well, then researchers should use multiple methods for this purpose and should not rely solely on self-reports ( Eid & Diener, 2006 ).
We also recommend that researchers not equate all individual differences with personality traits. Personality psychologists also study constructs such as motivation, interests, emotions, values, identities, life stories, and self-regulation (see Mayer, 2005 , and Roberts & Wood, 2006 , for reviews). Moreover, these different domains of personality are only modestly correlated (e.g., Ackerman & Heggested, 1997 ; Roberts & Robins, 2000 ). Thus, there are a wide range of additional constructs that may have independent effects on important life outcomes that are waiting to be studied.
Conclusions
In light of increasingly robust evidence that personality matters for a wide range of life outcomes, researchers need to turn their attention to several issues. First, we need to know more about the processes through which personality traits shape individuals’ functioning over time. Simply documenting that links exist between personality traits and life outcomes does not clarify the mechanisms through which personality exerts its effects. In this article, we have suggested a number of potential processes that may be at work in the domains of health, relationships, and educational and occupational success. Undoubtedly, other personality processes will turn out to influence these outcomes as well.
Second, we need a greater understanding of the relationship between personality and the social environmental factors already known to affect health and development. Looking over the studies reviewed above, one can see that specific personality traits such as Conscientiousness predict occupational and marital outcomes that, in turn, predict longevity. Thus, it may be that Conscientiousness has both direct and indirect effects on mortality, as it contributes to following life paths that afford better health, and may also directly affect the ways in which people handle health-related issues, such as whether they exercise or eat a healthy diet ( Bogg & Roberts, 2004 ). One idea that has not been entertained is the potential synergistic relation between personality traits and social environmental factors. It may be the case that the combination of certain personality traits and certain social conditions creates a potent cocktail of factors that either promotes or undermines specific outcomes. Finally, certain social contexts may wash out the effect of individual difference factors, and, in turn, people possessing certain personality characteristics may be resilient to seemingly toxic environmental influences. A systematic understanding of the relations between personality traits and social environmental factors associated with important life outcomes would be very helpful.
Third, the present results drive home the point that we need to know much more about the development of personality traits at all stages in the life course. How does a person arrive in adulthood as an optimistic or conscientious person? If personality traits affect the ways that individuals negotiate the tasks they face across the course of their lives, then the processes contributing to the development of those traits are worthy of study ( Caspi & Shiner, 2006 ; Caspi & Shiner, in press ; Rothbart & Bates, 2006 ). However, there has been a tendency in personality and developmental research to focus on personality traits as the causes of various outcomes without fully considering personality differences as an outcome worthy of study ( Roberts, 2005 ). In contrast, research shows that personality traits continue to change in adulthood (e.g., Roberts, Walton, & Viechtbauer, 2006 ) and that these changes may be important for health and mortality. For example, changes in personality traits such as Neuroticism have been linked to poor health outcomes and even mortality ( Mroczek & Spiro, 2007 ).
Fourth, our results raise fundamental questions about how personality should be addressed in prevention and intervention efforts. Skeptical readers may doubt the relevance of the present results for prevention and intervention in light of the common assumption that personality is highly stable and immutable. However, personality traits do change in adulthood ( Roberts, Walton, & Viechtbauer, 2006 ) and can be changed through therapeutic intervention ( De Fruyt, Van Leeuwen, Bagby, Rolland, & Rouillon, 2006 ). Therefore, one possibility would be to focus on socializing factors that may affect changes in personality traits, as the resulting changes would then be leveraged across multiple domains of life. Further, the findings for personality traits should be of considerable interest to professionals dedicated to promoting healthy, happy marriages and socioeconomic success. Some individuals will clearly be at a heightened risk of problems in these life domains, and it may be possible to target prevention and intervention efforts to the subsets of individuals at the greatest risk. Such research can likewise inform the processes that need to be targeted in prevention and intervention. As we gain greater understanding of how personality exerts its effects on adaptation, we will achieve new insights into the most relevant processes to change. Moreover, it is essential to recognize that it may be possible to improve individuals’ lives by targeting those processes without directly changing the personality traits driving those processes (e.g., see Rapee, Kennedy, Ingram, Edwards, & Sweeney, 2005 , for an interesting example of how this may occur). In all prevention and intervention work, it will be important to attend to the possibility that most personality traits can have positive or negative effects, depending on the outcomes in question, the presence of other psychological attributes, and the environmental context ( Caspi & Shiner, 2006 ; Shiner, 2005 ).
Personality research has had a contentious history, and there are still vestiges of doubt about the importance of personality traits. We thus reviewed the comparative predictive validity of personality traits, SES, and IQ across three objective criteria: mortality, divorce, and occupational attainment. We found that personality traits are just as important as SES and IQ in predicting these important life outcomes. We believe these metaanalytic findings should quell lingering doubts. The closing of a chapter in the history of personality psychology is also an opportunity to open a new chapter. We thus invite new research to test and document how personality traits “work” to shape life outcomes. A useful lead may be taken from cognate research on social disparities in health ( Adler & Snibbe, 2003 ). Just as researchers are seeking to understand how SES “gets under the skin” to influence health, personality researchers need to partner with other branches of psychology to understand how personality traits “get outside the skin” to influence important life outcomes.

Average effects (in the correlation metric) of low socioeconomic status (SES), low Conscientiousness (C), Neuroticism (N), and low Agreeableness (A) on divorce. Error bars represent standard error.
Acknowledgments
Preparation of this paper was supported by National Institute of Aging Grants AG19414 and AG20048; National Institute of Mental Health Grants MH49414, MH45070, MH49227; United Kingdom Medical Research Council Grant G0100527; and by grants from the Colgate Research Council. We would like to thank Howard Friedman, David Funder, George Davie Smth, Ian Deary, Chris Fraley, Linda Gottfredson, Josh Jackson, and Ben Karney for their comments on earlier drafts of this article.
1 This situation is in no way particular to epidemiological or medical studies using odds, rate, and hazard ratios as outcomes. The field of psychology reports results in a Babylonian array of test statistics and effect sizes also.
2 The population effects for the rate ratio and correlation metric were not based on identical data because in some cases the authors did not report rate ratio information or did not report enough information to compute a rate ratio and a CI.
3 Most of the studies of SES and mortality were compiled from an exhaustive review of the literature on the effect of childhood SES and mortality ( Galobardes et al., 2004 ). We added several of the largest studies examining the effect of adult SES on mortality (e.g., Steenland et al., 2002 ), and to these we added the results from the studies on cognitive ability and personality that reported SES effects. We also did standard electronic literature searches using the terms socioeconomic status, cognitive ability , and all-cause mortality . We also examined the reference sections from the list of studies and searched for papers that cited these studies. Experts in the field of epidemiology were also contacted and asked to identify missing studies. The resulting SES data base is representative of the field, and as the effects are based on over 3 million data points, the effect sizes and CIs are very stable. The studies of cognitive ability and mortality represent all of the studies found that reported usable data.
4 We identified studies through electronic searches that included the terms personality traits, extroversion, agreeableness, hostility, conscientiousness, emotional stability, neuroticism, openness to experience , and all-cause mortality . We also identified studies through reference sections of the list of studies and through studies that cited each study. A number of studies were not included in this review because we focused on studies that were prospective and controlled for background factors.
5 We did not examine the domain of Openness to Experience because there were only two studies that tested the association with mortality.
6 We identified studies using electronic searches including the terms divorce, socioeconomic status , and cognitive ability . We also identified studies through examining the reference sections of the studies and through studies that cited each study.
7 We did not transform the standardized beta weights into the correlation metric because almost all authors failed to provide the necessary information for the transformation (CIs or standard errors). Therefore, we averaged the results in the beta weight metric instead. As the sampling distribution of beta weights is unknown, we used the formula for the standard error of the partial correlation (√ N −k−2) to estimate CIs.
8 In making comparisons between correlations and regression weights, it should be kept in mind that although the two are identical for orthogonal predictors, most regression weights tend to be smaller than the corresponding zero-order validity correlations because of predictor redundancy (R.A. Peterson & Brown, 2005 ).
- Abas M, Hotopf M, Prince M. Depression and mortality in a high-risk population. British Journal of Psychiatry. 2002; 181 :123–128. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Abelson RP. A variance explanation paradox: When a little is a lot. Psychological Bulletin. 1985; 97 :129–133. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ackerman PL, Heggestad ED. Intelligence, personality, and interests: Evidence for overlapping traits. Psychological Bulletin. 1997; 121 :219–245. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Adler NE, Boyce T, Chesney MA, Cohen S, Folkman S, Kahn RL, Syme SL. Socioeconomic status and health: The challenge of the gradient. American Psychologist. 1994; 49 :15–24. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Adler NE, Snibbe AC. The role of psychosocial processes in explaining the gradient between socioeconomic status and health. Current Directions in Psychological Science. 2003; 12 :119–123. [ Google Scholar ]
- Allison PJ, Guichard C, Fung K, Gilain L. Dispositional optimism predicts survival status 1 year after diagnosis in head and neck cancer patients. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2003; 21 :543–548. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Almada SJ, Zonderman AB, Shekelle RB, Dyer AR, Daviglus ML, Costa PT, Stamler J. Neuroticism and cynicism and risk of death in middle-aged men: The Western Electric Study. Psychosomatic Medicine. 1991; 53 :165–175. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Amato PR, Rogers SJ. A longitudinal study of marital problems and subsequent divorce. Journal of Marriage and the Family. 1997; 59 :612–624. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ashby FG, Isen AM, Turken AU. A neuropsychological theory of positive affect and its influence on cognition. Psychological Review. 1999; 106 :529–550. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ashton MC. Personality and job performance: The importance of narrow traits. Journal of Organizational Behavior. 1998; 19 :289–303. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bandura A. Social cognitive theory of personality. In: Pervin LA, John OR, editors. Handbook of personality: Theory and research. 2nd ed. New York: Guilford Press; 1999. pp. 154–196. [ Google Scholar ]
- Barefoot JC, Dahlstrom WG, Williams RB. Hostility, CHD incidence, and total mortality: A 25-year follow-up study of 255 physicians. Psychosomatic Medicine. 1983; 45 :59–63. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Barefoot JC, Dodge KA, Peterson BL, Dahlstrom WG, Williams RB. The Cook-Medley hostility scale: Item content and ability to predict survival. Psychosomatic Medicine. 1989; 51 :46–57. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Barefoot JC, Larsen S, von der Lieth L, Schroll M. Hostility, incidence of acute myocardial infarction, and mortality in a sample of older Danish men and women. American Journal of Epidemiology. 1995; 142 :477–484. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Barefoot JC, Maynard KE, Beckham JC, Brummett BH, Hooker K, Siegler IC. Trust, health, and longevity. Journal of Behavioral Medicine. 1998; 21 :517–526. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Barefoot JC, Siegler IC, Nowlin JB, Peterson BL, Haney TL, Williams RB. Suspiciousness, health, and mortality: A follow-up stuffy of 500 older adults. Psychosomatic Medicine. 1987; 49 :450–457. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bassuk SS, Berkman LF, Amick BC. Socioeconomic status and mortality among the elderly: Findings from four U.S. Communities. American Journal of Epidemiology. 2002; 155 :520–533. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Beebe-Dimmer J, Lynch JW, Turrell G, Lustgarten S, Raghunathan T, Kaplan GA. Childhood and adult socioeconomic conditions and 31-year mortality risk in women. American Journal of Epidemiology. 2004; 159 :481–490. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bell NE, Staw BM. People as sculptors versus sculpture: The roles of personality and personal control in organizations. In: Arthur MB, Hall DT, Lawrence BS, editors. Handbook of career theory. New York: Cambridge University Press; 1989. pp. 232–251. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bentler PM, Newcomb MD. Longitudinal study of marital success and failure. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 1978; 46 :1053–1070. [ Google Scholar ]
- Berkman LF, Glass T, Brissette I, Seeman TE. From social integration to health. Social Science Medicine. 2000; 51 :843–857. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Birch SH, Ladd GW. Children’s interpersonal behaviors and the teacher-child relationship. Developmental Psychology. 1998; 34 :934–946. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Blau PM, Duncan OD. The American occupational structure. New York: Wiley; 1967. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bogg T, Roberts BW. Conscientiousness and health behaviors: A meta-analysis of the leading behavioral contributors to mortality. Psychological Bulletin. 2004; 130 :887–919. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bolger N, Zuckerman A. A framework for studying personality in the stress process. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1995; 69 :890–902. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bornstein RF. Criterion validity of objective and projective dependency tests: A meta-analytic assessment of behavioral prediction. Psychological Assessment. 1999; 11 :48–57. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bosworth HB, Schaie KW. Survival effects in cognitive function, cognitive style, and sociodemographic variables in the Seattle Longitudinal Study. Experimental Aging Research. 1999; 25 :121–139. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Boyle SH, Williams RB, Mark DB, Brummett BH, Siegler IC, Barefoot JC. Hostility, age, and mortality in a sample of cardiac patients. American Journal of Cardiology. 2005; 96 :64–66. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Boyle SH, Williams RB, Mark DB, Brummett BH, Siegler IC, Helms MJ, Barefoot JC. Hostility as a predictor of survival in patients with coronary artery disease. Psychosomatic Medicine. 2004; 66 :629–632. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bradley RH, Corwyn RF. Socioeconomic status and child development. Annual Review of Psychology. 2002; 53 :371–399. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bucher HC, Ragland DR. Socioeconomic indicators and mortality from coronary heart disease and cancer: A 22-year follow-up of middle-aged men. American Journal of Public Health. 1995; 85 :1231–1236. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cairns RB, Cairns BD. Lifelines and risks: Pathways of youth in our time. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press; 1994. [ Google Scholar ]
- Caspi A, Elder GH, Bern DJ. Moving against the world: Life-course patterns of explosive children. Developmental Psychology. 1987; 23 :308–313. [ Google Scholar ]
- Caspi A, Elder GH, Bern DJ. Moving away from the world: Life-course patterns of shy children. Developmental Psychology. 1988; 24 :824–831. [ Google Scholar ]
- Caspi A, Roberts BW, Shiner R. Personality development. Annual Review of Psychology. 2005; 56 :453–484. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Caspi A, Shiner RL. Personality development. In: Damon W, Lerner R, Eisenberg N, editors. Handbook of child psychology: Vol. 3. Social, emotional, and personality development. 6th ed. New York: Wiley; 2006. pp. 300–365. (Vol. Ed.) [ Google Scholar ]
- Caspi A, Shiner RL. Temperament and personality. In: Rutter M, Bishop D, Pine D, Scott S, Stevenson J, Taylor E, Thapar A, editors. Rutter’s child and adolescent psychiatry. 5th ed. London: Blackwell; (in press) [ Google Scholar ]
- Caspi A, Wright BR, Moffitt TE, Silva PA. Early failure in the labor market: Childhood and adolescent predictors of unemployment in the transition to adulthood. American Sociological Preview. 1998; 63 :424–451. [ Google Scholar ]
- Christensen AJ, Ehlers SL, Wiebe JS, Moran PJ, Raichle K, Ferneyhough K, Lawton WJ. Patient personality and mortality: A 4-year prospective examination of chronic renal insufficiency. Health Psychology. 2002; 21 :315–320. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Claussen B, Davey-Smith G, Thelle D. Impact of childhood and adulthood socioeconomic position on cause specific mortality: The Oslo Mortality Study. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health. 2003; 57 :40–45. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- The Cochrane Collaboration. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions 4.2.5. 2005 May; Retrieved June 1, 2006, from http://www.cochrane.org/resources/handbook/handbook.pdf .
- Cohen S, Doyle WJ, Turner RB, Alper CM, Skoner DR. Emotional style and susceptibility to the common cold. Psychosomatic Medicine. 2003a; 65 :652–657. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cohen S, Doyle WJ, Turner RB, Alper CM, Skoner DR. Sociability and susceptibility to the common cold. Psychological Science. 2003b; 14 :389–395. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Conger RD, Donnellan MB. An interactionist perspective on the socioeconomic context of human development. Annual Review of Psychology. 2007; 58 :175–199. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Contrada RJ, Cather C, O’Leary A. Personality and health: Dispositions and processes in disease susceptibility and adaptation to illness. In: Pervin LA, John OR, editors. Handbook of personality: Theory and research. 2nd ed. New York: Guilford Press; 1999. pp. 576–604. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cook KW, Vance CA, Spector RE. The relation of candidate personality with selection-interview outcomes. Journal of Applied Social Psychology. 2000; 30 :867–885. [ Google Scholar ]
- Curtis S, Southall H, Congdon P, Dodgeon B. Area effects on health variation over the life-course: Analysis of the longitudinal study sample in England using new data on are of residence in childhood. Social Science & Medicine. 2004; 58 :57–74. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Danner DD, Snowden DA, Friesen WV. Positive emotions in early life and longevity: Findings from the Nun Study. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 2001; 80 :804–813. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Davey-Smith G, Hart C, Blane D, Hole D. Adverse socioeconomic conditions in childhood and cause specific adult mortality: Prospective observational study. British Medical Journal. 1998; 316 :1631–1635. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Deary IJ, Batty D, Gottfredson LS. Human hierarchies, health, and IQ: Comment. Science. 2005; 309 :703. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Deary IJ, Der G. Reaction time explains IQ’s association with death. Psychological Science. 2005; 16 :64–69. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- De Fruyt F, Denollet J. Type D personality: A five-factor model perspective. Psychology and Health. 2002; 17 :671–683. [ Google Scholar ]
- De Fruyt F, Van Leeuwen K, Bagby RM, Rolland J, Rouillon F. Assessing and interpreting personality change and continuity in patients treated for major depression. Psychological Assessment. 2006; 18 :71–80. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Denollet J, Sys SU, Stroobant N, Rombouts H, Gillebert TC, Brutsaert DL. Personality as independent predictor of long-term mortality in patients with coronary heart disease. Lancet. 1996; 347 :417–421. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Donnellan MB, Conger RD, Bryant CM. The Big Five and enduring marriages. Journal of Research in Personality. 2004; 38 :481–504. [ Google Scholar ]
- Doornbos G, Kromhout D. Educational level and mortality in a 32-year follow-up study of 18-year old men in the Netherlands. International Journal of Epidemiology. 1990; 19 :374–379. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Eid M, Diener E. Handbook of psychological assessment: A multimethod perspective. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association; 2006. [ Google Scholar ]
- Erez A, Judge TA. Relationship of core self-evaluations to goal setting, motivation, and performance. Journal of Applied Psychology. 2001; 86 :1270–1279. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Everson SA, Kauhanen J, Kaplan GA, Goldberg DE, Julkunen J, Tuomilehto J, Salonen JT. Hostility and increased risk of mortality and acute myocardial infarction: The mediating role of behavioral risk factors. American Journal of Epidemiology. 1997; 146 :142–152. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fergusson DM, Horwood LJ, Shannon FT. A proportional hazards model of family breakdown. Journal of Marriage and the Family. 1984; 46 :539–549. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fiscella K, Franks P. Individual income, income inequality, health, and mortality: What are the relationships? Health Services Research. 2000; 35 :307–318. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Friedman HS. Long-term relations of personality and health: Dynamisms, mechanisms, tropisms. Journal of Personality. 2000; 68 :1089–1108. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Friedman HS, Tucker JS, Tomlinson-Keasey C, Schwartz JE, Wingard DL, Criqui MH. Does childhood personality predict longevity? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1993; 65 :176–185. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Funder DC. The personality puzzle. New York: Norton; 2004. [ Google Scholar ]
- Funder DC, Ozer DJ. Behavior as a function of the situation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1983; 44 :107–112. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gallo LC, Matthews KA. Understanding the association between socioeconomic status and physical health: Do negative emotions play a role? Psychological Bulletin. 2003; 129 :10–51. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Galobardes B, Lynch JW, Smith GD. Childhood socioeconomic circumstances and cause-specific mortality in adulthood: Systematic review and interpretation. Epidemiologic Reviews. 2004; 26 :7–21. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ganguli M, Dodge HH, Mulsant BH. Rates and predictors of mortality in an aging, rural, community-based cohort. Archives of General Psychiatry. 2002; 59 :1046–1052. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Giltay EJ, Geleijnse JM, Zitman EG, Hoekstra T, Schouten EG. Dispositional optimism and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in a prospective cohort of elderly Dutch men and women. Archives of General Psychiatry. 2004; 61 :1126–1135. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Goldberg LR. The structure of personality traits: Vertical and horizontal aspects. In: Funder DC, Parke RD, Tomlinson-Keasey C, Widaman K, editors. Studying lives through time: Personality and development. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association; 1993a. pp. 169–188. [ Google Scholar ]
- Goldberg LR. The structure of phenotypic personality traits. American Psychologist. 1993b; 48 :26–34. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gottfredson GD, Jones EM, Holland JL. Personality and vocational interests: The relation of Holland’s six interest dimensions to five robust dimensions of personality. Journal of Counseling Psychology. 1993; 40 :518–524. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gottman JM. What predicts divorce? The relationship between marital processes and marital outcomes. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum; 1994. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gottman JM, Coan J, Carrere S, Swanson C. Predicting marital happiness and stability from newlywed interactions. Journal of Marriage and Family. 1998; 60 :5–22. [ Google Scholar ]
- Grossarth-Maticek R, Bastianns J, Kanazir DT. Psychosocial factors as strong predictors of mortality from cancer, ischaemic heart disease and stroke: The Yugoslav prospective study. Journal of Psychosomatic Research. 1985; 29 :167–176. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Haller AO, Portes A. Status attainment processes. Sociology of Education. 1973; 46 :51–91. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hardarson T, Gardarsdottir M, Gudmundsson KT, Thorgeirsson G, Sigvaldason H, Sigfusson N. The relationship between educational level and mortality: The Reykjavik Study. Journal of Internal Medicine. 2001; 249 :495–502. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Harms PD, Roberts BW, Winter D. Becoming the Harvard man: Person-environment fit, personality development, and academic success. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin. 2006; 32 :851–865. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hart CL, Taylor MD, Davey-Smith G, Whalley LJ, Starr JM, Hole DJ, et al. Childhood IQ, social class, deprivation, and their relationships with mortality and morbidity risk in later life: Prospective observational study linking the Scottish Mental Survey 1932 and the Midspan Studies. Psychosomatic Medicine. 2003; 65 :877–883. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hauser RM, Tsai S, Sewell WH. A model of stratification with response error in social and psychological variables. Sociology of Education. 1983; 56 :20–46. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hearn MD, Murray DM, Luepker RV. Hostility, coronary heart disease, and total mortality: A 33-year follow-up study of university students. Journal of Behavioral Medicine. 1989; 12 :105–121. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hedges LV, Olkin I. Statistical methods for meta-analysis. San Diego, CA: Academic Press; 1985. [ Google Scholar ]
- Helson R. [Unpublished data from the Mills Longitudinal Study] Berkeley: University of California; 2006. Unpublished raw data. [ Google Scholar ]
- Helson R, Roberts BW. Personality of young adult couples and wives’ work patterns. Journal of Personality. 1992; 60 :575–597. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Helson R, Roberts BW, Agronick G. Enduringness and change in creative personality and the prediction of occupational creativity. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1995; 69 :1173–1183. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hemphill JF. Interpreting the magnitude of correlation coefficients. American Psychologist. 2003; 58 :78–79. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Heslop P, Smith GD, Macleod J, Hart C. The socioeconomic position of employed women, risk factors and mortality. Social Science and Medicine. 2001; 53 :477–485. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hirokawa K, Nagata C, Takatsuka N, Shimizu H. The relationships of a rationality/antiemotionality personality scale to mortalities of cancer and cardiovascular disease in a community population in Japan. Journal of Psychosomatic Research. 2004; 56 :103–111. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hogan J, Holland B. Using theory to evaluate personality and job-performance relations: A socioanalytic perspective. Journal of Applied Psychology. 2003; 88 :100–112. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Holley P, Yabiku S, Benin M. The relationship between intelligence and divorce. Journal of Family Issues. 2006; 27 :1723–1748. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hollis JF, Connett JE, Stevens VJ, Greenlick MR. Stressful life events, Type A behavior, and the prediction of cardiovascular and total mortality over six years. Journal of Behavioral Medicine. 1990; 13 :263–280. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hosegood V, Campbell OMR. Body mass index, height, weight, arm circumference, and mortality in rural Bangladeshi women: A 19-year longitudinal study. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2003; 77 :341–347. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hurtz GM, Donovan JJ. Personality and job performance: The Big Five revisited. Journal of Applied Psychology. 2000; 85 :869–879. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Huston TL, Caughlin JP, Houts RM, Smith SE, George LJ. The connubial crucible: Newlywed years as predictors of marital delight, distress, and divorce. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 2001; 80 :237–252. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Iribarren C, Jacobs DR, Kiefe CI, Lewis CE, Matthews KA, Roseman JM, Hulley SB. Causes and demographic, medical, lifestyle and psychosocial predictors of premature mortality: the CARDIA study. Social Science & Medicine. 2005; 60 :471–482. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jalovaara M. Socio-economic status and divorce in first marriages in Finland 1991–1993. Population Studies. 2001; 55 :119–133. [ Google Scholar ]
- Jencks C, Crouse J, Mueser P. The Wisconsin model of status attainment: A national replication with improved measures of ability and aspiration. Sociology of Education. 1983; 56 :3–19. [ Google Scholar ]
- Jensen-Campbell LA, Graziano WG. Agreeableness as a moderator of interpersonal conflict. Journal of Personality. 2001; 69 :323–361. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jockin V, McGue M, Lykken DT. Personality and divorce: A genetic analysis. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1996; 71 :288–299. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Johnson W, Krueger RF. How money buys happiness: Genetic and environmental processes linking finances and life satisfaction. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 2006; 90 :680–691. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Judge TA, Bono JE, Ilies R, Gerhardt MW. Personality and leadership: A qualitative and quantitative review. Journal of Applied Psychology. 2002; 87 :765–780. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Judge TA, Higgins CA, Thoresen CJ, Barrick MR. The big five personality traits, general mental ability, and career success across the life span. Personnel Psychology. 1999; 52 :621–652. [ Google Scholar ]
- Judge TA, Ilies R. Relationship of personality to performance motivation: A meta-analytic review. Journal of Applied Psychology. 2002; 87 :797–807. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kaplan GA, Wilson TW, Cohen RD, Kauhanen J, Wu M, Salonen JT. Social functioning and overall mortality: Prospective evidence from the Kuopio Ischemic Heart Disease Risk Factor Study. Epidemiology. 1994; 5 :495–500. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Karney BR, Bradbury TN. The longitudinal course of marital quality and stability: A review of theory, methods, and research. Psychological Bulletin. 1995; 118 :3–34. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kelly EL, Conley JJ. Personality and compatibility: A prospective analysis of marital stability and marital satisfaction. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1987; 52 :27–40. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kenford SL, Smith SS, Wetter DW, Jorenby DE, Fiore MC, Baker TB. Predicting relapse back to smoking: Contrasting affective and physical models of dependence. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 2002; 70 :216–227. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Khang Y, Kim HR. Explaining socioeconomic inequality in mortality among South Koreans: An examination of multiple pathways in a nationally representative longitudinal study. International Journal of Epidemiology. 2005; 34 :630–637. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kinnunen U, Pulkkinen L. Childhood socio-emotional characteristics as antecedents of marital stability and quality. European Psychologist. 2003; 8 :223–237. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kokko K, Bergman LR, Pulkkinen L. Child personality characteristics and selection into long-term unemployment in Finnish and Swedish longitudinal samples. International Journal of Behavioral Development. 2003; 27 :134–144. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kokko K, Pulkkinen L. Aggression in childhood and long-term unemployment in adulthood: A cycle of maladaptation and some protective factors. Developmental Psychology. 2000; 36 :463–472. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Korten AE, Jorm AF, Jaio Z, Letenneur L, Jacomb PA, Henderson AS, et al. Health, cognitive, and psychosocial factors as predictors of mortality in an elderly community sample. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health. 1999; 53 :83–88. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Koskenvuo M, Kaprio J, Rose RJ, Kesaniemi A, Sarna S, Heikkila K, Langinvainio H. Hostility as a risk factor for mortality and ischemic heart disease in men. Psychosomatic Medicine. 1988; 50 :330–340. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kuh D, Hardy R, Langenberg C, Richards M, Wadsworth MEJ. Mortality in adults aged 26–54 years related to socioeconomic conditions in childhood and adulthood: Post war birth cohort study. British Medical Journal. 2002; 325 :1076–1080. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kuh D, Maclean M. Women’s childhood experience of parental separation and their subsequent health and socioeconomic status in adulthood. Journal of Biosocial Science. 1990; 22 :121–135. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kuh D, Richards M, Hardy R, Butterworth S, Wadsworth MEJ. Childhood cognitive ability and deaths up until middle age: A post-war birth cohort study. International Journal of Epidemiology. 2004; 33 :408–413. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kuncel NR, Crede M, Thomas LL. A comprehensive meta-analysis of the predictive validity of the Graduate Management Admission Test (GMAT) and undergraduate grade point average (UGPA) Academy of Management Learning and Education. 2007; 6 :51–68. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kuncel NR, Hezlett SA, Ones DS. A comprehensive meta-analysis of the predictive validity of the Graduate Record Examinations: Implications for graduate student selection and performance. Psychological Bulletin. 2001; 127 :162–181. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kuncel NR, Hezlett SA, Ones DS. Academic performance, career potential, creativity, and job performance: Can one construct predict them all? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 2004; 86 :148–161. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kurdek LA. Predicting marital dissolution: A 5-year prospective longitudinal study of newlywed couples. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1993; 64 :221–242. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lantz PM, House JS, Lepkowski JM, Williams DR, Mero RP, Chen J. Socioeconomic factors, health behaviors, and mortality. Journal of the American Medical Association. 1998; 279 :1703–1708. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lawrence E, Bradbury TN. Physical aggression and marital dysfunction: A longitudinal analysis. Journal of Family Psychology. 2001; 15 :135–154. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lee WE, Wadsorth MEJ, Hotopf M. The protective role of trait anxiety: S longitudinal cohort study. Psychological Medicine. 2006; 36 :345–351. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- LePine JA, Hollenbeck JR, Ilgen DR, Hedlund J. Effects of individual differences on the performance of hierarchical decision-making teams: Much more than g . Journal of Applied Psychology. 1997; 82 :803–811. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lewis M. Issues in the study of personality development. Psychological Inquiry. 2001; 12 :67–83. [ Google Scholar ]
- Loeb J. The personality factor in divorce. Journal of Consulting Psychology. 1966; 30 :562. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lund R, Holstein BE, Osler M. Marital history from age 15 to 40 years and subsequent 10-year mortality: A longitudinal study of Danish males born in 1953. International Journal of Epidemiology. 2004; 33 :389–397. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Luster T, McAdoo H. Family and child influences on educational attainment: A secondary analysis of the High/Scope Perry preschool data. Developmental Psychology. 1996; 32 :26–39. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lynch JW, Kaplan GA, Cohen RD, Kauhanen J, Wilson TW, Smith NL, Salonen JT. Childhood and adult socioeconomic status as predictors of mortality in Finland. Lancet. 1994; 343 :424–527. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Maier H, Smith J. Psychological predictors of mortality in old age. Journal of Gerontology: Psychological Sciences. 1999; 54B :44–54. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Martin LT, Friedman HS. Comparing personality scales across time: An illustrative study of validity and consistency in life-span archival data. Journal of Personality. 2000; 68 :85–110. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Martin LT, Kubzansky LD. Childhood cognitive performance and risk of mortality: A prospective cohort study of gifted individuals. American Journal of Epidemiology. 2005; 162 :887–890. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Maruta T, Colligan RC, Malinchoc M, Offord KP. Optimists vs. pessimists: Survival rate among medical patients over a 30-year period. Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 2000; 75 :140–143. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Maruta T, Hamburgen ME, Jennings CA, Offord KP, Colligan RC, Frye RL, Malinchoc M. Keeping hostility in perspective: Coronary heart disease and the hostility scale on the Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory. Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 1993; 68 :109–114. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mayer JD. A tale of two visions: Can a new view of personality help integrate psychology? American Psychologist. 2005; 60 :294–307. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McCarron P, Gunnell D, Harrison GL, Okasha M, Davey-Smith G. Temperament in young adulthood and later mortality: Prospective observational study. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health. 2003; 57 :888–892. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McCranie EW, Kahan J. Personality and multiple divorce. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease. 1986; 174 :161–164. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McCrainie EW, Watkins LO, Brandsma JM, Sisson BD. Hostility, coronary heart disease (CHD) incidence, and total mortality: Lack of association in a 25-year follow-up study of 478 physicians. Journal of Behavioral Medicine. 1986; 9 :119–125. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Meehl RE. High school yearbooks: A reply to Schwarz. Journal of Abnormal Psychology. 1971; 77 :143–148. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mershon B, Gorsuch RL. Number of factors in personality sphere: Does increase in factors increase predictability of real life criteria? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1988; 55 :675–680. [ Google Scholar ]
- Meyer GJ, Finn SE, Eyde LD, Kay GG, Moreland KL, Dies RR, et al. Psychological testing and psychological assessment. American Psychologist. 2001; 56 :128–165. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Miller GE, Cohen S, Rabin BS, Skoner DR, Doyle WJ. Personality and tonic cardiovascular, neuroendocrine, and immune parameters. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity. 1999; 13 :109–123. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mischel W. Personality and assessment. New York: Wiley; 1968. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mroczek DK, Spiro A. Personality change influences mortality in older men. Psychological Science. 2007; 18 :371–376. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Murberg TA, Bru E, Aarsland T. Personality as predictor of mortality among patients with congestive heart failure: A two-year follow-up study. Personality and Individual Differences. 2001; 30 :749–757. [ Google Scholar ]
- Myers DG. The American paradox: Spiritual hunger in an age of plenty. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press; 2000. [ Google Scholar ]
- Orbuch TL, Veroff J, Hassan H, Horrocks J. Who will divorce: A 14-year longitudinal study of black couples and white couples. Journal of Social and Personal Relationships. 2002; 19 :179–202. [ Google Scholar ]
- Osler M, Andersen AN, Due P, Lund R, Damsgaard MT, Holstein BE. Socioeconomic position in early life, birth weight, childhood cognitive function, and adult mortality. A longitudinal study of Danish men born in 1953. Journal of Epidemiology Community Health. 2003; 57 :681–686. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Osler M, Prescott E, Gronbaek M, Christensen U, Due P, Enghorn G. Income inequality, individual income, and mortality in Danish adults: Analysis of pooled data from two cohort studies. British Medical Journal. 2002; 324 :1–4. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ozer DJ, Benet-Martinez V. Personality and the prediction of consequential outcomes. Annual Review of Psychology. 2006; 57 :401–421. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Paul AM. The cult of personality. New York: Free Press; 2004. [ Google Scholar ]
- Paunonen SV. Hierarchical organization of personality and prediction of behavior. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1998; 74 :538–556. [ Google Scholar ]
- Paunonen SV, Ashton MC. Big Five factors and facets and the prediction of behavior. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 2001; 81 :524–539. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pervin LA, John OP. Handbook of personality theory and research. New York: Guilford Press; 1999. [ Google Scholar ]
- Peterson C, Seligman MER, Yurko KH, Martin LR, Friedman HS. Catastrophizing and untimely death. Psychological Science. 1998; 2 :127–130. [ Google Scholar ]
- Peterson RA, Brown SR. On the use of beta coefficients in meta-analysis. Journal of Applied Psychology. 2005; 90 :175–181. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pressman SD, Cohen S. Does positive affect influence health? Psychological Bulletin. 2005; 131 :925–971. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pudaric S, Sundquist J, Johansson S. Country of birth, instrumental activities of daily living, self-rated health and mortality: A Swedish population-based survey of people aged 55–74. Social Science and Medicine. 2003; 56 :2439–2503. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rapee RM, Kennedy S, Ingram M, Edwards S, Sweeney L. Prevention and early intervention of anxiety disorders in inhibited preschool children. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 2005; 73 :488–497. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Reiss HT, Capobianco A, Tsai FT. Finding the person in personal relationships. Journal of Personality. 2002; 70 :813–850. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Roberts BW. Blessings, banes, and possibilities in the study of childhood personality. Merrill Palmer Quarterly. 2005; 51 :367–378. [ Google Scholar ]
- Roberts BW. Personality development and organizational behavior. In: Staw BM, editor. Research on organizational behavior. Greenwich, CT: Elsevier Science/JAI Press; 2006. pp. 1–41. [ Google Scholar ]
- Roberts BW, Bogg T. A 30-year longitudinal study of the relationships between conscientiousness-related traits, and the family structure and health-behavior factors that affect health. Journal of Personality. 2004; 72 :325–354. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Roberts BW, Caspi A, Moffitt T. Work experiences and personality development in young adulthood. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 2003; 84 :582–593. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Roberts BW, Robins RW. Broad dispositions, broad aspirations: The intersection of the Big Five dimensions and major life goals. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin. 2000; 26 :1284–1296. [ Google Scholar ]
- Roberts BW, Walton K, Viechtbauer W. Patterns of mean-level change in personality traits across the life course: A meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Psychological Bulletin. 2006; 132 :1–25. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Roberts BW, Wood D. Personality development in the context of the neo-socioanalytic model of personality. In: Mroczek D, Little T, editors. Handbook of personality development. Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum; 2006. pp. 11–39. [ Google Scholar ]
- Robins RW, Caspi A, Moffitt TE. Two personalities, one relationship: Both partners’ personality traits shape the quality of a relationship. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 2000; 79 :251–259. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Robins RW, Caspi A, Moffitt TE. It’s not just who you’re with, it’s who you are: Personality and relationship experiences across multiple relationships. Journal of Personality. 2002; 70 :925–964. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Roisman GE, Masten AS, Coatsworth D, Tellegen A. Salient and emerging developmental tasks in the transition to adulthood. Child Development. 2004; 75 :123–133. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosenthal R. How are we doing in soft psychology. American Psychologist. 1990; 45 :775–777. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosenthal R. Meta-analytic procedures for social research. Rev. ed. Newbury Park, CA: Sage; 1991. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosenthal R. Effect sizes in behavioral and biomedical research. In: Bicman L, editor. Validity and social experimentation: Don Campbell’s legacy. Newbury Park, CA: Sage; 2000. pp. 121–139. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosenthal R, Rubin DB. R equivalent : A simple effect size indicator. Psychological Methods. 2003; 8 :492–496. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ross L, Nisbett RE. The person and the situation: Perspectives of social psychology. New York: McGraw-Hill Book Company; 1991. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rothbart MK, Bates JE. Temperament. In: Damon W, Lerner R, Eisenberg N, editors. Handbook of child psychology: Vol. 3. Social, emotional, and personality development. 6th ed. New York: Wiley; 2006. pp. 99–166. (Vol. Ed.) [ Google Scholar ]
- Rozanski A, Blumenthal JA, Kaplan J. Impact of psychological factors on the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease and implications for therapy. Circulation. 1999; 99 :2192–2217. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sapolsky RM. The influence of social hierarchy on primate health. Science. 2005; 308 :648–652. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sarason IG, Smith RE, Diener E. Personality research: Components of variance attributable to the person and the situation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1975; 32 :199–204. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Saucier G. An alternative multi-language structure for personality attributes. European Journal of Personality. 2003; 76 :179–205. [ Google Scholar ]
- Schaie KW. The course of adult intellectual development. American Psychologist. 1994; 49 :304–313. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Scheier MF, Carver CS. On the power of positive thinking. Current Directions in Psychological Science. 1993; 2 :26–30. [ Google Scholar ]
- Schmidt FL, Hunter JE. The validity and utility of selection methods in personnel psychology: Practical and theoretical implications of 85 years of research findings. Psychological Bulletin. 1998; 124 :262–274. [ Google Scholar ]
- Schulz R, Bookwala J, Knapp JE, Scheier M, Williamson GM. Pessimism, age, and cancer mortality. Psychology and Aging. 1996; 11 :304–309. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Seibert SE, Kraimer ML, Crant JM. What do proactive people do? A longitudinal model linking proactive personality and career success. Personnel Psychology. 2001; 54 :845–874. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sewell WH, Haller AO, Portes A. The educational and early occupational process. American Sociological Review. 1969; 34 :82–92. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sewell WH, Hauser RM. The Wisconsin longitudinal study of social and psychological factors in aspirations and achievements. Research in Sociology of Education and Socialization. 1980; 1 :59–101. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sewell WH, Hauser RM. The influence of The American Occupational Structure on the Wisconsin model. Contemporary Sociology. 1992; 21 :598–603. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shiner RL. An emerging developmental science of personality: Current progress and future prospects. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly. 2005; 51 :379–387. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shipley BA, Der G, Taylor MD, Deary IJ. Cognition and all-cause mortality across the entire adult age range: Health and lifestyle survey. Psychosomatic Medicine. 2006; 68 :17–24. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Skolnick A. Married lives: Longitudinal perspectives on marriage. In: Eichorn DH, Clausen JA, Haan N, Honzik MP, Mussen PH, editors. Present and past in midlife. New York: Academic Press; 1981. pp. 270–300. [ Google Scholar ]
- Smith AW, Meitz JEG. Vanishing supermoms and other trends in marital dissolution, 1969–1978. Journal of Marriage and the Family. 1985; 47 :53–65. [ Google Scholar ]
- Smith TW. Personality as risk and resilience in physical health. Current Directions in Psychological Science. 2006; 15 :227–231. [ Google Scholar ]
- Smith TW, Gallo L. Personality traits as risk factors for physical illness. In: Baum A, Evenson T, Singer J, editors. Handbook of health psychology. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum; 2001. pp. 139–174. [ Google Scholar ]
- Snyder M, Stukas A. Interpersonal processes: The interplay of cognitive, motivational, and behavioral activities in social interaction. Annual Review of Psychology. 1999; 50 :273–303. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Steenland K, Henley J, Thun M. All-cause and cause-specific death rates by educational status for two million people in two American Cancer Society cohorts, 1959–1996. American Journal of Epidemiology. 2002; 156 :11–21. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- St. John PD, Montgomery PR, Kristjansson B, McDowell I. Cognitive scores, even with the normal range, predict death and institutionalization. Age and Ageing. 2002; 31 :373–378. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Suls J, Martin R. The daily life of the garden-variety neurotic: Reactivity, stressor exposure, mood spillover, and maladaptive coping. Journal of Personality. 2005; 73 :1485–1509. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Surtees PG, Wainwright NWJ, Luben R, Day NE, Khaw K. Prospective cohort study of hostility and the risk of cardiovascular disease mortality. International Journal of Cardiology. 2005; 100 :155–161. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Surtees PG, Wainwright NWJ, Luben R, Khaw K, Day NE. Sense of coherence and mortality in men and women in the EPIC-Norfolk United Kingdom prospective cohort study. American Journal of Epidemiology. 2003; 158 :1202–1209. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Taylor MD, Hart CL, Davey-Smith G, Whalley LJ, Hole DJ, Wilson V, Deary IJ. Childhood IQ and marriage by mid-life: The Scottish Mental Survey 1932 and the Midspan studies. Personality and Individual Differences. 2005; 38 :1621–1630. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tenconi MT, Devoti G, Comelli M RIFLE Research Group. Role of socioeconomic indicators in the prediction of all causes and coronary heart disease mortality in over 12,000 men—The Italian RIFLE pooling project. European Journal of Epidemiology. 2000; 16 :565–571. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tharenou P. Going up? Do traits and informal social processes predict advancing in management? Academy of Management Journal. 2001; 44 :1005–1017. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tucker JS, Kressin NR, Spiro A, Ruscio J. Intrapersonal characteristics and the timing of divorce: A prospective investigation. Journal of Social and Personal Relationships. 1998; 15 :211–225. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tzeng JM, Mare RD. Labor market and socioeconomic effects on marital stability. Social Science Research. 1995; 24 :329–351. [ Google Scholar ]
- Vagero D, Leon D. Effect of social class in childhood and adulthood on adult mortality. Lancet. 1994; 343 :1224–1225. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Watson D, Hubbard B, Wiese D. General traits of personality and affectivity as predictors of satisfaction in intimate relationships: Evidence from self-and partner-ratings. Journal of Personality. 2000; 68 :413–449. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Weiss A, Costa PT. Domain and facet personality predictors of all-cause mortality among Medicare patients aged 65 to 100. Psychosomatic Medicine. 2005; 67 :1–10. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Whalley LJ, Deary IJ. Longitudinal cohort study of childhood IQ and survival up to age 76. British Medical Journal. 2001; 322 :1–5. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wilson RS, Bienias JL, Mendes de Leon CF, Evans DA, Bennet DA. Negative affect and mortality in older persons. American Journal of Epidemiology. 2003; 9 :827–835. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wilson RS, Krueger KR, Gu L, Bienas JL, Mendes de Leon CF, Evans DA. Neuroticism, extraversion, and mortality in a defined population of older persons. Psychosomatic Medicine. 2005; 67 :841–845. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wilson RS, Mendes de Leon CF, Bienias JL, Evans DA, Bennett DA. Personality and mortality in old age. Journal of Gerontology: Psychological Sciences. 2004; 59 :110–116. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wrzesniewski A, Dutton JE. Crafting a job: Revisioning employees as active crafters of their work. Academy of Management Review. 2001; 26 :179–201. [ Google Scholar ]
Can Personal Identity Be Changed? Essay
A person’s personality is a unique combination of spiritual and physical characteristics based on personal and behavioral tendencies. Changing one’s personality is a complex and irreparable process, but nonetheless achievable. In practice, there are many ways to change a person’s personality based on their goals, desires, and needs.
Personality is a combination of many traits, including feelings, thoughts, behavior, and opinions. Sometimes our traits change on their own or due to causes beyond our control. For example, we may change our habits due to a new job or family (Noonan 89). But this does not mean that we can completely change our personalities.
In fact, it is possible to change one’s personality, although it takes a lot of time and effort to do so. Some linguists believe that we can change our personalities by using certain techniques. For example, techniques such as thought transformation, behavior modification, etc (Verhoeven et al. 42). All of these techniques can help a person transform their personality.
For example, if you want to change your personality, you can try new things. You can visit new places, try new types of food, etc. These new experiences will help you acquire new habits and can change your thinking patterns. Additionally, you can study new topics and observe the behavior of others (Noonan 208). These actions will help you learn the behavior you want to emulate.
One of the most effective ways to change one’s personality is self-development. A person needs to take responsibility for their personality and begin to work on their development. They need to understand what changes they need to make to their personality to reach their goal. It is important to understand that self-development should become a habit (Verhoeven et al. 54). To become better, one must constantly strive for improvement.
Learning techniques of self-motivation and emotional control can also help a person change their personality. Self-motivation can help a person in making decisions and achieving desired results. It can help people understand and accept their behavior and actions (Verhoeven et al. 51). With self-motivation, people can learn to achieve their goals, make the right decisions, and generally succeed in life.
Also, psychological technologies can be used to change one’s personality. Many people use psychotherapy to work through their problems and change their personalities. Psychotherapy helps a person make more rational decisions and get used to new behavioral models (Noonan 39). In addition, psychotherapy can help a person change their thoughts, feelings, and emotions and help them accept themselves as they are.
Finally, changing one’s personality can be done with the help of artificial intelligence. Artificial intelligence helps people understand themselves and change their behavior. Many artificial intelligence programs can understand a person’s personality traits and help them change them so they can reach their goals (Verhoeven et al. 49). Additionally, artificial intelligence can help people realize their shortcomings and weaknesses and find more effective ways to change their personalities.
In conclusion, it can be said that changing one’s personality is a complex process but achievable. A person can use many methods to change their personality, including self-development, learning motivation techniques, psychotherapy, and using artificial intelligence. All these techniques will help a person to change their personality and become the best version of themselves; one just needs to understand and accept themselves as they are and keep moving forward.
Works Cited
Noonan, Harold W. Personal identity . Routledge, 2019.
Verhoeven, Monique, Astrid MG Poorthuis, and Monique Volman. “The role of school in adolescents’ identity development. A literature review.” Educational Psychology Review 31 (2019): 35-63.
- Changing Behavior for Exercise Maintenance
- Development of Management Capability
- Leadership Principles for Effectiveness
- Personality and Cultural Groups Analysis
- Shared Identity vs. Fluidity of Racial Classifications
- Identity in the "Beyond the Veil" Video Analysis
- Immigration, Race, and Ethnicity
- Asian American and Hispanic Identities in the US
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, May 23). Can Personal Identity Be Changed? https://ivypanda.com/essays/can-personal-identity-be-changed/
"Can Personal Identity Be Changed?" IvyPanda , 23 May 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/can-personal-identity-be-changed/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'Can Personal Identity Be Changed'. 23 May.
IvyPanda . 2024. "Can Personal Identity Be Changed?" May 23, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/can-personal-identity-be-changed/.
1. IvyPanda . "Can Personal Identity Be Changed?" May 23, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/can-personal-identity-be-changed/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Can Personal Identity Be Changed?" May 23, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/can-personal-identity-be-changed/.

Does your personality change as you get older?
Good news: we get better over time.

Between adolescence and adulthood, you go through a host of changes — jobs, regrettable haircuts and relationships that come and go. But what about who you are at your core? As you grow older, does your personality change?
Personality is the pattern of thoughts, feelings and behaviors unique to a person. People tend to think of personality as fixed. But according to psychologists, that's not how it works. "Personality is a developmental phenomenon. It's not just a static thing that you're stuck with and can't get over," said Brent Roberts, a psychologist at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
That's not to say that you're a different person each day you wake up. In the short term, change can be nearly imperceptible, Roberts told Live Science. Longitudinal studies, in which researchers survey the personalities of participants regularly over many years, suggest that our personality is actually stable on shorter time scales.
Related: Why do people have different personalities?
In one study, published in 2000 in the journal Psychological Bulletin , researchers analyzed the results of 152 longitudinal studies on personality, which followed participants ranging in age from childhood to their early 70s. Each of these studies measured trends in the Big Five personality traits. This cluster of traits, which include extroversion, agreeableness, conscientiousness, openness to experience, and neuroticism, are a mainstay of personality research. The researchers found that individuals' levels of each personality trait, relative to other participants, tended to stay consistent within each decade of life.
That pattern of consistency begins around age 3, and perhaps even earlier, said Brent Donnellan, professor and chair of psychology at Michigan State University. When psychologists study children, they don't measure personality traits in the same way they do for adults. Instead, they look at temperament — the intensity of a person's reactions to the world. We come into the world with unique temperaments, and research suggests that our temperaments as children — for example, whether we're easy going or prone to temper tantrums, eager or more reluctant to approach strangers — correspond to adult personality traits. "A shy 3-year-old acts a lot different from a shy 20-something. But there's an underlying core," Donnellan told Live Science.
Earlier temperament seems to affect later life experience. For example, one 1995 study published in the journal Child Development followed children from the age of 3 until the age of 18. The researchers found, for instance, that children who were shyer and more withdrawn tended to grow into unhappier teenagers.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
But those decades add up. Throughout all those years, our personality is still changing, but slowly, Roberts said. "It's something that's subtle," he added. You don't notice it on that five-to-10-year time scale, but in the long term, it becomes pronounced. In 1960, psychologists surveyed over 440,000 high school students — around 5% of all students in the country at that time. The students answered questions about everything from how they reacted to emotional situations to how efficiently they got work done. Fifty years later, researchers tracked down 1,952 of these former students and gave them the same survey. The results, published in 2018 in the Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , found that in their 60s, participants scored much higher than they had as teenagers on questions measuring calmness, self-confidence, leadership and social sensitivity.
Again and again, longitudinal studies have found similar results. Personality tends to get "better" over time. Psychologists call it "the maturity principle." People become more extraverted, emotionally stable, agreeable and conscientious as they grow older. Over the long haul, these changes are often pronounced.
Some individuals might change less than others, but in general, the maturity principle applies to everyone. That makes personality change even harder to recognize in ourselves — how your personality compares with that of your peers doesn't change as much as our overall change in personality, because everyone else is changing right along with you. "There's good evidence that the average self-control of a 30-year-old is higher than a 20-year-old," Donnellan said. "At the same time, people who are relatively self-controlled at 18 also tend to be relatively self-controlled at age 30."
— Which personality types are most likely to be happy?
— What is consciousness?
— Can we ever stop thinking?
So why do we change so much? Evidence suggests it's not dramatic life events, such as marriage, the birth of a child or loss of a loved one. Some psychologists actually suggest these events reinforce your personality as you bring your characteristics with you to that particular situation, Donnellan said.
Related: How accurate is the Myers-Briggs personality test?
Instead, changing expectations placed on us — as we adjust to university, the work force, starting a family — slowly wears us in, almost like a pair of shoes, Roberts said. "Over time you are asked in many contexts across life to do things a bit differently," he said. "There's not a user manual for how to act, but there's very clear implicit norms for how we should behave in these situations." So we adapt.
Depending on how you look at it, it's a revelation that's either unsettling or hopeful. Over time, personality does change, progressively and consistently — like tectonic plates shifting rather than an earthquake . "That opens up the question: Over the life course, how much of a different person do we become?" Roberts said.
Originally published on Live Science .
Isobel Whitcomb is a contributing writer for Live Science who covers the environment, animals and health. Her work has appeared in the New York Times, Fatherly, Atlas Obscura, Hakai Magazine and Scholastic's Science World Magazine. Isobel's roots are in science. She studied biology at Scripps College in Claremont, California, while working in two different labs and completing a fellowship at Crater Lake National Park. She completed her master's degree in journalism at NYU's Science, Health, and Environmental Reporting Program. She currently lives in Portland, Oregon.
Many kids are unsure if Alexa and Siri have feelings or think like people, study finds
'Scent therapy' helps unlock memories in people with depression, trial finds
AI can 'fake' empathy but also encourage Nazism, disturbing study suggests
Most Popular
- 2 10 surprising things that are made from petroleum
- 3 What's the highest place on Earth that humans live?
- 4 Scientists just discovered an enormous lithium reservoir under Pennsylvania
- 5 DeepMind's AI program AlphaFold3 can predict the structure of every protein in the universe — and show how they function
- 2 Neanderthals could talk — but how sophisticated was their language?
- 3 Things are finally looking up for the Voyager 1 interstellar spacecraft
- 4 New display tech paves the way for 'most realistic' holograms in regular eyeglasses
- 5 Auroras could paint Earth's skies again in early June. Here are the key nights to watch for.
How to Masterfully Describe Your Personality in an Essay: A Step-by-Step Guide 2023

Introduction
Step 1: self-reflection and introspection, step 2: identifying core values and beliefs, step 3: gathering evidence and examples.
- Step 4: Show, don't tell
Step 5: Structuring your essay effectively
Step 6: balancing self-awareness and humility, step 7: seeking feedback and editing.
Describing your personality in an essay is not simply an exercise in self-expression; it is a transformative process that allows you to artfully communicate and convey the intricate nuances of your character to the reader. By delving into the depths of your self-awareness, personal growth, and the values that serve as the compass guiding your actions and decisions, you embark on a journey of self-discovery and introspection. In this comprehensive step-by-step guide , we will navigate the intricacies of crafting a compelling personality description in your essay, providing you with the necessary tools to masterfully articulate your unique qualities, experiences, and perspectives.
At its core, the act of describing your personality in an essay is an opportunity to authentically showcase who you are. It is a platform to illuminate the multifaceted nature of your being, unveiling the layers that make you distinct and individual. Through self-reflection and introspection , you delve into the recesses of your soul, gaining a deeper understanding of your own personality traits and characteristics. This process of self-exploration allows you to unearth the strengths that define you and the weaknesses that provide opportunities for growth.
Identifying your core values and beliefs is another essential step in effectively describing your personality. By exploring your fundamental principles and ideals, you gain insight into the motivations behind your actions and the driving force behind your decisions . These values serve as the undercurrent that weaves together the fabric of your personality, giving coherence and purpose to your thoughts and behaviors. Understanding how your personality traits align with your core values enables you to articulate a more comprehensive and authentic depiction of yourself.
To breathe life into your personality description, it is crucial to gather evidence and examples that showcase your traits in action. Recall specific instances where your personality has manifested itself, and examine the behaviors, thoughts, and emotions that were present. By drawing on these concrete examples, you provide tangible proof of your personality claims, allowing the reader to envision your character in vivid detail.
However, it is not enough to simply tell the reader about your personality traits; you must show them through vivid and descriptive language. By employing sensory details and evocative storytelling, you paint a vibrant picture that engages the reader’s imagination. It is through this artful depiction that your personality comes to life on the page, leaving a lasting impression.
Crafting an effective structure for your essay is also paramount to conveying your personality in a coherent and engaging manner. A well-structured essay captivates the reader from the outset with an engaging introduction that sets the tone and grabs their attention. Organizing your essay around key personality traits or themes creates a logical progression of ideas, enabling a seamless flow from one aspect of your personality to the next. This careful structuring enhances the readability and impact of your essay, allowing the reader to follow your journey of self-expression with ease.
In describing your personality, it is essential to strike a delicate balance between self-awareness and humility. While it is important to acknowledge your strengths and accomplishments, it is equally crucial to avoid sounding arrogant. Honesty about your weaknesse s and areas for growth demonstrates humility and a willingness to learn from experiences, fostering personal growth and development.
Also, seeking feedback and diligently editing your essay play a vital role in refining your personality description. Sharing your work with trusted individuals allows for constructive criticism, providing valuable insights into how effectively your personality is being portrayed. By carefully incorporating this feedback and paying attention to grammar, punctuation, and clarity, you can ensure that your essay is polished and ready to make a lasting impression . Below are the step by step guide on how to masterfully describe your personality in an essay

Before diving into writing, take the time to deeply understand your own personality traits and characteristics. Reflect on your strengths and weaknesses , considering how they have influenced your actions and interactions with others. Additionally, contemplate significant life experiences that have shaped your personality, providing valuable insights into who you are today.
Your core values and beliefs are the guiding principles that define your character. Explore what truly matters to you and the ideals that drive your decisions . By connecting your personality traits to these fundamental values, you create a more comprehensive understanding of yourself, providing a solid foundation for your essay.
To effectively describe your personality, draw upon specific instances where your traits were on display. Recall experiences that highlight your behavior, thoughts, and emotions. By utilizing concrete examples, you lend credibility to your claims about your personality, allowing the reader to envision your character in action.
Step 4: Show, don’t tell
Avoid falling into the trap of generic and vague descriptions. Instead, use vivid language and sensory details to bring your personality to life. Engage the reader’s imagination by painting a clear picture through storytelling. Let them experience your traits firsthand, making your essay more engaging and memorable.
Crafting a well-structured essay is crucial for conveying your personality in a coherent and engaging manner. Begin with an attention-grabbing introduction that captivates the reader’s interest. Organize your essay around key personality traits or themes, ensuring a logical progression of ideas. Maintain a smooth flow between paragraphs, enhancing the overall readability of your essay.
While it’s essential to highlight your strengths, be careful not to come across as arrogant. Emphasize your accomplishments and positive attributes without boasting. Simultaneously, be honest about your weaknesses and areas for growth , demonstrating humility and a willingness to learn from experiences. This balance showcases maturity and self-awareness.
Sharing your essay with trusted individuals can provide valuable perspectives and constructive criticism. Seek feedback from mentors, teachers, or friends who can offer insights into your essay’s strengths and areas that need improvement. Revise and refine your essay based on this feedback, paying close attention to grammar, punctuation, and clarity.
Incorporating these steps and techniques will allow you to masterfully describe your personality in an essay, capturing the essence of who you are in a compelling and authentic manner. Whether you are writing personality essays, an essay about personalities, or an essay on personality, the introduction of your personality essay should create a strong impression. It serves as a gateway for the reader to delve into your unique characteristics and perspectives. By effectively integrating these steps and maintaining a balanced approach, you can create a personality essay introduction that sets the stage for a captivating exploration of your individuality. So, how would you describe yourself? Use these guidelines and examples to express your personality with confidence and authenticity in your essay.
Mastering the art of describing your personality in an essay allows you to authentically express yourself and connect with readers on a deeper level. By embracing self-reflection and emphasizing personal growth, you create a c ompelling narrative that showcases your unique qualities. So, embark on this journey of self-expression and let your personality shine through your writing. Embrace authenticity, as it is through effective self-expression that personal growth and understanding can flourish.
If you’re looking for professional essay writing and editing services, GradeSmiths is here to help. With a team of experienced writers and editors, GradeSmiths offers reliable and high-quality assistance to students in need of essay support. Whether you need help with essay writing, editing, proofreading, or refining your content, GradeSmiths can provide the expertise you require. Their dedicated team is committed to delivering well-crafted essays that meet academic standards and showcase your unique ideas and voice. With GradeSmiths, you can trust that your essay will receive the attention and care it deserves.
- RESEARCH PAPER FOR SALE
- RESEARCH PAPER WRITER
- RESEARCH PROPOSAL WRITING SERVICES
- SCHOLARSHIP ESSAY HELP
- SPEECH HELP
- STATISTICS HOMEWORK HELP
- TERM PAPER WRITING HELP
- THESIS EDITING SERVICES
- THESIS PROPOSAL WRITING SERVICE
- TRIGONOMETRY HOMEWORK HELP
- ADMISSION ESSAY WRITING HELP
- BIOLOGY PAPER WRITING SERVICE
- BOOK REPORT WRITING HELP
- BUY BOOK REVIEW
- BUY COURSEWORKS
- BUY DISCUSSION POST
- BUY TERM PAPER
- CAPSTONE PROJECT WRITING SERVICE
- COURSEWORK WRITING SERVICE
- CRITIQUE MY ESSAY
- CUSTOM RESEARCH PAPER
- CUSTOMER CONDUCT
- DISSERTATION EDITING SERVICE
- DISSERTATION WRITERS
- DO MY DISSERTATION FOR ME
- DO MY POWERPOINT PRESENTATION
- EDIT MY PAPER
- English Research Paper Writing Service
- ENGLISH RESEARCH PAPER WRITING SERVICE
- ESSAY WRITING HELP
- ESSAYS FOR SALE
- GRADUATE PAPER WRITING SERVICE
- LAW ASSIGNMENT WRITING HELP
- MARKETING ASSIGNMENT WRITING HELP
- NON-PLAGIARIZED ESSAYS
- NURSING ASSIGNMENT HELP
- PAY FOR COURSEWORK
- PAY FOR ESSAYS
- PAY FOR LITERATURE REVIEW
- PAY FOR PAPERS
- PAY FOR RESEARCH PAPERS
- PERSONAL STATEMENT EDITING SERVICE
- PERSONAL STATEMENT WRITER
- PERSUASIVE ESSAY WRITING HELP
- PERSUASIVE ESSAY WRITING SERVICES
- PHD THESIS WRITING SERVICE
- PROOFREAD MY PAPER
- PSYCHOLOGY ESSAY WRITING SERVICES
- THESIS STATEMENT HELP
- WRITE MY ANNOTATED BIBLIOGRAPHY FOR ME
- WRITE MY CASE STUDY
- WRITE MY DISCUSSION BOARD POST
- WRITE MY LAB REPORT

Personality Change
The surprising truth is that people change all the time, we likely underestimate how much people can change..
Updated May 28, 2024 | Reviewed by Michelle Quirk
- A tendency to underestimate how much people change can lead to pessimism about addressing conflicts.
- Research shows that personality changes are not only possible but more common than believed.
- To change conflict patterns, we can think about changing situations, perspectives, or even labels we're using.

I’ve had the chance to talk to thousands of people about conflicts, and not one has ever said to me, “I'm the primary driver of the problem. Why am I so difficult?” Instead, they invariably ask how to change other people’s beliefs or bad behavior. And a lot of the time, they feel like they already know the answer: That other person will never change. They’re unreachable. They’re awful. They’re the problem .
What’s fascinating is that all sides can find ways to think this.
Picture this common scene: You meet up with a friend for coffee and soon they’re explaining to you in detail why their co-worker is so impossible to work with. In that moment have you ever wondered what that co-worker is telling their friends?
When you see the other side as “the problem,” that can preserve destructive conflict patterns. The conflict feels fated to continue, you imagine, because people don’t change.
Except they do. All the time.
Daniel Aires began dreaming of a career as a soldier when he was 10. He joined the Canadian Armed Forces at 16. One day, he was given a book about peace issues.
I remember reading the book and being absolutely enraged. How could anyone be so peaceful? How could they live their life where everyone is their brother and everyone is their sister?... I’m thinking, “This is complete lunacy!” And I took the book and I threw it in the bottom of the vehicle and drove around and it got all full of gunpowder and gasoline and I read it again, and again, and again and it wore a hole in my side pocket. I had it on me all the time. And within six months I was out of the military.
Somehow, what seemed impossible happened, and a single book changed Daniel’s life. But he had to go through a months-long invisible process first.
Most of us underestimate the likelihood of such changes. A major study found that the average person surveyed thinks their personality is far more constant than it actually is. “People, it seems, regard the present as a watershed moment at which they have finally become the person they will be for the rest of their lives.” But the study found that this just isn’t true. Most of us are closer to Daniel Aires—changing in many ways as we age.
Research into people trying to change their own personalities has found that, while difficult, it is possible. For instance two studies done with students found that many succeeded, at least over the course of four months. These students tested differently both on personality tests and on reports about their daily behaviors.
Systematic examination of the evidence on personality change highlights that there are many factors required. It’s not easy. But, then again, there are many factors required to not change.
Where we don’t change, it might be more because of repeated habits and being in the same situations over and over. Therefore, one important way to address a difficult conflict pattern is to change the situation. For instance, go for a walk together instead of staying seated .
Another way to change the situation is to think about it differently. Find common values , feelings, and needs. And try not to fix the person in your mind with all sorts of simple labels .
Researchers suggest that words that portray a situation as more fixed or straightforward than it really is come with serious costs. They reduce accuracy and understanding. They can lead to more entrenched and less rewarding conflicts.
An example is the label “toxic masculinity.” Such broad terms can make for frustrating conversations in part because people actually mean very different things by them. What’s worse, evidence shows that masculinity is actually changing—even amongst groups of men who traditionally felt strong pressures to be rugged and stoic individualists. So a term like “toxic masculinity” might harmfully oversimplify what’s happening, making it feel more stuck than it is.

There are no guarantees that a given conflict can be positively transformed. But it can be empowering to stop expecting that nothing will change. Lots of changes are happening. You have more power to impact them than you might think.
Richard Gater. Why ‘toxic masculinity’ isn’t a useful term for understanding all of the ways to be a man . The Conversation. October 11, 2023.

Matthew Legge is the author of Are We Done Fighting? Building Understanding in a World of Hate and Division. He is a Peace Program Coordinator at Canadian Friends Service Committee.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- International
- New Zealand
- South Africa
- Switzerland
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
More From Forbes
How to build a strengths-based career through personality assessments.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Side view of a business woman imagining to be a super hero looking aspired.
What are your superpowers? I always ask my coachees this question during our first encounter. Surprisingly, many don't know what to say. I believe aligning your professional path with your inherent strengths and personality traits is crucial for achieving long-term success and happiness, to be honest. Unfortunately, this is not how many career paths are designed at companies nowadays. Performance reviews focus too much on what is wrong, what is missing, and what needs to be improved but too little on what your strengths are and what you should continue unlocking.
The rise of artificial intelligence (AI) has transformed industries, reshaped job markets, and raised concerns about job displacement. As AI continues to automate routine tasks and decision-making processes, the future of work increasingly favors skills and attributes that machines cannot easily replicate. Building a career based on your strengths is a powerful strategy to stay relevant in this evolving landscape and thrive.
A holistic approach is required to consider individual strengths, emotional intelligence , and personality insights. Personality assessments are pivotal in this process, offering deep insights into one's unique traits and preferences. However, the true power of these assessments is unlocked when paired with professional coaching.
Understanding and Leveraging Your Strengths
Identifying and leveraging your strengths is fundamental to achieving excellence and fulfillment in your career. Individuals engaging in activities that align with their natural talents are more likely to experience heightened engagement, productivity, and satisfaction. Recognizing and developing these strengths leads to a state of "flow," where work feels effortless and enjoyable and where stressful situations can be overcome more easily.
Once you have a clear understanding of your strengths, personality traits, and emotional intelligence, you can integrate these insights into your career development by focusing on developing skills that enhance your strengths, tailoring your current role to better align with your strengths, or moving to a role where your strengths are needed.
Apple Brings Back iPhone 14 Pro For First Time At Lower Price Refurbished
Trump lashes out at robert de niro after actor calls him a ‘tyrant’ outside courthouse, trump trial prosecutor ends closing argument after nearly 5 hours jury instructions set for wednesday.
You can also improve your personal branding by highlighting your strengths in your resume, LinkedIn profile, and during job interviews. Communicating what you do best can help you stand out to potential employers and increase your chances of finding a role that fits you well.
The Role of Personality Assessments
A proficient coach can help you identify your superpowers without a self-assessment, but personality assessments can provide more a structured approach to understanding individual strengths and preferences. Here are three widely recognized assessments:
1. DISC Assessment:
The DISC assessment categorizes behavior into four primary styles: Dominance, Influence, Steadiness, and Conscientiousness. It helps individuals understand their behavior patterns, communication styles, and responses to various situations. Knowing your DISC profile can guide you in selecting roles and environments where your natural tendencies are most effective.
2. CliftonStrengths (formerly StrengthsFinder)
Developed by Gallup, this assessment identifies 34 talent themes and highlights an individual's top strengths. It focuses on what people naturally do best and encourages them to build on these talents to achieve professional excellence.
3. Emotional Intelligence (EIQ) Assessments
Emotional intelligence is the ability to recognize, understand, and manage one's emotions and those of others. EQ assessments provide insights into emotional competencies like self-awareness, self-regulation, empathy, and social skills so that you can react to what happens in your environment in a more productive way. High emotional intelligence is linked to better workplace leadership, teamwork, stress management and even time management, and it is not a genetic trait, it can be improved over time.
The Importance of a Debrief with a Coach
Personality assessments offer valuable insights, but it's important to have a debrief with a coach to fully benefit from them. Keep in mind that personality assessments are not set in stone and can change over time. They are designed to assess consistent patterns and are not heavily influenced by your current mood, unless you are going through a serious trauma, anxiety, or depression, according to Psychology Today . However, your responses may vary based on the context in which you are answering, such as whether you are considering your behavior at home or at work, or if you are responding for self-reflection or a job interview.
John Johnson from Psychology Today affirms that while some people may lie on personality tests, it's less common than you might think, even in situations like job interviews. A coach can help you interpret your assessment results, provide personalized feedback, and help you develop actionable strategies based on the insights. They can also help you avoid common pitfalls, such as relying too much on strengths without addressing weaknesses or misinterpreting the assessment results.
Building a career based on your strengths is a powerful strategy for achieving long-term success and satisfaction. Personality assessments like DISC, CliftonStrengths, and emotional intelligence assessments provide valuable insights into your unique traits and preferences. However, the true value of these assessments is realized through a debrief with a professional coach who can help interpret results, develop actionable strategies, and set realistic goals. By understanding and leveraging your strengths, you can confidently navigate your career path, avoid common pitfalls, and build a career where you don't feel like working anymore.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.
- Patient Care & Health Information
- Diseases & Conditions
- Frontotemporal dementia
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) is an umbrella term for a group of brain diseases that mainly affect the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain. These areas of the brain are associated with personality, behavior and language.
In frontotemporal dementia, parts of these lobes shrink, known as atrophy. Symptoms depend on which part of the brain is affected. Some people with frontotemporal dementia have changes in their personalities. They become socially inappropriate and may be impulsive or emotionally indifferent. Others lose the ability to properly use language.
Frontotemporal dementia can be misdiagnosed as a mental health condition or as Alzheimer's disease. But FTD tends to occur at a younger age than does Alzheimer's disease. It often begins between the ages of 40 and 65, although it can occur later in life as well. FTD is the cause of dementia about 10% to 20% of the time.
Products & Services
- A Book: Day to Day: Living With Dementia
- A Book: Mayo Clinic on Alzheimer's Disease
Symptoms of frontotemporal dementia differ from one person to the next. Symptoms get worse over time, usually over years.
People with frontotemporal dementia tend to have clusters of symptom types that occur together. They also may have more than one cluster of symptom types.
Behavioral changes
The most common symptoms of frontotemporal dementia involve extreme changes in behavior and personality. These include:
- Increasingly inappropriate social behavior.
- Loss of empathy and other interpersonal skills. For example, not being sensitive to another person's feelings.
- Lack of judgment.
- Loss of inhibition.
- Lack of interest, also known as apathy. Apathy can be mistaken for depression.
- Compulsive behaviors such as tapping, clapping, or smacking lips over and over.
- A decline in personal hygiene.
- Changes in eating habits. People with FTD typically overeat or prefer to eat sweets and carbohydrates.
- Eating objects.
- Compulsively wanting to put things in the mouth.
Speech and language symptoms
Some subtypes of frontotemporal dementia lead to changes in language ability or loss of speech. Subtypes include primary progressive aphasia, semantic dementia and progressive agrammatic aphasia, also known as progressive nonfluent aphasia.
These conditions can cause:
- Increasing trouble using and understanding written and spoken language. People with FTD may not be able to find the right word to use in speech.
- Trouble naming things. People with FTD may replace a specific word with a more general word, such as using "it" for pen.
- No longer knowing word meanings.
- Having hesitant speech that may sound telegraphic by using simple, two-word sentences.
- Making mistakes in sentence building.
Movement conditions
Rare subtypes of frontotemporal dementia cause movements similar to those seen in Parkinson's disease or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Movement symptoms may include:
- Muscle spasms or twitches.
- Poor coordination.
- Trouble swallowing.
- Muscle weakness.
- Inappropriate laughing or crying.
- Falls or trouble walking.
In frontotemporal dementia, the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain shrink and certain substances build up in the brain. What causes these changes is usually not known.
Some genetic changes have been linked to frontotemporal dementia. But more than half of the people with FTD have no family history of dementia.
Researchers have confirmed that some frontotemporal dementia gene changes also are seen in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). More research is being done to understand the connection between the conditions.
Risk factors
Your risk of getting frontotemporal dementia is higher if you have a family history of dementia. There are no other known risk factors.
Frontotemporal dementia care at Mayo Clinic
- Frontotemporal disorders. National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. https://www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/all-disorders/frontotemporal-dementia-information-page. Accessed Aug. 30, 2023.
- Loscalzo J, et al., eds. Frontotemporal dementia. In: Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine. 21st ed. McGraw Hill; 2022. https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com. Accessed Aug. 30, 2023.
- Ulugut H, et al. Frontotemporal dementia: Past, present and future. Alzheimer's & Dementia. 2023; doi:10.1002/alz.13363.
- Grossman M, et al. Frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Nature Reviews: Disease Primers. 2023; doi:10.1038/s41572-023-00447-0.
- Antonioni A, et al. Frontotemporal dementia, where do we stand? A narrative review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; doi:10.3390/ijms241411732.
- Diagnosing FTD. The Association for Frontotemporal Degeneration. https://www.theaftd.org/for-health-professionals/diagnosing-ftd/. Accessed Aug. 30, 2023.
- What are frontotemporal disorders? Causes, symptoms and treatment. National Institute on Aging. https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/what-causes-frontotemporal-disorders. Accessed Aug. 30, 2023.
- Lee SE, et al. Frontotemporal dementia: Treatment. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Accessed Aug. 30, 2023.
- Ferri FF. Frontotemporal dementia. In: Ferri's Clinical Advisor 2024. Elsevier; 2024. https://www.clinicalkey.com. Accessed Aug. 30, 2023.
- The ALLFTD team. ARTFL LEFTDS Longitudinal Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration. https://www.allftd.org/allftd-executive-team. Accessed Sept. 6, 2023.
- Providing care for a person with a frontotemporal disorder. National Institute on Aging. https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/providing-care-person-frontotemporal-disorder. Accessed Aug. 30, 2023.
- Ami TR. Allscripts EPSi. Mayo Clinic. Sept. 4, 2023.
- Alzheimer's disease research centers. National Institute on Aging. https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/alzheimers-disease-research-centers. Accessed Aug. 30, 2023.
- Participating institutions. Arizona Alzheimer's Consortium. http://azalz.org/about-us/participating-institutions/. Accessed Aug. 30, 2023.
- MRI comparison
Associated Procedures
- Positron emission tomography scan
News from Mayo Clinic
- Global consortium to study Pick's disease, rare form of early-onset dementia April 24, 2024, 03:15 p.m. CDT
- Untangling the threads of early onset dementia March 29, 2024, 03:01 p.m. CDT
- What is frontotemporal dementia? Feb. 23, 2024, 04:15 p.m. CDT
- Symptoms & causes
- Diagnosis & treatment
- Doctors & departments
- Care at Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
- Opportunities
Mayo Clinic Press
Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press .
- Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence
- The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book
- Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance
- FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment
- Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book
Your gift holds great power – donate today!
Make your tax-deductible gift and be a part of the cutting-edge research and care that's changing medicine.
- Sports Betting
- Sports Entertainment
Recommended
Rory mcilroy had private investigator serve wife with divorce papers.
- View Author Archive
- Email the Author
- Get author RSS feed
Contact The Author
Thanks for contacting us. We've received your submission.
Thanks for contacting us. We've received your submission.
Rory McIlroy’s estranged wife Erica Stoll was served divorce papers by a private investigator while at their family home in the members-only development, The Bear’s Club, in Jupiter, Fla., on May 13, according to court documents obtained by Irish newspaper The Belfast Telegraph .
McIlroy filed for divorce from Stoll, his wife of seven years, stating the marriage was “irretrievably broken,” and the documents stated the pair has a prenup.
Stoll was served the legal documents by Carl Woods — a former Palm Beach police officer, who now runs a private practice , CW Services & Associates, which serves the legal community — at 10.30 a.m. on May 13, according to the summons.

In it, Woods described Stoll as being white with blonde hair, in her 30s, thin, and standing between 5-foot-7 and 5-foot-8 in height. He said she was not wearing glasses.
McIlroy signed the divorce papers digitally while he was playing in the Wells Fargo Championship at Quail Hallow in North Carolina, which he went on to win, on May 9, per court records.
The 35-year-old Northern Irishman filed the papers in Palm Beach County Court through attorney Thomas Sasser, who represented Tiger Woods in his high-profile divorce with Elin Nordegren in 2010.

Stoll has 20 days to file a written response to McIlroy’s petition with the circuit court clerk from the day she was served, according to the documents.
“A phone call will not protect you,” the summons read. “Your written response, including the case number given above and the names of the parties, must be filed if you want the court to hear your side of the case.
“If you do not file your response on time, you may lose the case, and your wages, money and property may thereafter be taken without further warning from the court.
“There are other legal requirements. You may want to call an attorney right away. If you do not know an attorney, you may call an attorney referral service or a legal aid office (listed in the phone book.”

Stoll has yet to respond to McIlroy’s divorce filing as of May 26, when the report was published.
McIlroy and Stoll are seeking split custody of their daughter Poppy, now 3, whom they welcomed in August 2020, according to his divorce filing.
A week after the split was made public, a report by The Daily Mail said McIlroy and CBS reporter Amanda Balionis were “the talk of the links” on the PGA Tour and the two were stirring romance rumors.
The pair has yet to address that report.
McIlroy’s camp released a statement at the time that “stressed Rory’s desire to ensure this difficult time is as respectful and amicable as possible.”
His team added that he would not be commenting further on the matter.

McIlroy is set to compete at this week’s RBC Canadian Open, which runs through June 2 at Hamilton Golf and Country Club in Hamilton, Ontario.
Share this article:

Advertisement
NCAA signs off on deal that would change landscape of college sports — paying student-athletes
A major change could be coming for college athletes — they may soon start getting paid.
A tentative agreement announced Thursday by the NCAA and the country’s five biggest conferences to a series of antitrust lawsuits could direct millions of dollars directly to athletes as soon as fall 2025.
The nearly $2.8 billion settlement, which would be paid out over the next decade to 14,000 former and current student-athletes, “is an important step in the continuing reform of college sports that will provide benefits to student-athletes and provide clarity in college athletics across all divisions for years to come,” NCAA President Charlie Baker said in a joint statement Thursday night with the commissioners of the ACC, the Big 10, the Big 12, the Pac-12 and the SEC.
The federal judge overseeing the case must still sign off on the agreement, but if it is approved, it would signal a major shift in college sports in which students would play for compensation, not just scholarships, exposure and opportunities.
“This landmark settlement will bring college sports into the 21st century, with college athletes finally able to receive a fair share of the billions of dollars of revenue that they generate for their schools,” said Steve Berman, one of the lead attorneys for the plaintiffs. “Our clients are the bedrock of the NCAA’s multibillion-dollar business and finally can be compensated in an equitable and just manner for their extraordinary athletic talents.”
The NCAA and power conferences called the settlement a “road map” that would allow the uniquely American institution to provide unmatched opportunity for millions of students and write the “next chapter of college sports.”
The case, which was set to go to trial early next year, was brought by a former and a current college athlete who said the NCAA and the five wealthiest conferences improperly barred athletes from earning endorsement money. Former Arizona State swimmer Grant House and Sedona Prince, a former Oregon and current TCU basketball player, also contended in their suit that athletes were entitled to a piece of the billions of dollars the NCAA and those conferences earn from media rights agreements with television networks.
Michael McCann, a legal analyst and sports reporter at Sportico , told NBC News in an interview on Top Story with Tom Llamas the case has two components that “move away from amateurism” — one that deals with how players are paid for the past loss of earnings, including money they could have made for name, image and likeness.
“The going forward part is that colleges can opt in, conferences can opt in, as well, to pay players, to share revenue with them, to have direct pay, and that would be of course a radical from the traditions of college sports,” McCann said, adding many would say that change is warranted. “Now the athletes, at least at some schools, will get a direct stake.”

Terms of the deal were not disclosed, though some details have emerged in the past few weeks. They signal the end of the NCAA’s bedrock amateurism model that dates to its founding in 1906. Indeed, the days of NCAA punishment for athletes driving booster-provided cars started vanishing three years ago when the organization lifted restrictions on endorsement deals backed by so-called name, image and likeness, or NIL, money.
Now it is not far-fetched to look ahead to seasons when a star quarterback or a top prospect on a college basketball team not only is cashing in big-money NIL deals but also has a $100,000 school payment in the bank to play.
A host of details are still to be determined . The agreement calls for the NCAA and the conferences to pay $2.77 billion over 10 years to more than 14,000 former and current college athletes who say now-defunct rules prevented them from earning money from endorsement and sponsorship deals dating to 2016.
Some of the money would come from NCAA reserve funds and insurance, but even though the lawsuit specifically targeted five conferences that comprise 69 schools (including Notre Dame), dozens of other NCAA member schools would get smaller distributions from the NCAA to cover the mammoth payout.
Schools in the Big Ten, the Big 12 and the Atlantic Coast and Southeastern conferences would end up bearing the brunt of the settlement at a cost of about $300 million apiece over 10 years, the majority of which would be paid to athletes going forward.
The Pac-12 is also part of the settlement, with all 12 current schools sharing responsibility even though Washington State and Oregon State will be the only league members left by this fall after the 10 other schools leave.
Paying athletes
In the new compensation model, each school would be permitted but not required to set aside up to $21 million in revenue to share with athletes per year, though as revenues rose, so could the cap.
Athletes in all sports would be eligible for payments, and schools would be given the freedom to decide how the money is divvied up among sports programs. Roster restrictions would replace scholarship limits by sport.
McCann said the back pay would disproportionately go to some sports — such as football and basketball.
“The schools that I think that are certainly big football schools will probably opt in because they’re going to want to compete, they’re going to want to get the best players, because college football generates a lot of revenue,” he said.
Whether the new compensation model is subject to the Title IX gender equity law is unknown, along with whether schools would be able to bring NIL activities in-house as they hope and squeeze out the booster-run collectives that have sprouted up in the last few years to pay athletes. Both topics could lead to more lawsuits.
“There are all sorts of areas of turbulence that could present themselves,” McCann said of roadblocks that could arise.
More sports coverage
- Four decades after Michael Jordan, Caitlin Clark is getting her own line of Wilson basketballs
- Mario Andretti: Formula 1 owner personally threatened to shut out team Andretti
- Student-athletes are inking lucrative endorsement deals, but a patchwork of laws has created chaos in college sports
Other cases
The settlement is expected to cover two other antitrust cases facing the NCAA and major conferences that challenge athlete compensation rules. Hubbard v. the NCAA and Carter v. the NCAA are also in front of judges in the Northern District of California.
A fourth case, Fontenot v. NCAA, creates a potential complication, as it remains in a Colorado court after a judge denied a request to combine it with Carter. Whether Fontenot becomes part of the settlement is unknown, and it matters because the NCAA and its conferences don’t want to be on the hook for more damages should they lose in court.
“We’re going to continue to litigate our case in Colorado and look forward to hearing about the terms of a settlement proposal once they’re actually released and put in front of a court,” said George Zelcs, a plaintiffs’ attorney in Fontenot.
Headed in that direction
The solution agreed to in the settlement is a landmark but not surprising. College sports have been trending in this direction for years, with athletes receiving more and more monetary benefits and rights they say were long overdue.
In December, Baker, the former governor of Massachusetts who has been on the job for 14 months, proposed creating a new tier of Division I athletics in which the schools with the most resources would be required to pay at least half their athletes $30,000 per year. That suggestion, along with many other possibilities, remains under discussion.
The settlement would not make every issue facing college sports go away. There is still a question of whether athletes should be deemed employees of their schools, which Baker and other college sports leaders are fighting.
Some type of federal legislation or antitrust exemption would most likely still be needed to codify the terms of the settlement, protect the NCAA from future litigation and pre-empt state laws that attempt to neuter the organization’s authority. As it is, the NCAA still faces lawsuits that challenge its ability to govern itself, including setting rules limiting multiple-time transfers.
“This settlement is also a road map for college sports leaders and Congress to ensure this uniquely American institution can continue to provide unmatched opportunity for millions of students,” the joint statement said. “All of Division I made today’s progress possible, and we all have work to do to implement the terms of the agreement as the legal process continues. We look forward to working with our various student-athlete leadership groups to write the next chapter of college sports.”
Federal lawmakers have indicated they would like to get something done, but while several bills have been introduced , none have gone anywhere.
Despite the unanswered questions, one thing is clear: Major college athletics is about to become more like professional sports than ever before.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Beliefs and belief systems. While changing certain aspects of your personality might be challenging, you can realistically tackle changing some of the underlying beliefs that help shape and control how your personality is expressed. Goals and coping strategies. For example, while you might have more of a Type A personality, you can learn new ...
They found that 98 percent of the participants had changed at least one personality trait. Even our career interests are more stable than our personalities, though our jobs can also change us: In ...
What's more, those changes are usually for the better. Many studies, including some of my own, show that most adults become more agreeable, conscientious and emotionally resilient as they age. But ...
Personality traits can be defined as broad patterns of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors (Lucas & Donnellan, 2011).Early empirical research on personality mainly focused on the structure, measurement, and consequences of traits (e.g., Digman, 1990).Stability and change in traits were less common topics, largely because traits were regarded as highly stable once people reach adulthood (McCrae ...
This potential for change is important because many individuals want to change aspects of their personality and because personality influences important life outcomes. In this Review, we examine ...
Yes. While personality disorders are thought of as long-term patterns of maladaptive thinking and behavior, there is evidence that over time, symptoms of a personality disorder can decrease—even ...
Certain personality traits represent an important target for policy interventions designed to improve human welfare and life outcomes, UC Davis researchers suggest. It has long been believed that people can't change their personalities, which are largely stable and inherited. But a review of recent research in personality science points to ...
Serious diseases like dementia, addiction, or mental illness can change personality and behavior. For example, alcoholism over time triggers depression and may lead to abusive behavior. On the ...
In my work, I study when people change in their broader personality traits, how they change in their broader personality traits, and, ideally, we are also trying to get answers as to why personality traits change. Let me give you an example. I am interested in, for example, people's self-esteem.
Most notably, people's personality traits did not always stay the same over the five decades, with many people showing quite dramatic changes. "Some of the changes we saw in personality traits over the 50 years were very, very large," says the lead author of the study, Rodica Damian of the University of Houston.
In one of the strongest studies yet, the personality traits of thousands of Dutch adults were followed for several years. There was little evidence that life events like marriage, childbirth ...
Change is associated with danger and is met with suspicion; even if the change is positive. Many people see things as "being," something that "is", or at least "should be", static and stable (Schwartz, 2009). We will write a custom essay on your topic. This same opinion is often applied to a human being. Comprehending change in a ...
Personality theories seek to explain how personality forms, changes, and impacts behavior. Five key personality theories focus on biological, behavioral, psychodynamic, humanistic, and trait approaches. While these theories offer different explanations for personality, each offers important insights that help us better understand ourselves.
In contrast, research shows that personality traits continue to change in adulthood (e.g., Roberts, Walton, & Viechtbauer, 2006) and that these changes may be important for health and mortality. For example, changes in personality traits such as Neuroticism have been linked to poor health outcomes and even mortality (Mroczek & Spiro, 2007).
Focus on a specific moment, and describe the scene using your five senses. Mention objects that have special significance to you. Instead of following a common story arc, include a surprising twist or insight. Your unique voice can shed new perspective on a common human experience while also revealing your personality.
The continuity theory is one of the approaches to the understanding of the way people change with age. Thus, many scholars believed that actions that occurred in childhood and influenced the development of personality had a substantial impact on personality. The primary idea of the continuity theory is that people have the same inner drivers ...
Organize your essay around key personality traits or themes, ensuring a logical progression of ideas. Maintain a smooth flow between paragraphs, enhancing the overall readability of your essay ...
Personality is a combination of many traits, including feelings, thoughts, behavior, and opinions. Sometimes our traits change on their own or due to causes beyond our control. For example, we may change our habits due to a new job or family (Noonan 89). But this does not mean that we can completely change our personalities.
Personality tends to get "better" over time. Psychologists call it "the maturity principle." People become more extraverted, emotionally stable, agreeable and conscientious as they grow older ...
The evidence is accumulating that contends individuals maintain the ability to adapt personality traits through all stages of life. Roberts and Mroczek (2008) emphasize that personality changes in middle and old age may appear subtle, however, they are apparent which supports a growing census that personality traits continue to evolve throughout one's lifetime.
Personality change. Personality change refers to the different forms of change in various aspects of personality. These changes include how we experience things, how our perception of experiences changes, and how we react in situations. [1] An individual's personality may stay somewhat consistent throughout their life.
Describing your personality in an essay is not simply an exercise in self-expression; it is a transformative process that allows you to artfully communicate and convey the intricate nuances of your character to the reader. By delving into the depths of your self-awareness, personal growth, and the values that serve as the compass guiding your ...
Most of us underestimate the likelihood of such changes. A major study found that the average person surveyed thinks their personality is far more constant than it actually is. "People, it seems ...
An Individual 's Personality Change Essay. Satisfactory Essays. 1353 Words. 6 Pages. Open Document. Over the years, there has been a debate over whether or not personality can be changed. Growing older, experiencing life, and seeking personality change are all factors that play a part in this change. Throughout an individual's life, they are ...
Here are three widely recognized assessments: 1. DISC Assessment: The DISC assessment categorizes behavior into four primary styles: Dominance, Influence, Steadiness, and Conscientiousness. It ...
The most common symptoms of frontotemporal dementia involve extreme changes in behavior and personality. These include: Increasingly inappropriate social behavior. Loss of empathy and other interpersonal skills. For example, not being sensitive to another person's feelings. Lack of judgment. Loss of inhibition.
The benefits of gender diversity are well known - it increases effectiveness and efficiency and strengthens decision-making. Yet, the IMF Executive Board continues to fall short of reaching gender balance, with women constituting a small minority of the Executive Directors and Alternate Executive Directors. There is a clear need for change. The IMFC has called on the membership to take ...
Published May 29, 2024, 12:13 p.m. ET. Rory McIlroy's estranged wife Erica Stoll was served divorce papers by a private investigator while at their family home in the members-only development ...
The debut of an AI iPhone could also entice consumers to upgrade at a time when they've been holding onto older models longer. Apple reported first-quarter revenue of $90.8 billion, down 4% year ...
A tentative agreement announced Thursday by the NCAA and the country's five biggest conferences to a series of antitrust lawsuits could direct millions of dollars directly to athletes as soon as ...