11.4 The Business Plan
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the different purposes of a business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a brief business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a full business plan
Unlike the brief or lean formats introduced so far, the business plan is a formal document used for the long-range planning of a company’s operation. It typically includes background information, financial information, and a summary of the business. Investors nearly always request a formal business plan because it is an integral part of their evaluation of whether to invest in a company. Although nothing in business is permanent, a business plan typically has components that are more “set in stone” than a business model canvas , which is more commonly used as a first step in the planning process and throughout the early stages of a nascent business. A business plan is likely to describe the business and industry, market strategies, sales potential, and competitive analysis, as well as the company’s long-term goals and objectives. An in-depth formal business plan would follow at later stages after various iterations to business model canvases. The business plan usually projects financial data over a three-year period and is typically required by banks or other investors to secure funding. The business plan is a roadmap for the company to follow over multiple years.
Some entrepreneurs prefer to use the canvas process instead of the business plan, whereas others use a shorter version of the business plan, submitting it to investors after several iterations. There are also entrepreneurs who use the business plan earlier in the entrepreneurial process, either preceding or concurrently with a canvas. For instance, Chris Guillebeau has a one-page business plan template in his book The $100 Startup . 48 His version is basically an extension of a napkin sketch without the detail of a full business plan. As you progress, you can also consider a brief business plan (about two pages)—if you want to support a rapid business launch—and/or a standard business plan.
As with many aspects of entrepreneurship, there are no clear hard and fast rules to achieving entrepreneurial success. You may encounter different people who want different things (canvas, summary, full business plan), and you also have flexibility in following whatever tool works best for you. Like the canvas, the various versions of the business plan are tools that will aid you in your entrepreneurial endeavor.

Business Plan Overview
Most business plans have several distinct sections ( Figure 11.16 ). The business plan can range from a few pages to twenty-five pages or more, depending on the purpose and the intended audience. For our discussion, we’ll describe a brief business plan and a standard business plan. If you are able to successfully design a business model canvas, then you will have the structure for developing a clear business plan that you can submit for financial consideration.
Both types of business plans aim at providing a picture and roadmap to follow from conception to creation. If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept.
The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, dealing with the proverbial devil in the details. Developing a full business plan will assist those of you who need a more detailed and structured roadmap, or those of you with little to no background in business. The business planning process includes the business model, a feasibility analysis, and a full business plan, which we will discuss later in this section. Next, we explore how a business plan can meet several different needs.
Purposes of a Business Plan
A business plan can serve many different purposes—some internal, others external. As we discussed previously, you can use a business plan as an internal early planning device, an extension of a napkin sketch, and as a follow-up to one of the canvas tools. A business plan can be an organizational roadmap , that is, an internal planning tool and working plan that you can apply to your business in order to reach your desired goals over the course of several years. The business plan should be written by the owners of the venture, since it forces a firsthand examination of the business operations and allows them to focus on areas that need improvement.
Refer to the business venture throughout the document. Generally speaking, a business plan should not be written in the first person.
A major external purpose for the business plan is as an investment tool that outlines financial projections, becoming a document designed to attract investors. In many instances, a business plan can complement a formal investor’s pitch. In this context, the business plan is a presentation plan, intended for an outside audience that may or may not be familiar with your industry, your business, and your competitors.
You can also use your business plan as a contingency plan by outlining some “what-if” scenarios and exploring how you might respond if these scenarios unfold. Pretty Young Professional launched in November 2010 as an online resource to guide an emerging generation of female leaders. The site focused on recent female college graduates and current students searching for professional roles and those in their first professional roles. It was founded by four friends who were coworkers at the global consultancy firm McKinsey. But after positions and equity were decided among them, fundamental differences of opinion about the direction of the business emerged between two factions, according to the cofounder and former CEO Kathryn Minshew . “I think, naively, we assumed that if we kicked the can down the road on some of those things, we’d be able to sort them out,” Minshew said. Minshew went on to found a different professional site, The Muse , and took much of the editorial team of Pretty Young Professional with her. 49 Whereas greater planning potentially could have prevented the early demise of Pretty Young Professional, a change in planning led to overnight success for Joshua Esnard and The Cut Buddy team. Esnard invented and patented the plastic hair template that he was selling online out of his Fort Lauderdale garage while working a full-time job at Broward College and running a side business. Esnard had hundreds of boxes of Cut Buddies sitting in his home when he changed his marketing plan to enlist companies specializing in making videos go viral. It worked so well that a promotional video for the product garnered 8 million views in hours. The Cut Buddy sold over 4,000 products in a few hours when Esnard only had hundreds remaining. Demand greatly exceeded his supply, so Esnard had to scramble to increase manufacturing and offered customers two-for-one deals to make up for delays. This led to selling 55,000 units, generating $700,000 in sales in 2017. 50 After appearing on Shark Tank and landing a deal with Daymond John that gave the “shark” a 20-percent equity stake in return for $300,000, The Cut Buddy has added new distribution channels to include retail sales along with online commerce. Changing one aspect of a business plan—the marketing plan—yielded success for The Cut Buddy.
Link to Learning
Watch this video of Cut Buddy’s founder, Joshua Esnard, telling his company’s story to learn more.
If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept. This version is used to interest potential investors, employees, and other stakeholders, and will include a financial summary “box,” but it must have a disclaimer, and the founder/entrepreneur may need to have the people who receive it sign a nondisclosure agreement (NDA) . The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, providing supporting details, and would be required by financial institutions and others as they formally become stakeholders in the venture. Both are aimed at providing a picture and roadmap to go from conception to creation.
Types of Business Plans
The brief business plan is similar to an extended executive summary from the full business plan. This concise document provides a broad overview of your entrepreneurial concept, your team members, how and why you will execute on your plans, and why you are the ones to do so. You can think of a brief business plan as a scene setter or—since we began this chapter with a film reference—as a trailer to the full movie. The brief business plan is the commercial equivalent to a trailer for Field of Dreams , whereas the full plan is the full-length movie equivalent.
Brief Business Plan or Executive Summary
As the name implies, the brief business plan or executive summary summarizes key elements of the entire business plan, such as the business concept, financial features, and current business position. The executive summary version of the business plan is your opportunity to broadly articulate the overall concept and vision of the company for yourself, for prospective investors, and for current and future employees.
A typical executive summary is generally no longer than a page, but because the brief business plan is essentially an extended executive summary, the executive summary section is vital. This is the “ask” to an investor. You should begin by clearly stating what you are asking for in the summary.
In the business concept phase, you’ll describe the business, its product, and its markets. Describe the customer segment it serves and why your company will hold a competitive advantage. This section may align roughly with the customer segments and value-proposition segments of a canvas.
Next, highlight the important financial features, including sales, profits, cash flows, and return on investment. Like the financial portion of a feasibility analysis, the financial analysis component of a business plan may typically include items like a twelve-month profit and loss projection, a three- or four-year profit and loss projection, a cash-flow projection, a projected balance sheet, and a breakeven calculation. You can explore a feasibility study and financial projections in more depth in the formal business plan. Here, you want to focus on the big picture of your numbers and what they mean.
The current business position section can furnish relevant information about you and your team members and the company at large. This is your opportunity to tell the story of how you formed the company, to describe its legal status (form of operation), and to list the principal players. In one part of the extended executive summary, you can cover your reasons for starting the business: Here is an opportunity to clearly define the needs you think you can meet and perhaps get into the pains and gains of customers. You also can provide a summary of the overall strategic direction in which you intend to take the company. Describe the company’s mission, vision, goals and objectives, overall business model, and value proposition.
Rice University’s Student Business Plan Competition, one of the largest and overall best-regarded graduate school business-plan competitions (see Telling Your Entrepreneurial Story and Pitching the Idea ), requires an executive summary of up to five pages to apply. 51 , 52 Its suggested sections are shown in Table 11.2 .
Are You Ready?
Create a brief business plan.
Fill out a canvas of your choosing for a well-known startup: Uber, Netflix, Dropbox, Etsy, Airbnb, Bird/Lime, Warby Parker, or any of the companies featured throughout this chapter or one of your choice. Then create a brief business plan for that business. See if you can find a version of the company’s actual executive summary, business plan, or canvas. Compare and contrast your vision with what the company has articulated.
- These companies are well established but is there a component of what you charted that you would advise the company to change to ensure future viability?
- Map out a contingency plan for a “what-if” scenario if one key aspect of the company or the environment it operates in were drastically is altered?
Full Business Plan
Even full business plans can vary in length, scale, and scope. Rice University sets a ten-page cap on business plans submitted for the full competition. The IndUS Entrepreneurs , one of the largest global networks of entrepreneurs, also holds business plan competitions for students through its Tie Young Entrepreneurs program. In contrast, business plans submitted for that competition can usually be up to twenty-five pages. These are just two examples. Some components may differ slightly; common elements are typically found in a formal business plan outline. The next section will provide sample components of a full business plan for a fictional business.
Executive Summary
The executive summary should provide an overview of your business with key points and issues. Because the summary is intended to summarize the entire document, it is most helpful to write this section last, even though it comes first in sequence. The writing in this section should be especially concise. Readers should be able to understand your needs and capabilities at first glance. The section should tell the reader what you want and your “ask” should be explicitly stated in the summary.
Describe your business, its product or service, and the intended customers. Explain what will be sold, who it will be sold to, and what competitive advantages the business has. Table 11.3 shows a sample executive summary for the fictional company La Vida Lola.
Business Description
This section describes the industry, your product, and the business and success factors. It should provide a current outlook as well as future trends and developments. You also should address your company’s mission, vision, goals, and objectives. Summarize your overall strategic direction, your reasons for starting the business, a description of your products and services, your business model, and your company’s value proposition. Consider including the Standard Industrial Classification/North American Industry Classification System (SIC/NAICS) code to specify the industry and insure correct identification. The industry extends beyond where the business is located and operates, and should include national and global dynamics. Table 11.4 shows a sample business description for La Vida Lola.
Industry Analysis and Market Strategies
Here you should define your market in terms of size, structure, growth prospects, trends, and sales potential. You’ll want to include your TAM and forecast the SAM . (Both these terms are discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis .) This is a place to address market segmentation strategies by geography, customer attributes, or product orientation. Describe your positioning relative to your competitors’ in terms of pricing, distribution, promotion plan, and sales potential. Table 11.5 shows an example industry analysis and market strategy for La Vida Lola.
Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis is a statement of the business strategy as it relates to the competition. You want to be able to identify who are your major competitors and assess what are their market shares, markets served, strategies employed, and expected response to entry? You likely want to conduct a classic SWOT analysis (Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats) and complete a competitive-strength grid or competitive matrix. Outline your company’s competitive strengths relative to those of the competition in regard to product, distribution, pricing, promotion, and advertising. What are your company’s competitive advantages and their likely impacts on its success? The key is to construct it properly for the relevant features/benefits (by weight, according to customers) and how the startup compares to incumbents. The competitive matrix should show clearly how and why the startup has a clear (if not currently measurable) competitive advantage. Some common features in the example include price, benefits, quality, type of features, locations, and distribution/sales. Sample templates are shown in Figure 11.17 and Figure 11.18 . A competitive analysis helps you create a marketing strategy that will identify assets or skills that your competitors are lacking so you can plan to fill those gaps, giving you a distinct competitive advantage. When creating a competitor analysis, it is important to focus on the key features and elements that matter to customers, rather than focusing too heavily on the entrepreneur’s idea and desires.
Operations and Management Plan
In this section, outline how you will manage your company. Describe its organizational structure. Here you can address the form of ownership and, if warranted, include an organizational chart/structure. Highlight the backgrounds, experiences, qualifications, areas of expertise, and roles of members of the management team. This is also the place to mention any other stakeholders, such as a board of directors or advisory board(s), and their relevant relationship to the founder, experience and value to help make the venture successful, and professional service firms providing management support, such as accounting services and legal counsel.
Table 11.6 shows a sample operations and management plan for La Vida Lola.
Marketing Plan
Here you should outline and describe an effective overall marketing strategy for your venture, providing details regarding pricing, promotion, advertising, distribution, media usage, public relations, and a digital presence. Fully describe your sales management plan and the composition of your sales force, along with a comprehensive and detailed budget for the marketing plan. Table 11.7 shows a sample marketing plan for La Vida Lola.
Financial Plan
A financial plan seeks to forecast revenue and expenses; project a financial narrative; and estimate project costs, valuations, and cash flow projections. This section should present an accurate, realistic, and achievable financial plan for your venture (see Entrepreneurial Finance and Accounting for detailed discussions about conducting these projections). Include sales forecasts and income projections, pro forma financial statements ( Building the Entrepreneurial Dream Team , a breakeven analysis, and a capital budget. Identify your possible sources of financing (discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis ). Figure 11.19 shows a template of cash-flow needs for La Vida Lola.
Entrepreneur In Action
Laughing man coffee.
Hugh Jackman ( Figure 11.20 ) may best be known for portraying a comic-book superhero who used his mutant abilities to protect the world from villains. But the Wolverine actor is also working to make the planet a better place for real, not through adamantium claws but through social entrepreneurship.
A love of java jolted Jackman into action in 2009, when he traveled to Ethiopia with a Christian humanitarian group to shoot a documentary about the impact of fair-trade certification on coffee growers there. He decided to launch a business and follow in the footsteps of the late Paul Newman, another famous actor turned philanthropist via food ventures.
Jackman launched Laughing Man Coffee two years later; he sold the line to Keurig in 2015. One Laughing Man Coffee café in New York continues to operate independently, investing its proceeds into charitable programs that support better housing, health, and educational initiatives within fair-trade farming communities. 55 Although the New York location is the only café, the coffee brand is still distributed, with Keurig donating an undisclosed portion of Laughing Man proceeds to those causes (whereas Jackman donates all his profits). The company initially donated its profits to World Vision, the Christian humanitarian group Jackman accompanied in 2009. In 2017, it created the Laughing Man Foundation to be more active with its money management and distribution.
- You be the entrepreneur. If you were Jackman, would you have sold the company to Keurig? Why or why not?
- Would you have started the Laughing Man Foundation?
- What else can Jackman do to aid fair-trade practices for coffee growers?
What Can You Do?
Textbooks for change.
Founded in 2014, Textbooks for Change uses a cross-compensation model, in which one customer segment pays for a product or service, and the profit from that revenue is used to provide the same product or service to another, underserved segment. Textbooks for Change partners with student organizations to collect used college textbooks, some of which are re-sold while others are donated to students in need at underserved universities across the globe. The organization has reused or recycled 250,000 textbooks, providing 220,000 students with access through seven campus partners in East Africa. This B-corp social enterprise tackles a problem and offers a solution that is directly relevant to college students like yourself. Have you observed a problem on your college campus or other campuses that is not being served properly? Could it result in a social enterprise?
Work It Out
Franchisee set out.
A franchisee of East Coast Wings, a chain with dozens of restaurants in the United States, has decided to part ways with the chain. The new store will feature the same basic sports-bar-and-restaurant concept and serve the same basic foods: chicken wings, burgers, sandwiches, and the like. The new restaurant can’t rely on the same distributors and suppliers. A new business plan is needed.
- What steps should the new restaurant take to create a new business plan?
- Should it attempt to serve the same customers? Why or why not?
This New York Times video, “An Unlikely Business Plan,” describes entrepreneurial resurgence in Detroit, Michigan.
- 48 Chris Guillebeau. The $100 Startup: Reinvent the Way You Make a Living, Do What You Love, and Create a New Future . New York: Crown Business/Random House, 2012.
- 49 Jonathan Chan. “What These 4 Startup Case Studies Can Teach You about Failure.” Foundr.com . July 12, 2015. https://foundr.com/4-startup-case-studies-failure/
- 50 Amy Feldman. “Inventor of the Cut Buddy Paid YouTubers to Spark Sales. He Wasn’t Ready for a Video to Go Viral.” Forbes. February 15, 2017. https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestreptalks/2017/02/15/inventor-of-the-cut-buddy-paid-youtubers-to-spark-sales-he-wasnt-ready-for-a-video-to-go-viral/#3eb540ce798a
- 51 Jennifer Post. “National Business Plan Competitions for Entrepreneurs.” Business News Daily . August 30, 2018. https://www.businessnewsdaily.com/6902-business-plan-competitions-entrepreneurs.html
- 52 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition . March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf
- 53 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition. March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf; Based on 2019 RBPC Competition Rules and Format April 4–6, 2019. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2019-RBPC-Competition-Rules%20-Format.pdf
- 54 Foodstart. http://foodstart.com
- 55 “Hugh Jackman Journey to Starting a Social Enterprise Coffee Company.” Giving Compass. April 8, 2018. https://givingcompass.org/article/hugh-jackman-journey-to-starting-a-social-enterprise-coffee-company/
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Michael Laverty, Chris Littel
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Entrepreneurship
- Publication date: Jan 16, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/11-4-the-business-plan
© Jan 4, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Free PDF Business Plan Templates and Samples
By Joe Weller | September 9, 2020
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
We’ve gathered the most useful collection of business plan PDF templates and samples, including options for organizations of any size and type.
On this page, you’ll find free PDF templates for a simple business plan , small business plan , startup business plan , and more.
Simple Business Plan PDF Templates
These simple business plan PDF templates are ready to use and customizable to fit the needs of any organization.
Simple Business Plan Template PDF

This template contains a traditional business plan layout to help you map out each aspect, from a company overview to sales projections and a marketing strategy. This template includes a table of contents, as well as space for financing details that startups looking for funding may need to provide.
Download Simple Business Plan Template - PDF
Lean Business Plan Template PDF

This scannable business plan template allows you to easily identify the most important elements of your plan. Use this template to outline key details pertaining to your business and industry, product or service offerings, target customer segments (and channels to reach them), and to identify sources of revenue. There is also space to include key performance metrics and a timeline of activities.
Download Lean Business Plan Template - PDF
Simple 30-60-90 Day Business Plan Template PDF

This template is designed to help you develop and implement a 90-day business plan by breaking it down into manageable chunks of time. Use the space provided to detail your main goals and deliverables for each timeframe, and then add the steps necessary to achieve your objectives. Assign task ownership and enter deadlines to ensure your plan stays on track every step of the way.
Download Simple 30-60-90 Day Business Plan Template
PDF | Smartsheet
One-Page Business Plan PDF Templates
The following single page business plan templates are designed to help you download your key ideas on paper, and can be used to create a pitch document to gain buy-in from partners, investors, and stakeholders.
One-Page Business Plan Template PDF
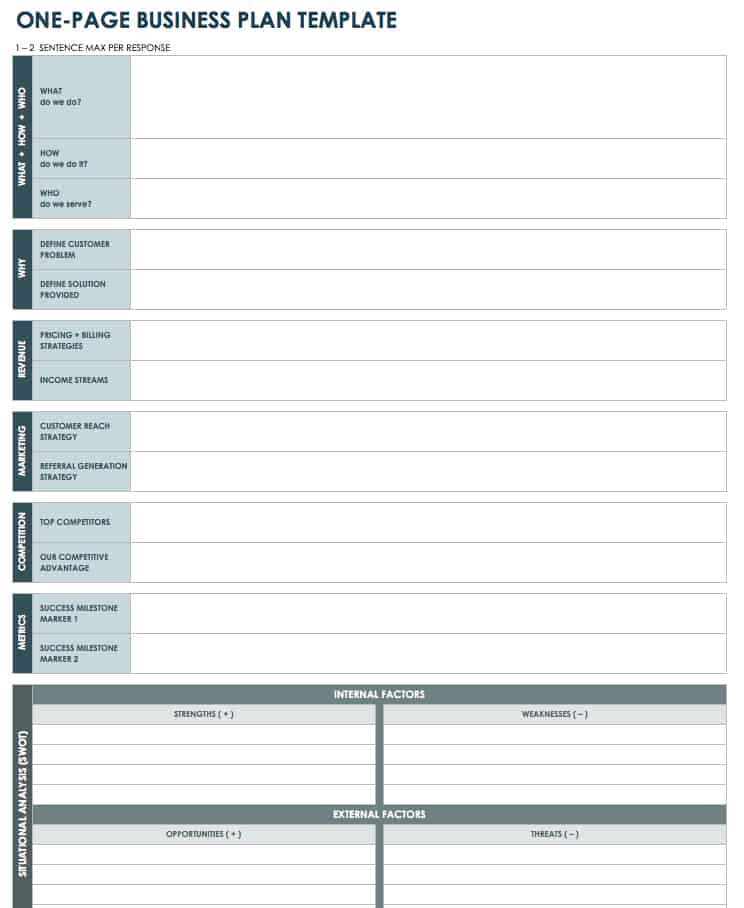
Use this one-page template to summarize each aspect of your business concept in a clear and concise manner. Define the who, what, why, and how of your idea, and use the space at the bottom to create a SWOT analysis (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) for your business.
Download One-Page Business Plan Template
If you’re looking for a specific type of analysis, check out our collection of SWOT templates .
One-Page Lean Business Plan PDF

This one-page business plan template employs the Lean management concept, and encourages you to focus on the key assumptions of your business idea. A Lean plan is not stagnant, so update it as goals and objectives change — the visual timeline at the bottom is ideal for detailing milestones.
Download One-Page Lean Business Plan Template - PDF
One-Page 30-60-90 Day Business Plan Template
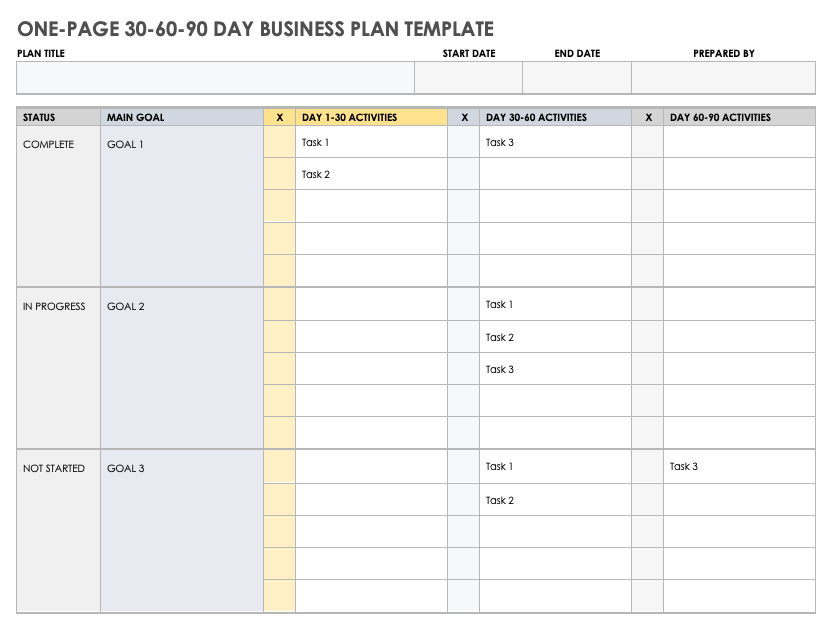
Use this business plan template to identify main goals and outline the necessary activities to achieve those goals in 30, 60, and 90-day increments. Easily customize this template to fit your needs while you track the status of each task and goal to keep your business plan on target.
Download One-Page 30-60-90 Day Business Plan Template
For additional single page plans, including an example of a one-page business plan , visit " One-Page Business Plan Templates with a Quick How-To Guide ."
Small Business Plan PDF Templates
These business plan templates are useful for small businesses that want to map out a way to meet organizational objectives, including how to structure, operate, and expand their business.
Simple Small Business Plan Template PDF
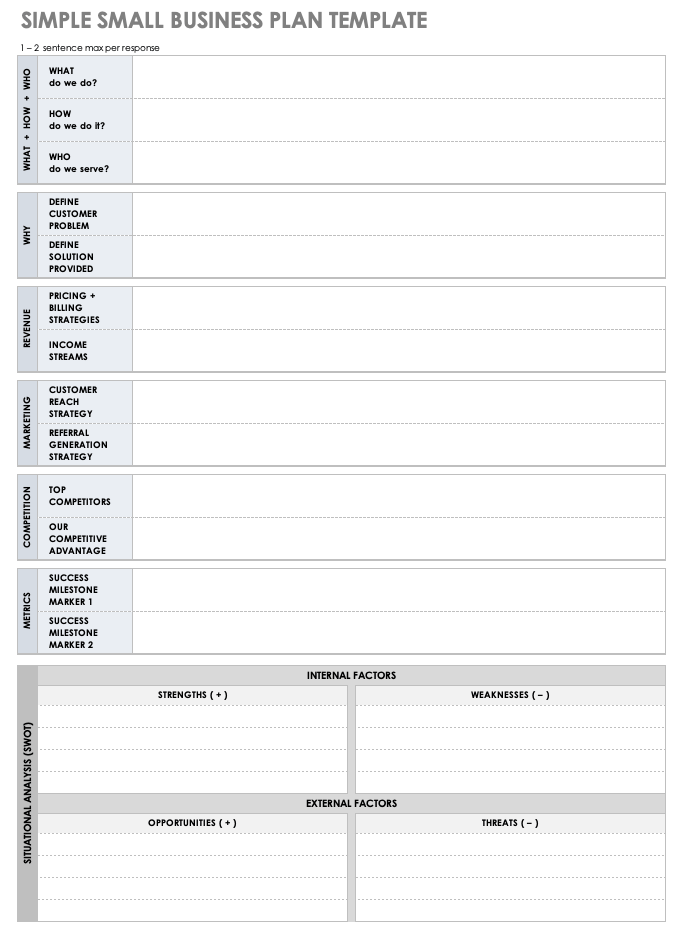
A small business can use this template to outline each critical component of a business plan. There is space to provide details about product or service offerings, target audience, customer reach strategy, competitive advantage, and more. Plus, there is space at the bottom of the document to include a SWOT analysis. Once complete, you can use the template as a basis to build out a more elaborate plan.
Download Simple Small Business Plan Template
Fill-In-the-Blank Small Business Plan Template PDF
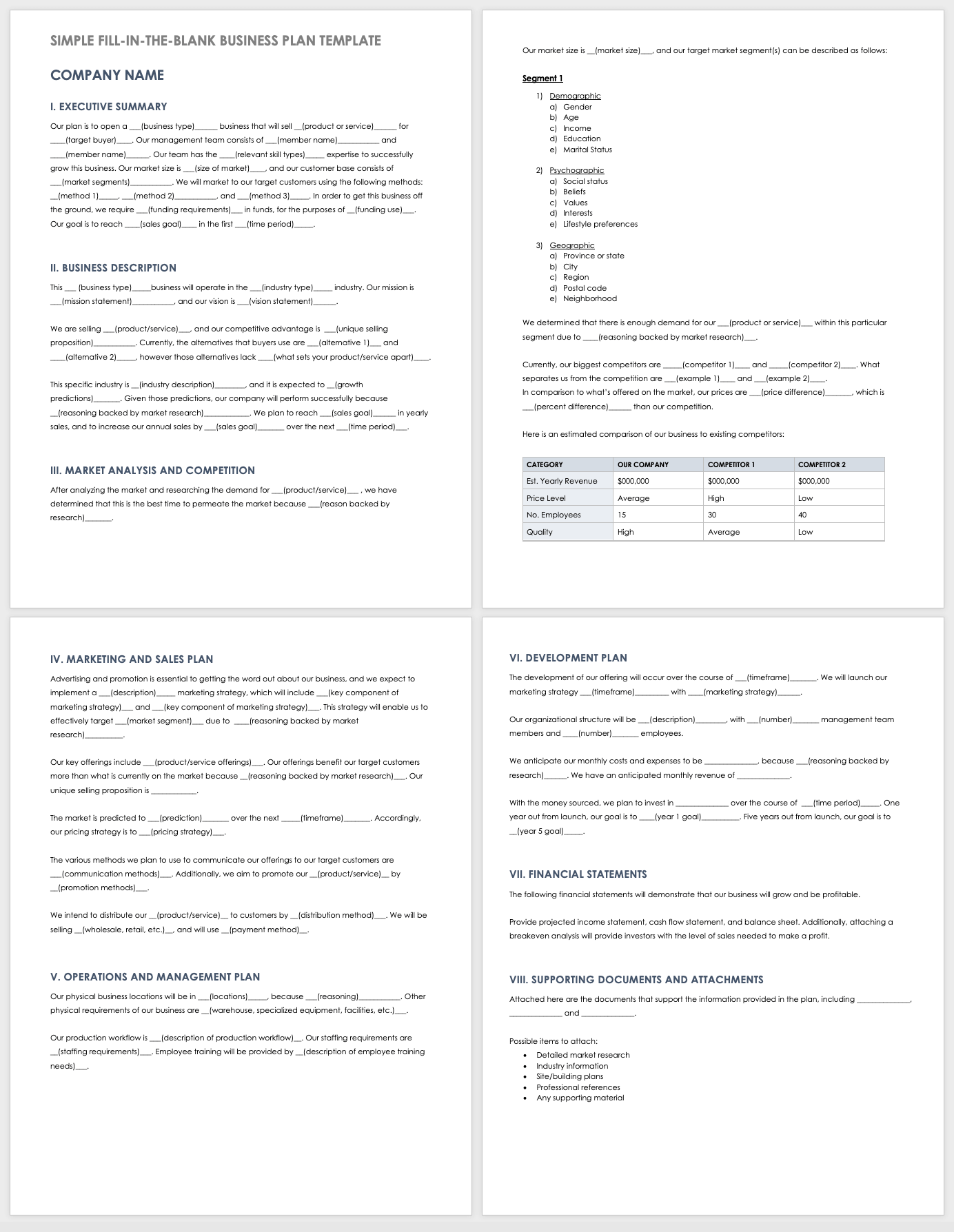
This fill-in-the-blank template walks you through each section of a business plan. Build upon the fill-in-the-blank content provided in each section to add information about your company, business idea, market analysis, implementation plan, timeline of milestones, and much more.
Download Fill-In-the-Blank Small Business Plan Template - PDF
One-Page Small Business Plan Template PDF

Use this one-page template to create a scannable business plan that highlights the most essential parts of your organization’s strategy. Provide your business overview and management team details at the top, and then outline the target market, market size, competitive offerings, key objectives and success metrics, financial plan, and more.
Download One-Page Business Plan for Small Business - PDF
Startup Business Plan PDF Templates
Startups can use these business plan templates to check the feasibility of their idea, and articulate their vision to potential investors.
Startup Business Plan Template
Use this business plan template to organize and prepare each essential component of your startup plan. Outline key details relevant to your concept and organization, including your mission and vision statement, product or services offered, pricing structure, marketing strategy, financial plan, and more.
Download Startup Business Plan Template
Sample 30-60-90 Day Business Plan for Startup
Startups can use this sample 30-60-90 day plan to establish main goals and deliverables spanning a 90-day period. Customize the sample goals, deliverables, and activities provided on this template according to the needs of your business. Then, assign task owners and set due dates to help ensure your 90-day plan stays on track.
Download Sample 30-60-90 Day Business Plan for Startup Template
For additional resources to create your plan, visit “ Free Startup Business Plan Templates and Examples .”
Nonprofit Business Plan PDF Templates
Use these business plan PDF templates to outline your organization’s mission, your plan to make a positive impact in your community, and the steps you will take to achieve your nonprofit’s goals.
Nonprofit Business Plan Template PDF
Use this customizable PDF template to develop a plan that details your organization’s purpose, objectives, and strategy. This template features a table of contents, with room to include your nonprofit’s mission and vision, key team and board members, program offerings, a market and industry analysis, promotional plan, financial plan, and more. This template also contains a visual timeline to display historic and future milestones.
Download Nonprofit Business Plan Template - PDF
One-Page Business Plan for Nonprofit Organization PDF
This one-page plan serves as a good starting point for established and startup nonprofit organizations to jot down their fundamental goals and objectives. This template contains all the essential aspects of a business plan in a concise and scannable format, including the organizational overview, purpose, promotional plan, key objectives and success metrics, fundraising goals, and more.
Download One-Page Business Plan for Nonprofit Organization Template - PDF
Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan PDF Templates
Use these fill-in-the-blank templates as a foundation for creating a comprehensive roadmap that aligns your business strategy with your marketing, sales, and financial goals.
Simple Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan PDF
The fill-in-the-blank template contains all the vital parts of a business plan, with sample content that you can customize to fit your needs. There is room to include an executive summary, business description, market analysis, marketing plan, operations plan, financial statements, and more.
Download Simple Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan Template - PDF
Lean Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan PDF
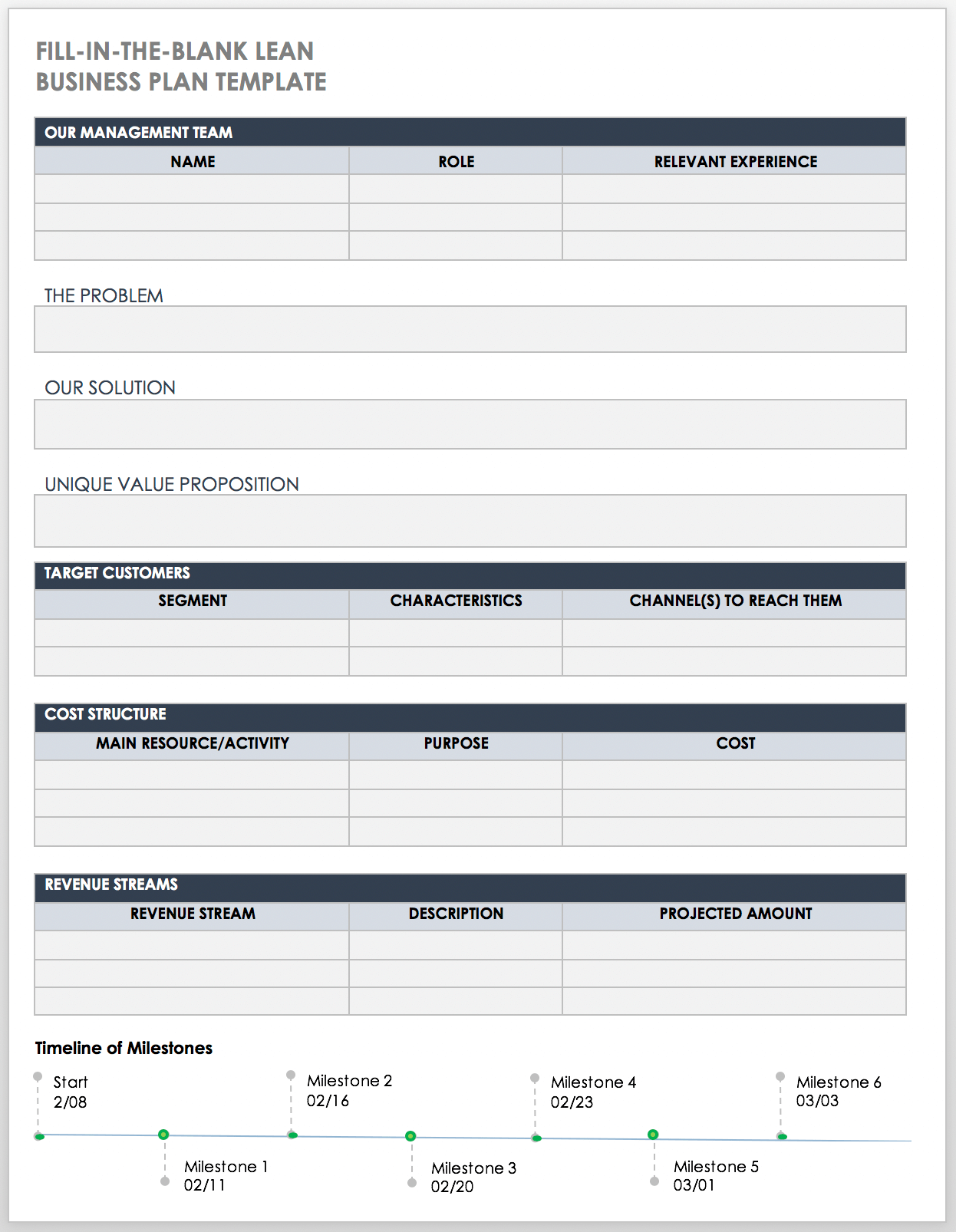
This business plan is designed with a Lean approach that encourages you to clarify and communicate your business idea in a clear and concise manner. This single page fill-in-the-blank template includes space to provide details about your management team, the problem you're solving, the solution, target customers, cost structure, and revenue streams. Use the timeline at the bottom to produce a visual illustration of key milestones.
Download Fill-In-the-Blank Lean Business Plan Template - PDF
For additional resources, take a look at " Free Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan Templates ."
Sample Business Plan PDF Templates
These sample business plan PDF templates can help you to develop an organized, thorough, and professional business plan.
Business Plan Sample
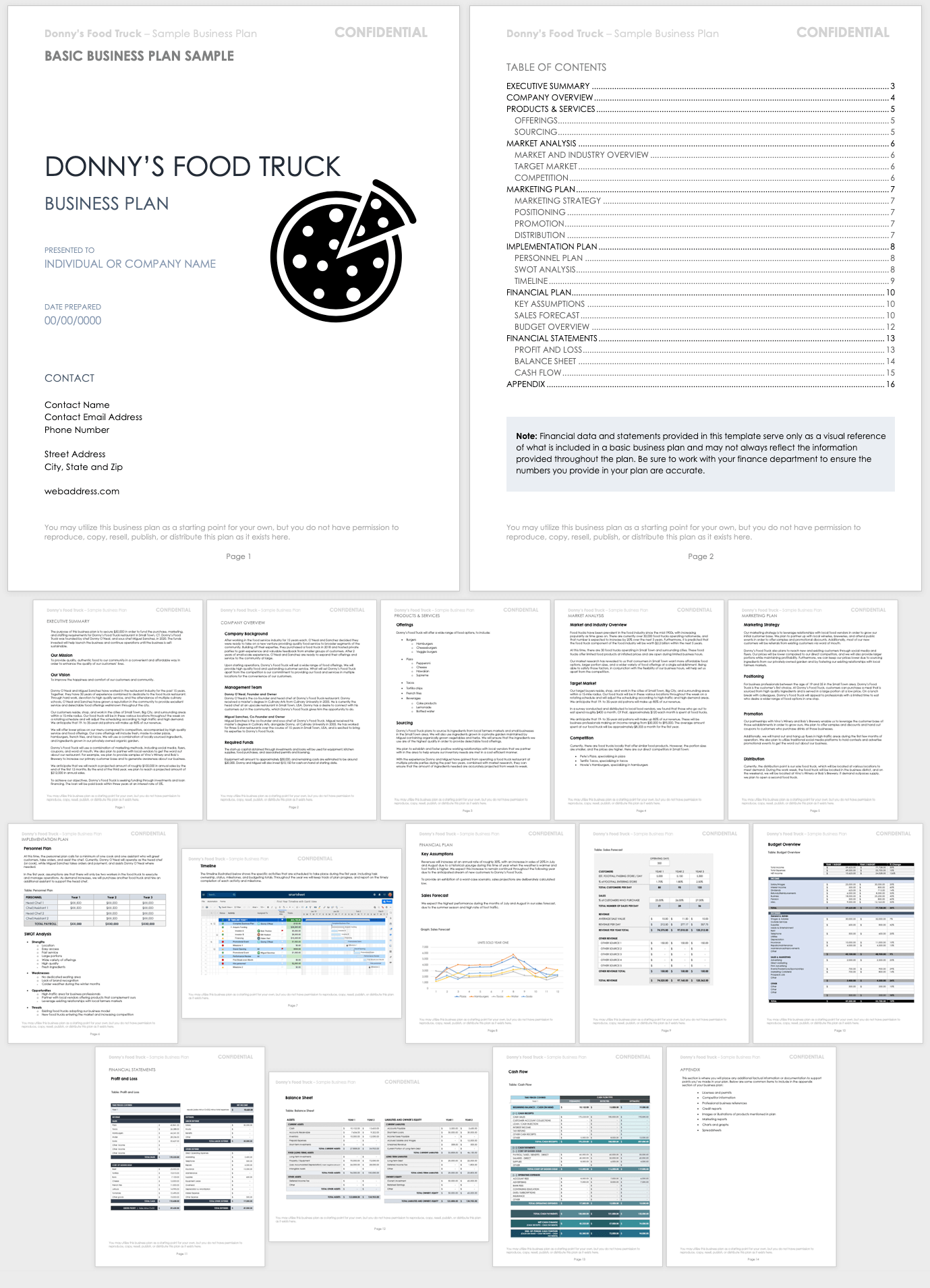
This business plan example demonstrates a plan for a fictional food truck company. The sample includes all of the elements in a traditional business plan, which makes it a useful starting point for developing a plan specific to your business needs.
Download Basic Business Plan Sample - PDF
Sample Business Plan Outline Template

Use this sample outline as a starting point for your business plan. Shorten or expand the outline depending on your organization’s needs, and use it to develop a table of contents for your finalized plan.
Download Sample Business Plan Outline Template - PDF
Sample Business Financial Plan Template
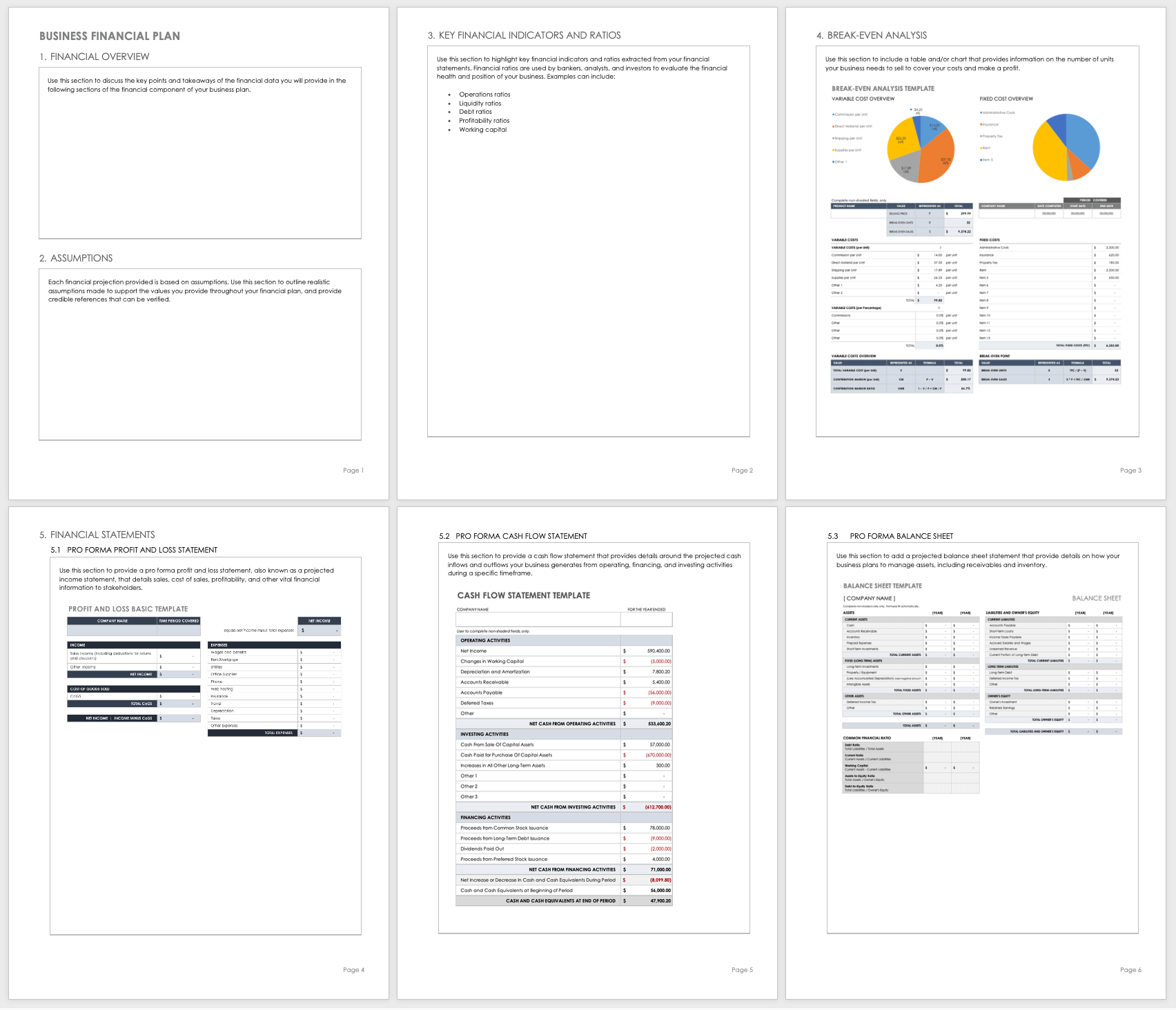
Use this sample template to develop the financial portion of your business plan. The template provides space to include a financial overview, key assumptions, financial indicators, and business ratios. Complete the break-even analysis and add your financial statements to help prove the viability of your organization’s business plan.
Download Business Financial Plan Template
PDF | Smartsheet
For more free, downloadable templates for all aspects of your business, check out “ Free Business Templates for Organizations of All Sizes .”
Improve Business Planning with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.

Free Business Plan Workbook (PDF) for Entrepreneurs
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Are you an aspiring entrepreneur looking to start your own business? Do you have a brilliant business idea but don’t know where to start with planning? Look no further! We are here to help you with our free business planning workbook (PDF) for entrepreneurs. This comprehensive workbook will guide you through the process of developing a solid business plan, which is crucial for the success of any business venture.
The Importance of a Business Plan
A business plan is like a roadmap that outlines your business goals, strategies, and financial projections. It serves as a blueprint for your business and helps you stay focused and organized as you navigate the challenges of starting and running a successful venture. A well-structured business plan is not only essential for securing funding from investors or lenders but also provides you with a clear direction and a solid foundation for making informed decisions for your business.
How Our Business Planning Workbook Can Help
Our free business planning workbook (PDF) is designed to assist entrepreneurs like you in creating a well-structured and comprehensive business plan. This workbook provides step-by-step guidance and exercises to help you gather and organize the necessary information for your business plan. It covers each of the key aspects of business planning, including customer analysis, competitive analysis, marketing strategies, financial projections, and more. Our workbook is easy to use and will save you time and effort in creating a professional business plan that meets the needs of your business.
Get Started with Our Free Business Planning Workbook
Ready to take your business idea to the next level? Download our free business planning workbook (PDF) now and start creating a comprehensive business plan that will set you up for success.
Benefits of Using Our Business Plan Workbook
When it comes to business planning, using our business plan workbook can be a game-changer. It provides a structured approach to developing a comprehensive business plan, ensuring that you cover all the essential elements of a successful plan. Here are some benefits of using our business plan workbook:
- Organized approach: Our business plan workbook provides a step-by-step guide, helping you organize your thoughts and ideas in a systematic manner. It prompts you to think critically about different aspects of your business and ensures that you do not overlook any crucial details.
- Time-saving: Writing a business plan from scratch can be time-consuming, but our business plan workbook streamlines the process by providing pre-designed prompts. This saves you time and effort, allowing you to focus on the content of your plan rather than the formatting.
- Flexibility: Our business plan workbook allows you to customize your plan according to your specific business needs. You can add, remove, or modify sections based on your unique business model, market research, and financial projections.
- Comprehensive coverage: A well-designed business plan workbook like ours covers all the essential elements of a business plan, including market analysis, marketing strategies, financial projections, and more. This ensures that you develop a thorough and well-rounded plan that addresses all aspects of your business.
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!


- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.1: Chapter 1 – Developing a Business Plan
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 21274

- Lee A. Swanson
- University of Saskatchewan
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Learning Objectives
After completing this chapter, you will be able to
- Describe the purposes for business planning
- Describe common business planning principles
- Explain common business plan development guidelines and tools
- List and explain the elements of the business plan development process
- Explain the purposes of each element of the business plan development process
- Explain how applying the business plan development process can aid in developing a business plan that will meet entrepreneurs’ goals
This chapter describes the purposes, principles, and the general concepts and tools for business planning, and the process for developing a business plan.
Purposes for Developing Business Plans
Business plans are developed for both internal and external purposes. Internally, entrepreneurs develop business plans to help put the pieces of their business together. Externally, the most common purpose is to raise capital.
Internal Purposes
As the road map for a business’s development, the business plan
- Defines the vision for the company
- Establishes the company’s strategy
- Describes how the strategy will be implemented
- Provides a framework for analysis of key issues
- Provides a plan for the development of the business
- Helps the entrepreneur develop and measure critical success factors
- Helps the entrepreneur to be realistic and test theories
External Purposes
The business plan provides the most complete source of information for valuation of the business. Thus, it is often the main method of describing a company to external audiences such as potential sources for financing and key personnel being recruited. It should assist outside parties to understand the current status of the company, its opportunities, and its needs for resources such as capital and personnel.
Business Plan Development Principles
Hindle and Mainprize (2006) suggested that business plan writers must strive to effectively communicate their expectations about the nature of an uncertain future and to project credibility. The liabilities of newness make communicating the expected future of new ventures much more difficult than for existing businesses. Consequently, business plan writers should adhere to five specific communication principles .
First, business plans must be written to meet the expectations of targeted readers in terms of what they need to know to support the proposed business. They should also lay out the milestones that investors or other targeted readers need to know. Finally, writers must clearly outline the opportunity , the context within the proposed venture will operate (internal and external environment), and the business model (Hindle & Mainprize, 2006).
There are also five business plan credibility principles that writers should consider. Business plan writers should build and establish their credibility by highlighting important and relevant information about the venture team . Writers need to elaborate on the plans they outline in their document so that targeted readers have the information they need to assess the plan’s credibility. To build and establish credibility, they must integrate scenarios to show that the entrepreneur has made realistic assumptions and has effectively anticipated what the future holds for their proposed venture. Writers need to provide comprehensive and realistic financial links between all relevant components of the plan. Finally, they must outline the deal , or the value that targeted readers should expect to derive from their involvement with the venture (Hindle & Mainprize, 2006).
General Guidelines for Developing Business Plans
Many businesses must have a business plan to achieve their goals. Using a standard format helps the reader understand that the you have thought everything through, and that the returns justify the risk. The following are some basic guidelines for business plan development.
As You Write Your Business Plan
1. If appropriate, include nice, catchy, professional graphics on your title page to make it appealing to targeted readers, but don’t go overboard.
2. Bind your document so readers can go through it easily without it falling apart. You might use a three-ring binder, coil binding, or a similar method. Make sure the binding method you use does not obscure the information next to where it is bound.
3. Make certain all of your pages are ordered and numbered correctly.
4. The usual business plan convention is to number all major sections and subsections within your plan using the format as follows:
1. First main heading
1.1 First subheading under the first main heading
1.1.1. First sub-subheading under the first subheading
2. Second main heading
2.1 First subheading under the second main heading
Use the styles and references features in Word to automatically number and format your section titles and to generate your table of contents. Be sure that the last thing you do before printing your document is update your automatic numbering and automatically generated tables. If you fail to do this, your numbering may be incorrect.
5. Prior to submitting your plan, be 100% certain each of the following requirements are met:
- Everything must be completely integrated. The written part must say exactly the same thing as the financial part.
- All financial statements must be completely linked and valid. Make sure all of your balance sheets balance.
- Everything must be correct. There should be NO spelling, grammar, sentence structure, referencing, or calculation errors.
- Your document must be well organized and formatted. The layout you choose should make the document easy to read and comprehend. All of your diagrams, charts, statements, and other additions should be easy to find and be located in the parts of the plan best suited to them.
- In some cases it can strengthen your business plan to show some information in both text and table or figure formats. You should avoid unnecessary repetition , however, as it is usually unnecessary—and even damaging—to state the same thing more than once.
- You should include all the information necessary for readers to understand everything in your document.
- The terms you use in your plan should be clear and consistent. For example, the following statement in a business plan would leave a reader completely confused: “There is a shortage of 100,000 units with competitors currently producing 25,000. We can help fill this huge gap in demand with our capacity to produce 5,000 units.”
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
Simple Business Plan Template for Entrepreneurs
Follow This Business Plan Outline to Write Your Own
Susan Ward wrote about small businesses for The Balance for 18 years. She has run an IT consulting firm and designed and presented courses on how to promote small businesses.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SusanWardLaptop2crop1-57aa62eb5f9b58974a12bac9.jpg)
Pros and Cons of Using a Business Plan Template
Do i need a simple or detailed business plan, how to use this business plan template, table of contents, section 1: executive summary, section 2: business/industry overview.
- Section 3: Market Analysis and Competition
Section 4: Sales and Marketing Plan
Section 5: ownership and management plan, section 6: operating plan, section 7: financial plan.
- Section 8: Appendices and Exhibits
Ariel Skelley / Getty Images
Think you have a great idea for a business? The best way to find out whether your idea is feasible is to create a business plan .
A solid, well-researched business plan provides a practical overview of your vision. It can be used to ground your ideas into workable actions and to help pitch your idea to financial institutions or potential investors when looking for funding.
The standard business plan consists of a single document divided into several sections for distinct elements, such as a description of the organization, market research, competitive analysis, sales strategies, capital and labor requirements, and financial data. Your plan may include more or fewer sections to best represent your business.
The template presented here will get you well on your way toward your simple business plan.
Ready-made layouts
Free downloads
Generic, not customized
No financial guidance
Additional skills needed
- Ready-made layouts : Templates offer general guidance about what information is needed and how to organize it, so you’re not stuck looking at a blank page when getting started. Especially detailed templates may offer instructions or helpful text prompts along the way.
- Variations : If you know what type of business plan you need—traditional, lean, industry-specific—chances are you can find a specialized template.
- Free downloads : There are many free business plan templates available online, which can be useful for comparing formats and features, or refining your own.
- Generic, not customized : Templates typically contain just the basics, and there will still be a lot of work involved to tailor the template to your business. For instance, you'll have to reformat, refine copy, and populate tables.
- No financial guidance : You’ll need enough industry knowledge to apply financial models to your specific business, and the math skills to generate formulas and calculate figures.
- Additional skills needed : Some degree of tech savvy is required to integrate charts and graphs, merge data from spreadsheets, and keep it all up-to-date.
A corporate business plan for a large organization can be hundreds of pages long. However, for a small business, it's best to keep the plan short and concise, especially if you're submitting it to bankers or investors . Around 35 to 50 pages should be sufficient, and more allowed for extras, such as photos of products, equipment, logos, or business premises or site plans. Your audience will likely prefer solid research and analysis over long, wordy descriptions.
An entrepreneur who creates a business plan is nearly twice as likely to secure financing and grow their business compared with those who do not have a plan.
The business plan template below is divided into sections as described in the table of contents. Each section can be copied into a document of your own; you may need to add or delete sections or make adjustments to fit your specific needs.
Once complete, be sure to format it attractively and get it professionally printed and bound. You want your business plan to convey the best possible impression. Make it engaging, something people will to want to pick up and peruse.
Enter your business information, including the legal name and address. If you already have a business logo, you can add it at the top or bottom of the title page.
- Business Plan for "Business Name"
- Business address
- Website URL
If you're addressing it to a company or individual, include:
- Presented to "Name"
- At "Company"
- Executive Summary................................................Page #
- Business/Industry Overview.................................Page #
- Market Analysis and Competition.........................Page #
- Sales and Marketing Plan.......................................Page #
- Ownership and Management Plan.......................Page #
- Operating Plan..........................................................Page #
- Financial Plan............................................................Page #
- Appendices and Exhibits........................................Page #
The executive summary introduces the plan, but it is written last. It provides a concise and optimistic overview of your business and should capture the reader's attention and create a desire to learn more. The executive summary should be no more than two pages long, with highlights or brief summaries of other sections of the plan.
- Describe your mission —what is the need for your new business? Sell your vision.
- Introduce your company briefly, sticking to vital details such as size, location, management, and ownership.
- Describe your main product(s) and/or service(s).
- Identify the customer base you plan to target and how your business will serve those customers.
- Summarize the competition and how you will get market share. What is your competitive advantage?
- Outline your financial projections for the first few years of operation.
- State your startup financing requirements.
This section provides an overview of the industry and explains in detail what makes your business stand out.
- Describe the overall nature of the industry, including sales and other statistics. Note trends and demographics, as well as economic, cultural, and governmental influences.
- Explain your business and how it fits into the industry.
- Mention the existing competition, which you'll expand upon in the following section.
- Identify what area(s) of the market you will target and what unique, improved, or lower-cost products and/or services you will offer.
Many business plans cover their products/services in a standalone section to add more detail or emphasize unique aspects.
Section 3: Market Analysis and Competition
This section focuses on the competitive factor of your business and justifies it with financial models and statistics. You need to demonstrate that you have thoroughly analyzed the target market, assessed the competition, and concluded that there is enough demand for your products/services to make your business viable.
- Define the target market(s) for your products/services in your geographic locale.
- Explain the need for your products/services.
- Estimate the overall size of the market and the units of your products/services that the target market might buy. Include forecasts of potential repeat-purchase volume and how the market might be affected by economic or demographic changes.
- Estimate the volume and value of your sales in comparison with any existing competitors. Highlight any key strengths over the competition in easily digestible charts and tables.
- Describe any helpful barriers to entry that may protect your business from competition, such as access to capital, technology, regulations, employee skill sets, or location.
You may opt to split the target market description and competitive analysis into two separate sections, if either (or both) portray your business especially favorably.
Here's where you dive into profits, giving detailed strategic view of how you intend to entice customers to buy your products and/or services, including advertising or promotion, pricing, sales, distribution, and post-sales support.
Product or Service Offerings
If your products and/or services don't take up a standalone section earlier in the plan, here is where you can answer the question: What is your unique selling proposition? Describe your products and/or services, how they benefit the customer and what sets them apart from competitor offerings.
Pricing Strategy
How will you price your products/services? Pricing must be low enough to attract customers, yet high enough to cover costs and generate a profit. You can base pricing decisions on a number of financial models, such as markup from cost or value to the buyer, or in comparison with similar products and/or services in the marketplace.
Sales and Distribution
For products, describe how you plan to distribute to the customer. Will you be selling wholesale or retail? What type of packaging will be required? How will products be shipped? If you offer a service, how will it be delivered to the customer? What methods will be used for payment?
Advertising and Promotion
List the various forms of media you will use to get your message to customers (e.g., website, email, social media, or newspapers). Will you use sales promotional methods such as free samples and product demonstrations? What about product launches and trade shows? Don't forget more everyday marketing materials such as business cards, flyers, or brochures. Include an approximate budget.
This section describes the legal structure, ownership, and (if applicable) management and staffing requirements of your business.
- Ownership structure : Describe the legal structure of your company (e.g., corporation, partnership, LLC, or sole proprietorship ). List ownership percentages, if applicable. If the business is a sole proprietorship, this is the only section required.
- Management team : Describe managers and their roles, key employee positions, and how each will be compensated. Include brief résumés.
- External resources and services : List any external professional resources required, such as accountants, lawyers, or consultants.
- Human resources : List the type and number of employees or contractors you will need, and estimate the salary and benefit costs of each.
- Advisory board : Include an advisory board as a supplemental management resource, if applicable.
The operating plan outlines the physical requirements of your business, such as office, warehouse, or retail space; equipment; supplies; or labor. This section will vary greatly by industry; a large manufacturer, for instance, should provide full details about supply chain or specialty equipment, while a therapist's office can get by with a much shorter list.
If your business is a small operation (like a one-person, home-based consulting firm), you might choose to eliminate the operating plan section altogether and include the operating essentials in the business overview.
- Development : Explain what you have done to date to identify possible locations, sources of equipment, supply chains, and other relevant relationships. Describe your production workflow.
- Production : For manufacturing, explain how long it takes to produce a unit and when you'll be ready to start production. Include factors that may affect the time frame of production and how you'll deal with potential problems, such as rush orders.
- Facilities : Describe the physical location of the business. Include geographical or building requirements; square footage estimates (with room for expansion if expected); mortgage or leasing costs; and estimates of maintenance, utilities, and related overhead costs . Include zoning approvals and other permissions that are necessary in order to operate.
- Staffing : Outline expected staffing needs and the main duties of staff members, especially the key employees. Describe how the employees will be sourced and the employment relationship (i.e., contract, full-time, part-time) as well as any training needs and how these will be provided.
- Equipment : Include a list of any specialized equipment needed, along with cost, whether it will be leased or purchased, and sources.
- Supplies : If your business is, for example, manufacturing, retail, or food services, include a description of the materials needed, reliable sources, major suppliers, and how you will manage inventory.
The financial plan is the most important section for lenders or investors. The goal is to demonstrate that your business will grow and be profitable. To do this, you will need to create realistic predictions or forecasts.
To avoid inflated expectations, a prudent financial plan underestimates revenues and overestimates expenses.
- Income statements : The income statement displays projected revenues, expenses, and profit. Do this on a monthly basis for at least the first year for a startup business.
- Cash-flow projections : The cash-flow projection shows your monthly anticipated cash revenues and disbursements for expenses. To be considered a good credit risk, it is important to demonstrate that you can manage your cash flow.
- Balance sheet : The balance sheet is a snapshot summary of the assets, liabilities, and equity of your business at a particular point in time. For a startup, this would be on the day the business opens.
- Breakeven analysis : Including a breakeven analysis will demonstrate to lenders or investors what level of sales you need to achieve to make a profit.
Section 8: Appendices and Exhibits
The appendices and exhibits section contains any detailed information needed to support other sections of the plan.
Possible Appendix or Exhibit items include:
- Credit histories for the business owners
- Detailed market research and analysis of competitors
- Résumés of the owners and key employees
- Diagrams and/or research about your products and/or services
- Site, building, or office plans
- Copies of mortgage documents or equipment leases (or quotes)
- Marketing brochures and other materials
- References from business colleagues
- Links to your business website
- Any other material that may impress potential lenders or investors
SCORE. " Business Plan Template for a Startup Business ." Accessed April 28, 2021.
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write your business plan ." Accessed April 28, 2021.
U.S. Small Business Administration. " SBA Recommended Business Plans and Length ." Accessed April 28, 2021.
Bplans. " Why Plan Your Business? Look at This Data ." Accessed April 28, 2021.
Marketing MO. " Pricing Strategy ." Accessed April 28, 2021.
Incorporate.com. " Write a Business Plan, a Step-by-Step Guide ." Accessed April 29, 2021.
Startup Nation. " The Five Costs You're Most Likely to Underestimate in Your Business Plan ." Accessed April 28, 2021.

Business Plan Development Guide
(6 reviews)
Lee Swanson, University of Saskatchewan
Copyright Year: 2017
Publisher: OPENPRESS.USASK.CA
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Kevin Heupel, Affiliate Faculty, Metropolitan State University of Denver on 3/4/20
The text does a good job of providing a general outline about writing and developing a written business plan. All of the important steps and components are included. However, the text is light on details, examples, and rationale for each element... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 3 see less
The text does a good job of providing a general outline about writing and developing a written business plan. All of the important steps and components are included. However, the text is light on details, examples, and rationale for each element of the business plan. Some examples from actual business plans would be helpful.
Content Accuracy rating: 4
For the most part, the content is accurate. The content covers all important aspects of drafting a business plan. I thought the industry analysis could use more information about collecting primary and secondary sources; instead, this information was referenced in the marketing plan section.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
Most of the content relies on cites as far back as 2006; however, when it comes to developing and writing a business plan nothing has changed. Thus, the content is current and there is no concern about it becoming obsolete in the near future.
Clarity rating: 4
The text is clear. There are no difficult terms used and the writing is simple. The text uses a lot of bullet points though, which gets tedious to read for a few pages.
Consistency rating: 5
The text does a good job of maintaining consistency in terms of framework and terminology. The text is organized where it's easy to find the information you want in a quick manner.
Modularity rating: 3
The text has a lot of bullet points and the paragraphs are dense. However, the use of subheading is excellent.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
The book is organized as if you're writing a business plan from start to finish, which is helpful as a practical guide.
Interface rating: 5
There are no navigation problems, distortion of images/charts, or any other display features that may distract or confuse the reader.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
The text is free of grammatical errors. The sentence structure is simple with many bullet points, which helps to avoid any grammatical issues.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
This book was written by a Canadian professor and provides references to Canadian sources. However, the information in this text can be used for U.S. schools.
This book is very short and provides a good, general overview about the process of creating and writing a business plan. It won't help a reader if he/she is confused about a certain part of the business plan. The reader will have to find another source, such as "Preparing Effective Business Plans" by Bruce Barringer, Ph.D. The book provides links to good resources and a finished business plan that the reader can reference. I would recommend the book for undergraduate courses.
Reviewed by Kenneth Lacho, Professor of Management, The University of New Orleans on 6/19/18
1. Text is relevant to Canada. Not the United States 2. Needs to cover resources available to entrepreneur, e.g., federal government agencies, trade associations, chambers of commerce, economic development agencies. 3. Discuss local economy or... read more
1. Text is relevant to Canada. Not the United States 2. Needs to cover resources available to entrepreneur, e.g., federal government agencies, trade associations, chambers of commerce, economic development agencies. 3. Discuss local economy or economic area relevant to this proposed business. 4. Business model ok as a guide. 5. Suggested mission statement to cover: product/business, target customer, geographical area covered. 6. Need detailed promotion plan, e.g., personal selling, advertising, sales promotion, networking publicity, and social media. 7. How do you find the target market? 8. Chapter 6 too much detail on debt and equity financing. 9. Discuss how to find sources of financing, e.g., angels. 10. Expand coverage of bootstring, crowdfunding. 11. Chapter 4 – good checklist. 12. Chapter 3 - overlaps. 13. Chapter 7 – 3 pages of executive summary – double or single spaced typing. Number all tables, graphs. 14. Some references out-of-date, mostly academic. Bring in trade magazines such as Entrepreneur.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
In my opinion, the content is accurate and error free.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 4
The material is relevant to writing a business plan. I wonder if the Porter, SWOT VRIO, etc. material is too high level for students who may not be seniors or have non-business degrees (e.g., liberal arts). Porter has been around for a while and does have longevity. The author has to be more alert to changes in promotion, e.g., social media and sources of financing, e.g., crowdfunding.
Clarity rating: 3
As noted in No. 9, the tone of the writing is too academic, thus making the material difficult to understand. Paragraphs are too long. Need to define: Porter, TOWS Matrix, VRIO, PESTEL. A student less from a senior or a non-business major would not be familiar with these terms.
Consistency rating: 4
The text is internally consistent. The model approach helps keep the process consistent.
Modularity rating: 4
The process of developing a business plan is divided into blocks which are parts of the business plan. Paragraphs tend to be too long in some spots.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
The topics are presented in a logical step-wise flow. The language style is too academic in parts, paragraphs too long. Leaves out the citations. Provides excellent check lists.
There are no display features which confuse the reader.
Grammatical Errors rating: 4
The text has no grammatical errors. On the other hand, I found the writing to be too academic in nature. Some paragraphs are too long. The material is more like an academic conference paper or journal submission. Academic citations references are not needed. The material is not exciting to read.
The text is culturally neutral. There are no examples which are inclusive of a variety of races, ethnicities, and backgrounds.
This book best for a graduate class.
Reviewed by Louis Bruneau, Part Time Faculty, Portland Community College on 6/19/18
The text provides appropriate discussion and illustration of all major concepts and useful references to source and resource materials. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
The text provides appropriate discussion and illustration of all major concepts and useful references to source and resource materials.
Contents of the book were accurate, although it could have benefited from editing/proofreading; there was no evidence of bias. As to editing/proofreading, a couple of examples: A. “Figure 1 – Business Plan… “ is shown at the top of the page following the diagram vs. the bottom of the page the diagram is on. (There are other problems with what is placed on each page.) B. First paragraph under heading “Essential Initial Research” there is reference to pages 21 to 30 though page numbering is missing from the book. (Page numbers are used in the Table of Contents.)
The book is current in that business planning has been stable for sometime. The references and resources will age in time, but are limited and look easy to update.
Clarity rating: 5
The book is written in a straightforward way, technical terms that needed explanations got them, jargon was avoided and generally it was an easy read.
The text is internally consistent in terms of terminology and framework.
Modularity rating: 5
The book lends itself to a multi-week course. A chapter could be presented and students could work on that stage of Plan development. It could also be pre-meeting reading for a workshop presentation. Reorganizing the book would be inappropriate.
The topics in the text are presented in a logical, clear fashion.
Generally, the book is free of interface problems. The financial tables in the Sample Plan were turned 90° to maintain legibility. One potential problem was with Figure 6 – Business Model Canvas. The print within the cells was too small to read; the author mitigated the problem by presenting the information, following Figure 6, in the type font of the text.
I found no grammatical errors.
The text is not culturally insensitive or offensive in any way.
I require a business plan in a course I teach; for most of the students the assignment is a course project that they do not intend to pursue in real life. I shared the book with five students that intended to develop an actual start-up business; three of them found it helpful while the other two decided not to do that much work on their plans. If I were planning a start-up, I would use/follow the book.
Reviewed by Todd Johnson, Faculty of Business, North Hennepin Community College on 5/21/18
The text is a thorough overview of all elements of a business plan. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
The text is a thorough overview of all elements of a business plan.
The content is accurate and seems to lack bias.
Content seems relevant and useful . It does not help an entrepreneur generate ideas, and is very light on crowdfunding and other novel funding source content. It is more traditional. This can be easily updated in future versions, however. "Social Media" appears once in the book, as does "Crowd Funding".
The book is comprehensive, but perhaps not written in the most lucid, accessible prose. I am not sure any college student could pick this up and just read and learn. It would be best used as a "teach along guide" for students to process with an instructor.
The text seems consistent. The author does a nice job of consistently staying on task and using bullets and brevity.
Here I am not so certain. The table of contents is not a good guide for this book. It does make the book look nicely laid out, but there is a lot of complexity within these sections. I read it uncertain that it was well organized. Yes there are many good bits of information, however it is not as if I could spend time on one swathe of text at a time. I would need to go back and forth throughout the text.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 2
Similar to the above. I did not like the flow and organization of this. An editor would help things be in a more logical order.
Interface rating: 2
The interface is just OK. It is not an attractice interface, as it presents text in a very dense manner. The images and charts are hard to follow.
I did not find any grammatical errors.
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
I a not certain of the origins of Saskatchewan, but I do feel this is a different read. It is more formal and dense than it has to be. This would be a difficult read for my students. I do not feel it is insensitive in any way, or offensive in any way.
I would not adopt this book if given the chance. It is too dense, and not organized very well, even though the information is very good. The density and lack of modularity are barriers to understanding what is obviously very good information.
Reviewed by Mariana Mitova, Lecturer, Bowling Green State University on 2/1/18
Though this textbook has a prescriptive nature, it is quite comprehensive. The author strikes a good balance between presenting concepts in a concise way and providing enough information to explain them. Many every-day examples and live links to... read more
Though this textbook has a prescriptive nature, it is quite comprehensive. The author strikes a good balance between presenting concepts in a concise way and providing enough information to explain them. Many every-day examples and live links to other resources add to the completeness of the textbook.
Content seems accurate.
Since the content is somewhat conceptual, the text will not become obsolete quickly. In addition, the author seems to be updating and editing content often hence the relevance to current developments is on target.
The text is very clear, written in clear and straight-to-the point language.
The organization of content is consistent throughout the entire text.
The textbook is organized by chapters, beginning with overview of the model used and followed by chapters for each concept within the model. Nicely done.
The flow is clear, logical and easy to follow.
Overall, images, links, and text are well organized. Some headlines were misaligned but still easy to follow.
No concerns for grammar.
No concerns for cultural irrelevance.
Reviewed by Darlene Weibye, Cosmetology Instructor, Minnesota State Community and Technical College on 2/1/18
The text is comprehensive and covers the information needed to develop a business plan. The book provides all the means necessary in business planning. read more
The text is comprehensive and covers the information needed to develop a business plan. The book provides all the means necessary in business planning.
The text was accurate, and error-free. I did not find the book to be biased.
The content is up-to-date. I am reviewing the book in 2017, the same year the book was published.
The content was very clear. A business plan sample included operation timelines, start up costs, and all relevant material in starting a business.
The book is very consistent and is well organized.
The book has a table of contents and is broken down into specific chapters. The chapters are not divided into sub topics. I do not feel it is necessary for sub topics because the chapters are brief and to the point.
There is a great flow from chapter to chapter. One topic clearly leads into the next without repeating.
The table of contents has direct links to each chapter. The appearance of the chapters are easy to read and the charts are very beneficial.
Does not appear to have any grammatical errors.
The text is not culturally insensitive or offensive.
I am incorporating some of the text into the salon business course. Very well written book.
Table of Contents
Introduction
- Chapter 1 – Developing a Business Plan
- Chapter 2 – Essential Initial Research
- Chapter 3 – Business Models
- Chapter 4 – Initial Business Plan Draft
- Chapter 5 – Making the Business Plan Realistic
- Chapter 6 – Making the Plan Appeal to Stakeholders and Desirable to the Entrepreneur
- Chapter 7 – Finishing the Business Plan
- Chapter 8 – Business Plan Pitches
References Appendix A – Business Plan Development Checklist and Project Planner Appendix B – Fashion Importers Inc. Business Plan Business Plan Excel Template
Ancillary Material
About the book.
This textbook and its accompanying spreadsheet templates were designed with and for students wanting a practical and easy-to-follow guide for developing a business plan. It follows a unique format that both explains what to do and demonstrates how to do it.
About the Contributors
Dr. Lee Swanson is an Associate Professor of Management and Marketing at the Edwards School of Business at the University of Saskatchewan. His research focuses on entrepreneurship, social entrepreneurship, Aboriginal entrepreneurship, community capacity-building through entrepreneurship, and institutional-stakeholder engagement. Dr. Swanson’s current research is funded through a Social Sciences Humanities Research Council grant and focuses on social and economic capacity building in Northern Saskatchewan and Northern Scandinavia. He is also actively studying Aboriginal community partnerships with resource based companies, entrepreneurship centres at universities, community-based entrepreneurship, and entrepreneurial attitudes and intentions. He teaches upper-year and MBA entrepreneurship classes and conducts seminars on business planning and business development.
Contribute to this Page
- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax
How to Write a Business Plan in 9 Steps (+ Template and Examples)
Every successful business has one thing in common, a good and well-executed business plan. A business plan is more than a document, it is a complete guide that outlines the goals your business wants to achieve, including its financial goals . It helps you analyze results, make strategic decisions, show your business operations and growth.
If you want to start a business or already have one and need to pitch it to investors for funding, writing a good business plan improves your chances of attracting financiers. As a startup, if you want to secure loans from financial institutions, part of the requirements involve submitting your business plan.
Writing a business plan does not have to be a complicated or time-consuming process. In this article, you will learn the step-by-step process for writing a successful business plan.
You will also learn what you need a business plan for, tips and strategies for writing a convincing business plan, business plan examples and templates that will save you tons of time, and the alternatives to the traditional business plan.
Let’s get started.
What Do You Need A Business Plan For?
Businesses create business plans for different purposes such as to secure funds, monitor business growth, measure your marketing strategies, and measure your business success.
1. Secure Funds
One of the primary reasons for writing a business plan is to secure funds, either from financial institutions/agencies or investors.
For you to effectively acquire funds, your business plan must contain the key elements of your business plan . For example, your business plan should include your growth plans, goals you want to achieve, and milestones you have recorded.
A business plan can also attract new business partners that are willing to contribute financially and intellectually. If you are writing a business plan to a bank, your project must show your traction , that is, the proof that you can pay back any loan borrowed.
Also, if you are writing to an investor, your plan must contain evidence that you can effectively utilize the funds you want them to invest in your business. Here, you are using your business plan to persuade a group or an individual that your business is a source of a good investment.
2. Monitor Business Growth
A business plan can help you track cash flows in your business. It steers your business to greater heights. A business plan capable of tracking business growth should contain:
- The business goals
- Methods to achieve the goals
- Time-frame for attaining those goals
A good business plan should guide you through every step in achieving your goals. It can also track the allocation of assets to every aspect of the business. You can tell when you are spending more than you should on a project.
You can compare a business plan to a written GPS. It helps you manage your business and hints at the right time to expand your business.
3. Measure Business Success
A business plan can help you measure your business success rate. Some small-scale businesses are thriving better than more prominent companies because of their track record of success.
Right from the onset of your business operation, set goals and work towards them. Write a plan to guide you through your procedures. Use your plan to measure how much you have achieved and how much is left to attain.
You can also weigh your success by monitoring the position of your brand relative to competitors. On the other hand, a business plan can also show you why you have not achieved a goal. It can tell if you have elapsed the time frame you set to attain a goal.
4. Document Your Marketing Strategies
You can use a business plan to document your marketing plans. Every business should have an effective marketing plan.
Competition mandates every business owner to go the extraordinary mile to remain relevant in the market. Your business plan should contain your marketing strategies that work. You can measure the success rate of your marketing plans.
In your business plan, your marketing strategy must answer the questions:
- How do you want to reach your target audience?
- How do you plan to retain your customers?
- What is/are your pricing plans?
- What is your budget for marketing?

How to Write a Business Plan Step-by-Step
1. create your executive summary.
The executive summary is a snapshot of your business or a high-level overview of your business purposes and plans . Although the executive summary is the first section in your business plan, most people write it last. The length of the executive summary is not more than two pages.

Generally, there are nine sections in a business plan, the executive summary should condense essential ideas from the other eight sections.
A good executive summary should do the following:
- A Snapshot of Growth Potential. Briefly inform the reader about your company and why it will be successful)
- Contain your Mission Statement which explains what the main objective or focus of your business is.
- Product Description and Differentiation. Brief description of your products or services and why it is different from other solutions in the market.
- The Team. Basic information about your company’s leadership team and employees
- Business Concept. A solid description of what your business does.
- Target Market. The customers you plan to sell to.
- Marketing Strategy. Your plans on reaching and selling to your customers
- Current Financial State. Brief information about what revenue your business currently generates.
- Projected Financial State. Brief information about what you foresee your business revenue to be in the future.
The executive summary is the make-or-break section of your business plan. If your summary cannot in less than two pages cannot clearly describe how your business will solve a particular problem of your target audience and make a profit, your business plan is set on a faulty foundation.
Avoid using the executive summary to hype your business, instead, focus on helping the reader understand the what and how of your plan.
View the executive summary as an opportunity to introduce your vision for your company. You know your executive summary is powerful when it can answer these key questions:
- Who is your target audience?
- What sector or industry are you in?
- What are your products and services?
- What is the future of your industry?
- Is your company scaleable?
- Who are the owners and leaders of your company? What are their backgrounds and experience levels?
- What is the motivation for starting your company?
- What are the next steps?
Writing the executive summary last although it is the most important section of your business plan is an excellent idea. The reason why is because it is a high-level overview of your business plan. It is the section that determines whether potential investors and lenders will read further or not.
The executive summary can be a stand-alone document that covers everything in your business plan. It is not uncommon for investors to request only the executive summary when evaluating your business. If the information in the executive summary impresses them, they will ask for the complete business plan.
If you are writing your business plan for your planning purposes, you do not need to write the executive summary.
2. Add Your Company Overview
The company overview or description is the next section in your business plan after the executive summary. It describes what your business does.
Adding your company overview can be tricky especially when your business is still in the planning stages. Existing businesses can easily summarize their current operations but may encounter difficulties trying to explain what they plan to become.
Your company overview should contain the following:
- What products and services you will provide
- Geographical markets and locations your company have a presence
- What you need to run your business
- Who your target audience or customers are
- Who will service your customers
- Your company’s purpose, mission, and vision
- Information about your company’s founders
- Who the founders are
- Notable achievements of your company so far
When creating a company overview, you have to focus on three basics: identifying your industry, identifying your customer, and explaining the problem you solve.
If you are stuck when creating your company overview, try to answer some of these questions that pertain to you.
- Who are you targeting? (The answer is not everyone)
- What pain point does your product or service solve for your customers that they will be willing to spend money on resolving?
- How does your product or service overcome that pain point?
- Where is the location of your business?
- What products, equipment, and services do you need to run your business?
- How is your company’s product or service different from your competition in the eyes of your customers?
- How many employees do you need and what skills do you require them to have?
After answering some or all of these questions, you will get more than enough information you need to write your company overview or description section. When writing this section, describe what your company does for your customers.

The company description or overview section contains three elements: mission statement, history, and objectives.
- Mission Statement
The mission statement refers to the reason why your business or company is existing. It goes beyond what you do or sell, it is about the ‘why’. A good mission statement should be emotional and inspirational.
Your mission statement should follow the KISS rule (Keep It Simple, Stupid). For example, Shopify’s mission statement is “Make commerce better for everyone.”
When describing your company’s history, make it simple and avoid the temptation of tying it to a defensive narrative. Write it in the manner you would a profile. Your company’s history should include the following information:
- Founding Date
- Major Milestones
- Location(s)
- Flagship Products or Services
- Number of Employees
- Executive Leadership Roles
When you fill in this information, you use it to write one or two paragraphs about your company’s history.
Business Objectives
Your business objective must be SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound.) Failure to clearly identify your business objectives does not inspire confidence and makes it hard for your team members to work towards a common purpose.
3. Perform Market and Competitive Analyses to Proof a Big Enough Business Opportunity
The third step in writing a business plan is the market and competitive analysis section. Every business, no matter the size, needs to perform comprehensive market and competitive analyses before it enters into a market.
Performing market and competitive analyses are critical for the success of your business. It helps you avoid entering the right market with the wrong product, or vice versa. Anyone reading your business plans, especially financiers and financial institutions will want to see proof that there is a big enough business opportunity you are targeting.
This section is where you describe the market and industry you want to operate in and show the big opportunities in the market that your business can leverage to make a profit. If you noticed any unique trends when doing your research, show them in this section.
Market analysis alone is not enough, you have to add competitive analysis to strengthen this section. There are already businesses in the industry or market, how do you plan to take a share of the market from them?
You have to clearly illustrate the competitive landscape in your business plan. Are there areas your competitors are doing well? Are there areas where they are not doing so well? Show it.
Make it clear in this section why you are moving into the industry and what weaknesses are present there that you plan to explain. How are your competitors going to react to your market entry? How do you plan to get customers? Do you plan on taking your competitors' competitors, tap into other sources for customers, or both?
Illustrate the competitive landscape as well. What are your competitors doing well and not so well?
Answering these questions and thoughts will aid your market and competitive analysis of the opportunities in your space. Depending on how sophisticated your industry is, or the expectations of your financiers, you may need to carry out a more comprehensive market and competitive analysis to prove that big business opportunity.
Instead of looking at the market and competitive analyses as one entity, separating them will make the research even more comprehensive.
Market Analysis
Market analysis, boarding speaking, refers to research a business carried out on its industry, market, and competitors. It helps businesses gain a good understanding of their target market and the outlook of their industry. Before starting a company, it is vital to carry out market research to find out if the market is viable.

The market analysis section is a key part of the business plan. It is the section where you identify who your best clients or customers are. You cannot omit this section, without it your business plan is incomplete.
A good market analysis will tell your readers how you fit into the existing market and what makes you stand out. This section requires in-depth research, it will probably be the most time-consuming part of the business plan to write.
- Market Research
To create a compelling market analysis that will win over investors and financial institutions, you have to carry out thorough market research . Your market research should be targeted at your primary target market for your products or services. Here is what you want to find out about your target market.
- Your target market’s needs or pain points
- The existing solutions for their pain points
- Geographic Location
- Demographics
The purpose of carrying out a marketing analysis is to get all the information you need to show that you have a solid and thorough understanding of your target audience.
Only after you have fully understood the people you plan to sell your products or services to, can you evaluate correctly if your target market will be interested in your products or services.
You can easily convince interested parties to invest in your business if you can show them you thoroughly understand the market and show them that there is a market for your products or services.
How to Quantify Your Target Market
One of the goals of your marketing research is to understand who your ideal customers are and their purchasing power. To quantify your target market, you have to determine the following:
- Your Potential Customers: They are the people you plan to target. For example, if you sell accounting software for small businesses , then anyone who runs an enterprise or large business is unlikely to be your customers. Also, individuals who do not have a business will most likely not be interested in your product.
- Total Households: If you are selling household products such as heating and air conditioning systems, determining the number of total households is more important than finding out the total population in the area you want to sell to. The logic is simple, people buy the product but it is the household that uses it.
- Median Income: You need to know the median income of your target market. If you target a market that cannot afford to buy your products and services, your business will not last long.
- Income by Demographics: If your potential customers belong to a certain age group or gender, determining income levels by demographics is necessary. For example, if you sell men's clothes, your target audience is men.
What Does a Good Market Analysis Entail?
Your business does not exist on its own, it can only flourish within an industry and alongside competitors. Market analysis takes into consideration your industry, target market, and competitors. Understanding these three entities will drastically improve your company’s chances of success.

You can view your market analysis as an examination of the market you want to break into and an education on the emerging trends and themes in that market. Good market analyses include the following:
- Industry Description. You find out about the history of your industry, the current and future market size, and who the largest players/companies are in your industry.
- Overview of Target Market. You research your target market and its characteristics. Who are you targeting? Note, it cannot be everyone, it has to be a specific group. You also have to find out all information possible about your customers that can help you understand how and why they make buying decisions.
- Size of Target Market: You need to know the size of your target market, how frequently they buy, and the expected quantity they buy so you do not risk overproducing and having lots of bad inventory. Researching the size of your target market will help you determine if it is big enough for sustained business or not.
- Growth Potential: Before picking a target market, you want to be sure there are lots of potential for future growth. You want to avoid going for an industry that is declining slowly or rapidly with almost zero growth potential.
- Market Share Potential: Does your business stand a good chance of taking a good share of the market?
- Market Pricing and Promotional Strategies: Your market analysis should give you an idea of the price point you can expect to charge for your products and services. Researching your target market will also give you ideas of pricing strategies you can implement to break into the market or to enjoy maximum profits.
- Potential Barriers to Entry: One of the biggest benefits of conducting market analysis is that it shows you every potential barrier to entry your business will likely encounter. It is a good idea to discuss potential barriers to entry such as changing technology. It informs readers of your business plan that you understand the market.
- Research on Competitors: You need to know the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors and how you can exploit them for the benefit of your business. Find patterns and trends among your competitors that make them successful, discover what works and what doesn’t, and see what you can do better.
The market analysis section is not just for talking about your target market, industry, and competitors. You also have to explain how your company can fill the hole you have identified in the market.
Here are some questions you can answer that can help you position your product or service in a positive light to your readers.
- Is your product or service of superior quality?
- What additional features do you offer that your competitors do not offer?
- Are you targeting a ‘new’ market?
Basically, your market analysis should include an analysis of what already exists in the market and an explanation of how your company fits into the market.
Competitive Analysis
In the competitive analysis section, y ou have to understand who your direct and indirect competitions are, and how successful they are in the marketplace. It is the section where you assess the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors, the advantage(s) they possess in the market and show the unique features or qualities that make you different from your competitors.

Many businesses do market analysis and competitive analysis together. However, to fully understand what the competitive analysis entails, it is essential to separate it from the market analysis.
Competitive analysis for your business can also include analysis on how to overcome barriers to entry in your target market.
The primary goal of conducting a competitive analysis is to distinguish your business from your competitors. A strong competitive analysis is essential if you want to convince potential funding sources to invest in your business. You have to show potential investors and lenders that your business has what it takes to compete in the marketplace successfully.
Competitive analysis will s how you what the strengths of your competition are and what they are doing to maintain that advantage.
When doing your competitive research, you first have to identify your competitor and then get all the information you can about them. The idea of spending time to identify your competitor and learn everything about them may seem daunting but it is well worth it.
Find answers to the following questions after you have identified who your competitors are.
- What are your successful competitors doing?
- Why is what they are doing working?
- Can your business do it better?
- What are the weaknesses of your successful competitors?
- What are they not doing well?
- Can your business turn its weaknesses into strengths?
- How good is your competitors’ customer service?
- Where do your competitors invest in advertising?
- What sales and pricing strategies are they using?
- What marketing strategies are they using?
- What kind of press coverage do they get?
- What are their customers saying about your competitors (both the positive and negative)?
If your competitors have a website, it is a good idea to visit their websites for more competitors’ research. Check their “About Us” page for more information.

If you are presenting your business plan to investors, you need to clearly distinguish yourself from your competitors. Investors can easily tell when you have not properly researched your competitors.
Take time to think about what unique qualities or features set you apart from your competitors. If you do not have any direct competition offering your product to the market, it does not mean you leave out the competitor analysis section blank. Instead research on other companies that are providing a similar product, or whose product is solving the problem your product solves.
The next step is to create a table listing the top competitors you want to include in your business plan. Ensure you list your business as the last and on the right. What you just created is known as the competitor analysis table.
Direct vs Indirect Competition
You cannot know if your product or service will be a fit for your target market if you have not understood your business and the competitive landscape.
There is no market you want to target where you will not encounter competition, even if your product is innovative. Including competitive analysis in your business plan is essential.
If you are entering an established market, you need to explain how you plan to differentiate your products from the available options in the market. Also, include a list of few companies that you view as your direct competitors The competition you face in an established market is your direct competition.
In situations where you are entering a market with no direct competition, it does not mean there is no competition there. Consider your indirect competition that offers substitutes for the products or services you offer.
For example, if you sell an innovative SaaS product, let us say a project management software , a company offering time management software is your indirect competition.
There is an easy way to find out who your indirect competitors are in the absence of no direct competitors. You simply have to research how your potential customers are solving the problems that your product or service seeks to solve. That is your direct competition.
Factors that Differentiate Your Business from the Competition
There are three main factors that any business can use to differentiate itself from its competition. They are cost leadership, product differentiation, and market segmentation.
1. Cost Leadership
A strategy you can impose to maximize your profits and gain an edge over your competitors. It involves offering lower prices than what the majority of your competitors are offering.
A common practice among businesses looking to enter into a market where there are dominant players is to use free trials or pricing to attract as many customers as possible to their offer.
2. Product Differentiation
Your product or service should have a unique selling proposition (USP) that your competitors do not have or do not stress in their marketing.
Part of the marketing strategy should involve making your products unique and different from your competitors. It does not have to be different from your competitors, it can be the addition to a feature or benefit that your competitors do not currently have.
3. Market Segmentation
As a new business seeking to break into an industry, you will gain more success from focusing on a specific niche or target market, and not the whole industry.
If your competitors are focused on a general need or target market, you can differentiate yourself from them by having a small and hyper-targeted audience. For example, if your competitors are selling men’s clothes in their online stores , you can sell hoodies for men.
4. Define Your Business and Management Structure
The next step in your business plan is your business and management structure. It is the section where you describe the legal structure of your business and the team running it.
Your business is only as good as the management team that runs it, while the management team can only strive when there is a proper business and management structure in place.
If your company is a sole proprietor or a limited liability company (LLC), a general or limited partnership, or a C or an S corporation, state it clearly in this section.
Use an organizational chart to show the management structure in your business. Clearly show who is in charge of what area in your company. It is where you show how each key manager or team leader’s unique experience can contribute immensely to the success of your company. You can also opt to add the resumes and CVs of the key players in your company.
The business and management structure section should show who the owner is, and other owners of the businesses (if the business has other owners). For businesses or companies with multiple owners, include the percent ownership of the various owners and clearly show the extent of each others’ involvement in the company.
Investors want to know who is behind the company and the team running it to determine if it has the right management to achieve its set goals.
Management Team
The management team section is where you show that you have the right team in place to successfully execute the business operations and ideas. Take time to create the management structure for your business. Think about all the important roles and responsibilities that you need managers for to grow your business.
Include brief bios of each key team member and ensure you highlight only the relevant information that is needed. If your team members have background industry experience or have held top positions for other companies and achieved success while filling that role, highlight it in this section.

A common mistake that many startups make is assigning C-level titles such as (CMO and CEO) to everyone on their team. It is unrealistic for a small business to have those titles. While it may look good on paper for the ego of your team members, it can prevent investors from investing in your business.
Instead of building an unrealistic management structure that does not fit your business reality, it is best to allow business titles to grow as the business grows. Starting everyone at the top leaves no room for future change or growth, which is bad for productivity.
Your management team does not have to be complete before you start writing your business plan. You can have a complete business plan even when there are managerial positions that are empty and need filling.
If you have management gaps in your team, simply show the gaps and indicate you are searching for the right candidates for the role(s). Investors do not expect you to have a full management team when you are just starting your business.
Key Questions to Answer When Structuring Your Management Team
- Who are the key leaders?
- What experiences, skills, and educational backgrounds do you expect your key leaders to have?
- Do your key leaders have industry experience?
- What positions will they fill and what duties will they perform in those positions?
- What level of authority do the key leaders have and what are their responsibilities?
- What is the salary for the various management positions that will attract the ideal candidates?
Additional Tips for Writing the Management Structure Section
1. Avoid Adding ‘Ghost’ Names to Your Management Team
There is always that temptation to include a ‘ghost’ name to your management team to attract and influence investors to invest in your business. Although the presence of these celebrity management team members may attract the attention of investors, it can cause your business to lose any credibility if you get found out.
Seasoned investors will investigate further the members of your management team before committing fully to your business If they find out that the celebrity name used does not play any actual role in your business, they will not invest and may write you off as dishonest.
2. Focus on Credentials But Pay Extra Attention to the Roles
Investors want to know the experience that your key team members have to determine if they can successfully reach the company’s growth and financial goals.
While it is an excellent boost for your key management team to have the right credentials, you also want to pay extra attention to the roles they will play in your company.
Organizational Chart

Adding an organizational chart in this section of your business plan is not necessary, you can do it in your business plan’s appendix.
If you are exploring funding options, it is not uncommon to get asked for your organizational chart. The function of an organizational chart goes beyond raising money, you can also use it as a useful planning tool for your business.
An organizational chart can help you identify how best to structure your management team for maximum productivity and point you towards key roles you need to fill in the future.
You can use the organizational chart to show your company’s internal management structure such as the roles and responsibilities of your management team, and relationships that exist between them.
5. Describe Your Product and Service Offering
In your business plan, you have to describe what you sell or the service you plan to offer. It is the next step after defining your business and management structure. The products and services section is where you sell the benefits of your business.
Here you have to explain how your product or service will benefit your customers and describe your product lifecycle. It is also the section where you write down your plans for intellectual property like patent filings and copyrighting.
The research and development that you are undertaking for your product or service need to be explained in detail in this section. However, do not get too technical, sell the general idea and its benefits.
If you have any diagrams or intricate designs of your product or service, do not include them in the products and services section. Instead, leave them for the addendum page. Also, if you are leaving out diagrams or designs for the addendum, ensure you add this phrase “For more detail, visit the addendum Page #.”
Your product and service section in your business plan should include the following:
- A detailed explanation that clearly shows how your product or service works.
- The pricing model for your product or service.
- Your business’ sales and distribution strategy.
- The ideal customers that want your product or service.
- The benefits of your products and services.
- Reason(s) why your product or service is a better alternative to what your competitors are currently offering in the market.
- Plans for filling the orders you receive
- If you have current or pending patents, copyrights, and trademarks for your product or service, you can also discuss them in this section.
What to Focus On When Describing the Benefits, Lifecycle, and Production Process of Your Products or Services
In the products and services section, you have to distill the benefits, lifecycle, and production process of your products and services.
When describing the benefits of your products or services, here are some key factors to focus on.
- Unique features
- Translating the unique features into benefits
- The emotional, psychological, and practical payoffs to attract customers
- Intellectual property rights or any patents
When describing the product life cycle of your products or services, here are some key factors to focus on.
- Upsells, cross-sells, and down-sells
- Time between purchases
- Plans for research and development.
When describing the production process for your products or services, you need to think about the following:
- The creation of new or existing products and services.
- The sources for the raw materials or components you need for production.
- Assembling the products
- Maintaining quality control
- Supply-chain logistics (receiving the raw materials and delivering the finished products)
- The day-to-day management of the production processes, bookkeeping, and inventory.
Tips for Writing the Products or Services Section of Your Business Plan
1. Avoid Technical Descriptions and Industry Buzzwords
The products and services section of your business plan should clearly describe the products and services that your company provides. However, it is not a section to include technical jargons that anyone outside your industry will not understand.
A good practice is to remove highly detailed or technical descriptions in favor of simple terms. Industry buzzwords are not necessary, if there are simpler terms you can use, then use them. If you plan to use your business plan to source funds, making the product or service section so technical will do you no favors.
2. Describe How Your Products or Services Differ from Your Competitors
When potential investors look at your business plan, they want to know how the products and services you are offering differ from that of your competition. Differentiating your products or services from your competition in a way that makes your solution more attractive is critical.
If you are going the innovative path and there is no market currently for your product or service, you need to describe in this section why the market needs your product or service.
For example, overnight delivery was a niche business that only a few companies were participating in. Federal Express (FedEx) had to show in its business plan that there was a large opportunity for that service and they justified why the market needed that service.
3. Long or Short Products or Services Section
Should your products or services section be short? Does the long products or services section attract more investors?
There are no straightforward answers to these questions. Whether your products or services section should be long or relatively short depends on the nature of your business.
If your business is product-focused, then automatically you need to use more space to describe the details of your products. However, if the product your business sells is a commodity item that relies on competitive pricing or other pricing strategies, you do not have to use up so much space to provide significant details about the product.
Likewise, if you are selling a commodity that is available in numerous outlets, then you do not have to spend time on writing a long products or services section.
The key to the success of your business is most likely the effectiveness of your marketing strategies compared to your competitors. Use more space to address that section.
If you are creating a new product or service that the market does not know about, your products or services section can be lengthy. The reason why is because you need to explain everything about the product or service such as the nature of the product, its use case, and values.
A short products or services section for an innovative product or service will not give the readers enough information to properly evaluate your business.
4. Describe Your Relationships with Vendors or Suppliers
Your business will rely on vendors or suppliers to supply raw materials or the components needed to make your products. In your products and services section, describe your relationships with your vendors and suppliers fully.
Avoid the mistake of relying on only one supplier or vendor. If that supplier or vendor fails to supply or goes out of business, you can easily face supply problems and struggle to meet your demands. Plan to set up multiple vendor or supplier relationships for better business stability.
5. Your Primary Goal Is to Convince Your Readers
The primary goal of your business plan is to convince your readers that your business is viable and to create a guide for your business to follow. It applies to the products and services section.
When drafting this section, think like the reader. See your reader as someone who has no idea about your products and services. You are using the products and services section to provide the needed information to help your reader understand your products and services. As a result, you have to be clear and to the point.
While you want to educate your readers about your products or services, you also do not want to bore them with lots of technical details. Show your products and services and not your fancy choice of words.
Your products and services section should provide the answer to the “what” question for your business. You and your management team may run the business, but it is your products and services that are the lifeblood of the business.
Key Questions to Answer When Writing your Products and Services Section
Answering these questions can help you write your products and services section quickly and in a way that will appeal to your readers.
- Are your products existing on the market or are they still in the development stage?
- What is your timeline for adding new products and services to the market?
- What are the positives that make your products and services different from your competitors?
- Do your products and services have any competitive advantage that your competitors’ products and services do not currently have?
- Do your products or services have any competitive disadvantages that you need to overcome to compete with your competitors? If your answer is yes, state how you plan to overcome them,
- How much does it cost to produce your products or services? How much do you plan to sell it for?
- What is the price for your products and services compared to your competitors? Is pricing an issue?
- What are your operating costs and will it be low enough for you to compete with your competitors and still take home a reasonable profit margin?
- What is your plan for acquiring your products? Are you involved in the production of your products or services?
- Are you the manufacturer and produce all the components you need to create your products? Do you assemble your products by using components supplied by other manufacturers? Do you purchase your products directly from suppliers or wholesalers?
- Do you have a steady supply of products that you need to start your business? (If your business is yet to kick-off)
- How do you plan to distribute your products or services to the market?
You can also hint at the marketing or promotion plans you have for your products or services such as how you plan to build awareness or retain customers. The next section is where you can go fully into details about your business’s marketing and sales plan.
6. Show and Explain Your Marketing and Sales Plan
Providing great products and services is wonderful, but it means nothing if you do not have a marketing and sales plan to inform your customers about them. Your marketing and sales plan is critical to the success of your business.
The sales and marketing section is where you show and offer a detailed explanation of your marketing and sales plan and how you plan to execute it. It covers your pricing plan, proposed advertising and promotion activities, activities and partnerships you need to make your business a success, and the benefits of your products and services.
There are several ways you can approach your marketing and sales strategy. Ideally, your marketing and sales strategy has to fit the unique needs of your business.
In this section, you describe how the plans your business has for attracting and retaining customers, and the exact process for making a sale happen. It is essential to thoroughly describe your complete marketing and sales plans because you are still going to reference this section when you are making financial projections for your business.
Outline Your Business’ Unique Selling Proposition (USP)

The sales and marketing section is where you outline your business’s unique selling proposition (USP). When you are developing your unique selling proposition, think about the strongest reasons why people should buy from you over your competition. That reason(s) is most likely a good fit to serve as your unique selling proposition (USP).
Target Market and Target Audience
Plans on how to get your products or services to your target market and how to get your target audience to buy them go into this section. You also highlight the strengths of your business here, particularly what sets them apart from your competition.

Before you start writing your marketing and sales plan, you need to have properly defined your target audience and fleshed out your buyer persona. If you do not first understand the individual you are marketing to, your marketing and sales plan will lack any substance and easily fall.
Creating a Smart Marketing and Sales Plan
Marketing your products and services is an investment that requires you to spend money. Like any other investment, you have to generate a good return on investment (ROI) to justify using that marketing and sales plan. Good marketing and sales plans bring in high sales and profits to your company.
Avoid spending money on unproductive marketing channels. Do your research and find out the best marketing and sales plan that works best for your company.
Your marketing and sales plan can be broken into different parts: your positioning statement, pricing, promotion, packaging, advertising, public relations, content marketing, social media, and strategic alliances.
Your Positioning Statement
Your positioning statement is the first part of your marketing and sales plan. It refers to the way you present your company to your customers.
Are you the premium solution, the low-price solution, or are you the intermediary between the two extremes in the market? What do you offer that your competitors do not that can give you leverage in the market?
Before you start writing your positioning statement, you need to spend some time evaluating the current market conditions. Here are some questions that can help you to evaluate the market
- What are the unique features or benefits that you offer that your competitors lack?
- What are your customers’ primary needs and wants?
- Why should a customer choose you over your competition? How do you plan to differentiate yourself from the competition?
- How does your company’s solution compare with other solutions in the market?
After answering these questions, then you can start writing your positioning statement. Your positioning statement does not have to be in-depth or too long.
All you need to explain with your positioning statement are two focus areas. The first is the position of your company within the competitive landscape. The other focus area is the core value proposition that sets your company apart from other alternatives that your ideal customer might consider.
Here is a simple template you can use to develop a positioning statement.
For [description of target market] who [need of target market], [product or service] [how it meets the need]. Unlike [top competition], it [most essential distinguishing feature].
For example, let’s create the positioning statement for fictional accounting software and QuickBooks alternative , TBooks.
“For small business owners who need accounting services, TBooks is an accounting software that helps small businesses handle their small business bookkeeping basics quickly and easily. Unlike Wave, TBooks gives small businesses access to live sessions with top accountants.”
You can edit this positioning statement sample and fill it with your business details.
After writing your positioning statement, the next step is the pricing of your offerings. The overall positioning strategy you set in your positioning statement will often determine how you price your products or services.
Pricing is a powerful tool that sends a strong message to your customers. Failure to get your pricing strategy right can make or mar your business. If you are targeting a low-income audience, setting a premium price can result in low sales.
You can use pricing to communicate your positioning to your customers. For example, if you are offering a product at a premium price, you are sending a message to your customers that the product belongs to the premium category.
Basic Rules to Follow When Pricing Your Offering
Setting a price for your offering involves more than just putting a price tag on it. Deciding on the right pricing for your offering requires following some basic rules. They include covering your costs, primary and secondary profit center pricing, and matching the market rate.
- Covering Your Costs: The price you set for your products or service should be more than it costs you to produce and deliver them. Every business has the same goal, to make a profit. Depending on the strategy you want to use, there are exceptions to this rule. However, the vast majority of businesses follow this rule.
- Primary and Secondary Profit Center Pricing: When a company sets its price above the cost of production, it is making that product its primary profit center. A company can also decide not to make its initial price its primary profit center by selling below or at even with its production cost. It rather depends on the support product or even maintenance that is associated with the initial purchase to make its profit. The initial price thus became its secondary profit center.
- Matching the Market Rate: A good rule to follow when pricing your products or services is to match your pricing with consumer demand and expectations. If you price your products or services beyond the price your customer perceives as the ideal price range, you may end up with no customers. Pricing your products too low below what your customer perceives as the ideal price range may lead to them undervaluing your offering.
Pricing Strategy
Your pricing strategy influences the price of your offering. There are several pricing strategies available for you to choose from when examining the right pricing strategy for your business. They include cost-plus pricing, market-based pricing, value pricing, and more.

- Cost-plus Pricing: This strategy is one of the simplest and oldest pricing strategies. Here you consider the cost of producing a unit of your product and then add a profit to it to arrive at your market price. It is an effective pricing strategy for manufacturers because it helps them cover their initial costs. Another name for the cost-plus pricing strategy is the markup pricing strategy.
- Market-based Pricing: This pricing strategy analyses the market including competitors’ pricing and then sets a price based on what the market is expecting. With this pricing strategy, you can either set your price at the low-end or high-end of the market.
- Value Pricing: This pricing strategy involves setting a price based on the value you are providing to your customer. When adopting a value-based pricing strategy, you have to set a price that your customers are willing to pay. Service-based businesses such as small business insurance providers , luxury goods sellers, and the fashion industry use this pricing strategy.
After carefully sorting out your positioning statement and pricing, the next item to look at is your promotional strategy. Your promotional strategy explains how you plan on communicating with your customers and prospects.
As a business, you must measure all your costs, including the cost of your promotions. You also want to measure how much sales your promotions bring for your business to determine its usefulness. Promotional strategies or programs that do not lead to profit need to be removed.
There are different types of promotional strategies you can adopt for your business, they include advertising, public relations, and content marketing.
Advertising
Your business plan should include your advertising plan which can be found in the marketing and sales plan section. You need to include an overview of your advertising plans such as the areas you plan to spend money on to advertise your business and offers.
Ensure that you make it clear in this section if your business will be advertising online or using the more traditional offline media, or the combination of both online and offline media. You can also include the advertising medium you want to use to raise awareness about your business and offers.
Some common online advertising mediums you can use include social media ads, landing pages, sales pages, SEO, Pay-Per-Click, emails, Google Ads, and others. Some common traditional and offline advertising mediums include word of mouth, radios, direct mail, televisions, flyers, billboards, posters, and others.
A key component of your advertising strategy is how you plan to measure the effectiveness and success of your advertising campaign. There is no point in sticking with an advertising plan or medium that does not produce results for your business in the long run.
Public Relations
A great way to reach your customers is to get the media to cover your business or product. Publicity, especially good ones, should be a part of your marketing and sales plan. In this section, show your plans for getting prominent reviews of your product from reputable publications and sources.
Your business needs that exposure to grow. If public relations is a crucial part of your promotional strategy, provide details about your public relations plan here.
Content Marketing
Content marketing is a popular promotional strategy used by businesses to inform and attract their customers. It is about teaching and educating your prospects on various topics of interest in your niche, it does not just involve informing them about the benefits and features of the products and services you have,

Businesses publish content usually for free where they provide useful information, tips, and advice so that their target market can be made aware of the importance of their products and services. Content marketing strategies seek to nurture prospects into buyers over time by simply providing value.
Your company can create a blog where it will be publishing content for its target market. You will need to use the best website builder such as Wix and Squarespace and the best web hosting services such as Bluehost, Hostinger, and other Bluehost alternatives to create a functional blog or website.
If content marketing is a crucial part of your promotional strategy (as it should be), detail your plans under promotions.
Including high-quality images of the packaging of your product in your business plan is a lovely idea. You can add the images of the packaging of that product in the marketing and sales plan section. If you are not selling a product, then you do not need to include any worry about the physical packaging of your product.
When organizing the packaging section of your business plan, you can answer the following questions to make maximum use of this section.
- Is your choice of packaging consistent with your positioning strategy?
- What key value proposition does your packaging communicate? (It should reflect the key value proposition of your business)
- How does your packaging compare to that of your competitors?
Social Media
Your 21st-century business needs to have a good social media presence. Not having one is leaving out opportunities for growth and reaching out to your prospect.
You do not have to join the thousands of social media platforms out there. What you need to do is join the ones that your customers are active on and be active there.

Businesses use social media to provide information about their products such as promotions, discounts, the benefits of their products, and content on their blogs.
Social media is also a platform for engaging with your customers and getting feedback about your products or services. Make no mistake, more and more of your prospects are using social media channels to find more information about companies.
You need to consider the social media channels you want to prioritize your business (prioritize the ones your customers are active in) and your branding plans in this section.

Strategic Alliances
If your company plans to work closely with other companies as part of your sales and marketing plan, include it in this section. Prove details about those partnerships in your business plan if you have already established them.
Strategic alliances can be beneficial for all parties involved including your company. Working closely with another company in the form of a partnership can provide access to a different target market segment for your company.
The company you are partnering with may also gain access to your target market or simply offer a new product or service (that of your company) to its customers.
Mutually beneficial partnerships can cover the weaknesses of one company with the strength of another. You should consider strategic alliances with companies that sell complimentary products to yours. For example, if you provide printers, you can partner with a company that produces ink since the customers that buy printers from you will also need inks for printing.
Steps Involved in Creating a Marketing and Sales Plan
1. Focus on Your Target Market
Identify who your customers are, the market you want to target. Then determine the best ways to get your products or services to your potential customers.
2. Evaluate Your Competition
One of the goals of having a marketing plan is to distinguish yourself from your competition. You cannot stand out from them without first knowing them in and out.
You can know your competitors by gathering information about their products, pricing, service, and advertising campaigns.
These questions can help you know your competition.
- What makes your competition successful?
- What are their weaknesses?
- What are customers saying about your competition?
3. Consider Your Brand
Customers' perception of your brand has a strong impact on your sales. Your marketing and sales plan should seek to bolster the image of your brand. Before you start marketing your business, think about the message you want to pass across about your business and your products and services.
4. Focus on Benefits
The majority of your customers do not view your product in terms of features, what they want to know is the benefits and solutions your product offers. Think about the problems your product solves and the benefits it delivers, and use it to create the right sales and marketing message.
Your marketing plan should focus on what you want your customer to get instead of what you provide. Identify those benefits in your marketing and sales plan.
5. Focus on Differentiation
Your marketing and sales plan should look for a unique angle they can take that differentiates your business from the competition, even if the products offered are similar. Some good areas of differentiation you can use are your benefits, pricing, and features.
Key Questions to Answer When Writing Your Marketing and Sales Plan
- What is your company’s budget for sales and marketing campaigns?
- What key metrics will you use to determine if your marketing plans are successful?
- What are your alternatives if your initial marketing efforts do not succeed?
- Who are the sales representatives you need to promote your products or services?
- What are the marketing and sales channels you plan to use? How do you plan to get your products in front of your ideal customers?
- Where will you sell your products?
You may want to include samples of marketing materials you plan to use such as print ads, website descriptions, and social media ads. While it is not compulsory to include these samples, it can help you better communicate your marketing and sales plan and objectives.
The purpose of the marketing and sales section is to answer this question “How will you reach your customers?” If you cannot convincingly provide an answer to this question, you need to rework your marketing and sales section.
7. Clearly Show Your Funding Request
If you are writing your business plan to ask for funding from investors or financial institutions, the funding request section is where you will outline your funding requirements. The funding request section should answer the question ‘How much money will your business need in the near future (3 to 5 years)?’
A good funding request section will clearly outline and explain the amount of funding your business needs over the next five years. You need to know the amount of money your business needs to make an accurate funding request.
Also, when writing your funding request, provide details of how the funds will be used over the period. Specify if you want to use the funds to buy raw materials or machinery, pay salaries, pay for advertisements, and cover specific bills such as rent and electricity.
In addition to explaining what you want to use the funds requested for, you need to clearly state the projected return on investment (ROI) . Investors and creditors want to know if your business can generate profit for them if they put funds into it.
Ensure you do not inflate the figures and stay as realistic as possible. Investors and financial institutions you are seeking funds from will do their research before investing money in your business.
If you are not sure of an exact number to request from, you can use some range of numbers as rough estimates. Add a best-case scenario and a work-case scenario to your funding request. Also, include a description of your strategic future financial plans such as selling your business or paying off debts.
Funding Request: Debt or Equity?
When making your funding request, specify the type of funding you want. Do you want debt or equity? Draw out the terms that will be applicable for the funding, and the length of time the funding request will cover.
Case for Equity
If your new business has not yet started generating profits, you are most likely preparing to sell equity in your business to raise capital at the early stage. Equity here refers to ownership. In this case, you are selling a portion of your company to raise capital.
Although this method of raising capital for your business does not put your business in debt, keep in mind that an equity owner may expect to play a key role in company decisions even if he does not hold a major stake in the company.
Most equity sales for startups are usually private transactions . If you are making a funding request by offering equity in exchange for funding, let the investor know that they will be paid a dividend (a share of the company’s profit). Also, let the investor know the process for selling their equity in your business.
Case for Debt
You may decide not to offer equity in exchange for funds, instead, you make a funding request with the promise to pay back the money borrowed at the agreed time frame.
When making a funding request with an agreement to pay back, note that you will have to repay your creditors both the principal amount borrowed and the interest on it. Financial institutions offer this type of funding for businesses.
Large companies combine both equity and debt in their capital structure. When drafting your business plan, decide if you want to offer both or one over the other.
Before you sell equity in exchange for funding in your business, consider if you are willing to accept not being in total control of your business. Also, before you seek loans in your funding request section, ensure that the terms of repayment are favorable.
You should set a clear timeline in your funding request so that potential investors and creditors can know what you are expecting. Some investors and creditors may agree to your funding request and then delay payment for longer than 30 days, meanwhile, your business needs an immediate cash injection to operate efficiently.
Additional Tips for Writing the Funding Request Section of your Business Plan
The funding request section is not necessary for every business, it is only needed by businesses who plan to use their business plan to secure funding.
If you are adding the funding request section to your business plan, provide an itemized summary of how you plan to use the funds requested. Hiring a lawyer, accountant, or other professionals may be necessary for the proper development of this section.
You should also gather and use financial statements that add credibility and support to your funding requests. Ensure that the financial statements you use should include your projected financial data such as projected cash flows, forecast statements, and expenditure budgets.
If you are an existing business, include all historical financial statements such as cash flow statements, balance sheets and income statements .
Provide monthly and quarterly financial statements for a year. If your business has records that date back beyond the one-year mark, add the yearly statements of those years. These documents are for the appendix section of your business plan.
8. Detail Your Financial Plan, Metrics, and Projections
If you used the funding request section in your business plan, supplement it with a financial plan, metrics, and projections. This section paints a picture of the past performance of your business and then goes ahead to make an informed projection about its future.
The goal of this section is to convince readers that your business is going to be a financial success. It outlines your business plan to generate enough profit to repay the loan (with interest if applicable) and to generate a decent return on investment for investors.
If you have an existing business already in operation, use this section to demonstrate stability through finance. This section should include your cash flow statements, balance sheets, and income statements covering the last three to five years. If your business has some acceptable collateral that you can use to acquire loans, list it in the financial plan, metrics, and projection section.
Apart from current financial statements, this section should also contain a prospective financial outlook that spans the next five years. Include forecasted income statements, cash flow statements, balance sheets, and capital expenditure budget.
If your business is new and is not yet generating profit, use clear and realistic projections to show the potentials of your business.
When drafting this section, research industry norms and the performance of comparable businesses. Your financial projections should cover at least five years. State the logic behind your financial projections. Remember you can always make adjustments to this section as the variables change.
The financial plan, metrics, and projection section create a baseline which your business can either exceed or fail to reach. If your business fails to reach your projections in this section, you need to understand why it failed.
Investors and loan managers spend a lot of time going through the financial plan, metrics, and projection section compared to other parts of the business plan. Ensure you spend time creating credible financial analyses for your business in this section.
Many entrepreneurs find this section daunting to write. You do not need a business degree to create a solid financial forecast for your business. Business finances, especially for startups, are not as complicated as they seem. There are several online tools and templates that make writing this section so much easier.
Use Graphs and Charts
The financial plan, metrics, and projection section is a great place to use graphs and charts to tell the financial story of your business. Charts and images make it easier to communicate your finances.
Accuracy in this section is key, ensure you carefully analyze your past financial statements properly before making financial projects.
Address the Risk Factors and Show Realistic Financial Projections
Keep your financial plan, metrics, and projection realistic. It is okay to be optimistic in your financial projection, however, you have to justify it.
You should also address the various risk factors associated with your business in this section. Investors want to know the potential risks involved, show them. You should also show your plans for mitigating those risks.
What You Should In The Financial Plan, Metrics, and Projection Section of Your Business Plan
The financial plan, metrics, and projection section of your business plan should have monthly sales and revenue forecasts for the first year. It should also include annual projections that cover 3 to 5 years.
A three-year projection is a basic requirement to have in your business plan. However, some investors may request a five-year forecast.
Your business plan should include the following financial statements: sales forecast, personnel plan, income statement, income statement, cash flow statement, balance sheet, and an exit strategy.
1. Sales Forecast
Sales forecast refers to your projections about the number of sales your business is going to record over the next few years. It is typically broken into several rows, with each row assigned to a core product or service that your business is offering.
One common mistake people make in their business plan is to break down the sales forecast section into long details. A sales forecast should forecast the high-level details.
For example, if you are forecasting sales for a payroll software provider, you could break down your forecast into target market segments or subscription categories.

Your sales forecast section should also have a corresponding row for each sales row to cover the direct cost or Cost of Goods Sold (COGS). The objective of these rows is to show the expenses that your business incurs in making and delivering your product or service.
Note that your Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) should only cover those direct costs incurred when making your products. Other indirect expenses such as insurance, salaries, payroll tax, and rent should not be included.
For example, the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) for a restaurant is the cost of ingredients while for a consulting company it will be the cost of paper and other presentation materials.

2. Personnel Plan
The personnel plan section is where you provide details about the payment plan for your employees. For a small business, you can easily list every position in your company and how much you plan to pay in the personnel plan.
However, for larger businesses, you have to break the personnel plan into functional groups such as sales and marketing.
The personnel plan will also include the cost of an employee beyond salary, commonly referred to as the employee burden. These costs include insurance, payroll taxes , and other essential costs incurred monthly as a result of having employees on your payroll.

3. Income Statement
The income statement section shows if your business is making a profit or taking a loss. Another name for the income statement is the profit and loss (P&L). It takes data from your sales forecast and personnel plan and adds other ongoing expenses you incur while running your business.

Every business plan should have an income statement. It subtracts your business expenses from its earnings to show if your business is generating profit or incurring losses.
The income statement has the following items: sales, Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), gross margin, operating expenses, total operating expenses, operating income , total expenses, and net profit.
- Sales refer to the revenue your business generates from selling its products or services. Other names for sales are income or revenue.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) refers to the total cost of selling your products. Other names for COGS are direct costs or cost of sales. Manufacturing businesses use the Costs of Goods Manufactured (COGM) .
- Gross Margin is the figure you get when you subtract your COGS from your sales. In your income statement, you can express it as a percentage of total sales (Gross margin / Sales = Gross Margin Percent).
- Operating Expenses refer to all the expenses you incur from running your business. It exempts the COGS because it stands alone as a core part of your income statement. You also have to exclude taxes, depreciation, and amortization. Your operating expenses include salaries, marketing expenses, research and development (R&D) expenses, and other expenses.
- Total Operating Expenses refers to the sum of all your operating expenses including those exemptions named above under operating expenses.
- Operating Income refers to earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. It is simply known as the acronym EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization). Calculating your operating income is simple, all you need to do is to subtract your COGS and total operating expenses from your sales.
- Total Expenses refer to the sum of your operating expenses and your business’ interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization.
- Net profit shows whether your business has made a profit or taken a loss during a given timeframe.
4. Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement tracks the money you have in the bank at any given point. It is often confused with the income statement or the profit and loss statement. They are both different types of financial statements. The income statement calculates your profits and losses while the cash flow statement shows you how much you have in the bank.

5. Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is a financial statement that provides an overview of the financial health of your business. It contains information about the assets and liabilities of your company, and owner’s or shareholders’ equity.
You can get the net worth of your company by subtracting your company’s liabilities from its assets.

6. Exit Strategy
The exit strategy refers to a probable plan for selling your business either to the public in an IPO or to another company. It is the last thing you include in the financial plan, metrics, and projection section.
You can choose to omit the exit strategy from your business plan if you plan to maintain full ownership of your business and do not plan on seeking angel investment or virtual capitalist (VC) funding.
Investors may want to know what your exit plan is. They invest in your business to get a good return on investment.
Your exit strategy does not have to include long and boring details. Ensure you identify some interested parties who may be interested in buying the company if it becomes a success.

Key Questions to Answer with Your Financial Plan, Metrics, and Projection
Your financial plan, metrics, and projection section helps investors, creditors, or your internal managers to understand what your expenses are, the amount of cash you need, and what it takes to make your company profitable. It also shows what you will be doing with any funding.
You do not need to show actual financial data if you do not have one. Adding forecasts and projections to your financial statements is added proof that your strategy is feasible and shows investors you have planned properly.
Here are some key questions to answer to help you develop this section.
- What is your sales forecast for the next year?
- When will your company achieve a positive cash flow?
- What are the core expenses you need to operate?
- How much money do you need upfront to operate or grow your company?
- How will you use the loans or investments?
9. Add an Appendix to Your Business Plan
Adding an appendix to your business plan is optional. It is a useful place to put any charts, tables, legal notes, definitions, permits, résumés, and other critical information that do not fit into other sections of your business plan.
The appendix section is where you would want to include details of a patent or patent-pending if you have one. You can always add illustrations or images of your products here. It is the last section of your business plan.
When writing your business plan, there are details you cut short or remove to prevent the entire section from becoming too lengthy. There are also details you want to include in the business plan but are not a good fit for any of the previous sections. You can add that additional information to the appendix section.
Businesses also use the appendix section to include supporting documents or other materials specially requested by investors or lenders.
You can include just about any information that supports the assumptions and statements you made in the business plan under the appendix. It is the one place in the business plan where unrelated data and information can coexist amicably.
If your appendix section is lengthy, try organizing it by adding a table of contents at the beginning of the appendix section. It is also advisable to group similar information to make it easier for the reader to access them.
A well-organized appendix section makes it easier to share your information clearly and concisely. Add footnotes throughout the rest of the business plan or make references in the plan to the documents in the appendix.
The appendix section is usually only necessary if you are seeking funding from investors or lenders, or hoping to attract partners.
People reading business plans do not want to spend time going through a heap of backup information, numbers, and charts. Keep these documents or information in the Appendix section in case the reader wants to dig deeper.
Common Items to Include in the Appendix Section of Your Business Plan
The appendix section includes documents that supplement or support the information or claims given in other sections of the business plans. Common items you can include in the appendix section include:
- Additional data about the process of manufacturing or creation
- Additional description of products or services such as product schematics
- Additional financial documents or projections
- Articles of incorporation and status
- Backup for market research or competitive analysis
- Bank statements
- Business registries
- Client testimonials (if your business is already running)
- Copies of insurances
- Credit histories (personal or/and business)
- Deeds and permits
- Equipment leases
- Examples of marketing and advertising collateral
- Industry associations and memberships
- Images of product
- Intellectual property
- Key customer contracts
- Legal documents and other contracts
- Letters of reference
- Links to references
- Market research data
- Organizational charts
- Photographs of potential facilities
- Professional licenses pertaining to your legal structure or type of business
- Purchase orders
- Resumes of the founder(s) and key managers
- State and federal identification numbers or codes
- Trademarks or patents’ registrations
Avoid using the appendix section as a place to dump any document or information you feel like adding. Only add documents or information that you support or increase the credibility of your business plan.

Tips and Strategies for Writing a Convincing Business Plan
To achieve a perfect business plan, you need to consider some key tips and strategies. These tips will raise the efficiency of your business plan above average.
1. Know Your Audience
When writing a business plan, you need to know your audience . Business owners write business plans for different reasons. Your business plan has to be specific. For example, you can write business plans to potential investors, banks, and even fellow board members of the company.
The audience you are writing to determines the structure of the business plan. As a business owner, you have to know your audience. Not everyone will be your audience. Knowing your audience will help you to narrow the scope of your business plan.
Consider what your audience wants to see in your projects, the likely questions they might ask, and what interests them.
- A business plan used to address a company's board members will center on its employment schemes, internal affairs, projects, stakeholders, etc.
- A business plan for financial institutions will talk about the size of your market and the chances for you to pay back any loans you demand.
- A business plan for investors will show proof that you can return the investment capital within a specific time. In addition, it discusses your financial projections, tractions, and market size.
2. Get Inspiration from People
Writing a business plan from scratch as an entrepreneur can be daunting. That is why you need the right inspiration to push you to write one. You can gain inspiration from the successful business plans of other businesses. Look at their business plans, the style they use, the structure of the project, etc.
To make your business plan easier to create, search companies related to your business to get an exact copy of what you need to create an effective business plan. You can also make references while citing examples in your business plans.
When drafting your business plan, get as much help from others as you possibly can. By getting inspiration from people, you can create something better than what they have.
3. Avoid Being Over Optimistic
Many business owners make use of strong adjectives to qualify their content. One of the big mistakes entrepreneurs make when preparing a business plan is promising too much.
The use of superlatives and over-optimistic claims can prepare the audience for more than you can offer. In the end, you disappoint the confidence they have in you.
In most cases, the best option is to be realistic with your claims and statistics. Most of the investors can sense a bit of incompetency from the overuse of superlatives. As a new entrepreneur, do not be tempted to over-promise to get the interests of investors.
The concept of entrepreneurship centers on risks, nothing is certain when you make future analyses. What separates the best is the ability to do careful research and work towards achieving that, not promising more than you can achieve.
To make an excellent first impression as an entrepreneur, replace superlatives with compelling data-driven content. In this way, you are more specific than someone promising a huge ROI from an investment.
4. Keep it Simple and Short
When writing business plans, ensure you keep them simple throughout. Irrespective of the purpose of the business plan, your goal is to convince the audience.
One way to achieve this goal is to make them understand your proposal. Therefore, it would be best if you avoid the use of complex grammar to express yourself. It would be a huge turn-off if the people you want to convince are not familiar with your use of words.
Another thing to note is the length of your business plan. It would be best if you made it as brief as possible.
You hardly see investors or agencies that read through an extremely long document. In that case, if your first few pages can’t convince them, then you have lost it. The more pages you write, the higher the chances of you derailing from the essential contents.
To ensure your business plan has a high conversion rate, you need to dispose of every unnecessary information. For example, if you have a strategy that you are not sure of, it would be best to leave it out of the plan.
5. Make an Outline and Follow Through
A perfect business plan must have touched every part needed to convince the audience. Business owners get easily tempted to concentrate more on their products than on other sections. Doing this can be detrimental to the efficiency of the business plan.
For example, imagine you talking about a product but omitting or providing very little information about the target audience. You will leave your clients confused.
To ensure that your business plan communicates your full business model to readers, you have to input all the necessary information in it. One of the best ways to achieve this is to design a structure and stick to it.
This structure is what guides you throughout the writing. To make your work easier, you can assign an estimated word count or page limit to every section to avoid making it too bulky for easy reading. As a guide, the necessary things your business plan must contain are:
- Table of contents
- Introduction
- Product or service description
- Target audience
- Market size
- Competition analysis
- Financial projections
Some specific businesses can include some other essential sections, but these are the key sections that must be in every business plan.
6. Ask a Professional to Proofread
When writing a business plan, you must tie all loose ends to get a perfect result. When you are done with writing, call a professional to go through the document for you. You are bound to make mistakes, and the way to correct them is to get external help.
You should get a professional in your field who can relate to every section of your business plan. It would be easier for the professional to notice the inner flaws in the document than an editor with no knowledge of your business.
In addition to getting a professional to proofread, get an editor to proofread and edit your document. The editor will help you identify grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and inappropriate writing styles.
Writing a business plan can be daunting, but you can surmount that obstacle and get the best out of it with these tips.
Business Plan Examples and Templates That’ll Save You Tons of Time
1. hubspot's one-page business plan.

The one-page business plan template by HubSpot is the perfect guide for businesses of any size, irrespective of their business strategy. Although the template is condensed into a page, your final business plan should not be a page long! The template is designed to ask helpful questions that can help you develop your business plan.
Hubspot’s one-page business plan template is divided into nine fields:
- Business opportunity
- Company description
- Industry analysis
- Target market
- Implementation timeline
- Marketing plan
- Financial summary
- Funding required
2. Bplan’s Free Business Plan Template

Bplans' free business plan template is investor-approved. It is a rich template used by prestigious educational institutions such as Babson College and Princeton University to teach entrepreneurs how to create a business plan.
The template has six sections: the executive summary, opportunity, execution, company, financial plan, and appendix. There is a step-by-step guide for writing every little detail in the business plan. Follow the instructions each step of the way and you will create a business plan that impresses investors or lenders easily.
3. HubSpot's Downloadable Business Plan Template

HubSpot’s downloadable business plan template is a more comprehensive option compared to the one-page business template by HubSpot. This free and downloadable business plan template is designed for entrepreneurs.
The template is a comprehensive guide and checklist for business owners just starting their businesses. It tells you everything you need to fill in each section of the business plan and how to do it.
There are nine sections in this business plan template: an executive summary, company and business description, product and services line, market analysis, marketing plan, sales plan, legal notes, financial considerations, and appendix.
4. Business Plan by My Own Business Institute

My Own Business Institute (MOBI) which is a part of Santa Clara University's Center for Innovation and Entrepreneurship offers a free business plan template. You can either copy the free business template from the link provided above or download it as a Word document.
The comprehensive template consists of a whopping 15 sections.
- The Business Profile
- The Vision and the People
- Home-Based Business and Freelance Business Opportunities
- Organization
- Licenses and Permits
- Business Insurance
- Communication Tools
- Acquisitions
- Location and Leasing
- Accounting and Cash Flow
- Opening and Marketing
- Managing Employees
- Expanding and Handling Problems
There are lots of helpful tips on how to fill each section in the free business plan template by MOBI.
5. Score's Business Plan Template for Startups

Score is an American nonprofit organization that helps entrepreneurs build successful companies. This business plan template for startups by Score is available for free download. The business plan template asks a whooping 150 generic questions that help entrepreneurs from different fields to set up the perfect business plan.
The business plan template for startups contains clear instructions and worksheets, all you have to do is answer the questions and fill the worksheets.
There are nine sections in the business plan template: executive summary, company description, products and services, marketing plan, operational plan, management and organization, startup expenses and capitalization, financial plan, and appendices.
The ‘refining the plan’ resource contains instructions that help you modify your business plan to suit your specific needs, industry, and target audience. After you have completed Score’s business plan template, you can work with a SCORE mentor for expert advice in business planning.
6. Minimalist Architecture Business Plan Template by Venngage

The minimalist architecture business plan template is a simple template by Venngage that you can customize to suit your business needs .
There are five sections in the template: an executive summary, statement of problem, approach and methodology, qualifications, and schedule and benchmark. The business plan template has instructions that guide users on what to fill in each section.
7. Small Business Administration Free Business Plan Template

The Small Business Administration (SBA) offers two free business plan templates, filled with practical real-life examples that you can model to create your business plan. Both free business plan templates are written by fictional business owners: Rebecca who owns a consulting firm, and Andrew who owns a toy company.
There are five sections in the two SBA’s free business plan templates.
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Service Line
- Marketing and Sales
8. The $100 Startup's One-Page Business Plan

The one-page business plan by the $100 startup is a simple business plan template for entrepreneurs who do not want to create a long and complicated plan . You can include more details in the appendices for funders who want more information beyond what you can put in the one-page business plan.
There are five sections in the one-page business plan such as overview, ka-ching, hustling, success, and obstacles or challenges or open questions. You can answer all the questions using one or two sentences.
9. PandaDoc’s Free Business Plan Template

The free business plan template by PandaDoc is a comprehensive 15-page document that describes the information you should include in every section.
There are 11 sections in PandaDoc’s free business plan template.
- Executive summary
- Business description
- Products and services
- Operations plan
- Management organization
- Financial plan
- Conclusion / Call to action
- Confidentiality statement
You have to sign up for its 14-day free trial to access the template. You will find different business plan templates on PandaDoc once you sign up (including templates for general businesses and specific businesses such as bakeries, startups, restaurants, salons, hotels, and coffee shops)
PandaDoc allows you to customize its business plan templates to fit the needs of your business. After editing the template, you can send it to interested parties and track opens and views through PandaDoc.
10. Invoiceberry Templates for Word, Open Office, Excel, or PPT

InvoiceBerry is a U.K based online invoicing and tracking platform that offers free business plan templates in .docx, .odt, .xlsx, and .pptx formats for freelancers and small businesses.
Before you can download the free business plan template, it will ask you to give it your email address. After you complete the little task, it will send the download link to your inbox for you to download. It also provides a business plan checklist in .xlsx file format that ensures you add the right information to the business plan.
Alternatives to the Traditional Business Plan
A business plan is very important in mapping out how one expects their business to grow over a set number of years, particularly when they need external investment in their business. However, many investors do not have the time to watch you present your business plan. It is a long and boring read.
Luckily, there are three alternatives to the traditional business plan (the Business Model Canvas, Lean Canvas, and Startup Pitch Deck). These alternatives are less laborious and easier and quicker to present to investors.
Business Model Canvas (BMC)
The business model canvas is a business tool used to present all the important components of setting up a business, such as customers, route to market, value proposition, and finance in a single sheet. It provides a very focused blueprint that defines your business initially which you can later expand on if needed.

The sheet is divided mainly into company, industry, and consumer models that are interconnected in how they find problems and proffer solutions.
Segments of the Business Model Canvas
The business model canvas was developed by founder Alexander Osterwalder to answer important business questions. It contains nine segments.

- Key Partners: Who will be occupying important executive positions in your business? What do they bring to the table? Will there be a third party involved with the company?
- Key Activities: What important activities will production entail? What activities will be carried out to ensure the smooth running of the company?
- The Product’s Value Propositions: What does your product do? How will it be different from other products?
- Customer Segments: What demography of consumers are you targeting? What are the habits of these consumers? Who are the MVPs of your target consumers?
- Customer Relationships: How will the team support and work with its customer base? How do you intend to build and maintain trust with the customer?
- Key Resources: What type of personnel and tools will be needed? What size of the budget will they need access to?
- Channels: How do you plan to create awareness of your products? How do you intend to transport your product to the customer?
- Cost Structure: What is the estimated cost of production? How much will distribution cost?
- Revenue Streams: For what value are customers willing to pay? How do they prefer to pay for the product? Are there any external revenues attached apart from the main source? How do the revenue streams contribute to the overall revenue?
Lean Canvas
The lean canvas is a problem-oriented alternative to the standard business model canvas. It was proposed by Ash Maurya, creator of Lean Stack as a development of the business model generation. It uses a more problem-focused approach and it majorly targets entrepreneurs and startup businesses.

Lean Canvas uses the same 9 blocks concept as the business model canvas, however, they have been modified slightly to suit the needs and purpose of a small startup. The key partners, key activities, customer relationships, and key resources are replaced by new segments which are:
- Problem: Simple and straightforward number of problems you have identified, ideally three.
- Solution: The solutions to each problem.
- Unfair Advantage: Something you possess that can't be easily bought or replicated.
- Key Metrics: Important numbers that will tell how your business is doing.
Startup Pitch Deck
While the business model canvas compresses into a factual sheet, startup pitch decks expand flamboyantly.
Pitch decks, through slides, convey your business plan, often through graphs and images used to emphasize estimations and observations in your presentation. Entrepreneurs often use pitch decks to fully convince their target audience of their plans before discussing funding arrangements.

Considering the likelihood of it being used in a small time frame, a good startup pitch deck should ideally contain 20 slides or less to have enough time to answer questions from the audience.
Unlike the standard and lean business model canvases, a pitch deck doesn't have a set template on how to present your business plan but there are still important components to it. These components often mirror those of the business model canvas except that they are in slide form and contain more details.

Using Airbnb (one of the most successful start-ups in recent history) for reference, the important components of a good slide are listed below.
- Cover/Introduction Slide: Here, you should include your company's name and mission statement. Your mission statement should be a very catchy tagline. Also, include personal information and contact details to provide an easy link for potential investors.
- Problem Slide: This slide requires you to create a connection with the audience or the investor that you are pitching. For example in their pitch, Airbnb summarized the most important problems it would solve in three brief points – pricing of hotels, disconnection from city culture, and connection problems for local bookings.
- Solution Slide: This slide includes your core value proposition. List simple and direct solutions to the problems you have mentioned
- Customer Analysis: Here you will provide information on the customers you will be offering your service to. The identity of your customers plays an important part in fundraising as well as the long-run viability of the business.
- Market Validation: Use competitive analysis to show numbers that prove the presence of a market for your product, industry behavior in the present and the long run, as well as the percentage of the market you aim to attract. It shows that you understand your competitors and customers and convinces investors of the opportunities presented in the market.
- Business Model: Your business model is the hook of your presentation. It may vary in complexity but it should generally include a pricing system informed by your market analysis. The goal of the slide is to confirm your business model is easy to implement.
- Marketing Strategy: This slide should summarize a few customer acquisition methods that you plan to use to grow the business.
- Competitive Advantage: What this slide will do is provide information on what will set you apart and make you a more attractive option to customers. It could be the possession of technology that is not widely known in the market.
- Team Slide: Here you will give a brief description of your team. Include your key management personnel here and their specific roles in the company. Include their educational background, job history, and skillsets. Also, talk about their accomplishments in their careers so far to build investors' confidence in members of your team.
- Traction Slide: This validates the company’s business model by showing growth through early sales and support. The slide aims to reduce any lingering fears in potential investors by showing realistic periodic milestones and profit margins. It can include current sales, growth, valuable customers, pre-orders, or data from surveys outlining current consumer interest.
- Funding Slide: This slide is popularly referred to as ‘the ask'. Here you will include important details like how much is needed to get your business off the ground and how the funding will be spent to help the company reach its goals.
- Appendix Slides: Your pitch deck appendix should always be included alongside a standard pitch presentation. It consists of additional slides you could not show in the pitch deck but you need to complement your presentation.
It is important to support your calculations with pictorial renditions. Infographics, such as pie charts or bar graphs, will be more effective in presenting the information than just listing numbers. For example, a six-month graph that shows rising profit margins will easily look more impressive than merely writing it.
Lastly, since a pitch deck is primarily used to secure meetings and you may be sharing your pitch with several investors, it is advisable to keep a separate public version that doesn't include financials. Only disclose the one with projections once you have secured a link with an investor.
Advantages of the Business Model Canvas, Lean Canvas, and Startup Pitch Deck over the Traditional Business Plan
- Time-Saving: Writing a detailed traditional business plan could take weeks or months. On the other hand, all three alternatives can be done in a few days or even one night of brainstorming if you have a comprehensive understanding of your business.
- Easier to Understand: Since the information presented is almost entirely factual, it puts focus on what is most important in running the business. They cut away the excess pages of fillers in a traditional business plan and allow investors to see what is driving the business and what is getting in the way.
- Easy to Update: Businesses typically present their business plans to many potential investors before they secure funding. What this means is that you may regularly have to amend your presentation to update statistics or adjust to audience-specific needs. For a traditional business plan, this could mean rewriting a whole section of your plan. For the three alternatives, updating is much easier because they are not voluminous.
- Guide for a More In-depth Business Plan: All three alternatives have the added benefit of being able to double as a sketch of your business plan if the need to create one arises in the future.
Business Plan FAQ
Business plans are important for any entrepreneur who is looking for a framework to run their company over some time or seeking external support. Although they are essential for new businesses, every company should ideally have a business plan to track their growth from time to time. They can be used by startups seeking investments or loans to convey their business ideas or an employee to convince his boss of the feasibility of starting a new project. They can also be used by companies seeking to recruit high-profile employee targets into key positions or trying to secure partnerships with other firms.
Business plans often vary depending on your target audience, the scope, and the goals for the plan. Startup plans are the most common among the different types of business plans. A start-up plan is used by a new business to present all the necessary information to help get the business up and running. They are usually used by entrepreneurs who are seeking funding from investors or bank loans. The established company alternative to a start-up plan is a feasibility plan. A feasibility plan is often used by an established company looking for new business opportunities. They are used to show the upsides of creating a new product for a consumer base. Because the audience is usually company people, it requires less company analysis. The third type of business plan is the lean business plan. A lean business plan is a brief, straight-to-the-point breakdown of your ideas and analysis for your business. It does not contain details of your proposal and can be written on one page. Finally, you have the what-if plan. As it implies, a what-if plan is a preparation for the worst-case scenario. You must always be prepared for the possibility of your original plan being rejected. A good what-if plan will serve as a good plan B to the original.
A good business plan has 10 key components. They include an executive plan, product analysis, desired customer base, company analysis, industry analysis, marketing strategy, sales strategy, financial projection, funding, and appendix. Executive Plan Your business should begin with your executive plan. An executive plan will provide early insight into what you are planning to achieve with your business. It should include your mission statement and highlight some of the important points which you will explain later. Product Analysis The next component of your business plan is your product analysis. A key part of this section is explaining the type of item or service you are going to offer as well as the market problems your product will solve. Desired Consumer Base Your product analysis should be supplemented with a detailed breakdown of your desired consumer base. Investors are always interested in knowing the economic power of your market as well as potential MVP customers. Company Analysis The next component of your business plan is your company analysis. Here, you explain how you want to run your business. It will include your operational strategy, an insight into the workforce needed to keep the company running, and important executive positions. It will also provide a calculation of expected operational costs. Industry Analysis A good business plan should also contain well laid out industry analysis. It is important to convince potential investors you know the companies you will be competing with, as well as your plans to gain an edge on the competition. Marketing Strategy Your business plan should also include your marketing strategy. This is how you intend to spread awareness of your product. It should include a detailed explanation of the company brand as well as your advertising methods. Sales Strategy Your sales strategy comes after the market strategy. Here you give an overview of your company's pricing strategy and how you aim to maximize profits. You can also explain how your prices will adapt to market behaviors. Financial Projection The financial projection is the next component of your business plan. It explains your company's expected running cost and revenue earned during the tenure of the business plan. Financial projection gives a clear idea of how your company will develop in the future. Funding The next component of your business plan is funding. You have to detail how much external investment you need to get your business idea off the ground here. Appendix The last component of your plan is the appendix. This is where you put licenses, graphs, or key information that does not fit in any of the other components.
The business model canvas is a business management tool used to quickly define your business idea and model. It is often used when investors need you to pitch your business idea during a brief window.
A pitch deck is similar to a business model canvas except that it makes use of slides in its presentation. A pitch is not primarily used to secure funding, rather its main purpose is to entice potential investors by selling a very optimistic outlook on the business.
Business plan competitions help you evaluate the strength of your business plan. By participating in business plan competitions, you are improving your experience. The experience provides you with a degree of validation while practicing important skills. The main motivation for entering into the competitions is often to secure funding by finishing in podium positions. There is also the chance that you may catch the eye of a casual observer outside of the competition. These competitions also provide good networking opportunities. You could meet mentors who will take a keen interest in guiding you in your business journey. You also have the opportunity to meet other entrepreneurs whose ideas can complement yours.
Exlore Further
- 12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
- 13 Sources of Business Finance For Companies & Sole Traders
- 5 Common Types of Business Structures (+ Pros & Cons)
- How to Buy a Business in 8 Steps (+ Due Diligence Checklist)
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.

Free Download
Business Plan Template for Small Businesses
Business planning can feel complicated. it doesn't have to be. start putting pen to paper today with your free business plan template download..
Available formats:
Downloads: 938,938
Our free template includes:
- Fill-in-the-blanks simplicity
You don't need to be an expert. This template makes business planning easy.
All 100% free. We're here to help you succeed in business, no strings attached.
Why you need a business plan
Writing a business plan can seem like a big task, especially if you’re starting a business for the first time and don’t have a financial background. After all, business plans have changed over the years, and what lenders and investors expect now is different than it was even just 10 years ago.
What hasn’t changed is that writing a business plan will help you:
- Develop a strategy for success
- Reduce the risk of starting a business
- Explore new business ideas
- Attract investors and get funding
Learn more about how you can get value out of your business plan .
What is included in this business plan template?
This template includes definitions, guidance, and examples for every business plan component needed to start, fund, and grow your business.
After downloading the full template, you’ll receive instructions on how to fill out each of the following sections.
Executive summary
The brief summary of your business plan introduces everyone to your business, the problem you solve, and what you’re asking from your readers. It’s the first chapter of your business plan and the last thing you write once you have the details from your full plan.
Problem & solution
More than a simple description of your products and services – here you define the problem you’re solving and the value you provide. It’s also your chance to showcase any initial traction that shows you’re on the right track.
Market analysis and target market
A detailed assessment of the market you intend to enter, including the size and value of the market, potential customer segments, and their buying patterns.
Competition
Show that you know who your competitors are, what advantages you have, and how you’re positioning your business to be competitive.
Marketing & sales
Describe how you’ll reach and sell to potential customers with a detailed sales plan and chosen marketing channels.
What makes your business run? Outline the day-to-day workflows and what needs to be set up for your business to deliver a product or service.
Milestones & metrics
Set goals for your business that include the dates and people responsible for accomplishing them. This is what you’ll use to manage responsibilities, track growth, and execute your larger strategy.
Company overview and team
Provide a brief rundown of the legal and structural components of your company, including your history, current team, and gaps you need to fill.
Financial plan
Create well-structured and accurate financial statements to help you pitch to investors, land funding, and achieve long-term success. All without the help of a financial advisor or a degree in accounting.
While not required, this last section of your business plan is a great place to drop in additional documents that support and strengthen the rest of your plan.
How do you write a simple business plan?
If you’re exploring a business idea and don’t plan to pursue funding, then you actually don’t need to write a traditional business plan. Instead, opt for a one-page plan , which is far easier to create but just as effective.
To write a simple one-page business plan, follow the same core sections as a traditional plan. But instead of lengthy paragraphs and multiple pages covering each area of your business, stick with single sentences and bulleted lists.
If a one-page plan sounds like a better option, download our free simple business plan template to get started.
Start your business plan today
Whether you're writing a business plan to validate your business idea, secure funding, or grow your existing business – our template will help you achieve your goals.

Business plan template FAQ
What file formats are available for this business plan template?
You can download and use this business plan template as a Google Doc, .docx (Microsoft Word), or PDF.
Can you print out this template?
This is a printable business plan template that can be downloaded and printed no matter which format you choose.
Why should you start with a business plan template?
Starting with a good business plan template (like this one) includes everything you need to get started. It helps you organize your thoughts, and provides guidance, instructions, and examples to create an investor-ready and SBA-approved business plan format. It really speeds up the planning process. Oh, and it's 100% free!
Is writing a business plan easy?
Using a business plan template can make writing a business plan easier. Additionally, if you focus on just getting your information down quickly, with the expectation that you'll revisit and revise your plan, you can speed up and simplify the process .
Can someone write your business plan for you?
If you're still struggling to write your business plan even when using a template, you can look into hiring a professional business plan writer. We even have a free resource to help you ask just the right questions to make sure you find the right plan writer.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
Related Resources

Work With a Professional Plan Writer
Download your template now
Need to validate your idea, secure funding, or grow your business this template is for you..
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
Your business plan template is ready
Find a download link in your email too.
Edit in Google Docs
Download as Docx
Download as PDF

Finish your business plan faster
Get an exclusive 14 day free trial to the world's #1 business planning software.

From template to plan in 30 minutes
- Step-by-step guidance
- Crystal clear financials
- Expert advice at your fingertips
- Funding & lender ready formats
- PLUS all the tools to manage & grow

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

- Customer Reviews
- Net 30 Account
- Wise Services
- Steps & Timeline
- Work at a Glance
- Market Research at a Glance
- Business Plan Writing Services
- Bank Business Plan
- Investor Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Cannabis Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Corporate Business Plan
- Merge and Acquisition Business Plan (M&A)
- Private Placement Memorandums (PPM)
- Sample Business Plans
- Professional Feasibility Study
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Pitch Deck Presentation Services
- Business Plan Printing
- Market Research
- L-1 Business Plan
- E-2 Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- EB-5 Regional Centers
- Immigration Attorneys
- Nonprofit Business Plan
- Exit Business Planning
- Business Planning
- Business Formation
- Business License
- Business Website
- Business Branding
- Business Bank Account
- Digital Marketing
- Business Funding Resources
- Small Business Loans
- Venture Capital
- Net 30 Apply

14 Professional Business Plan Samples [Downloadable pdf]
Looking for business plan examples for inspiration? Download or view 14 business plans examples/samples, vetted by our MBA business plan writers. Download in PDF format or read like a book. These real business plan samples would help in writing your own business plan.

- View Real Business Plan Examples/Samples

As an entrepreneur, effectively pitching your idea to attract investors and secure funding can be a challenge. Moreover, when launching a business, creating a comprehensive business plan is paramount.
To aid you in these crucial tasks, we offer a collection of real-world and sample business plan examples across diverse industries. A well-structured business plan is indispensable in the fast-paced entrepreneurial landscape, as it delineates your goals, strategies, and financial projections, providing a clear roadmap for your venture.
Our aim is to facilitate the creation of an effective business plan by integrating real-life examples to elucidate the key elements involved. Below, you’ll find a range of 14 detailed business plan examples available for download and use.
Important Sections to Include in Business Plan
Practical business plan examples illustrating strategies for startup success, 1. e-commerce plan sample or example, 2. online marketplace business plan example or sample, 3. snack bar business plan sample / business plan example, 4. coffee shop business plan sample/business plan example pdf, 5. food hall business plan sample/business plan example pdf, 6. printing shop business plan sample/business plan example plan, 7. acquisition business plan sample/ example pdf, 8. l-1 visa business plan example with sample pdf, 9. e-2 visa business plan sample/ example pdf, 10. eb-5 business plan sample/ example pdf, 11. investor business plan sample/ example pdf, 12. nonprofit business plan sample/ example pdf, 13. bank business plan sample/ example pdf, 14. cannabis business plan sample/ example pdf, detailed overview of key components of a business plan, 1. executive summary, tips for writing executive summary, 2. company overview or description, tips for writing company description, 3. market analysis, tips for writing market analysis, 4. product and services, tips for writing product and services, 5. marketing and sales plan, tips for writing marketing and sales plan, 6. operation planning, tips for writing operational planning, 7. organization and management, tips for writing organization and management summary, 8. financial plan, tips for writing financial plan, 9. key external drivers, tips for writing key external drivers, 10. startup summary, tips for writing startup summary, 11. projected industry growth, tips for writing projected industry growth, 12. break-even analysis, tips for writing break-even analysis, 13. management summary, tips for writing management summary, 14. financial indicators, tips for writing financial indicators, discover business plan formats and free templates, business plan examples for students pdf, common types of business plan, 1. one page business plan, 2. start-up business plan, 3. strategic business plan, 4. feasibility business plan, 5. internal business plan, conclusion, frequently asked questions, download pack of 14 business plan examples, are you looking for top business plan writer.
To create a robust business plan, ensure inclusion of the following key sections:
- Executive Summary: A brief snapshot of your business and the key highlights of your business plan. Read more
- Product and Services: An elaborate description of the offerings you will provide to your customers. Read more
- Marketing and Sales Plan: A strategic roadmap outlining how you intend to promote and market your business before, during, and after its launch. Read more
- Operating Planning: An explanation of the systems, processes, and tools necessary to efficiently run your business behind the scenes. Read more
- Organization and Management: Organization and management in a business plan outline the structure and leadership of the company. Read more
- Financial Plan: A comprehensive plan mapping out your short-term and long-term financial goals and the associated costs of running your business. If you require funding, this section is where you can outline your request and financial needs. Read more
- Key External Drivers: External drivers encompass factors like outsourcing, economic changes, industry competition, and business legislation complexity. Read more
- Startup Summary: The startup summary offers a comprehensive financial overview of , detailing expenses, asset value, and total requirements, crucial for transparency with entrepreneurs and investors. Read more
- Projected Industry Growth : Projected industry growth forecasts the sector’s expansion, offering a 10-year perspective and average annual growth rate, providing clarity to investors. Read more
- Break-even analysis: The break-even analysis visually presents key metrics and a 12-month revenue forecast to help stakeholders grasp the point where the business covers costs and starts generating profit . Read more
- Management Summary: The management summary provides a concise overview of organizational structure, key personnel, their roles, and financial commitments, ensuring stakeholders understand the business’s operational strength and leadership capability. Read more
- Financial Indicators: The financial indicators section evaluates organizational fiscal health, focusing on year-over-year profitability metrics, leverage ratios, liquidity ratios, and additional metrics, providing a comprehensive understanding of the business’s financial performance and efficiency in revenue generation from equity investments. Read more

Something Borrowed Something New is a burgeoning e-commerce enterprise specializing in wedding accessories and personalized gifts. Operating on a drop-shipping model, this business has the capability to make a significant impact in the market.
Moreover, leveraging social networking and blogging can be instrumental in generating awareness and capturing interest, thereby creating a robust online marketing strategy for Something Old and Something New.
To enhance their business operations, they are contemplating the integration of a WhatsApp CRM system. This initiative aims to optimize communication with potential customers, ensuring prompt responses to inquiries and fostering a seamless interaction process.

EPlace Solutions will be an innovative online marketplace business portal offering a variety of products to consumers throughout the globe. Founded by Mr. John Jones, a seasoned business visionary with an eye toward profit and achievement, the organization is set to enter the market in 2023.
Online shopping is at an all-time high with new consumer mindsets calling for them to shop for the types of deals and bargains that will be so much a part of the online marketplace business model.

There is an increasing demand for snack-type fast food to be consumed while window shopping and walking around inside a shopping mall.
Do you plan to start a snack bar business? Then here’s a complete snack bar startup business plan template and feasibility report you can use FREE of charge. It sounds easy to open a snack bar, but in reality, you need well-planned strategies to ensure that your business stands the test of time.
Our snack bar business plan sample includes a detailed description of the products and services offered, as well as a market a nalysis and competitive analysis.
It also includes a financial plan that outlines the startup costs, revenue projections, and break-even analysis. We like this sample plan because it demonstrates how to build a profitable snack bar business by creating a unique menu and offering healthy, high-quality snac ks that meet custome r demand.
Your snack shop business plan can look as polished and professional as the sample plan. It’s fun and easy, with Wise Business Plan. Let’s review the snack shop business plan sample and adjust them according to your audience for the best results.

A coffee shop business plan is a document that outlines what your business idea is and how it will be implemented. Its purpose is to answer questions such as what it costs to start a coffee shop, how these costs will be financed, and how much money you can expect to earn from your cafe.
Are you looking for the right business plan for your cafe? Let’s review the Coffee shop business plan sample to find out how cloud-based software can make your day-to-day work more efficient.
Our coffee shop business plan sample includes a detailed description of the products and services offered, as well as a market analysis and competitive analysis.
It also includes a financial plan that outlines the startup costs, revenue projections, and break-even analysis. We like this sample plan because it demonstrates how to build a profitable coffee shop business by creating a unique brand and offering high-quality products a nd customer service.

In the food industry, there is fierce competition. To ensure success, you need to hit the ground running with the right pitch. Our food house business plan is the ideal solution with an attractive design highlighting key information and conveying the right message.
This food business plan example features food images intended to tantalize the taste buds. It captures the theme perfectly and will convey the ultimate message to investors, clients and customers.
It is important to remember that the business plan template can be customized to meet your company’s specific needs and requirements. It will help showcase your business as a leader in the modern industry.
This food business plan template provides key slides to showcase everything from finances to marketing and key competitors. If you prefer, you can alter the content displayed to meet your specific needs, but this is a good starting point.
Ultimately, this food house business plan will be suitable for any business operating in the food industry and keen to get interested from key individuals. It will ensure that you can build up the rep of your company.
We provide a one-of-a-kind sales pitch deck designed to appeal to your prospective audience, as well as a custom presentation tailored to their information requirements.

When establishing a think tank, you will need to develop a business plan and document it properly. As a mass think tank, you need a special strategy to legalize the think tank as a non-profit organization and to raise funds for your project successfully.
Copy and print businesses offer a variety of services to both businesses and consumers. A copy and print shop can handle everything from single-page printing to large-volume jobs using several types of media.
Our printing shop business plan sample includes a detailed description of the products and services offered, as well as a market analysis and competitive analysis. It also includes a financial plan that outlines the startup costs, revenue projections, and break-even analysis. We like this sample plan because it demonstrates how to build a profitable printing shop business by offering high-quality, customized printing services with a focus on customer s ervice and efficient operations.
Let’s take a look at Printing and Photocopy Business Plan Sample that you can use to inspire your own and easily create one.

The acquisition business plan sample is intended for businesses seeking to acquire another company or merge with a competitor. This plan includes an analysis of the target company, a valuation, and a strategy for integrating the acquired business into the existing operations. We like this sample plan because it provides a clear roadmap for the acquisition process and demonstrates the potential benefits of the deal.

At Wisebusinessplans, we understand that obtaining an L1 visa for an executive or manager requires a thorough and compelling business plan.
Our L1 business plan sample includes all the necessary components to satisfy USCIS requirements and demonstrate your qualifications and your company’s viability in the US market.
The L1 business plan sample is a comprehensive plan for a new business seeking L1 visa approval for an executive or manager. This plan focuses on demonstrating the applicant’s qualifications and the company’s viability in the US market.
We like this sample plan because it is specific to the L1 visa process and includes all the necessary components to satisfy USCIS requirements.

If you’re an entrepreneur seeking E-2 visa approval, Wise Business Plans can help you create a persuasive business plan.
Our E-2 business plan sample outlines your investment, business operations, and financial projections, providing a clear and compelling case for your ability to successfully run a business and make a significant economic impact.
The E-2 business plan sample is designed for entrepreneurs seeking E-2 visa approval, which allows individuals to invest in and manage a business in the United States. This plan outlines the applicant’s investment, business operations, and financial projections. We like this sample plan because it provides a clear and compelling case for the applicant’s ability to successfully run a business and make a significant economic impact.

If you’re looking to obtain an EB-5 visa by investing in a new commercial enterprise in the United States, Wise Business Plans can help you create a compelling business plan.
Our EB-5 business plan sample includes a description of your business, a market analysis, and financial projections, providing a detailed and persuasive case for the potential success of your venture.
The EB-5 business plan sample is designed for individuals seeking to obtain an EB-5 visa by investing in a new commercial enterprise in the United States. This plan includes a description of the business, a market analysis, and financial projections. We like this sample plan because it provides a detailed and persuasive case for the potential success of the business, which is crucial for obtaining EB-5 visa approval.

If you’re seeking investment from angel investors, venture capitalists, or other private equity firms, Wise Business Plans can help you create a compelling pitch.
Our investor business plan sample includes a pitch deck, financial projections, and a detailed analysis of the market the potential return on investment and the scalability of your business.
The investor business plan sample is intended for businesses seeking to attract investment from angel investors, venture capitalists, or other private equity firms. This plan includes a pitch deck, financial projections, and a detailed analysis of the market opportunity. We like this sample plan because it emphasizes the potential return on investment and the scalability of the business.

At Wisebusinessplans, we’re committed to helping non-profit organizations achieve their social impact goals.
Our non-profit business plan sample includes a mission statement, programs and services, marketing and outreach strategies, and a financial analysis, providing a clear roadmap for establishing or expanding your organization.
The non-profit business plan sample is designed for organizations seeking to establish or expand a non-profit entity. This plan includes a mission statement, programs and services, marketing and outreach strategies, and a financial analysis. We like this sample plan because it demonstrates a strong commitment to social impact and outlines a clear strategy for achieving the organization’s goals.

Whether you’re seeking financing from a bank or other financial institution, Wise Business Plans can help you create a detailed and persuasive business plan.
Our bank business plan sample includes a thorough financial analysis, market research, and a strategy for achieving profitability, highlighting the key factors that banks consider when evaluating loan applications.
The bank business plan sample is tailored for businesses seeking financing from a bank or other financial institution. This plan includes a detailed financial analysis, market research, and a strategy for achieving profitability. We like this sample plan because it highlights the key factors that banks consider when evaluating loan applications, and provides a strong case for the borrower’s ability to repay the loan.

The cannabis industry is rapidly growing, and Wise Business Plans can help you enter it with confidence.
Our cannabis business plan sample includes a market analysis, operational strategy, and regulatory compliance a comprehensive overview of the unique challenges and opportunities in the industry and offering a clear roadmap for success.
The cannabis business plan sample is tailored for entrepreneurs seeking to enter the rapidly growing cannabis industry. This plan includes a market analysis, operational strategy, and regulatory compliance plan. We like this sample plan because it provides a comprehensive overview of the unique challenges and opportunities in the cannabis industry, and offers a clear roadmap for success.
The executive summary is a concise overview of your business plan, highlighting the key points of each section. It should capture the essence of your business, its mission, and the purpose of the business plan. This section should be written last, but it’s placed at the beginning of the business plan. Here is an example executive summary from our professional business plan written for Eplace Solution , an innovative e-commerce portal.

- Keep it brief and focused on key points.
- Clearly define the problem and your solution.
- Highlight market opportunities and growth potential.
- Showcase your team’s qualifications.
- Include financial projections.
- End with a clear call to action.
- Tailor it to your audience.
- Review and update regularly.

In this section, provide a detailed description of your company, including its history, legal structure, location, and vision. Explain your mission statement and core values that guide your business decisions. Use real-life examples of successful companies and how their strong company descriptions have contributed to their growth. In addition, you can reuse your company description on your About page, Instagram page, or other properties that ask for a boilerplate description of your business.
This section also allows you to describe how you register your business . Here you must choose whether your business is a corporation, sole proprietorship, LLC , or another type of business .

- Describe your company’s mission and vision.
- Explain what your business does and the problems it solves.
- Mention your target market and customer base.
- Highlight your unique selling points.
- Provide a brief history and background.
A market analysis analyzes how you are positioned in the market, who your target customers are, what your product or service will offer them, and industry trends. It might be useful to do a SWOT analysis to discover your strengths and weaknesses to identify market gaps that you may be able to exploit to build your business.
As part of your market research, you’ll also need to perform a competitive analysis. It will give you an idea of who your competition is and how to differentiate your brand. Here’s an example of a competitive analysis we did for a food business.

- Research and understand your industry thoroughly.
- Identify market trends and growth opportunities.
- Analyze your competitors and their strengths and weaknesses.
- Define your target audience and their needs.
- Include data and statistics to support your analysis.

Adding products and services to a business plan involves more than listing your company’s offerings. If you intend to gain funding or partner with another business, your products, and services section needs to demonstrate your company’s quality, value, and benefits.
Here’s an example of a product and service section in the business plan we wrote for an e-commerce business that offers wedding accessories.

- Clearly describe your offerings and their features.
- Explain how your products/services address customer needs.
- Highlight any unique qualities or advantages.
- Discuss your pricing strategy.
- Mention any future product/service development plans.
Here is example of services section of a bank.

It is always a good idea to have a marketing plan before launching your business. A potential investor will want to know how you will advertise your business. Therefore, you should create a marketing plan that explains your planned promotion and customer acquisition strategies.
Discuss how you will make a sale. How will you attract customers and maximize their lifetime value? Ensure your marketing and sales forecasts align with your financial forecasts Marketing plans are usually based on the four Ps : product, price, place, and promotion. Breaking it down by marketing channels makes it easier. Discuss how you intend to market your business via blogs, email, social media, and word-of-mouth. Here is an example of marketing strategies we develop for a restaurant business.

- Define your marketing goals and objectives.
- Outline your marketing strategies, including channels and tactics.
- Explain your sales strategy and target sales goals.
- Include a budget for marketing and sales activities.
- Discuss your sales team and their roles.
- Detail your customer acquisition and retention strategies.
- Mention any partnerships or collaborations for marketing and sales.
Example of marketing and sales plan section of a bank

The operation plan should include all the steps needed to run the business in the long run. The plan should include details about logistics, duties for each department of the company, and responsibilities for the team.
The main aspect of running a business is its costs. Whether it’s machinery or services, each requires capital.
how to write an operation plan in a business plan
- Describe your day-to-day business operations.
- Explain your supply chain and production processes.
- Outline your facility and equipment requirements.
- Discuss your quality control and efficiency measures.
- Mention any legal and regulatory compliance considerations.
- Detail your staffing and management structure.
- Include contingency plans for potential disruptions.
In this section, you can describe your current team and the people you need to hire. You will need to highlight your team’s relevant experience if you intend to seek funding. Basically, this is where you demonstrate that this team can be successful in starting and growing the business.

- Introduce your leadership team and their roles.
- Highlight their relevant experience and qualifications.
- Explain your organizational structure and hierarchy.
- Discuss key personnel responsibilities and functions.
- Mention any plans for team growth or development.
- Address any advisory boards or external support.
Management summary of coffee shoppe business.

A financial plan should include sales and revenue forecasts, profit and loss statements , cash flow statements , and balance sheets .
Now, if you plan to pitch investors or submit a loan application, you’ll also need a “use of funds” report. Here you outline how you plan to leverage any funding you might acquire for your business.
With our business templates , you can create your own income statement, cash flow statement, and balance sheet.

- Include detailed financial projections (income statement, cash flow, balance sheet).
- Explain your funding requirements and sources.
- Discuss your pricing and revenue model.
- Describe your expense management and cost controls.
- Mention any financial risks and mitigation strategies.
- Highlight key financial milestones and goals.
Financial highlights of foodShack business.

External drivers refer to the external factors or influences that significantly impact the activity and growth of an industry. These drivers include outsourcing of non-core activities, changes in economic activity, competition from other industries, and the complexity of business legislation.
Additionally, external drivers encompass the effects of changes in new business formation, especially among small businesses, which directly affect the demand for services within the industry.

- Identify and analyze current and emerging market trends in your industry.
- Assess potential positive or negative impacts these trends may have on your business.
- Evaluate broader economic conditions, including inflation rates, interest rates, and GDP growth.
- Elucidate how changes in economic conditions could influence consumer behavior, product demand, and overall cost structure.
- Outline key industry regulations and compliance requirements, discussing potential impacts on operations, costs, and market access.
- Highlight relevant technological advancements and explain their potential effects on your product or service offerings, operations, and competitiveness.
- Analyze current and potential future competitors, emphasizing the evolving competitive landscape’s impact on market share, pricing strategy, and overall business strategy.
- Consider social and cultural factors influencing consumer preferences and behaviors, exploring how societal changes can affect product demand.
- Evaluate environmental trends and regulations, discussing potential impacts on operations, supply chain, and customer perceptions.
- Assess political stability, government policies, and geopolitical factors, exploring potential risks and opportunities from political changes.
- Discuss global market conditions, analyzing how global economic trends, trade policies, and currency fluctuations may affect operations and expansion plans.
- Identify and discuss potential risks in the supply chain, such as disruptions, shortages, or geopolitical issues.
- Consider demographic shifts affecting your target market and discuss how changes may impact your customer base and marketing strategies.
- Highlight key legal and regulatory factors affecting the business, discussing potential legal challenges, compliance costs, and regulatory changes.
- Outline comprehensive risk management strategies, including contingency plans and risk mitigation strategies.
- Explain how you will monitor external drivers and emphasize the importance of staying agile and responsive to changes in the external environment.

The startup summary serves as a comprehensive overview of essential financial aspects, encompassing total startup expenses, the overall value of startup assets, and the total requirements, which is the cumulative sum of all expenses and startup investments.
It provides a clear financial snapshot, outlining the costs involved in launching the business, the value of assets acquired, and the overall financial needs for the startup.
This section is crucial for entrepreneurs and potential investors, offering a transparent understanding of the financial foundation required to initiate and sustain the business successfully.
This roadmap ensures a realistic evaluation of the business idea, identifying potential challenges and offering solutions.To write an effective plan, focus on what sets your venture apart from competitors, maintain conciseness, and embrace flexibility as a living document.
Answer fundamental questions about your business, create actionable checklists, execute the plan, and continually revise and update based on experiences and feedback.This iterative process fosters continuous improvement, helping entrepreneurs stay adaptable and enhance their business strategies over time.

- Clearly state the startup’s name and provide a concise description of its activities.
- Include a succinct mission statement capturing the startup’s purpose and goals, reflecting its core values.
- Specify the founding date and offer brief bios of key founders, highlighting relevant experience.
- Summarize the startup’s concept, explaining offered products or services and key distinguishing features.
- Clearly articulate the problem or need in the market that the startup addresses, defining the target audience.
- State what makes the startup unique, whether it’s a special feature, market gap, or competitive advantage.
- Provide a brief description of the market opportunity, covering target market size, trends, and growth prospects.
- Outline how the startup plans to generate revenue, detailing streams, pricing strategy, and potential partnerships.
- Offer a snapshot of the startup’s current status, highlighting key achievements such as product development or partnerships.
- If seeking funding, clearly state the amount sought and its allocation, covering areas like product development and marketing.
- Include a high-level financial summary with key projections for revenue, expenses, and profitability.
- Briefly outline future aspirations and plans, encompassing areas like expansion, product development, or strategic partnerships.
The projected industry growth is a pivotal aspect that forecasts the expansion of a specific sector over a defined timeframe.
For instance, it could provide an estimate of where that particular business will be standing in the next 10 years, and what will be the average annual growth rate of that industry.
This information provides prospective investors and stakeholders with a clear understanding of the industry’s potential and positions the startup within a dynamic and flourishing market.

- Emphasize the importance of industry trends and growth to your business.
- Provide a concise overview, including market size, major players, and recent trends.
- Briefly explain how you gathered data on industry growth projections (e.g., market research reports, expert interviews).
- Identify and discuss prevailing trends, such as technological advancements, changes in consumer behavior, and regulatory shifts.
- Summarize the industry’s historical growth, highlighting growth rates, market expansion, and notable milestones.
- Highlight key factors expected to drive industry growth, such as emerging markets, technological innovations, and demographic shifts.
- Discuss specific opportunities within the industry, including gaps in the market, underserved segments, or areas of competitive advantage.
- Acknowledge potential challenges or risks that could impact industry growth, demonstrating a realistic understanding.
- Present projections for future growth rates based on historical data, expert opinions, and your analysis. Include short-term and long-term projections.
- Discuss how key competitors are positioned to leverage industry growth, emphasizing your business’s differentiation strategies.
- Consider the regulatory landscape impacting growth, discussing anticipated changes and their potential effects on the industry.
- Explore international trends and their implications for industry growth, including factors like global economic conditions and geopolitical influences.
Here is example of market analysis section of a bank.

The break-even analysis serves as a vital financial tool, offering a detailed estimation of key metrics such as Sales Revenue, Cost of Sales, Gross Profit, Fixed Expenses, and Income Before Tax.
These critical components are visually presented through a bar graph, providing a clear and concise overview of the financial dynamics.
Additionally, the break-even analysis delves into a 12-month forecast, outlining the projected amount of revenue generated and the corresponding fixed costs.
This section is instrumental in helping stakeholders understand the financial threshold at which the business covers its costs and begins to generate profit.

- Define break-even analysis as a financial calculation where total revenue equals total costs.
- Identify constant costs regardless of production or sales levels.
- Enumerate and explain costs changing with production or sales.
- Present the break-even analysis formula, indicating the units needed to cover costs.
- Perform a practical break-even calculation using business-specific fixed costs, selling price, and variable cost per unit.
- Include a break-even chart or graph for a visual understanding of cost-revenue dynamics.
- Conduct a proactive sensitivity analysis to explore how changes in variables impact the break-even point.
- Specify the anticipated timeframe to reach the break-even point in terms of months or units sold.
- Clearly outline assumptions made in the analysis and provide justifications for transparency and credibility.
- Acknowledge potential risks or challenges that may affect the accuracy of the break-even analysis.
- Briefly mention contingency plans for difficulties in reaching the break-even point within the projected timeframe.
The management summary within the business plan provides a concise overview of the organizational structure and key personnel.
This includes a count of individuals, specifying the number of founders and operational team members integral to the organization.
The summary delves into the roles and responsibilities of each key figure, offering insights into the leadership dynamics driving the business.
Furthermore, the management summary sheds light on the financial aspect by presenting details about personal wages and payroll allocations for both founders and operational staff.
This comprehensive section ensures a clear understanding of the human resource framework and the financial commitments associated with the management team, crucial for stakeholders evaluating the business’s operational strength and leadership capability.

- Highlighting the critical role the management team plays in the business’s success, the introduction emphasizes their significance.
- Listing each key member with names, positions, and brief role summaries introduces the core of the management team.
- Providing brief biographies for each team member underscores their relevant experience, skills, achievements, and industry-specific expertise.
- Clearly outlining roles and responsibilities emphasizes how each team member’s skills contribute to the overall success of the business.
- Sharing the team’s vision and strategy involves discussing key strategic goals and outlining the plans to achieve them.
- Highlighting notable achievements or milestones showcases the team members’ successful ventures, industry recognition, or career accomplishments.
- Discussing team dynamics emphasizes collaboration and the complementary nature of their skills in driving the business forward.
- Introducing advisory board members, if applicable, underscores the additional guidance and expertise they bring to the business.
- Discussing how the team plans to contribute to future growth and development includes strategies for talent acquisition, leadership development, and succession planning.
- Touching on the team’s culture and values emphasizes their role in shaping the overall ethos of the business.
- If seeking investment, briefly mentioning how the management team plans to use funding for business growth and development provides insight into their financial strategy.
Here is example of marketing and sales plan section of a bank.

The financial indicators section within the business plan helps in evaluating the fiscal health and performance of the organization.
Year-after-year profitability estimates take center stage, encompassing key metrics such as gross margin, net profit margin, and EBITDA to revenue.
These indicators provide a comprehensive understanding of the business’s ability to generate profit relative to its revenue.
Furthermore, the financial indicators extend to leverage ratios, including the critical Debt to Equity ratio, Debt to Assets ratio, and Interest Coverage ratio.
These metrics illuminate the organization’s capital structure, debt management, and its capacity to meet interest obligations.
Liquidity ratios includes the Current Ratio and Current Debt to Total Asset Ratio.
These ratios provide insights into the company’s short-term financial health and its ability to meet immediate obligations.
The financial indicator toolbox is enriched with additional metrics, notably the Revenue to Equity ratio, which sheds light on the efficiency of generating revenue from equity investments.

- Detailed revenue forecasts for the next 3-5 years. Breakdown by product/service and geographical regions.
- Detailed breakdown of anticipated expenses. Include fixed and variable costs, operational expenses, and other relevant expenditures.
- Historical P&L statements if available. Projected future profits and losses based on revenue and expense projections.
- Outline of expected cash inflows and outflows. Emphasis on the ability to meet short-term obligations.
- Snapshot of the company’s financial position. Includes assets, liabilities, and equity.
- Calculation and presentation of key financial ratios (liquidity, solvency, profitability). Discussion on the significance of these ratios.
- Identification and explanation of relevant KPIs. Highlighting alignment with the overall business strategy.
- Discussion of potential financial risks. Mitigation strategies and addressing uncertainties.
- Clear statement of the amount and purpose of funds required.
- Outline of key assumptions underlying financial projections. Rationale for these assumptions.
- Summary of industry financial trends and business positioning. Outlook on future financial prospects considering market dynamics.

Looking For The Right Business Plan Format?
These sample business plans will provide you with a complete structure and format for your business plan, which will give you a head start on developing your document, so you won’t be stuck seeing an empty page and wondering what to write.
Simply going through the process of writing a business plan is one of its key benefits. If you sit down to write, you’ll naturally think about your startup costs, your target market , and any market analysis or research you’ll need to conduct. In addition to defining your position among your competitors, you will establish your goals and milestones.
You can see what should be included in a sample financial plan, but It is wrong to assume that a sample company’s financial projections will fit your own. If you need more resources to get you started, we recommend this guide on how to write a business plan .
In addition, you can download our 40+ free business plan templates covering a range of industries.
One-page business plans are short, compact, and to the point and are designed to make the plan easy to read at a glance. Make sure to include all of the sections, but truncate and summarize them
Start-up business plans are for businesses that are just getting started. They are usually developed to secure outside funding. In this regard, financials are of increased importance, as well as other sections that determine whether your business idea is viable, such as market research.
A strategic business plan lays out a company’s goals and how it will achieve them at a high level. It is a foundational document for the company as a whole. A strategic business plan allows all levels of the business to see the big picture, inspiring employees to work together to reach the company’s goals.
Developing a feasibility plan answers two primary questions about a business venture: who would purchase the service or product the company wants to sell, and if the venture is profitable.
Internal Business plans are geared to a specific audience within a company to keep your team on the same page and focused on the same goals.
In conclusion, whether you’re venturing into a traditional business or creating an innovative startup, the significance of a well-crafted business plan cannot be overstated. Different types of business plans cater to specific needs, from internal alignment to strategic expansion. Employing a template in MS Word ensures a polished presentation. The process of writing an executive summary, creating a plan, and defining the components of your business plan is essential.
Recognizing the need for a comprehensive and standard business plan can help guide your endeavors. Whether you choose to write a full business plan or opt for a one-page business overview, leveraging templates in MS Word can simplify the process. In essence, understanding the types of business plans and utilizing an executive summary template provides a structured approach to showcase your business overview.
Take inspiration from example business plans to tailor your strategy, ensuring a roadmap for success in the dynamic world of entrepreneurship. Always remember, a meticulously crafted business plan not only communicates your vision effectively but also serves as a valuable resource that can help secure investments and guide your business’s growth trajectory.
Begin with an executive summary, delve into market analysis, outline your strategies, create financial projections, and use available business plan examples as templates to guide your writing.
A comprehensive business plan template should encompass key sections such as an executive summary, business description, market analysis, marketing strategy, organizational structure, and financial projections. Seek templates online that cover these elements.
Tailor your business plan to the scale of your small business. Define your objectives clearly, outline cost-effective strategies, and emphasize agility in adapting to market changes.
Explore well-crafted business plan examples you can visit our website wisebusinessplan.
The fundamental components include an executive summary, business description, market analysis, marketing and sales strategy, organizational structure, product/service description, and financial projections.
Investors focus on growth potential, detailed financial projections, market analysis, competition analysis, and the qualifications and experience of your management team when reviewing a business plan.
To find a business plan example for a tech startup,you can visit our visit wisebusinessplan .
A business plan provides a comprehensive overview of your entire business, including strategies, operations, and financials. In contrast, a business proposal typically focuses on a specific project or offer, outlining the details and benefits to a potential client.
Craft an engaging executive summary by summarizing your business’s mission, highlighting the market opportunity, showcasing your product or service, and providing a concise overview of your financial projections.
Seek tailored business plan examples for nonprofit organizations you can visit wisebusinessplan .
These business plans are written by MBA writers. Real-world use cases were used in these plans.
Get our business plan writing and consultation service.
Quick Links

- Investor Business Plans
- M&A Business Plan
- Private Placement
- Feasibility Study
- Hire a Business Plan Writer
- Business Valuation Calculator
- Business Plan Examples
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Plan Template
- Business Plan Pricing Guide
- Business Plan Makeover
- SBA Loans, Bank Funding & Business Credit
- Finding & Qualifying for Business Grants
- Leadership for the New Manager
- Content Marketing for Beginners
- All About Crowdfunding
- EB-5 Regional Centers, A Step-By-Step Guide
- Logo Designer
- Landing Page
- PPC Advertising

- Business Entity
- Business Licensing
- Virtual Assistant
- Business Phone
- Business Address
- E-1 Visa Business Plan
- EB1-A Visa Business Plan
- EB1-C Visa Business Plan
- EB2-NIW Business Plan
- H1B Visa Business Plan
- O1 Visa Business Plan
- Business Brokers
- Merger & Acquisition Advisors
- Franchisors
Proud Sponsor of
- 1-800-496-1056

- (613) 800-0227

- +44 (1549) 409190

- +61 (2) 72510077

Download 14 Professional Business Plan Samples
Your Full Name
- Skip to search box
- Skip to main content
Princeton University Library
Entrepreneurship.
- Idea Generation
- Industry Research
- Market Research
- Intellectual Property
- Social Entrepreneurship
Print Resources
- Additional Books and Entrepreneurship Videos
- Online Resources
- SBA: Create a Business Plan A tool provided by the Small Business Administration to help entrepreneurs write out their initial business plan. Walks you through completing each section. Save you plan as a PDF file, or saved in-progress on their website for up to six months from last login.
- Entrepreneur.com - Business Plan From Entrepreneur.com, an article that serves as a starting point, linking to things you should consider before writing your plan, practical suggestions for writing your plan, and tools to assist you.
- Bplans The Bplans site includes free sample business plans, helpful tools and guides to help you manage your business better, practical advice on planning, interactive tools and calculators, and publishes daily advice to help you grow your business.
This is only a very small selection of the books, both online and print, that are available. Go to the library homepage to search for more .
- << Previous: Social Entrepreneurship
- Next: Additional Books and Entrepreneurship Videos >>
- Last Updated: Feb 23, 2024 5:03 PM
- URL: https://libguides.princeton.edu/entrepreneurship
Newsmoor.com is an educational website for online learning. It Provides information: on verbal and nonverbal communication elements, noise, models, and theories, print, broadcast, and online journalism, and feature article writing. It also includes business models, theories, plans, profile examples, advantages and disadvantages of several models, facts, research methodology, research proposal writing, assignment writing, a study abroad, including top public and private universities and educational consultants.
Business Plan Examples and Sample For Students
Business Plan Examples For Students. Business Proposal Examples for Students. Also, Business Plan Sample pdf for Students. Business Plan Examples For Students Entrepreneurship PDF.
Business Plan
The business plan refers to the company’s written statement explaining the company's background and business details. This plan includes the executive summary of the company, product and service, operation, marketing, and financial plan.
The employee creates the business plan to represent and improve the organization's image to stakeholders, customers, and affiliates. It proposes the business strategy entirely mentioning how the company profits and survives in markets. So, a business plan is also known as a business proposal that is crucial for corporate branding. The business plan is essential for every company to build rapport with stakeholders and business partners as well as achieve competitiveness.
The key elements of a business plan or proposal are an executive summary, background, product and service, organizational structure , sales and marketing strategy, financial and operational plan, and more.
Business Plan Examples
A business plan example refers to a business proposal sample that thoroughly explains the business, including the executive summary of the financial statement. It is also known as a business report example or business proposal format. An example of a business plan certainly includes the executive summary of the business, operating strategy, start-up financial projections, financial projections, etc. The business plan example for students is also known as the business report format.
Business plan writing is a mandatory assignment for students in entrepreneurship. It is also a compulsory assignment for business students. The importance of a business plan is growing day by day for selling products on digital platforms and managing the organization virtually.
The business proposal is also compulsory for getting a bank loan. The organization needs it to make agreements with other organizations. The bank authority surely asks the organization to submit a business plan with the bank loan application. The other names of a business plan are business proposal, report, profile, and more. A business plan example is also known as an example of a company profile , business proposal example, sample, and format.
Elements of Business Plan Example
The Nine Components of a Business Plan are as follows:
Business Plan Examples For Student Entrepreneurship
Today, the authors present a business plan example for students. They wrote it while they were students in entrepreneurship courses at the Faculty of Economics and Management University Putra Malaysia (UPM). The lecturer sets group assignments for the students; therefore, the students make the business plan example to complete the group assignment. Thus, this business plan or proposal example for students certainly assists business administration students. It also assists students in BBA, MBA, economics, finance, and business communication courses and researchers.
The author also wrote business plan examples for students about food and an Example of Business Report.

The students set the company name “BambooS.” It sells reusable and eco-friendly bamboo straws. Straws are a unique product in Malaysia that can be customized for length and diameter. Besides, the company offers engraving services for customers. So, customers can customize a meaningful word on the bamboo straw for engraving. In addition, it provides a designed pouch as packaging for our straw that looks smart.
Business Plan Example For Students

1.0 Executive Summary Of Business Plan
BambooS Sdn. Bhd. company was created by a group of 10 students in the Basic Entrepreneurship course. This company is named BambooS. It produces and sells bamboo-based products. The capital S in the company’s name stands for straw. The original idea came from a student. And we chose Bamboo as the main ingredient of the products. Currently, we focus on producing eco-friendly straws to serve our customers. The products are the best quality yet affordable straws.
Our product is also biodegradable as it is made from Bamboo. We also guarantee that customers can use our products many times. It is reusable and easy to wash and carry. The straw size is customizable. So customers choose the size based on their preferences. In addition, our specialty is not only in our product but also in our packaging.
There are ten members in a group and each member will contribute RM 100. The total paid-up capital is RM 1000. We set up our warehouse in the Serdang area to produce, package, and store our products. We are making the straw as per the customer’s demand and request. For the marketing part, we are advertising and promoting our product through social media sites, such as WhatsApp, Instagram, and Facebook, and e-commerce, such as Shopee. We adopt the lean canvas business model tool to assess the outcome of the business.
2.0 Background of the Company

2.2 Company overview

2.3 Vision And Mission Statement
2.3.1 vision statement.
To become the most notable company in Malaysia for producing eco-friendly bamboo straws.
2.3.2 Mission Statement
We want to fulfill the objective of satisfying customers with our eco-friendly products. We want to reduce pollution by using reusable straws anywhere and anytime.
2.4 Keys To Success
The Keys to Success for BambooS Include the following:
Table: 4 Keys of Success
2.5 Organizational Chart

3.0 Administration anD Human Resource Plan
3.1 business strategies.
Business strategy is crucial to maintain business growth.
The personal preferences of corporate management do not influence good business strategies. We emphasize every department's function. It ensures the plans run smoothly to meet goals. We need to achieve them. We have put as much emphasis on the efficiency of each Department.
Our company has set several strategies to achieve the company objectives. However, these strategies have been made based on every Department’s suggestion.
a. Administration and Human Resources Department
- The admin and human resource department monitors all the business operations. It manages employees' and management problems.
- It also solves problems that affect people management programs in the long run.
- Moreover, it follows the five-gap model of service quality to ensure service quality.
b. Marketing Department
- This department handles marketing of the product and promotional activities in order to reach the products to a vast amount of potential clients.
- It also promotes the business and mission of an organization through social media.
c. Operational Department
- This department ensures that all the equipment and material are ready to run the operation smoothly. It ensures that all products are of good quality. This department follows the eight principles of TQM to ensure product and service quality.
- Additionally, this department has the ultimate accountability for profit and loss and seeks to maximize shareholder return on investment.
3.2 Management Team

3.3 Job Descriptions

4.0 Market Plan
4.1 introduction.
BambooS Sdn. Bhd. support the “Save The Earth” campaign by producing eco-friendly Bamboo straws. These straws are environmentally friendly products. Therefore, these products are alternatives to plastic straws. The government has imposed restrictions on the use of plastic straws. They also create social awareness of to use of natural products.
Hence, It is an important driving factor of our market strategy. In addition, the surging demand for drinking beverages, including juices and Boba drinks and then the save the turtle campaign, is also propelling the demand for bamboo straws across the globe. Bamboo straws are reusable compared to plastic; they are better for health, durable & robust, and it is an environmentally friendly product. The products will contribute to reducing global warming and preventing climate change globally .
4.2 Objective of Marketing
Our objective in producing Bamboo straws is to encourage consumers to use natural, eco-friendly products. Why are bamboo straws better than metal? Firstly, Bamboo comes from a natural source. So it is naturally sturdy and easy to collect. We do not need to use chemicals to make straws.
Additionally, metal straws are not pocket-friendly compared to Bamboo. Moreover, metal will rust when in contact with water and oxygen. Bamboo stock is much cheaper, less work, and easy to collect. Our marketing strategy will focus mainly on reusable principles and are much more trendy to youngsters because we have an engraving service to attract them.
4.3 Analysis of Marketing
4.3.1 market trend.
The demand for bamboo straws has risen due to growing environmental attention. Additionally, plastic straws have been reduced due to state restrictions. However, the bamboo straw market is expected to achieve high growth shortly. In addition, BambooS Sdn. Bhd is a unique company in Malaysia. We produce our straw ourselves, and we provide safety and hygiene assurance. The buyer can engrave their name on the straw. Nowadays, customers want recognition for something they buy or support. They are also sincere about ‘Save the Earth’ and deserve to flex.
4.3.2 External Environment Analysis
Our first demographic psychographic and geographic target market is the University Putra Malaysia (UPM). Since we are students of UPM, it is easier to approach our target customers, including students and staff. Students tend to bring their water bottles or flasks to classes. It is one step toward being environmentally friendly; thus, we promote their effort by selling bamboo straws. In addition, we will promote our product at cafes or food courts at the faculty and library. We also establish a booth at super shops.
4.3.3 Internal Environment Analysis
(SWOT ANALYSIS)

4.3.4 Market Opportunities
Our bamboo straw comes with a pouch; thus, it is hygienic and easy to bring everywhere. We also provide a small brush to ensure deep cleaning of the inner straw. Our product is able to be used again and again. So students and staff can save money. They do not need to bring straws in large volumes. The structure of our bamboo straw is strong and sturdy; thus, it will not break if soaked in water for a long time, unlike paper straws.
4.4 Target Market
4.4.1 segmentation.
- S size is fit for ordinary drinks, fully liquid
- L size is suited for Boba drink or any drink that has topping.
- People use straws for drinking tea, juice, frappe, and Boba.
- Restaurants, cafes, food court, canteen, food stalls, super shops around UPM
4.4.2 Consumer Market and Buyer Behaviour
(i) Students and staff at UPM (ii) Cafe and Restaurant at UPM
4.4.3 Positioning
- New business strategy for eco-friendly products in the market.
- Our production, process, and packaging materials match zero pollution.
- Providing Engraved service
- Customized and Eco-friendly bamboo straws of different sizes
- Made of organic material
- Unique punch made by the jute bag.
4.5 4 P's Marketing Strategy
4.5.1 product strategy.
To make our product unique, we ensure the quality and safety of our products always satisfy our customers.
Our product comes neatly packaged in a unique eco-friendly punch. It is made of a jute bag. The natural bag is designed to make people use bamboo straws every day.
Labeling/Customised
Our company provides customized products. We resize and engrave the bamboo straws to attract more customers. So, our customers can request any size and imprint their straw with any logo or design they like. Our product comes in two sizes: the regular size for the standard drink, fully liquid, and the large size for the Boba drink or drink that has topped. Customers can send us their logo or name on social media sites. Personalized bamboo straws look fantastic across social media.
4.5.2 Price Strategy
Price is the payment given by one party to the other in order to get the return for goods or services. It is necessary as it determines our profit and business survival. Two factors affect our pricing strategy to increase our profits. The internal factor that affects our pricing strategy is production and management cost. At the same time, the external factor is the competitive environment.
Our management team decided to sell the straw in four sets: A, B, C, and D. Our company decided to set the price at RM 10.00 for set A. This set includes the common Bamboo straw, brush, and pouch. Then SET B cost RM 12.00, including the Boba size straw, brush, and pouch. SET C and SET D are more special because they include the engraving service. The engraving cost is RM 8.00 for each Set. As we mentioned before, we resize products for clients. So our customers can personally request to resize the straw. We charge it costs RM 9.00 per set.
4.5.3 Place Strategy
Place strategy is also known as distribution strategy, wherein the organization decides the mode of distribution for the product. The pacing strategy plays an important role in selling the products. We have chosen the market, cafe, or restaurant adjacent to the University Putra Malaysia. Our main target market is UPM staff and students.
Furthermore, we also decided to make it easy for our customers to find our product by using the shopping app, Shopee apps. We chose these apps because Shopee is the best option if you want to start selling online at a low cost and big money.
4.5.4 Promotion Strategy
Promotion is the advertising process to provide information to different parties about the products. It is a communication process that influences the customer to buy products. In order to get customers' attention and obtain a more significant market share, Bamboos Sdn. Bhd uses digital and internet marketing.
We have set up social media accounts, Instagram, Facebook, Shopee, and Blogspot, to promote our business. The marketing team will upload the promotional content to social media sites. This is because most people stay on social media sites mostly. With that, social media sites are the easiest way to buy anything we want without going out. Moreover, online shopping has become popular in this era, and all these social media sites have become the hottest sites, especially Instagram, which has a high rating in advertisements. Many companies use social media to sell their products and services by putting corporate information in their accounts.
Social Media Advantages
Social media are free sites where we can reach a large number of customers. Hence, we use social media to do hard and soft selling.
We fully develop every post to attract customers. In addition, we will always update our posts and story feeds. We ensure that customers are more exposed to our product. Next, we also use social media hashtags. We use hashtags such as #Bamboos, #SafeTheEarth, and more to make it easier for customers. The marketing team uses social media for the ordering process.
Similarly, we will place the generated links on each social media to encourage the product ordering process. Our company also makes sure transactions with our customers are easy. Finally, we also produce videos to promote our sales. The video will achieve the highest social media reach for views and engagement.
We tend to focus more on WhatsApp groups, Shopee, and Instagram since our target audience is UPM students. Many students are involved in WhatsApp groups, such as on faculty, college, hostels, and clubs. WhatsApp and Instagram are more popular among students as the places they spend most of their time. WhatsApp is the most popular social media site in Malaysia.
5.0 operations planning
5.1 location and address.
We will mainly sell the straw on social media sites. The production team will handle the production process. They resize and wash the Bamboo at the warehouse in Selangor, Malaysia. The social media sites are Instagram, Facebook, Shopee, Blogspot, and WhatsApp. Supplies will be directly delivered to the responsible members for further processing based on our buyer's order.
5.2 Objective of Operations
We aim to produce and deliver good quality Bamboo Straw. Our team ensures that all products are effective and attractive. We also must gain customers' trust and happiness with our service, including price and delivery. We also make sure our products are cleaned and safe for use. Our team is very responsive to making good-quality straws. In addition, our company has ultimate responsibility for profit and loss. However, we seek partners for more investment.
5.3 Operation Strategies
A few strategies have been set up to ensure that our business runs smoothly throughout the week and meets our objectives.

5.4 Supplier
The bamboo stock was from a supplier via the Shopee platform, and the pouch supplies were from Giftstalk Sdn. Bhd. The company logo's printing service was also included when we ordered the pouch from suppliers. Moreover, we order coconut fiber cleaning brush stock and packing Boxes from Shopee. We also surveyed purchasing and made sure that our supplies were reasonable. All the supplies are ordered online and delivered to our company via specialized courier service companies.
The bamboo straw will be customized and delivered to the customer using J&T Express, Ninja Van, and cash-on-delivery service, which will ease our delivery.
Thus, we have decided on the following suppliers as our supply providers:
- Wing.DIY – Shopee- For Bamboo Stock
- GIFTSTALK SDN BHD)- For Pouch Supplies
- Gd. Pack -Shopee)- For Paper Boxes Stock - Sandpaper Holder with Plastic.
5.5 Process Planning

5.6 Implementation Schedule

5.7 Machinery and Equipment Including GST
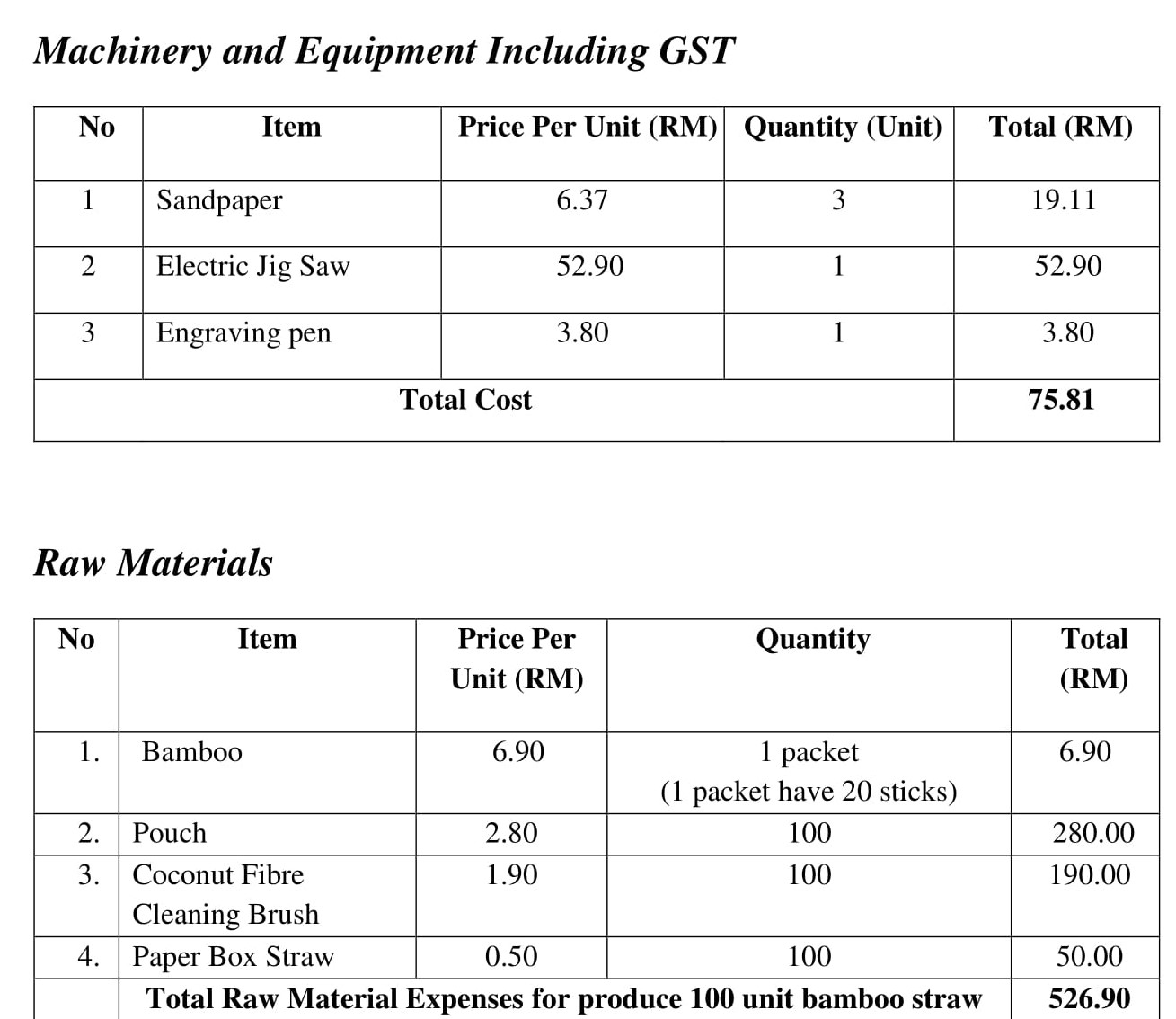
6.0 Financial Plan
6.1 introduction.
A financial plan can be defined as a process of framing procedures and budgets regarding the financial activities of concern. This is done to ensure good financial and investment procedures.
Generally, the financial plan is used to know an investor's current pay and future financial state by using current known variables to predict future income, asset values, and withdrawal plans.
A financial plan is one of the most crucial parts of a business. Some of the importance of a financial plan are:
- A financial plan provides the direction of one's business.
- It also helps understand how finances impact one's business.
- Additionally, it helps to manage income better.
6.2 Purpose of the Financial Department
A few purposes are as below:
- Firstly, it determines capital conditions.
- Secondly, it operates the fund nicely for different purposes.
- Finally, it maintains proper cash flow.
6.3 Project Implementation Cost

Source of Fund
Our money is used as the start-up capital with a contribution of RM100.00 per shareholder, bringing the total investment to RM 1000.00.
6.4 List of Expenses
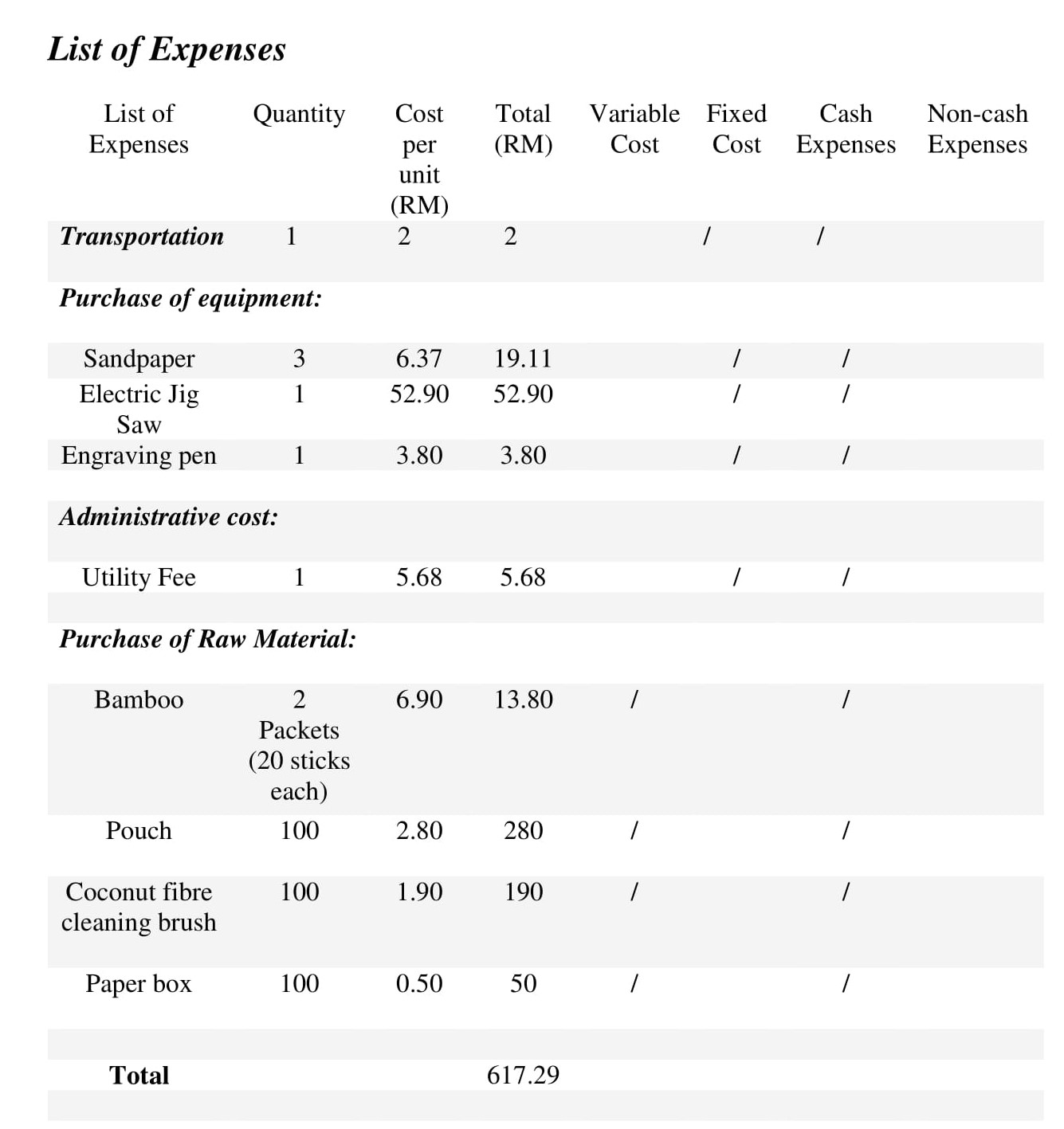
Twelve partners funded a total of RM1000.00 to cover all business costs, which is RM 617.29. Expenses are in terms of buying raw materials, equipment, and delivery fees. We will not invest all amount to the business.
The equipment is counted as fixed cost as they are bought in bulk. Refer to 6.4 (List of Expenses) for detailed information.
6.5 Record of List of Sales
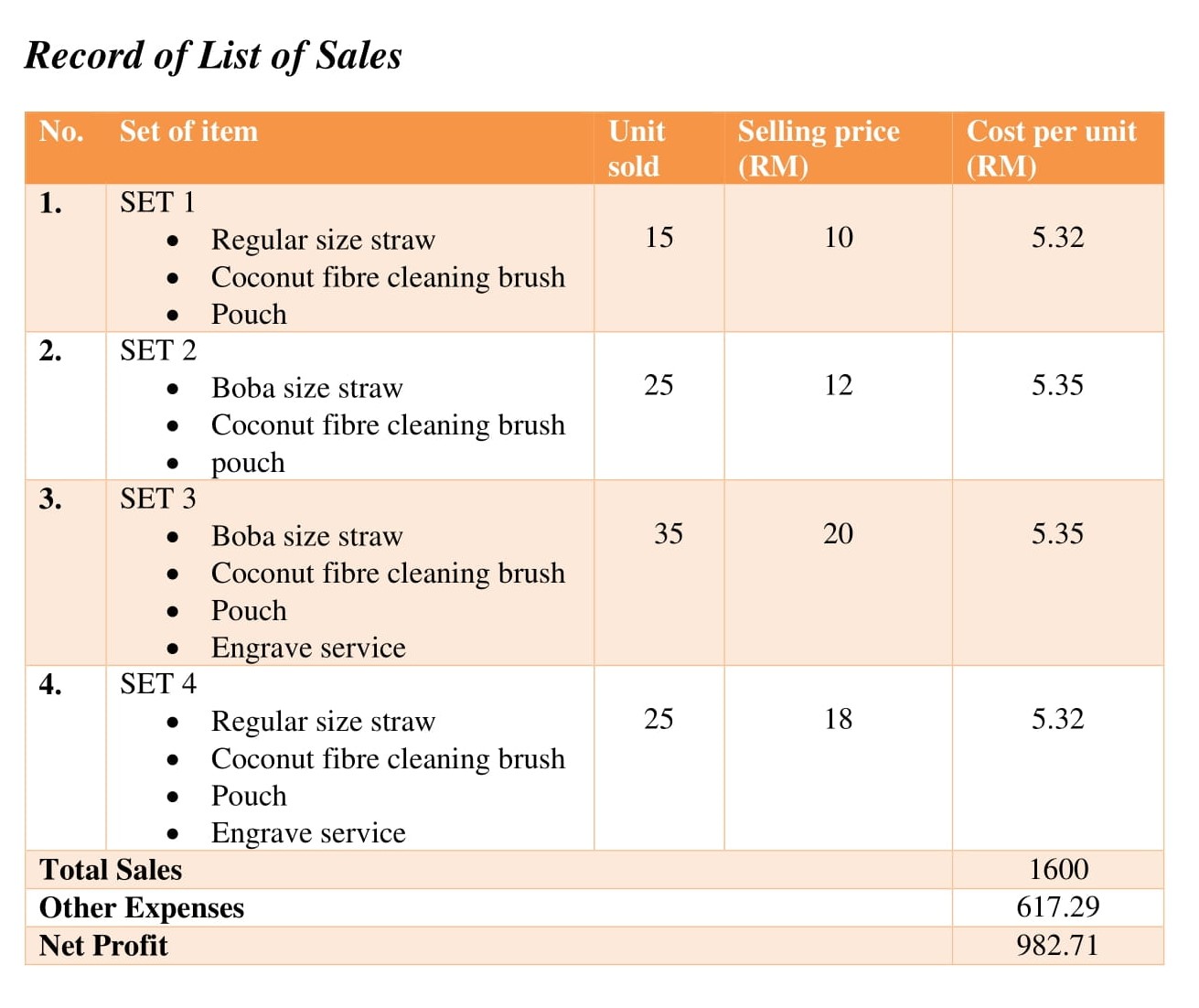
6.6 Income Statement
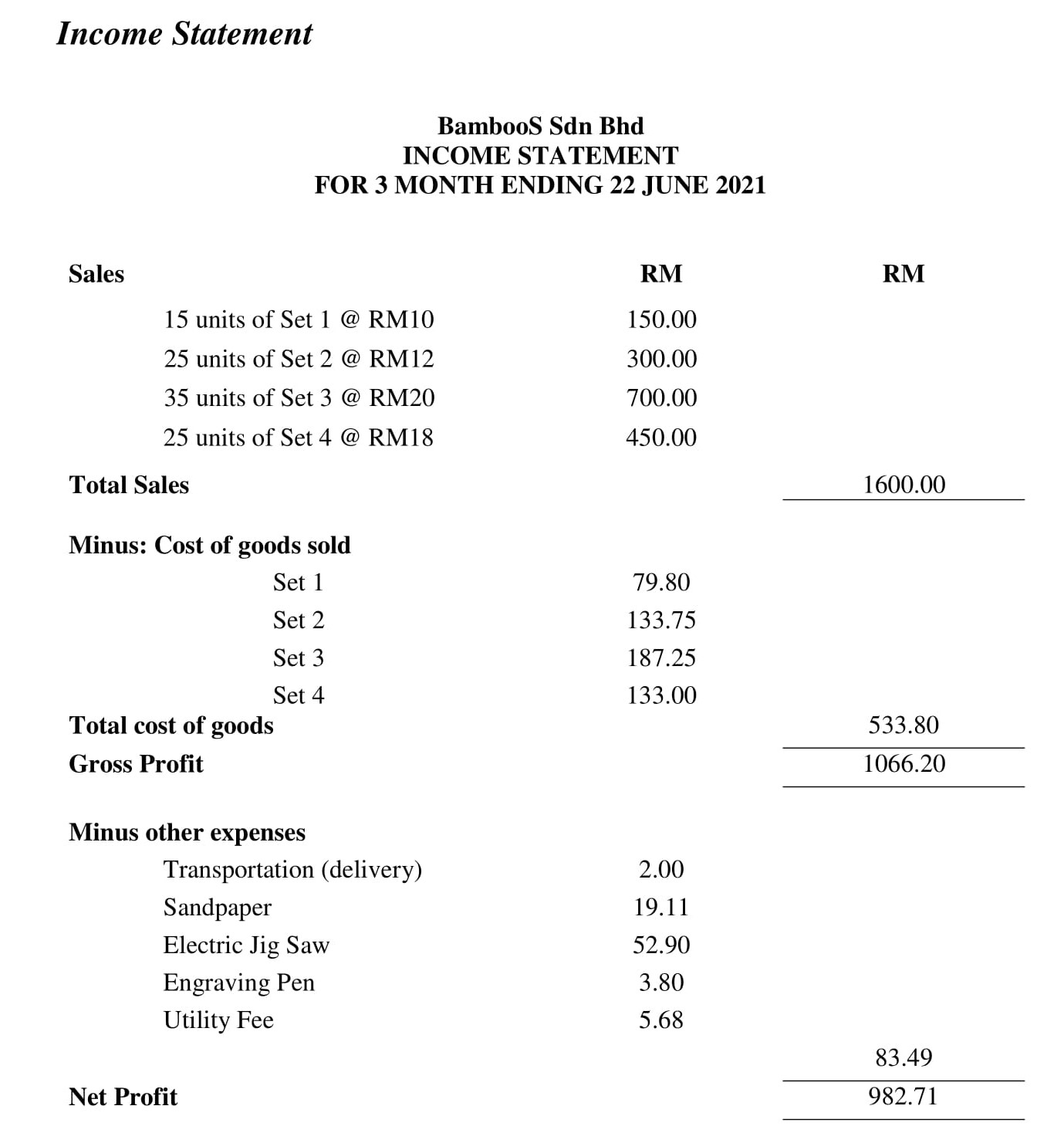
After one month of business, BambooS ended up with RM 1600.00 from 7 different products. This includes selling 15 units of Set 1, 25 of Set 2, 35 of Set 3, and 30 of Set 4. Leftovers for bamboo straws are found. The income statement shows that the business's net profit after one month of operation is RM 988.39, approximately 98.8% of capital invested into the business.
6.7 Cash Flow Statement

The case flow statement shows that the initial capital on hand is RM 1000.00, and at the end of the business, the total surplus (after deducting all expenses) is RM 1982.71.
The RM 1982.71 includes RM 100 capital invested by every shareholder at the beginning of the business. By dividing the remaining money after deduction, each shareholder would find themselves receiving an extra RM 98.27. Hence, every
6.8 Balance Sheet
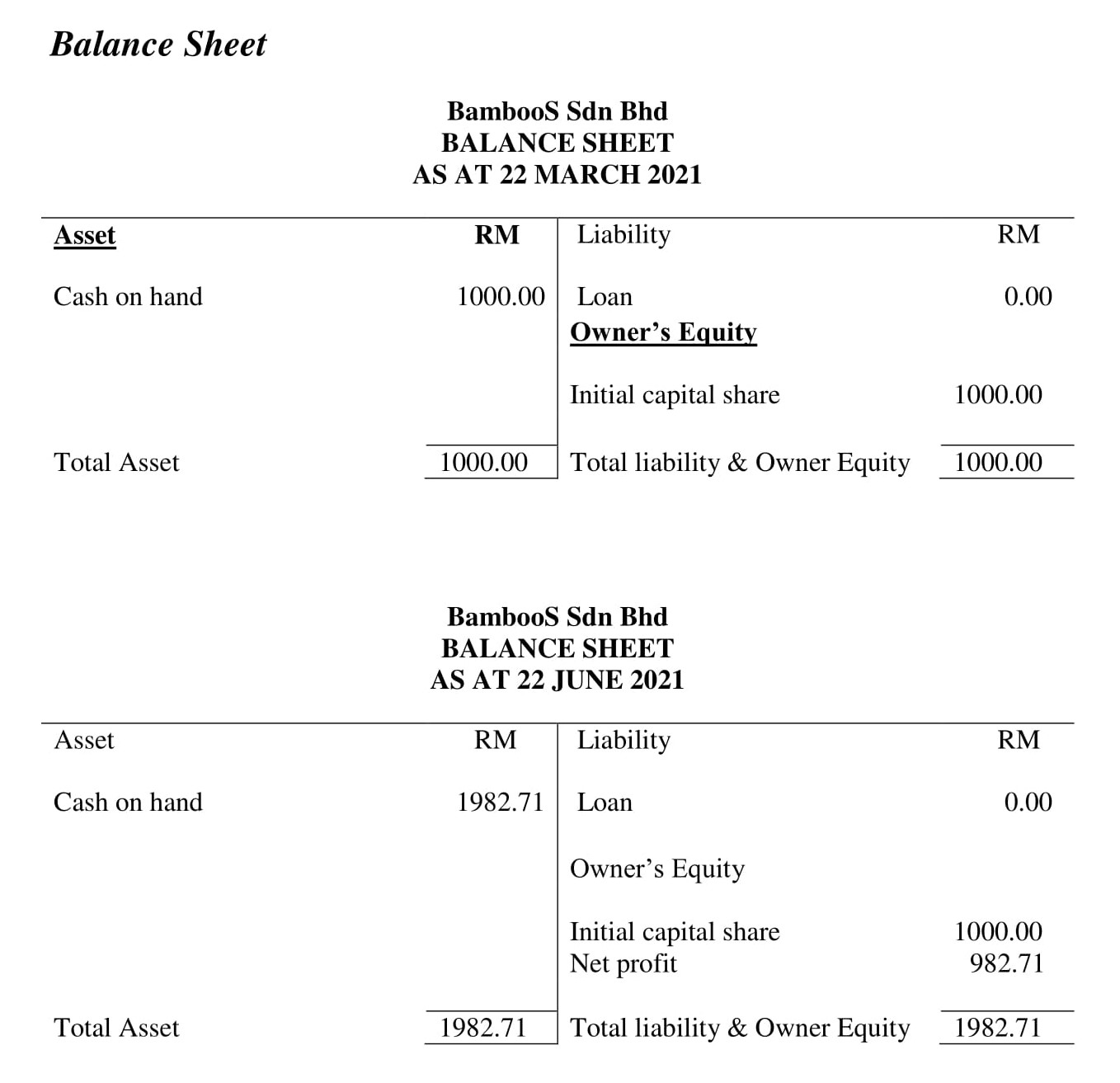
At the start of the business (22 March 2021), the initial capital share is RM 300.00. There is no liability such as a loan.
At the end of 9 weeks’ business (22 June 2021), the cash on hand increased to RM 1982.71, as well as the owner’s equity. The firm's net worth is RM 1982.71, done by subtracting liabilities from assets.
6.9 Financial Analysis
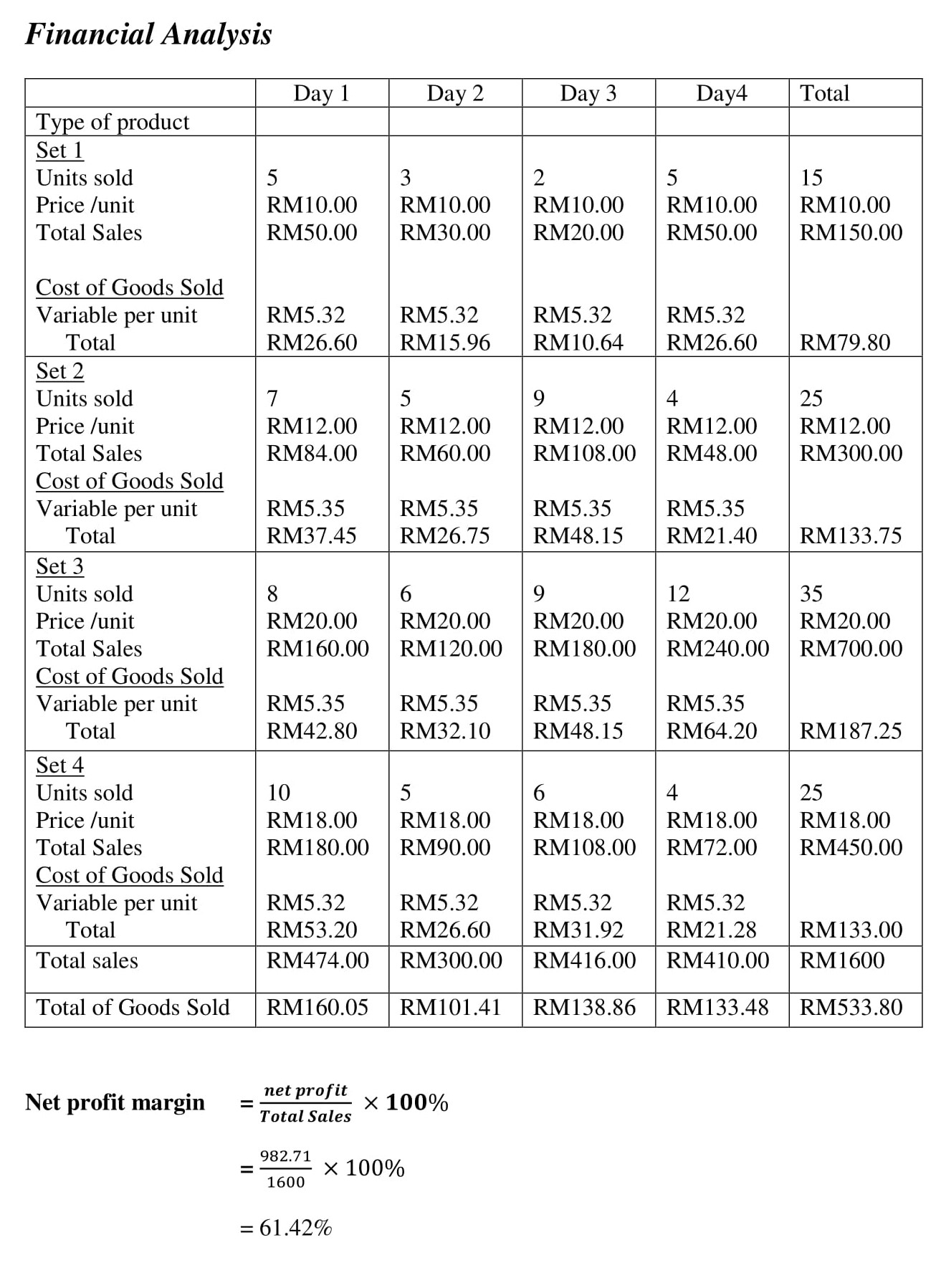
BambooS has a net profit margin of 61.42%. BambooS also has a break-even point of RM 126.50. Sales passing this break-even point means that BambooS can start making profits.
Set 1 has a break-even point of RM 11.90, and set 2 have it at RM 23.72. The break-even point for set 3 is RM 55.34, while set 4 has a break-even point of RM 35.58.
The interest for the business is 0.9827 or 98.27%. This means for every RM 1 capital invested in the business; the shareholders can get back RM 0.98 as profit.
7.0 Conclusion
Based on the business plan template or business proposal example that we have made, BambooS will give us profitable returns. The assumptions we made for these three months are conservative as we know that our company is still in the beginning, and the marketing and promotion are still in the early phase. The company sets systematic planning to reach the target. Thus, BambooS is very confident that our company will be able to grow in the future and become the most popular brand in the world.
We will always ensure that everyone in the company cooperates well in order to achieve the business target profit. We hope that BambooS will be the best company for producing eco-friendly straws in Malaysia. Our company assists UPM students and staff in reducing plastic usage.
Problem Faced and Solutions in Business
Every business will need to face many challenges to sustain success. As a new business, we also must face many things to achieve our business goal.
Firstly, we confirmed the product we would sell; everyone gave their opinions and ideas. This leads to 10 different products and services on the list. So we need to vote for the best one. We had faced a healthy argument on picking the best product. After discussion, we finally came out with the idea of producing an eco-friendly product. We focused on global warming issues and finally decided to produce and sell bamboo straws.
Moreover, we also have to face a conflict in fixing the vendors. We need to find the best vendors that offer the most reasonable price for us to produce the bamboo straw. The cost must be tele with our starting capital. In order to solve this, everyone has done their research on all the possible suppliers until we find the best one to choose from.
To avoid extreme market competitors, our team chose a blue ocean strategy to create a new market to achieve competitive advantages.
Business Proposal Examples For Students PDF
A business proposal is a short business plan. The business proposal describes the business process. However, a business proposal includes an executive summary, problem statements, product, finance, and solution. The example of a business proposal for students certainly guides others to create a business plan. This business plan sample teaches how to write business plan assignments for students. Students might learn how to write a simple business plan and proposal.
The importance of a business plan is crucial to stakeholders, employees, students, and entrepreneurs. Additionally, the business plan example assists employees in creating a professional business proposal.
Author: M M Kobiruzzaman
M M Kobiruzzaman, Content Writer View all posts by M M Kobiruzzaman
16 thoughts on “Business Plan Examples and Sample For Students”
this is wonderful ,,nice work
I need more info
Nice work keep on educating me I bet your help
Good Day! Can I ask your permission to use your template in my class discussion? It is very detailed and all the components present in this format.
Yes, You Can.
Great work,keep it up
great article . check out datatoleas.com
This template is the best I have seen It's so detailed You have everything you are looking for
It's a good sample for up coming entrepreneurs,keep it up 👍🏻
Mr Kobiruzzaman thanks so much am Kimera Kenneth from Uganda but your content is so useful.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
For instance, Chris Guillebeau has a one-page business plan template in his book The $100 Startup. 48 His version is basically an extension of a napkin sketch without the detail of a full business plan. As you progress, you can also consider a brief business plan (about two pages)—if you want to support a rapid business launch—and/or a ...
Lean Business Plan Template PDF. This scannable business plan template allows you to easily identify the most important elements of your plan. Use this template to outline key details pertaining to your business and industry, product or service offerings, target customer segments (and channels to reach them), and to identify sources of revenue.
Provide projections for two to four years in the future, including: 1. Forecasted income (monthly for first two years, then by quarter or year thereafter), 2. Forecasted cash flows by month (monthly for first two years, then by quarter or year thereafter), 3. Forecasted balance sheet for all years (year-end), and. 4.
Our free business planning workbook (PDF) is designed to assist entrepreneurs like you in creating a well-structured and comprehensive business plan. This workbook provides step-by-step guidance and exercises to help you gather and organize the necessary information for your business plan. It covers each of the key aspects of business planning ...
As the road map for a business's development, the business plan. Defines the vision for the company. Establishes the company's strategy. Describes how the strategy will be implemented. Provides a framework for analysis of key issues. Provides a plan for the development of the business. Helps the entrepreneur develop and measure critical ...
What You'll Get: A complete business plan Unlike other blank templates, our business plan examples are complete business plans with all of the text and financial forecasts already filled out. Edit the text to make the plan your own and save hundreds of hours. A professional business plan template All 550 of our business plans are in the SBA-approved format that's proven to raise money from ...
Common items to include are credit histories, resumes, product pictures, letters of reference, licenses, permits, patents, legal documents, and other contracts. Example traditional business plans. Before you write your business plan, read the following example business plans written by fictional business owners.
business owners /operators in fourteen countries by Jonathan T. Scott The Entrepreneur's Guide to Building a Successful Business Everything you need to build your successful business: • Finding a profitable business idea • Choosing a location • Writing a business plan • Business model examples • Determining costs and revenues
Simple Business Plan Template for Entrepreneurs. Follow This Business Plan Outline to Write Your Own. By. Susan Ward. Updated on October 13, 2022. Reviewed by. Thomas J. Catalano. Fact checked by Leila Najafi. In This Article.
Introduction. Chapter 1 - Developing a Business Plan. Chapter 2 - Essential Initial Research. Chapter 3 - Business Models. Chapter 4 - Initial Business Plan Draft. Chapter 5 - Making the Business Plan Realistic. Chapter 6 - Making the Plan Appeal to Stakeholders and Desirable to the Entrepreneur. Chapter 7 - Finishing the Business ...
1. Create Your Executive Summary. The executive summary is a snapshot of your business or a high-level overview of your business purposes and plans. Although the executive summary is the first section in your business plan, most people write it last. The length of the executive summary is not more than two pages.
To write a simple one-page business plan, follow the same core sections as a traditional plan. But instead of lengthy paragraphs and multiple pages covering each area of your business, stick with single sentences and bulleted lists. If a one-page plan sounds like a better option, download our free simple business plan template to get started.
A few minutes on Google will provide plenty of free business plan template options. The following is adapted from the SCORE Association's recommended outline of categories, which covers most of ...
EB-5 Business Plan. Acquisition Business Plan. Private Placement Memorandum. L-1 Visa Business Plan. EB2-NIW Visa Business Plan. EB-5 Regional Center. Exit Business Plan. Franchise Business Plans. As an entrepreneur, effectively pitching your idea to attract investors and secure funding can be a challenge.
Impact. Indicators should link back to your mission, theory of change and strategy. Just enough indicators, and no more: i.e., the critical ones. Adapt measures and process to the stage of the organization. Set and measure interim milestones on the way to longer-term goals. Use measures to improve your program and organization.
ISBN: 9780749467104. Publication Date: 2013-03-28. How to Write a Business Plan, 4th edition gives you the expert guidance you need to make an impact with your written plan, including advice on researching competitors, how to present your management skills and experience and how to effectively communicate your strategic vision.
The Business Plan •Vary in depth, detail, and quality •Tech vs. low tech businesses •Examples •www.bplans.com •WCU Library •"The business planning guide : creating a plan for success in your own business" by David H. Bangs, Jr. •"Business plans handbook. Volume 10 : a compilation of actual business plans developed by
1. It allowed the entrepreneur to view and evaluate the proposed business venture in an objective, critical and practical manner . The business plan can shows the entrepreneur the potential of the business and it can be a guideline for the business management. 2. The function of a business plan is to convince relevant parties of the investment ...
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
A. Synopsis: Entrepreneurship has become a major force i n the global economy. Policy makers across th e world are discovering. that economic growth and prosperity lie in the hands of ...
Sample Entrepreneurship Business Plan - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. This document is a business plan for Bilk Bags Co., a proposed company that will manufacture and sell eco-friendly bags. The plan outlines the company's executive summary, marketing plan, operational plan, human resources plan, and financial plan.
Sample Business Plan mindanao state university iligan institute of technology college of business administration and accountancy department of marketing alibata. ... Entrepreneurship (Entrep 100) 7 Documents. Students shared 7 documents in this course. University Samar College. Academic year: 2021/2022. Uploaded by: MS. Megumin Sato.
An example of a business plan certainly includes the executive summary of the business, operating strategy, start-up financial projections, financial projections, etc. The business plan example for students is also known as the business report format. Business plan writing is a mandatory assignment for students in entrepreneurship.