Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Data Collection Methods | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples

Data Collection Methods | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
Published on 4 May 2022 by Pritha Bhandari .
Data collection is a systematic process of gathering observations or measurements. Whether you are performing research for business, governmental, or academic purposes, data collection allows you to gain first-hand knowledge and original insights into your research problem .
While methods and aims may differ between fields, the overall process of data collection remains largely the same. Before you begin collecting data, you need to consider:
- The aim of the research
- The type of data that you will collect
- The methods and procedures you will use to collect, store, and process the data
To collect high-quality data that is relevant to your purposes, follow these four steps.
Table of contents
Step 1: define the aim of your research, step 2: choose your data collection method, step 3: plan your data collection procedures, step 4: collect the data, frequently asked questions about data collection.
Before you start the process of data collection, you need to identify exactly what you want to achieve. You can start by writing a problem statement : what is the practical or scientific issue that you want to address, and why does it matter?
Next, formulate one or more research questions that precisely define what you want to find out. Depending on your research questions, you might need to collect quantitative or qualitative data :
- Quantitative data is expressed in numbers and graphs and is analysed through statistical methods .
- Qualitative data is expressed in words and analysed through interpretations and categorisations.
If your aim is to test a hypothesis , measure something precisely, or gain large-scale statistical insights, collect quantitative data. If your aim is to explore ideas, understand experiences, or gain detailed insights into a specific context, collect qualitative data.
If you have several aims, you can use a mixed methods approach that collects both types of data.
- Your first aim is to assess whether there are significant differences in perceptions of managers across different departments and office locations.
- Your second aim is to gather meaningful feedback from employees to explore new ideas for how managers can improve.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Based on the data you want to collect, decide which method is best suited for your research.
- Experimental research is primarily a quantitative method.
- Interviews , focus groups , and ethnographies are qualitative methods.
- Surveys , observations, archival research, and secondary data collection can be quantitative or qualitative methods.
Carefully consider what method you will use to gather data that helps you directly answer your research questions.
When you know which method(s) you are using, you need to plan exactly how you will implement them. What procedures will you follow to make accurate observations or measurements of the variables you are interested in?
For instance, if you’re conducting surveys or interviews, decide what form the questions will take; if you’re conducting an experiment, make decisions about your experimental design .
Operationalisation
Sometimes your variables can be measured directly: for example, you can collect data on the average age of employees simply by asking for dates of birth. However, often you’ll be interested in collecting data on more abstract concepts or variables that can’t be directly observed.
Operationalisation means turning abstract conceptual ideas into measurable observations. When planning how you will collect data, you need to translate the conceptual definition of what you want to study into the operational definition of what you will actually measure.
- You ask managers to rate their own leadership skills on 5-point scales assessing the ability to delegate, decisiveness, and dependability.
- You ask their direct employees to provide anonymous feedback on the managers regarding the same topics.
You may need to develop a sampling plan to obtain data systematically. This involves defining a population , the group you want to draw conclusions about, and a sample, the group you will actually collect data from.
Your sampling method will determine how you recruit participants or obtain measurements for your study. To decide on a sampling method you will need to consider factors like the required sample size, accessibility of the sample, and time frame of the data collection.
Standardising procedures
If multiple researchers are involved, write a detailed manual to standardise data collection procedures in your study.
This means laying out specific step-by-step instructions so that everyone in your research team collects data in a consistent way – for example, by conducting experiments under the same conditions and using objective criteria to record and categorise observations.
This helps ensure the reliability of your data, and you can also use it to replicate the study in the future.
Creating a data management plan
Before beginning data collection, you should also decide how you will organise and store your data.
- If you are collecting data from people, you will likely need to anonymise and safeguard the data to prevent leaks of sensitive information (e.g. names or identity numbers).
- If you are collecting data via interviews or pencil-and-paper formats, you will need to perform transcriptions or data entry in systematic ways to minimise distortion.
- You can prevent loss of data by having an organisation system that is routinely backed up.
Finally, you can implement your chosen methods to measure or observe the variables you are interested in.
The closed-ended questions ask participants to rate their manager’s leadership skills on scales from 1 to 5. The data produced is numerical and can be statistically analysed for averages and patterns.
To ensure that high-quality data is recorded in a systematic way, here are some best practices:
- Record all relevant information as and when you obtain data. For example, note down whether or how lab equipment is recalibrated during an experimental study.
- Double-check manual data entry for errors.
- If you collect quantitative data, you can assess the reliability and validity to get an indication of your data quality.
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organisations.
When conducting research, collecting original data has significant advantages:
- You can tailor data collection to your specific research aims (e.g., understanding the needs of your consumers or user testing your website).
- You can control and standardise the process for high reliability and validity (e.g., choosing appropriate measurements and sampling methods ).
However, there are also some drawbacks: data collection can be time-consuming, labour-intensive, and expensive. In some cases, it’s more efficient to use secondary data that has already been collected by someone else, but the data might be less reliable.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analysing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
Reliability and validity are both about how well a method measures something:
- Reliability refers to the consistency of a measure (whether the results can be reproduced under the same conditions).
- Validity refers to the accuracy of a measure (whether the results really do represent what they are supposed to measure).
If you are doing experimental research , you also have to consider the internal and external validity of your experiment.
In mixed methods research , you use both qualitative and quantitative data collection and analysis methods to answer your research question .
Operationalisation means turning abstract conceptual ideas into measurable observations.
For example, the concept of social anxiety isn’t directly observable, but it can be operationally defined in terms of self-rating scores, behavioural avoidance of crowded places, or physical anxiety symptoms in social situations.
Before collecting data , it’s important to consider how you will operationalise the variables that you want to measure.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2022, May 04). Data Collection Methods | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 7 June 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/data-collection-guide/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Other students also liked, qualitative vs quantitative research | examples & methods, triangulation in research | guide, types, examples, what is a conceptual framework | tips & examples.

Data Collection Methods
Data collection is a process of collecting information from all the relevant sources to find answers to the research problem, test the hypothesis (if you are following deductive approach ) and evaluate the outcomes. Data collection methods can be divided into two categories: secondary methods of data collection and primary methods of data collection.
Secondary Data Collection Methods
Secondary data is a type of data that has already been published in books, newspapers, magazines, journals, online portals etc. There is an abundance of data available in these sources about your research area in business studies, almost regardless of the nature of the research area. Therefore, application of appropriate set of criteria to select secondary data to be used in the study plays an important role in terms of increasing the levels of research validity and reliability.
These criteria include, but not limited to date of publication, credential of the author, reliability of the source, quality of discussions, depth of analyses, the extent of contribution of the text to the development of the research area etc. Secondary data collection is discussed in greater depth in Literature Review chapter.
Secondary data collection methods offer a range of advantages such as saving time, effort and expenses. However they have a major disadvantage. Specifically, secondary research does not make contribution to the expansion of the literature by producing fresh (new) data.
Primary Data Collection Methods
Primary data is the type of data that has not been around before. Primary data is unique findings of your research. Primary data collection and analysis typically requires more time and effort to conduct compared to the secondary data research. Primary data collection methods can be divided into two groups: quantitative and qualitative.
Quantitative data collection methods are based on mathematical calculations in various formats. Methods of quantitative data collection and analysis include questionnaires with closed-ended questions, methods of correlation and regression, mean, mode and median and others.
Quantitative methods are cheaper to apply and they can be applied within shorter duration of time compared to qualitative methods. Moreover, due to a high level of standardisation of quantitative methods, it is easy to make comparisons of findings.
Qualitative research methods , on the contrary, do not involve numbers or mathematical calculations. Qualitative research is closely associated with words, sounds, feeling, emotions, colours and other elements that are non-quantifiable.
Qualitative studies aim to ensure greater level of depth of understanding and qualitative data collection methods include interviews, questionnaires with open-ended questions, focus groups, observation, game or role-playing, case studies etc.
Your choice between quantitative or qualitative methods of data collection depends on the area of your research and the nature of research aims and objectives.
My e-book, The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Dissertation in Business Studies: a step by step assistance offers practical assistance to complete a dissertation with minimum or no stress. The e-book covers all stages of writing a dissertation starting from the selection to the research area to submitting the completed version of the work within the deadline.
John Dudovskiy

Fastest Nurse Insight Engine
- MEDICAL ASSISSTANT
- Abdominal Key
- Anesthesia Key
- Basicmedical Key
- Otolaryngology & Ophthalmology
- Musculoskeletal Key
- Obstetric, Gynecology and Pediatric
- Oncology & Hematology
- Plastic Surgery & Dermatology
- Clinical Dentistry
- Radiology Key
- Thoracic Key
- Veterinary Medicine
- Gold Membership
The Research Proposal: Collecting Data
Introduction This chapter is linked to the data collection section of the web program. ‘All research relies on data to underpin new discoveries or discussions of well-established trains of thought. Whether we term them data, evidence, findings or outcomes, they provide the reader with insight into a research project and allow us to critically assess the project itself’ (Serrant-Green 2008: 3). Now your research is becoming really interesting because you are at the stage of interacting with your participants, particularly if you are undertaking your research study within a qualitative paradigm. The data collection stage is crucial to the success of your research study. If you collect poor data or the wrong data, then your results will be meaningless or, worse, false. Importantly, it is crucial when writing your research proposal to be very clear about what data you are going to collect as well as how you are going to collect them. Data collection is simply the formal term for how we gather information. There are many different ways of doing this for both quantitative and qualitative research studies and it is essential that you choose the method that is best suited to your needs. In other words, it must be able to answer your research question or allow you to prove/disprove your hypothesis. It is also important to bear in mind that, as Cormack (2000) points out, no method of collecting data is perfect because every method has its limitations and strengths. Your role as a researcher is to select or adapt a method which is as near perfect as possible for your particular research study, and then you must be able to discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the method you have chosen as well as giving a rationale for why you chose it. Once you have selected your data collection method, you will need to construct a data collection plan so that you can determine step-by-step: how you intend to collect the data; the sequence in which the data will be collected; the time and cost of collecting the data. This will include the actual use of your data collection instrument(s), but you will also need to configure within your plan how much time you will require for: identifying potential subjects for your sample (see chapter 7); explaining the study to your participants; obtaining their consent (Burns & Grove 2005). Once you start your data collection – including the points mentioned above – you may find that practicalities will intrude and that you have to modify your plan. For example, you may find that potential participants need longer to reach a decision as to whether or not they wish to take part, or you may find that interviews are so exhausting that you need longer between them to analyse the data and/or to recover from the previous interview. Interviews can be mentally draining because you have to listen attentively, whilst at the same time thinking of your next question, trying to work out the direction the interview is taking or assessing if the interviewee is fit enough to continue, and so on. Depending on the subject matter, the interview can also be emotionally draining for both the interviewer and the interviewee; the interviewer later faces the same emotions when he/she transcribes the interview. Another point that is very important to bear in mind when thinking about data collection is the importance of ensuring its consistency, particularly in research studies where there is interaction between the researcher and the participants (Burns & Grove 2005). If more than one person is going to take on the role of data collector (e.g. interviewer), it is important to ensure that there is consistency between them as regards interviewing technique, questions asked and approach to participants. This is known as interrater reliability. In addition, it is important that all the data collectors receive the same information about your research study, that they are familiar with the data collection instruments you are using and that they have received adequate and equal training (Burns & Grove 2005). Collecting data One way of characterising the differences between quantitative and qualitative research is by means of the methods that we use (Dodd 2008). In essence, methods of obtaining data for quantitative research studies include tests/experiments and questionnaires, as well as an examination of existing databases (electronic or otherwise). Whereas, methods of obtaining data for qualitative research include interviewing, observations and focus group work (Dodd 2008). No matter what type of research is being carried out, all researchers need to think about (and later perform during the conduct of the actual study) four tasks concerning the process of data collection when writing the research proposal. These are: selecting the subjects; collecting data consistently; maintaining research controls – criteria of sample participants, methodological controls, elimination/admission of bias; solving problems/conflicts that may arise and jeopardise your study throughout the duration of the research project (Burns & Grove 2005). If you have been lucky with the design of your research study, you may have decided to use an established data collection instrument (there are many available for both quantitative and qualitative research studies). However, you may not find something that is suitable for your particular research study, in which case you may decide to develop your own data collection instrument. If you do, it is very important that you test it rigorously, systematically and honestly before the study begins. This will enable you to determine whether the instrument can collect the data you require. In addition, it will allow you to identify any parts that are difficult for participants to understand and/or to answer. Another benefit of pre-testing your data collection instrument is that it allows you to estimate how long it will take to collect the data using that instrument, which, of course, has a bearing on the time allowance in your data collection plan. In fact, for this very reason, it is often considered a good idea to pre-test all the data collection instruments that you may be using (Polit & Hungler 1999). So, now it is time for us to look at the selection of data collection instruments and methods for use in both the quantitative and qualitative research paradigms. Quantitative research – data collection ‘The fundamental principles guiding data collection in quantitative research are that data are derived in a way that is independent of the expectations of the observer and that the data are true representations of a phenomenon’ (Botti & Endacott 2005: 188). According to Botti & Endacott (2005) there are just two approaches to answering quantitative research questions, namely: descriptive; and experimental. Descriptive quantitative research is concerned with the observation of phenomena that occur without any interference on the part of the researcher – there is no manipulation of the observed phenomena. Experimental quantitative research, on the other hand, is concerned with the manipulation of phenomena in order to observe the effects that this manipulation or interference has on other phenomena. The methods of data collection for both types of quantitative research have many similarities. In theoretical terms, quantitative data collection is underscored by four principles: 1. empiricism; 2. measurement; 3. replicability; 4. objectivity. Empiricism is observation and measurement – and whatever is observed or measured must be able to be replicated by others. Replicability is important because it ensures that any results found in the research can be repeated in replication studies by other researchers. Measurement requires the explicit definition of data collection tools and of instruments that have been used to measure the phenomena, whilst objectivity is essential in order to eliminate any biases arising in the data collection and interpretation (Botti & Endacott 2005). In practice, there is a variety of techniques that can be used to collect data in a quantitative research study. However, all of them are geared to numerical collection. These numerical data can be collected by means of: 1. observation; 2. interview; 3. questionnaires; 4. scales; 5. physiological measurement. In quantitative research, the data are collected and recorded systematically, and these are then organised so that they can be entered into a computer database (Burns & Grove 2005). Variables The term ‘variable’ occurs at several points in this and previous chapters and is a very important element of quantitative research, so before we turn to the different data collection methods, a few words about variables are in order, because these are often what are being measured during the collection of data, particularly when using scales and other physiological measurements in experimental research. When you look at many experimental quantitative research studies you will find that the phenomenon of interest is linked to various differences between people or within people, both before and after certain events or treatments. This phenomenon is what we call a ‘variable’. There are two types of variables that we use in quantitative research, namely: independent variables; dependent variables. An independent variable is the experimental factor in the research study that is manipulated by the researcher, whilst the dependent variable is what is being studied to see if the experimental factor has had any effect (Lanoë 2002). For example, if you want to study the effects of two ways of reducing a high temperature in a baby (e.g. tepid sponging and anti-pyretic drug) in order to see which is the more effective, then the different ways of trying to reduce temperature would be the independent variables, and the rate of reduction of temperature would be the dependent variable (i.e. it is dependent on the effectiveness of the independent variables). Observation In quantitative research, the observation must be structured so that there is a defined purpose to it. The first step in structured observational measurement is to define what is to be observed. A definition of observational measurement is ‘the use of structured and unstructured observation to measure study variables’ (Burns & Grove 2005: 744). Once the decision has been made as to what is to be observed, the next step is to decide how the observations are to be made, recorded and coded. Observations can be made in a laboratory or a natural setting, and each can give rise to its own problems. For example, a laboratory is an artificial setting and may alter the behaviour of the participants, either making them more constrained and inhibited than they otherwise would be, or giving them licence to overact and adopt a false persona. Within a natural setting, the same problems of influencing behaviour can arise if the participants are aware that they are being observed. If they are not aware that they are being observed, then there are problems linked to privacy and ethics (see chapter 6). Making observations using a data collection instrument/tool can lead to varying degrees of structure that are imposed by you the researcher – for example, there may be an unstructured observation of interactions between participants (more of a qualitative study), or there may be a more structured collection of data by tabulating such quantitative concepts as frequency of an action or degree of response to an action or treatment (definitely a quantitative study). Polit & Hungler (1999: 314) discuss a serious problem that can arise from the use of observation as a data collection tool, namely its vulnerability to observer bias. They detail a number of biases which can affect the validity and reliability of objective observations: emotions, prejudices, attitudes and values, which may unconsciously colour what the observer is witnessing; personal interest and commitment, which may cause the observer to see what he/she wants to see; anticipation of what is to be observed naturally, which affects what the observer has actually seen; making too hasty decisions on what has been seen before all information has been gathered.’ Polit & Hungler (1999) conclude that it is probably impossible to eliminate observation biases altogether, but the aim should be to minimise them as far as possible. In most cases, a category system is developed for organising and sorting the behaviour or events that are being observed. The categories that are to be observed should be mutually exclusive. The observer may use checklists as an aid to the structured observation (Burns & Grove 2005). Checklists are techniques to indicate whether or not a behaviour or event/happening occurred during the observation. Usually the checklist contains a number of defined behaviours/happenings/events that it has previously been decided will be the units of data that the researcher is interested in for a particular research project. A mark is usually then placed against that behaviour, happening or event, if they do occur. Behaviour that does not appear on the checklist is ignored. Interviews Although interviews are usually associated with qualitative research, they can have a role to play in quantitative research as well. In the case of quantitative research, the interview will be totally structured, with the interviewee being able to choose a response (usually one word) from a series on the interview form. Often the reply can be a simple ‘yes’ or ‘no’, or it may be a number. Alternatively, the interviewee may be asked to choose one item from a list. These replies can then be coded and entered into a database for statistical analysis. The interview may well be linked to a checklist. In quantitative research, an interview is often used in these cases because of the poor return rate of postal questionnaires and checklists. Questionnaires Questionnaires may seem to be an easy option for a researcher, but actually are very difficult to devise and use correctly. However, they can be useful for collecting data on simple and well-defined issues. The design of questionnaires should be carefully planned and piloted to ensure that they provide: the required data; data that can be analysed and used; an unbiased response. Questionnaires should ideally be developed from a pilot study (see chapter 5). There are two types of questions that you can include, depending on whether it is going to be a quantitative or a qualitative questionnaire. These are: closed questions – usually quantitative; open-ended questions – usually qualitative. Often, we are warned against putting ‘leading’ questions in questionnaires. All questions are ‘leading’ in some respect though, but some lead more than others. However, they all lead towards an answer. If you wish to construct your own reliable and valid questionnaire in order to collect high quality data, you have to accept that this is a subtle and sophisticated art. It is all too easy to devise a poor questionnaire, but much more testing to devise a high-quality one, but it is essential that you do, because poorly designed questionnaires produce poor quality data. Lydeard (1991, cited in Mathers & Huang 2004) describes the steps necessary in the process of developing a questionnaire for use as a research tool: Define the area of investigation. Formulate the questions. Choose the sample and maximise the response rate. Pilot and test for validity and reliability. Recognise sources of error. Hagerty & Patusky (1995) describe the process of developing a questionnaire that they went through in order to measure ‘sense of belonging’ through a number of steps: The area of investigation was defined by reviewing the relevant literature. The questions were formulated from a number of sources, including a literature review and clinical experiences, and statements by people who participated in earlier focus group interviews. The process of sampling and piloting was undertaken with community college students and clients diagnosed with major depression in hospital. A third group of Roman Catholic nuns were subsequently sampled. Details of how the response rate was maximised (e.g. paying respondents for completed questionnaires) are also given. A good description of how the validity and reliability testing of the questionnaire was established is also included, for example, a panel of experts assessed content validity, and retest reliability was examined through the studies with the three subject groups. Finally, some consideration was given to the possible sources of error in the whole process of developing the instrument. If you come across a detailed description of how a particular questionnaire was developed such as the one above, you can have confidence in the rigour of the study. But it also gives you some idea of what you have to do if you are developing your own questionnaire, so our advice would be, wherever possible, use an accepted questionnaire, or failing that, to discuss what you want to achieve with an experienced researcher. In any research study which has used a self-developed instrument for data collection, sufficient detail should be given to allow for an appraisal of how it was developed before it was applied in the study. However, what is important is that you recognise that whether or not a questionnaire is an appropriate data collection method depends on the research question that has been asked. Indeed, you should always ask whether the method of collecting data was appropriate whenever you come across a research paper or a paper describing evidence-based care. You also need to ask whether the research methodology the researchers used was the right one for the research question that was being asked. This is why it is important that the authors of a research paper state what the research question or hypothesis is at the very beginning of the paper, in order for you to be able to decide whether or not they are using the correct research methodology and method of data collection. Finally, when you become involved in a research study yourself, you must make sure that you know exactly what your research question is (or hypothesis is if it is experimental quantitative research), and also that it is the correct question for what you want to achieve. Summary of questionnaires Careful questionnaire design is essential in quantitative and qualitative research for the collection of good quality data. You should look for evidence that research methods have been piloted and modified accordingly. Scales Scales are a very common data collection tool for quantitative research studies because they lend themselves to the simple collection of data from a very large sample/population; they also give rise to statistics. You now know that quantitative research involves numbers, and we can define the numerical values with respect to the following measurement scales: nominal scales; ordinal scales; interval scales; ratio scales. Nominal scales A nominal scale is a type of measurement which has only a limited number of possible outcomes which cannot be placed in any order that represents what are considered to be intrinsic properties of the measurements. On a nominal scale, numbers are present in order to establish identity only (e.g. male or female). Nominal scales classify data into distinct categories in which there is no implied ranking. Note that ranking means placing objects, etc. in order – 1st, 2nd … 30th and so on. In nominal scales: Values are assigned to categories, e.g. in a sample, there are 50 men and 39 women. The categories cannot be placed in ranks of 1st, 2nd, 3rd and so on. The numbers assigned have no intrinsic meaning – for example, you may give each of the participants in your research study a number (1, 2, 3, 4 …), in order to make it easier for you to analyse data from your research. Data that are collected here represent categories of a particular variable, for example, gender, where females could be categorised as ‘1’ and males as ‘2’. These numbers have no numerical significance. Ordinal scales An ordinal scale is a type of measurement that classifies data into distinct categories. Here ranking (or ordering) is implied and utilised in the research study. In these scales, the relative values of data are defined in terms of being less than, equal to or greater than other data on the scale. In ordinal scales: Numbers are assigned to categories that correspond to order/ranks (1st, 2nd, and so on). Responses on the scale can be ranked from high to low, or vice versa. The distance between the first and second category does not have to be the same as that between the second and third, or the third and fourth categories. For example, you may want to rank the ages of participants in your research study, and you could do it as an ordinal scale with the nominal numbers (which are assigned when the participants are recruited for the research) below the ages:
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
Related posts:
- The Research Proposal:Research Design
- The Research Proposal: Current Research Issues in Healthcare
- The Research Proposal: Developing the Research Question
- The Research Proposal: Analysing Data
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Comments are closed for this page.

Full access? Get Clinical Tree

- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home QuestionPro QuestionPro Products
Data Collection Methods: Types & Examples
Data is a collection of facts, figures, objects, symbols, and events gathered from different sources. Organizations collect data using various methods to make better decisions. Without data, it would be difficult for organizations to make appropriate decisions, so data is collected from different audiences at various times.
For example, an organization must collect data on product demand, customer preferences, and competitors before launching a new product. If data is not collected beforehand, the organization’s newly launched product may fail for many reasons, such as less demand and inability to meet customer needs.
Although data is a valuable asset for every organization, it does not serve any purpose until it is analyzed or processed to achieve the desired results.
What are Data Collection Methods?
Data collection methods are techniques and procedures for gathering information for research purposes. They can range from simple self-reported surveys to more complex quantitative or qualitative experiments.
Some common data collection methods include surveys , interviews, observations, focus groups, experiments, and secondary data analysis . The data collected through these methods can then be analyzed and used to support or refute research hypotheses and draw conclusions about the study’s subject matter.
Understanding Data Collection Methods
Data collection methods encompass a variety of techniques and tools for gathering quantitative and qualitative data. These methods are integral to the data collection process and ensure accurate and comprehensive data acquisition.
Quantitative data collection methods involve systematic approaches to collecting data, like numerical data, such as surveys, polls, and statistical analysis, aimed at quantifying phenomena and trends.
Conversely, qualitative data collection methods focus on capturing non-numerical information, such as interviews, focus groups, and observations, to delve deeper into understanding attitudes, behaviors, and motivations.
Combining quantitative and qualitative data collection techniques can enrich organizations’ datasets and gain comprehensive insights into complex phenomena.
Effective utilization of accurate data collection tools and techniques enhances the accuracy and reliability of collected data, facilitating informed decision-making and strategic planning.
LEARN ABOUT: Self-Selection Bias
Importance of Data Collection Methods
Data collection methods play a crucial role in the research process as they determine the quality and accuracy of the data collected. Here are some major importance of data collection methods.
- Quality and Accuracy: The choice of data collection technique directly impacts the quality and accuracy of the data obtained. Properly designed methods help ensure that the data collected is error-free and relevant to the research questions.
- Relevance, Validity, and Reliability: Effective data collection methods help ensure that the data collected is relevant to the research objectives, valid (measuring what it intends to measure), and reliable (consistent and reproducible).
- Bias Reduction and Representativeness: Carefully chosen data collection methods can help minimize biases inherent in the research process, such as sampling bias or response bias. They also aid in achieving a representative sample, enhancing the findings’ generalizability.
- Informed Decision Making: Accurate and reliable data collected through appropriate methods provide a solid foundation for making informed decisions based on research findings. This is crucial for both academic research and practical applications in various fields.
- Achievement of Research Objectives: Data collection methods should align with the research objectives to ensure that the collected data effectively addresses the research questions or hypotheses. Properly collected data facilitates the attainment of these objectives.
- Support for Validity and Reliability: Validity and reliability are essential to research validity. The choice of data collection methods can either enhance or detract from the validity and reliability of research findings. Therefore, selecting appropriate methods is critical for ensuring the credibility of the research.
The importance of data collection methods cannot be overstated, as they play a key role in the research study’s overall success and internal validity .
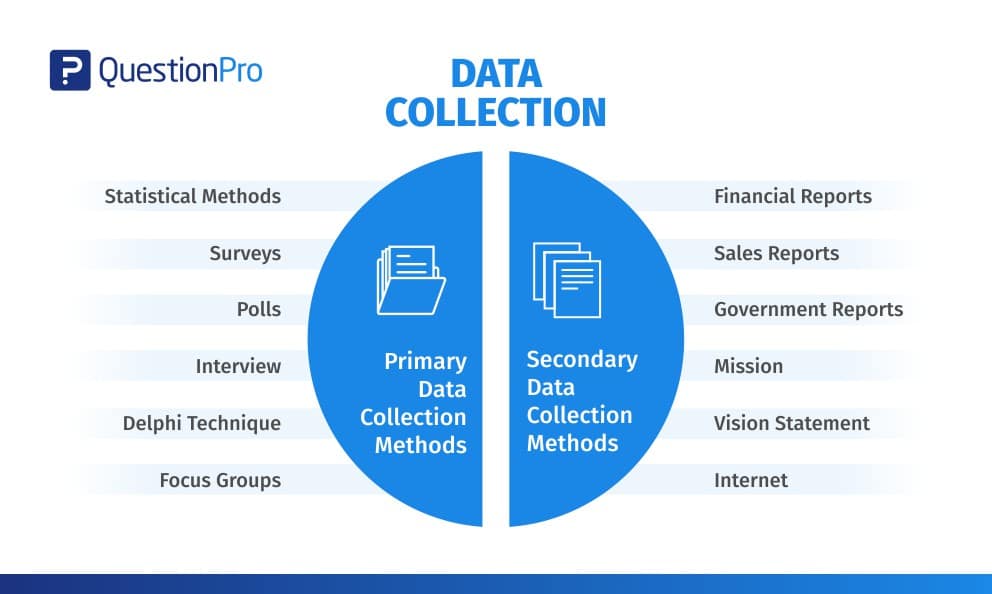
Types of Data Collection Methods
The choice of data collection method depends on the research question being addressed, the type of data needed, and the resources and time available. Data collection methods can be categorized into primary and secondary methods.
1. Primary Data Collection Methods
Primary data is collected from first-hand experience and is not used in the past. The data gathered by primary data collection methods are highly accurate and specific to the research’s motive.
Primary data collection methods can be divided into two categories: quantitative methods and qualitative methods .
Quantitative Methods:
Quantitative techniques for market research and demand forecasting usually use statistical tools. In these techniques, demand is forecasted based on historical data. These methods of primary data collection are generally used to make long-term forecasts. Statistical analysis methods are highly reliable as subjectivity is minimal.

- Time Series Analysis: A time series refers to a sequential order of values of a variable, known as a trend, at equal time intervals. Using patterns, an organization can predict the demand for its products and services over a projected time period.
- Smoothing Techniques: Smoothing techniques can be used in cases where the time series lacks significant trends. They eliminate random variation from the historical demand, helping identify patterns and demand levels to estimate future demand. The most common methods used in smoothing demand forecasting are the simple moving average and weighted moving average methods.
- Barometric Method: Also known as the leading indicators approach, researchers use this method to speculate future trends based on current developments. When past events are considered to predict future events, they act as leading indicators.
Qualitative Methods:
Qualitative data collection methods are especially useful when historical data is unavailable or when numbers or mathematical calculations are unnecessary.
Qualitative research is closely associated with words, sounds, feelings, emotions, colors, and non-quantifiable elements. These techniques are based on experience, judgment, intuition, conjecture, emotion, etc.
Quantitative methods do not provide the motive behind participants’ responses, often don’t reach underrepresented populations, and require long periods of time to collect the data. Hence, it is best to combine quantitative methods with qualitative methods.
1. Surveys: Surveys collect data from the target audience and gather insights into their preferences, opinions, choices, and feedback related to their products and services. Most survey software offers a wide range of question types.
You can also use a ready-made survey template to save time and effort. Online surveys can be customized to match the business’s brand by changing the theme, logo, etc. They can be distributed through several channels, such as email, website, offline app, QR code, social media, etc.
You can select the channel based on your audience’s type and source. Once the data is collected, survey software can generate various reports and run analytics algorithms to discover hidden insights.
A survey dashboard can give you statistics related to response rate, completion rate, demographics-based filters, export and sharing options, etc. Integrating survey builders with third-party apps can maximize the effort spent on online real-time data collection .
Practical business intelligence relies on the synergy between analytics and reporting , where analytics uncovers valuable insights, and reporting communicates these findings to stakeholders.
2. Polls: Polls comprise one single or multiple-choice question . They are useful when you need to get a quick pulse of the audience’s sentiments. Because they are short, it is easier to get responses from people.
Like surveys, online polls can be embedded into various platforms. Once the respondents answer the question, they can also be shown how they compare to others’ responses.
Interviews: In this method, the interviewer asks the respondents face-to-face or by telephone.
3. Interviews: In face-to-face interviews, the interviewer asks a series of questions to the interviewee in person and notes down responses. If it is not feasible to meet the person, the interviewer can go for a telephone interview.
This form of data collection is suitable for only a few respondents. It is too time-consuming and tedious to repeat the same process if there are many participants.

4. Delphi Technique: In the Delphi method, market experts are provided with the estimates and assumptions of other industry experts’ forecasts. Experts may reconsider and revise their estimates and assumptions based on this information. The consensus of all experts on demand forecasts constitutes the final demand forecast.
5. Focus Groups: Focus groups are one example of qualitative data in education . In a focus group, a small group of people, around 8-10 members, discuss the common areas of the research problem. Each individual provides his or her insights on the issue concerned.
A moderator regulates the discussion among the group members. At the end of the discussion, the group reaches a consensus.
6. Questionnaire: A questionnaire is a printed set of open-ended or closed-ended questions that respondents must answer based on their knowledge and experience with the issue. The questionnaire is part of the survey, whereas the questionnaire’s end goal may or may not be a survey.
2. Secondary Data Collection Methods
Secondary data is data that has been used in the past. The researcher can obtain data from the data sources , both internal and external, to the organizational data .
Internal sources of secondary data:
- Organization’s health and safety records
- Mission and vision statements
- Financial Statements
- Sales Report
- CRM Software
- Executive summaries
External sources of secondary data:
- Government reports
- Press releases
- Business journals
Secondary data collection methods can also involve quantitative and qualitative techniques. Secondary data is easily available, less time-consuming, and expensive than primary data. However, the authenticity of the data gathered cannot be verified using these methods.
Secondary data collection methods can also involve quantitative and qualitative observation techniques. Secondary data is easily available, less time-consuming, and more expensive than primary data.
However, the authenticity of the data gathered cannot be verified using these methods.
Regardless of the data collection method of your choice, there must be direct communication with decision-makers so that they understand and commit to acting according to the results.
For this reason, we must pay special attention to the analysis and presentation of the information obtained. Remember that these data must be useful and functional to us, so the data collection method has much to do with it.
LEARN ABOUT: Data Asset Management
How Can QuestionPro Help to Create Effective Data Collection?
QuestionPro is a comprehensive online survey software platform that can greatly assist in various data collection methods. Here’s how it can help:
- Survey Creation: QuestionPro offers a user-friendly interface for creating surveys with various question types, including multiple-choice, open-ended, Likert scale, and more. Researchers can customize surveys to fit their specific research needs and objectives.
- Diverse Distribution Channels: The platform provides multiple channels for distributing surveys, including email, web links, social media, and website embedding surveys. This enables researchers to reach a wide audience and collect data efficiently.
- Panel Management: QuestionPro offers panel management features, allowing researchers to create and manage panels of respondents for targeted data collection. This is particularly useful for longitudinal studies or when targeting specific demographics.
- Data Analysis Tools: The platform includes robust data analysis tools that enable researchers to analyze survey responses in real-time. Researchers can generate customizable reports, visualize data through charts and graphs, and identify trends and patterns within the data.
- Data Security and Compliance: QuestionPro prioritizes data security and compliance with regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA. The platform offers features such as SSL encryption, data masking, and secure data storage to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of collected data.
- Mobile Compatibility: With the increasing use of mobile devices, QuestionPro ensures that surveys are mobile-responsive, allowing respondents to participate in surveys conveniently from their smartphones or tablets.
- Integration Capabilities: QuestionPro integrates with various third-party tools and platforms, including CRMs, email marketing software, and analytics tools. This allows researchers to streamline their data collection processes and incorporate survey data into their existing workflows.
- Customization and Branding: Researchers can customize surveys with their branding elements, such as logos, colors, and themes, enhancing the professional appearance of surveys and increasing respondent engagement.
The conclusion you obtain from your investigation will set the course of the company’s decision-making, so present your report clearly and list the steps you followed to obtain those results.
Make sure that whoever will take the corresponding actions understands the importance of the information collected and that it gives them the solutions they expect.
QuestionPro offers a comprehensive suite of features and tools that can significantly streamline the data collection process, from survey creation to analysis, while ensuring data security and compliance. Remember that at QuestionPro, we can help you collect data easily and efficiently. Request a demo and learn about all the tools we have for you.
MORE LIKE THIS

Life@QuestionPro: The Journey of Kristie Lawrence
Jun 7, 2024

How Can I Help You? — Tuesday CX Thoughts
Jun 5, 2024

Why Multilingual 360 Feedback Surveys Provide Better Insights
Jun 3, 2024

Raked Weighting: A Key Tool for Accurate Survey Results
May 31, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Anaesth
- v.60(9); 2016 Sep
How to write a research proposal?
Department of Anaesthesiology, Bangalore Medical College and Research Institute, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India
Devika Rani Duggappa
Writing the proposal of a research work in the present era is a challenging task due to the constantly evolving trends in the qualitative research design and the need to incorporate medical advances into the methodology. The proposal is a detailed plan or ‘blueprint’ for the intended study, and once it is completed, the research project should flow smoothly. Even today, many of the proposals at post-graduate evaluation committees and application proposals for funding are substandard. A search was conducted with keywords such as research proposal, writing proposal and qualitative using search engines, namely, PubMed and Google Scholar, and an attempt has been made to provide broad guidelines for writing a scientifically appropriate research proposal.
INTRODUCTION
A clean, well-thought-out proposal forms the backbone for the research itself and hence becomes the most important step in the process of conduct of research.[ 1 ] The objective of preparing a research proposal would be to obtain approvals from various committees including ethics committee [details under ‘Research methodology II’ section [ Table 1 ] in this issue of IJA) and to request for grants. However, there are very few universally accepted guidelines for preparation of a good quality research proposal. A search was performed with keywords such as research proposal, funding, qualitative and writing proposals using search engines, namely, PubMed, Google Scholar and Scopus.
Five ‘C’s while writing a literature review

BASIC REQUIREMENTS OF A RESEARCH PROPOSAL
A proposal needs to show how your work fits into what is already known about the topic and what new paradigm will it add to the literature, while specifying the question that the research will answer, establishing its significance, and the implications of the answer.[ 2 ] The proposal must be capable of convincing the evaluation committee about the credibility, achievability, practicality and reproducibility (repeatability) of the research design.[ 3 ] Four categories of audience with different expectations may be present in the evaluation committees, namely academic colleagues, policy-makers, practitioners and lay audiences who evaluate the research proposal. Tips for preparation of a good research proposal include; ‘be practical, be persuasive, make broader links, aim for crystal clarity and plan before you write’. A researcher must be balanced, with a realistic understanding of what can be achieved. Being persuasive implies that researcher must be able to convince other researchers, research funding agencies, educational institutions and supervisors that the research is worth getting approval. The aim of the researcher should be clearly stated in simple language that describes the research in a way that non-specialists can comprehend, without use of jargons. The proposal must not only demonstrate that it is based on an intelligent understanding of the existing literature but also show that the writer has thought about the time needed to conduct each stage of the research.[ 4 , 5 ]
CONTENTS OF A RESEARCH PROPOSAL
The contents or formats of a research proposal vary depending on the requirements of evaluation committee and are generally provided by the evaluation committee or the institution.
In general, a cover page should contain the (i) title of the proposal, (ii) name and affiliation of the researcher (principal investigator) and co-investigators, (iii) institutional affiliation (degree of the investigator and the name of institution where the study will be performed), details of contact such as phone numbers, E-mail id's and lines for signatures of investigators.
The main contents of the proposal may be presented under the following headings: (i) introduction, (ii) review of literature, (iii) aims and objectives, (iv) research design and methods, (v) ethical considerations, (vi) budget, (vii) appendices and (viii) citations.[ 4 ]
Introduction
It is also sometimes termed as ‘need for study’ or ‘abstract’. Introduction is an initial pitch of an idea; it sets the scene and puts the research in context.[ 6 ] The introduction should be designed to create interest in the reader about the topic and proposal. It should convey to the reader, what you want to do, what necessitates the study and your passion for the topic.[ 7 ] Some questions that can be used to assess the significance of the study are: (i) Who has an interest in the domain of inquiry? (ii) What do we already know about the topic? (iii) What has not been answered adequately in previous research and practice? (iv) How will this research add to knowledge, practice and policy in this area? Some of the evaluation committees, expect the last two questions, elaborated under a separate heading of ‘background and significance’.[ 8 ] Introduction should also contain the hypothesis behind the research design. If hypothesis cannot be constructed, the line of inquiry to be used in the research must be indicated.
Review of literature
It refers to all sources of scientific evidence pertaining to the topic in interest. In the present era of digitalisation and easy accessibility, there is an enormous amount of relevant data available, making it a challenge for the researcher to include all of it in his/her review.[ 9 ] It is crucial to structure this section intelligently so that the reader can grasp the argument related to your study in relation to that of other researchers, while still demonstrating to your readers that your work is original and innovative. It is preferable to summarise each article in a paragraph, highlighting the details pertinent to the topic of interest. The progression of review can move from the more general to the more focused studies, or a historical progression can be used to develop the story, without making it exhaustive.[ 1 ] Literature should include supporting data, disagreements and controversies. Five ‘C's may be kept in mind while writing a literature review[ 10 ] [ Table 1 ].
Aims and objectives
The research purpose (or goal or aim) gives a broad indication of what the researcher wishes to achieve in the research. The hypothesis to be tested can be the aim of the study. The objectives related to parameters or tools used to achieve the aim are generally categorised as primary and secondary objectives.
Research design and method
The objective here is to convince the reader that the overall research design and methods of analysis will correctly address the research problem and to impress upon the reader that the methodology/sources chosen are appropriate for the specific topic. It should be unmistakably tied to the specific aims of your study.
In this section, the methods and sources used to conduct the research must be discussed, including specific references to sites, databases, key texts or authors that will be indispensable to the project. There should be specific mention about the methodological approaches to be undertaken to gather information, about the techniques to be used to analyse it and about the tests of external validity to which researcher is committed.[ 10 , 11 ]
The components of this section include the following:[ 4 ]
Population and sample
Population refers to all the elements (individuals, objects or substances) that meet certain criteria for inclusion in a given universe,[ 12 ] and sample refers to subset of population which meets the inclusion criteria for enrolment into the study. The inclusion and exclusion criteria should be clearly defined. The details pertaining to sample size are discussed in the article “Sample size calculation: Basic priniciples” published in this issue of IJA.
Data collection
The researcher is expected to give a detailed account of the methodology adopted for collection of data, which include the time frame required for the research. The methodology should be tested for its validity and ensure that, in pursuit of achieving the results, the participant's life is not jeopardised. The author should anticipate and acknowledge any potential barrier and pitfall in carrying out the research design and explain plans to address them, thereby avoiding lacunae due to incomplete data collection. If the researcher is planning to acquire data through interviews or questionnaires, copy of the questions used for the same should be attached as an annexure with the proposal.
Rigor (soundness of the research)
This addresses the strength of the research with respect to its neutrality, consistency and applicability. Rigor must be reflected throughout the proposal.
It refers to the robustness of a research method against bias. The author should convey the measures taken to avoid bias, viz. blinding and randomisation, in an elaborate way, thus ensuring that the result obtained from the adopted method is purely as chance and not influenced by other confounding variables.

Consistency
Consistency considers whether the findings will be consistent if the inquiry was replicated with the same participants and in a similar context. This can be achieved by adopting standard and universally accepted methods and scales.
Applicability
Applicability refers to the degree to which the findings can be applied to different contexts and groups.[ 13 ]
Data analysis
This section deals with the reduction and reconstruction of data and its analysis including sample size calculation. The researcher is expected to explain the steps adopted for coding and sorting the data obtained. Various tests to be used to analyse the data for its robustness, significance should be clearly stated. Author should also mention the names of statistician and suitable software which will be used in due course of data analysis and their contribution to data analysis and sample calculation.[ 9 ]
Ethical considerations
Medical research introduces special moral and ethical problems that are not usually encountered by other researchers during data collection, and hence, the researcher should take special care in ensuring that ethical standards are met. Ethical considerations refer to the protection of the participants' rights (right to self-determination, right to privacy, right to autonomy and confidentiality, right to fair treatment and right to protection from discomfort and harm), obtaining informed consent and the institutional review process (ethical approval). The researcher needs to provide adequate information on each of these aspects.
Informed consent needs to be obtained from the participants (details discussed in further chapters), as well as the research site and the relevant authorities.
When the researcher prepares a research budget, he/she should predict and cost all aspects of the research and then add an additional allowance for unpredictable disasters, delays and rising costs. All items in the budget should be justified.
Appendices are documents that support the proposal and application. The appendices will be specific for each proposal but documents that are usually required include informed consent form, supporting documents, questionnaires, measurement tools and patient information of the study in layman's language.
As with any scholarly research paper, you must cite the sources you used in composing your proposal. Although the words ‘references and bibliography’ are different, they are used interchangeably. It refers to all references cited in the research proposal.
Successful, qualitative research proposals should communicate the researcher's knowledge of the field and method and convey the emergent nature of the qualitative design. The proposal should follow a discernible logic from the introduction to presentation of the appendices.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business How to Write a Research Proposal: A Step-by-Step
How to Write a Research Proposal: A Step-by-Step
Written by: Danesh Ramuthi Nov 29, 2023

A research proposal is a structured outline for a planned study on a specific topic. It serves as a roadmap, guiding researchers through the process of converting their research idea into a feasible project.
The aim of a research proposal is multifold: it articulates the research problem, establishes a theoretical framework, outlines the research methodology and highlights the potential significance of the study. Importantly, it’s a critical tool for scholars seeking grant funding or approval for their research projects.
Crafting a good research proposal requires not only understanding your research topic and methodological approaches but also the ability to present your ideas clearly and persuasively. Explore Venngage’s Proposal Maker and Research Proposals Templates to begin your journey in writing a compelling research proposal.
What to include in a research proposal?
In a research proposal, include a clear statement of your research question or problem, along with an explanation of its significance. This should be followed by a literature review that situates your proposed study within the context of existing research.
Your proposal should also outline the research methodology, detailing how you plan to conduct your study, including data collection and analysis methods.
Additionally, include a theoretical framework that guides your research approach, a timeline or research schedule, and a budget if applicable. It’s important to also address the anticipated outcomes and potential implications of your study. A well-structured research proposal will clearly communicate your research objectives, methods and significance to the readers.

How to format a research proposal?
Formatting a research proposal involves adhering to a structured outline to ensure clarity and coherence. While specific requirements may vary, a standard research proposal typically includes the following elements:
- Title Page: Must include the title of your research proposal, your name and affiliations. The title should be concise and descriptive of your proposed research.
- Abstract: A brief summary of your proposal, usually not exceeding 250 words. It should highlight the research question, methodology and the potential impact of the study.
- Introduction: Introduces your research question or problem, explains its significance, and states the objectives of your study.
- Literature review: Here, you contextualize your research within existing scholarship, demonstrating your knowledge of the field and how your research will contribute to it.
- Methodology: Outline your research methods, including how you will collect and analyze data. This section should be detailed enough to show the feasibility and thoughtfulness of your approach.
- Timeline: Provide an estimated schedule for your research, breaking down the process into stages with a realistic timeline for each.
- Budget (if applicable): If your research requires funding, include a detailed budget outlining expected cost.
- References/Bibliography: List all sources referenced in your proposal in a consistent citation style.

How to write a research proposal in 11 steps?
Writing a research proposal template in structured steps ensures a comprehensive and coherent presentation of your research project. Let’s look at the explanation for each of the steps here:
Step 1: Title and Abstract Step 2: Introduction Step 3: Research objectives Step 4: Literature review Step 5: Methodology Step 6: Timeline Step 7: Resources Step 8: Ethical considerations Step 9: Expected outcomes and significance Step 10: References Step 11: Appendices
Step 1: title and abstract.
Select a concise, descriptive title and write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology and expected outcomes. The abstract should include your research question, the objectives you aim to achieve, the methodology you plan to employ and the anticipated outcomes.
Step 2: Introduction
In this section, introduce the topic of your research, emphasizing its significance and relevance to the field. Articulate the research problem or question in clear terms and provide background context, which should include an overview of previous research in the field.
Step 3: Research objectives
Here, you’ll need to outline specific, clear and achievable objectives that align with your research problem. These objectives should be well-defined, focused and measurable, serving as the guiding pillars for your study. They help in establishing what you intend to accomplish through your research and provide a clear direction for your investigation.
Step 4: Literature review
In this part, conduct a thorough review of existing literature related to your research topic. This involves a detailed summary of key findings and major contributions from previous research. Identify existing gaps in the literature and articulate how your research aims to fill these gaps. The literature review not only shows your grasp of the subject matter but also how your research will contribute new insights or perspectives to the field.
Step 5: Methodology
Describe the design of your research and the methodologies you will employ. This should include detailed information on data collection methods, instruments to be used and analysis techniques. Justify the appropriateness of these methods for your research.
Step 6: Timeline
Construct a detailed timeline that maps out the major milestones and activities of your research project. Break the entire research process into smaller, manageable tasks and assign realistic time frames to each. This timeline should cover everything from the initial research phase to the final submission, including periods for data collection, analysis and report writing.
It helps in ensuring your project stays on track and demonstrates to reviewers that you have a well-thought-out plan for completing your research efficiently.
Step 7: Resources
Identify all the resources that will be required for your research, such as specific databases, laboratory equipment, software or funding. Provide details on how these resources will be accessed or acquired.
If your research requires funding, explain how it will be utilized effectively to support various aspects of the project.
Step 8: Ethical considerations
Address any ethical issues that may arise during your research. This is particularly important for research involving human subjects. Describe the measures you will take to ensure ethical standards are maintained, such as obtaining informed consent, ensuring participant privacy, and adhering to data protection regulations.
Here, in this section you should reassure reviewers that you are committed to conducting your research responsibly and ethically.
Step 9: Expected outcomes and significance
Articulate the expected outcomes or results of your research. Explain the potential impact and significance of these outcomes, whether in advancing academic knowledge, influencing policy or addressing specific societal or practical issues.
Step 10: References
Compile a comprehensive list of all the references cited in your proposal. Adhere to a consistent citation style (like APA or MLA) throughout your document. The reference section not only gives credit to the original authors of your sourced information but also strengthens the credibility of your proposal.
Step 11: Appendices
Include additional supporting materials that are pertinent to your research proposal. This can be survey questionnaires, interview guides, detailed data analysis plans or any supplementary information that supports the main text.
Appendices provide further depth to your proposal, showcasing the thoroughness of your preparation.

Research proposal FAQs
1. how long should a research proposal be.
The length of a research proposal can vary depending on the requirements of the academic institution, funding body or specific guidelines provided. Generally, research proposals range from 500 to 1500 words or about one to a few pages long. It’s important to provide enough detail to clearly convey your research idea, objectives and methodology, while being concise. Always check
2. Why is the research plan pivotal to a research project?
The research plan is pivotal to a research project because it acts as a blueprint, guiding every phase of the study. It outlines the objectives, methodology, timeline and expected outcomes, providing a structured approach and ensuring that the research is systematically conducted.
A well-crafted plan helps in identifying potential challenges, allocating resources efficiently and maintaining focus on the research goals. It is also essential for communicating the project’s feasibility and importance to stakeholders, such as funding bodies or academic supervisors.

Mastering how to write a research proposal is an essential skill for any scholar, whether in social and behavioral sciences, academic writing or any field requiring scholarly research. From this article, you have learned key components, from the literature review to the research design, helping you develop a persuasive and well-structured proposal.
Remember, a good research proposal not only highlights your proposed research and methodology but also demonstrates its relevance and potential impact.
For additional support, consider utilizing Venngage’s Proposal Maker and Research Proposals Templates , valuable tools in crafting a compelling proposal that stands out.
Whether it’s for grant funding, a research paper or a dissertation proposal, these resources can assist in transforming your research idea into a successful submission.
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Proposal – Types, Template and Example
Research Proposal – Types, Template and Example
Table of Contents

Research Proposal
Research proposal is a document that outlines a proposed research project . It is typically written by researchers, scholars, or students who intend to conduct research to address a specific research question or problem.
Types of Research Proposal
Research proposals can vary depending on the nature of the research project and the specific requirements of the funding agency, academic institution, or research program. Here are some common types of research proposals:
Academic Research Proposal
This is the most common type of research proposal, which is prepared by students, scholars, or researchers to seek approval and funding for an academic research project. It includes all the essential components mentioned earlier, such as the introduction, literature review , methodology , and expected outcomes.
Grant Proposal
A grant proposal is specifically designed to secure funding from external sources, such as government agencies, foundations, or private organizations. It typically includes additional sections, such as a detailed budget, project timeline, evaluation plan, and a description of the project’s alignment with the funding agency’s priorities and objectives.
Dissertation or Thesis Proposal
Students pursuing a master’s or doctoral degree often need to submit a proposal outlining their intended research for their dissertation or thesis. These proposals are usually more extensive and comprehensive, including an in-depth literature review, theoretical framework, research questions or hypotheses, and a detailed methodology.
Research Project Proposal
This type of proposal is often prepared by researchers or research teams within an organization or institution. It outlines a specific research project that aims to address a particular problem, explore a specific area of interest, or provide insights for decision-making. Research project proposals may include sections on project management, collaboration, and dissemination of results.
Research Fellowship Proposal
Researchers or scholars applying for research fellowships may be required to submit a proposal outlining their proposed research project. These proposals often emphasize the novelty and significance of the research and its alignment with the goals and objectives of the fellowship program.
Collaborative Research Proposal
In cases where researchers from multiple institutions or disciplines collaborate on a research project, a collaborative research proposal is prepared. This proposal highlights the objectives, responsibilities, and contributions of each collaborator, as well as the overall research plan and coordination mechanisms.
Research Proposal Outline
A research proposal typically follows a standard outline that helps structure the document and ensure all essential components are included. While the specific headings and subheadings may vary slightly depending on the requirements of your institution or funding agency, the following outline provides a general structure for a research proposal:
- Title of the research proposal
- Name of the researcher(s) or principal investigator(s)
- Affiliation or institution
- Date of submission
- A concise summary of the research proposal, typically limited to 200-300 words.
- Briefly introduce the research problem or question, state the objectives, summarize the methodology, and highlight the expected outcomes or significance of the research.
- Provide an overview of the subject area and the specific research problem or question.
- Present relevant background information, theories, or concepts to establish the need for the research.
- Clearly state the research objectives or research questions that the study aims to address.
- Indicate the significance or potential contributions of the research.
- Summarize and analyze relevant studies, theories, or scholarly works.
- Identify research gaps or unresolved issues that your study intends to address.
- Highlight the novelty or uniqueness of your research.
- Describe the overall approach or research design that will be used (e.g., experimental, qualitative, quantitative).
- Justify the chosen approach based on the research objectives and question.
- Explain how data will be collected (e.g., surveys, interviews, experiments).
- Describe the sampling strategy and sample size, if applicable.
- Address any ethical considerations related to data collection.
- Outline the data analysis techniques or statistical methods that will be applied.
- Explain how the data will be interpreted and analyzed to answer the research question(s).
- Provide a detailed schedule or timeline that outlines the various stages of the research project.
- Specify the estimated duration for each stage, including data collection, analysis, and report writing.
- State the potential outcomes or results of the research.
- Discuss the potential significance or contributions of the study to the field.
- Address any potential limitations or challenges that may be encountered.
- Identify the resources required to conduct the research, such as funding, equipment, or access to data.
- Specify any collaborations or partnerships necessary for the successful completion of the study.
- Include a list of cited references in the appropriate citation style (e.g., APA, MLA).
———————————————————————————————–
Research Proposal Example Template
Here’s an example of a research proposal to give you an idea of how it can be structured:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Adolescent Well-being: A Mixed-Methods Study
This research proposal aims to investigate the impact of social media on the well-being of adolescents. The study will employ a mixed-methods approach, combining quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews to gather comprehensive data. The research objectives include examining the relationship between social media use and mental health, exploring the role of peer influence in shaping online behaviors, and identifying strategies for promoting healthy social media use among adolescents. The findings of this study will contribute to the understanding of the effects of social media on adolescent well-being and inform the development of targeted interventions.
1. Introduction
1.1 Background and Context:
Adolescents today are immersed in social media platforms, which have become integral to their daily lives. However, concerns have been raised about the potential negative impact of social media on their well-being, including increased rates of depression, anxiety, and body dissatisfaction. It is crucial to investigate this phenomenon further and understand the underlying mechanisms to develop effective strategies for promoting healthy social media use among adolescents.
1.2 Research Objectives:
The main objectives of this study are:
- To examine the association between social media use and mental health outcomes among adolescents.
- To explore the influence of peer relationships and social comparison on online behaviors.
- To identify strategies and interventions to foster positive social media use and enhance adolescent well-being.
2. Literature Review
Extensive research has been conducted on the impact of social media on adolescents. Existing literature suggests that excessive social media use can contribute to negative outcomes, such as low self-esteem, cyberbullying, and addictive behaviors. However, some studies have also highlighted the positive aspects of social media, such as providing opportunities for self-expression and social support. This study will build upon this literature by incorporating both quantitative and qualitative approaches to gain a more nuanced understanding of the relationship between social media and adolescent well-being.
3. Methodology
3.1 Research Design:
This study will adopt a mixed-methods approach, combining quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews. The quantitative phase will involve administering standardized questionnaires to a representative sample of adolescents to assess their social media use, mental health indicators, and perceived social support. The qualitative phase will include in-depth interviews with a subset of participants to explore their experiences, motivations, and perceptions related to social media use.
3.2 Data Collection Methods:
Quantitative data will be collected through an online survey distributed to schools in the target region. The survey will include validated scales to measure social media use, mental health outcomes, and perceived social support. Qualitative data will be collected through semi-structured interviews with a purposive sample of participants. The interviews will be audio-recorded and transcribed for thematic analysis.
3.3 Data Analysis:
Quantitative data will be analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis to examine the relationships between variables. Qualitative data will be analyzed thematically to identify common themes and patterns within participants’ narratives. Integration of quantitative and qualitative findings will provide a comprehensive understanding of the research questions.
4. Timeline
The research project will be conducted over a period of 12 months, divided into specific phases, including literature review, study design, data collection, analysis, and report writing. A detailed timeline outlining the key milestones and activities is provided in Appendix A.
5. Expected Outcomes and Significance
This study aims to contribute to the existing literature on the impact of social media on adolescent well-being by employing a mixed-methods approach. The findings will inform the development of evidence-based interventions and guidelines to promote healthy social media use among adolescents. This research has the potential to benefit adolescents, parents, educators, and policymakers by providing insights into the complex relationship between social media and well-being and offering strategies for fostering positive online experiences.
6. Resources
The resources required for this research include access to a representative sample of adolescents, research assistants for data collection, statistical software for data analysis, and funding to cover survey administration and participant incentives. Ethical considerations will be taken into account, ensuring participant confidentiality and obtaining informed consent.
7. References
Research Proposal Writing Guide
Writing a research proposal can be a complex task, but with proper guidance and organization, you can create a compelling and well-structured proposal. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
- Understand the requirements: Familiarize yourself with the guidelines and requirements provided by your institution, funding agency, or program. Pay attention to formatting, page limits, specific sections or headings, and any other instructions.
- Identify your research topic: Choose a research topic that aligns with your interests, expertise, and the goals of your program or funding opportunity. Ensure that your topic is specific, focused, and relevant to the field of study.
- Conduct a literature review : Review existing literature and research relevant to your topic. Identify key theories, concepts, methodologies, and findings related to your research question. This will help you establish the context, identify research gaps, and demonstrate the significance of your proposed study.
- Define your research objectives and research question(s): Clearly state the objectives you aim to achieve with your research. Formulate research questions that address the gaps identified in the literature review. Your research objectives and questions should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Develop a research methodology: Determine the most appropriate research design and methodology for your study. Consider whether quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-methods approaches will best address your research question(s). Describe the data collection methods, sampling strategy, data analysis techniques, and any ethical considerations associated with your research.
- Create a research plan and timeline: Outline the various stages of your research project, including tasks, milestones, and deadlines. Develop a realistic timeline that considers factors such as data collection, analysis, and report writing. This plan will help you stay organized and manage your time effectively throughout the research process.
- A. Introduction: Provide background information on the research problem, highlight its significance, and introduce your research objectives and questions.
- B. Literature review: Summarize relevant literature, identify gaps, and justify the need for your proposed research.
- C . Methodology: Describe your research design, data collection methods, sampling strategy, data analysis techniques, and any ethical considerations.
- D . Expected outcomes and significance: Explain the potential outcomes, contributions, and implications of your research.
- E. Resources: Identify the resources required to conduct your research, such as funding, equipment, or access to data.
- F . References: Include a list of cited references in the appropriate citation style.
- Revise and proofread: Review your proposal for clarity, coherence, and logical flow. Check for grammar and spelling errors. Seek feedback from mentors, colleagues, or advisors to refine and improve your proposal.
- Finalize and submit: Make any necessary revisions based on feedback and finalize your research proposal. Ensure that you have met all the requirements and formatting guidelines. Submit your proposal within the specified deadline.
Research Proposal Length
The length of a research proposal can vary depending on the specific guidelines provided by your institution or funding agency. However, research proposals typically range from 1,500 to 3,000 words, excluding references and any additional supporting documents.
Purpose of Research Proposal
The purpose of a research proposal is to outline and communicate your research project to others, such as academic institutions, funding agencies, or potential collaborators. It serves several important purposes:
- Demonstrate the significance of the research: A research proposal explains the importance and relevance of your research project. It outlines the research problem or question, highlights the gaps in existing knowledge, and explains how your study will contribute to the field. By clearly articulating the significance of your research, you can convince others of its value and potential impact.
- Provide a clear research plan: A research proposal outlines the methodology, design, and approach you will use to conduct your study. It describes the research objectives, data collection methods, data analysis techniques, and potential outcomes. By presenting a clear research plan, you demonstrate that your study is well-thought-out, feasible, and likely to produce meaningful results.
- Secure funding or support: For researchers seeking funding or support for their projects, a research proposal is essential. It allows you to make a persuasive case for why your research is deserving of financial resources or institutional backing. The proposal explains the budgetary requirements, resources needed, and potential benefits of the research, helping you secure the necessary funding or support.
- Seek feedback and guidance: Presenting a research proposal provides an opportunity to receive feedback and guidance from experts in your field. It allows you to engage in discussions and receive suggestions for refining your research plan, improving the methodology, or addressing any potential limitations. This feedback can enhance the quality of your study and increase its chances of success.
- Establish ethical considerations: A research proposal also addresses ethical considerations associated with your study. It outlines how you will ensure participant confidentiality, obtain informed consent, and adhere to ethical guidelines and regulations. By demonstrating your awareness and commitment to ethical research practices, you build trust and credibility in your proposed study.
Importance of Research Proposal
The research proposal holds significant importance in the research process. Here are some key reasons why research proposals are important:
- Planning and organization: A research proposal requires careful planning and organization of your research project. It forces you to think through the research objectives, research questions, methodology, and potential outcomes before embarking on the actual study. This planning phase helps you establish a clear direction and framework for your research, ensuring that your efforts are focused and purposeful.
- Demonstrating the significance of the research: A research proposal allows you to articulate the significance and relevance of your study. By providing a thorough literature review and clearly defining the research problem or question, you can showcase the gaps in existing knowledge that your research aims to address. This demonstrates to others, such as funding agencies or academic institutions, why your research is important and deserving of support.
- Obtaining funding and resources: Research proposals are often required to secure funding for your research project. Funding agencies and organizations need to evaluate the feasibility and potential impact of the proposed research before allocating resources. A well-crafted research proposal helps convince funders of the value of your research and increases the likelihood of securing financial support, grants, or scholarships.
- Receiving feedback and guidance: Presenting a research proposal provides an opportunity to seek feedback and guidance from experts in your field. By sharing your research plan and objectives with others, you can benefit from their insights and suggestions. This feedback can help refine your research design, strengthen your methodology, and ensure that your study is rigorous and well-informed.
- Ethical considerations: A research proposal addresses ethical considerations associated with your study. It outlines how you will protect the rights and welfare of participants, maintain confidentiality, obtain informed consent, and adhere to ethical guidelines and regulations. This emphasis on ethical practices ensures that your research is conducted responsibly and with integrity.
- Enhancing collaboration and partnerships: A research proposal can facilitate collaborations and partnerships with other researchers, institutions, or organizations. When presenting your research plan, you may attract the interest of potential collaborators who share similar research interests or possess complementary expertise. Collaborative partnerships can enrich your study, expand your resources, and foster knowledge exchange.
- Establishing a research trajectory: A research proposal serves as a foundation for your research project. Once approved, it becomes a roadmap that guides your study’s implementation, data collection, analysis, and reporting. It helps maintain focus and ensures that your research stays on track and aligned with the initial objectives.
When to Write Research Proposal
The timing of when to write a research proposal can vary depending on the specific requirements and circumstances. However, here are a few common situations when it is appropriate to write a research proposal:
- Academic research: If you are a student pursuing a research degree, such as a Ph.D. or Master’s by research, you will typically be required to write a research proposal as part of the application process. This is usually done before starting the research program to outline your proposed study and seek approval from the academic institution.
- Funding applications: When applying for research grants, scholarships, or funding from organizations or institutions, you will often need to submit a research proposal. Funding agencies require a detailed description of your research project, including its objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. Writing a research proposal in this context is necessary to secure financial support for your study.
- Research collaborations: When collaborating with other researchers, institutions, or organizations on a research project, it is common to prepare a research proposal. This helps outline the research objectives, roles and responsibilities, and expected contributions from each party. Writing a research proposal in this case allows all collaborators to align their efforts and ensure a shared understanding of the project.
- Research project within an organization: If you are conducting research within an organization, such as a company or government agency, you may be required to write a research proposal to gain approval and support for your study. This proposal outlines the research objectives, methodology, resources needed, and expected outcomes, ensuring that the project aligns with the organization’s goals and objectives.
- Independent research projects: Even if you are not required to write a research proposal, it can still be beneficial to develop one for your independent research projects. Writing a research proposal helps you plan and structure your study, clarify your research objectives, and anticipate potential challenges or limitations. It also allows you to communicate your research plans effectively to supervisors, mentors, or collaborators.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Business Proposal – Templates, Examples and Guide

How To Write A Grant Proposal – Step-by-Step...

How To Write A Business Proposal – Step-by-Step...

How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step...

How To Write A Proposal – Step By Step Guide...

Grant Proposal – Example, Template and Guide

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 2: Choose your data collection method. Based on the data you want to collect, decide which method is best suited for your research. Experimental research is primarily a quantitative method. Interviews, focus groups, and ethnographies are qualitative methods. Surveys, observations, archival research, and secondary data collection can be ...
Data collection is the process of gathering and collecting information from various sources to analyze and make informed decisions based on the data collected. This can involve various methods, such as surveys, interviews, experiments, and observation. In order for data collection to be effective, it is important to have a clear understanding ...
Data Collection Methods. Data collection is a process of collecting information from all the relevant sources to find answers to the research problem, test the hypothesis (if you are following deductive approach) and evaluate the outcomes. Data collection methods can be divided into two categories: secondary methods of data collection and ...
PDF | Learn how to choose the best data collection methods and tools for your research project, with examples and tips from ResearchGate experts. | Download and read the full-text PDF.
A research proposal aims to show why your project is worthwhile. It should explain the context, objectives, and methods of your research. FAQ About us . Our editors ... Finalize sampling methods and data analysis methods; 13th February: 3. Data collection and preparation:
Types of Data Collection Methods. Data collection methods are important, because how the information collected is used and what explanations it can generate are determined by the methodology and analytical approach applied by the researcher. 1, 2 Five key data collection methods are presented here, with their strengths and limitations described ...
There are actually two kinds of mixing of the six major methods of data collection (Johnson & Turner, 2003). The first is intermethod mixing, which means two or more of the different methods of data collection are used in a research study. This is seen in the two examples in the previous paragraph.
on data collection (we refer to several at the end of this chapter). Its pur-pose is to guide the proposal writer in stipulating the methods of choice for his study and in describing for the reader how the data will inform his research questions. How the researcher plans to use these methods, however, depends on several considerations.
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about: Your overall research objectives and approach. Whether you'll rely on primary research or secondary research. Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects. Your data collection methods.
Data Collection, Research Methodology, Data Collection Methods, Academic Research Paper, Data Collection Techniques. I. INTRODUCTION Different methods for gathering information regarding specific variables of the study aiming to employ them in the data analysis phase to achieve the results of the study, gain the answer of the research
The Research Proposal: Collecting Data. This chapter is linked to the data collection section of the web program. 'All research relies on data to underpin new discoveries or discussions of well-established trains of thought. Whether we term them data, evidence, findings or outcomes, they provide the reader with insight into a research project ...
Here is an explanation of each step: 1. Title and Abstract. Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research. Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal. 2.
Data Collection | Definition, Methods & Examples. Published on June 5, 2020 by Pritha Bhandari.Revised on June 21, 2023. Data collection is a systematic process of gathering observations or measurements. Whether you are performing research for business, governmental or academic purposes, data collection allows you to gain first-hand knowledge and original insights into your research problem.
It puts the proposal in context. 3. The introduction typically begins with a statement of the research problem in precise and clear terms. 1. The importance of the statement of the research problem 5: The statement of the problem is the essential basis for the construction of a research proposal (research objectives, hypotheses, methodology ...
The importance of data collection methods cannot be overstated, as they play a key role in the research study's overall success and internal validity. Types of Data Collection Methods. The choice of data collection method depends on the research question being addressed, the type of data needed, and the resources and time available.
Gustave Flaubert. CHAPTER 3: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY. 3.1 Introduction. As it is indicated in the title, this chapter includes the research methodology of. the dissertation. In more details, in this ...
A proposal needs to show how your work fits into what is already known about the topic and what new paradigm will it add to the literature, while specifying the question that the research will answer, establishing its significance, and the implications of the answer. [ 2] The proposal must be capable of convincing the evaluation committee about ...
Data Collection Methods. Describe the methods used to collect data (e.g., surveys, interviews, observations) ... Research methodology is typically written after the research proposal has been approved and before the actual research is conducted. It should be written prior to data collection and analysis, as it provides a clear roadmap for the ...
Learn about the concept, types, and issues of data collection methods, with examples and tips from ResearchGate's experts. Download the PDF for free.
Answer: The methods section of a research proposal contains details about how you will conduct your research. It includes your study design - the methodology and methods that you plan to use - as well as your work plan - the activities that you plan to undertake to complete your project. The methods section of a research proposal must contain ...
research proposal is the formal description of this process. The first part of the proposal will include the research question to be answered along with a statement of why the area of research is important and what is known already. The second part of the proposal is the methods section, where the plan for answering the research question is given.
While many books and articles guide various qualitative research methods and analyses, there is currently no concise resource that explains and differentiates among the most common qualitative approaches. We believe novice qualitative researchers, students planning the design of a qualitative study or taking an introductory qualitative research course, and faculty teaching such courses can ...
Writing a research proposal template in structured steps ensures a comprehensive and coherent presentation of your research project. Let's look at the explanation for each of the steps here: Step 1: Title and Abstract. Step 2: Introduction. Step 3: Research objectives. Step 4: Literature review.
Research proposals can vary depending on the nature of the research project and the specific requirements of the funding agency, academic institution, or research program. ... and approach you will use to conduct your study. It describes the research objectives, data collection methods, data analysis techniques, and potential outcomes. By ...
Currently, there are more methods to obtain human motion data with different features, such as depth, skeleton, optical flow, point cloud, and other human motion data with various modal features widely used in gesture recognition. (a) Depth image data features. Depth images contain important 3D spatial information.