- Email: [email protected]

- Medical Tourism
- Health and Nutrition

Navigating Vertex Presentation: Unveiling Types, Positions, Complications, and Risks
Brace yourself for a journey through the enigmatic realm of vertex presentation in pregnancy. This captivating voyage will unravel the mysteries surrounding the positioning of your little one inside the womb. Picture this: your baby, like a seasoned traveler, assumes various positions as they gear up for their grand entrance into the world. But with every journey, there are tales of twists and turns. In this article, we’ll embark on an exploration of the different types and positions of vertex presentation, shedding light on the complications that might arise along the way. Are you ready to embark on this adventure of knowledge? Let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
Introduction to Vertex Presentation
Understanding fetal presentation.
Imagine the baby nestled in the womb, getting ready for the world outside. How they position themselves matters, not just for their comfort, but also for a safe and smooth journey into the world. Vertex presentation refers to the baby’s head pointing downward towards the birth canal. This is the ideal position for a vaginal birth, setting the stage for an awe-inspiring dance of nature.
Importance of Vertex Presentation
Why does vertex presentation take center stage? Well, think of the baby’s head as the ultimate pioneer. When the head leads the way, it paves a path that minimizes complications during delivery. This isn’t just any head-first journey; it’s a strategic masterpiece that nature has perfected over eons. But like any grand performance, there are variations, surprises, and even a touch of drama.
Types of Vertex Presentation
Occiput anterior: the optimal position.
Imagine the baby facing your spine, with their head slightly tilted downwards, chin tucked in. This is the occiput anterior position—the gold standard of vertex presentation. It’s like a skilled explorer charting the best route through uncharted territories. This position eases the baby’s descent through the birth canal, a journey your little one is about to undertake with vigor.
Occiput Posterior: The Adventurous Flip
In the occiput posterior position, the baby’s head is still leading the way, but with a twist. The back of their head faces your spine, making this journey a bit more adventurous. It’s as if your baby decided to take in the scenic route. While this position can pose challenges, the body knows how to adapt, turning this expedition into a remarkable tale of resilience.
Face Presentation: The Expressive Arrival
Picture your baby’s face taking the lead, gazing at the world they’re about to enter. Face presentation is like a theatrical entrance—an expression of eagerness. While relatively rare, it adds a touch of uniqueness to your baby’s birth story. It’s as if your little one wanted to make sure their arrival was unforgettable.
Brow Presentation: The Furrowed Path
In the brow presentation, the baby’s forehead assumes the lead. This can be compared to a bold adventurer choosing an unconventional route. While brow presentations are less common, they remind us that the journey to birth is as diverse as the individuals taking it. Nature’s unpredictability is part of what makes this experience so awe-inspiring.
Positions of Vertex Presentation
Engaging in engagement.
As the due date draws near, your baby is gearing up for their grand entrance. The engagement phase marks the beginning of the final countdown. The baby’s head starts to settle into the pelvis, aligning itself with the birth canal. It’s like a pilot preparing to land a plane—a critical phase that sets the stage for a safe touchdown.
The Dance of Descent
Once engaged, the baby starts their descent. This is where gravity takes on a crucial role, guiding your little one towards the exit. It’s like watching a skilled mountaineer descending a steep slope—each movement calculated, every step an achievement. The body’s intricate mechanisms ensure that the journey is gradual and controlled.
Navigating Through Flexion and Extension
As the baby journeys through the birth canal, their head flexes and extends, adapting to the twists and turns of the passage. Flexion allows the smallest part of the head to lead the way, while extension aids in navigating corners. It’s like a skilled dancer adjusting their moves to fit the rhythm of the music, ensuring a harmonious performance.
Complications During Vertex Presentation
Shoulder dystocia: when the passage narrows.
While nature has its plan, sometimes the path encounters unexpected obstacles. Shoulder dystocia occurs when the baby’s head passes through the birth canal, but their shoulders get stuck behind the pelvic bone. It’s like a car stuck in a narrow alley—requiring quick thinking and skilled maneuvers to overcome.
Prolapsed Umbilical Cord: An Urgent Twist
Imagine the umbilical cord, that lifeline connecting your baby to nourishment, taking an unexpected turn. In cases of prolapsed umbilical cord, the cord slips through the cervix ahead of the baby. It’s like the thread connecting two worlds suddenly getting tangled. Immediate action is crucial, akin to untangling a delicate knot.
Perineal Tears: The Aftermath of Delivery
As your baby triumphantly emerges into the world, the journey leaves its mark. Perineal tears, though common, are like battle scars of childbirth. These tears occur when the tissue between the vaginal opening and anus stretches or tears during delivery. Healing these tears is like tending to a precious garden—requiring care and time.
Risks and Challenges
Maternal risks: a careful balancing act.
While nature orchestrates the dance of birth, it’s not without its challenges. In vertex presentation, certain positions might increase the risk of maternal complications. Pressure on the back or prolonged labor can lead to discomfort or even back pain. However, healthcare providers are adept at managing such situations, ensuring the safety and well-being of both mother and baby.
Fetal Risks: Navigating the Unknown
As your baby navigates their journey through the birth canal, there’s a delicate balance between the baby’s needs and the challenges they might encounter. For example, prolonged labor might lead to oxygen deprivation for the baby. But fret not—this is where vigilant monitoring and expert guidance come into play, safeguarding your baby’s welfare.
Medical Interventions: When Nature Needs a Helping Hand
In the grand tapestry of childbirth, medical interventions occasionally play a vital role. Sometimes, the baby’s journey might need a nudge in the right direction. This could involve gentle manipulation or even assistance using instruments. Think of it as a gentle breeze guiding a kite—it’s a collaborative effort between nature and science.
Preparing for a Smooth Presentation
Optimal fetal positioning techniques.
Just as you might prepare for a long journey, your baby can benefit from optimal positioning techniques. Engaging in activities that promote a balanced pelvis, like sitting on an exercise ball, can encourage the baby into the ideal position. It’s like setting the stage for a well-choreographed performance.
Exercises and Posture Adjustments
Prenatal exercises, such as pelvic tilts and lunges, can help keep your baby in an optimal position. It’s akin to practicing dance moves before a big recital—your baby is learning the steps for their grand entrance.
Role of Healthcare Providers
Your healthcare provider is your guiding star throughout this journey. They’re the experts who will monitor the baby’s position, offer guidance, and ensure your well-being. Trust them like you would trust a seasoned captain navigating uncharted waters.
Epidurals and Their Impact
How epidurals influence presentation.
Epidurals, those miraculous pain-relief interventions, can also impact how the baby positions itself. Sometimes, epidurals can lead to a baby settling into a posterior position. This isn’t a cause for alarm; it’s just nature’s way of adapting to the circumstances.
Weighing the Pros and Cons
As you consider pain relief options, remember that each choice has its benefits and potential impacts. Epidurals offer relief, but they can influence the baby’s positioning. Discuss your preferences and concerns with your healthcare provider, finding the balance that suits you best.
Navigating Complications: A Personal Story
Real-life account of overcoming complications.
Birth stories are like individual masterpieces, each with its unique brushstrokes. Listen to Sarah’s journey—a tale of unexpected challenges, quick decisions, and the unwavering spirit of resilience. Sarah’s story reminds us that even when complications arise, the human spirit has a remarkable capacity to triumph.
The Strength of Resilience
Sarah’s story echoes the strength that resides within every mother. It’s as if adversity sharpens our resolve, transforming challenges into stepping stones towards victory. Her journey serves as a beacon of hope, illustrating the power of determination in the face of the unknown.
When the Unexpected Strikes
Dealing with emergency situations.
Life has its own rhythm, occasionally punctuated by unexpected beats. In childbirth, emergencies might arise—situations where quick decisions and expert responses are essential. Just as a captain navigates through rough seas, healthcare providers adeptly steer through the storms, ensuring the safety of both mother and baby.
The Triumph of Quick Decisions
In the realm of childbirth, split-second decisions can make all the difference. Whether it’s addressing fetal distress or managing complications, healthcare providers are like skilled conductors—orchestrating a symphony of actions to ensure a safe delivery.
The Role of Technology
Ultrasounds: peeking into the womb.
Ultrasounds offer a magical glimpse into the womb’s mysteries. They provide insights into the baby’s position, allowing healthcare providers to make informed decisions. It’s like getting a sneak peek of a breathtaking sunrise before it graces the horizon.
Monitoring Fetal Well-Being
Throughout the journey of vertex presentation, technology acts as a vigilant guardian. Electronic fetal monitoring keeps track of the baby’s heart rate, ensuring their well-being. Think of it as a safety net, always ready to catch any unexpected twists in the tale.
Cesarean Birth: A Safe Haven
When vaginal delivery isn’t an option.
In the grand play of childbirth, sometimes the script takes an unexpected turn. If vaginal delivery poses risks or complications, a cesarean birth becomes the hero of the day. It’s like a well-planned escape route, ensuring both mother and baby reach the destination safely.
The Surgical Marvel of Cesarean Birth
Cesarean births are a marvel of modern medicine, a testament to the leaps humanity has taken. Like a skilled craftsman, the surgeon carefully brings the baby into the world. While it might not be the anticipated path, it’s a journey towards a new chapter in the story of life.
Postpartum Care and Healing
Recovery after vertex presentation.
As the curtain falls on the stage of childbirth, a new act begins—the postpartum period. Just as a dancer needs time to rest after a performance, your body requires healing. Postpartum care involves nurturing your physical and emotional well-being, stepping into the role of both mother and self-care advocate.
Emotional and Physical Healing
Birth is a profound experience that leaves an imprint on both body and soul. Embrace the whirlwind of emotions, from joy to exhaustion. Surround yourself with a supportive network, allowing yourself the time and space to heal and flourish.
Creating a Supportive Birth Plan
Communicating your preferences.
A birth plan is like a roadmap for your childbirth journey—a document that outlines your preferences and desires. Discuss your wishes with your healthcare provider, ensuring that your voice is heard in the symphony of birth.
Building a Solid Birth Team
Just as a ship needs a skilled crew, your birth journey thrives with a supportive team. From healthcare providers to partners, each plays a unique role. Craft a team that understands and supports your choices, creating an atmosphere of trust and comfort.
Partner’s Guide to Supporting Vertex Presentation
Standing strong in the delivery room.
Partners, you’re not just spectators—you’re co-captains of this voyage. Your presence, support, and encouragement can be the wind in the sails, propelling your partner forward. Be the anchor of strength, ready to weather any storm.
Providing Emotional and Physical Support
Birth is an emotional rollercoaster, and your partner might need a steady hand to hold onto. Comfort, reassure, and advocate for her needs. Whether it’s offering a word of encouragement or a soothing touch, your role is irreplaceable.
In the tapestry of childbirth, vertex presentation is a thread woven with awe and wonder. It’s a journey of discovery, a dance of adaptation, and a celebration of life’s marvels. As mothers and families embrace the unpredictability of this voyage, they embody the essence of courage and resilience. So, here’s to the adventure—the adventure of vertex presentation—where twists and turns lead to triumph, and every challenge becomes a stepping stone towards the greatest gift of all: a new life.
FAQ’s
Absolutely! Babies are like explorers, and their journey is dynamic. It’s not uncommon for a baby to shift positions during labor, guided by the dance of nature.
While it can make labor a bit more challenging, the body often adapts to facilitate delivery. Healthcare providers are skilled at assisting in such scenarios.
Yes, certain exercises, posture adjustments, and even prenatal yoga can help encourage the baby into an ideal position for birth.
Medical technology, like ultrasounds, provides insights into fetal positioning and well-being, allowing healthcare providers to make informed decisions.
Not necessarily. Many non-optimal positions can still result in vaginal births, with the right support and guidance from healthcare professionals.
Note: Remember, it’s always a good idea to consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before making significant changes to your diet, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or specific dietary requirements.
Book an Appointment
Recent articles.

Find Best Doctors In India
- Top Cardiologist
- Top Oncologist
- Top Orthopaedic
- Top Gastrologist
- Top Spine Specialist
- Top Obstetrics and Gynecologist
- Top Paediatrician
Find Top Hospitals
- Top Hospitals In Chennai
- Top Hospitals In Bangalore
- Top Hospitals In Hyderabad
- Top Hospitals In Delhi
- Top Hospitals In Mumbai
- Top Hospitals In Ahmedabad
- Top Hospitals In Indore
- Top Hospitals In Kolkata
Top Doctors
- Nurse at Home
- Doctor at Home
- Physiotherapy at Home
- Rehab at Home
- Ortho Rehab
- Heart Rehab
Book Doctor Appointment
- Book Health Check-up
- Book Nurse at Home
- Book Physio at Home
- Book Doctor at Home
- Buy/Rent Medical Equipments
- Angioplasty
- Kidney Stones
Quick Links
- Medicine Info
- Preventive Health
- Privacy Policy
© 2023 MaxinHealth. All Rights Reserved.
- Terms & Conditions
Appointments at Mayo Clinic
- Pregnancy week by week
- Fetal presentation before birth
The way a baby is positioned in the uterus just before birth can have a big effect on labor and delivery. This positioning is called fetal presentation.
Babies twist, stretch and tumble quite a bit during pregnancy. Before labor starts, however, they usually come to rest in a way that allows them to be delivered through the birth canal headfirst. This position is called cephalic presentation. But there are other ways a baby may settle just before labor begins.
Following are some of the possible ways a baby may be positioned at the end of pregnancy.
Head down, face down
When a baby is head down, face down, the medical term for it is the cephalic occiput anterior position. This the most common position for a baby to be born in. With the face down and turned slightly to the side, the smallest part of the baby's head leads the way through the birth canal. It is the easiest way for a baby to be born.
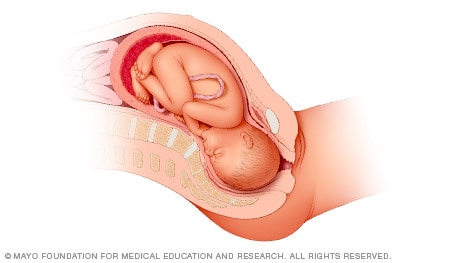
Head down, face up
When a baby is head down, face up, the medical term for it is the cephalic occiput posterior position. In this position, it might be harder for a baby's head to go under the pubic bone during delivery. That can make labor take longer.
Most babies who begin labor in this position eventually turn to be face down. If that doesn't happen, and the second stage of labor is taking a long time, a member of the health care team may reach through the vagina to help the baby turn. This is called manual rotation.
In some cases, a baby can be born in the head-down, face-up position. Use of forceps or a vacuum device to help with delivery is more common when a baby is in this position than in the head-down, face-down position. In some cases, a C-section delivery may be needed.
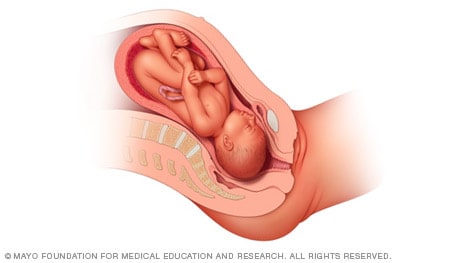
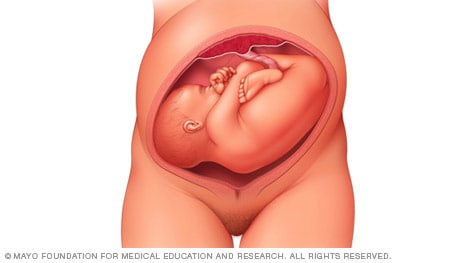
Frank breech
When a baby's feet or buttocks are in place to come out first during birth, it's called a breech presentation. This happens in about 3% to 4% of babies close to the time of birth. The baby shown below is in a frank breech presentation. That's when the knees aren't bent, and the feet are close to the baby's head. This is the most common type of breech presentation.
If you are more than 36 weeks into your pregnancy and your baby is in a frank breech presentation, your health care professional may try to move the baby into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. It involves one or two members of the health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
If the procedure isn't successful, or if the baby moves back into a breech position, talk with a member of your health care team about the choices you have for delivery. Most babies in a frank breech position are born by planned C-section.

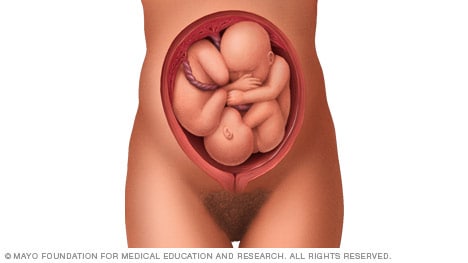
Complete and incomplete breech
A complete breech presentation, as shown below, is when the baby has both knees bent and both legs pulled close to the body. In an incomplete breech, one or both of the legs are not pulled close to the body, and one or both of the feet or knees are below the baby's buttocks. If a baby is in either of these positions, you might feel kicking in the lower part of your belly.
If you are more than 36 weeks into your pregnancy and your baby is in a complete or incomplete breech presentation, your health care professional may try to move the baby into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. It involves one or two members of the health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
If the procedure isn't successful, or if the baby moves back into a breech position, talk with a member of your health care team about the choices you have for delivery. Many babies in a complete or incomplete breech position are born by planned C-section.

When a baby is sideways — lying horizontal across the uterus, rather than vertical — it's called a transverse lie. In this position, the baby's back might be:
- Down, with the back facing the birth canal.
- Sideways, with one shoulder pointing toward the birth canal.
- Up, with the hands and feet facing the birth canal.
Although many babies are sideways early in pregnancy, few stay this way when labor begins.
If your baby is in a transverse lie during week 37 of your pregnancy, your health care professional may try to move the baby into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. External cephalic version involves one or two members of your health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
If the procedure isn't successful, or if the baby moves back into a transverse lie, talk with a member of your health care team about the choices you have for delivery. Many babies who are in a transverse lie are born by C-section.
If you're pregnant with twins and only the twin that's lower in the uterus is head down, as shown below, your health care provider may first deliver that baby vaginally.
Then, in some cases, your health care team may suggest delivering the second twin in the breech position. Or they may try to move the second twin into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. External cephalic version involves one or two members of the health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
Your health care team may suggest delivery by C-section for the second twin if:
- An attempt to deliver the baby in the breech position is not successful.
- You do not want to try to have the baby delivered vaginally in the breech position.
- An attempt to move the baby into a head-down position is not successful.
- You do not want to try to move the baby to a head-down position.
In some cases, your health care team may advise that you have both twins delivered by C-section. That might happen if the lower twin is not head down, the second twin has low or high birth weight as compared to the first twin, or if preterm labor starts.
- Landon MB, et al., eds. Normal labor and delivery. In: Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2021. https://www.clinicalkey.com. Accessed May 19, 2023.
- Holcroft Argani C, et al. Occiput posterior position. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 19, 2023.
- Frequently asked questions: If your baby is breech. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/if-your-baby-is-breech. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Hofmeyr GJ. Overview of breech presentation. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Strauss RA, et al. Transverse fetal lie. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Chasen ST, et al. Twin pregnancy: Labor and delivery. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Cohen R, et al. Is vaginal delivery of a breech second twin safe? A comparison between delivery of vertex and non-vertex second twins. The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine. 2021; doi:10.1080/14767058.2021.2005569.
- Marnach ML (expert opinion). Mayo Clinic. May 31, 2023.
Products and Services
- A Book: Obstetricks
- A Book: Mayo Clinic Guide to a Healthy Pregnancy
- 3rd trimester pregnancy
- Fetal development: The 3rd trimester
- Overdue pregnancy
- Pregnancy due date calculator
- Prenatal care: 3rd trimester
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
- Opportunities
Mayo Clinic Press
Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press .
- Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence
- The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book
- Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance
- FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment
- Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book
- Healthy Lifestyle
Your gift holds great power – donate today!
Make your tax-deductible gift and be a part of the cutting-edge research and care that's changing medicine.
Labour and Delivery Care Module: 8. Abnormal Presentations and Multiple Pregnancies
Study session 8 abnormal presentations and multiple pregnancies, introduction.
In previous study sessions of this module, you have been introduced to the definitions, signs, symptoms and stages of normal labour, and about the ‘normal’ vertex presentation of the fetus during delivery. In this study session, you will learn about the most common abnormal presentations (breech, shoulder, face or brow), their diagnostic criteria and the required actions you need to take to prevent complications developing during labour. Taking prompt action may save the life of the mother and her baby if the delivery becomes obstructed because the baby is in an abnormal presentation. We will also tell you about twin births and the complications that may result if the two babies become ‘locked’ together, preventing either of them from being born.
Learning Outcomes for Study Session 8
After studying this session, you should be able to:
8.1 Define and use correctly all of the key words printed in bold . (SAQs 8.1 and 8.2)
8.2 Describe how you would identify a fetus in the vertex presentation and distinguish this from common malpresentations and malpositions. (SAQs 8.1 and 8.2)
8.3 Describe the causes and complications for the fetus and the mother of fetal malpresentation during full term labour. (SAQ 8.3)
8.4 Describe how you would identify a multiple pregnancy and the complications that may arise. (SAQ 8.4)
8.5 Explain when and how you would refer a woman in labour due to abnormal fetal presentation or multiple pregnancy. (SAQ 8.4)
8.1 Normal and abnormal presentations
8.1.1 vertex presentation.
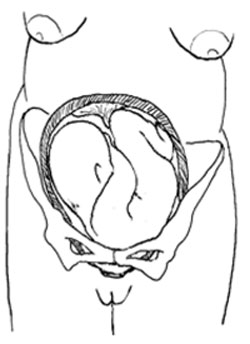
In about 95% of deliveries, the part of the fetus which arrives first at the mother’s pelvic brim is the highest part of the fetal head, which is called the vertex (Figure 8.1). This presentation is called the vertex presentation . Notice that the baby’s chin is tucked down towards its chest, so that the vertex is the leading part entering the mother’s pelvis. The baby’s head is said to be ‘well-flexed’ in this position.
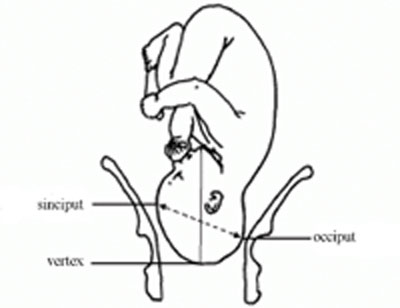
During early pregnancy, the baby is the other way up — with its bottom pointing down towards the mother’s cervix — which is called the breech presentation . This is because during its early development, the head of the fetus is bigger than its buttocks; so in the majority of cases, the head occupies the widest cavity, i.e. the fundus (rounded top) of the uterus. As the fetus grows larger, the buttocks become bigger than the head and the baby spontaneously reverses its position, so its buttocks occupy the fundus. In short, in early pregnancy, the majority of fetuses are in the breech presentation and later in pregnancy most of them make a spontaneous transition to the vertex presentation.
8.1.2 Malpresentations
You will learn about obstructed labour in Study Session 9.
When the baby presents itself in the mother’s pelvis in any position other than the vertex presentation, this is termed an abnormal presentation, or m alpresentation . The reason for referring to this as ‘abnormal’ is because it is associated with a much higher risk of obstruction and other birth complications than the vertex presentation. The most common types of malpresentation are termed breech, shoulder, face or brow. We will discuss each of these in turn later. Notice that the baby can be ‘head-down’ but in an abnormal presentation, as in face or brow presentations, when the baby’s face or forehead (brow) is the presenting part.
8.1.3 Malposition
Although it may not be so easy for you to identify this, the baby can also be in an abnormal position even when it is in the vertex presentation. In a normal delivery, when the baby’s head has engaged in the mother’s pelvis, the back of the baby’s skull (the occiput ) points towards the front of the mother’s pelvis (the pubic symphysis ), where the two pubic bones are fused together. This orientation of the fetal skull is called the occipito-anterior position (Figure 8.2a). If the occiput (back) of the fetal skull is towards the mother’s back, this occipito-posterior position (Figure 8.2b) is a vertex malposition , because it is more difficult for the baby to be born in this orientation. The good thing is that more than 90% of babies in vertex malpositions undergo rotation to the occipito-anterior position and are delivered normally.
You learned the directional positions: anterior/in front of and posterior/behind or in the back of, in the Antenatal Care Module, Part 1, Study Session 3.
Note that the fetal skull can also be tilted to the left or to the right in either the occipito-anterior or occipito-posterior positions.

8.2 Causes and consequences of malpresentations and malpositions
In the majority of individual cases it may not be possible to identify what caused the baby to be in an abnormal presentation or position during delivery. However, the general conditions that are thought to increase the risk of malpresentation or malposition are listed below:
Multiple pregnancy is the subject of Section 8.7 of this study session. You learned about placenta previa in the Antenatal Care Module, Study Session 21.
- Abnormally increased or decreased amount of amniotic fluid
- A tumour (abnormal tissue growth) in the uterus preventing the spontaneous inversion of the fetus from breech to vertex presentation during late pregnancy
- Abnormal shape of the pelvis
- Laxity (slackness) of muscular layer in the walls of the uterus
- Multiple pregnancy (more than one baby in the uterus)
- Placenta previa (placenta partly or completely covering the cervical opening).
If the baby presents at the dilating cervix in an abnormal presentation or malposition, it will more difficult (and may be impossible) for it to complete the seven cardinal movements that you learned about in Study Sessions 3 and 5. As a result, birth is more difficult and there is an increased risk of complications, including:
You learned about PROM in Study Session 17 of the Antenatal Care Module, Part 2.
- Premature rupture of the fetal membranes (PROM)
- Premature labour
- Slow, erratic, short-lived contractions
- Uncoordinated and extremely painful contractions, with slow or no progress of labour
- Prolonged and obstructed labour, leading to a ruptured uterus (see Study Sessions 9 and 10 of this Module)
- Postpartum haemorrhage (see Study Session 11)
- Fetal and maternal distress, which may lead to the death of the baby and/or the mother.
With these complications in mind, we now turn your attention to the commonest types of malpresentation and how to recognise them.
8.3 Breech presentation
In a b reech presentation , the fetus lies with its buttocks in the lower part of the uterus, and its buttocks and/or the feet are the presenting parts during delivery. Breech presentation occurs on average in 3–4% of deliveries after 34 weeks of pregnancy.
When is the breech position the normal position for the fetus?
During early pregnancy the baby’s bottom points down towards the mother’s cervix, and its head (the largest part of the fetus at this stage of development) occupies the fundus (rounded top) of the uterus, which is the widest part of the uterine cavity.
8.3.1 Causes of breech presentation
You can see a transverse lie in Figure 8.7 later in this study session.
In the majority of cases there is no obvious reason why the fetus should present by the breech at full term. In practice, what is commonly observed is the association of breech presentation at delivery with a transverse lie earlier in the pregnancy, i.e. the fetus lies sideways across the mother’s abdomen, facing a sideways implanted placenta. It is thought that when the placenta is in front of the baby’s face, it may obstruct the normal process of inversion, when the baby turns head-down as it gets bigger during the pregnancy. As a result, the fetus turns in the other direction and ends in the breech presentation. Some other circumstances that are thought to favour a breech presentation during labour include:
- Premature labour, beginning before the baby undergoes spontanous inversion from breech to vertex presentation
- Multiple pregnancy, preventing the normal inversion of one or both babies
- Polyhydramnios: excessive amount of amniotic fluid, which makes it more difficult for the fetal head to ‘engage’ with the mother’s cervix (polyhydramnios is pronounced ‘poll-ee-hy-dram-nee-oss’. Hydrocephaly is pronounced ‘hy-droh-keff-all-ee’)
- Hydrocephaly (‘water on the brain’) i.e. an abnormally large fetal head due to excessive accumulation of fluid around the brain
- Placenta praevia
- Breech delivery in the previous pregnancy
- Abnormal formation of the uterus.
8.3.2 Diagnosis of breech presentation
On abdominal palpation the fetal head is found above the mother’s umbilicus as a hard, smooth, rounded mass, which gently ‘ballots’ (can be rocked) between your hands.
Why do you think a mass that ‘ballots’ high up in the abdomen is a sign of breech presentation? (You learned about this in Study Session 11 of the Antenatal Care Module.)
The baby’s head can ‘rock’ a little bit because of the flexibility of the baby’s neck, so if there is a rounded, ballotable mass above the mother’s umbilicus it is very likely to be the baby’s head. If the baby was ‘bottom-up’ (vertex presentation) the whole of its back will move of you try to rock the fetal parts at the fundus (Figure 8.3).
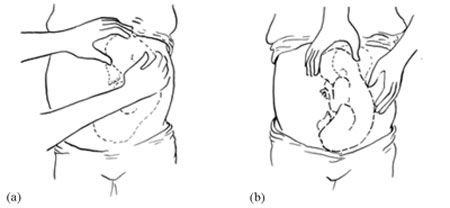
Once the fetus has engaged and labour has begun, the breech baby’s buttocks can be felt as soft and irregular on vaginal examination. They feel very different to the relatively hard rounded mass of the fetal skull in a vertex presentation. When the fetal membranes rupture, the buttocks and/or feet can be felt more clearly. The baby’s anus may be felt and fresh thick, dark meconium may be seen on your examining finger. If the baby’s legs are extended, you may be able to feel the external genitalia and even tell the sex of the baby before it is born.
8.3.3 Types of breech presentation
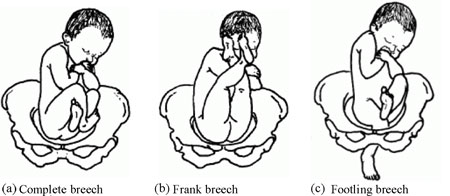
There are three types of breech presentation, as illustrated in Figure 8.4. They are:
- Complete breech is characterised by flexion of the legs at both hips and knee joints, so the legs are bent underneath the baby.
- Frank breech is the commonest type of breech presentation, and is characterised by flexion at the hip joints and extension at the knee joints, so both the baby’s legs point straight upwards.
- Footling breech is when one or both legs are extended at the hip and knee joint and the baby presents ‘foot first’.
8.3.4 Risks of breech presentation
Regardless of the type of breech presentation, there are significant associated risks to the baby. They include:
- The fetal head gets stuck (arrested) before delivery
- Labour becomes obstructed when the fetus is disproportionately large for the size of the maternal pelvis
- Cord prolapse may occur, i.e. the umbilical cord is pushed out ahead of the baby and may get compressed against the wall of the cervix or vagina
- Premature separation of the placenta (placental abruption)
- Birth injury to the baby, e.g. fracture of the arms or legs, nerve damage, trauma to the internal organs, spinal cord damage, etc.
A breech birth may also result in trauma to the mother’s birth canal or external genitalia through being overstretched by the poorly fitting fetal parts.
Cord prolapse in a normal (vertex) presentation was illustrated in Study Session 17 of the Antenatal Care Module, and placental abruption was covered in Study Session 21.
What will be the effect on the baby if it gets stuck, the labour is obstructed, the cord prolapses, or placental abruption occurs?
The result will be hypoxia , i.e. it will be deprived of oxygen, and may suffer permanent brain damage or die.
You learned about the causes and consequences of hypoxia in the Antenatal Care Module.
8.4 Face presentation
Face presentation occurs when the baby’s neck is so completely extended (bent backwards) that the occiput at the back of the fetal skull touches the baby’s own spine (see Figure 8.5). In this position, the baby’s face will present to you during delivery.
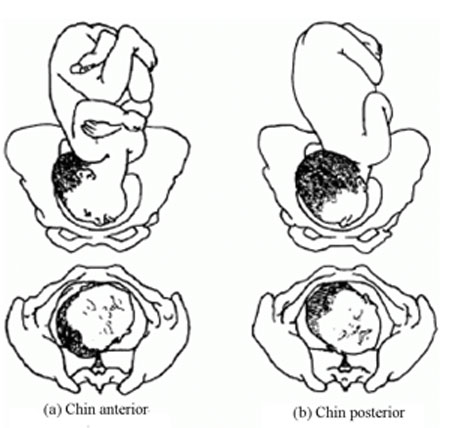
Refer the mother if a baby in the chin posterior face presentation does not rotate and the labour is prolonged.
The incidence of face presentation is about 1 in 500 pregnancies in full term labours. In Figure 8.5, you can see how flexed the head is at the neck. Babies who present in the ‘chin posterior’ position (on the right in Figure 8.5) usually rotate spontaneously during labour, and assume the ‘chin anterior’ position, which makes it easier for them to be born. However, they are unlikely to be delivered vaginally if they fail to undergo spontaneous rotation to the chin anterior position, because the baby’s chin usually gets stuck against the mother’s sacrum (the bony prominence at the back of her pelvis). A baby in this position will have to be delivered by caesarean surgery.
8.4.1 Causes of face presentation
The causes of face presentation are similar to those already described for breech births:
- Laxity (slackness) of the uterus after many previous full-term pregnancies
- Multiple pregnancy
- Polyhydramnios (excessive amniotic fluid)
- Congenital abnormality of the fetus (e.g. anencephaly, which means no or incomplete skull bones)
- Abnormal shape of the mother’s pelvis.
8.4.2 Diagnosis of face presentation
Face presentation may not be easily detected by abdominal palpation, especially if the chin is in the posterior position. On abdominal examination, you may feel irregular shapes, formed because the fetal spine is curved in an ‘S’ shape. However, on vaginal examination, you can detect face presentation because:
- The presenting part will be high, soft and irregular.
- When the cervix is sufficiently dilated, you may be able to feel parts of the face, such as the orbital ridges above the eyes, the nose or mouth, gums, or bony chin.
- If the membranes are ruptured, the baby may suck your examining finger!
But as labour progresses, the baby’s face becomes o edematous (swollen with fluid), making it more difficult to distinguish from the soft shape you will feel in a breech presentation.
8.4.3 Complications of face presentation
Complications for the fetus include:
- Obstructed labour and ruptured uterus
- Cord prolapse
- Facial bruising
- Cerebral haemorrhage (bleeding inside the fetal skull).
8.5 Brow presentation

In brow presentation , the baby’s head is only partially extended at the neck (compare this with face presentation), so its brow (forehead) is the presenting part (Figure 8.6). This presentation is rare, with an incidence of 1 in 1000 deliveries at full term.
8.5.1 Possible causes of brow presentation
You have seen all of these factors before, as causes of other malpresentations:
- Lax uterus due to repeated full term pregnancy
- Polyhydramnios
8.5.2 Diagnosis of brow presentation
Brow presentation is not usually detected before the onset of labour, except by very experienced birth attendants. On abdominal examination, the head is high in the mother’s abdomen, appears unduly large and does not descend into the pelvis, despite good uterine contractions. On vaginal examination, the presenting part is high and may be difficult to reach. You may be able to feel the root of the nose, eyes, but not the mouth, tip of the nose or chin. You may also feel the anterior fontanel, but a large caput (swelling) towards the front of the fetal skull may mask this landmark if the woman has been in labour for some hours.
Recall the appearance of a normal caput over the posterior fontanel shown in Figure 4.4 earlier in this Module.
8.5.3 Complications of brow presentation
The complications of brow presentation are much the same as for other malpresentations:
- Cerebral haemorrhage.
Which are you more likely to encounter — face or brow presentations?
Face presentation, which occurs in 1 in 500 full term labours. Brow presentation is more rare, at 1 in 1,000 full term labours.
8.6 Shoulder presentation
Shoulder presentation is rare at full term, but may occur when the fetus lies transversely across the uterus (Figure 8.7), if it stopped part-way through spontaneous inversion from breech to vertex, or it may lie transversely from early pregnancy. If the baby lies facing upwards, its back may be the presenting part; if facing downwards its hand may emerge through the cervix. A baby in the transverse position cannot be born through the vagina and the labour will be obstructed. Refer babies in shoulder presentation urgently.
8.6.1 Causes of shoulder presentation
Causes of shoulder presentation could be maternal or fetal factors.
Maternal factors include:
- Lax abdominal and uterine muscles: most often after several previous pregnancies
- Uterine abnormality
- Contracted (abnormally narrow) pelvis.
Fetal factors include:
- Preterm labour
- Placenta previa.
What do ‘placenta previa’ and ‘polyhydramnios’ indicate?
Placenta previa is when the placenta is partly or completely covering the cervical opening. Polyhydramnios is an excess of amniotic fluid. They are both potential causes of malpresentation.
8.6.2 Diagnosis of shoulder presentation
On abdominal palpation, the uterus appears broader and the height of the fundus is less than expected for the period of gestation, because the fundus is not occupied by either the baby’s head or buttocks. You can usually feel the head on one side of the mother’s abdomen. On vaginal examination, in early labour, the presenting part may not be felt, but when the labour is well progressed, you may feel the baby’s ribs. When the shoulder enters the pelvic brim, the baby’s arm may prolapse and become visible outside the vagina.
8.6.3 Complications of shoulder presentation
Complications include:
- Trauma to a prolapsed arm
- Fetal hypoxia and death.
Remember that a shoulder presentation means the baby cannot be born through the vagina; if you detect it in a woman who is already in labour, refer her urgently to a higher health facility.
8.7 Multiple pregnancy
In this section, we turn to the subject of multiple pregnancy , when there is more than one fetus in the uterus. More than 95% of multiple pregnancies are twins (two fetuses), but there can also be triplets (three fetuses), quadruplets (four fetuses), quintuplets (five fetuses), and other higher order multiples with a declining chance of occurrence. The spontaneous occurrence of twins varies by country : it is lowest in East Asia n countries like Japan and China (1 out of 1000 pregnancies are fraternal or non-identical twins), and highest in black Africans , particularly in Nigeria , where 1 in 20 pr egnancies are fraternal twins. In general, compared to single babies, multiple pregnancies are highly associated with early pregnancy loss and high perinatal mortality, mainly due to prematurity.
8.7.1 Types of twin pregnancy
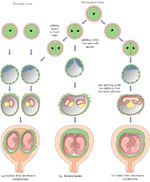
Twins may be identical (monozygotic) or non-identical and fraternal (dizigotic). Monozygotic twins develop from a single fertilised ovum (the zygote), so they are always the same sex and they share the same placenta . By contrast, dizygotic twins develop from two different zygotes, so they can have the same or different sex, and they have separate placenta s . Figure 8.8 shows the types of twin pregnancy and the processes by which they are formed.
8.7.2 Diagnosis of twin pregnancy
On abdominal examination you may notice that:
- The size of the uterus is larger than the expected for the period for gestation.
- The uterus looks round and broad, and fetal movement may be seen over a large area. (The shape of the uterus at term in a singleton pregnancy in the vertex presentation appears heart-shaped rounder at the top and narrower at the bottom.)
- Two heads can be felt.
- Two fetal heart beats may be heard if two people listen at the same time, and they can detect at least 10 beats different (Figure 8.6).
- Ultrasound examination can make an absolute diagnosis of twin pregnancy.

8.7.3 Consequences of twin pregnancy
Women who are pregnant with twins are more prone to suffer with the minor disorders of pregnancy, like morning sickness, nausea and heartburn. Twin pregnancy is one cause of hyperemesis gravidarum (persistent, severe nausea and vomiting). Mothers of twins are also more at risk of developing iron and folate-deficiency anaemia during pregnancy.
Can you suggest why anaemia is a greater risk in multiple pregnancies?
The mother has to supply the nutrients to feed two (or more) babies; if she is not getting enough iron and folate in her diet, or through supplements, she will become anaemic.
Other complications include the following:
- Pregnancy-related hypertensive disorders like pre-eclampsia and eclampsia are more common in twin pregnancies.
- Pressure symptoms may occur in late pregnancy due to the increased weight and size of the uterus.
- Labour often occurs spontaneously before term, with p remature delivery or premature rupture of membranes (PROM) .
- Respiratory deficit ( shortness of breath, because of fast growing uterus) is another common problem.
Twin babies may be small in comparison to their gestational age and more prone to the complications associated with low birth weight (increased vulnerability to infection, losing heat, difficulty breastfeeding).
You will learn about low birth weight babies in detail in the Postnatal Care Module.
- Malpresentation is more common in twin pregnancies, and they may also be ‘locked’ at the neck with one twin in the vertex presentation and the other in breech. The risks associated with malpresentations already described also apply: prolapsed cord, poor uterine contraction, prolonged or obstructed labour, postpartum haemorrhage, and fetal hypoxia and death.
- Conjoined twins (fused twins, joined at the head, chest, or abdomen, or through the back) may also rarely occur.
8.8 Management of women with malpresentation or multiple pregnancy
As you have seen in this study session, any presentation other than vertex has its own dangers for the mother and baby. For this reason, all women who develop abnormal presentation or multiple pregnancy should ideally have skilled care by senior health professionals in a health facility where there is a comprehensive emergency obstetric service. Early detection and referral of a woman in any of these situations can save her life and that of her baby.
What can you do to reduce the risks arising from malpresentation or multiple pregnancy in women in your care?
During focused antenatal care of the pregnant women in your community, at every visit after 36 weeks of gestation you should check for the presence of abnormal fetal presentation. If you detect abnormal presentation or multiple pregnancy, you should refer the woman before the onset of labour.
Summary of Study Session 8
In Study Session 8, you learned that:
- During early pregnancy, babies are naturally in the breech position, but in 95% of cases they spontaneously reverse into the vertex presentation before labour begins.
- Malpresentation or malposition of the fetus at full term increases the risk of obstructed labour and other birth complications.
- Common causes of malpresentations/malpositions include: excess amniotic fluid, abnormal shape and size of the pelvis; uterine tumour; placenta praevia; slackness of uterine muscles (after many previous pregnancies); or multiple pregnancy.
- Common complications include: premature rupture of membranes, premature labour, prolonged/obstructed labour; ruptured uterus; postpartum haemorrhage; fetal and maternal distress which may lead to death.
- Vertex malposition is when the fetal head is in the occipito-posterior position — i.e. the back of the fetal skull is towards the mother’s back instead of pointing towards the front of the mother’s pelvis. 90% of vertex malpositions rotate and deliver normally.
- Breech presentation (complete, frank or footling) is when the baby’s buttocks present during labour. It occurs in 3–4% of labours after 34 weeks of pregnancy and may lead to obstructed labour, cord prolapse, hypoxia, premature separation of the placenta, birth injury to the baby or to the birth canal.
- Face presentation is when the fetal head is bent so far backwards that the face presents during labour. It occurs in about 1 in 500 full term labours. ‘Chin posterior’ face presentations usually rotate spontaneously to the ‘chin anterior’ position and deliver normally. If rotation does not occur, a caesarean delivery is likely to be necessary.
- Brow presentation is when the baby’s forehead is the presenting part. It occurs in about 1 in 1000 full term labours and is difficult to detect before the onset of labour. Caesarean delivery is likely to be necessary.
- Shoulder presentation occurs when the fetal lie during labour is transverse. Once labour is well progressed, vaginal examination may feel the baby’s ribs, and an arm may sometimes prolapse. Caesarean delivery is always required unless a doctor or midwife can turn the baby head-down.
- Multiple pregnancies are always at high risk of malpresentation. Mothers need greater antenatal care, and twins are more prone to complications associated with low birth weight and prematurity.
- Any presentation other than vertex after 34 weeks of gestation is considered as high risk to the mother and to her baby. Do not attempt to turn a malpresenting or malpositioned baby! Refer the mother for emergency obstetric care.
Self-Assessment Questions (SAQs) for Study Session 8
Now that you have completed this study session, you can assess how well you have achieved its Learning Outcomes by answering the following questions. Write your answers in your Study Diary and discuss them with your Tutor at the next Study Support Meeting. You can check your answers with the Notes on the Self-Assessment Questions at the end of this Module.
SAQ 8.1 (tests Learning Outcomes 8.1, 8.2 and 8.4)
Which of the following definitions are true and which are false? Write down the correct definition for any which you think are false.
A Fundus — the ‘rounded top’ and widest cavity of the uterus.
B Complete breech — where the legs are bent at both hips and knee joints and are folded underneath the baby.
C Frank breech — where the breech is so difficult to treat that you have to be very frank and open with the mother about the difficulties she will face in the birth.
D Footling breech — when one or both legs are extended so that the baby presents ‘foot first’.
E Hypoxia — the baby gets too much oxygen.
F Multiple pregnancy — when a mother has had many babies previously.
G Monozygotic twins — develop from a single fertilised ovum (the zygote). They can be different sexes but they share the same placenta.
H Dizygotic twins — develop from two zygotes. They have separate placentas, and can be of the same sex or different sexes.
A is true. The fundus is the ‘rounded top’ and widest cavity of the uterus.
B is true. Complete breech is where the legs are bent at both hips and knee joints and are folded underneath the baby.
C is false . A frank breech is the most common type of breech presentation and is when the baby’s legs point straight upwards (see Figure 8.4).
D is true. A footling breech is when one or both legs are extended so that the baby presents ‘foot first’.
E is false . Hypoxia is when the baby is deprived of oxygen and risks permanent brain damage or death.
F is false. Multiple pregnancy is when there is more than one fetus in the uterus.
G is false. Monozygotic twins develop from a single fertilised ovum (the zygote), and they are always the same sex , as well as sharing the same placenta.
H is true. Dizygotic twins develop from two zygotes, have separate placentas, and can be of the same or different sexes.
SAQ 8.2 (tests Learning Outcomes 8.1 and 8.2)
What are the main differences between normal and abnormal fetal presentations? Use the correct medical terms in bold in your explanation.
In a normal presentation, the vertex (the highest part of the fetal head) arrives first at the mother’s pelvic brim, with the occiput (the back of the baby’s skull) pointing towards the front of the mother’s pelvis (the pubic symphysis ).
Abnormal presentations are when there is either a vertex malposition (the occiput of the fetal skull points towards the mother’s back instead towards of the pubic symphysis), or a malpresentation (when anything other than the vertex is presenting): e.g. breech presentation (buttocks first); face presentation (face first); brow presentation (forehead first); and shoulder presentation (transverse fetal).
SAQ 8.3 (tests Learning Outcomes 8.3 and 8.5)
- a. List the common complications of malpresentations or malposition of the fetus at full term.
- b. What action should you take if you identify that the fetus is presenting abnormally and labour has not yet begun?
- c. What should you not attempt to do?
- a. The common complications of malpresentation or malposition of the fetus at full term include: premature rupture of membranes, premature labour, prolonged/obstructed labour; ruptured uterus; postpartum haemorrhage; fetal and maternal distress which may lead to death.
- b. You should refer the mother to a higher health facility – she may need emergency obstetric care.
- c. You should not attempt to turn the baby by hand. This should only be attempted by a specially trained doctor or midwife and should only be done at a health facility.
SAQ 8.4 (tests Learning Outcomes 8.4 and 8.5)
A pregnant woman moves into your village who is already at 37 weeks gestation. You haven’t seen her before. She tells you that she gave birth to twins three years ago and wants to know if she is having twins again this time.
- a. How would you check this?
- b. If you diagnose twins, what would you do to reduce the risks during labour and delivery?
- Is the uterus larger than expected for the period of gestation?
- What is its shape – is it round (indicative of twins) or heart-shaped (as in a singleton pregnancy)?
- Can you feel more than one head?
- Can you hear two fetal heartbeats (two people listening at the same time) with at least 10 beats difference?
- If there is access to a higher health facility, and you are still not sure, try and get the woman to it for an ultrasound scan.
- Be extra careful to check that the mother is not anaemic.
- Encourage her to rest and put her feet up to reduce the risk of increased blood pressure or swelling in her legs and feet.
- Be alert to the increased risk of pre-eclampsia.
- Expect her to go into labour before term, and be ready to get her to the health facility before she goes into labour, going with her if at all possible.
- Get in early touch with that health facility to warn them to expect a referral from you.
- Make sure that transport is ready to take her to a health facility when needed.
Except for third party materials and/or otherwise stated (see terms and conditions ) the content in OpenLearn is released for use under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Sharealike 2.0 licence . In short this allows you to use the content throughout the world without payment for non-commercial purposes in accordance with the Creative Commons non commercial sharealike licence. Please read this licence in full along with OpenLearn terms and conditions before making use of the content.
When using the content you must attribute us (The Open University) (the OU) and any identified author in accordance with the terms of the Creative Commons Licence.
The Acknowledgements section is used to list, amongst other things, third party (Proprietary), licensed content which is not subject to Creative Commons licensing. Proprietary content must be used (retained) intact and in context to the content at all times. The Acknowledgements section is also used to bring to your attention any other Special Restrictions which may apply to the content. For example there may be times when the Creative Commons Non-Commercial Sharealike licence does not apply to any of the content even if owned by us (the OU). In these stances, unless stated otherwise, the content may be used for personal and non-commercial use. We have also identified as Proprietary other material included in the content which is not subject to Creative Commons Licence. These are: OU logos, trading names and may extend to certain photographic and video images and sound recordings and any other material as may be brought to your attention.
Unauthorised use of any of the content may constitute a breach of the terms and conditions and/or intellectual property laws.
We reserve the right to alter, amend or bring to an end any terms and conditions provided here without notice.
All rights falling outside the terms of the Creative Commons licence are retained or controlled by The Open University.
Head of Intellectual Property, The Open University
Fetal Presentation, Position, and Lie (Including Breech Presentation)
- Variations in Fetal Position and Presentation |
During pregnancy, the fetus can be positioned in many different ways inside the mother's uterus. The fetus may be head up or down or facing the mother's back or front. At first, the fetus can move around easily or shift position as the mother moves. Toward the end of the pregnancy the fetus is larger, has less room to move, and stays in one position. How the fetus is positioned has an important effect on delivery and, for certain positions, a cesarean delivery is necessary. There are medical terms that describe precisely how the fetus is positioned, and identifying the fetal position helps doctors to anticipate potential difficulties during labor and delivery.
Presentation refers to the part of the fetus’s body that leads the way out through the birth canal (called the presenting part). Usually, the head leads the way, but sometimes the buttocks (breech presentation), shoulder, or face leads the way.
Position refers to whether the fetus is facing backward (occiput anterior) or forward (occiput posterior). The occiput is a bone at the back of the baby's head. Therefore, facing backward is called occiput anterior (facing the mother’s back and facing down when the mother lies on her back). Facing forward is called occiput posterior (facing toward the mother's pubic bone and facing up when the mother lies on her back).
Lie refers to the angle of the fetus in relation to the mother and the uterus. Up-and-down (with the baby's spine parallel to mother's spine, called longitudinal) is normal, but sometimes the lie is sideways (transverse) or at an angle (oblique).
For these aspects of fetal positioning, the combination that is the most common, safest, and easiest for the mother to deliver is the following:
Head first (called vertex or cephalic presentation)
Facing backward (occiput anterior position)
Spine parallel to mother's spine (longitudinal lie)
Neck bent forward with chin tucked
Arms folded across the chest
If the fetus is in a different position, lie, or presentation, labor may be more difficult, and a normal vaginal delivery may not be possible.
Variations in fetal presentation, position, or lie may occur when
The fetus is too large for the mother's pelvis (fetopelvic disproportion).
The uterus is abnormally shaped or contains growths such as fibroids .
The fetus has a birth defect .
There is more than one fetus (multiple gestation).

Position and Presentation of the Fetus
Variations in fetal position and presentation.
Some variations in position and presentation that make delivery difficult occur frequently.
Occiput posterior position
In occiput posterior position (sometimes called sunny-side up), the fetus is head first (vertex presentation) but is facing forward (toward the mother's pubic bone—that is, facing up when the mother lies on her back). This is a very common position that is not abnormal, but it makes delivery more difficult than when the fetus is in the occiput anterior position (facing toward the mother's spine—that is facing down when the mother lies on her back).
When a fetus faces up, the neck is often straightened rather than bent,which requires more room for the head to pass through the birth canal. Delivery assisted by a vacuum device or forceps or cesarean delivery may be necessary.
Breech presentation
In breech presentation, the baby's buttocks or sometimes the feet are positioned to deliver first (before the head).
When delivered vaginally, babies that present buttocks first are more at risk of injury or even death than those that present head first.
The reason for the risks to babies in breech presentation is that the baby's hips and buttocks are not as wide as the head. Therefore, when the hips and buttocks pass through the cervix first, the passageway may not be wide enough for the head to pass through. In addition, when the head follows the buttocks, the neck may be bent slightly backwards. The neck being bent backward increases the width required for delivery as compared to when the head is angled forward with the chin tucked, which is the position that is easiest for delivery. Thus, the baby’s body may be delivered and then the head may get caught and not be able to pass through the birth canal. When the baby’s head is caught, this puts pressure on the umbilical cord in the birth canal, so that very little oxygen can reach the baby. Brain damage due to lack of oxygen is more common among breech babies than among those presenting head first.
In a first delivery, these problems may occur more frequently because a woman’s tissues have not been stretched by previous deliveries. Because of risk of injury or even death to the baby, cesarean delivery is preferred when the fetus is in breech presentation, unless the doctor is very experienced with and skilled at delivering breech babies or there is not an adequate facility or equipment to safely perform a cesarean delivery.
Breech presentation is more likely to occur in the following circumstances:
Labor starts too soon (preterm labor).
The uterus is abnormally shaped or contains abnormal growths such as fibroids .
Other presentations
In face presentation, the baby's neck arches back so that the face presents first rather than the top of the head.
In brow presentation, the neck is moderately arched so that the brow presents first.
Usually, fetuses do not stay in a face or brow presentation. These presentations often change to a vertex (top of the head) presentation before or during labor. If they do not, a cesarean delivery is usually recommended.
In transverse lie, the fetus lies horizontally across the birth canal and presents shoulder first. A cesarean delivery is done, unless the fetus is the second in a set of twins. In such a case, the fetus may be turned to be delivered through the vagina.

- Cookie Preferences

Copyright © 2024 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and its affiliates. All rights reserved.

Fetal Presentation, Position, and Lie (Including Breech Presentation)
- Key Points |
Abnormal fetal lie or presentation may occur due to fetal size, fetal anomalies, uterine structural abnormalities, multiple gestation, or other factors. Diagnosis is by examination or ultrasonography. Management is with physical maneuvers to reposition the fetus, operative vaginal delivery , or cesarean delivery .
Terms that describe the fetus in relation to the uterus, cervix, and maternal pelvis are
Fetal presentation: Fetal part that overlies the maternal pelvic inlet; vertex (cephalic), face, brow, breech, shoulder, funic (umbilical cord), or compound (more than one part, eg, shoulder and hand)
Fetal position: Relation of the presenting part to an anatomic axis; for transverse presentation, occiput anterior, occiput posterior, occiput transverse
Fetal lie: Relation of the fetus to the long axis of the uterus; longitudinal, oblique, or transverse
Normal fetal lie is longitudinal, normal presentation is vertex, and occiput anterior is the most common position.
Abnormal fetal lie, presentation, or position may occur with
Fetopelvic disproportion (fetus too large for the pelvic inlet)
Fetal congenital anomalies
Uterine structural abnormalities (eg, fibroids, synechiae)
Multiple gestation
Several common types of abnormal lie or presentation are discussed here.

Transverse lie
Fetal position is transverse, with the fetal long axis oblique or perpendicular rather than parallel to the maternal long axis. Transverse lie is often accompanied by shoulder presentation, which requires cesarean delivery.
Breech presentation
There are several types of breech presentation.
Frank breech: The fetal hips are flexed, and the knees extended (pike position).
Complete breech: The fetus seems to be sitting with hips and knees flexed.
Single or double footling presentation: One or both legs are completely extended and present before the buttocks.
Types of breech presentations
Breech presentation makes delivery difficult ,primarily because the presenting part is a poor dilating wedge. Having a poor dilating wedge can lead to incomplete cervical dilation, because the presenting part is narrower than the head that follows. The head, which is the part with the largest diameter, can then be trapped during delivery.
Additionally, the trapped fetal head can compress the umbilical cord if the fetal umbilicus is visible at the introitus, particularly in primiparas whose pelvic tissues have not been dilated by previous deliveries. Umbilical cord compression may cause fetal hypoxemia.

Predisposing factors for breech presentation include
Preterm labor
Uterine abnormalities
Fetal anomalies
If delivery is vaginal, breech presentation may increase risk of
Umbilical cord prolapse
Birth trauma
Perinatal death

Face or brow presentation
In face presentation, the head is hyperextended, and position is designated by the position of the chin (mentum). When the chin is posterior, the head is less likely to rotate and less likely to deliver vaginally, necessitating cesarean delivery.
Brow presentation usually converts spontaneously to vertex or face presentation.
Occiput posterior position
The most common abnormal position is occiput posterior.
The fetal neck is usually somewhat deflexed; thus, a larger diameter of the head must pass through the pelvis.
Progress may arrest in the second phase of labor. Operative vaginal delivery or cesarean delivery is often required.
Position and Presentation of the Fetus
If a fetus is in the occiput posterior position, operative vaginal delivery or cesarean delivery is often required.
In breech presentation, the presenting part is a poor dilating wedge, which can cause the head to be trapped during delivery, often compressing the umbilical cord.
For breech presentation, usually do cesarean delivery at 39 weeks or during labor, but external cephalic version is sometimes successful before labor, usually at 37 or 38 weeks.

- Cookie Preferences

Copyright © 2024 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and its affiliates. All rights reserved.
- Search Please fill out this field.
- Newsletters
- Sweepstakes
- Labor & Delivery
What Causes Breech Presentation?
Learn more about the types, causes, and risks of breech presentation, along with how breech babies are typically delivered.
What Is Breech Presentation?
Types of breech presentation, what causes a breech baby, can you turn a breech baby, how are breech babies delivered.
FatCamera/Getty Images
Toward the end of pregnancy, your baby will start to get into position for delivery, with their head pointed down toward the vagina. This is otherwise known as vertex presentation. However, some babies turn inside the womb so that their feet or buttocks are poised to be delivered first, which is commonly referred to as breech presentation, or a breech baby.
As you near the end of your pregnancy journey, an OB-GYN or health care provider will check your baby's positioning. You might find yourself wondering: What causes breech presentation? Are there risks involved? And how are breech babies delivered? We turned to experts and research to answer some of the most common questions surrounding breech presentation, along with what causes this positioning in the first place.
During your pregnancy, your baby constantly moves around the uterus. Indeed, most babies do somersaults up until the 36th week of pregnancy , when they pick their final position in the womb, says Laura Riley , MD, an OB-GYN in New York City. Approximately 3-4% of babies end up “upside-down” in breech presentation, with their feet or buttocks near the cervix.
Breech presentation is typically diagnosed during a visit to an OB-GYN, midwife, or health care provider. Your physician can feel the position of your baby's head through your abdominal wall—or they can conduct a vaginal exam if your cervix is open. A suspected breech presentation should ultimately be confirmed via an ultrasound, after which you and your provider would have a discussion about delivery options, potential issues, and risks.
There are three types of breech babies: frank, footling, and complete. Learn about the differences between these breech presentations.
Frank Breech
With frank breech presentation, your baby’s bottom faces the cervix and their legs are straight up. This is the most common type of breech presentation.
Footling Breech
Like its name suggests, a footling breech is when one (single footling) or both (double footling) of the baby's feet are in the birth canal, where they’re positioned to be delivered first .
Complete Breech
In a complete breech presentation, baby’s bottom faces the cervix. Their legs are bent at the knees, and their feet are near their bottom. A complete breech is the least common type of breech presentation.
Other Types of Mal Presentations
The baby can also be in a transverse position, meaning that they're sideways in the uterus. Another type is called oblique presentation, which means they're pointing toward one of the pregnant person’s hips.
Typically, your baby's positioning is determined by the fetus itself and the shape of your uterus. Because you can't can’t control either of these factors, breech presentation typically isn’t considered preventable. And while the cause often isn't known, there are certain risk factors that may increase your risk of a breech baby, including the following:
- The fetus may have abnormalities involving the muscular or central nervous system
- The uterus may have abnormal growths or fibroids
- There might be insufficient amniotic fluid in the uterus (too much or too little)
- This isn’t your first pregnancy
- You have a history of premature delivery
- You have placenta previa (the placenta partially or fully covers the cervix)
- You’re pregnant with multiples
- You’ve had a previous breech baby
In some cases, your health care provider may attempt to help turn a baby in breech presentation through a procedure known as external cephalic version (ECV). This is when a health care professional applies gentle pressure on your lower abdomen to try and coax your baby into a head-down position. During the entire procedure, the fetus's health will be monitored, and an ECV is often performed near a delivery room, in the event of any potential issues or complications.
However, it's important to note that ECVs aren't for everyone. If you're carrying multiples, there's health concerns about you or the baby, or you've experienced certain complications with your placenta or based on placental location, a health care provider will not attempt an ECV.
The majority of breech babies are born through C-sections . These are usually scheduled between 38 and 39 weeks of pregnancy, before labor can begin naturally. However, with a health care provider experienced in delivering breech babies vaginally, a natural delivery might be a safe option for some people. In fact, a 2017 study showed similar complication and success rates with vaginal and C-section deliveries of breech babies.
That said, there are certain known risks and complications that can arise with an attempt to deliver a breech baby vaginally, many of which relate to problems with the umbilical cord. If you and your medical team decide on a vaginal delivery, your baby will be monitored closely for any potential signs of distress.
Ultimately, it's important to know that most breech babies are born healthy. Your provider will consider your specific medical condition and the position of your baby to determine which type of delivery will be the safest option for a healthy and successful birth.
ACOG. If Your Baby Is Breech .
American Pregnancy Association. Breech Presentation .
Gray CJ, Shanahan MM. Breech Presentation . [Updated 2022 Nov 6]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-.
Mount Sinai. Breech Babies .
Takeda J, Ishikawa G, Takeda S. Clinical Tips of Cesarean Section in Case of Breech, Transverse Presentation, and Incarcerated Uterus . Surg J (N Y). 2020 Mar 18;6(Suppl 2):S81-S91. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1702985. PMID: 32760790; PMCID: PMC7396468.
Shanahan MM, Gray CJ. External Cephalic Version . [Updated 2022 Nov 6]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-.
Fonseca A, Silva R, Rato I, Neves AR, Peixoto C, Ferraz Z, Ramalho I, Carocha A, Félix N, Valdoleiros S, Galvão A, Gonçalves D, Curado J, Palma MJ, Antunes IL, Clode N, Graça LM. Breech Presentation: Vaginal Versus Cesarean Delivery, Which Intervention Leads to the Best Outcomes? Acta Med Port. 2017 Jun 30;30(6):479-484. doi: 10.20344/amp.7920. Epub 2017 Jun 30. PMID: 28898615.
Related Articles

- Pregnancy Classes

Breech Births
In the last weeks of pregnancy, a baby usually moves so his or her head is positioned to come out of the vagina first during birth. This is called a vertex presentation. A breech presentation occurs when the baby’s buttocks, feet, or both are positioned to come out first during birth. This happens in 3–4% of full-term births.
What are the different types of breech birth presentations?
- Complete breech: Here, the buttocks are pointing downward with the legs folded at the knees and feet near the buttocks.
- Frank breech: In this position, the baby’s buttocks are aimed at the birth canal with its legs sticking straight up in front of his or her body and the feet near the head.
- Footling breech: In this position, one or both of the baby’s feet point downward and will deliver before the rest of the body.
What causes a breech presentation?
The causes of breech presentations are not fully understood. However, the data show that breech birth is more common when:
- You have been pregnant before
- In pregnancies of multiples
- When there is a history of premature delivery
- When the uterus has too much or too little amniotic fluid
- When there is an abnormally shaped uterus or a uterus with abnormal growths, such as fibroids
- The placenta covers all or part of the opening of the uterus placenta previa
How is a breech presentation diagnosed?
A few weeks prior to the due date, the health care provider will place her hands on the mother’s lower abdomen to locate the baby’s head, back, and buttocks. If it appears that the baby might be in a breech position, they can use ultrasound or pelvic exam to confirm the position. Special x-rays can also be used to determine the baby’s position and the size of the pelvis to determine if a vaginal delivery of a breech baby can be safely attempted.
Can a breech presentation mean something is wrong?
Even though most breech babies are born healthy, there is a slightly elevated risk for certain problems. Birth defects are slightly more common in breech babies and the defect might be the reason that the baby failed to move into the right position prior to delivery.
Can a breech presentation be changed?
It is preferable to try to turn a breech baby between the 32nd and 37th weeks of pregnancy . The methods of turning a baby will vary and the success rate for each method can also vary. It is best to discuss the options with the health care provider to see which method she recommends.
Medical Techniques
External Cephalic Version (EVC) is a non-surgical technique to move the baby in the uterus. In this procedure, a medication is given to help relax the uterus. There might also be the use of an ultrasound to determine the position of the baby, the location of the placenta and the amount of amniotic fluid in the uterus.
Gentle pushing on the lower abdomen can turn the baby into the head-down position. Throughout the external version the baby’s heartbeat will be closely monitored so that if a problem develops, the health care provider will immediately stop the procedure. ECV usually is done near a delivery room so if a problem occurs, a cesarean delivery can be performed quickly. The external version has a high success rate and can be considered if you have had a previous cesarean delivery.
ECV will not be tried if:
- You are carrying more than one fetus
- There are concerns about the health of the fetus
- You have certain abnormalities of the reproductive system
- The placenta is in the wrong place
- The placenta has come away from the wall of the uterus ( placental abruption )
Complications of EVC include:
- Prelabor rupture of membranes
- Changes in the fetus’s heart rate
- Placental abruption
- Preterm labor
Vaginal delivery versus cesarean for breech birth?
Most health care providers do not believe in attempting a vaginal delivery for a breech position. However, some will delay making a final decision until the woman is in labor. The following conditions are considered necessary in order to attempt a vaginal birth:
- The baby is full-term and in the frank breech presentation
- The baby does not show signs of distress while its heart rate is closely monitored.
- The process of labor is smooth and steady with the cervix widening as the baby descends.
- The health care provider estimates that the baby is not too big or the mother’s pelvis too narrow for the baby to pass safely through the birth canal.
- Anesthesia is available and a cesarean delivery possible on short notice
What are the risks and complications of a vaginal delivery?
In a breech birth, the baby’s head is the last part of its body to emerge making it more difficult to ease it through the birth canal. Sometimes forceps are used to guide the baby’s head out of the birth canal. Another potential problem is cord prolapse . In this situation the umbilical cord is squeezed as the baby moves toward the birth canal, thus slowing the baby’s supply of oxygen and blood. In a vaginal breech delivery, electronic fetal monitoring will be used to monitor the baby’s heartbeat throughout the course of labor. Cesarean delivery may be an option if signs develop that the baby may be in distress.
When is a cesarean delivery used with a breech presentation?
Most health care providers recommend a cesarean delivery for all babies in a breech position, especially babies that are premature. Since premature babies are small and more fragile, and because the head of a premature baby is relatively larger in proportion to its body, the baby is unlikely to stretch the cervix as much as a full-term baby. This means that there might be less room for the head to emerge.
Want to Know More?
- Creating Your Birth Plan
- Labor & Birth Terms to Know
- Cesarean Birth After Care
Compiled using information from the following sources:
- ACOG: If Your Baby is Breech
- William’s Obstetrics Twenty-Second Ed. Cunningham, F. Gary, et al, Ch. 24.
- Danforth’s Obstetrics and Gynecology Ninth Ed. Scott, James R., et al, Ch. 21.
BLOG CATEGORIES
- Can I get pregnant if… ? 3
- Child Adoption 19
- Fertility 54
- Pregnancy Loss 11
- Breastfeeding 29
- Changes In Your Body 5
- Cord Blood 4
- Genetic Disorders & Birth Defects 17
- Health & Nutrition 2
- Is it Safe While Pregnant 54
- Labor and Birth 65
- Multiple Births 10
- Planning and Preparing 24
- Pregnancy Complications 68
- Pregnancy Concerns 62
- Pregnancy Health and Wellness 149
- Pregnancy Products & Tests 8
- Pregnancy Supplements & Medications 14
- The First Year 41
- Week by Week Newsletter 40
- Your Developing Baby 16
- Options for Unplanned Pregnancy 18
- Paternity Tests 2
- Pregnancy Symptoms 5
- Prenatal Testing 16
- The Bumpy Truth Blog 7
- Uncategorized 4
- Abstinence 3
- Birth Control Pills, Patches & Devices 21
- Women's Health 34
- Thank You for Your Donation
- Unplanned Pregnancy
- Getting Pregnant
- Healthy Pregnancy
- Privacy Policy
Share this post:
Similar post.

Episiotomy: Advantages & Complications

Retained Placenta

What is Dilation in Pregnancy?
Track your baby’s development, subscribe to our week-by-week pregnancy newsletter.
- The Bumpy Truth Blog
- Fertility Products Resource Guide
Pregnancy Tools
- Ovulation Calendar
- Baby Names Directory
- Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
- Pregnancy Quiz
Pregnancy Journeys
- Partner With Us
- Corporate Sponsors
- >> Post Created: February 11, 2022
- >> Last Updated: June 4, 2024
Vertex Position - Table of Contents
As you approach the due date for your baby’s delivery, the excitement and apprehensions are at their peak! What probably adds to the anxieties are the medical terms describing the baby, its ‘position’ and ‘presentation.’ Let’s strike that out from the list now!
In simple words, ‘ position ’ of the baby is always in reference to the mother ; on what side of the mother’s pelvis does the baby lean more (left or right) and if the baby is facing the mother’s spine or belly (anterior or posterior) – for eg.: Left Occiput Anterior , Right Occiput Anterior , Right Occiput Posterior and so on.
On the other hand, ‘ presentation’ is the body part of baby (head, shoulder, feet, and buttocks) that will enter the mother’s pelvic region first at the beginning of labor.
As ‘ presentation’ depends on the ‘ position’ of the baby, the terms cannot be used interchangeably, which is often mistakenly done. If you are told by your doctor that your baby is in a head-down position , which means its head will enter the pelvic region first , then it means the baby is in ‘vertex’ presentation or even sometimes loosely referred to as vertex position of baby though its conceptually incorrect however it means the same.
With this article, we aim to explain how exactly vertex presentation affects your labor and delivery.
Understanding Vertex Presentation
If your baby is in the head-down position by the third trimester, then you are one of the 95% mothers who have a vertex baby or a vertex delivery. When the baby enters the birth canal head first, then the top part of the head is called the ‘vertex.’
In exact medical terms, we give you the definition of vertex presentation by the American College of Obstetrics and Gynecologists (ACOG) – “a fetal presentation where the head is presenting first in the pelvic inlet.”
Besides vertex presentation (also sometimes referred to as vertex position of baby or vertex fetal position also), the other occasional presentations (non-vertex presentations) include –
- Breech – baby’s feet or buttocks are down and first to enter the mother’s pelvic region. Head is near the mother’s ribs
- Transverse – baby’s shoulder, arm or even the trunk are the first to enter the pelvis, as the baby is laying on the side and not in a vertical position
It is common that babies turn to a particular position (hence, affecting the presentation) by 34 -36 weeks of pregnancy. Nevertheless, some babies have ‘unstable lies’ ; – wherein the baby keeps changing positions towards the end of the pregnancy and not remaining in any one position for long.
Should you be worried if the baby is in vertex presentation?
Absolutely not! The vertex presentation is not only the most common, but also the best for a smooth delivery. In fact, the chances of a vaginal delivery are better if you have a vertex fetal position.
By 36 weeks into pregnancy, about 95% of the babies position themselves to have the vertex presentation. However, if your baby hasn’t come into the vertex fetal position by this time, then you can talk to your doctor about the options.
You may be suggested a cephalic version procedure also known as the version procedure /external cephalic version (ECV procedure) – which is used to turn the baby/ fetus from a malpresentation – like breech, oblique or transverse (which occur just about 3-4% times) to the cephalic position (head down).
This is how your doctor will try to turn your baby manually by pushing on your belly to get the baby into the vertex presentation. But it is necessary for you to know that this procedure does involve some risk and is successful only 60-70% of the time.
Continue reading below ↓
Read this next

Everything you need to know about Placenta Position & Placenta Health – with FAQs

The Ultimate List of Baby Must Haves

Looking for Diapers on Sale? Here’s where you can get great diaper deals on buying bulk diapers
Risks of vertex position of baby: can there be any complications for the baby in the vertex presentation.
As discussed above, the vertex fetal position/presentation is the best for labor and delivery, but there can be some complications as the baby makes its way through the birth canal. One such complication can arise if the baby is on the larger side. The baby can face difficulty while passing through the birth canal even if it is in the head-down position because of the size.
Babies who weigh over 9 to 10 pounds are called ‘ macrosomic’ or even referred to as fetal macrosomia , and they are at a higher risk of getting their shoulders stuck in the birth canal during delivery, despite being in the head-down position.
In such cases, to avoid birth trauma for the baby, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) suggests that cesarean deliveries should be limited to estimated fetal weights of at least 11 pounds in women without diabetes and about 9 pounds in women with diabetes.
In case of fetal macrosomia, your doctor will monitor your pregnancy more often and work out a particular birth plan for you subject to your age (mothers age) and size of your baby.
How will I deliver a baby in the vertex fetal position?
Even unborn human babies can astonish you if you observe the way they make their way through the birth canal during delivery.
A vertex baby may be in the optimal position ( head-down first in pelvis) for labor and delivery, but it does its own twisting and turning while passing through the birth canal to fit through. In humans, unlike other mammals, the ratio of the baby’s head to the space in the birth canal is quite limited.
The baby has to flex and turn its head in different positions to fit through and ultimately arrive in this world. And it does so successfully! It is a wonder how they know how to do this so naturally.
And to answer the question ‘how will I deliver a baby in the vertex position?’ – Simply NATURALLY i.e. vaginal delivery. Don’t worry, follow your doctor’s instructions, do your breathing and PUSH.
FAQs to keep ready: How can my doctor help me prepare as I approach my due date?
As your due date nears, apart from bodily discomfort, you may experience nervousness about the big day. Your doctor can help by clearing your doubts and putting you at ease. You can ask them the following questions to understand the process better.
Q1) How will I know if my baby is in vertex fetal position?
A doctor can confidently tell you whether or not your baby is in the vertex presentation. Many medical professionals will be able to determine your baby’s position merely by using their hands; this is called ‘Leopold’s maneuvers.’
However, in case they aren’t very confident about the baby’s position even after this, then an ultrasound can confirm the exact position of the baby.
You can also understand this through belly mapping . You are sure to feel the kicks towards the top of your stomach and head (distinct hard circular feel) towards your pelvis.
Q2)Is there any risk of my vertex baby turning and changing positions?
Yes, in case of some women, the baby who has a vertex presentation may turn at the last moment.
What may cause this? Women who have extra amniotic fluid (polyhydramnios) have increased chances of a vertex baby turning into a breech baby at the last minute.
Discuss this with your doctor to understand what are the chances this might happen to you and what all you can do to keep the baby in the vertex presentation for delivery.
Q3) Is there need to be worried if my baby has a breech presentation?
Not really! There are loads of exercises which you which can help you get your baby in the right position.
Then there are the ECV (external cephalic version) procedure which can help in changing the position of your baby into the desired vertex position. Speak with your doctor.
Having a baby in breech position just before labor will require you to have a C-section . Let your doctor guide you. But there is nothing to worry about.
Q4) What may cause babies to come into breech position?
A few circumstances may cause the baby to come into breech position even after 36 weeks into pregnancy.
- If you are carrying twins or multiple babies , in which case there is limited space for each baby to move around.
- Low levels of amniotic fluid which restricts the free movement of the baby or even high levels of amniotic fluid that does not permit the baby to remain in any one position.
- If there are abnormalities in the uterus or other conditions like low-lying placenta or large fibroids in the lower part of the uterus.
Chances of breech babies are higher in births that are pre-term as the baby does not get enough time to flip into a head-down position – cephalic position – vertex presentation (vertex position of baby/ vertex fetal position).
Q5) Can a baby turn from breech position to vertex presentation?
Yes, a baby can turn from a breech position to vertex position / vertex fetal position over time with exercises and sometimes through ECV.
If an ultrasound has confirmed you have a breech baby, then you can do the following to turn it to a vertex baby. Try the following –
- Do not underestimate the wonders of daily walks of about 45-60 mins when it comes to bringing your baby in vertex presentation from breech presentation.
- Talk to your doctor about certain exercises that can help turn your baby in the head-down position. Exercises like ‘ high bridge’ or ‘cat and camel’ can help here. We recommend you to learn and try this only in the presence of a professional.
- External Cephalic Version (ECV ) is a way to manually maneuver the baby to vertex presentation. It is done with the help of an ultrasound and generally after 36 weeks into pregnancy. However, it has the success rate of just 50%. Discuss the risks, if any, with your gynecologist before opting for this procedure.
There are a couple of other unscientific methods that may not be safe to try –
- Light : Placing a torch near your vagina may guide the baby toward the light, and hence, get it in the vertex presentation.
- Music : Playing music near your belly’s bottom may urge the baby to move itself in the head-down position.
Q6) What all can I do to ensure I have a healthy delivery?
A healthy delivery requires the mother to be active, eating well, and staying happy. For any apprehensions regarding labor and delivery, do not hesitate to talk to your doctor and clarify your doubts.
Your doctor can help you understand your baby’s position and presentation, and then based on that they can plan your delivery to ensure your baby’s birth will happen in the safest possible way.
Try and maintain a healthy lifestyle which will also help in overall of your child and placenta health .
Key Takeaway
Yes, vertex presentation or vertex position of baby and vertex delivery are very common, normal, safe, and the best for labor and delivery of the baby. There is probability of complications sometimes, but that is only subject to certain conditions that we discussed above.
However, understand that any other baby position is also safe. The only thing with other positions and presentations is that the chances of a cesarean delivery goes up. Nevertheless, know what matters at the end of it all is a happy and healthy baby in your arms!
Happy pregnancy!
Khushboo Kirale
You may also be interested in.

Sequential Screening – Why is it so important for you to get it done?

Placenta Previa or Low Lying Placenta: How much should you be concerned?
Lateral Placenta: How does this placenta position impact pregnancy and delivery?

hCG levels twins vs. singleton – What’s the difference?
Fundal Placenta: Does Placenta on Top Make Pregnancy Difficult?

Anterior Placenta Position – How It Affects Pregnancy, Labor and Delivery
Subscribe to get our latest posts on parenting and we will make sure you don’t miss a thing!
Privacy Policy - Terms and Conditions
- Getting Pregnant
- Registry Builder
- Baby Products
- Birth Clubs
- See all in Community
- Ovulation Calculator
- How To Get Pregnant
- How To Get Pregnant Fast
- Ovulation Discharge
- Implantation Bleeding
- Ovulation Symptoms
- Pregnancy Symptoms
- Am I Pregnant?
- Pregnancy Tests
- See all in Getting Pregnant
- Due Date Calculator
- Pregnancy Week by Week
- Pregnant Sex
- Weight Gain Tracker
- Signs of Labor
- Morning Sickness
- COVID Vaccine and Pregnancy
- Fetal Weight Chart
- Fetal Development
- Pregnancy Discharge
- Find Out Baby Gender
- Chinese Gender Predictor
- See all in Pregnancy
- Baby Name Generator
- Top Baby Names 2023
- Top Baby Names 2024
- How to Pick a Baby Name
- Most Popular Baby Names
- Baby Names by Letter
- Gender Neutral Names
- Unique Boy Names
- Unique Girl Names
- Top baby names by year
- See all in Baby Names
- Baby Development
- Baby Feeding Guide
- Newborn Sleep
- When Babies Roll Over
- First-Year Baby Costs Calculator
- Postpartum Health
- Baby Poop Chart
- See all in Baby
- Average Weight & Height
- Autism Signs
- Child Growth Chart
- Night Terrors
- Moving from Crib to Bed
- Toddler Feeding Guide
- Potty Training
- Bathing and Grooming
- See all in Toddler
- Height Predictor
- Potty Training: Boys
- Potty training: Girls
- How Much Sleep? (Ages 3+)
- Ready for Preschool?
- Thumb-Sucking
- Gross Motor Skills
- Napping (Ages 2 to 3)
- See all in Child
- Photos: Rashes & Skin Conditions
- Symptom Checker
- Vaccine Scheduler
- Reducing a Fever
- Acetaminophen Dosage Chart
- Constipation in Babies
- Ear Infection Symptoms
- Head Lice 101
- See all in Health
- Second Pregnancy
- Daycare Costs
- Family Finance
- Stay-At-Home Parents
- Breastfeeding Positions
- See all in Family
- Baby Sleep Training
- Preparing For Baby
- My Custom Checklist
- My Registries
- Take the Quiz
- Best Baby Products
- Best Breast Pump
- Best Convertible Car Seat
- Best Infant Car Seat
- Best Baby Bottle
- Best Baby Monitor
- Best Stroller
- Best Diapers
- Best Baby Carrier
- Best Diaper Bag
- Best Highchair
- See all in Baby Products
- Why Pregnant Belly Feels Tight
- Early Signs of Twins
- Teas During Pregnancy
- Baby Head Circumference Chart
- How Many Months Pregnant Am I
- What is a Rainbow Baby
- Braxton Hicks Contractions
- HCG Levels By Week
- When to Take a Pregnancy Test
- Am I Pregnant
- Why is Poop Green
- Can Pregnant Women Eat Shrimp
- Insemination
- UTI During Pregnancy
- Vitamin D Drops
- Best Baby Forumla
- Postpartum Depression
- Low Progesterone During Pregnancy
- Baby Shower
- Baby Shower Games
How your twins’ fetal positions affect labor and delivery

Twin fetal presentation – also known as the position of your babies in the womb – dictates whether you'll have a vaginal or c-section birth. Toward the end of pregnancy, most twins will move in the head-down position (vertex), but there's a risk that the second twin will change position after the first twin is born. While there are options to change the second twin's position, this can increase the risk of c-section and other health issues. Learn about the six possible twin fetal presentations: vertex-vertex, vertex-breech, breech-breech, vertex-transverse, breech-transverse, and transverse-transverse – and how they'll impact your delivery and risks for complications.
What is fetal presentation and what does it mean for your twins?
As your due date approaches, you might be wondering how your twins are currently positioned in the womb, also known as the fetal presentation, and what that means for your delivery. Throughout your pregnancy, your twin babies will move in the uterus, but sometime during the third trimester – usually between 32 and 36 weeks – their fetal presentation changes as they prepare to go down the birth canal.
The good news is that at most twin births, both babies are head-down (vertex), which means you can have a vaginal delivery. In fact, nearly 40 percent of twins are delivered vaginally.
But if one baby has feet or bottom first (breech) or is sideways (transverse), your doctor might deliver the lower twin vaginally and then try to rotate the other twin so that they face head-down (also called external cephalic version or internal podalic version) and can be delivered vaginally. But if that doesn't work, there's still a chance that your doctor will be able to deliver the second twin feet first vaginally via breech extraction (delivering the breech baby feet or butt first through the vagina).
That said, a breech extraction depends on a variety of factors – including how experienced your doctor is in the procedure and how much the second twin weighs. Studies show that the higher rate of vaginal births among nonvertex second twins is associated with labor induction and more experienced doctors, suggesting that proper delivery planning may increase your chances of a vaginal birth .
That said, you shouldn't totally rule out a Cesarean delivery with twins . If the first twin is breech or neither of the twins are head-down, then you'll most likely have a Cesarean delivery.
Research also shows that twin babies who are born at less than 34 weeks and have moms with multiple children are associated with intrapartum presentation change (when the fetal presentation of the second twin changes from head-down to feet first after the delivery of the first twin) of the second twin. Women who have intrapartum presentation change are more likely to undergo a Cesarean delivery for their second twin.
Here's a breakdown of the different fetal presentations for twin births and how they will affect your delivery.
Head down, head down (vertex, vertex)
This fetal presentation is the most promising for a vaginal delivery because both twins are head-down. Twins can change positions, but if they're head-down at 28 weeks, they're likely to stay that way.
When delivering twins vaginally, there is a risk that the second twin will change position after the delivery of the first. Research shows that second twins change positions in 20 percent of planned vaginal deliveries. If this happens, your doctor may try to rotate the second twin so it faces head-down or consider a breech extraction. But if neither of these work or are an option, then a Cesarean delivery is likely.
In vertex-vertex pairs, the rate of Cesarean delivery for the second twin after a vaginal delivery of the first one is 16.9 percent.
Like all vaginal deliveries, there's also a chance you'll have an assisted birth, where forceps or a vacuum are needed to help deliver your twins.
Head down, bottom down (vertex, breech)
When the first twin's (the lower one) head is down, but the second twin isn't, your doctor may attempt a vaginal delivery by changing the baby's position or doing breech extraction, which isn't possible if the second twin weighs much more than the first twin.
The rates of emergency C-section deliveries for the second twin after a vaginal delivery of the first twin are higher in second twins who have a very low birth weight. Small babies may not tolerate labor as well.
Head down, sideways (vertex, transverse)
If one twin is lying sideways or diagonally (oblique), there's a chance the baby may shift position as your labor progresses, or your doctor may try to turn the baby head-down via external cephalic version or internal podalic version (changing position in the uterus), which means you may be able to deliver both vaginally.
Bottom down, bottom down (breech, breech)
When both twins are breech, a planned C-section is recommended because your doctor isn't able to turn the fetuses. Studies also show that there are fewer negative neonatal outcomes for planned C-sections than planned vaginal births in breech babies.
As with any C-section, the risks for a planned one with twins include infection, loss of blood, blood clots, injury to the bowel or bladder, a weak uterine wall, placenta abnormalities in future pregnancies and fetal injury.
Bottom down, sideways (breech, transverse)
When the twin lowest in your uterus is breech or transverse (which happens in 25 percent of cases), you'll need to have a c-section.
Sideways, sideways (transverse, transverse)
This fetal presentation is rare with less than 1 percent of cases. If both babies are lying horizontally, you'll almost definitely have a C-section.
Learn more:
- Twin fetal development month by month
- Your likelihood of having twins or more
- When and how to find out if you’re carrying twins or more
Was this article helpful?
28 weeks pregnant with twins

32 weeks pregnant with twins

36 weeks pregnant with twins

24 weeks pregnant with twins

BabyCenter's editorial team is committed to providing the most helpful and trustworthy pregnancy and parenting information in the world. When creating and updating content, we rely on credible sources: respected health organizations, professional groups of doctors and other experts, and published studies in peer-reviewed journals. We believe you should always know the source of the information you're seeing. Learn more about our editorial and medical review policies .
Cleveland Clinic. Fetal Positions for Birth: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/9677-fetal-positions-for-birth Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
Mayo Clinic. Fetal Presentation Before Birth: https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/pregnancy-week-by-week/multimedia/fetal-positions/sls-20076615?s=7 Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
NHS. Giving Birth to Twins or More: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29016498/ Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
Science Direct. Breech Extraction: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/breech-extraction Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
Obstetrics & Gynecology. Clinical Factors Associated With Presentation Change of the Second Twin After Vaginal Delivery of the First Twin https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29016498/ Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. Fetal presentation and successful twin vaginal delivery: https://www.ajog.org/article/S0002-9378(04)00482-X/fulltext [Accessed July 2021]
The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine. Changes in fetal presentation in twin pregnancies https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/14767050400028592 Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
Reviews in Obstetrics & Gynecology. An Evidence-Based Approach to Determining Route of Delivery for Twin Gestations https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3252881/ Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
Nature. Neonatal mortality and morbidity in vertex–vertex second twins according to mode of delivery and birth weight: https://www.nature.com/articles/7211408 Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
Cochrane. Planned cesarean for a twin pregnancy: https://www.cochrane.org/CD006553/PREG_planned-caesarean-section-twin-pregnancy Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
Kids Health. What Is the Apgar Score?: https://www.kidshealth.org/Nemours/en/parents/apgar0.html Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology. Neonatal mortality in second twin according to cause of death, gestational age, and mode of delivery https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15467540/ Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
Lancet. Planned cesarean section versus planned vaginal birth for breech presentation at term: a randomised multicentre trial. Term Breech Trial Collaborative Group https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11052579/ Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
Cleveland Clinic. Cesarean Birth (C-Section): https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/7246-cesarean-birth-c-section Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
St. Jude Medical Staff. Delivery of Twin Gestation: http://www.sjmedstaff.org/documents/Delivery-of-twins.pdf Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]

Where to go next

Fastest Obstetric, Gynecology and Pediatric Insight Engine
- Abdominal Key
- Anesthesia Key
- Basicmedical Key
- Otolaryngology & Ophthalmology
- Musculoskeletal Key
- Obstetric, Gynecology and Pediatric
- Oncology & Hematology
- Plastic Surgery & Dermatology
- Clinical Dentistry
- Radiology Key
- Thoracic Key
- Veterinary Medicine
- Gold Membership
Malpresentations
Fetal malpresentation exists when the presenting part is other than the normal vertex of the fetal head. This includes two malpresentations that are covered in other chapters: breech ( Chapter 16 ) and cord presentation ( Chapter 18 ). The remaining malpresentations that will be covered in this chapter are face, brow, transverse lie with shoulder or arm presentation, and compound presentations. In modern obstetrics, particularly in the developed world, the incidence of malpresentations has fallen. This is due to the association of many malpresentations with high parity and the fact that women are having fewer children. The various anteroposterior diameters ( Fig 11-1 ) of the term fetal head vary depending upon the position: normal flexed vertex (9.5 cm), deflexed occipito-posterior position (11–12 cm) and malpresentation: face presentation, submento-bregmatic (9.5 cm) and brow, mento-vertical (13.5 cm). These are illustrated in Figure 11-2 . FIGURE 11-1 Diameters and landmarks of the fetal skull. FIGURE 11-2 Positions and malpresentations of the fetal head. Face Presentation In face presentation the attitude of the fetal head is one of complete extension with the chin as the denominator and leading pole. The presenting diameter is the submento-bregmatic, which in the term fetus is about 9.5 cm. This is the same as the favourable flexed vertex presentation, but the facial bones do not mould to the same extent as the cranial vault does in vertex presentation. The incidence of face presentation is about 1 in 500 births. Causes • Fetal anomalies are found in about 15% of face presentations. The commonest are major CNS anomalies such as anencephaly and meningomyelocoele. Tumours of the neck may also cause extension and face presentation. • Prematurity. • Mild cephalopelvic disproportion has been incriminated. It is probable that in some cases of deflexed occipito-posterior position with relative disproportion the fetal head may extend completely to a face presentation. • It has been postulated that excessive tone in the extensor muscles may predispose to face presentation. This theory has been used to explain cases of primary face presentation which occur before the onset of labour. The development of face presentation during labour is called secondary face presentation. • High parity is associated in the majority of cases. • In most cases, other than parity, no obvious cause is found. Diagnosis The presenting part of the face is between the chin and supraorbital ridges. Usually the characteristic landmarks of the eyes, nose, mouth and chin can be felt with the examining finger during labour. Considerable oedema often develops which may, to a degree, obscure these landmarks. Although the distinction is usually obvious there may be confusion in distinguishing between the mouth and the anus. If this is so, the finger is inserted into the orifice and the gum ridges can easily be felt as a distinguishing landmark. Diagnosis before labour is rare but may be suspected if on abdominal examination the fetus is easily palpated and its back is lying dorsoanterior. In cases with a normally flexed vertex, palpation of the back and head will reveal only a slight depression at the neck between the back and occiput. In face presentations on the other hand, with the head extended, there is a marked depression between the back and occiput. If there is clinical suspicion, ultrasound will establish or refute the diagnosis. The position of a face presentation is defined with the chin as the denominator and is therefore recorded as mento-anterior, mento-posterior or mento-transverse, left or right accordingly. The majority of cases are mento-anterior. Management On the rare occasions that face presentation is diagnosed before labour a careful ultrasound examination should be made to exclude structural fetal anomalies. One can make the case for observation until the onset of labour or full term, on the grounds that a number of these cases will revert spontaneously to a normal flexed vertex position. However, if face presentation persists and the fetus is normal, it should be delivered by elective caesarean section. When the diagnosis is made in labour a gross fetal anomaly should be excluded and clinical pelvimetry should rule out obvious pelvic contraction or deformity. The position of the face presentation is then assessed. Depending upon the estimated fetal weight, the position, station, clinical assessment of pelvic capacity and the progress of labour the following guidelines may be used: If the fetus has an anomaly incompatible with life then progress to vaginal delivery should be followed. If the position is mento-anterior, which presents the same diameters as a flexed vertex, if the fetus is normal or small in size and the pelvis is of good capacity, progress can be followed with the expectation of spontaneous vaginal delivery. The majority of cases with mento-transverse position will rotate to the more favourable anterior position. Fifty years ago, when the morbidity and mortality associated with caesarean section was high, vaginal manipulation was used to try and convert face presentations to a vertex presentation. This was carried out at advanced or full cervical dilatation and usually done under deep general anaesthesia with uterine relaxation. In a previous edition of this book Chassar Moir (1964) described his technique: ‘In cases discovered early in labour (mentolateral) positions, I succeeded in five consecutive cases in correcting the position to a vertex position by the simple intrauterine manipulation of hooking down the occiput with the fingers and simultaneously pressing up the chin and brow with the thumb, labour then proceeded normally in each case.’ Nowadays, we would not advise such manipulation, except perhaps a tentative attempt which is most likely to succeed with a small fetus and a large pelvis. One would only continue with such a manoeuvre if it proved easy and atraumatic. ‘When the chin is turned towards the pubis, at the lower part of that bone, the woman must be laid on her back, the forceps introduced … and when the chin is brought out from under the pubis, the head must be pulled half round upwards; by which means, the fore and hind head will be raised from the perineum.’ William Smellie A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Midwifery. London: D. Wilson, 1752, p281 Provided labour continues normally and there is good progress in the second stage with mento-anterior positions, spontaneous delivery is likely. If progress is inadequate with mento-anterior positions consideration of forceps delivery is appropriate. One has to be very careful that there is adequate descent for safe forceps assisted delivery. Even when the face is visible at the vulva the cranium may not be fully through the pelvic brim. The guiding dictum is ‘the head is higher than you think’. If forceps delivery is to be considered there should be no head palpable at the pelvic brim and the sacral hollow should be filled with the cranium. Either classical or Kielland’s forceps can be used and in face presentations the chin replaces the occiput for orientation. If Kielland’s forceps are used the directional buttons on the shanks should point toward the chin. With both types of forceps the blades are applied as for classical forceps to the occiput anterior positions (see Chapter 10 ). The orientation is along the mento-occipital diameter of the head. With the pelvic curve of the classical forceps the chin is between the heels of the blades and the face is beneath the level of the shanks ( Fig 11-3 ). With Kielland’s forceps the upper part of the blades is at the level of the supraorbital ridges with the face above the level of the shanks ( Fig 11-4 ).
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
Related posts:
- Human Birth
- Shoulder Dystocia
- Antepartum Haemorrhage
- Analgesia and Anaesthesia
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Comments are closed for this page.

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Vertex Presentation Definition

Vertex presentation refers to the manner in which a baby’s head is positioned inside the mother’s womb, which determines the points of contact on the baby’s head as they are being born. When the baby is in the vertex position, this means that the baby’s head is the first part of the body to be born. This is the most common presentation and is considered the best position for the baby to be born in. It occurs in about 97% of all births.
This position is also known as the cephalic position. However, vertex presentation is but one of the different types of cephalic presentations.
This presentation has three types. Occiput anterior is the most common, where the baby’s head is facing forward, towards the mother’s rectum. Occiput posterior is the least common, where the baby’s head is facing backward, facing the mother’s spine. Mentum anterior is a variation of occiput anterior, where the chin is leading instead of the forehead, also known as the face presentation.
The most important thing to consider during a vertex presentation is the baby’s position. If the baby is in an occiput posterior position, it may need to be turned to the occiput anterior position in order to be born. Failure to turn will result in prolonged labor. If the baby is in a mentum anterior position, it may need to be turned to the occiput posterior position in order to be born.
This image shows how often the term ‘Vertex Presentation’ is used in relation to other, similar birth terms:

[RELATED TERMS GRAPH]
Importance of the Vertex Presentation
A vertex presentation is generally a good sign that the baby is ready to be born, but there are some risks associated with it. The most common risk is cord prolapse, where the umbilical cord slips out of the baby’s vagina before the baby is born. This can cause the baby to lose its oxygen supply and can be fatal. Other risks include shoulder dystocia, where the baby’s shoulder gets stuck in the birth canal, and the nuchal cord, where the umbilical cord gets wrapped around the baby’s neck.
If the baby is in a vertex presentation and their head is not engaged in the pelvis, that means that they are not ready to be born yet. In this case, the doctor or midwife will usually try to encourage the baby to move down into the pelvis by pushing on the mother’s belly or using a vacuum extractor. If the baby does not move down into the pelvis after a certain amount of time, a cesarean section may be necessary albeit an undesirable option.
Do you know a man who wants to learn more about birth? Send him our way ! Also, men and women are welcome to join our free public community of Dads helping Dads be better at birth.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc
- v.56(211); May-Jun 2018

Predisposing Factors and Outcome of Malpresentations in an Institute
Smrity maskey.
1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, KIST Medical College and Teaching Hospital, Lalitpur, Nepal
Introduction
This study was done to find out the incidence of malpresentation among all deliveries with various types of Malpresentations, its mode of delivery, maternal and fetal predisposing factors with outcome.
This was a cross sectional descriptive study done at KIST Medical College and Teaching Hospital. Review cases of women admitted in labor after 22 weeks with malpresentation was done. Maternal/fetal predisposing factors were recorded.
Total delivery in study period was 4009 where 101 (2.5%) were of malpresentation. Breech was the commonest malpresentation 83 (82.1%). Assisted vaginal delivery occurred in 16 (15.8%) and 953 (84.2%) caesarian section. Malpresentations was common in primigravida 62 (61.3%). Half (47.2%) cases had one/more predisposing factors, commonest being oligohydramnious 7 (6.9%). Out of 108 babies with malpresentation, 10 had perinatal deaths and 10 had NICU admissions. Congenital anomaly was found in 4 babies.
Conclusions
The most common type of malpresentation was breech common in primigravida with oligohydramnios as contributing factor.
INTRODUCTION
Malposition is abnormal positions of fetal vertex in relation to maternal pelvis. At onset of labor, the incidence is about 10% of all vertex presentation. 1 Malpresentation is presentation other than vertex. Breech presentation being the commonest (3%-4%) at term but more common in earlier gestations. 2 Many studies were conducted to find the cause of malpresentation and its maternal / fetal outcome 3 – 5 focused on gravida, malpresentation, 4 and association with their route of delivery. 3 – 5 Malpresentations usually ends increasing operative delivery, 6 leading to increased adverse outcome for mother and baby. The incidence of cord prolapse is 5-10% in transverse lie, 3% in breech (flexed leg) 7 and 10% in compound presentation.
Taking prompt action may save life of mother and baby if the delivery becomes obstructed due to abnormal presentation. 7 The risk of cord prolapse is 1 in 300 deliveries which decreases with elective caeserian section. 8 Malpresentation is quite common in multiple pregnancies (10%). 9
This study aims in finding the commonest type of malpresentation, its diagnosis with prompt management and outcome.
A cross sectional descriptive study was conducted in KIST medical college from December 2013 to February 2014. Ethical approval was taken. Data were collected from medical record of all the pregnant women between June 2008 to January 2014. All delivery with malpresentation and malposition that occurred during the study period was included. On the other hand those gestation before after age of viability (22 weeks) with diagnosis of malpresentation were not included in the study. All parameters like age, gravida, parity, gestation age, ANC visits, type of malpresentation, mode of delivery, baby's birth weight, Apgar score, neonatal outcome, maternal complications were noted. Similarly any maternal or fetal predisposing factors were also looked for and recorded. Descriptive analysis were done using Microsoft Excel.
The total number of delivery in the study period of five and half years was 4009. Among them 101 (2.5%) cases were of malpresentation. Breech was the most common malpresentation 83 (82.1%) among these malpresentations ( Figure 1 ).

Out of these cases of malpresentation, assisted vaginal delivery occurred in 16 (15.8%) and 953 (84.2%) underwent caesarian section ( Figure 2 ).

The mean age of these women were 23.4 years. Malpresentation was more common in primigravida 62 (61.3%) as compared to multigravida ( Table 1 ). Most of the malpresentations were diagnosed at ANC before the onset of labor; only 5 (4.9%) had no ANC and were diagnosed as malpresentation at labor. About half (47.2%) of the cases had one or more associated predisposing factors for malpresentation. The most common associated factor mentioned was Oligohydramnious 7 (6.9%) followed by IUGR, twin, IUFD, APH, Cord prolapse, abnormality and previous section. None of the cases had uterine anomalies documented though it is a common associated factor. Only 2 (1.9%) of cases had placenta previa.
Total 108 babies were born including seven sets of twins. Among these babies 10 had perinatal deaths (5 IUFD and 5 early Neonatal Deaths), 10 babies had NICU admissions for birth asphyxia. Low birth weight (less than 2.5 kg) baby's rate was 40.74%. Congenital anomaly was found in 4 babies.
Malpresentation and malposition is commonly encountered obstetric problem which accounts of 3-4%. In this study in a span of five and half years its incidence was 2.5%.
Breech was the most common malpresentation in our hospital study accounting for 82.1% which is consistent to the study from U.K. 1 in which breech as malpresentation was 85%. In present study the most common mode of delivery was caesarian section i.e. 84.2%. Assisted vaginal delivery accounted for 15.8% which was seen only in breech presentation. The incidence of breech vaginal delivery is low than a CS rate which corresponds with the study of Nordin NM. 10 This also supports the study of reference. 10 – 12 For most of the examined parameters statistically significant differences were found in mortality and morbidity between the vaginally delivered group and the caesarean section group in three birth weight categories which corresponds to the study of de Leeuw JP.4
In the study malpresentation with complication was the most common cause that increased caesarian rate. The commonest causes were twin and oligohydramnious 7 ( 6.9%) each. Because we include only studies that compared non-cephalic presenting twins with each other, these reports were excluded which is supported by the reverence. 9 A limitation of this study was no uterine anomaly was detected despite it is the most common cause of malpresentation. In the study cord prolapsed was seen in 2 cases (2%) out of 101 malpresentation cases which is very high in contrast to study of Kouam L where 39 ( 0.1%) cases of cord prolapsed were found out of 20,000 cases. This disparity can be because of the sample size.
Due to good ANC, 95.1% patient were diagnosed with malpresentation antenatally and were managed electively in contrast to 4.9% patient who had no ANC. This indicates that good ANC can detect malpresentation which will have good prognosis for mother and baby. Malpresentation was more common in primi gravida which was 61.3%. This might indicate that the patient coming to hospital for deliveries were mostly primi.
NICU admissions were 5 patients for birth asphyxia and were seen in emergency LSCS patients only. Elective LSCS had good neonatal outcome. Among the 3 category of baby birth weight in the study very low birth weight was found only in pre-term pregnancy whereas it was more than 2.5kg in term and post term pregnancies.
CONCLUSIONS
Malpresentation accounted for 2.5% in the study with breech as the most common type. Most malpresentations were diagnosed at ANC through clinical finding and ultrasonography while only 4.9% had no ANC and diagnosed at labor. The most common associated factor of malpresentation was oligohydramnios and twins. The most common mode of delivery was Caesarian section. In caesarian section emergency section was more compared to elective section due to associated complications and late detection of malpresentation. The maternal and fetal outcome was good with no maternal mortality and 10 perinatal morbidity. Anencephaly was the only congenital abnormality encountered in the study (4 cases). Future research about this subject might be useful.
Conflict of Interest
Face Presentation
- First Online: 02 August 2023
Cite this chapter

- Shubhra Agarwal 2 &
- Suchitra Pandit 3
562 Accesses
Face presentation is defined as a cephalic presentation in which the presenting part is face and it occurs due to factors that lead to extension of of fetal head. It is a rare obstetric presentation and may not be encountered even in the entire carrier of an obstetrician.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Shaffer BL. Face presentation: predictors and delivery route. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2006;194:e10–2.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Schwartz Z, Dgani R, Lancet M, Kessler I. Face presentation. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 1986;26:172–6.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Westgren M, et al. Face presentation in modern obstetrics-a study with special reference to fetal long term morbidity. Z Geburtshilfe Perinatol. 1984;188(2):87–9.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, TMMC&RC, Moradabad, India
Shubhra Agarwal
Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Surya Hospital, Mumbai, India
Suchitra Pandit
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Sarojini Naidu Medical College, Agra, Uttar Pradesh, India
Ruchika Garg
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Agarwal, S., Pandit, S. (2023). Face Presentation. In: Garg, R. (eds) Labour and Delivery. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-6145-8_6
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-6145-8_6
Published : 02 August 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-19-6144-1
Online ISBN : 978-981-19-6145-8
eBook Packages : Medicine Medicine (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Types of Vertex Presentation Occiput Anterior: The Optimal Position. Imagine the baby facing your spine, with their head slightly tilted downwards, chin tucked in. This is the occiput anterior position—the gold standard of vertex presentation. It's like a skilled explorer charting the best route through uncharted territories.
Is vertex presentation the same as cephalic position? Yes, they essentially mean the same thing. Cephalic presentation means a fetus is in a head-down position. Vertex refers to the fetus's neck being tucked in. There are other types of cephalic presentations like brow and face. These mainly describe how the fetus's neck is flexed.
This positioning is called fetal presentation. ... presentation. That's when the knees aren't bent, and the feet are close to the baby's head. This is the most common type of breech presentation. ... A comparison between delivery of vertex and non-vertex second twins. The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine. 2021; doi:10.1080/14767058 ...
8.1 Normal and abnormal presentations 8.1.1 Vertex presentation. In about 95% of deliveries, the part of the fetus which arrives first at the mother's pelvic brim is the highest part of the fetal head, which is called the vertex (Figure 8.1).This presentation is called the vertex presentation.Notice that the baby's chin is tucked down towards its chest, so that the vertex is the leading ...
In face presentation, the baby's neck arches back so that the face presents first rather than the top of the head.. In brow presentation, the neck is moderately arched so that the brow presents first.. Usually, fetuses do not stay in a face or brow presentation. These presentations often change to a vertex (top of the head) presentation before or during labor.
Toward the end of pregnancy, the fetus moves into position for delivery. Normally, the presentation is vertex (head first), and the position is occiput anterior (facing toward the pregnant patient's spine) with the face and body angled to one side and the neck flexed. Abnormal presentations include face, brow, breech, and shoulder.
This has been described as "prolapse of an extremity alongside of the presenting part, both entering the pelvic canal simultaneously." 8 The incidence of this type of presentation has been reported to range from 0.15% 9 to 0.4%. 10 The most frequent is a vertex and hand combination, which accounts for 58% of the cases. 9 This is followed in ...
Learn more about the types, causes, and risks of breech presentation, along with how breech babies are typically delivered. By Elizabeth Stein, CNM and Laura Riley, M.D.
Breech Births. In the last weeks of pregnancy, a baby usually moves so his or her head is positioned to come out of the vagina first during birth. This is called a vertex presentation. A breech presentation occurs when the baby's buttocks, feet, or both are positioned to come out first during birth. This happens in 3-4% of full-term births.
As mentioned earlier, a vertex position is a baby's position during vaginal delivery. The baby moves into the vertex position between the 33 rd - 36 th week of pregnancy. In this position, the baby's head comes out first through the vagina during delivery. However, it is vital to know that the baby can present with other positions like ...
Vertex presentation indicates that the crown of the head or vertex of the baby is presenting towards the cervix. Vertex presentation is the most common presentation observed in the third trimester. The definition of vertex presentation, according to the American College of Obstetrics and Gynecologists is, "A fetal presentation where the head ...
The incidence of breech presentation varies according to gestation: 20% at 30 weeks falling to 4% by term. The aetiology of most breech presentations at term is unclear but known factors to consider include placenta praevia, polyhydramnios, bicornuate uterus, fibroids and, rarely, spina bifida or hydrocephaly. Types of breech presentation
Most common are the "incomplete" types of breech presentation, such as footling breech presentations (Fig. 3, Tables 5 and 6). Deflexion of the fetal head, more commonly seen in preterm fetuses, results in the potential for further compromise at delivery. ... % Vertex at delivery % Vertex controls. Brocks et al., 1984 15. 41. 100. 14.
Absolutely not! The vertex presentation is not only the most common, but also the best for a smooth delivery. In fact, the chances of a vaginal delivery are better if you have a vertex fetal position. By 36 weeks into pregnancy, about 95% of the babies position themselves to have the vertex presentation. However, if your baby hasn't come into ...
Presentation of twins in Der Rosengarten ("The Rose Garden"), a standard medical text for midwives published in 1513. In obstetrics, the presentation of a fetus about to be born specifies which anatomical part of the fetus is leading, that is, is closest to the pelvic inlet of the birth canal. According to the leading part, this is identified as a cephalic, breech, or shoulder presentation.
Breech presentation refers to the fetus in the longitudinal lie with the buttocks or lower extremity entering the pelvis first. The three types of breech presentation include frank breech, complete breech, and incomplete breech. In a frank breech, the fetus has flexion of both hips, and the legs are straight with the feet near the fetal face, in a pike position. The complete breech has the ...
Occiput or cephalic anterior: This is the best fetal position for childbirth. It means the fetus is head down, facing the birth parent's spine (facing backward). Its chin is tucked towards its chest. The fetus will also be slightly off-center, with the back of its head facing the right or left. This is called left occiput anterior or right ...
Twin fetal presentation - also known as the position of your babies in the womb - dictates whether you'll have a vaginal or c-section birth. Toward the end of pregnancy, most twins will move in the head-down position (vertex), but there's a risk that the second twin will change position after the first twin is born.
Fetal malpresentation exists when the presenting part is other than the normal vertex of the fetal head. This includes two malpresentations that are covered in other chapters: breech ( Chapter 16 ) and cord presentation ( Chapter 18 ).The remaining malpresentations that will be covered in this chapter are face, brow, transverse lie with shoulder or arm presentation, and compound presentations.
Vertex Presentation Definition. April 24, 2022. Vertex presentation refers to the manner in which a baby's head is positioned inside the mother's womb, which determines the points of contact on the baby's head as they are being born. When the baby is in the vertex position, this means that the baby's head is the first part of the body ...
At onset of labor, the incidence is about 10% of all vertex presentation. 1 Malpresentation is presentation other than vertex. Breech presentation being the commonest ... This study aims in finding the commonest type of malpresentation, its diagnosis with prompt management and outcome.
387 likes • 100,485 views. AI-enhanced description. Shrooti Shah. This document discusses various types of malpresentations that can occur during labor, including face presentation, brow presentation, breech presentation, shoulder presentation, and unstable lie. It provides details on the diagnosis, management, and potential complications of ...
A type of cephalic presentation in which the presenting part is the face, the area between chin and glabella. The incidence varies from 1 in 500 to 1 in 1000 deliveries. Primary face presentation is rare. Secondary face presentation caused by extension of head during labor is common. Thus, the diagnosis is usually made during active phase of ...
Follow. KING OF PRUSSIA, Pa., May 30, 2024 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Vertex, Inc. (NASDAQ:VERX), a global provider of tax technology solutions, today announced that management will present at the ...