Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments

Definition and Introduction
Case analysis is a problem-based teaching and learning method that involves critically analyzing complex scenarios within an organizational setting for the purpose of placing the student in a “real world” situation and applying reflection and critical thinking skills to contemplate appropriate solutions, decisions, or recommended courses of action. It is considered a more effective teaching technique than in-class role playing or simulation activities. The analytical process is often guided by questions provided by the instructor that ask students to contemplate relationships between the facts and critical incidents described in the case.
Cases generally include both descriptive and statistical elements and rely on students applying abductive reasoning to develop and argue for preferred or best outcomes [i.e., case scenarios rarely have a single correct or perfect answer based on the evidence provided]. Rather than emphasizing theories or concepts, case analysis assignments emphasize building a bridge of relevancy between abstract thinking and practical application and, by so doing, teaches the value of both within a specific area of professional practice.
Given this, the purpose of a case analysis paper is to present a structured and logically organized format for analyzing the case situation. It can be assigned to students individually or as a small group assignment and it may include an in-class presentation component. Case analysis is predominately taught in economics and business-related courses, but it is also a method of teaching and learning found in other applied social sciences disciplines, such as, social work, public relations, education, journalism, and public administration.
Ellet, William. The Case Study Handbook: A Student's Guide . Revised Edition. Boston, MA: Harvard Business School Publishing, 2018; Christoph Rasche and Achim Seisreiner. Guidelines for Business Case Analysis . University of Potsdam; Writing a Case Analysis . Writing Center, Baruch College; Volpe, Guglielmo. "Case Teaching in Economics: History, Practice and Evidence." Cogent Economics and Finance 3 (December 2015). doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/23322039.2015.1120977.
How to Approach Writing a Case Analysis Paper
The organization and structure of a case analysis paper can vary depending on the organizational setting, the situation, and how your professor wants you to approach the assignment. Nevertheless, preparing to write a case analysis paper involves several important steps. As Hawes notes, a case analysis assignment “...is useful in developing the ability to get to the heart of a problem, analyze it thoroughly, and to indicate the appropriate solution as well as how it should be implemented” [p.48]. This statement encapsulates how you should approach preparing to write a case analysis paper.
Before you begin to write your paper, consider the following analytical procedures:
- Review the case to get an overview of the situation . A case can be only a few pages in length, however, it is most often very lengthy and contains a significant amount of detailed background information and statistics, with multilayered descriptions of the scenario, the roles and behaviors of various stakeholder groups, and situational events. Therefore, a quick reading of the case will help you gain an overall sense of the situation and illuminate the types of issues and problems that you will need to address in your paper. If your professor has provided questions intended to help frame your analysis, use them to guide your initial reading of the case.
- Read the case thoroughly . After gaining a general overview of the case, carefully read the content again with the purpose of understanding key circumstances, events, and behaviors among stakeholder groups. Look for information or data that appears contradictory, extraneous, or misleading. At this point, you should be taking notes as you read because this will help you develop a general outline of your paper. The aim is to obtain a complete understanding of the situation so that you can begin contemplating tentative answers to any questions your professor has provided or, if they have not provided, developing answers to your own questions about the case scenario and its connection to the course readings,lectures, and class discussions.
- Determine key stakeholder groups, issues, and events and the relationships they all have to each other . As you analyze the content, pay particular attention to identifying individuals, groups, or organizations described in the case and identify evidence of any problems or issues of concern that impact the situation in a negative way. Other things to look for include identifying any assumptions being made by or about each stakeholder, potential biased explanations or actions, explicit demands or ultimatums , and the underlying concerns that motivate these behaviors among stakeholders. The goal at this stage is to develop a comprehensive understanding of the situational and behavioral dynamics of the case and the explicit and implicit consequences of each of these actions.
- Identify the core problems . The next step in most case analysis assignments is to discern what the core [i.e., most damaging, detrimental, injurious] problems are within the organizational setting and to determine their implications. The purpose at this stage of preparing to write your analysis paper is to distinguish between the symptoms of core problems and the core problems themselves and to decide which of these must be addressed immediately and which problems do not appear critical but may escalate over time. Identify evidence from the case to support your decisions by determining what information or data is essential to addressing the core problems and what information is not relevant or is misleading.
- Explore alternative solutions . As noted, case analysis scenarios rarely have only one correct answer. Therefore, it is important to keep in mind that the process of analyzing the case and diagnosing core problems, while based on evidence, is a subjective process open to various avenues of interpretation. This means that you must consider alternative solutions or courses of action by critically examining strengths and weaknesses, risk factors, and the differences between short and long-term solutions. For each possible solution or course of action, consider the consequences they may have related to their implementation and how these recommendations might lead to new problems. Also, consider thinking about your recommended solutions or courses of action in relation to issues of fairness, equity, and inclusion.
- Decide on a final set of recommendations . The last stage in preparing to write a case analysis paper is to assert an opinion or viewpoint about the recommendations needed to help resolve the core problems as you see them and to make a persuasive argument for supporting this point of view. Prepare a clear rationale for your recommendations based on examining each element of your analysis. Anticipate possible obstacles that could derail their implementation. Consider any counter-arguments that could be made concerning the validity of your recommended actions. Finally, describe a set of criteria and measurable indicators that could be applied to evaluating the effectiveness of your implementation plan.
Use these steps as the framework for writing your paper. Remember that the more detailed you are in taking notes as you critically examine each element of the case, the more information you will have to draw from when you begin to write. This will save you time.
NOTE : If the process of preparing to write a case analysis paper is assigned as a student group project, consider having each member of the group analyze a specific element of the case, including drafting answers to the corresponding questions used by your professor to frame the analysis. This will help make the analytical process more efficient and ensure that the distribution of work is equitable. This can also facilitate who is responsible for drafting each part of the final case analysis paper and, if applicable, the in-class presentation.
Framework for Case Analysis . College of Management. University of Massachusetts; Hawes, Jon M. "Teaching is Not Telling: The Case Method as a Form of Interactive Learning." Journal for Advancement of Marketing Education 5 (Winter 2004): 47-54; Rasche, Christoph and Achim Seisreiner. Guidelines for Business Case Analysis . University of Potsdam; Writing a Case Study Analysis . University of Arizona Global Campus Writing Center; Van Ness, Raymond K. A Guide to Case Analysis . School of Business. State University of New York, Albany; Writing a Case Analysis . Business School, University of New South Wales.
Structure and Writing Style
A case analysis paper should be detailed, concise, persuasive, clearly written, and professional in tone and in the use of language . As with other forms of college-level academic writing, declarative statements that convey information, provide a fact, or offer an explanation or any recommended courses of action should be based on evidence. If allowed by your professor, any external sources used to support your analysis, such as course readings, should be properly cited under a list of references. The organization and structure of case analysis papers can vary depending on your professor’s preferred format, but its structure generally follows the steps used for analyzing the case.
Introduction
The introduction should provide a succinct but thorough descriptive overview of the main facts, issues, and core problems of the case . The introduction should also include a brief summary of the most relevant details about the situation and organizational setting. This includes defining the theoretical framework or conceptual model on which any questions were used to frame your analysis.
Following the rules of most college-level research papers, the introduction should then inform the reader how the paper will be organized. This includes describing the major sections of the paper and the order in which they will be presented. Unless you are told to do so by your professor, you do not need to preview your final recommendations in the introduction. U nlike most college-level research papers , the introduction does not include a statement about the significance of your findings because a case analysis assignment does not involve contributing new knowledge about a research problem.
Background Analysis
Background analysis can vary depending on any guiding questions provided by your professor and the underlying concept or theory that the case is based upon. In general, however, this section of your paper should focus on:
- Providing an overarching analysis of problems identified from the case scenario, including identifying events that stakeholders find challenging or troublesome,
- Identifying assumptions made by each stakeholder and any apparent biases they may exhibit,
- Describing any demands or claims made by or forced upon key stakeholders, and
- Highlighting any issues of concern or complaints expressed by stakeholders in response to those demands or claims.
These aspects of the case are often in the form of behavioral responses expressed by individuals or groups within the organizational setting. However, note that problems in a case situation can also be reflected in data [or the lack thereof] and in the decision-making, operational, cultural, or institutional structure of the organization. Additionally, demands or claims can be either internal and external to the organization [e.g., a case analysis involving a president considering arms sales to Saudi Arabia could include managing internal demands from White House advisors as well as demands from members of Congress].
Throughout this section, present all relevant evidence from the case that supports your analysis. Do not simply claim there is a problem, an assumption, a demand, or a concern; tell the reader what part of the case informed how you identified these background elements.
Identification of Problems
In most case analysis assignments, there are problems, and then there are problems . Each problem can reflect a multitude of underlying symptoms that are detrimental to the interests of the organization. The purpose of identifying problems is to teach students how to differentiate between problems that vary in severity, impact, and relative importance. Given this, problems can be described in three general forms: those that must be addressed immediately, those that should be addressed but the impact is not severe, and those that do not require immediate attention and can be set aside for the time being.
All of the problems you identify from the case should be identified in this section of your paper, with a description based on evidence explaining the problem variances. If the assignment asks you to conduct research to further support your assessment of the problems, include this in your explanation. Remember to cite those sources in a list of references. Use specific evidence from the case and apply appropriate concepts, theories, and models discussed in class or in relevant course readings to highlight and explain the key problems [or problem] that you believe must be solved immediately and describe the underlying symptoms and why they are so critical.
Alternative Solutions
This section is where you provide specific, realistic, and evidence-based solutions to the problems you have identified and make recommendations about how to alleviate the underlying symptomatic conditions impacting the organizational setting. For each solution, you must explain why it was chosen and provide clear evidence to support your reasoning. This can include, for example, course readings and class discussions as well as research resources, such as, books, journal articles, research reports, or government documents. In some cases, your professor may encourage you to include personal, anecdotal experiences as evidence to support why you chose a particular solution or set of solutions. Using anecdotal evidence helps promote reflective thinking about the process of determining what qualifies as a core problem and relevant solution .
Throughout this part of the paper, keep in mind the entire array of problems that must be addressed and describe in detail the solutions that might be implemented to resolve these problems.
Recommended Courses of Action
In some case analysis assignments, your professor may ask you to combine the alternative solutions section with your recommended courses of action. However, it is important to know the difference between the two. A solution refers to the answer to a problem. A course of action refers to a procedure or deliberate sequence of activities adopted to proactively confront a situation, often in the context of accomplishing a goal. In this context, proposed courses of action are based on your analysis of alternative solutions. Your description and justification for pursuing each course of action should represent the overall plan for implementing your recommendations.
For each course of action, you need to explain the rationale for your recommendation in a way that confronts challenges, explains risks, and anticipates any counter-arguments from stakeholders. Do this by considering the strengths and weaknesses of each course of action framed in relation to how the action is expected to resolve the core problems presented, the possible ways the action may affect remaining problems, and how the recommended action will be perceived by each stakeholder.
In addition, you should describe the criteria needed to measure how well the implementation of these actions is working and explain which individuals or groups are responsible for ensuring your recommendations are successful. In addition, always consider the law of unintended consequences. Outline difficulties that may arise in implementing each course of action and describe how implementing the proposed courses of action [either individually or collectively] may lead to new problems [both large and small].
Throughout this section, you must consider the costs and benefits of recommending your courses of action in relation to uncertainties or missing information and the negative consequences of success.
The conclusion should be brief and introspective. Unlike a research paper, the conclusion in a case analysis paper does not include a summary of key findings and their significance, a statement about how the study contributed to existing knowledge, or indicate opportunities for future research.
Begin by synthesizing the core problems presented in the case and the relevance of your recommended solutions. This can include an explanation of what you have learned about the case in the context of your answers to the questions provided by your professor. The conclusion is also where you link what you learned from analyzing the case with the course readings or class discussions. This can further demonstrate your understanding of the relationships between the practical case situation and the theoretical and abstract content of assigned readings and other course content.
Problems to Avoid
The literature on case analysis assignments often includes examples of difficulties students have with applying methods of critical analysis and effectively reporting the results of their assessment of the situation. A common reason cited by scholars is that the application of this type of teaching and learning method is limited to applied fields of social and behavioral sciences and, as a result, writing a case analysis paper can be unfamiliar to most students entering college.
After you have drafted your paper, proofread the narrative flow and revise any of these common errors:
- Unnecessary detail in the background section . The background section should highlight the essential elements of the case based on your analysis. Focus on summarizing the facts and highlighting the key factors that become relevant in the other sections of the paper by eliminating any unnecessary information.
- Analysis relies too much on opinion . Your analysis is interpretive, but the narrative must be connected clearly to evidence from the case and any models and theories discussed in class or in course readings. Any positions or arguments you make should be supported by evidence.
- Analysis does not focus on the most important elements of the case . Your paper should provide a thorough overview of the case. However, the analysis should focus on providing evidence about what you identify are the key events, stakeholders, issues, and problems. Emphasize what you identify as the most critical aspects of the case to be developed throughout your analysis. Be thorough but succinct.
- Writing is too descriptive . A paper with too much descriptive information detracts from your analysis of the complexities of the case situation. Questions about what happened, where, when, and by whom should only be included as essential information leading to your examination of questions related to why, how, and for what purpose.
- Inadequate definition of a core problem and associated symptoms . A common error found in case analysis papers is recommending a solution or course of action without adequately defining or demonstrating that you understand the problem. Make sure you have clearly described the problem and its impact and scope within the organizational setting. Ensure that you have adequately described the root causes w hen describing the symptoms of the problem.
- Recommendations lack specificity . Identify any use of vague statements and indeterminate terminology, such as, “A particular experience” or “a large increase to the budget.” These statements cannot be measured and, as a result, there is no way to evaluate their successful implementation. Provide specific data and use direct language in describing recommended actions.
- Unrealistic, exaggerated, or unattainable recommendations . Review your recommendations to ensure that they are based on the situational facts of the case. Your recommended solutions and courses of action must be based on realistic assumptions and fit within the constraints of the situation. Also note that the case scenario has already happened, therefore, any speculation or arguments about what could have occurred if the circumstances were different should be revised or eliminated.
Bee, Lian Song et al. "Business Students' Perspectives on Case Method Coaching for Problem-Based Learning: Impacts on Student Engagement and Learning Performance in Higher Education." Education & Training 64 (2022): 416-432; The Case Analysis . Fred Meijer Center for Writing and Michigan Authors. Grand Valley State University; Georgallis, Panikos and Kayleigh Bruijn. "Sustainability Teaching using Case-Based Debates." Journal of International Education in Business 15 (2022): 147-163; Hawes, Jon M. "Teaching is Not Telling: The Case Method as a Form of Interactive Learning." Journal for Advancement of Marketing Education 5 (Winter 2004): 47-54; Georgallis, Panikos, and Kayleigh Bruijn. "Sustainability Teaching Using Case-based Debates." Journal of International Education in Business 15 (2022): 147-163; .Dean, Kathy Lund and Charles J. Fornaciari. "How to Create and Use Experiential Case-Based Exercises in a Management Classroom." Journal of Management Education 26 (October 2002): 586-603; Klebba, Joanne M. and Janet G. Hamilton. "Structured Case Analysis: Developing Critical Thinking Skills in a Marketing Case Course." Journal of Marketing Education 29 (August 2007): 132-137, 139; Klein, Norman. "The Case Discussion Method Revisited: Some Questions about Student Skills." Exchange: The Organizational Behavior Teaching Journal 6 (November 1981): 30-32; Mukherjee, Arup. "Effective Use of In-Class Mini Case Analysis for Discovery Learning in an Undergraduate MIS Course." The Journal of Computer Information Systems 40 (Spring 2000): 15-23; Pessoa, Silviaet al. "Scaffolding the Case Analysis in an Organizational Behavior Course: Making Analytical Language Explicit." Journal of Management Education 46 (2022): 226-251: Ramsey, V. J. and L. D. Dodge. "Case Analysis: A Structured Approach." Exchange: The Organizational Behavior Teaching Journal 6 (November 1981): 27-29; Schweitzer, Karen. "How to Write and Format a Business Case Study." ThoughtCo. https://www.thoughtco.com/how-to-write-and-format-a-business-case-study-466324 (accessed December 5, 2022); Reddy, C. D. "Teaching Research Methodology: Everything's a Case." Electronic Journal of Business Research Methods 18 (December 2020): 178-188; Volpe, Guglielmo. "Case Teaching in Economics: History, Practice and Evidence." Cogent Economics and Finance 3 (December 2015). doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/23322039.2015.1120977.
Writing Tip
Ca se Study and Case Analysis Are Not the Same!
Confusion often exists between what it means to write a paper that uses a case study research design and writing a paper that analyzes a case; they are two different types of approaches to learning in the social and behavioral sciences. Professors as well as educational researchers contribute to this confusion because they often use the term "case study" when describing the subject of analysis for a case analysis paper. But you are not studying a case for the purpose of generating a comprehensive, multi-faceted understanding of a research problem. R ather, you are critically analyzing a specific scenario to argue logically for recommended solutions and courses of action that lead to optimal outcomes applicable to professional practice.
To avoid any confusion, here are twelve characteristics that delineate the differences between writing a paper using the case study research method and writing a case analysis paper:
- Case study is a method of in-depth research and rigorous inquiry ; case analysis is a reliable method of teaching and learning . A case study is a modality of research that investigates a phenomenon for the purpose of creating new knowledge, solving a problem, or testing a hypothesis using empirical evidence derived from the case being studied. Often, the results are used to generalize about a larger population or within a wider context. The writing adheres to the traditional standards of a scholarly research study. A case analysis is a pedagogical tool used to teach students how to reflect and think critically about a practical, real-life problem in an organizational setting.
- The researcher is responsible for identifying the case to study; a case analysis is assigned by your professor . As the researcher, you choose the case study to investigate in support of obtaining new knowledge and understanding about the research problem. The case in a case analysis assignment is almost always provided, and sometimes written, by your professor and either given to every student in class to analyze individually or to a small group of students, or students select a case to analyze from a predetermined list.
- A case study is indeterminate and boundless; a case analysis is predetermined and confined . A case study can be almost anything [see item 9 below] as long as it relates directly to examining the research problem. This relationship is the only limit to what a researcher can choose as the subject of their case study. The content of a case analysis is determined by your professor and its parameters are well-defined and limited to elucidating insights of practical value applied to practice.
- Case study is fact-based and describes actual events or situations; case analysis can be entirely fictional or adapted from an actual situation . The entire content of a case study must be grounded in reality to be a valid subject of investigation in an empirical research study. A case analysis only needs to set the stage for critically examining a situation in practice and, therefore, can be entirely fictional or adapted, all or in-part, from an actual situation.
- Research using a case study method must adhere to principles of intellectual honesty and academic integrity; a case analysis scenario can include misleading or false information . A case study paper must report research objectively and factually to ensure that any findings are understood to be logically correct and trustworthy. A case analysis scenario may include misleading or false information intended to deliberately distract from the central issues of the case. The purpose is to teach students how to sort through conflicting or useless information in order to come up with the preferred solution. Any use of misleading or false information in academic research is considered unethical.
- Case study is linked to a research problem; case analysis is linked to a practical situation or scenario . In the social sciences, the subject of an investigation is most often framed as a problem that must be researched in order to generate new knowledge leading to a solution. Case analysis narratives are grounded in real life scenarios for the purpose of examining the realities of decision-making behavior and processes within organizational settings. A case analysis assignments include a problem or set of problems to be analyzed. However, the goal is centered around the act of identifying and evaluating courses of action leading to best possible outcomes.
- The purpose of a case study is to create new knowledge through research; the purpose of a case analysis is to teach new understanding . Case studies are a choice of methodological design intended to create new knowledge about resolving a research problem. A case analysis is a mode of teaching and learning intended to create new understanding and an awareness of uncertainty applied to practice through acts of critical thinking and reflection.
- A case study seeks to identify the best possible solution to a research problem; case analysis can have an indeterminate set of solutions or outcomes . Your role in studying a case is to discover the most logical, evidence-based ways to address a research problem. A case analysis assignment rarely has a single correct answer because one of the goals is to force students to confront the real life dynamics of uncertainly, ambiguity, and missing or conflicting information within professional practice. Under these conditions, a perfect outcome or solution almost never exists.
- Case study is unbounded and relies on gathering external information; case analysis is a self-contained subject of analysis . The scope of a case study chosen as a method of research is bounded. However, the researcher is free to gather whatever information and data is necessary to investigate its relevance to understanding the research problem. For a case analysis assignment, your professor will often ask you to examine solutions or recommended courses of action based solely on facts and information from the case.
- Case study can be a person, place, object, issue, event, condition, or phenomenon; a case analysis is a carefully constructed synopsis of events, situations, and behaviors . The research problem dictates the type of case being studied and, therefore, the design can encompass almost anything tangible as long as it fulfills the objective of generating new knowledge and understanding. A case analysis is in the form of a narrative containing descriptions of facts, situations, processes, rules, and behaviors within a particular setting and under a specific set of circumstances.
- Case study can represent an open-ended subject of inquiry; a case analysis is a narrative about something that has happened in the past . A case study is not restricted by time and can encompass an event or issue with no temporal limit or end. For example, the current war in Ukraine can be used as a case study of how medical personnel help civilians during a large military conflict, even though circumstances around this event are still evolving. A case analysis can be used to elicit critical thinking about current or future situations in practice, but the case itself is a narrative about something finite and that has taken place in the past.
- Multiple case studies can be used in a research study; case analysis involves examining a single scenario . Case study research can use two or more cases to examine a problem, often for the purpose of conducting a comparative investigation intended to discover hidden relationships, document emerging trends, or determine variations among different examples. A case analysis assignment typically describes a stand-alone, self-contained situation and any comparisons among cases are conducted during in-class discussions and/or student presentations.
The Case Analysis . Fred Meijer Center for Writing and Michigan Authors. Grand Valley State University; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Ramsey, V. J. and L. D. Dodge. "Case Analysis: A Structured Approach." Exchange: The Organizational Behavior Teaching Journal 6 (November 1981): 27-29; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . 6th edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2017; Crowe, Sarah et al. “The Case Study Approach.” BMC Medical Research Methodology 11 (2011): doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-11-100; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods . 4th edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publishing; 1994.
- << Previous: Reviewing Collected Works
- Next: Writing a Case Study >>
- Last Updated: Jun 3, 2024 9:44 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- Browse by collection
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Online First
- Towards regulatory generative AI in ophthalmology healthcare: a security and privacy perspective
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- http://orcid.org/0009-0008-5169-5857 Yueye Wang 1 ,
- Chi Liu 2 ,
- Keyao Zhou 3 , 4 ,
- Tianqing Zhu 2 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6836-3447 Xiaotong Han 1
- 1 Sun Yat-sen University Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center State Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology , Guangzhou , Guangdong , China
- 2 Faculty of Data Science, City University of Macau , Macao SAR , China
- 3 Department of Ophthalmology , Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital , Guangzhou , Guangdong , China
- 4 Department of Neurosurgery , Huashan Hospital, Fudan University , Shanghai , China
- Correspondence to Dr Xiaotong Han, Sun Yat-Sen University Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center State Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China; lh.201205{at}aliyun.com ; Dr Chi Liu, Faculty of Data Science, City University of Macau, Macao SAR, China; chiliu{at}cityu.edu.mo
As the healthcare community increasingly harnesses the power of generative artificial intelligence (AI), critical issues of security, privacy and regulation take centre stage. In this paper, we explore the security and privacy risks of generative AI from model-level and data-level perspectives. Moreover, we elucidate the potential consequences and case studies within the domain of ophthalmology. Model-level risks include knowledge leakage from the model and model safety under AI-specific attacks, while data-level risks involve unauthorised data collection and data accuracy concerns. Within the healthcare context, these risks can bear severe consequences, encompassing potential breaches of sensitive information, violating privacy rights and threats to patient safety. This paper not only highlights these challenges but also elucidates governance-driven solutions that adhere to AI and healthcare regulations. We advocate for preparedness against potential threats, call for transparency enhancements and underscore the necessity of clinical validation before real-world implementation. The objective of security and privacy improvement in generative AI warrants emphasising the role of ophthalmologists and other healthcare providers, and the timely introduction of comprehensive regulations.
- Public health
Data availability statement
Data sharing not applicable as no data sets generated and/or analysed for this study. Not applicable.
https://doi.org/10.1136/bjo-2024-325167
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
Introduction
Over the past decade, the field of medicine has grasped opportunities from artificial intelligence (AI). 1 2 There is growing optimism regarding the promise of this technology to transform healthcare. 3 The image-centric nature of ophthalmology renders the development and application of AI within this field tremendous progress. 4 While alongside its huge potential, security and privacy issues arising from AI are of paramount importance. The powerful capabilities and extensive data consumption behind the AI raise concerns that without proper development and regulation, this technology may present risks and potential harm to individual privacy and security. 5 Nowhere are these concerns more critical than in the healthcare industry, where data leakage or model misuse can have severe consequences. To ensure the responsible use of this technology for the public’s benefit, the European Union (EU) published the first AI-specific regulation in 2021—the EU AI Act and other regulatory institutions like WHO and Food and Drug Administration (FDA) are catching up in recent years. 6–8
Generative AI, which enables the creation of various synthetic contexts based on users’ input, can highly speed up information translation and technological innovation. 9 Large language models (LLM), such as ChatGPT and Bard, showed great performance in the ophthalmology question–answering domain, even superior to historical human marks. 10 11 However, as we embrace the wave of generative AI, we are just starting to grasp the risks that come with it. Differing from regulated AI, generative AI presents unique characteristics such as extensive training data, broad applications, interactive data flow and synthetic contents. These features can pose new challenges that current regulations have not fully addressed. The extensive and diverse use of large generative AI models necessitates specific guidelines to protect security and privacy. 12
This paper aims to discuss the security and privacy challenges of generative AI in the context of healthcare. We present vulnerabilities at both the model and data levels, argue the consequences of such risk in ophthalmology and the broader medical fields and propose solutions and regulatory approaches to harness the full potential of this technology.
Security and privacy risks
Model-level risk, knowledge leakage.
The development of large generative models requires substantial data, expert knowledge, computational resources and trial and error, leading to substantial expenses for the developers. This is especially pronounced in the medical domain where data is highly sensitive and difficult to collect, coupled with the elevated costs for expert knowledge acquisition. Therefore, well-trained models are valuable digital assets whose safety should be protected. Traditionally, due to the ‘black box’ nature of AI, it is assumed that a deployed model is complicated to penetrate and reproduce without explicit knowledge of model architecture, training set and parameters. However, attacks like reverse engineering, model inversion attack and model extraction attack can still put the trained model at risk of being stolen during the inference time. 13–15 In the case of generative AI, network architecture and model hyperparameters can be inferred from the outputs (eg, synthetic images generated by the model). 16
Data used for training a generative AI model is also at risk of leakage. A membership inference attack is a way to expose the training data only from the queried outputs of a model. 17 For example, by deducing the participation of individuals in the training set from the output of a generative model, up to over 80% of the training set data can be inferred under a membership inference attack. 18 The risk of data leakage is amplified in generative models than in traditional medical AI models such as image-based classification models (eg, diagnostic models for eye diseases). This is because traditional models merely output abstract decisions based on prediction probabilities, and thus attackers are only able to infer approximate distributional information of training set with particular attacks. In contrast, generative models directly generate exact data points that belong to the same distribution of the training set, wherein the original training knowledge may leak spontaneously. For instance, with deliberate prompt decoys, an LLM can disclose the texts it has learnt in its responses. 19
Model corruption
Given the heightened expectations regarding AI’s role in supporting clinical decision-making, the integrity and reliability of the models should be prerequisites for healthcare practices. Unfortunately, current AI techniques, including generative AI, are vulnerable to orchestrated attacks. For instance, adversarial attacks, test-time attacks that perturb a clean test sample with imperceptible adversarial noises, can misguide a well-trained AI model to give a wrong prediction. 20 Another typical attack is known as a poisoning attack, where an attacker intentionally manipulates the training data of an AI model when they gain access to the training data set. The model trained with the poisoned data set becomes corrupted and, consequently would make inaccurate or biased predictions controlled by the triggering signals from the attacker during inference. 21
Model corruption can be especially impactful for generative AI, given the increasing reliance on it as a primary source of medical information. A corrupted model could be manipulated to generate toxic, biased or misleading content. What is worse, such problematic outputs are harder for humans to identify than detecting incorrect predictions from traditional medical AI, since LLMs present information interactively in natural language. Additionally, common AI attack vectors like adversarial attacks, backdoors and data poisoning are shifting focus from training-time attacks to prompt-level and fine-tuning attacks that no longer require data set access. This reduces attack costs, expanding and diversifying attack surfaces, necessitating urgent research attention.
Data-level risk
Unauthorised data collection.
Numerous data privacy breaches involving AI have been reported in the healthcare sector. 22 In the era of generative AI, the risk of healthcare data privacy violation has been significantly aggravated, as the information channels are greatly expanded through human-AI interaction. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act calls for attention to the heightened risk of healthcare data breaches due to generative AI. 23 For example, synthetic content from generative AI can abused for healthcare fraud. Additionally, conversational AI chatbots released by unauthorised services can be manipulated to steal patients’ data. The risk is particularly noteworthy in the field of ophthalmology, as the eye is usually considered a window to the body. Even from the input of a single retinal image, one’s demographic characteristics (eg, age, sex) and systematic conditions (eg, circulatory, neurological ageing and diseases) would be at risk of leakage.
Notably, LLMs like ChatGPT involve reinforcement learning from human feedback, which by default uses user-entered information for continuous training. 24 This poses an unwitting risk of exposing sensitive data at various stages of generative AI use. When being implemented for medical use, the models may receive sensitive prompts such as personal information and medical conditions without explicit and proper consent obtained from patients, which might violate the users’ original purpose.
Is seeing always believing?
Generative AI can synthesise content that looks highly realistic. For instance, a diffusion model can perform text-to-image translation, yielding high-fidelity output. 25 A generative adversarial network also makes it possible for transmodality from a fundus photograph to retinal angiography images with explicit microvasculature details. 26 However, it is essential to acknowledge that in medical practice, accuracy is critical besides fidelity. Content created by generative AI can have mistakes that do not align with science. 27 Another concern is the use of LLMs as medical databases; LLMs may provide persuasive yet fake citations when asked about data sources. 5
Unfortunately, clinical validation for generative AI is extremely challenging right now, primarily due to the massive content the model can generate. This unpredictability hinders generative models from meeting the regulation standards of the FDA as medical devices. Although we already have models that can generate fundus images featuring detailed retinal lesions, ascertaining the reliability of these lesions poses a challenge. The clinical application of such generative models also requires further validation.
Consequences in healthcare practice and case studies
Patient information breaches.
Generative AI has shown its value to be deployed in enhancing clinical documentation and workflow, supporting decision-making and improving interaction with patients. 12 In the diagnosis of ophthalmological diseases and in generating proficient operative notes, LLMs showed parallel performance to ophthalmology trainees or interns, indicating a promising way to reduce ophthalmologist workload. 28 However, as a potential consequence of relying on these models, the inevitable risk of sensitive information breach, such as biological data or clinical records, can severely violate patients’ privacy. The leading LLM, ChatGPT, experienced its first data breach on 20 March this year, affecting approximately 1.2 million users with exposed data. 29 This incident resulted from a bug in the open-source code, enabling some users to access others’ personal information (name, address, payment information and chat history).
This situation underscores the high risk regarding the application of generative models in clinical workflows. General LLMs, particularly cloud-based models, may harbour massive and dynamic patient information, making them vulnerable to potential breaches of sensitive data. To address this concern, one mitigation approach is to employ a locally customised LLM (such as Microsoft’s AutoGen), not relying on third-party servers. This strategy ensures that sensitive patient data remains confidential and secure within the context of the local health system. One alternative is to use a dedicated service such as Azure OpenAI services, where patient data is not available to be copied to the LLM or other customers or models, minimising the risk of data breaches.
Moreover, if malicious users manage to retrieve the training data or even the generative model itself through leaked information, the model’s integrity can be compromised. Recently, researchers from Google’s DeepMind used only simple prompts and extracted private training data from ChatGPT, breaking the model’s safeguards. 30 Any response lag in generative AI due to such a model attack may result in delayed patient management. Additionally, incorrect output generated from a corrupted model may contribute to misdiagnosis and inappropriate treatments.
Violation of the ‘Right to be Forgotten’
The ‘right to be forgotten’ under Article 17 of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is an essential consideration for human privacy. It addresses the need to mitigate prolonged storage of private medical information, which can be risky. This rule also acknowledges patients’ entitlement to request the removal of their data from AI models. Nevertheless, generative AI, especially LLMs, confronts obstacles in complying with this rule. The model requires massive amounts of clinical data for training, while the source of the training data is essentially unknown to both clinicians and patients. Even if removing personal data from the training data set, the trained model can produce outputs containing patient-specific information. In one case, researchers showed that ChatGPT provided the personal information of individual A in a request for a non-related individual B. 31 This case proved that LLM can memorise personal data and generate this data in future output.
Prolonged data retention or the failure to delete data on request may heighten the risk of unauthorised access or the unintended use of sensitive personal information. Even the training interval of Llama 2 family, the LLMs from Meta, was only around 2 months, this timespan still failed the requirement of GDPR’s ‘undue delay’—around 1 month. Lack of transparency is another critical concern in the use of generative AI that may harm the ‘right to be forgotten’. Patients entrust their personal data to healthcare providers and have the right to comprehensive information about data collection, processing and storage. Unfortunately, existing data processing disclosures have proven inadequate in this regard.
Is synthetic data safe for patient?
In digital modelling for trends assessment and prediction of disease risks, using synthetic data can augment sample sizes or enhance data set diversity, overcome challenges posed by insufficient real-world data or simulation on rare conditions. A recent study adopted Synthea, a well-documented and peer-reviewed generative AI to generate a 1.2 million Massachusetts patient cohort. 32 This study indicated that high-fidelity synthetic data performed well in modelling demographics, showing promise as a valuable analytics tool for aiding decision-making processes. However, it is noteworthy that synthetic data may not act well when simulating positive cases or reflecting disease-related metrics like mortality rates or complication rates. It is also challenging for synthetic data to monitor specific trends related to novel treatments or patient prognoses. This limitation of synthetic data may result in an underestimation of actual clinical outcomes.
Synthetic information from LLMs may also not be suitable for real-world medical use. Though studies are showing LLM can pass medical examinations such as the US Medical Licensing Examination. 33 Healthcare providers still express major concerns about accuracy and reliability regarding synthetic answers. 34 In the case of ChatGPT, it was found able to manage appropriately in retinal diseases, yet showed significant mistakes in other subdomain diseases such as lacrimal drainage disorders and anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy. 35–37
Based on the current evidence, synthetic data may not yet be a reliable proxy for real patient data. Inaccurate synthetic data may yield misleading or biased outcomes in medical research and practice, thereby exacerbating the potential for unsafe clinical management. 38 Before the clinical application of synthetic data, it is imperative to ensure its comparability to real-world data, safeguarding against potential harm to patients. Looking ahead, researchers are optimistic about this cutting-edge tool but stress the need for rigorous external clinical validation and accurate information.
Solutions under regulation
Be prepared for the attack.
In the latest updates, the first regulation on AI, the EU AI Act requires providers of generative AI to deploy the model with adequate training and design safeguards (Article 28). Prior to deployment in real clinical practice, anti-attack techniques such as adversarial training and robust model validation can help identify and mitigate model-level attacks. 39 The German Federal Office for Information and Security suggested several ways to reduce vulnerability to model attacks, 40 including avoiding identifiable and sensitive data, specifying training on sensitive data, restricting the user group, etc. In short, model providers and users need to be aware of the potential risk of model attacks and prepare plans for these attacks, such as model pre-training and user training.
Informed consent, data share and transparency
When using generative AI, it is vital for both model providers and users to comply with GDPR guidelines regarding lawful personal data collection and processing. This includes obtaining explicit consent from patients, providing transparent information about how data will be used, ensuring data security and enabling patients to exercise their data-related rights. Healthcare organisations must diligently train their staff to ensure compliance with patient security and privacy laws before deploying generative AI tools. Also, decentralisation technologies like blockchain, and federated learning, can be integrated with generative AI to enhance security in data share and storage.
Regarding the transparency of AI tools, research from Stanford University highlights that major providers of foundational models in the market have not strictly complied with the EU’s regulations. 41 Model providers may be reluctant to adhere strictly to transparency regulations, citing concerns related to both competitive factors and security considerations. To address these concerns and enhance transparency, regulators should also provide appropriate safeguards and guidance to model providers when regulating their activities.
Clinical validation
EU AI law mandates that synthetic content generation must adhere to legal requirements. However, within the healthcare context, legality alone is insufficient. Authentication and accuracy should also be put on the table. The Data Protection and Privacy Authorities (DPA) G7 underscores the importance of meticulously examining the interaction of individuals with generative AI and the processing of the content generated by generative AI tools. Cases with the data of minors should gain specific attention. Given that current models are typically trained on data from the general population, clinicians need to take care to determine whether a patient belongs to a vulnerable group or has characteristics that might make the model’s use inappropriate, to ensure patient safety.
Currently, clinical evaluations of LLMs primarily focus on accuracy. 42 To justify the use of LLMs for clinical applications, it is also essential to define other appropriate procedures and endpoints beyond effectiveness evaluation. Robust protocols are required to address security and privacy concerns. Before data is fed into the LLM, it is crucial to assess the success rate of pre-processing procedures, such as replacing, masking or anonymising to remove any personally identifiable information. Continuous monitoring of incoming requests in real-time helps to identify any instances where personally identifiable information reaches the LLM. This ensures that the LLM is working with data that has been thoroughly sanitised. In addition, the output generated by an LLM needs to be thoroughly evaluated against standard clinical practices. Content filtering and abuse monitoring can help evaluate every decision made by an LLM to detect and mitigate instances of harmful content generation. The most important part is clinician involvement in the quality appraisal process, as the unsupervised deployment of LLMs is considered impractical. 43 Clinicians need to evaluate whether the output of LLM is harmful to patients, may disclose individual information and introduce bias or discrimination into downstream clinical decisions.
Future perspectives
‘Many of the problems caused by AI can also be managed with the help of AI’, as said by Bill Gates. 44 During model development, data protection should be integrated into the system. DPA G7 suggested generative AI models to embed data protection throughout the product total lifecycle, based on the concept of ‘Privacy by Design’. Yang et al proposed using a digital mask to erase identifiable features while preserving the main features for ocular condition diagnosis. 45 By constructing synthetic data that behaves similarly to real clinical data, this privacy-protecting approach can be further enhanced with the help of generative AI. 45 46
The upcoming trend involves pre-trained large foundational models that serve as the cornerstone for various downstream AI applications. Two foundation models in ophthalmology, RETFound and VisionFM, have undergone training on millions of retinal images. They have effectively learnt general features from unlabeled data, showcasing remarkable capabilities in downstream tasks related to diagnosing ocular and systemic diseases. 47 48 The interaction of generative AI and the large foundation model may introduce new threats. For example, the frequently used pre-trained self-supervised learning encoder in foundational model techniques is susceptible to model stealing attacks. 49 These attacks not only endanger the model’s intellectual property but also potentially act as foreshadowing for subsequent attacks.
Current regulations are inadequate to address AI-related security and privacy concerns as they have already fallen outside the scope of national regulation for patient information protection. 50 Without expanding the regulatory framework, keeping up with the evolving landscape of generative AI can be difficult. Future regulatory perspectives may involve classifying AI software as medical devices, as the FDA has done, or shifting the regulatory focus from the AI models themselves to the providers, as the EU has pursued. Healthcare providers are the first line of defence for patient security and privacy. Generative AI and foundational models are ultimately tools designed to support healthcare services. It is important for future regulations to emphasise education for first-line healthcare service providers, on the responsible use of patient data to mitigate risks while maintaining accessibility and efficacy.
The full potential of generative AI technology can only be realised under effective governance. The principle of technology neutrality, where no specific technology is favoured or imposed, becomes crucial in the global competition to establish timely regulations for the burgeoning field of generative AI. There have been calls that AI regulations such as the EU AI Act need to take measures for sustainable development and innovation. 51 The Cyberspace Administration of China encourages innovation in generative AI services and lends support to the development of experimental research, while simultaneously emphasise responsibility for security and privacy. In the most recent recommendations from WHO, regulatory sandboxes are getting popular among regulators. 52 The Spanish government has approved the first AI regulatory sandbox pilot in 2023 as it allows the flexibility to test innovative products or services with minimal regulatory requirements and may foster AI innovation. 53 Achieving a trade-off between the advantages and risks associated with generative AI presents a tangible challenge for regulatory bodies in the near future.
Generative AI holds the potential to facilitate various aspects of clinical practice in ophthalmology and other healthcare domains. Prior to the implementation of this technology, it is essential to recognise the potential security and privacy risks associated with these models. Susceptible to both model-level and data-level attacks, generative models may cause severe consequences like extensive breaches of personal data, violation of patients’ privacy rights and safety. To address these concerns, it is crucial for model providers and users to proactively develop strategies that counteract attacks, enhance transparency and ensure robust validation throughout the entire product lifecycle, thus aligning with existing regulations. Furthermore, it is imperative to update the regulatory framework to keep pace with the ever-evolving landscape of generative AI, striking a balance between effective regulation and continued innovation.
Ethics statements
Patient consent for publication.
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
Acknowledgments.
We would like to acknowledge Professor Mingguang He and his research team for their kind suggestions during this study.
- Gulshan V ,
- Coram M , et al
- Pasquale LR ,
- Peng L , et al
- Gilbert S ,
- Melvin T , et al
- World Health Organization
- Zuiderveen Borgesius F
- Evgeniou T , et al
- Bockting CL ,
- van Dis EAM ,
- van Rooij R , et al
- Chia MA , et al
- Pei H , et al
- Hassner T , et al
- Sun L , et al
- Danezis G , et al
- Xu K , et al
- Ye D , et al
- Liang J , et al
- Ziegler DM ,
- Stiennon N ,
- Wu J , et al
- Saharia C ,
- Saxena S , et al
- Tavakkoli A ,
- Kamran SA ,
- Hossain KF , et al
- Reis-Filho JS ,
- Pushpanathan K , et al
- Carlini N ,
- Hayase J , et al
- Finckenberg-Broman P ,
- Hoang T , et al
- Patel M , et al
- Mihalache A ,
- Popovic MM , et al
- Temsah M-H ,
- Aljamaan F ,
- Malki KH , et al
- Potapenko I ,
- Boberg-Ans LC ,
- Stormly Hansen M , et al
- Waisberg E ,
- Masalkhi M , et al
- Giuffrè M ,
- Sajeeda A ,
- Hossain BMM
- Security FOfI
- Bommasani R ,
- Zhang D , et al
- Milad J , et al
- Thirunavukarasu AJ ,
- Elangovan K , et al
- Wang R , et al
- Plawinski J ,
- Subramaniam S , et al
- Wagner SK , et al
- Wei H , et al
- Benedikt Kohn LVN
- World Health O
YW and CL are joint first authors.
Contributors YW and CL developed the concept of the manuscript. YW, CL and KZ drafted the manuscript. XH and TZ made critical revisions of the manuscript. XH and TZ supervised the entire work. All authors approved the completed version. We used ChatGPT-4 only for proofreading and grammar checking of this review, but have not relied on the tool for any thinking or material presentation in this paper.
Funding This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82000901, 82101171), the Global STEM Professorship Scheme (P0046113), the Fundamental Research Funds of the State Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology (303060202400201209), the Outstanding PI Research Funds of the State Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology (3030902113083).
Competing interests None declared.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Read the full text or download the PDF:
Your cart is empty.
Sorry, there is insufficient stock for your cart.
Remove a Product
Without this product, applied coupon or promotion code cannot be redeemed. Are you sure to remove this product?
Privacy Policy
Tick this box to proceed to Samsung.com.
Samsung.com Services and marketing information, new product and service announcements as well as special offers, events and newsletters.
Check Preferences
Help us to make recommendations for you by updating your product preferences.
What are you looking for?
No suggestions, suggested searches, popular keyword, search history, recommended search.
Samsung for Business
Transforming businesses. Empowering owners.
Find the right solutions and exclusive benefits for businesses of all sizes.

See how Samsung makes an impact
Samsung's devices and solutions create tangible results.
Schneider needed a provider that could integrate its proprietary software with relevant third-party applications for connected fleets.
Duty Free Americas
Duty Free Americas, the largest duty-free retailer in the Americas, began its digital transformation a few years ago.
Lucid Motors
The design team at Lucid Motors was looking for a new, state-of-the-art display to take their design process to the next level.
Take the next step
Get connected today with volume discount offers on employee smartphones, monitors, displays, digital signage, appliances and more.
Stay in the know
* By submitting your email, you agree to receive periodic emails from Samsung on exclusive discounts, new product announcements, our latest technology insights, special events and more. Please consult our Privacy Policy to understand how we protect your privacy
Contact a sales expert
Get in touch with our sales team to discuss tailored solutions for your business. You can call (866) 726-4249 to talk to an expert now, or use the form below to submit your requests.
Get product support
Find manuals, downloads, warranty information and more. We also offer FAQs and demos to help with business product questions.
We will help you find the right solution for your business.
Sales Enquiries
Technical support, you are entering.
By selecting CONTINUE, you will be entering a website of
website is governed by its own privacy policy, level of security and terms of use
Your enquiry has been successfully submitted. We will get back to you shortly.
- Accessibility Policy
- Skip to content
- QUICK LINKS
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
- Oracle Fusion Cloud Applications
- Download Java
- Careers at Oracle
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI)
The next-generation cloud designed to run any application, faster and more securely, for less.
Stay at the forefront of the AI revolution. Get certified on OCI Generative AI for free until July 31.

Developers can now incorporate semantic and generative AI search within their applications, as well as in their observability and security analytics dashboards.

Address AI sovereignty needs with Oracle’s distributed cloud. Deploy Oracle’s full AI stack in the public cloud or in your data center for increased control of data and AI infrastructure.

Oracle and NVIDIA to Deliver Sovereign AI Worldwide
Oracle and NVIDIA are collaborating to put accelerated computing and generative AI services wherever countries must meet digital sovereignty requirements.

Clay Magouyrk, executive vice president of OCI development, shares how Oracle is bringing the cloud and AI to industries worldwide during his keynote at Oracle CloudWorld.

The expanded Oracle-Microsoft partnership, announced by Larry Ellison and Satya Nadella, delivers Oracle database services on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure in Microsoft Azure.
Learn how to get the most of AI for your business at an Oracle Data and AI Forum.
A distributed cloud that can be wherever you need it
The only cloud that delivers complete cloud services around the world, across clouds, or in your data center.
1. Multicloud
Make multiple clouds work as one. Oracle offers direct database integration with Microsoft Azure as well as high performance interconnection.
2. Public cloud
The only cloud with a consistent set of services and consistent low prices across commercial and government public cloud regions.
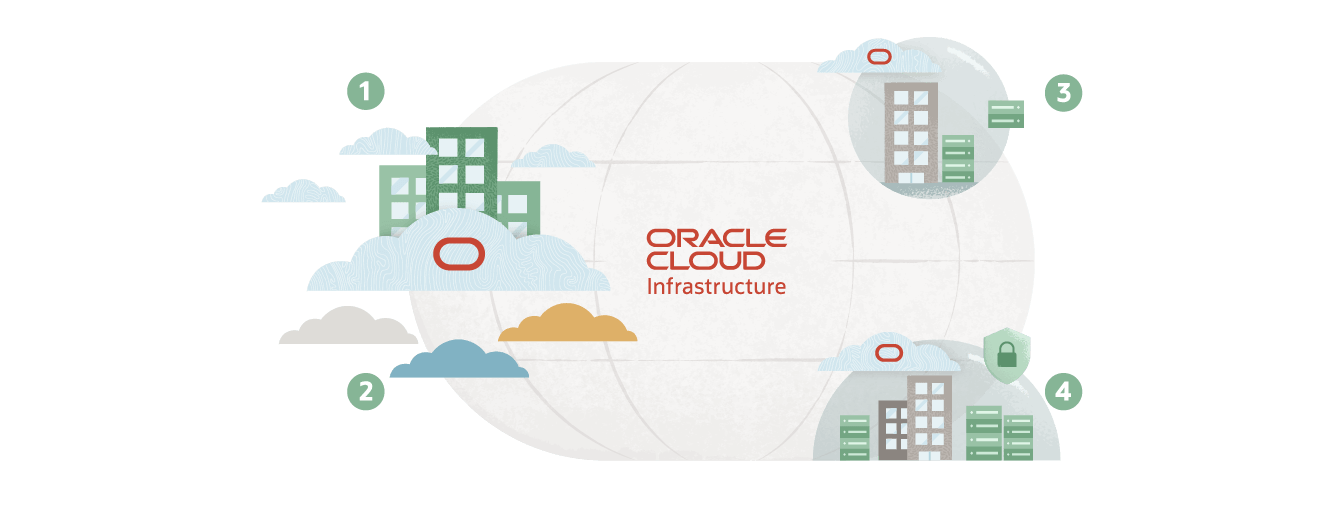
3. Hybrid cloud
Trusted cloud solutions for nearly any location, including Oracle Exadata Cloud@Customer, a highly optimized database as a service already deployed in more than 60 countries.
4. Dedicated cloud
OCI Dedicated Region and Oracle Alloy are the only products that provide more than 100 cloud services at public cloud pricing entirely within your data centers.
Complete cloud infrastructure and platform services for every workload
OCI offers a common set of 100+ services in each cloud region. Get all the services you need—from containers and VMware to AI—to migrate, modernize, build, and scale your IT. Automate all your workloads, including both existing and new applications and data platforms.
Developer Services
Build, deploy, and manage modern cloud applications using developer-friendly tools and services.
Build and run
- API Gateway
- API Management
- Blockchain Platform
- Notifications
- Resource Manager
- Visual Builder Studio
- Application Integration
- Content Management
- Digital Assistant
Integration Services
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure integration services connect any application and data source to automate end-to-end processes and centralize management. The broad array of integrations, with prebuilt adapters and low-code customization, simplify migration to the cloud while streamlining hybrid and multicloud operations.
Application integration
- Service Oriented Architecture (SOA)
Data integration
- Data Integration
- Autonomous Database Data Studio
- Data Integrator
Process automation
- Process Automation
API full lifecycle management
Event-driven, analytics and bi.
Gain comprehensive business intelligence with augmented analytics to help your organization grow through unique insights.
- Oracle Analytics Platform
- Oracle Fusion CX Analytics
- Oracle Fusion ERP Analytics
- Oracle Fusion HCM Analytics
- Oracle Analytics mobile app
AI and Machine Learning
Easily add intelligence to your applications and workloads with prebuilt perception and decision models and out-of-the-box chatbots, or build and train your own models with our data science services.
AI Services
- Document Understanding
ML Services
- Data Science
- In-Database Machine Learning
- HeatWave AutoML
Media Services
- Media Streams
Big Data and Data Lake
Gain new insights across all of your data with our comprehensive platform of managed Spark, Hadoop, Elasticsearch, and Kafka-compatible services, combined with best-in-class data warehouse and data management services.
- Big Data Service
- Data Catalog
Secure and elastic compute capacity in the cloud that ranges from flexible virtual machines (Flex VMs) and high-performance bare metal servers to HPC and GPUs.
- Arm-based Compute
- Bare Metal Servers
- GPU-Accelerated Compute
- HPC Compute
- Virtual Machines
Address key use cases with on-demand local, object, file, block, and archive storage.
- Archive Storage
- Block Volumes
- Data Transfer Service
- File Storage
- Object Storage
- Storage Gateway
Containers and Functions
Deploy microservices applications on high-performance, managed, open source Docker, Kubernetes, and Fn Functions services.
- Container Instances
- Kubernetes Engine
- Service Mesh
Connect securely to a customizable, isolated virtual cloud network (VCN) as the heart of your cloud deployment. Move data at 25% of the cost of other cloud providers.
- Customer-Premises Equipment
- DNS Management
- FastConnect
- Load Balancers
- Networking Gateways
- Private Endpoint
- Site-to-Site VPN
- Virtual Cloud Networks
Oracle Databases
Run cost-optimized, high-performance, and autonomous versions of Oracle Database, the world's leading converged, multimodel database management system in the cloud.
- Autonomous Database
- Autonomous Database on Exadata Cloud@Customer
- Database Management
- Database Migration
- Oracle Database@Azure
- Database Service for Azure
- Enterprise Database Service
- Exadata Cloud@Customer
- Exadata Database Service
- Globally Distributed Autonomous Database
- Ops Insights
- Standard Database Service
- Zero Data Loss Autonomous Recovery Service
Open Source Databases
MySQL HeatWave is a fully managed database service, powered by the integrated HeatWave in-memory query accelerator. It’s the only cloud database service that combines transactions, analytics, and machine learning services in one MySQL Database, delivering real-time, secure analytics without the complexity, latency, and cost of ETL duplication.
- Database with PostgreSQL
- MySQL HeatWave
- Search with OpenSearch
Security, Observability and Management, Compliance, and Cost Management and Governance
Protect your most valuable data in the cloud with Oracle’s security-first approach and comprehensive compliance programs. Oracle provides visibility and machine-learning–driven insights to ease management across all layers of the stack deployed on any technology, anywhere.
Cloud Infrastructure Security
- Access Governance
- Autonomous Linux
- Certificates
- Cloud Guard
- Hardware Root of Trust
- Identity and Access Management
- Isolated Network Virtualization
- Key Management
- Network Firewall
- Security Zones
- Threat Intelligence
- Vulnerability Scanning
Cloud Database Security
- Autonomous Database Security (PDF)
Cloud Application Security
- Web Application Firewall
Observability and Management
- Application Performance Monitoring
- Connector Hub
- Full Stack Disaster Recovery
- Java Management
- Logging Analytics
- OS Management Hub
- OS Management Service
Cost Management and Governance
- Cloud Advisor
- Cost Analysis
- License Manager
- Organization Management
- Support Rewards
- Oracle Cloud Compliance
- Oracle Corporate Security
Global Cloud Data Center Infrastructure
Global, secure, high-performance environments to move, build, and run all your workloads. Hybrid and edge offerings provide specialized deployment, disconnected and intermittently connected operation, low latency and high performance, as well as data locality and security.
- Multicloud solutions
- Database Service for Microsoft Azure
- Interconnect for Microsoft Azure
Public cloud
- Global cloud regions
- Oracle EU Sovereign Cloud
- UK government regions
- US Department of Defense regions
- US FedRAMP regions
Hybrid Cloud
- Hybrid cloud solutions
- Roving Edge Infrastructure
Dedicated cloud
- Dedicated Regions
Run IT for a lot less with ease
Save money without inflexible up-front commitments. In contrast to others, OCI has the same low price in all cloud regions, including government and dedicated regions. We offer innovative features, such as flexible compute, auto-tuning storage, up to 10X lower data egress fees, and free tools and reports to help eliminate needless overpayment and billing surprises. Committed use discounts, software license portability, and loyalty rewards are also available.
The cost for outbound bandwidth 1,2
Better price-performance 2,3
Base IOPS for half the price 4,5
Pricing comparison as of April 9, 2023 1. OCI Network Pricing 2. AWS Compute and Network Pricing 3. OCI Compute Pricing 4. AWS Storage Pricing 5. OCI Storage Pricing
Cloud infrastructure and applications everywhere
Oracle Cloud spans 48 interconnected geographic commercial and government cloud regions. Unlike other providers, each region offers a consistent set of more than 100 Oracle Cloud Infrastructure services, with consistent low pricing worldwide. For more complete support of customer cloud strategies, Oracle Cloud also offers a full suite of Oracle Cloud Applications and direct interconnection with Microsoft Azure.

Oracle data centers are distributed around the world.

Technology and industry solutions
Resolve your organization’s unique challenges, make data-driven decisions, and increase efficiency with OCI’s purpose-built solutions.
- Telecommunications
Financial services institutions benefit from OCI’s secure, reliable, and highly scalable multicloud platform, which offers robust services and an accelerated AI infrastructure with the broadest set of deployment options to meet your data residency requirements.
Meet all your business and technology objectives for an on-premises database cloud deployment with Oracle Exadata Cloud@Customer.
Benefit from a single unified platform to run every healthcare workload—from legacy applications to AI/ML-enabled services—to enhance the patient experience, decrease the cost of care, and enable precision medicine.
Realize the value of data—use all the available data sources to help improve patient outcomes and provide a seamless healthcare experience.
Many defense, intelligence community, and federal civilian agencies across the globe rely on Oracle Cloud for Government to modernize and innovate faster for better mission outcomes. Oracle Cloud provides world-class security and compliance, consistent high performance, and simple and predictable pricing.
Dedicated to serving governments and safeguarding global defense missions at hyperscale, this innovative cloud solution includes a fully integrated infrastructure with IaaS/PaaS/SaaS and industry-leading price-performance.
Oracle Cloud for telcos is a comprehensive set of cloud solutions built on OCI to help telcos become more agile, reduce capital investments and operating costs, and establish a flexible foundation for innovation.
Use Oracle’s database clustering and massive I/O to maintain near zero-downtime environments while improving performance by 50% or more compared with on-premises or other clouds.
Get started with OCI
- Free OCI services
- Hands-on labs
- Reference architectures
- Events and webinars
Contact sales
Try 20+ always free cloud services, with a 30-day trial for even more.
Oracle offers a Free Tier with no time limits on more than 20 services such as Autonomous Database, Arm Compute, and Storage, as well as US$300 in free credits to try additional cloud services. Get the details and sign up for your free account today.
What’s included with Oracle Cloud Free Tier?
- 2 Autonomous Databases, 20 GB each
- AMD and Arm Compute VMs
- 200 GB total block storage
- 10 GB object storage
- 10 TB outbound data transfer per month
- 10+ more Always Free services
- US$300 in free credits for 30 days for even more
Learn with step-by-step guidance
Experience a wide range of OCI services through tutorials and hands-on labs. Whether you're a developer, admin, or analyst, we can help you see how OCI works. Many labs run on the Oracle Cloud Free Tier or an Oracle-provided free lab environment.
Get started with OCI core services
The labs in this workshop cover an introduction to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) core services including virtual cloud networks (VCN) and compute and storage services.
Autonomous Database quick start
In this workshop, you’ll go through the steps to get started using Oracle Autonomous Database.
Build an app from a spreadsheet
This lab walks you through uploading a spreadsheet into an Oracle Database table, and then creating an application based on this new table.
Deploy an HA application on OCI
In this lab you’ll deploy web servers on two compute instances in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), configured in High Availability mode by using a Load Balancer.
Explore over 150 best practice designs
See how our architects and other customers deploy a wide range of workloads, from enterprise apps to HPC, from microservices to data lakes. Understand the best practices, hear from other customer architects in our Built & Deployed series, and even deploy many workloads with our "click to deploy" capability or do it yourself from our GitHub repo.
Popular architectures
- Apache Tomcat with MySQL Database Service
- Oracle Weblogic on Kubernetes with Jenkins
- Machine-learning (ML) and AI environments
- Tomcat on Arm with Oracle Autonomous Database
- Log analysis with ELK Stack
- HPC with OpenFOAM
Explore our informative events series featuring the latest announcements, customer conversations, product-specific insights, technical sessions, and hands-on labs.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure events
Get more out of OCI with a wide range of live and on-demand events.
Oracle CloudWorld
Join us at Oracle’s new global customer and partner conference for cloud infrastructure and applications.
Interested in learning more about Oracle Cloud Infrastructure? Let one of our experts help.
They can answer questions like:
- What workloads run best on OCI?
- How do I get the most out of my overall Oracle investments?
- How does OCI compare to other cloud computing providers?
- How can OCI support your IaaS and PaaS goals?
Why the Pandemic Probably Started in a Lab, in 5 Key Points

By Alina Chan
Dr. Chan is a molecular biologist at the Broad Institute of M.I.T. and Harvard, and a co-author of “Viral: The Search for the Origin of Covid-19.”
This article has been updated to reflect news developments.
On Monday, Dr. Anthony Fauci returned to the halls of Congress and testified before the House subcommittee investigating the Covid-19 pandemic. He was questioned about several topics related to the government’s handling of Covid-19, including how the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, which he directed until retiring in 2022, supported risky virus work at a Chinese institute whose research may have caused the pandemic.
For more than four years, reflexive partisan politics have derailed the search for the truth about a catastrophe that has touched us all. It has been estimated that at least 25 million people around the world have died because of Covid-19, with over a million of those deaths in the United States.
Although how the pandemic started has been hotly debated, a growing volume of evidence — gleaned from public records released under the Freedom of Information Act, digital sleuthing through online databases, scientific papers analyzing the virus and its spread, and leaks from within the U.S. government — suggests that the pandemic most likely occurred because a virus escaped from a research lab in Wuhan, China. If so, it would be the most costly accident in the history of science.
Here’s what we now know:
1 The SARS-like virus that caused the pandemic emerged in Wuhan, the city where the world’s foremost research lab for SARS-like viruses is located.
- At the Wuhan Institute of Virology, a team of scientists had been hunting for SARS-like viruses for over a decade, led by Shi Zhengli.
- Their research showed that the viruses most similar to SARS‑CoV‑2, the virus that caused the pandemic, circulate in bats that live r oughly 1,000 miles away from Wuhan. Scientists from Dr. Shi’s team traveled repeatedly to Yunnan province to collect these viruses and had expanded their search to Southeast Asia. Bats in other parts of China have not been found to carry viruses that are as closely related to SARS-CoV-2.

The closest known relatives to SARS-CoV-2 were found in southwestern China and in Laos.
Large cities
Mine in Yunnan province
Cave in Laos
South China Sea

The closest known relatives to SARS-CoV-2
were found in southwestern China and in Laos.
philippines

The closest known relatives to SARS-CoV-2 were found
in southwestern China and Laos.
Sources: Sarah Temmam et al., Nature; SimpleMaps
Note: Cities shown have a population of at least 200,000.

There are hundreds of large cities in China and Southeast Asia.

There are hundreds of large cities in China
and Southeast Asia.

The pandemic started roughly 1,000 miles away, in Wuhan, home to the world’s foremost SARS-like virus research lab.

The pandemic started roughly 1,000 miles away,
in Wuhan, home to the world’s foremost SARS-like virus research lab.

The pandemic started roughly 1,000 miles away, in Wuhan,
home to the world’s foremost SARS-like virus research lab.
- Even at hot spots where these viruses exist naturally near the cave bats of southwestern China and Southeast Asia, the scientists argued, as recently as 2019 , that bat coronavirus spillover into humans is rare .
- When the Covid-19 outbreak was detected, Dr. Shi initially wondered if the novel coronavirus had come from her laboratory , saying she had never expected such an outbreak to occur in Wuhan.
- The SARS‑CoV‑2 virus is exceptionally contagious and can jump from species to species like wildfire . Yet it left no known trace of infection at its source or anywhere along what would have been a thousand-mile journey before emerging in Wuhan.
2 The year before the outbreak, the Wuhan institute, working with U.S. partners, had proposed creating viruses with SARS‑CoV‑2’s defining feature.
- Dr. Shi’s group was fascinated by how coronaviruses jump from species to species. To find viruses, they took samples from bats and other animals , as well as from sick people living near animals carrying these viruses or associated with the wildlife trade. Much of this work was conducted in partnership with the EcoHealth Alliance, a U.S.-based scientific organization that, since 2002, has been awarded over $80 million in federal funding to research the risks of emerging infectious diseases.
- The laboratory pursued risky research that resulted in viruses becoming more infectious : Coronaviruses were grown from samples from infected animals and genetically reconstructed and recombined to create new viruses unknown in nature. These new viruses were passed through cells from bats, pigs, primates and humans and were used to infect civets and humanized mice (mice modified with human genes). In essence, this process forced these viruses to adapt to new host species, and the viruses with mutations that allowed them to thrive emerged as victors.
- By 2019, Dr. Shi’s group had published a database describing more than 22,000 collected wildlife samples. But external access was shut off in the fall of 2019, and the database was not shared with American collaborators even after the pandemic started , when such a rich virus collection would have been most useful in tracking the origin of SARS‑CoV‑2. It remains unclear whether the Wuhan institute possessed a precursor of the pandemic virus.
- In 2021, The Intercept published a leaked 2018 grant proposal for a research project named Defuse , which had been written as a collaboration between EcoHealth, the Wuhan institute and Ralph Baric at the University of North Carolina, who had been on the cutting edge of coronavirus research for years. The proposal described plans to create viruses strikingly similar to SARS‑CoV‑2.
- Coronaviruses bear their name because their surface is studded with protein spikes, like a spiky crown, which they use to enter animal cells. T he Defuse project proposed to search for and create SARS-like viruses carrying spikes with a unique feature: a furin cleavage site — the same feature that enhances SARS‑CoV‑2’s infectiousness in humans, making it capable of causing a pandemic. Defuse was never funded by the United States . However, in his testimony on Monday, Dr. Fauci explained that the Wuhan institute would not need to rely on U.S. funding to pursue research independently.

The Wuhan lab ran risky experiments to learn about how SARS-like viruses might infect humans.
1. Collect SARS-like viruses from bats and other wild animals, as well as from people exposed to them.

2. Identify high-risk viruses by screening for spike proteins that facilitate infection of human cells.

2. Identify high-risk viruses by screening for spike proteins that facilitate infection of
human cells.

In Defuse, the scientists proposed to add a furin cleavage site to the spike protein.
3. Create new coronaviruses by inserting spike proteins or other features that could make the viruses more infectious in humans.

4. Infect human cells, civets and humanized mice with the new coronaviruses, to determine how dangerous they might be.

- While it’s possible that the furin cleavage site could have evolved naturally (as seen in some distantly related coronaviruses), out of the hundreds of SARS-like viruses cataloged by scientists, SARS‑CoV‑2 is the only one known to possess a furin cleavage site in its spike. And the genetic data suggest that the virus had only recently gained the furin cleavage site before it started the pandemic.
- Ultimately, a never-before-seen SARS-like virus with a newly introduced furin cleavage site, matching the description in the Wuhan institute’s Defuse proposal, caused an outbreak in Wuhan less than two years after the proposal was drafted.
- When the Wuhan scientists published their seminal paper about Covid-19 as the pandemic roared to life in 2020, they did not mention the virus’s furin cleavage site — a feature they should have been on the lookout for, according to their own grant proposal, and a feature quickly recognized by other scientists.
- Worse still, as the pandemic raged, their American collaborators failed to publicly reveal the existence of the Defuse proposal. The president of EcoHealth, Peter Daszak, recently admitted to Congress that he doesn’t know about virus samples collected by the Wuhan institute after 2015 and never asked the lab’s scientists if they had started the work described in Defuse. In May, citing failures in EcoHealth’s monitoring of risky experiments conducted at the Wuhan lab, the Biden administration suspended all federal funding for the organization and Dr. Daszak, and initiated proceedings to bar them from receiving future grants. In his testimony on Monday, Dr. Fauci said that he supported the decision to suspend and bar EcoHealth.
- Separately, Dr. Baric described the competitive dynamic between his research group and the institute when he told Congress that the Wuhan scientists would probably not have shared their most interesting newly discovered viruses with him . Documents and email correspondence between the institute and Dr. Baric are still being withheld from the public while their release is fiercely contested in litigation.
- In the end, American partners very likely knew of only a fraction of the research done in Wuhan. According to U.S. intelligence sources, some of the institute’s virus research was classified or conducted with or on behalf of the Chinese military . In the congressional hearing on Monday, Dr. Fauci repeatedly acknowledged the lack of visibility into experiments conducted at the Wuhan institute, saying, “None of us can know everything that’s going on in China, or in Wuhan, or what have you. And that’s the reason why — I say today, and I’ve said at the T.I.,” referring to his transcribed interview with the subcommittee, “I keep an open mind as to what the origin is.”
3 The Wuhan lab pursued this type of work under low biosafety conditions that could not have contained an airborne virus as infectious as SARS‑CoV‑2.
- Labs working with live viruses generally operate at one of four biosafety levels (known in ascending order of stringency as BSL-1, 2, 3 and 4) that describe the work practices that are considered sufficiently safe depending on the characteristics of each pathogen. The Wuhan institute’s scientists worked with SARS-like viruses under inappropriately low biosafety conditions .

In the United States, virologists generally use stricter Biosafety Level 3 protocols when working with SARS-like viruses.
Biosafety cabinets prevent
viral particles from escaping.
Viral particles
Personal respirators provide
a second layer of defense against breathing in the virus.
DIRECT CONTACT
Gloves prevent skin contact.
Disposable wraparound
gowns cover much of the rest of the body.

Personal respirators provide a second layer of defense against breathing in the virus.
Disposable wraparound gowns
cover much of the rest of the body.
Note: Biosafety levels are not internationally standardized, and some countries use more permissive protocols than others.

The Wuhan lab had been regularly working with SARS-like viruses under Biosafety Level 2 conditions, which could not prevent a highly infectious virus like SARS-CoV-2 from escaping.
Some work is done in the open air, and masks are not required.
Less protective equipment provides more opportunities
for contamination.

Some work is done in the open air,
and masks are not required.
Less protective equipment provides more opportunities for contamination.
- In one experiment, Dr. Shi’s group genetically engineered an unexpectedly deadly SARS-like virus (not closely related to SARS‑CoV‑2) that exhibited a 10,000-fold increase in the quantity of virus in the lungs and brains of humanized mice . Wuhan institute scientists handled these live viruses at low biosafet y levels , including BSL-2.
- Even the much more stringent containment at BSL-3 cannot fully prevent SARS‑CoV‑2 from escaping . Two years into the pandemic, the virus infected a scientist in a BSL-3 laboratory in Taiwan, which was, at the time, a zero-Covid country. The scientist had been vaccinated and was tested only after losing the sense of smell. By then, more than 100 close contacts had been exposed. Human error is a source of exposure even at the highest biosafety levels , and the risks are much greater for scientists working with infectious pathogens at low biosafety.
- An early draft of the Defuse proposal stated that the Wuhan lab would do their virus work at BSL-2 to make it “highly cost-effective.” Dr. Baric added a note to the draft highlighting the importance of using BSL-3 to contain SARS-like viruses that could infect human cells, writing that “U.S. researchers will likely freak out.” Years later, after SARS‑CoV‑2 had killed millions, Dr. Baric wrote to Dr. Daszak : “I have no doubt that they followed state determined rules and did the work under BSL-2. Yes China has the right to set their own policy. You believe this was appropriate containment if you want but don’t expect me to believe it. Moreover, don’t insult my intelligence by trying to feed me this load of BS.”
- SARS‑CoV‑2 is a stealthy virus that transmits effectively through the air, causes a range of symptoms similar to those of other common respiratory diseases and can be spread by infected people before symptoms even appear. If the virus had escaped from a BSL-2 laboratory in 2019, the leak most likely would have gone undetected until too late.
- One alarming detail — leaked to The Wall Street Journal and confirmed by current and former U.S. government officials — is that scientists on Dr. Shi’s team fell ill with Covid-like symptoms in the fall of 2019 . One of the scientists had been named in the Defuse proposal as the person in charge of virus discovery work. The scientists denied having been sick .
4 The hypothesis that Covid-19 came from an animal at the Huanan Seafood Market in Wuhan is not supported by strong evidence.
- In December 2019, Chinese investigators assumed the outbreak had started at a centrally located market frequented by thousands of visitors daily. This bias in their search for early cases meant that cases unlinked to or located far away from the market would very likely have been missed. To make things worse, the Chinese authorities blocked the reporting of early cases not linked to the market and, claiming biosafety precautions, ordered the destruction of patient samples on January 3, 2020, making it nearly impossible to see the complete picture of the earliest Covid-19 cases. Information about dozens of early cases from November and December 2019 remains inaccessible.
- A pair of papers published in Science in 2022 made the best case for SARS‑CoV‑2 having emerged naturally from human-animal contact at the Wuhan market by focusing on a map of the early cases and asserting that the virus had jumped from animals into humans twice at the market in 2019. More recently, the two papers have been countered by other virologists and scientists who convincingly demonstrate that the available market evidence does not distinguish between a human superspreader event and a natural spillover at the market.
- Furthermore, the existing genetic and early case data show that all known Covid-19 cases probably stem from a single introduction of SARS‑CoV‑2 into people, and the outbreak at the Wuhan market probably happened after the virus had already been circulating in humans.

An analysis of SARS-CoV-2’s evolutionary tree shows how the virus evolved as it started to spread through humans.
SARS-COV-2 Viruses closest
to bat coronaviruses
more mutations

Source: Lv et al., Virus Evolution (2024) , as reproduced by Jesse Bloom

The viruses that infected people linked to the market were most likely not the earliest form of the virus that started the pandemic.

- Not a single infected animal has ever been confirmed at the market or in its supply chain. Without good evidence that the pandemic started at the Huanan Seafood Market, the fact that the virus emerged in Wuhan points squarely at its unique SARS-like virus laboratory.
5 Key evidence that would be expected if the virus had emerged from the wildlife trade is still missing.

In previous outbreaks of coronaviruses, scientists were able to demonstrate natural origin by collecting multiple pieces of evidence linking infected humans to infected animals.
Infected animals
Earliest known
cases exposed to
live animals
Antibody evidence
of animals and
animal traders having
been infected
Ancestral variants
of the virus found in
Documented trade
of host animals
between the area
where bats carry
closely related viruses
and the outbreak site

Infected animals found
Earliest known cases exposed to live animals
Antibody evidence of animals and animal
traders having been infected
Ancestral variants of the virus found in animals
Documented trade of host animals
between the area where bats carry closely
related viruses and the outbreak site

For SARS-CoV-2, these same key pieces of evidence are still missing , more than four years after the virus emerged.

For SARS-CoV-2, these same key pieces of evidence are still missing ,
more than four years after the virus emerged.
- Despite the intense search trained on the animal trade and people linked to the market, investigators have not reported finding any animals infected with SARS‑CoV‑2 that had not been infected by humans. Yet, infected animal sources and other connective pieces of evidence were found for the earlier SARS and MERS outbreaks as quickly as within a few days, despite the less advanced viral forensic technologies of two decades ago.
- Even though Wuhan is the home base of virus hunters with world-leading expertise in tracking novel SARS-like viruses, investigators have either failed to collect or report key evidence that would be expected if Covid-19 emerged from the wildlife trade . For example, investigators have not determined that the earliest known cases had exposure to intermediate host animals before falling ill. No antibody evidence shows that animal traders in Wuhan are regularly exposed to SARS-like viruses, as would be expected in such situations.
- With today’s technology, scientists can detect how respiratory viruses — including SARS, MERS and the flu — circulate in animals while making repeated attempts to jump across species . Thankfully, these variants usually fail to transmit well after crossing over to a new species and tend to die off after a small number of infections. In contrast, virologists and other scientists agree that SARS‑CoV‑2 required little to no adaptation to spread rapidly in humans and other animals . The virus appears to have succeeded in causing a pandemic upon its only detected jump into humans.
The pandemic could have been caused by any of hundreds of virus species, at any of tens of thousands of wildlife markets, in any of thousands of cities, and in any year. But it was a SARS-like coronavirus with a unique furin cleavage site that emerged in Wuhan, less than two years after scientists, sometimes working under inadequate biosafety conditions, proposed collecting and creating viruses of that same design.
While several natural spillover scenarios remain plausible, and we still don’t know enough about the full extent of virus research conducted at the Wuhan institute by Dr. Shi’s team and other researchers, a laboratory accident is the most parsimonious explanation of how the pandemic began.
Given what we now know, investigators should follow their strongest leads and subpoena all exchanges between the Wuhan scientists and their international partners, including unpublished research proposals, manuscripts, data and commercial orders. In particular, exchanges from 2018 and 2019 — the critical two years before the emergence of Covid-19 — are very likely to be illuminating (and require no cooperation from the Chinese government to acquire), yet they remain beyond the public’s view more than four years after the pandemic began.
Whether the pandemic started on a lab bench or in a market stall, it is undeniable that U.S. federal funding helped to build an unprecedented collection of SARS-like viruses at the Wuhan institute, as well as contributing to research that enhanced them . Advocates and funders of the institute’s research, including Dr. Fauci, should cooperate with the investigation to help identify and close the loopholes that allowed such dangerous work to occur. The world must not continue to bear the intolerable risks of research with the potential to cause pandemics .
A successful investigation of the pandemic’s root cause would have the power to break a decades-long scientific impasse on pathogen research safety, determining how governments will spend billions of dollars to prevent future pandemics. A credible investigation would also deter future acts of negligence and deceit by demonstrating that it is indeed possible to be held accountable for causing a viral pandemic. Last but not least, people of all nations need to see their leaders — and especially, their scientists — heading the charge to find out what caused this world-shaking event. Restoring public trust in science and government leadership requires it.
A thorough investigation by the U.S. government could unearth more evidence while spurring whistleblowers to find their courage and seek their moment of opportunity. It would also show the world that U.S. leaders and scientists are not afraid of what the truth behind the pandemic may be.
More on how the pandemic may have started

Where Did the Coronavirus Come From? What We Already Know Is Troubling.
Even if the coronavirus did not emerge from a lab, the groundwork for a potential disaster had been laid for years, and learning its lessons is essential to preventing others.
By Zeynep Tufekci

Why Does Bad Science on Covid’s Origin Get Hyped?
If the raccoon dog was a smoking gun, it fired blanks.
By David Wallace-Wells

A Plea for Making Virus Research Safer
A way forward for lab safety.
By Jesse Bloom
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
Alina Chan ( @ayjchan ) is a molecular biologist at the Broad Institute of M.I.T. and Harvard, and a co-author of “ Viral : The Search for the Origin of Covid-19.” She was a member of the Pathogens Project , which the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists organized to generate new thinking on responsible, high-risk pathogen research.
- Share full article
Advertisement
- Skip to main content
- Skip to search
- Skip to footer
Products and Services
Routers and SD-WAN appliances
Connect and protect every network.
Connect and secure networks of any scale—from the edge to the cloud.
Discover smarter, more secure routing
Build an intelligent, self-defending network with advanced analytics, automated provisioning, and integrated security.
Protect your users and data
Boost security from the WAN to the cloud, with trusted authentication, robust encryption, and granular segmentation.
Accelerate your deployment
Deploy integrated network services on demand—anywhere, anytime.
Transform application experience
Get in-depth analytics, visibility, and control to make excellent application experience a cornerstone of your operations.
Centralize network management
Easily deploy SD-WAN and security while maintaining policy across thousands of sites.

Build a resilient and secure SD-WAN.

Future-ready routers for every network
cisco catalyst 8300 series edge platforms.
Get SASE-ready with SD-WAN, cloud-native agility, multilayer security, flexible routing, and edge intelligence.
Cisco Catalyst 8200 Series Edge Platforms
Move to secure access service edge (SASE) with secure and scalable SD-WAN and intelligent multicloud connectivity.
Cisco 1000 Series Integrated Services Routers
Boost performance with advanced security, multicloud access, and wireless capability—in one device.
Cisco Meraki MX security and SD-WAN appliances
Build a complete SD-branch on a cloud-first platform with secure SD-WAN, access, and IoT.
Fixed wireless access devices
Deliver secure, reliable, and scalable connectivity for remote and branch offices.
Hybrid work
Cisco remote worker gateways.
Experience reliable connectivity with enterprise Wi-Fi access at home without the need for a VPN.
Industrial
Cisco catalyst ir1100 rugged series routers.
Securely connect remote industrial operations with this rugged, compact, and modular SD-WAN-enabled router.
Cisco Catalyst IR1800 Rugged Series Routers
Speed digitization at the mobile edge, with high performance and industry-leading flexibility.
Cisco Catalyst IR8100 Heavy Duty Series Routers
Unite your outdoor edge with this IP67-rated and SD-WAN-enabled router that’s fully modular.
Cisco Catalyst IR8300 Rugged Series Routers
Deliver peak industrial networking and SD-WAN performance with rugged all-in-one routing and switching.
Service providers
Cisco 8000 series routers.
Deliver the performance and scale to build the internet of the future with cloud-enhanced systems.
Cisco Network Convergence System 5700 Series Routers
Scale with high-density 400G routers for long-term growth and segment routing for SLA-based services.
Cisco ASR 9000 Series Aggregation Services Routers
Support the application performance required to power your services with scalable routing systems.
Cisco Network Convergence System 500 Series Routers
Simplify your access network and converge services with these secure and programmable routers.
Small business
Streamline your small business with secure SD-WAN, access, and IoT on a cloud-first platform.
Cisco 1000 Series Integrated Services Routers
Boost performance with advanced security, multicloud access, and wireless capability—in one device.
Cisco 900 Series Integrated Services Routers
Combine WAN, switching, security, and advanced connectivity options in a compact, fanless platform.
Cisco Catalyst 8000V Edge Software
Optimize applications and enhance user experience with secure, multicloud connectivity.
Cisco Meraki vMX appliances
Securely extend SD-WAN to public and private cloud infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) environments in three clicks.
Cisco IOS XRd Virtual Router
Experience greater agility, improved network efficiency, and lower costs with virtual and containerized routers.

Find a fast route to value
Power your network with secure and reliable experiences for campus, branch, edge, and data center.
Explore routing solutions
Cisco catalyst sd-wan.
Lower costs and complexity, and enrich the user experience at your branches.
Secure access where users and applications reside, with one cloud-native service.
For service providers
Deliver quality services fast and easily with advanced network automation.
Support to get you started
Cisco Success Tracks
Make the most of your IT investment
Optimize the value of your routing solutions for faster results, with digital insights and services expertise.
Business Critical Services
Move your business forward faster
Modernize IT environments and boost agility with analytics-driven advisory services.
Find your router
Compare and contrast Cisco routers of all types and sizes. Quickly find the router to meet your needs.
The state of AI in early 2024: Gen AI adoption spikes and starts to generate value
If 2023 was the year the world discovered generative AI (gen AI) , 2024 is the year organizations truly began using—and deriving business value from—this new technology. In the latest McKinsey Global Survey on AI, 65 percent of respondents report that their organizations are regularly using gen AI, nearly double the percentage from our previous survey just ten months ago. Respondents’ expectations for gen AI’s impact remain as high as they were last year , with three-quarters predicting that gen AI will lead to significant or disruptive change in their industries in the years ahead.
About the authors
This article is a collaborative effort by Alex Singla , Alexander Sukharevsky , Lareina Yee , and Michael Chui , with Bryce Hall , representing views from QuantumBlack, AI by McKinsey, and McKinsey Digital.
Organizations are already seeing material benefits from gen AI use, reporting both cost decreases and revenue jumps in the business units deploying the technology. The survey also provides insights into the kinds of risks presented by gen AI—most notably, inaccuracy—as well as the emerging practices of top performers to mitigate those challenges and capture value.
AI adoption surges
Interest in generative AI has also brightened the spotlight on a broader set of AI capabilities. For the past six years, AI adoption by respondents’ organizations has hovered at about 50 percent. This year, the survey finds that adoption has jumped to 72 percent (Exhibit 1). And the interest is truly global in scope. Our 2023 survey found that AI adoption did not reach 66 percent in any region; however, this year more than two-thirds of respondents in nearly every region say their organizations are using AI. 1 Organizations based in Central and South America are the exception, with 58 percent of respondents working for organizations based in Central and South America reporting AI adoption. Looking by industry, the biggest increase in adoption can be found in professional services. 2 Includes respondents working for organizations focused on human resources, legal services, management consulting, market research, R&D, tax preparation, and training.
Also, responses suggest that companies are now using AI in more parts of the business. Half of respondents say their organizations have adopted AI in two or more business functions, up from less than a third of respondents in 2023 (Exhibit 2).
Gen AI adoption is most common in the functions where it can create the most value
Most respondents now report that their organizations—and they as individuals—are using gen AI. Sixty-five percent of respondents say their organizations are regularly using gen AI in at least one business function, up from one-third last year. The average organization using gen AI is doing so in two functions, most often in marketing and sales and in product and service development—two functions in which previous research determined that gen AI adoption could generate the most value 3 “ The economic potential of generative AI: The next productivity frontier ,” McKinsey, June 14, 2023. —as well as in IT (Exhibit 3). The biggest increase from 2023 is found in marketing and sales, where reported adoption has more than doubled. Yet across functions, only two use cases, both within marketing and sales, are reported by 15 percent or more of respondents.
Gen AI also is weaving its way into respondents’ personal lives. Compared with 2023, respondents are much more likely to be using gen AI at work and even more likely to be using gen AI both at work and in their personal lives (Exhibit 4). The survey finds upticks in gen AI use across all regions, with the largest increases in Asia–Pacific and Greater China. Respondents at the highest seniority levels, meanwhile, show larger jumps in the use of gen Al tools for work and outside of work compared with their midlevel-management peers. Looking at specific industries, respondents working in energy and materials and in professional services report the largest increase in gen AI use.
Investments in gen AI and analytical AI are beginning to create value
The latest survey also shows how different industries are budgeting for gen AI. Responses suggest that, in many industries, organizations are about equally as likely to be investing more than 5 percent of their digital budgets in gen AI as they are in nongenerative, analytical-AI solutions (Exhibit 5). Yet in most industries, larger shares of respondents report that their organizations spend more than 20 percent on analytical AI than on gen AI. Looking ahead, most respondents—67 percent—expect their organizations to invest more in AI over the next three years.
Where are those investments paying off? For the first time, our latest survey explored the value created by gen AI use by business function. The function in which the largest share of respondents report seeing cost decreases is human resources. Respondents most commonly report meaningful revenue increases (of more than 5 percent) in supply chain and inventory management (Exhibit 6). For analytical AI, respondents most often report seeing cost benefits in service operations—in line with what we found last year —as well as meaningful revenue increases from AI use in marketing and sales.
Inaccuracy: The most recognized and experienced risk of gen AI use
As businesses begin to see the benefits of gen AI, they’re also recognizing the diverse risks associated with the technology. These can range from data management risks such as data privacy, bias, or intellectual property (IP) infringement to model management risks, which tend to focus on inaccurate output or lack of explainability. A third big risk category is security and incorrect use.
Respondents to the latest survey are more likely than they were last year to say their organizations consider inaccuracy and IP infringement to be relevant to their use of gen AI, and about half continue to view cybersecurity as a risk (Exhibit 7).
Conversely, respondents are less likely than they were last year to say their organizations consider workforce and labor displacement to be relevant risks and are not increasing efforts to mitigate them.
In fact, inaccuracy— which can affect use cases across the gen AI value chain , ranging from customer journeys and summarization to coding and creative content—is the only risk that respondents are significantly more likely than last year to say their organizations are actively working to mitigate.
Some organizations have already experienced negative consequences from the use of gen AI, with 44 percent of respondents saying their organizations have experienced at least one consequence (Exhibit 8). Respondents most often report inaccuracy as a risk that has affected their organizations, followed by cybersecurity and explainability.
Our previous research has found that there are several elements of governance that can help in scaling gen AI use responsibly, yet few respondents report having these risk-related practices in place. 4 “ Implementing generative AI with speed and safety ,” McKinsey Quarterly , March 13, 2024. For example, just 18 percent say their organizations have an enterprise-wide council or board with the authority to make decisions involving responsible AI governance, and only one-third say gen AI risk awareness and risk mitigation controls are required skill sets for technical talent.
Bringing gen AI capabilities to bear
The latest survey also sought to understand how, and how quickly, organizations are deploying these new gen AI tools. We have found three archetypes for implementing gen AI solutions : takers use off-the-shelf, publicly available solutions; shapers customize those tools with proprietary data and systems; and makers develop their own foundation models from scratch. 5 “ Technology’s generational moment with generative AI: A CIO and CTO guide ,” McKinsey, July 11, 2023. Across most industries, the survey results suggest that organizations are finding off-the-shelf offerings applicable to their business needs—though many are pursuing opportunities to customize models or even develop their own (Exhibit 9). About half of reported gen AI uses within respondents’ business functions are utilizing off-the-shelf, publicly available models or tools, with little or no customization. Respondents in energy and materials, technology, and media and telecommunications are more likely to report significant customization or tuning of publicly available models or developing their own proprietary models to address specific business needs.
Respondents most often report that their organizations required one to four months from the start of a project to put gen AI into production, though the time it takes varies by business function (Exhibit 10). It also depends upon the approach for acquiring those capabilities. Not surprisingly, reported uses of highly customized or proprietary models are 1.5 times more likely than off-the-shelf, publicly available models to take five months or more to implement.
Gen AI high performers are excelling despite facing challenges
Gen AI is a new technology, and organizations are still early in the journey of pursuing its opportunities and scaling it across functions. So it’s little surprise that only a small subset of respondents (46 out of 876) report that a meaningful share of their organizations’ EBIT can be attributed to their deployment of gen AI. Still, these gen AI leaders are worth examining closely. These, after all, are the early movers, who already attribute more than 10 percent of their organizations’ EBIT to their use of gen AI. Forty-two percent of these high performers say more than 20 percent of their EBIT is attributable to their use of nongenerative, analytical AI, and they span industries and regions—though most are at organizations with less than $1 billion in annual revenue. The AI-related practices at these organizations can offer guidance to those looking to create value from gen AI adoption at their own organizations.
To start, gen AI high performers are using gen AI in more business functions—an average of three functions, while others average two. They, like other organizations, are most likely to use gen AI in marketing and sales and product or service development, but they’re much more likely than others to use gen AI solutions in risk, legal, and compliance; in strategy and corporate finance; and in supply chain and inventory management. They’re more than three times as likely as others to be using gen AI in activities ranging from processing of accounting documents and risk assessment to R&D testing and pricing and promotions. While, overall, about half of reported gen AI applications within business functions are utilizing publicly available models or tools, gen AI high performers are less likely to use those off-the-shelf options than to either implement significantly customized versions of those tools or to develop their own proprietary foundation models.
What else are these high performers doing differently? For one thing, they are paying more attention to gen-AI-related risks. Perhaps because they are further along on their journeys, they are more likely than others to say their organizations have experienced every negative consequence from gen AI we asked about, from cybersecurity and personal privacy to explainability and IP infringement. Given that, they are more likely than others to report that their organizations consider those risks, as well as regulatory compliance, environmental impacts, and political stability, to be relevant to their gen AI use, and they say they take steps to mitigate more risks than others do.
Gen AI high performers are also much more likely to say their organizations follow a set of risk-related best practices (Exhibit 11). For example, they are nearly twice as likely as others to involve the legal function and embed risk reviews early on in the development of gen AI solutions—that is, to “ shift left .” They’re also much more likely than others to employ a wide range of other best practices, from strategy-related practices to those related to scaling.
In addition to experiencing the risks of gen AI adoption, high performers have encountered other challenges that can serve as warnings to others (Exhibit 12). Seventy percent say they have experienced difficulties with data, including defining processes for data governance, developing the ability to quickly integrate data into AI models, and an insufficient amount of training data, highlighting the essential role that data play in capturing value. High performers are also more likely than others to report experiencing challenges with their operating models, such as implementing agile ways of working and effective sprint performance management.
About the research
The online survey was in the field from February 22 to March 5, 2024, and garnered responses from 1,363 participants representing the full range of regions, industries, company sizes, functional specialties, and tenures. Of those respondents, 981 said their organizations had adopted AI in at least one business function, and 878 said their organizations were regularly using gen AI in at least one function. To adjust for differences in response rates, the data are weighted by the contribution of each respondent’s nation to global GDP.
Alex Singla and Alexander Sukharevsky are global coleaders of QuantumBlack, AI by McKinsey, and senior partners in McKinsey’s Chicago and London offices, respectively; Lareina Yee is a senior partner in the Bay Area office, where Michael Chui , a McKinsey Global Institute partner, is a partner; and Bryce Hall is an associate partner in the Washington, DC, office.
They wish to thank Kaitlin Noe, Larry Kanter, Mallika Jhamb, and Shinjini Srivastava for their contributions to this work.
This article was edited by Heather Hanselman, a senior editor in McKinsey’s Atlanta office.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Moving past gen AI’s honeymoon phase: Seven hard truths for CIOs to get from pilot to scale

A generative AI reset: Rewiring to turn potential into value in 2024

Implementing generative AI with speed and safety

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This study employed a qualitative case study methodology. The case study method is a research strategy that aims to gain an in-depth understanding of a specific phenomenon by collecting and ...
This guide explains how to write a descriptive case study. A descriptive case study describes how an organization handled a specific issue. Case studies can vary in length and the amount of details provided. They can be fictional or based on true events. Why should you write one? Case studies can help others (e.g., students, other organizations,
Besides discussing case study design, data collection, and analysis, the refresher addresses several key features of case study research. First, an abbreviated definition of a "case study" will help identify the circumstances when you might choose to use the case study method instead of (or as a complement to) some other research method.
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemological strands which determine the particular case study type and approach adopted in the field, discusses the factors which can enhance the effectiveness of a case study research, and the debate ...
The purpose of a paper in the social sciences designed around a case study is to thoroughly investigate a subject of analysis in order to reveal a new understanding about the research problem and, in so doing, contributing new knowledge to what is already known from previous studies. In applied social sciences disciplines [e.g., education, social work, public administration, etc.], case ...
cipline-specific applications of case study methods and describe the appropriate research questions addressed by case studies. I follow this description with methods considerations, including case study design, research questions, sample size, data collection, and data analysis. Note that there are many approaches and styles to case study research.
Although case studies have been discussed extensively in the literature, little has been written about the specific steps one may use to conduct case study research effectively (Gagnon, 2010; Hancock & Algozzine, 2016).Baskarada (2014) also emphasized the need to have a succinct guideline that can be practically followed as it is actually tough to execute a case study well in practice.
1. Case study is a research strategy, and not just a method/technique/process of data collection. 2. A case study involves a detailed study of the concerned unit of analysis within its natural setting. A de-contextualised study has no relevance in a case study research. 3. Since an in-depth study is conducted, a case study research allows the
A case study paper must report research objectively and factually to ensure that any findings are understood to be logically correct and trustworthy. A case analysis scenario may include misleading or false information intended to deliberately distract from the central issues of the case. The purpose is to teach students how to sort through ...
Case study is a research methodology, typically seen in social and life sciences. There is no one definition of case study research.1 However, very simply... 'a case study can be defined as an intensive study about a person, a group of people or a unit, which is aimed to generalize over several units' .1 A case study has also been described ...
type of case study was normally a lot richer and of greater depth than could be found through other types of case study or experimental designs. Case Description Data used in this study included 101 students' pre and post-test scores, and four structured written reflection papers by four STEM classroom teachers who voluntarily joined the ...
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
Marzano (2003) studied the practices of effective teachers. and determined that "an effective teacher-student relationship may be. the keystone that allows the other aspects to work well" (p. 91). The relationships that teachers develop with their students have. an important role in a student's academic growth.
2. Develop Instruments. • Develop interview/survey protocols—the rules that guide the administration and implementation of the interview/survey. Put simply, these are the instructions that are followed to ensure consistency across interviews/surveys, and thus increase the reliability of the findings.
Case Study Example. This document shows how you might use an exemplar to inform your own original work. If you were writing your own case study, you might look at how an exemplar case study was organized and formatted, and you might look at what information was included in each section. The text in the left- hand column comes from a case study ...
Identify the key problems and issues in the case study. Formulate and include a thesis statement, summarizing the outcome of your analysis in 1-2 sentences. Background. Set the scene: background information, relevant facts, and the most important issues. Demonstrate that you have researched the problems in this case study. Evaluation of the Case
A COUNTRY CASE STUDY OF THE PHILIPPINES Author: STA. ROMANA, Leonardo L. 1. Introduction The typical analysis of poverty or international trade generally focuses solely either on one topic or the other. In this paper, however, we have a twin focus on both trade and poverty, and the linkages and connections between the two topics.
Case study examples. Case studies are proven marketing strategies in a wide variety of B2B industries. Here are just a few examples of a case study: Amazon Web Services, Inc. provides companies with cloud computing platforms and APIs on a metered, pay-as-you-go basis. This case study example illustrates the benefits Thomson Reuters experienced ...
major choice, study and social habits, remote learning experiences, current labor market participation, and expectations about future employment. Second, we study how these e ects di er along existing so-cioeconomic divides, and whether the pandemic has exacerbated existing inequalities. Finally, we present
Mission. The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives.
As the healthcare community increasingly harnesses the power of generative artificial intelligence (AI), critical issues of security, privacy and regulation take centre stage. In this paper, we explore the security and privacy risks of generative AI from model-level and data-level perspectives. Moreover, we elucidate the potential consequences and case studies within the domain of ophthalmology.
Contact a sales expert. Get in touch with our sales team to discuss tailored solutions for your business. You can call (866) 726-4249 to talk to an expert now, or use the form below to submit your requests. Contact sales.
Complete cloud infrastructure and platform services for every workload. OCI offers a common set of 100+ services in each cloud region. Get all the services you need—from containers and VMware to AI—to migrate, modernize, build, and scale your IT. Automate all your workloads, including both existing and new applications and data platforms.
Dr. Chan is a molecular biologist at the Broad Institute of M.I.T. and Harvard, and a co-author of "Viral: The Search for the Origin of Covid-19." This article has been updated to reflect news ...
Transform application experience. Get in-depth analytics, visibility, and control to make excellent application experience a cornerstone of your operations. Centralize network management. Easily deploy SD-WAN and security while maintaining policy across thousands of sites. Build a resilient and secure SD-WAN.
About the research. The online survey was in the field from February 22 to March 5, 2024, and garnered responses from 1,363 participants representing the full range of regions, industries, company sizes, functional specialties, and tenures. Of those respondents, 981 said their organizations had adopted AI in at least one business function, and ...