- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Finance and Business
- Business by Industry

How to Start a Computer Business
Last Updated: June 5, 2024 References
This article was co-authored by Luigi Oppido and by wikiHow staff writer, Christopher M. Osborne, PhD . Luigi Oppido is the Owner and Operator of Pleasure Point Computers in Santa Cruz, California. Luigi has over 25 years of experience in general computer repair, data recovery, virus removal, and upgrades. He is also the host of the Computer Man Show! broadcasted on KSQD covering central California for over two years. This article has been viewed 194,923 times.
While your dream may be to start the next Apple or Microsoft out of your garage, it is more likely that your desire to start a computer business involves dealing with existing systems via sales, service, or support. With the rapid changes in technology that have already led some to place us in the “post-PC era,” [1] X Research source the job of a computer repair person , for instance, has changed quite a bit from ten years ago and will surely be quite different ten years from now. Beyond keeping up with changing technology and maintaining your expertise, however, starting a computer business requires many of the same skills required of any other small business field — things like a clear business plan, a smart marketing strategy , and outstanding customer service.
Aligning Your Skills and Goals With the Market

- Have you ever dissected, reassembled, or repaired a computer? Are you familiar with all major operating systems? Have you worked in the computer field before? Honestly assess your readiness to start a computer business, or ask someone else with industry knowledge help you make the assessment.
- Completing a degree in the computer field will certainly help you in starting a business, but it is unlikely that most customers will ask to see your diploma. More important is your ongoing gathering of experience, whether through education, training, or employment.
- Certification is a good way to indicate expertise, though. You may want to seek A+ certification from the Computer Technology Industry Association (CompTIA), or the related N+ network certification, or become a Microsoft Certified System Engineer (MCSE). [2] X Research source These can help give your business card an air of legitimacy.

- In this so-called “post-PC era,” you may find demand for traditional computer sales, service, and/or support to be much reduced, especially among a younger, tech-savvy population. However, especially in areas with older populations and/or small-town and rural areas, you may find a greater percentage of people in need of PC repairs and support. Remember, you need to keep up with the latest technology; many of your potential customers do not (and will not). [3] X Research source [4] X Research source

- New technology is meant to make life easier, but many consumers find it to be just another layer of confusion. General set-up and troubleshooting tasks, like setting up printers and wireless networks, data recovery and wiping, and media archiving or editing, may remain a viable component of your business, even if PC repair requests decrease.
- If you can prove yourself to be an expert on computers and related technology, and can build a positive reputation, you should be able to find a niche for your computer business.

- If you’re looking to keep your computer business as a part-time job, then keeping your focus on repairs and troubleshooting may suffice.
- Building your business into a full-time occupation, however, may require further diversification of the products and services you offer, perhaps by selling parts, accessories, or entire systems. You’ll need to draw in a loyal client base and build a positive reputation in the community.
Brandon Phipps
Your core goal is to offer benefits to your customers for a fair price. By providing such a service, you can earn a significant income while doing something you are skilled at and helping others.
Succeeding in the Computer Business

- Even if computers are your focus, expect people to seek help and guidance with all sorts of mobile technology, from phones to tablets to watches. You may or may not want to get into the mobile tech sales and/or service business — consider the increased inventory demands, for instance — but being able to provide general troubleshooting, training, and support on the latest devices may prove quite useful. [6] X Research source
- If home service calls are part of your business, the essential toolkit you take with you will continue to shift along with technology. However, you can find a good list of basic equipment you’ll need (for the time being) at https://www.technibble.com/categories/starting-computer-repair-business/ .

- You’ll deal with panicked customers who think they’ve just lost all their important files, irate customers who want immediate help at 10 p.m., and hovering customers who want to supervise (and ask about) every move you make. You need to be able to remain calm , courteous, and patient. As a small business, you’re not likely to be able to match the prices of your larger competitors — the personalized service you offer needs to offset this disadvantage.

- Put some thought to your business name, logos , signage, marketing, etc. Create a professional look that presents your business as legitimate and lasting.
- Referrals will be essential to your business. Always hand out professional-looking business cards to existing customers, and consider offering referral discounts or rewards. Throwing in some free service or equipment is a small price to pay in order to build up your customer base. [8] X Research source
- Especially if you don’t have a storefront, make your business website and/or social media presence appear professional and interconnected to your overall brand.

- Working from home, for instance, offers more flexibility and less overhead costs, but also offers less visibility and possibly more distractions. A well-placed storefront adds to your visibility and helps legitimize your business in the public’s mind, but it comes at a cost and tends to lock you into a more rigid schedule.
- If you focus on computer repairs, working in your own shop may limit distractions and save you time and travel money, but customers may be more comfortable with you working on the equipment in their homes. (Your potential liability is also likely to be reduced when you don’t take the equipment with you.)
Starting a Small Business: Some Basics

- See How to Write a Business Plan for a good primer on the process of creating this important document.

- You may want to save on taxes by having customers pay cash “under the table” and not reporting the income, but this gives your business an air of illegitimacy (as well it should) for your customers. You are better off paying the taxes and appearing (and being) legitimate. [9] X Research source
- How to Open a Small Business offers some nice information on the legal requirements of establishing a business. The U.S. Small Business Administration website is also a great resource; see, for instance, https://www.sba.gov/content/follow-these-steps-starting-business .

- Volunteer some of your time and expertise. Be a supporting sponsor at community events (with the requisite public recognition, of course). Use your advertising and branding to develop a sense of stability and permanence for your business, even in a field that changes as rapidly as computers.
- No matter the nature of your small business, you need to be visible, you need to be reliable, and you need to provide a personalized experience that builds customer loyalty.
Expert Q&A

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.technibble.com/moving-wearable-mobile-repair-post-pc-era/
- ↑ http://www.computerhope.com/issues/ch001553.htm
- ↑ https://www.technibble.com/categories/starting-computer-repair-business/
- ↑ http://www.mytopbusinessideas.com/computer/
- ↑ http://www.tomshardware.com/answers/id-1813630/starting-computer-repair-setup-consulting-business-tips.html
About This Article

To start up a successful computer business, find a way to match your skills with the needs of your local computer market. Assess the training and experience that you have with computers to determine the type of computer business that is best suited to your talents. For example, if you have experience building personal computers, you can use your background to start up a business selling discounted computers that you assemble from parts that you acquire. In addition to your skills and experience, it’s important that you analyze the market around you to see if you can start a successful business. Consider the demographics in your area and think about what type of computer products or services they’re likely to purchase. For example, if you’re selling discounted computer systems, and your area has a large number of older people looking to buy a simple home computer, you may have a market for your business! For tips about how to build your brand identity when you’re starting a computer business, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Namgbenda Andrew
Oct 27, 2016
Did this article help you?

Sophia Tamayo
Jul 5, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
How to start a successful computer repair business

Table of contents:
Introduction
Step 1: build up your savings, step 2: create a business plan for your computer repair business, step 3: finance your computer repair business, step 4: choose a location, step 5: set your pricing for your computer repair services, step 6: get your computer repair and it certifications, step 7: market your computer repair business, step 8: protect your computer repair business with small business insurance.
The ability to configure a motherboard or coax a CPU into place are valuable skills, and those who have the technical chops can become a hot commodity. But what about tech experts who dream of being their own boss? If you have a knack for fixing electronics, starting a computer repair business could be a logical career move.
However, you shouldn’t take that decision lightly. Writing a business plan, securing financing, and taking several other key steps may be needed to put your best foot forward with your new IT company.
If you think you’re ready to open your doors and offer your tech expertise to customers directly, you can follow these helpful steps to successfully launch your computer repair business.
When starting a computer repair business, it’s important to shore up on your savings to help cover the essentials before working with your first customer. These expenses may include:
- Purchasing your own tools and equipment
- Leasing a storefront
- Registering your business
- Paying for professional certifications, business licenses, and training
- Marketing materials, such as business cards, flyers, and online advertisements
On top of these startup costs, it’s also a good idea to keep emergency cash on hand. This gives you some flexibility as your company grows, as it can cover your business expenses during months when you don’t hit your billable work goals.
Ideally, you should keep enough money to cover your expenses for at least six months before quitting your day job and starting your own computer repair business.
Your business plan will serve as the cornerstone of your small business – whether you run a laptop repair service from your kitchen table, or from the inside of a large IT repair and maintenance company with several employees.
When you write a business plan , it should include both your ideas for getting your new computer repair business up and running, as well as plans for how you’ll grow and adapt in the future. Here are some of the most important questions you should answer in your business plan to help guide your new company.
What services will you offer?
IT and computer repair is a broad field. Your business plan should include a “shortlist” of services that your computer repair company will specialize in. You could choose from several different specialties, including server maintenance, personal computer repair, and more.
Who is your target customer?
Deciding who your target customers are – individuals, businesses, or both – will help you better understand their needs and how your computer repair business can help them. Your business plan should include a profile of your target customers and a plan for reaching them.
What is your business structure?
How you choose to structure your business can affect both your taxes and legal liability. Most companies choose one of three options:
- Sole proprietorship
- Limited liability company (LLC)
Where will you work?
Where you choose to conduct business will directly impact your expenses, business insurance needs, and customer relationships. For example, if you decide to offer computer repair services from your home, you’ll likely need a business vehicle and commercial auto insurance .
Most computer repairs companies operate from their own home, a storefront, or on-site with clients.
How are you financing your business?
Your business plan should include a strategy for financing your startup costs and operational expenses until you’re profitable. Some small business financing options include small business loans, partnering with outside investors, and crowdfunding.
Who are your competitors?
You should accurately analyze your competition in your business plan. Understand their strengths, weaknesses, and how you could fill a gap in your market. You should also note their marketing strategies and how they might make it difficult for your new computer repair company to gain traction.
What are your projected income and expenses for the first five years?
Setting goals in your business plan shows that you’re committed to your computer repair business. It forces you to consider the costs involved and develop a vision for where you want your company to go in the future.
What is your marketing strategy?
Your business plan should cover how you’ll get the word out about your new company. This section should include both your strategy and the costs associated with it. Consider attending networking events, email marketing, and SEO-based advertising to help you get started.
Do you plan on hiring employees?
Hiring employees can help take some work off your plate and allow you to scale your business. If you think you’ll hire employees eventually, your business plan should answer when you will look to hire, what business goals you need to hit to afford that, and what types of employees you'll need.
After outlining your finance options in your business plan, the next step is to seek out what options are readily available to help get your computer repair business off the ground.
To start, one option you can consider is a loan through the Small Business Administration (SBA). The SBA partners with lenders, community development organizations, and microlending institutions to set guidelines and facilitate loans for small business owners.
The SBA’s support reduces overall risk for lenders, making it easier for you to get approved for financing than you would through a traditional bank loan.
However, an SBA loan may not cover all your needs. In that case, you could try to leverage any of these options to provide additional support:
- Find an investor, such as a venture capital firm or angel investor
- Use small business credit cards
- Tap into your 401(k)
- Crowdfunding
- Borrowing from friends and family
Each of these options comes with risks. For example, credit cards typically have high interest rates compared to other business loans, and borrowing from friends and family risks damaging your personal relationships if your business should fail. For this reason, you should try to run your computer repair business as lean as possible in the beginning. Doing so will minimize the amount of money you need to borrow and allow you to focus on building your business rather than repaying debt.
Depending on the types of services you’ll offer, you could have a lot of location flexibility when you start your new computer repair business. For example, if you fix computers online, you may only need a home office with a secure internet connection to get started. Or, if you decide to offer on-site repairs, you may not need a physical location at all.
How you choose to operate will ultimately determine your location needs, which you’ll eventually choose from one of these three options:
Running a home business reduces your overhead since you don’t need to pay for office space. On top of that, your commute is nonexistent, and you typically have more flexibility over your work hours.
However, there are some downsides. It may be tough to separate your professional life and personal life. Also, if you ever work with your customers face-to-face (IT consultations, dropping off laptops for repair, etc.), you’ll either need to meet them somewhere else, or invite them to your home. You’ll also need to purchase commercial property insurance as most homeowners’ policies don’t cover business property.
Because of this, running your computer repair business from your home is best if you fix computers online, offer in-home computer repair services, or work on-site with local businesses.
A storefront
A storefront lets people in your community see your business name and brand. It can draw foot traffic and gives you a set location to interact with customers who may be dropping off their computers for repairs or stopping in to ask questions.
The biggest downside of a storefront is the additional expense. Not only will you pay rent or a mortgage (if you decide to buy instead of lease), but you’ll also have other expenses such as utilities. On top of that, you’ll likely need to purchase general liability insurance and commercial property insurance to protect both you and your landlord from lawsuits and property damage .
If you include a retail section to sell computer accessories, you will also need to consider the wholesale costs of the products you plan to sell, as well as invest in product liability insurance .
On-site support
If you offer at-home computer repair services, you may not need a physical location for your business. Instead, you’ll go to your customers’ homes to repair their computers and troubleshoot other technical problems.
If you prefer to work with businesses instead of individuals, you can also run an on-site computer repair company where you’ll maintain their servers, install new hardware, and repair their company laptops and computers.
Limiting your repairs to on-site visits eliminates the added expense of a storefront while also separating your personal and professional lives. However, there are other factors to consider, including:
- Your customer’s scheduling constraints
- The possibility of jobs taking longer than expected
- Customers asking for extra work once you're already on location
- Transportation risks, such as car accidents or traffic delays
Since you’ll be driving to your customers, you’ll also need to purchase commercial auto insurance, since most personal auto policies exclude business-related driving.
It can be tempting to offer below-market pricing when you first start out. However, this strategy can backfire. Your customers will expect your low prices to continue, making it harder to raise your rates in the future.
Plus, you run the risk of being seen as the “cheaper” option rather than the high-quality one. This could attract customers who are more interested in the cheapest rate rather than high-quality service. Once your rates increase, these customers could disappear, forcing you to build your customer base from scratch.
When you get into this low-price cycle, you’ll have to take on more customers to cover your business expenses and pay your salary.
Research the typical rate for other repair shops in your area and set your prices accordingly. You should aim to be in line with what your competition is charging, while also accounting for your own expenses.

In most states, all you need to open a computer repair business is the expertise to do the work. However, you would likely benefit from obtaining certain certifications that prove your expertise and help you gain a competitive advantage. Some of the more common certifications for IT professionals include:
- CompTIA A+ Technician
- Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA)
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
- Microsoft Certified Systems Engineer (MCSE)
- Apple Certified Macintosh Technician (ACMT)
- Building Industry Consulting Service International (BICSI) Technician
Certifications can help businesses of all sizes – from large commercial IT companies to freelance computer technicians . However, these credentials and courses aren’t one-size-fits-all. Check to see which certifications are common among other repair shops in your area and search online for common certifications in your industry to learn about the latest trends.
Asking family and friends to spread the word about your new business can help you build some initial buzz, but you also need a comprehensive marketing strategy to help potential customers find you.
Your first priority should be creating a website for your computer repair business. Use the website to share information about what you do, who you work with, and how to contact you. Your website should be professional and mobile-friendly. To make sure it meets these standards, consider hiring a professional web designer to build it for you.
Your company website will also be your hub for search engine marketing (SEM), where you’ll optimize keywords and content on your site to help you show up in the search results when people look for terms like “computer repair company” or “freelance computer technician.”
But marketing doesn’t stop with your website. You’ll want to invest in other strategies as well. Some ideas for marketing a computer repair business include:
- Attending networking events with your target customers
- Joining a professional networking group
- Email marketing
- Promoting posts and ads on social media
It’s important to make marketing part of your regular schedule. Set aside a few hours each week to touch base with current and potential business clients, post on your social media accounts, and use email or other popular mediums to promote your business.
Lawsuits and other catastrophic events can cost you a lot of money – and could even bankrupt your business. Fortunately, small business insurance for computer repair shops will help protect all your hard work. Here’s a breakdown of all the policies you should consider purchasing for your new business.
General liability insurance
General liability insurance is typically the first insurance policy any small business purchases. It covers many common issues that you might face, including:
- Third-party bodily injuries
- Third-party property damage
- Advertising injuries like libel , slander , and copyright infringement
If you rent an office space, your landlord will likely require you to carry this insurance policy as part of your lease agreement.
Commercial property insurance
Commercial property insurance pays to repair or replace stolen, lost, or damaged business property. It covers both your office space (whether your rent or own) and any property that you use for business purposes. You can also add to your commercial property insurance to cover things like:
- Natural disasters
- Forced closures due to property damage
- Damage to mobile property
Even freelance computer repair technicians, home-based computer repair companies, and mobile repair services should consider commercial property insurance since most homeowners’ policies exclude business property from their coverage.
Business owner’s policy
Another policy that could benefit your computer repair business is a business owner’s policy (BOP). This insurance coverage combines general liability insurance and commercial property insurance in one package, making it an ideal option for most computer repair companies – especially those who rent a storefront.
You can also add bailee coverage to your business owner’s or general liability policies to cover your customers’ property when they leave it in your care.
Errors and omissions insurance
Errors and omissions insurance (also called E&O or professional liability insurance ) covers lawsuits over the quality of your work. If a customer believes you either didn’t provide the services you agreed to, or made mistakes that cost them money, they could file a lawsuit against you. Errors and omissions coverage pays for your legal fees, settlements, and other costs arising from the lawsuit.
Cyber liability insurance
Another critical policy for someone in your line of work is cyber liability insurance . This policy covers the cost of a data breach on your servers, or lawsuits when a customer blames you for failing to prevent a data breach on their computer. It pays for things like:
- Cyber extortion payments
- Data recovery
- Regulatory investigation and compliance
- Notifying affected customers
- Credit monitoring
- Business interruption expenses
Commercial auto insurance
If you travel to client sites, your personal auto policy likely won't cover an accident if you’re on company business. Most personal vehicle policies exclude business-related driving. Vehicles owned by a business must be covered by commercial auto insurance .
Or, you could invest in hired and non-owned auto insurance (HNOA) , which covers accidents in personal, leased, and rented vehicles used for work purposes.
For example, if you or an employee gets into an accident while driving a personal car to drop off a laptop for work, your HNOA coverage would help pay for any claims or lawsuits against your business. It’s worth noting that this would not cover damage to the vehicle used by your business.
Fidelity bonds
Computer repair specialists who take on jobs with banks or other financial institutions may be asked by their clients to purchase a fidelity bond . Also known as an employee dishonesty bond, it functions as a voucher to ensure that you or your employees won’t use your behind-the-scenes access to steal money. If a theft does occur, the bond can repay the stolen funds.
Workers’ compensation insurance
If you have employees, it might be necessary to purchase workers’ compensation insurance , which can pay for medical expenses and partial lost wages if an employee is hurt on the job. Whether or not you are required to buy it depends on where the business is based, since the laws covering workers’ comp requirements are governed at the state level .
If you're curious how much insurance might cost to protect your computer repair business, you can review Insureon’s estimates for IT businesses .
Complete Insureon’s easy online application today to compare insurance quotes from top-rated U.S. carriers. Once you find the right policy for your small business, you can begin coverage in less than 24 hours.
Christine Aebischer, Contributing Writer
Christine is a contributing writer who's experienced in a wide range of topics from personal finance and insurance to luxury lifestyles and wellness. She is an accomplished writer, editor, and content marketer with a specialization in service-driven content.
- Sample Business Plans
- IT, Staffing & Customer Service
Computer Repair Business Plan
Starting a computer repair business can be a lucrative and rewarding business venture for any tech enthusiast.
However, entering the marketplace without proper planning can put your business at risk. That’s where a business plan can help.
Need help writing a business plan for your computer repair business? You’re at the right place. Our computer repair business plan template will help you get started

Free Business Plan Template
Download our Free Computer Repair Business Plan Template now and pave the way to success. Let’s turn your vision into an actionable strategy!
- Fill in the blanks – Outline
- Financial Tables
How to Write a Computer Repair Business Plan?
Writing a computer repair business plan is a crucial step toward the success of your business. Here are the key steps to consider when writing a business plan:
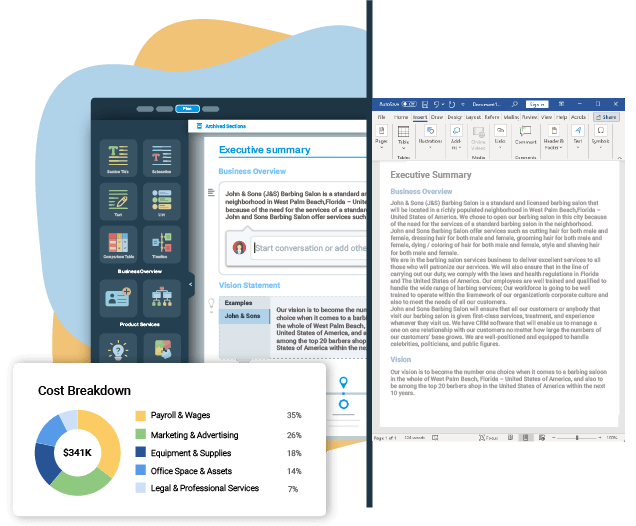
1. Executive Summary
An executive summary is the first section planned to offer an overview of the entire business plan. However, it is written after the entire business plan is ready and summarizes each section of your plan.
Here are a few key components to include in your executive summary:
- Introduce your Business: Start your executive summary by briefly introducing your business to your readers.
- This section may include the name of your computer repair business, its location, when it was founded, the type of computer repair business (E.g., general computer repair, mobile device repair, gaming console repair.), etc.
- Market Opportunity: Summarize your market research, including market size, growth potential, and marketing trends. Highlight the opportunities in the market and how your business will fit in to fill the gap.
- Products and Services: Highlight the computer repair services you offer your clients. The USPs and differentiators you offer are always a plus.
- Financial Highlights: Briefly summarize your financial projections for the initial years of business operations. Include any capital or investment requirements, associated startup costs, projected revenues, and profit forecasts.
- Call to Action: Summarize your executive summary section with a clear CTA, for example, inviting angel investors to discuss the potential business investment.
Ensure your executive summary is clear, concise, easy to understand, and jargon-free.
Say goodbye to boring templates
Build your business plan faster and easier with AI
Plans starting from $7/month

2. Business Overview
The business overview section of your business plan offers detailed information about your company. The details you add will depend on how important they are to your business. Yet, business name, location, business history, and future goals are some of the foundational elements you must consider adding to this section:
- General computer repair
- Laptop repair
- Mobile device repair
- Remote support services
- Gaming console repair
- On-site repair services
- Describe the legal structure of your computer repair company, whether it is a sole proprietorship, LLC, partnership, or others.
- Explain where your business is located and why you selected the place.
- Owners: List the names of your computer repair company’s founders or owners. Describe what shares they own and their responsibilities for efficiently managing the business.
- Mission Statement: Summarize your business’ objective, core principles, and values in your mission statement. This statement needs to be memorable, clear, and brief.
- Business History: If you’re an established computer repair service provider, briefly describe your business history, like—when it was founded, how it evolved over time, etc.
- Additionally, If you have received any awards or recognition for excellent work, describe them.
- Future Goals: It’s crucial to convey your aspirations and vision. Mention your short-term and long-term goals; they can be specific targets for revenue, market share, or expanding your services.
This section should provide a thorough understanding of your business, its history, and its future plans. Keep this section engaging, precise, and to the point.
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section of your business plan should offer a thorough understanding of the industry with the target market, competitors, and growth opportunities. You should include the following components in this section.
- Target market: Start this section by describing your target market. Define your ideal customer and explain what types of services they prefer. Creating a buyer persona will help you easily define your target market to your readers.
- For instance, computer educational institutes and IT offices can be an ideal target market for a computer repair business.
- Market size and growth potential: Describe your market size and growth potential and whether you will target a niche or a much broader market.
- Competitive Analysis: Identify and analyze your direct and indirect competitors. Identify their strengths and weaknesses, and describe what differentiates your computer repair services from them. Point out how you have a competitive edge in the market.
- Market Trends: Analyze emerging trends in the industry, such as technology disruptions, changes in customer behavior or preferences, etc. Explain how your business will cope with all the trends.
- For instance, there is a growing demand for mobile device repair services; explain how you plan to deal with this growing market trend.
- Regulatory Environment: List regulations and licensing requirements that may affect your computer repair company, such as business registration, insurance, trade and association memberships, data privacy and security, intellectual property rights, etc.
Here are a few tips for writing the market analysis section of your computer repair business plan:
- Conduct market research, industry reports, and surveys to gather data.
- Provide specific and detailed information whenever possible.
- Illustrate your points with charts and graphs.
- Write your business plan keeping your target audience in mind.
4. Products And Services
The product and services section should describe the specific services and products that will be offered to customers. To write this section should include the following:
- Diagnosis and troubleshooting
- Hardware repair and replacement
- Virus and malware removal
- Networking and connectivity solutions
- Software installation and configuration
- You might mention how customers request computer repair services, how you diagnose or troubleshoot issues, and when you deliver services.
- Quality Assurance: This section should explain how you maintain quality standards and consistently provide the highest quality service.
- This may include standardized procedures, timely quality audits, monitoring and testing equipment, and continuous improvement.
- Additional Services: Mention if your computer repair company offers any additional services. You may include services like IT consulting and support, data migration, cybersecurity solutions, cloud services, and e-waste recycling and disposal.
In short, this section of your computer repair plan must be informative, precise, and client-focused. By providing a clear and compelling description of your offerings, you can help potential investors and readers understand the value of your business.
5. Sales And Marketing Strategies
Writing the sales and marketing strategies section means a list of strategies you will use to attract and retain your clients. Here are some key elements to include in your sales & marketing plan:
- Unique Selling Proposition (USP): Define your business’s USPs depending on the market you serve, the equipment you use, and the unique services you provide. Identifying USPs will help you plan your marketing strategies.
- For example, fast turnaround times, on-site repairs, specialized expertise, and environment-friendly practices could be some of the great USPs for a computer repair company.
- Pricing Strategy: Describe your pricing strategy—how you plan to price your services and stay competitive in the local market. You can mention any discounts you plan on offering to attract new customers.
- Marketing Strategies: Discuss your marketing strategies to market your services. You may include some of these marketing strategies in your business plan—social media marketing, Google ads, local SEO, brochures, email marketing, and print marketing.
- Sales Strategies: Outline the strategies you’ll implement to maximize your sales. Your sales strategies may include offering free consultations, upselling and cross-selling, and forming strategic partnerships.
- Customer Retention: Describe your customer retention strategies and how you plan to execute them.
- For instance, your customer retention strategies may include providing excellent customer service, customer feedback and surveys, and follow-up calls.
Overall, this section of your computer repair business plan should focus on customer acquisition and retention.
Have a specific, realistic, and data-driven approach while planning sales and marketing strategies for your computer repair business, and be prepared to adapt or make strategic changes in your strategies based on feedback and results.
6. Operations Plan
The operations plan section of your business plan should outline the processes and procedures involved in your business operations, such as staffing requirements and operational processes. Here are a few components to add to your operations plan:
- Staffing & Training: Mention your business’s staffing requirements, including the number of employees or technicians needed. Include their qualifications, the training required, and the duties they will perform.
- Operational Process: Outline the processes and procedures you will use to run your computer repair business. Your operational processes may include equipment and inventory management, data and privacy protection, communication & customer service, and quality assurance & testing.
- Equipment & Machinery: Include the list of equipment and machinery required for computer repairs, such as workbench or repair tables, hand tools, diagnostic and testing tools, hardware components & repair parts, and software for data backup.
- Explain how these technologies help you maintain quality standards and improve the efficiency of your business operations.
Adding these components to your operations plan will help you lay out your business operations, which will eventually help you manage your business effectively.
7. Management Team
The management team section provides an overview of your computer repair business’s management team. This section should provide a detailed description of each manager’s experience and qualifications, as well as their responsibilities and roles.
- Founders/CEO: Mention the founders and CEO of your computer repair company, and describe their roles and responsibilities in successfully running the business.
- Key managers: Introduce your management and key members of your team, and explain their roles and responsibilities.
- It should include senior management and other key people involved in the computer repair business operations, including their education, professional background, and any relevant experience in the industry.
- Organizational structure: Explain the organizational structure of your management team. Include the reporting line and decision-making hierarchy.
- Compensation Plan: Describe your compensation plan for the management and staff. Include their salaries, incentives, and other benefits.
- Advisors/Consultants: Mentioning advisors or consultants in your business plans adds credibility to your business idea.
- So, if you have any advisors or consultants, include them with their names and brief information consisting of roles and years of experience.
This section should describe the key personnel for your computer repair services, highlighting how you have the perfect team to succeed.
8. Financial Plan
Your financial plan section should provide a summary of your business’s financial projections for the first few years. Here are some key elements to include in your financial plan:
- Profit & loss statement: Describe details such as projected revenue, operational costs, and service costs in your projected profit and loss statement. Make sure to include your business’s expected net profit or loss.
- Cash flow statement: The cash flow for the first few years of your operation should be estimated and described in this section. This may include billing invoices, payment receipts, loan payments, and any other cash flow statements.
- Balance Sheet: Create a projected balance sheet documenting your repair business’s assets, liabilities, and equity.
- Break-even point: Determine and mention your business’s break-even point—the point at which your business costs and revenue will be equal.
- This exercise will help you understand how much revenue you need to generate to sustain or be profitable.
- Financing Needs: Calculate costs associated with starting a computer repair business, and estimate your financing needs and how much capital you need to raise to operate your business. Be specific about your short-term and long-term financing requirements, such as investment capital or loans.
Be realistic with your financial projections, and make sure you offer relevant information and evidence to support your estimates.
9. Appendix
The appendix section of your plan should include any additional information supporting your business plan’s main content, such as market research, legal documentation, financial statements, and other relevant information.
- Add a table of contents for the appendix section to help readers easily find specific information or sections.
- In addition to your financial statements, provide additional financial documents like tax returns, a list of assets within the business, credit history, and more. These statements must be the latest and offer financial projections for at least the first three or five years of business operations.
- Provide data derived from market research, including stats about the computer repair industry, user demographics, and industry trends.
- Include any legal documents such as permits, licenses, and contracts.
- Include any additional documentation related to your business plan, such as product brochures, marketing materials, operational procedures, etc.
Use clear headings and labels for each section of the appendix so that readers can easily find the necessary information.
Remember, the appendix section of your computer repair business plan should only include relevant and important information supporting your plan’s main content.
The Quickest Way to turn a Business Idea into a Business Plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
This sample computer repair business plan will provide an idea for writing a successful computer repair plan, including all the essential components of your business.
After this, if you still need clarification about writing an investment-ready business plan to impress your audience, download our computer repair business plan pdf .
Related Posts
Software Company Business Plan
IT Consulting Business Plan
Why Customer Analysis Important
How to Choose Effective Business Location
10 Components of a Business Plan
Guide to Making a Business Plan Presentation
Frequently asked questions, why do you need a computer repair business plan.
A business plan is an essential tool for anyone looking to start or run a successful computer repair business. It helps to get clarity in your business, secures funding, and identifies potential challenges while starting and growing your business.
Overall, a well-written plan can help you make informed decisions, which can contribute to the long-term success of your computer repair company.
How to get funding for your computer repair business?
There are several ways to get funding for your computer repair business, but self-funding is one of the most efficient and speedy funding options. Other options for funding are:
- Bank loan – You may apply for a loan in government or private banks.
- Small Business Administration (SBA) loan – SBA loans and schemes are available at affordable interest rates, so check the eligibility criteria before applying for it.
- Crowdfunding – The process of supporting a project or business by getting a lot of people to invest in your business, usually online.
- Angel investors – Getting funds from angel investors is one of the most sought-after startup options.
Apart from all these options, there are small business grants available, Check for the same in your location and you can apply for it.
Where to find business plan writers for your computer repair business?
There are many business plan writers available, but no one knows your business and ideas better than you, so we recommend you write your computer repair business plan and outline your vision as you have in mind.
What is the easiest way to write your computer repair business plan?
A lot of research is necessary for writing a business plan, but you can write your plan most efficiently with the help of any computer repair business plan example and edit it as per your need. You can also quickly finish your plan in just a few hours or less with the help of our business plan software .
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more
Plan your business in the shortest time possible
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee

Create a great Business Plan with great price.
- 400+ Business plan templates & examples
- AI Assistance & step by step guidance
- 4.8 Star rating on Trustpilot
Streamline your business planning process with Upmetrics .

ZenBusinessPlans
Home » Sample Business Plans » Technology
How to Write a Computer Sales & Service Business Plan [Sample Template]
Are you about starting a computer sales & services business? If YES, here is a complete sample computer sales & services business plan template & feasibility report you can use for FREE . According to a recent report, computer sales and related services are expected to exceed $47 billion this year in the U.S. alone, with computer servicing leading the way.
This goes to show that any entrepreneur who properly positions himself or herself in computer sales and servicing industry would definitely enjoy good business turnover. As a matter of fact, almost all businesses and homes have computers, and these people may not have the skills, time or the desire to do their own computer servicing, repairs and upgrades, and that puts a computer physician right in the middle of one of the fastest-growing industries in the world.
A Sample Computer Sales & Services Business Plan Template
1. industry overview.
The computer sales and servicing industry includes operators that mainly sell and service all forms of computers such as desktops, laptops, notebooks, palmtops and software, as well as accessories like printers, scanners and keyboards. These goods are generally purchased from domestic and international manufacturers and wholesalers and then sold to end consumers, including households and businesses.
Computers have exploded throughout America and the world over the past 30 years – from 2,000 units shipped in 1960 to 900,000 in 1980 to 7 million in 1990 to over 15 million per year by 2003 to over 65 million per quarter in 2015. With this rapid growth, there has been a corresponding increase in the need for computer services.
If you are conversant with happenings in the Computer Sales and Services industry, you will notice that computers are rapidly becoming indispensable household and personal products. In spite of the growing ubiquity of these products, retailers of computers, peripherals and consumer electronics have experienced some time-consuming challenges over the past five years.
Swift technological change, increased production efficiency and a highly globalized supply chain have lowered computer retail prices, hampering the industry’s revenue potential.
In addition, the increasing adoption of e-commerce has reduced customer traffic in computer stores, further limiting revenue. More consumers are now taking advantage of online shopping, which facilitates product and price comparisons. Going forward, industry revenue is expected to decrease.
The Computer Sales and Services industry is indeed a large industry and pretty much active in most countries of the world. Statistics has it that in the united states of America alone, there are about 18,173 registered and licensed (big, medium scale and small) computer manufacturing companies scattered all across the United States responsible for employing about 94,791 people and the industry rakes in a whooping sum of $29 billion annually.
The industry is projected to enjoy -0.4 percent annual growth within 2012 and 2017. It is important to state that Apple Inc., Best Buy Co. Inc. and Fry’s have lion shares of the available market in this industry.
Computer sales account for an estimated 44.0 percent of industry revenue in 2017. Products in this segment include desktops and laptops, with laptop sales outpacing that of desktops. While desktops were historically the most commonly purchased computer product, the falling price of computers and computer components over the past five years reduced the premium that laptops once commanded over desktops.
A majority of consumers’ favor laptops for their portability, augmented by the increasingly wireless data infrastructure. However, desktops still maintain advantages in niche market, particularly with gaming enthusiasts and computer power users who prefer a desktop computer’s superior upgrade potential, ease of repair and customizability.
No doubt everybody will quite agree that the computer sales and services industry has come to stay and of course it is one industry that plays key roles not only in the business world, but also in almost all aspects of what goes around in our world today as long as computers are involved.
Over and above, the Computer Sales and Services industry is an open industry hence a low level of market share concentration. Even though large multiservice agencies operate in the industry, revenue is also spread among thousands of small computer stores and repair centers.
2. Executive Summary
Harry & Barry® Computer Sales & Services Center, LLC is a U.S based computer sales and services company. We have been able to secure a standard store facility in a central business district in Phillips Avenue, Sioux Falls – South Dakota. We are set to compete in the highly competitive computer sales and services industry not only in Sioux Falls – South Dakota, but also throughout the United States market.
Harry & Barry® Computer Sales & Services Center, LLC will engage in the sales and servicing of all forms of computers such as desktops, laptops, palmtops and software, as well as accessories like printers, scanners and keyboards. Our business goal is to become one of the top brands in the computer sales and services industry in the United States and we will make sure that we do all we can to compete favorably with leaders in the industry.
Our workers are going to be selected from a pool of certified and highly experienced computer sales and services engineers in and around Sioux Falls – South Dakota and also from any part of the United States of America as the business grows. We will make sure that we take all the members of our workforce through the required training that will position them to meet the expectations of the company.
At Harry & Barry® Computer Sales & Services Center, LLC, our client’s best interest will always come first, and everything we do will be guided by our values and professional ethics. We will ensure that we hold ourselves accountable to the highest standards by meeting our client’s needs precisely and completely.
Harry & Barry® Computer Sales & Services Center, LLC is a joint partnership business that is owned by Engr. Harry Jordan a computer engineer par excellence who graduated with from Illinois Institute of Technology (B.Engr. Computer Engineering), and his friend and business partner Barry Martins (B.Sc. Business Management).
They have a combined experience that can help them build Harry & Barry® Computer Sales & Services Center, LLC to favorably compete with other leading computer sales and services businesses in the United States of America.
3. Our Products and Services
Harry & Barry® Computer Sales & Services Center, LLC is established with the aim of maximizing profits in the computer sales and services industry. We want to compete favorably with companies in the United States which is why we have put in place a competent quality assurance team that will ensure that every service rendered meets and even surpasses our customers’ expectations.
We will work hard to ensure that Harry & Barry® Computer Sales & Services Center, LLC is not just accepted in Sioux Falls – South Dakota but also in other cities in the United States of America. Our products and services are listed below;
- Sales and servicing of all sort of computers
- Sales and servicing of computer peripherals (e.g. printers, monitors, keyboards, mouse and speakers)
- Sale of computer software
- Computer installation
- Computer Cloning/upgrade
- Offering other computer repair and installation related services
4. Our Mission and Vision Statement
- Our vision is to establish a one stop computer sales and service center whose services and brand will not only be accepted in Sioux Falls – South Dakota but also in other cities in the United States of America.
- Our mission is to retail computers and related products and also to provide professional computer services that will assist businesses and individuals in ensuring that their computers are always in good shape to help them carry out their business.
- We want to build a computer sales and services company that can favorably compete with other leading brands in the computer sales and services industry.
Our Business Structure
Harry & Barry® Computer Sales & Services Center, LLC, is a computer sales and services company that intend starting small in Phillips Avenue, Sioux Falls, but hopes to grow big in order to compete with leading computer sales and services companies in the United States.
We are aware of the importance of building a solid business structure that can support the picture of the kind of world class business we want to own. This is why we are committed to only hire the best hands within our area of operations.
At Harry & Barry® Computer Sales & Services Center, LLC, we will ensure that we hire people that are qualified, hardworking, creative, customer centric and are ready to work to help us build a prosperous business that will benefit all the stake holders.
As a matter of fact, profit-sharing arrangement will be made available to all our senior management staff and it will be based on their performance for a period of five years or more as agreed by the board of trustees of the company. In view of the above, we have decided to hire qualified and competent hands to occupy the following positions;
- Chief Executive Officer
- Store Manager
- Head, Technical Services
- Human Resources and Admin Manager
- Sales and Marketing Executive
- Computer Repair and Maintenance Engineers and Technicians (10)
- Client Service Executive
5. Job Roles and Responsibilities
Chief Executive Officer – CEO:
- Increases management’s effectiveness by employing, choosing, orientating, training, coaching, counseling, and disciplining managers; communicating values, strategies, and objectives; assigning accountabilities; planning, monitoring, and appraising job results; developing incentives; developing a climate for offering information and opinions; providing educational opportunities.
- Accountable for fixing prices and signing business deals
- Responsible for providing direction for the business
- Creates, communicates, and implements the organization’s vision, mission, and overall direction – i.e. leading the development and implementation of the overall organization’s strategy.
- Responsible for signing checks and documents on behalf of the company
- Evaluates the success of the organization
- Reports to the board
Admin and HR Manager
- Responsible for overseeing the smooth running of HR and administrative tasks for the organization
- Maintains office supplies by checking stocks; placing and expediting orders; evaluating new products.
- Ensures operation of equipment by completing preventive maintenance requirements; calling for repairs.
- Defines job positions for recruitment and managing interviewing process
- Carries out induction for new team members
- Responsible for training, evaluation and assessment of employees
- Responsible for arranging travel, meetings and appointments
- Oversees the smooth running of the daily office activities.
Store Manager:
- Responsible for managing the daily activities in the store
- Ensures that proper records of computers and computer parts are kept and warehouse does not run out of products
- Ensures that the store facility is in tip top shape and goods are properly arranged and easy to locate
- Controls distribution and supply chain inventory
- Supervises the workforce in the sales floor
- Helps to ensure consistent quality of computers and computer parts are purchased and retailed in good price that will ensure we make good profit
Head, Technical Services:
- Serves as project manager of the organization; works directly with employees
- Maintains quality service by establishing and enforcing organization standards.
- Makes certain that the technical department performs efficiently, coordinates employee efforts, facilitates communication between management and computer repairs and maintenance engineers and technicians
- Ensures that the organization work in line with international best practices.
Sales and Marketing Manager
- Manages external research and coordinate all the internal sources of information to retain the organizations’ best customers and attract new ones
- Models demographic information and analyze the volumes of transactional data generated by customer
- Identifies development opportunities; follows up on development leads and contacts; participates in the structuring and financing of projects; assures the completion of development projects.
- Writing winning proposal documents, negotiate fees and rates in line with organizations’ policy
- Responsible for handling business research, market surveys and feasibility studies for clients
- Responsible for supervising implementation, advocate for the customer’s needs, and communicate with clients
- Develops executes and evaluate new plans for expanding sales
- Creates new markets cum businesses for the organization
- Empower and motivates the sales team to meet and surpass agreed targets
Accountant/Cashier:
- Responsible for preparing financial reports, budgets, and financial statements for the organization
- Provides managements with financial analyses, development budgets, and accounting reports; analyzes financial feasibility for the most complex proposed projects; conducts market research to forecast trends and business conditions.
- Responsible for financial forecasting and risks analysis.
- Performs cash management, general ledger accounting, and financial reporting for one or more properties.
- Responsible for developing and managing financial systems and policies
- Responsible for administering payrolls
- Ensuring compliance with taxation legislation
- Handles all financial transactions for the organization
- Serves as internal auditor for the organization.
Computer Repair and Maintenance Engineers (2) and Technicians (8)
- Responsible for general computer repairs and maintenance services
- Carry out computer installation services for clients
- Responsible for carrying out computer cloning and upgrade
- Responsible for handling Networking of computer system
- Responsible for handling virus removal Data recovery
- Handles computer and accessories sales and supply for the organization
Help Desk Officers
- Welcomes clients and potential clients by greeting them in person or on the telephone; answering or directing inquiries.
- Ensures that all contacts with clients (e-mail, walk-In center, SMS or phone) provides the client with a personalized customer service experience of the highest level.
- Through interaction with clients on the phone, uses every opportunity to build client’s interest in the company’s products and services.
- Manages administrative duties assigned by the creative director in an effective and timely manner.
- Consistently stays abreast of any new information on the organizations’ products, promotional campaigns etc. to ensure accurate and helpful information are supplied to clients when they make enquiries.
- Find out the customer’s needs, recommend, select and help locate the right merchandise, describe a product’s features and benefits.
- Bag, package or gift-wrap merchandise as requested by customers.
6. SWOT Analysis
Because of our quest for excellence, Harry & Barry® Computer Sales & Services Center, LLC engaged the services of a core professional in the area of business consulting and structuring to assist our organization in building a well – structured computer sales and services business that can favorably compete in the industry in the United States.
Part of what the business consultant did was to work with the management of our organization in conducting a comprehensive SWOT analysis for Harry & Barry® Computer Sales & Services Center, LLC. Here is a summary from the result of the SWOT analysis that was conducted on behalf of Harry & Barry® Computer Sales & Services Center, LLC;
Our core strength lies in the power of our workforce. We have a team of trained and certified computer repair engineers and technicians, a team with excellent qualifications and experience in various niche areas in the industry. Aside from the synergy that exists in our carefully selected workforce, our services will be guided by best practices in the industry and we will ensure that we have all brands and types of computers in our store per time.
As a new computer sales and services center in Sioux Falls – South Dakota, it might take some time for our organization to break into the market and gain acceptance especially from top profile clients in the already highly competitive computer sales and services industry; that is perhaps our major weakness. Another weakness is that we may not have the required cash to pump into promoting our business the way we would want to.
- Opportunities:
No doubt, the opportunities in the computer sales and services industry is massive considering the number of individuals and businesses that own computers. So also, the launch of new tablets will likely drive consumers into stores to test and compare products. As a computer sales and services company, we are ready to take advantage of any opportunity that is available in the industry.
The increasing adoption of e-commerce has reduced customer traffic in computer stores, further limiting revenue and also, the domestic PC market has shrunk due to market saturation and greater competition from tablets, are some of the threats that will confront us.
So also, one major threat that we are likely going to face is economic downturn. Another threat that may likely confront us is the arrival of a new computer sales and services center in same location where our target market exists and who may want to adopt same Business model like us.
7. MARKET ANALYSIS
- Market Trends
The extent at which the internet and computer has taken over our world is a pure sign that every computer literate needs the services of a computer repairer when his/her computer malfunctions – be it hardware or software.
The very nature of the Computer Sales and Services industry, with its extraordinary rate of technological development, creates a constant need for businesses skilled in updating and advising customers on computer-related issues.
With every individual armed with a computer and with almost all valuable information in our daily lives being stored in the computer, the computer selling business is booming and with this booming comes a need for repair.
Everybody with a computer knows that moment of panic when the hard drive crashes–and for business people, it usually happens when they are staring into the eye of a deadline. The need for computer physicians is growing every day and more people are venturing into this field, making it a competitive and goal oriented industry.
Lastly, the computer sales and services industry will continue to evolve due to the advancement of computer technology and software designs et al.
8. Our Target Market
Before starting our computer sales and services business in Sioux Falls – South Dakota, we conducted a market survey and feasibility studies and we are certain that there is a wide range of both corporate and individual clients who cannot successfully run their businesses without computers.
In view of that, we have created strategies that will enable us reach out to various corporate organizations and individual who we know can’t afford to do without our products and services. Below is a list of people we will specifically market our products and services to;
- Banks, Insurance Companies and other related Financial Institutions
- Blue Chips Companies
- Corporate Organizations
- Real Estate Owners, Developers, and Contractors
- Research and Development Companies
- The Government (Public Sector)
- Schools (High Schools, Colleges and Universities)
- Celebrities, Politicians, Public Figures and Public Speakers
- Sport Organizations
- Religious Organizations
- Television Stations
- Printing Press (Publishing Houses) and Authors
- Branding and Advertising agencies
- Individuals and households who own computers
Our Competitive Advantage
Surviving in the business world as a computer sales and services company requires more than your expertise, knowing how to deliver standard repairs and maintenance but also how to network with key people that matter.
We are quite aware that to be highly competitive in the computer sales and services industry means that you are not only expected to deliver reliable computer supply, installation, repair, networking and maintenance jobs, but you must be able to meet set targets.
No one would want to continue to hire your services if don’t always meet up with the target date of completion of projects. Our competitive advantage lies in our ability to control stock at hand, our experienced work force and proximity to key markets.
We equally have a team of certified, highly trained and experienced computer repair engineers and technicians, a team with excellent qualifications and experience in various niche areas in the computer sales and service industry. Aside from the synergy that exists in our carefully selected workforce, our services will be guided by best practices in the industry.
Lastly, all our employees will be well taken care of, and their welfare package will be among the best within our category in the industry. It will enable them to be more than willing to build the business with us and help deliver our set goals and achieve all our business aims and objectives.
9. SALES AND MARKETING STRATEGY
- Sources of Income
Harry & Barry® Computer Sales & Services Center, LLC is established with the aim of maximizing profits in the computer sales and services industry and we are going to go all the way to ensure that we do all it takes to meet and surpass the expectations of all our clients.
Harry & Barry® Computer Sales & Services Center, LLC will generate income by;
- Computer Cloning and upgrade
10. Sales Forecast
One thing is certain, there would always be corporate organizations and individuals who would need to purchase computers and accessories. We are well positioned to take on the available market in Sioux Falls – South Dakota and we are quite optimistic that we will meet our set target of generating enough profits from our first six months of operation.
We have been able to critically examine the computer sales and services market, we have analyzed our chances in the industry and we have been able to come up with the following sales forecast. The sales projections are based on information gathered on the field and some assumptions that are peculiar to similar startups in Sioux Falls – South Dakota.
- First Year: $350,000
- Second Year: $750,000
- Third Year: $1.2 million
N.B : This projection is done based on what is obtainable in the industry and with the assumption that there won’t be any major economic meltdown and there won’t be any major competitor offering same products and services as we do within the same location. Please note that the above projection might be lower and at the same time it might be higher.
- Marketing Strategy and Sales Strategy
We are mindful of the fact that there are stiff competitions in the computer sales and services industry, hence we have been able to hire some of the best marketing experts to handle our sales and marketing.
Our sales and marketing team will be recruited based on their vast experience in the industry and they will be trained on a regular basis so as to be well equipped to meet their targets and the overall business goal of Harry & Barry® Computer Sales & Services Center, LLC.
Our corporate goal is to grow Harry & Barry® Computer Sales & Services Center, LLC to become one of the top 10 computer sales and services brands in the United States of America which is why we have mapped out strategies that will help us take advantage of the available market and grow to become a major force to reckon with not only in Sioux Falls – South Dakota but also in other cities in the United States of America.
Harry & Barry® Computer Sales & Services Center, LLC is set to make use of the following marketing and sales strategies to attract clients;
- Introduce our computer sales and services center by sending introductory letters alongside our brochure to individuals, corporate organizations and key stake holders in and around Sioux Falls – South Dakota.
- Promptness in bidding for computer supply, installation, repair, networking and maintenance contract from the government and other cooperate organizations
- Advertise our business in relevant business magazines, newspapers, TV and radio stations.
- List our business in yellow pages’ ads (local directories)
- Attend relevant international and local expos, seminars and business fairs et al
- Create different packages for different category of clients in order to work with their budgets and still deliver excellent services
- Leverage on the internet to promote our business
- Engage direct marketing approach
- Encourage word of mouth marketing from loyal and satisfied clients
11. Publicity and Advertising Strategy
We have been able to work with our in-house brand and publicity consultant to help us map out publicity and advertising strategies that will help us walk our way into the heart of our target market. We are set to become the number one choice for both corporate and individual clients in the whole of the Sioux Falls and beyond which is why we have made provisions for effective publicity and advertisement of our computer sales and services company.
Below are the platforms we intend to leverage on to promote and advertise Harry & Barry® Computer Sales & Services Center, LLC;
- Place adverts on both print (newspapers and magazines) and electronic media platforms
- Sponsor relevant community based events/programs
- Leverage on the internet and social media platforms like Instagram, Facebook, twitter, YouTube, Google + et al to promote our services.
- Install our billboards in strategic locations all around Sioux Falls – South Dakota.
- Engage in roadshows from time to time in targeted neighborhoods.
- Distribute our fliers and handbills in target areas.
- List our computer sales and services company in local directories/yellow pages
- Advertise our computer sales and services company in our official website and employ strategies that will help us pull traffic to the site.
- Ensure that all our staff members wear our branded shirts and all our vehicles are well branded with our company logo.
12. Our Pricing Strategy
At Harry & Barry® Computer Sales & Services Center, LLC we will keep the prices of our products and services below the average market rate by keeping our overhead low and by collecting payment in advance from corporate organizations who would purchase our products or hire our services. In addition, we will also offer special discounted rates to all our customers at regular intervals.
We are aware that there are some one – off jobs or government contracts like computer supply, installation, repair, networking and maintenance which are always lucrative, we will ensure that we abide by the pricing model that is expected from contractors or organizations that bid for such contracts.
- Payment Options
The payment policy adopted by Harry & Barry® Computer Sales & Services Center, LLC is all inclusive because we are quite aware that different customers prefer different payment options as it suits them but at the same time, we will ensure that we abide by the financial rules and regulation of the United States of America.
Here are the payment options that Harry & Barry® Computer Sales & Services Center, LLC will make available to her clients;
- Payment via bank transfer
- Payment with cash
- Payment via credit cards/Point of Sale Machines (POS Machines)
- Payment via online bank transfer
- Payment via check
- Payment via mobile money transfer
- Payment via bank draft
In view of the above, we have chosen banking platforms that will enable our clients make payments for the purchase of our products or our services without any stress on their part. Our bank account numbers will be made available on our website and promotional materials for this purpose.
13. Startup Expenditure (Budget)
From our market survey and feasibility studies, we have been able to come up with a detailed budget on achieving our aim of establishing a standard and highly competitive computer sales and services company in Sioux Falls – South Dakota and here are the key areas where we will spend our startup capital;
- The total fee for registering the business in the Unites States of America – $750 .
- Legal expenses for obtaining licenses and permits as well as the accounting services (software, P.O.S machines and other software) – $3,300.
- Marketing promotion expenses for the grand opening of Harry & Barry® Computer Sales & Services Center, LLC in the amount of $3,500 and as well as flyer printing (2,000 flyers at $0.04 per copy) for the total amount of $3,580.
- The cost for hiring business consultant – $2,500.
- Insurance (general liability, workers’ compensation and property casualty) coverage at a total premium – $2,400.
- The cost for payment of rent for 12 months at $1.76 per square feet in the total amount of $105,600.
- The cost for shop remodeling (construction of racks and shelves) – $20,000.
- Other start-up expenses including stationery ( $500 ) and phone and utility deposits ( $2,500 ).
- Operational cost for the first 3 months (salaries of employees, payments of bills et al) – $60,000.
- The cost for start-up inventory (stocking with a wide range of computers such as desktops, notebook computers and software, as well as accessories like printers, scanners and keyboards. et al from different manufacturing brands) – $200,000
- The cost for counter area equipment – $9,500.
- The cost for store equipment (cash register, security, ventilation, signage) – $13,750
- The cost of purchase and installation of CCTVs: $10,000 .
- The cost for the purchase of office furniture and gadgets (Computers, Printers, Telephone, TVs, Sound System, tables and chairs et al): $4,000.
- The cost of launching a website: $600 .
- The cost for our opening party: $7,000 .
- Miscellaneous: $10,000.
We would need an estimate of three hundred and fifty thousand dollars ( $350,000 ) to successfully set up our computer sales and services store in Sioux Falls – South Dakota.
Generating Startup Capital for Harry & Barry® Computer Sales & Services Center, LLC
Harry & Barry® Computer Sales & Services Center, LLC is a business that will be owned and managed by Engr. Harry Jordan and his friend and business partner Barry Martins. They are the financiers of the business which is why they decided to restrict the sourcing of the startup capital for the business to just three major sources.
These are the areas we intend generating our startup capital;
- Generate part of the startup capital from personal savings and sale of his stocks.
- Generate part of the startup capital from friends and other extended family members.
- Generate a larger chunk of the startup capital from the bank.
N.B: We have been able to generate about $150,000 ( Personal savings $120,000 and soft loan from family members $30,000 ) and we are at the final stages of obtaining a loan facility of $200,000 from our bank. All papers and documents have been duly signed and submitted, the loan has been approved and any moment from now our account will be credited.
14. Sustainability and Expansion Strategy
The future of a business lies in the number of loyal customers that they have, the capacity and competence of their employees, their investment strategy and business structure. If all of these factors are missing from a business, then it won’t be too long before the business close shop.
One of our major goals of starting Harry & Barry® Computer Sales & Services Center, LLC is to build a business that will survive off its own cash flow without injecting finance from external sources once the business is officially running.
We know that one of the ways of gaining approval and winning customers over is to sell or computers and accessories and offer our computer repair and maintenance services a little bit cheaper than what is obtainable in the market and we are well prepared to survive on lower profit margin for a while.
Harry & Barry® Computer Sales & Services Center, LLC will make sure that the right foundation, structures and processes are put in place to ensure that our staff welfare are well taken of. Our company’s corporate culture is designed to drive our business to greater heights and training and retraining of our workforce is at the top burner.
As a matter of fact, profit-sharing arrangement will be made available to all our management staff and it will be based on their performance for a period of three years or more. We know that if that is put in place, we will be able to successfully hire and retain the best hands we can get in the industry; they will be more committed to help us build the business of our dreams.
Check List/Milestone
- Business Name Availability Check: Completed
- Business Incorporation: Completed
- Opening of Corporate Bank Accounts: Completed
- Opening Online Payment Platforms: Completed
- Application and Obtaining Tax Payer’s ID: In Progress
- Securing a standard office facility for our studio: Completed
- Application for business license and permit: Completed
- Purchase of Insurance for the Business: Completed
- Conducting Feasibility Studies: Completed
- Generating part of the startup capital from the founders: Completed
- Writing of Business Plan: Completed
- Drafting of Employee’s Handbook: Completed
- Drafting of Contract Documents: In Progress
- Design of Logo for the business: Completed
- Secure trademark for our products: In Progress
- Printing of Promotional Materials: Completed
- Recruitment of employees: In Progress
- Purchase of the needed furniture, office equipment, software applications, electronic appliances and facility facelift: In progress
- Creating official website for the business: In Progress
- Creating Awareness for the business: In Progress
- Health and Safety and Fire Safety Arrangement: In Progress
- Opening party planning: In Progress
- Compilation of the list of products that will be available in our store: Completed
- Establishing business relationship with vendors – manufacturers and suppliers of computers, computer parts and accessories: In Progress
More on Technology


How to Start a Computer Repair Business

Starting a computer repair business can be very profitable. With proper planning, execution and hard work, you can enjoy great success. Below you will learn the keys to launching a successful computer repair business.
Importantly, a critical step in starting a computer repair business is to complete your business plan. To help you out, you should download Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template here .
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here
14 Steps To Start a Computer Repair Business :
- Choose the Name for Your Computer Repair Business
- Develop Your Computer Repair Business Plan
- Choose the Legal Structure for Your Computer Repair Business
- Secure Startup Funding for Your Computer Repair Business (If Needed)
- Secure a Location for Your Business
- Register Your Computer Repair Business with the IRS
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Get the Required Business Licenses and Permits
- Get Business Insurance for Your Computer Repair Business
- Buy or Lease the Right Computer Repair Business Equipment
- Develop Your Computer Repair Business Marketing Materials
- Purchase and Setup the Software Needed to Run Your Computer Repair Business
- Open for Business
1. Choose the Name for Your Computer Repair Business
The first step to starting a computer repair business is to choose your business’ name.
This is a very important choice since your company name is your brand and will last for the lifetime of your business. Ideally you choose a name that is meaningful and memorable. Here are some tips for choosing a name for your own computer repair business:
- Make sure the name is available . Check your desired name against trademark databases and your state’s list of registered business names to see if it’s available. Also check to see if a suitable domain name is available.
- Keep it simple . The best names are usually ones that are easy to remember, pronounce and spell.
- Think about marketing . Come up with a name that reflects the desired brand and/or focus of your computer repair business.
2. Develop Your Computer Repair Business Plan
One of the most important steps in starting a computer repair business is to develop your computer repair business plan . The process of creating your plan ensures that you fully understand your market and your business model. The plan also provides you with a roadmap to follow and if needed, to present to funding sources to raise capital for your business.
Your business plan should include the following sections:
- Executive Summary – this section should summarize your entire business plan so readers can quickly understand the key details of your new computer repair business.
- Company Overview – this section tells the reader about the history of your computer repair business and what type of computer repair business you operate. For example, are you a PC, Mac, mobile phone, or a tablet repair shop?
- Industry Analysis – here you will document key information about the computer repair industry. Conduct market research and document how big the industry is and what trends are affecting it.
- Customer Analysis – in this section, you will document who your ideal or target customers are and their demographics. For example, how old are they? Where do they live? What do they find important when purchasing products or services like the ones you will offer?
- Competitive Analysis – here you will document the key direct and indirect competitors you will face and how you will build competitive advantage.
- Marketing Plan – your marketing plan should address the 4Ps: Product, Price, Promotions and Place.
- Product : Determine and document what products/services you will offer
- Prices : Document the prices of your products/services
- Place : Where will your business be located and how will that location help you increase sales?
- Promotions : What promotional methods will you use to attract customers to your computer repair business? For example, you might decide to use pay-per-click advertising, public relations, search engine optimization and/or social media marketing.
- Operations Plan – here you will determine the key processes you will need to run your day-to-day operations. You will also determine your staffing needs. Finally, in this section of your plan, you will create a projected growth timeline showing the milestones you hope to achieve in the coming years.
- Management Team – this section details the background of your company’s management team.
- Financial Plan – finally, the financial plan answers questions including the following:
- What startup costs will you incur?
- How will your computer repair business make money?
- What are your projected sales and expenses for the next five years?
- Do you need to raise funding to launch your business?
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
3. choose the legal structure for your computer repair business.
Next you need to choose a legal structure for your computer repair business and register it and your business name with the Secretary of State in each state where you operate your business.
Below are the five most common legal structures:
1) Sole proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is a business entity in which the owner of the computer repair business and the business are the same legal person. The owner of a sole proprietorship is responsible for all debts and obligations of the business. There are no formalities required to establish a sole proprietorship, and it is easy to set up and operate. The main advantage of a sole proprietorship is that it is simple and inexpensive to establish. The main disadvantage is that the owner is liable for all debts and obligations of the business.
2) Partnerships
A partnership is a legal structure that is popular among small businesses. It is an agreement between two or more people who want to start a computer repair business together. The partners share in the profits and losses of the business.
The advantages of a partnership are that it is easy to set up, and the partners share in the profits and losses of the business. The disadvantages of a partnership are that the partners are jointly liable for the debts of the business, and disagreements between partners can be difficult to resolve.
3) Limited Liability Company (LLC)
A limited liability company, or LLC, is a type of business entity that provides limited liability to its owners. This means that the owners of an LLC are not personally responsible for the debts and liabilities of the business. The advantages of an LLC for a computer repair business include flexibility in management, pass-through taxation (avoids double taxation as explained below), and limited personal liability. The disadvantages of an LLC include lack of availability in some states and self-employment taxes.
4) C Corporation
A C Corporation is a business entity that is separate from its owners. It has its own tax ID and can have shareholders. The main advantage of a C Corporation for a computer repair business is that it offers limited liability to its owners. This means that the owners are not personally responsible for the debts and liabilities of the business. The disadvantage is that C Corporations are subject to double taxation. This means that the corporation pays taxes on its profits, and the shareholders also pay taxes on their dividends.
5) S Corporation
An S Corporation is a type of corporation that provides its owners with limited liability protection and allows them to pass their business income through to their personal income tax returns, thus avoiding double taxation. There are several limitations on S Corporations including the number of shareholders they can have among others.
Once you register your computer repair business, your state will send you your official “Articles of Incorporation.” You will need this among other documentation when establishing your banking account (see below). We recommend that you consult an attorney in determining which legal structure is best suited for your company.
Incorporate Your Business at the Guaranteed Lowest Price
We are proud to have partnered with Business Rocket to help you incorporate your business at the lowest price, guaranteed.
Not only does BusinessRocket have a 4.9 out of 5 rating on TrustPilot (with over 1,000 reviews) because of their amazing quality…but they also guarantee the most affordable incorporation packages and the fastest processing time in the industry.
4. Secure Startup Funding for Your Computer Repair Business (If Needed)
In developing your computer repair business plan , you might have determined that you need to raise funding to launch your business.
If so, the main sources of funding for a computer repair business to consider are personal savings, family and friends, credit card financing, bank loans, crowdfunding and angel investors. Angel investors are individuals who provide capital to early-stage businesses. Angel investors typically will invest in a computer repair business that they believe has high potential for growth.
5. Secure a Location for Your Business
When starting a computer repair business, or a commercial computer repair business, the first step is to find a business location. The best place for a computer repair business is in an area with many companies and people. A busy area will bring in more customers. It would help if you also looked for a location that is easy to get to and has plenty of parking. You can rent a space or buy a property. If you purchase a property, make sure it is zoned for commercial use.
6. Register Your Computer Repair Business with the IRS
Next, you need to register your business with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) which will result in the IRS issuing you an Employer Identification Number (EIN).
Most banks will require you to have an EIN in order to open up an account. In addition, in order to hire employees, you will need an EIN since that is how the IRS tracks your payroll tax payments.
Note that if you are a sole proprietor without employees, you generally do not need to get an EIN. Rather, you would use your social security number (instead of your EIN) as your taxpayer identification number.
7. Open a Business Bank Account
It is important to establish a bank account in your computer repair business’ name. This process is fairly simple and involves the following steps:
- Identify and contact the bank you want to use
- Gather and present the required documents (generally include your company’s Articles of Incorporation, driver’s license or passport, and proof of address)
- Complete the bank’s application form and provide all relevant information
- Meet with a banker to discuss your business needs and establish a relationship with them
8. Get a Business Credit Card
You should get a business credit card for your computer repair business to help you separate personal and business expenses.
You can either apply for a business credit card through your bank or apply for one through a credit card company.
When you’re applying for a business credit card, you’ll need to provide some information about your business. This includes the name of your business, the address of your business, and the type of business you’re running. You’ll also need to provide some information about yourself, including your name, Social Security number, and date of birth.
Once you’ve been approved for a business credit card, you’ll be able to use it to make purchases for your business. You can also use it to build your credit history which could be very important in securing loans and getting credit lines for your business in the future.
9. Get the Required Business Licenses and Permits
Licensing and permitting requirements may vary by location. Some licenses and permits you may need to start a computer repair business, or a commercial computer repair business include a business license, a vendor’s license, a seller’s permit, and a contractor’s license. Reach out to your local licensing office to determine which licenses and permits are required for your business.
10. Get Business Insurance for Your Computer Repair Business
The type of insurance you need to operate a computer repair business may vary depending on the scope of your operation. For instance, if you offer mobile computer repair services, you will need auto insurance for your business’s vehicle.
Some business insurance policies you should consider for your computer repair business include:
- General liability insurance : This covers accidents and injuries that occur on your property. It also covers damages caused by your employees or products.
- Auto insurance : If a vehicle is used in your business, this type of insurance will cover if a vehicle is damaged or stolen.
- Workers’ compensation insurance : If you have employees, this type of policy works with your general liability policy to protect against workplace injuries and accidents. It also covers medical expenses and lost wages.
- Commercial property insurance : This covers damage to your property caused by fire, theft, or vandalism.
- Business interruption insurance : This covers lost income and expenses if your business is forced to close due to a covered event.
- Professional liability insurance : This protects your business against claims of professional negligence.
Find an insurance agent, tell them about your business and its needs, and they will recommend policies that fit those needs.
11. Buy or Lease the Right Computer Repair Business Equipment
To run a computer repair business, you will need some basic office equipment including a computer, phone, and internet connection.
12. Develop Your Computer Repair Business Marketing Materials
Marketing materials will be required to attract and retain customers to your computer repair business.
The key marketing materials you will need are as follows:
- Logo : Spend some time developing a good logo for your computer repair business. Your logo will be printed on company stationery, business cards, marketing materials and so forth. The right logo can increase customer trust and awareness of your brand.
- Website : Likewise, a professional computer repair business website provides potential customers with information about the products and/or services you offer, your company’s history, and contact information. Importantly, remember that the look and feel of your website will affect how customers perceive you..
- Social Media Accounts : establish social media accounts in your company’s name. Accounts on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn and/or other social media networks will help customers and others find and interact with your computer repair business.
13. Purchase and Setup the Software Needed to Run Your Computer Repair Business
To start a computer repair business, you’ll need some essential business software. First, you’ll need business software such as QuickBooks to manage your finances. You may also want to invest in an inventory management system to track the parts and tools you need for repairs. Finally, a customer relationship management (CRM) system will be helpful for managing your customer information, and a website will be useful for promoting your business.
14. Open for Business
You are now ready to open your computer repair business. If you followed the steps above, you should be in a great position to build a successful business. Below are answers to frequently asked questions that might further help you.
How to Finish Your Ultimate Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your computer repair business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
How to Start a Computer Repair Business FAQs
Is it hard to start a computer repair business.
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question, as the difficulty of starting a computer repair business will vary depending on the specific niche, the amount of competition in your area, and your level of experience. However, if you have the skills and knowledge required to start a successful computer repair business and you can market your computer repair service effectively, you are off to a good start. Additionally, it is helpful to have a solid business plan before starting any business to ensure that all of your bases are covered and that you have a clear road map for success.
How can I start a computer repair business with no experience?
There are a few ways to start a computer repair business with no experience. You can start by doing research on the internet, attending computer repair classes, or reading books about computer repair. Additionally, you can network with other computer repair shops and learn from their experiences. Finally, you can offer free services to friends and family to get some experience before starting your own business.
What type of computer repair business is most profitable?
The profitability of computer repair businesses can vary depending on many factors. However, some of the most profitable computer repair businesses are those that offer services in high demand, such as data recovery or virus removal. Furthermore, businesses that offer a variety of services, as well as those that have a strong online presence, are likely to be more profitable than those that do not.
How much does it cost to start a computer repair business?
It costs about $1,000 to start a computer repair business. This includes setting up a small workshop, purchasing necessary tools and equipment, and advertising your new business. If you lease or purchase a space, the startup costs will be higher.
What are the ongoing expenses for a computer repair business?
There are a few ongoing expenses for a computer repair business. One is the cost of advertising and marketing. This cost may include flyers, online ads, and mailing lists. Another expense is the cost of parts and tools. A computer repair business may need to invest in new tools and parts as technology changes. Finally, there is the cost of insurance. This is important to protect the business and its employees in case of accidents or damage to equipment.
How does a computer repair business make money?
One way a computer repair business makes money is by charging a fee for each service provided. Many computer repair businesses also offer hardware and software sales, which can provide additional revenue. Finally, a computer repair business can make money by providing consulting services to businesses or individuals.
Is owning a computer repair business profitable?
There are several reasons owning a computer repair business can be profitable. One reason is that the demand for computer repair services is high. Many people rely on their computers every day to conduct business and stay connected with friends and family. Additionally, many companies outsource their computer repair needs, giving computer repair businesses great opportunities to generate revenue. Finally, computer repair is a relatively low-cost business to start, making it an attractive option for entrepreneurs.
Why do computer repair businesses fail?
There are many reasons computer repair businesses can fail. One of the most common reasons is a lack of understanding of the market. Companies need to understand what their target customers are looking for to succeed. Another reason is a lack of very strong technical background . A business needs to understand the products they're repairing and the technology behind them to be successful. Finally, a lack of customer service can be a death knell for a computer repair business. If customers don't feel like they're getting the help they need, they'll take their business elsewhere.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
US proposes rules to stop Americans from investing in Chinese technology with military uses
FILE - The Treasury Building is viewed in Washington, May 4, 2021. The Treasury Department has fleshed out its proposed rule that would restrict and monitor U.S. investments in China for artificial intelligence, computer chips and quantum computing. The proposed rule, released Friday, June 21, 2024, stems from President Joe Biden’s August 2023 executive order regarding the access that “countries of concern” have to American dollars funding advanced technologies that the U.S. government says would enhance their military, intelligence, surveillance, and cyber capabilities. (AP Photo/Patrick Semansky, File)
- Copy Link copied
WASHINGTON (AP) — The Treasury Department on Friday fleshed out a proposed rule that would restrict and monitor U.S. investments in China for artificial intelligence, computer chips and quantum computing.
The proposed rule stems from President Joe Biden’s August 2023 executive order regarding the access that “countries of concern” have to American dollars that fund advanced technologies, which the U.S. government says would enhance their military, intelligence, surveillance and cyber capabilities. The order identified China, Hong Kong and Macau as countries of concern.
The Biden administration has sought to stymie the development of technologies by China, the world’s second-largest economy, that could give it a military edge or enable it to dominate emerging sectors such as electric vehicles.
In addition to the proposed rule, Democrat Biden has also placed a stiff tariff on Chinese EVs , an issue with political implications as the president and Republican Donald Trump are both trying to show voters who can best stand up to China, a geopolitical rival and major trading partner.
The proposed rule outlines the required information that U.S. citizens and permanent residents must provide when engaging in transactions in this area, as well as what would be considered a violation of the restrictions.
It specifically would prohibit American investors from funding AI systems in China that could be used for weapons targeting, combat and location tracking, among other military applications, according to a senior Treasury official who previewed the rule for reporters on the condition of anonymity.
J. Philip Ludvigson, a partner at King & Spalding and a former Treasury official for Investment Security, said “companies and investors are now getting a much better look at what will be expected of them” under the new outbound investment program. “These added details are particularly important because the private sector will be shouldering the many due diligence and compliance burdens associated with making new investments,” he said.
Craig Allen, president of the U.S.-China Business Council, a nonprofit organization of American firms that do business in China, said his organization “supports the Biden administration’s efforts to protect U.S. national security while also ensuring robust commercial exchange with China for the benefit of American companies, workers and our economy.”
Treasury is seeking comment on the proposal through Aug. 4, 2024, and after that is expected to issue a final rule.
Biden administration officials, including Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen, have insisted that they have no interest in “decoupling” from China — however, tensions between the two nations have increased in recent years.
After the U.S. military in February 2023 shot down a suspected Chinese spy balloon off the Carolina coast after it traversed sensitive military sites across North America, China threatened repercussions.
Since then, incidents between the two nations based on national security concerns have regularly occurred.
For instance, Biden in May issued an order blocking a Chinese-backed cryptocurrency mining firm from owning land near a Wyoming nuclear missile base, calling its proximity to the base a “national security risk.”

Computer Repair Business Plan Template & Guidebook
How to write a computer repair business plan in 7 steps:, 1. describe the purpose of your computer repair business., 2. products & services offered by your computer repair business., 3. build a creative marketing stratgey., target market, customer base , product or service description, competitive analysis, marketing channels, form an llc in your state, 4. write your operational plan., what equipment, supplies, or permits are needed to run a computer repair business, 5. management & organization of your computer repair business., 6. computer repair business startup expenses & captial needed., 7. financial plan & projections, frequently asked questions about computer repair business plans:, why do you need a business plan for a computer repair business, who should you ask for help with your computer repair business plan, can you write a computer repair business plan yourself, related business plans, home inventory business plan template & guidebook, home inspection business plan template & guidebook, home decor business plan template & guidebook, health and wellness business plan template & guidebook, hauling business plan template & guidebook, hardware business plan template & guidebook, handyman business plan template & guidebook, hair extension business plan template & guidebook, handbag business plan template & guidebook.
I'm Nick, co-founder of newfoundr.com, dedicated to helping aspiring entrepreneurs succeed. As a small business owner with over five years of experience, I have garnered valuable knowledge and insights across a diverse range of industries. My passion for entrepreneurship drives me to share my expertise with aspiring entrepreneurs, empowering them to turn their business dreams into reality.
Edwardsville Police plan stepped-up traffic enforcement for July Fourth celebrations
Drive sober or get pulled over — drive high get a dui.

From June 21 through the early-morning hours of July 8, officers will be working tirelessly to keep impaired drivers off the road and ticketing unbuckled motorists.
“It’s a straightforward message: If you’re behind the wheel, stay sober. Don’t drink, use marijuana, or consume any other impairing substances before or while driving,” said Lt. Brandn Whittaker. “Our officers will be on duty around the clock, dedicated to enforcing traffic laws and, most importantly, saving lives.”
Driving under the influence not only poses a grave risk to oneself but also endangers passengers and fellow citizens. The financial and human costs of a DUI are immeasurable. The decision to avoid driving impaired is simple and could spare lives.
The Edwardsville Police Department is collaborating with the Illinois State Police and over 200 other local police and sheriffs’ departments in this unified effort to enhance statewide enforcement during this period.

- Designate a sober driver before heading
- Prevent friends and family members from driving under the
- If you find yourself impaired, use safe alternatives such as taxis, public transit and ride- sharing apps, or contact a sober friend or family member for a ride.
- Report suspected drunk drivers promptly to law enforcement by pulling over and dialing
- Ensure that all passengers in your vehicle buckle It’s not only the law, but also a crucial defense against impaired drivers.
The traffic safety enforcement effort, including the “Drive Sober or Get Pulled Over,” “Drive High Get a DUI,” and “Click It or Ticket” programs, is made possible through federal highway safety funds administered by the Illinois Department of Transportation. These efforts are complemented by IDOT’s “It’s Not a Game” media campaign, which emphasizes the serious consequences of impaired driving and other unsafe driving behaviors.
Leave a Comment
Related posts.

SIUE Veterans Upward Bound collaborates with Florissant, The Kaufman Fund, other VSOs for Resource and Job Fair

The Three Rivers Project of Sierra Club Illinois’ Urban Farm Tour is June 30

Hospital Sisters Health System introduces upfront tuition coverage program for full-, part-time colleagues

SLCL introduces eMedia service at airport, Metro Transit, Schnucks, St. Louis county offices

Duckworth holds recent conversation with United Congregations of the Metro East

- Open source software

Haris - stock.adobe.com
Executive interview: Open models pros and cons
We speak to meta’s vice-president of ai research about recent publicly released research and models, and the role of closed ai models.

- Cliff Saran, Managing Editor
Meta’s research arm has opened up a number of its internal artificial intelligence (AI) projects to the wider research community in a bid to help it improve its AI models.
Fundamental AI Research (Fair) is the open science research group at the social media company. It comprises between 500 to 600 people across Europe and North America, and is focused on solving core problems in AI.
Fair has recently released several new research artefacts it hopes will enable the research community to innovate, explore and discover new ways to apply AI at scale.
These include Chameleon, which provides a unified architecture for text and image input and output; multi-token prediction for training language models to predict multiple future words at once; and AudioSeal, an audio watermarking technique.
Looking at the role of Fair in the social media giant’s business, Joëlle Pineau, Meta’s vice-president of AI research, says, “We’re not necessarily the team that brings those innovations into product. We’re squarely focused on solving AI.”
Fair shares research publicly along with code bases, data sets, models, training recipes and safety guides. While the group is focused on fundamental innovation, the research is shared internally with Meta’s applied research team that she says takes the model and figures out how to go from a concept like the new Chameleon one and works with Meta’s product teams to make it into a product.
“Over the years, a number of our innovations have made it into products,” says Pineau. “If you’ve seen the Meta glasses – smart glasses – the AI model that it runs came out of our research. The first Llama model came out of our research lab. But as Llama 2 and 3 are product-focused , they are developed by Meta’s generative AI [GenAI] team, which is more of an applied research team.”
New open models
Meta Chameleon uses tokenisation for text and images. According to the company, this enables a more unified approach, and makes the model easier to design, maintain and scale. Application areas include generating creative captions for images or using a mix of text prompts and images to create an entirely new scene.
With Chameleon, Pineau says the model uses text and images to reason about specific properties. “We’ve trained Chameleon up to about 30 billion parameters, which is much smaller than, for example, models like Llama, GPT and so on,” she says. “But we have a proof of concept which works up to a particular size.
“Applied research teams have the ability either to scale it up more or make it work with different types of data, and under different constraints,” says Pineau.
The second piece of research that Meta has now made public is a new approach to tokenisation. Most modern large language models (LLMs) have a simple training objective: predicting the next word. While this approach is simple and scalable, Meta says that it is also inefficient. It requires several orders of magnitude more text than what children need to learn the same degree of language fluency.
Read more LLM articles
- Hype around GenAI will inevitably be followed by generative AI disillusionment. Experts ruminate on how to shorten the trough and prepare for the future.
- We speak to the head of the GenAI Innovation Center for Amazon Web Services about AI, tech innovation and IT challenge.
Pineau says multi-token prediction was directly inspired by the work on code generation. “There’s an opportunity to generate many tokens eventually in a structured way, not just in a linear way,” she says.
“Whereas classic LLMs just generate one word after the other, and product linearisation of the output tokens, for code, many people don’t write one token at a time. You write the code structure, then you write some of the sub-structures, and then you resolve the details in terms of the structures, and you go back and forth at different levels of abstraction as you’re building up the code.”
This, she adds, is much more complex than the linear approach used in LLMs.
Closed versus open debate
When asked about whether there is a place for closed AI models, Pineau believes an AI model should be made open when there are safeguards in place to ensure it doesn’t cause undue risk.
“In the case of our Chameleon model, we chose after going through a risk analysis not to release the image generation capabilities,” she says. “The model is able to generate images, but we felt the safety measures are not mature enough.”
Another model developed by Fair, which has been published but not released, is one for voice synthesis. “Within a few seconds of a voice recording from an individual, we can essentially generate speech that mimics someone’s voice to the point that it is misleading,” says Pineau.

In this case, she says authentication tools do not exist that can distinguish between the AI-generated voice and the genuine voice recording. However, Meta has been researching authentication, and she says AudioSeal’s watermarking technique was shared with a small cohort of academic researchers for third-party examination of the model. While the audio watermarking techniques are not quite mature enough to give Meta’s researchers the confidence they have sufficient safety to make its voice synthesis model publicly available, AudioSeal has been designed specifically for the localised detection of AI-generated speech.
So, should you give them a go? While the new AI models Meta has released are open, Pineau says there’s a reasonable learning curve to figure out how to get them to work – but people who are using models routinely, such as those available via Hugging Face, should be in a position to get up and running relatively easily.
“We have people who take a model such as Llama and fine-tune it, and within 48 hours there’s a fine-tuned version available that shows up on some of the [AI model] leaderboards,” she says. “It really depends on your level of proficiency.”
Getting started doesn’t require high-end hardware. She says that in some cases, models are made available in different sizes: the smaller models can run on a single graphics processing unit and are easier to get started with. “The bigger models require more knowledge of distributed systems to get the required level of performance,” says Pineau.
Read more on Open source software

An industry-wide agreement is needed to identify AI-generated content

SAP widens Business AI strategy with Meta open source models

Meta chief lays out long-term AI plan
Meta outage disrupts social media globally

The Biden administration's regulatory efforts have defined the U.S. approach to climate over the last four years. That could ...
AI adoption is reshaping technology skill sets in enterprises, while lingering economic uncertainty dampens some forms of ...
While there is disagreement in Congress over how to diversify the critical materials supply chain, there is bipartisan agreement ...
At re:Inforce 2024, AWS shared details of its secure-by-design measures to protect customer data.
The Biden administration announced a ban on Kaspersky Lab products inside the United States due to the antivirus vendor's ties ...
The Centre for Cybersecurity Belgium observed exploitation against CVE-2024-28995, a high-severity vulnerability in SolarWind's ...
Analysts Jim Frey and Jon Brown from Enterprise Strategy Group talk about their takeaways from the Cisco Live 2024 conference in ...
As Mass General Brigham updated its network and invested in other upgrades, the hospital ecosystem also developed a measured ...
Cisco Live 2024 will focus largely on AI and its potential to transform enterprise networking and IT. Use this guide to follow ...
A data center's UPS might not be overloaded. Check loads on the circuits and balance all three phases as closely as possible to ...
As climate change becomes a more pressing issue, these sustainability best practices can help your data center go greener, which ...
StorMagic looks to court customers with smaller data centers for SMBs and the edge with SvHCI, a new VMware alternative with a ...
The data management and analytics vendor's embeddable database now includes streaming capabilities via support for Kafka and ...
The vendor's latest update adds new customer insight capabilities, including an AI assistant, and industry-specific tools all ...
The data quality specialist's capabilities will enable customers to monitor unstructured text to ensure the health of data used ...
Don't bother with copy and paste.
Get this complete sample business plan as a free text document.
Computer Engineering Business Plan
Start your own computer engineering business plan
Todd, West, and Associates
Executive summary executive summary is a brief introduction to your business plan. it describes your business, the problem that it solves, your target market, and financial highlights.">.
Todd, West, and Associates specializes in modifications to inventory management systems of all types. The company’s connectivity and network engineering expertise assures a complete wireless solution to warehouse management issues. Todd, West, and Associates has over fifteen years of experience within the ADC (Automated Data Collection) marketplace.
Prior to starting this new company, the staff of Todd, West, and Associates worked within the industry’s major companies performing special wireless modification for customers. Their unique perspective has already led to two of the industry leaders, Symbol and CDS, outsourcing special modification orders to Todd, West, and Associates.

1.1 Objectives
The objectives of Todd, West, and Associates are as follows:
- Establish the company as a leader in warehouse wireless connectivity.
- Increase client base by 20% each year.
- Develop packaged solutions for warehouse management systems.
1.2 Mission
The mission of Todd, West, and Associates is to work directly with customers to improve their warehouse management systems. The development, modification, and/or improvement of warehouse data infrastructure will assure that the business will function efficiently and successfully.
Company Summary company overview ) is an overview of the most important points about your company—your history, management team, location, mission statement and legal structure.">
Todd, West, and Associates is a new start-up engineering contracting firm. Co-owners, Mary Todd and John West have over fifteen years of experience in connectivity and network engineering. The country’s economic growth over the last several years has resulted in increased opportunity for the installation of high-end warehouse management systems. Todd, West, and Associates is positioned to capitalize on the growing need of companies to better manage their inventory.
From 1996 to 2001, Mary Todd was senior engineer for the Special Modification Services unit of CDS, one of the country’s leading producers of Automatic Data Collection (ADC) products. Her primary responsibility was to travel to the customer’s warehouse site and perform custom wireless network modifications using CDS products.
John West has been a senior engineer for Symbol’s system installation services unit for the past five years. John’s responsibilities included custom wireless installation of Symbol networking equipment and ADC products at the customer’s warehouse site.
Todd, West, and Associates has signed outsourcing agreements with both CDS and Symbol to provide custom network installation services to their customers. Currently, these agreements represent $100,000 in scheduled assignments.
2.1 Company Ownership
Mary Todd and John West are co-owners of Todd, West, and Associates.
2.2 Start-up Summary
Mary Todd and John West will each equally invest in Todd, West, and Associates. In addition, they will secure a long-term loan. The following table and chart show projected initial start-up costs for Todd, West, and Associates.

| Start-up Funding | |
| Start-up Expenses to Fund | $9,000 |
| Start-up Assets to Fund | $61,000 |
| Total Funding Required | $70,000 |
| Assets | |
| Non-cash Assets from Start-up | $0 |
| Cash Requirements from Start-up | $61,000 |
| Additional Cash Raised | $0 |
| Cash Balance on Starting Date | $61,000 |
| Total Assets | $61,000 |
| Liabilities and Capital | |
| Liabilities | |
| Current Borrowing | $0 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $50,000 |
| Accounts Payable (Outstanding Bills) | $0 |
| Other Current Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 |
| Total Liabilities | $50,000 |
| Capital | |
| Planned Investment | |
| Mary Todd | $10,000 |
| John West | $10,000 |
| Additional Investment Requirement | $0 |
| Total Planned Investment | $20,000 |
| Loss at Start-up (Start-up Expenses) | ($9,000) |
| Total Capital | $11,000 |
| Total Capital and Liabilities | $61,000 |
| Total Funding | $70,000 |
| Start-up | |
| Requirements | |
| Start-up Expenses | |
| Legal | $1,000 |
| Stationery etc. | $1,000 |
| Rent | $1,000 |
| Expensed Equipment | $6,000 |
| Total Start-up Expenses | $9,000 |
| Start-up Assets | |
| Cash Required | $61,000 |
| Other Current Assets | $0 |
| Long-term Assets | $0 |
| Total Assets | $61,000 |
| Total Requirements | $70,000 |
Todd, West, and Associates’ services include the following:
- Automated data collection installation
- Database engineering/conversions (MS Access/SQL/Oracle)
- Data imports/exports
- Database links to accounting system (MAS-90/Solomon/Peachtree)
- Wireless networking
- Portable data terminal programming
- LAN/WAN infrastructure
- System consulting
The prices for services are as follows:
- On-site System Requirements Study : $1,000 a day plus travel and expenses.
- On-site Database/Network Engineering/Training : $1,000 a day plus travel and expenses.
- Phone Training/Assistance : $120 an hour.
- Database Modifications : Quoted based on job specifics.
- General Data Imports/Exports : $120 an hour.
Market Segmentation
Automated Data Collection (ADC) products and services is a $3 billion industry. The products are used in numerous companies with significant inventory and warehouse space. Approximately, 30% of the market is in wireless products and services but the demand is growing. It is estimated that wireless ADC products will dominate the market by 2005. Two of the industry leaders, Symbol and CDS, exceeded $600 million in sales for FY 2000. Wireless products represented 28% of their total sales.
Typically, with the installation of wireless products, there are associated costs for networking and connectivity issues. Most companies in the industry offer these additional services to their customers or outsource the service to engineering firms with expertise in their product line.
Todd, West, and Associates has extensive experience with both Symbol and CDS products. The company’s focus is to first meet the demands of the Symbol and CDS referred customers. Todd, West, and Associates will establish relationships with these companies and will work to receive referral business from them over time. The company estimates that 80% of revenues will come from outsourced clientele and 20% from new business. Over the next three years, Todd, West, and Associates estimates that new business will constitute 40% of revenue.

| Market Analysis | |||||||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 | |||
| Potential Customers | Growth | CAGR | |||||
| Outsourced Customers | 10% | 2,000 | 2,200 | 2,420 | 2,662 | 2,928 | 10.00% |
| New Customers | 5% | 10,000 | 10,500 | 11,025 | 11,576 | 12,155 | 5.00% |
| Total | 5.88% | 12,000 | 12,700 | 13,445 | 14,238 | 15,083 | 5.88% |
Strategy and Implementation Summary
Todd, West, and Associates will focus on companies utilizing Symbol and CDS wireless ADC products to manage their inventories. The targeted customer will have ten or more warehouse staff members using ADC wireless systems.
Initially, the company will receive 80% of its clients through Symbol and CDS outsource referrals. The remaining 20% will come from direct marketing.
Over the past five years, both Mary and John have built an extensive network of contacts with companies utilizing wireless ADC products. Todd, West, and Associates will market its services directly to these companies.
After its first three months of operation, the company expects to begin to receive installation contracts from new customers.
5.1 Competitive Edge
Todd, West, and Associates will sustain its competitive advantages to steadily gain market share. The first advantage is based on extensive knowledge of Symbol and CDS wireless ADC products. The second advantage is an established network of contacts among numerous companies that utilize wireless ADC products.
Todd, West, and Associates’ competitive edge is the five years Mary and John have spent installing Symbol and CDS wireless ADC systems. Both have excellent reputations with customers for quality work and effective communication skills. These established relationships create a trust bond that is significant when it comes to generating new referrals.
5.2 Sales Strategy
Todd, West, and Associates estimates that about 80% of revenues will come from outsourced clientele and 20% from new business. Over the next three years, Todd, West, and Associates estimates that new business will grow to eventually constitute 40% of revenue.
5.2.1 Sales Forecast
The following is the sales forecast for the next three years.

| Sales Forecast | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Sales | |||
| Symbol and CDS Customers | $283,377 | $310,000 | $330,000 |
| New Customers | $57,200 | $78,000 | $100,000 |
| Total Sales | $340,577 | $388,000 | $430,000 |
| Direct Cost of Sales | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Symbol and CDS Customers | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Customers | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Direct Cost of Sales | $0 | $0 | $0 |
Management Summary management summary will include information about who's on your team and why they're the right people for the job, as well as your future hiring plans.">
Todd, West, and Associates will be managed jointly by Mary Todd and John West. Initially, the company will have only three additional employees.
6.1 Personnel Plan

- Installation consultants (wireless installations)
- Office manager
| Personnel Plan | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Mary Todd | $60,000 | $63,000 | $66,000 |
| John West | $60,000 | $63,000 | $66,000 |
| Installation Consultants | $96,000 | $100,000 | $104,000 |
| Office Manager | $36,000 | $38,000 | $40,000 |
| Total People | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Total Payroll | $252,000 | $264,000 | $276,000 |
Financial Plan investor-ready personnel plan .">
The following is the financial plan for Todd, West, and Associates.
7.1 Break-even Analysis
The monthly break-even point is shown in the table and chart below.

| Break-even Analysis | |
| Monthly Revenue Break-even | $25,450 |
| Assumptions: | |
| Average Percent Variable Cost | 0% |
| Estimated Monthly Fixed Cost | $25,450 |
7.2 Projected Profit and Loss
The following table and charts highlight the projected profit and loss for the next three years.

| Pro Forma Profit and Loss | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Sales | $340,577 | $388,000 | $430,000 |
| Direct Cost of Sales | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Production Expenses | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Cost of Sales | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Gross Margin | $340,577 | $388,000 | $430,000 |
| Gross Margin % | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Expenses | |||
| Payroll | $252,000 | $264,000 | $276,000 |
| Sales and Marketing and Other Expenses | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Depreciation | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Leased Equipment | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Utilities | $3,600 | $3,600 | $3,600 |
| Insurance | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Rent | $12,000 | $12,000 | $12,000 |
| Payroll Taxes | $37,800 | $39,600 | $41,400 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Operating Expenses | $305,400 | $319,200 | $333,000 |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | $35,177 | $68,800 | $97,000 |
| EBITDA | $35,177 | $68,800 | $97,000 |
| Interest Expense | $2,883 | $2,676 | $2,460 |
| Taxes Incurred | $9,688 | $19,837 | $28,362 |
| Net Profit | $22,606 | $46,287 | $66,178 |
| Net Profit/Sales | 6.64% | 11.93% | 15.39% |
7.3 Projected Cash Flow
The following table and chart highlight the projected cash flow for the next three years.

| Pro Forma Cash Flow | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Cash Received | |||
| Cash from Operations | |||
| Cash Sales | $85,144 | $97,000 | $107,500 |
| Cash from Receivables | $209,420 | $284,593 | $316,826 |
| Subtotal Cash from Operations | $294,565 | $381,593 | $424,326 |
| Additional Cash Received | |||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Received | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Other Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Sales of Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Sales of Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Investment Received | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Cash Received | $294,565 | $381,593 | $424,326 |
| Expenditures | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Expenditures from Operations | |||
| Cash Spending | $252,000 | $264,000 | $276,000 |
| Bill Payments | $60,773 | $76,524 | $86,991 |
| Subtotal Spent on Operations | $312,773 | $340,524 | $362,991 |
| Additional Cash Spent | |||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Paid Out | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Principal Repayment of Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Long-term Liabilities Principal Repayment | $3,600 | $3,600 | $3,600 |
| Purchase Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Purchase Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Dividends | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Cash Spent | $316,373 | $344,124 | $366,591 |
| Net Cash Flow | ($21,809) | $37,469 | $57,735 |
| Cash Balance | $39,191 | $76,661 | $134,395 |
7.4 Projected Balance Sheet
The following table highlights the projected balance sheet for the next three years.
| Pro Forma Balance Sheet | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Assets | |||
| Current Assets | |||
| Cash | $39,191 | $76,661 | $134,395 |
| Accounts Receivable | $46,013 | $52,419 | $58,094 |
| Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Current Assets | $85,204 | $129,080 | $192,489 |
| Long-term Assets | |||
| Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Assets | $85,204 | $129,080 | $192,489 |
| Liabilities and Capital | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Current Liabilities | |||
| Accounts Payable | $5,198 | $6,387 | $7,218 |
| Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Current Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Current Liabilities | $5,198 | $6,387 | $7,218 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $46,400 | $42,800 | $39,200 |
| Total Liabilities | $51,598 | $49,187 | $46,418 |
| Paid-in Capital | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 |
| Retained Earnings | ($9,000) | $13,606 | $59,893 |
| Earnings | $22,606 | $46,287 | $66,178 |
| Total Capital | $33,606 | $79,893 | $146,071 |
| Total Liabilities and Capital | $85,204 | $129,080 | $192,489 |
| Net Worth | $33,606 | $79,893 | $146,071 |
7.5 Business Ratios
Business ratios for the years of this plan are shown below. Industry profile ratios based on the NAISC code 541614, Process, Physical Distribution, and Logistics Consulting, are shown for comparison.
| Ratio Analysis | ||||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Industry Profile | |
| Sales Growth | 0.00% | 13.92% | 10.82% | 7.23% |
| Percent of Total Assets | ||||
| Accounts Receivable | 54.00% | 40.61% | 30.18% | 19.37% |
| Other Current Assets | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 50.13% |
| Total Current Assets | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 70.99% |
| Long-term Assets | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 29.01% |
| Total Assets | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Current Liabilities | 6.10% | 4.95% | 3.75% | 34.21% |
| Long-term Liabilities | 54.46% | 33.16% | 20.36% | 15.24% |
| Total Liabilities | 60.56% | 38.11% | 24.11% | 49.45% |
| Net Worth | 39.44% | 61.89% | 75.89% | 50.55% |
| Percent of Sales | ||||
| Sales | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Gross Margin | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 23.92% |
| Selling, General & Administrative Expenses | 93.80% | 88.49% | 85.02% | 11.77% |
| Advertising Expenses | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.57% |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | 10.33% | 17.73% | 22.56% | 0.85% |
| Main Ratios | ||||
| Current | 16.39 | 20.21 | 26.67 | 1.60 |
| Quick | 16.39 | 20.21 | 26.67 | 1.31 |
| Total Debt to Total Assets | 60.56% | 38.11% | 24.11% | 56.90% |
| Pre-tax Return on Net Worth | 96.10% | 82.77% | 64.72% | 2.82% |
| Pre-tax Return on Assets | 37.90% | 51.23% | 49.11% | 6.54% |
| Additional Ratios | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Net Profit Margin | 6.64% | 11.93% | 15.39% | n.a |
| Return on Equity | 67.27% | 57.94% | 45.31% | n.a |
| Activity Ratios | ||||
| Accounts Receivable Turnover | 5.55 | 5.55 | 5.55 | n.a |
| Collection Days | 57 | 62 | 63 | n.a |
| Accounts Payable Turnover | 12.69 | 12.17 | 12.17 | n.a |
| Payment Days | 27 | 27 | 28 | n.a |
| Total Asset Turnover | 4.00 | 3.01 | 2.23 | n.a |
| Debt Ratios | ||||
| Debt to Net Worth | 1.54 | 0.62 | 0.32 | n.a |
| Current Liab. to Liab. | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.16 | n.a |
| Liquidity Ratios | ||||
| Net Working Capital | $80,006 | $122,693 | $185,271 | n.a |
| Interest Coverage | 12.20 | 25.71 | 39.43 | n.a |
| Additional Ratios | ||||
| Assets to Sales | 0.25 | 0.33 | 0.45 | n.a |
| Current Debt/Total Assets | 6% | 5% | 4% | n.a |
| Acid Test | 7.54 | 12.00 | 18.62 | n.a |
| Sales/Net Worth | 10.13 | 4.86 | 2.94 | n.a |
| Dividend Payout | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | n.a |
| Sales Forecast | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Sales | |||||||||||||
| Symbol and CDS Customers | 0% | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,785 | $21,890 | $21,400 | $24,200 | $24,302 | $25,000 | $27,400 | $28,900 | $27,500 | $22,000 |
| New Customers | 0% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $6,000 | $7,500 | $8,000 | $9,700 | $6,000 | $7,000 | $7,000 | $6,000 |
| Total Sales | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,785 | $21,890 | $27,400 | $31,700 | $32,302 | $34,700 | $33,400 | $35,900 | $34,500 | $28,000 | |
| Direct Cost of Sales | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Symbol and CDS Customers | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Customers | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Subtotal Direct Cost of Sales | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Personnel Plan | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Mary Todd | 0% | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 |
| John West | 0% | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 |
| Installation Consultants | 0% | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 |
| Office Manager | 0% | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 |
| Total People | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Total Payroll | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | |
| General Assumptions | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Plan Month | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | |
| Current Interest Rate | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | |
| Long-term Interest Rate | 6.00% | 6.00% | 6.00% | 6.00% | 6.00% | 6.00% | 6.00% | 6.00% | 6.00% | 6.00% | 6.00% | 6.00% | |
| Tax Rate | 30.00% | 30.00% | 30.00% | 30.00% | 30.00% | 30.00% | 30.00% | 30.00% | 30.00% | 30.00% | 30.00% | 30.00% | |
| Other | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pro Forma Profit and Loss | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Sales | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,785 | $21,890 | $27,400 | $31,700 | $32,302 | $34,700 | $33,400 | $35,900 | $34,500 | $28,000 | |
| Direct Cost of Sales | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Other Production Expenses | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Cost of Sales | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Gross Margin | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,785 | $21,890 | $27,400 | $31,700 | $32,302 | $34,700 | $33,400 | $35,900 | $34,500 | $28,000 | |
| Gross Margin % | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | |
| Expenses | |||||||||||||
| Payroll | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | |
| Sales and Marketing and Other Expenses | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Depreciation | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Leased Equipment | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Utilities | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | |
| Insurance | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Rent | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | |
| Payroll Taxes | 15% | $3,150 | $3,150 | $3,150 | $3,150 | $3,150 | $3,150 | $3,150 | $3,150 | $3,150 | $3,150 | $3,150 | $3,150 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Operating Expenses | $25,450 | $25,450 | $25,450 | $25,450 | $25,450 | $25,450 | $25,450 | $25,450 | $25,450 | $25,450 | $25,450 | $25,450 | |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | ($5,450) | ($5,450) | ($4,665) | ($3,560) | $1,950 | $6,250 | $6,852 | $9,250 | $7,950 | $10,450 | $9,050 | $2,550 | |
| EBITDA | ($5,450) | ($5,450) | ($4,665) | ($3,560) | $1,950 | $6,250 | $6,852 | $9,250 | $7,950 | $10,450 | $9,050 | $2,550 | |
| Interest Expense | $249 | $247 | $246 | $244 | $243 | $241 | $240 | $238 | $237 | $235 | $234 | $232 | |
| Taxes Incurred | ($1,710) | ($1,709) | ($1,473) | ($1,141) | $512 | $1,803 | $1,984 | $2,704 | $2,314 | $3,065 | $2,645 | $695 | |
| Net Profit | ($3,989) | ($3,988) | ($3,437) | ($2,663) | $1,195 | $4,206 | $4,629 | $6,308 | $5,399 | $7,151 | $6,172 | $1,623 | |
| Net Profit/Sales | -19.94% | -19.94% | -16.54% | -12.16% | 4.36% | 13.27% | 14.33% | 18.18% | 16.17% | 19.92% | 17.89% | 5.79% | |
| Pro Forma Cash Flow | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Cash Received | |||||||||||||
| Cash from Operations | |||||||||||||
| Cash Sales | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,196 | $5,473 | $6,850 | $7,925 | $8,076 | $8,675 | $8,350 | $8,975 | $8,625 | $7,000 | |
| Cash from Receivables | $0 | $500 | $15,000 | $15,020 | $15,616 | $16,555 | $20,658 | $23,790 | $24,286 | $25,993 | $25,113 | $26,890 | |
| Subtotal Cash from Operations | $5,000 | $5,500 | $20,196 | $20,492 | $22,466 | $24,480 | $28,733 | $32,465 | $32,636 | $34,968 | $33,738 | $33,890 | |
| Additional Cash Received | |||||||||||||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Received | 0.00% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Other Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Sales of Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Sales of Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Investment Received | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Subtotal Cash Received | $5,000 | $5,500 | $20,196 | $20,492 | $22,466 | $24,480 | $28,733 | $32,465 | $32,636 | $34,968 | $33,738 | $33,890 | |
| Expenditures | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Expenditures from Operations | |||||||||||||
| Cash Spending | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | $21,000 | |
| Bill Payments | $100 | $2,989 | $2,996 | $3,233 | $3,608 | $5,248 | $6,500 | $6,697 | $7,379 | $7,026 | $7,735 | $7,263 | |
| Subtotal Spent on Operations | $21,100 | $23,989 | $23,996 | $24,233 | $24,608 | $26,248 | $27,500 | $27,697 | $28,379 | $28,026 | $28,735 | $28,263 | |
| Additional Cash Spent | |||||||||||||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Paid Out | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Principal Repayment of Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Other Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Long-term Liabilities Principal Repayment | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | |
| Purchase Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Purchase Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Dividends | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Subtotal Cash Spent | $21,400 | $24,289 | $24,296 | $24,533 | $24,908 | $26,548 | $27,800 | $27,997 | $28,679 | $28,326 | $29,035 | $28,563 | |
| Net Cash Flow | ($16,400) | ($18,789) | ($4,099) | ($4,041) | ($2,441) | ($2,067) | $933 | $4,468 | $3,958 | $6,642 | $4,702 | $5,327 | |
| Cash Balance | $44,600 | $25,811 | $21,712 | $17,671 | $15,229 | $13,162 | $14,095 | $18,563 | $22,521 | $29,163 | $33,865 | $39,191 | |
| Pro Forma Balance Sheet | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Assets | Starting Balances | ||||||||||||
| Current Assets | |||||||||||||
| Cash | $61,000 | $44,600 | $25,811 | $21,712 | $17,671 | $15,229 | $13,162 | $14,095 | $18,563 | $22,521 | $29,163 | $33,865 | $39,191 |
| Accounts Receivable | $0 | $15,000 | $29,500 | $30,089 | $31,487 | $36,420 | $43,640 | $47,209 | $49,444 | $50,208 | $51,140 | $51,903 | $46,013 |
| Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Current Assets | $61,000 | $59,600 | $55,311 | $51,801 | $49,157 | $51,650 | $56,802 | $61,304 | $68,007 | $72,728 | $80,303 | $85,767 | $85,204 |
| Long-term Assets | |||||||||||||
| Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Assets | $61,000 | $59,600 | $55,311 | $51,801 | $49,157 | $51,650 | $56,802 | $61,304 | $68,007 | $72,728 | $80,303 | $85,767 | $85,204 |
| Liabilities and Capital | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Current Liabilities | |||||||||||||
| Accounts Payable | $0 | $2,889 | $2,888 | $3,115 | $3,434 | $5,031 | $6,277 | $6,451 | $7,145 | $6,767 | $7,491 | $7,084 | $5,198 |
| Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Current Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Current Liabilities | $0 | $2,889 | $2,888 | $3,115 | $3,434 | $5,031 | $6,277 | $6,451 | $7,145 | $6,767 | $7,491 | $7,084 | $5,198 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $50,000 | $49,700 | $49,400 | $49,100 | $48,800 | $48,500 | $48,200 | $47,900 | $47,600 | $47,300 | $47,000 | $46,700 | $46,400 |
| Total Liabilities | $50,000 | $52,589 | $52,288 | $52,215 | $52,234 | $53,531 | $54,477 | $54,351 | $54,745 | $54,067 | $54,491 | $53,784 | $51,598 |
| Paid-in Capital | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 |
| Retained Earnings | ($9,000) | ($9,000) | ($9,000) | ($9,000) | ($9,000) | ($9,000) | ($9,000) | ($9,000) | ($9,000) | ($9,000) | ($9,000) | ($9,000) | ($9,000) |
| Earnings | $0 | ($3,989) | ($7,977) | ($11,414) | ($14,077) | ($12,882) | ($8,675) | ($4,047) | $2,262 | $7,661 | $14,812 | $20,983 | $22,606 |
| Total Capital | $11,000 | $7,011 | $3,023 | ($414) | ($3,077) | ($1,882) | $2,325 | $6,953 | $13,262 | $18,661 | $25,812 | $31,983 | $33,606 |
| Total Liabilities and Capital | $61,000 | $59,600 | $55,311 | $51,801 | $49,157 | $51,650 | $56,802 | $61,304 | $68,007 | $72,728 | $80,303 | $85,767 | $85,204 |
| Net Worth | $11,000 | $7,011 | $3,023 | ($414) | ($3,077) | ($1,882) | $2,325 | $6,953 | $13,262 | $18,661 | $25,812 | $31,983 | $33,606 |

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
As a small business, you're not likely to be able to match the prices of your larger competitors — the personalized service you offer needs to offset this disadvantage. 3. Build your brand identity. A new computer business, like any other small business, needs to make a quick and lasting impression in order to survive.
1. Describe the Purpose of Your Computer Business. The first step to writing your business plan is to describe the purpose of your computer business. This includes describing why you are starting this type of business, and what problems it will solve for customers. This is a quick way to get your mind thinking about the customers' problems.
Banks and other funders will want to see a traditional business plan before they loan your company money. A traditional computer repair business plan includes: an executive summary. a company description. a competitive market analysis. business structure and service offerings information. marketing and sales plans.
Creating a business plan is a critical step in laying the foundation for a successful computer business. It serves as a roadmap, detailing your business goals, strategies, and how you plan to achieve them. Here are key elements to include in your draft: Executive Summary: Summarize your business concept, vision, and key objectives.
Introduction. Step 1: Build up your savings. Step 2: Create a business plan for your computer repair business. Step 3: Finance your computer repair business. Step 4: Choose a location. Step 5: Set your pricing for your computer repair services. Step 6: Get your computer repair and IT certifications.
For example, give a brief overview of the computer repair industry. Discuss the type of computer repair business you are operating. Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target customers. Provide a snapshot of your marketing plan. Identify the key members of your team.
Amount required to purchase the needed software applications - $ 3,500. Launching an official Website will cost - $500. Amount need to pay bills and staff members for at least 2 to 3 months - $70,000. Additional Expenditure such as Business cards, Signage, Adverts and Promotions will cost - $5,000.
P36,549. P71,702. P106,946. P142,281. Download This Plan. Explore a real-world computer support business plan example and download a free template with this information to start writing your own business plan.
Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows. Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your IT business, including answering calls, meeting with new clients, billing and collecting payments from clients, etc. Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve.
Marketing Plan. Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P's: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a technology business plan, your marketing plan should include the following: Product: In the product section, you should reiterate the type of technology company that you documented in your Company Analysis.
Writing a computer repair business plan is a crucial step toward the success of your business. Here are the key steps to consider when writing a business plan: 1. Executive Summary. An executive summary is the first section planned to offer an overview of the entire business plan. However, it is written after the entire business plan is ready ...
1. Don't worry about finding an exact match. We have over 550 sample business plan templates. So, make sure the plan is a close match, but don't get hung up on the details. Your business is unique and will differ from any example or template you come across. So, use this example as a starting point and customize it to your needs.
If YES, here is a complete sample computer sales & services business plan template & feasibility report you can use for FREE. According to a recent report, computer sales and related services are expected to exceed $47 billion this year in the U.S. alone, with computer servicing leading the way. This goes to show that any entrepreneur who ...
A business plan has 2 main parts: a financial forecast outlining the funding requirements of your computer store and the expected growth, profits and cash flows for the next 3 to 5 years; and a written part which gives the reader the information needed to decide if they believe the forecast is achievable.
Lastly, address any funding needs in the "ask" section of your executive summary. 2. The presentation of the company. In your computer repair shop business plan, the second section should focus on the structure and ownership, location, and management team of your company.
2.3 Start-up Summary. The start-up expense for the Gaming Futures is focused primarily on equipment and office space. William, Diane, Marcus, Jillian, and Jeremy will each invest $35,000. In addition, Gaming Futures will secure a $100,000 long term loan. Start-up Funding.
The computer shop will sell desktops, laptops, servers, printers, accessories, and offer IT consulting services. It aims to capitalize on competitor weaknesses and gain market share through advertising, promotions, and sales tactics like in-store, phone, and online sales. The business plan provides details on suppliers, staffing, budgets, and 3 ...
The 10 online business plan software solutions examined in this roundup —Atlas Business Solutions Ultimate Business Planner 5.0, Enloop, EquityNet, NetEkspert iPlanner.NET, OnePlace, Palo Alto ...
4. Secure Startup Funding for Your Computer Repair Business (If Needed) In developing your computer repair business plan, you might have determined that you need to raise funding to launch your business.. If so, the main sources of funding for a computer repair business to consider are personal savings, family and friends, credit card financing, bank loans, crowdfunding and angel investors.
Business plans might seem like an old-school stiff-collared practice, but they deserve a place in the startup realm, too. It's probably not going to be the frame-worthy document you hang in the office—yet, it may one day be deserving of the privilege. Whether you're looking to win the heart of an angel investor or convince
The Boston Business Journal features local business news about Boston. We also provide tools to help businesses grow, network and hire.
We expect the local consumer market segment to provide 50% of the business income. The remaining 40% of our business income will be generated by the small business market segment. 77% of the businesses in Hawaii are small businesses with less than 10 employees. These small businesses are large enough to need the high-quality computer technology ...
With Microsoft 365 Business Basic, Microsoft 365 Business Standard, and Microsoft 365 Business Premium plans, you can host online meetings and video calls for up to 300 people using Microsoft Teams. With Microsoft 365 E3 and E5, Microsoft 365 A3 and A5, and Microsoft 365 Government G3 and G5 plans, this limit increases up to 1,000 people.
Craig Allen, president of the U.S.-China Business Council, a nonprofit organization of American firms that do business in China, said his organization "supports the Biden administration's efforts to protect U.S. national security while also ensuring robust commercial exchange with China for the benefit of American companies, workers and our economy."
Super Micro Computer on Wednesday introduced liquid-cooled AI data center systems running the latest Nvidia chips that are quick to deploy and can save on electricity usage. SMCI stock rose on the ...
How to Write a Computer Repair Business Plan in 7 Steps: 1. Describe the Purpose of Your Computer Repair Business. The first step to writing your business plan is to describe the purpose of your computer repair business. This includes describing why you are starting this type of business, and what problems it will solve for customers.
Drive Sober or Get Pulled Over — Drive High Get a DUI. As Independence Day approaches, the Edwardsville Police Department is gearing up for increased traffic enforcement to ensure the safety of all residents and motorists.
This business plan leads the way. It renews our vision and strategic focus: adding value to our target market segments, the small business and high-end home office users, in our local market. It also provides the step-by-step plan for improving our sales, gross margin, and profitability.
Looking at the role of Fair in the social media giant's business, Joëlle Pineau, Meta's vice-president of AI research, says, "We're not necessarily the team that brings those innovations ...
5.1 Competitive Edge. Todd, West, and Associates will sustain its competitive advantages to steadily gain market share. The first advantage is based on extensive knowledge of Symbol and CDS wireless ADC products. The second advantage is an established network of contacts among numerous companies that utilize wireless ADC products.