We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business How to Write Business Proposal (Examples + Free Templates)

How to Write Business Proposal (Examples + Free Templates)
Written by: Aditya Sheth Jan 25, 2024

The great Mark Cuban once said, “Sales cure all.” If a business doesn’t sell, it doesn’t make money and by extension the business fails. That’s why you need to write business proposals .
A well-written business proposal can often mean the difference between winning or losing a prospective client.
In this in-depth guide to creating business proposals, we show you how to close more deals, make more sales and crush your business goals — all by using easy-to-edit professional business proposal templates .
Here’s what this guide will cover (click to jump ahead):
What is a business proposal, what are the components of a business proposal.
- How to write a business proposal step by step
What should you include in a business proposal?
What are the types of business proposals, more business proposal examples + writing and design tips.
- FAQs about business proposals
Looking for a shortcut? Watch this quick video for an overview of everything to include in your business proposal:
A business proposal is a document designed to outline a business plan to convince potential client, investor or partner to engage in a business agreement with you or your company. It’s basically a sales pitch in writing to persuade potential clients to show them benefits of working with you or your company for their business success.
A business proposal outlines what your business does and what you can do for your client . It can be general like this business proposal example:

Or it can be more specific, like this business proposal template which focuses on proposing a project for the Newton Center Rail:

Or this business proposal sample, which presents a plan for a social media strategy and campaign:

To design a business proposal that holds the client’s attention, identify their pain points . Then provide your buyer with the right solution to alleviate those frustrations.
Working on a new project? These project proposal examples might come in handy for you.
The components of a business proposal can change depending on the field, company size and client needs. While details may differ, strong proposals typically introduce your company, explain the problem, offer a solution and its benefits, highlight your team’s skills, and outline timeline, cost and next steps.
How to write a business proposal step by step
Before you start creating your business proposal template, you need to understand the business proposal format. At a high level, your effective business proposal should include the following:
- Create a compelling business proposal title
- Build a table of contents
- Craft the executive summary
- Write a detailed problem statement
- Propose your solutions
- Showcase your team’s expertise
- Create a realistic timeline
- Present your payment structure
- Specify the terms and conditions
- Receiving the decision
Below, you can see business proposal examples that demonstrate how to include these 10 sections.
1. Create a compelling business proposal title
A compelling title could mean the difference between someone reading your proposal or ignoring it in favor of a competitor’s .
What makes a good title page? Here are the essential elements to include:
- Your name along with your company’s name
- The name of the prospect (or their business)
- The date you’re submitting the proposal

The gray business consulting proposal template above contains all the details a prospect would want to know. The title also offers a strong tangible benefit to the prospective buyer. Honestly, “Who doesn’t want to grow their business?”
2. Build a table of contents
The table of contents is a fundamental part of every winning business proposal template. It makes your proposal scannable and easy to read.
The people you will be pitching to are usually C-level executives. These are busy people who don’t have time to read your entire proposal in one go.
That’s why most of the business proposal examples in this list include a table of contents.
Adding a table of contents to your document makes it easy for them to go through it at their own pace. They can also skim through parts of the proposal that they deem more important. You can see how this abstract business proposal template uses the table of contents:

You can also make your business proposal template easier to navigate by adding hyperlinks to the document, particularly in the table of contents. This way your clients can jump to specific sections without having to scroll through the entire document. Ensuring your business plan format follows a clear structure can greatly enhance readability and comprehension for potential investors or partners.
It’s easy to add hyperlinks in the Venngage editor. Select the text you’d like to turn into a link, then click the link icon in the top bar. From there, select the page you want to link to! Then download your completed design as an Interactive PDF .

3. Craft the executive summary
The executive summary is a staple in all kinds of annual reports , leadership development plan , project plans and even marketing plans . It is a concise summary of the entire contents of your document. In other words, write a business proposal outline that is easy to glance over and that highlights your value proposition.
The goals of your executive summary are:
- Introduce your company to your buyer
- Provide an overview of your company goals
- Showcase your company’s milestones, overall vision and future plans
- Include any other relevant details
This gray business proposal example has a detailed yet short executive summary including some social proof in the form of clients they’ve worked with:

Take note of how precise this business proposal example is. You want to keep your executive summary concise and clear from the get-go. This sets the right tone for the rest of your proposal. It also gives your buyer a reason to continue reading your proposal.
Crafting an executive summary and keeping it concise and compelling can be challenging. but you can use an AI summarizer online to generate an executive summary. Such tools are trained on relevant AI models that can extract core points from a given text. You can get such a point either in bullet form or in abstract summary form.
Pro Tip: Try to write an executive summary such that, even if your prospective client doesn’t read the entire proposal (with a good executive summary, they most likely will), they should have a clear idea about what your company does and how you can help them.
4. Write a detailed problem statement
The point of writing a business proposal is to solve a buyer’s problem. Your goal is to outline the problem statement as clearly as possible. This develops a sense of urgency in your prospect. They will want to find a solution to the problem. And you have that solution.
A well-defined problem statement does two things:
- It shows the prospect you have done your homework instead of sending a generic pitch
- It creates an opportunity for you to point out a problem your prospect might not be aware they had in the first place.

This bold business proposal template above clearly outlines the problem at hand and also offers a ray of hope i.e. how you can solve your prospect’s problem. This brings me to…
5. P ropose your solutions
The good stuff. In the proposed solution section, you show how you can alleviate your prospective buyer’s pain points. This can fit onto the problem statement section but if you have a comprehensive solution or prefer to elaborate on the details, a separate section is a good idea.
Spare no details regarding the solution you will provide. When you write a business proposal, explain how you plan to deliver the solution. Include an estimated timeline of when they can expect your solution and other relevant details.
For inspiration, look at how this business proposal template quickly and succinctly outlines the project plan, deliverables and metrics :

6. Showcase your team’s expertise
At this point, the prospect you’re pitching your solution to likes what they’re reading. But they may not trust you to deliver on your promises. Why is this?
It’s because they don’t know you. Your job is to convince them that you can fix their problem. This section is important because it acts as social proof. You can highlight what your company does best and how qualified your team is when you write a business proposal for a potential client.

This free business proposal template showcases the company’s accolades, client testimonials, relevant case studies, and industry awards. You can also include other forms of social proof to establish yourself as a credible business. This makes it that much more likely that they will say yes!
Pro Tip: Attaching in-depth case studies of your work is a great way to build trust with a potential client by showcasing how you’ve solved similar problems for other clients in the past. Our case study examples post can show you how to do just that.
7. Create a realistic timeline
To further demonstrate just how prepared you are, it’s important to outline the next steps you will take should your buyer decide to work with you.
Provide a timeline of how and when you will complete all your deliverables. You can do this by designing a flow chart . Or add a roadmap with deadlines. Pitching a long-term project? A timeline infographic would be a better fit.
If you look at this abstract business proposal template below, even something as simple as a table can do the trick.

The timeline is not always set in stone, rather it’s an estimation. The goal is to clarify any questions your potential client might have about how you will deliver for the underlying B2B sales process.
8. Present your payment and terms
On this page, you can outline your fees, payment schedule, invoice payment terms , as well as legal aspects involved in this deal. You can even use the Excel Invoice Template to create professional-looking invoices (including brand logo and other elements) and add them to this page.
The key to good pricing is to provide your buyer with options. A pricing comparison table can help with this. You want to give your client some room to work with. Make sure you’re not scaring off your client with a high price, nor undervaluing yourself.
Breaking up your pricing in stages is another great way to make sure your potential client knows what he’s paying for. Look at how this simple business proposal template does this:

The legal aspects can slot right into the terms and conditions section. Alternatively, you can add them to the signature section of the proposal to keep things simple.
9. Specify the terms and conditions
Summarize everything you have promised to deliver so far. Include what you expect from your prospective buyer in return. Add the overall project timeline from start to end, as well as payment methods and payment schedule, incorporating these details into an online digital project management tool. This way, both of you will be clear on what is being agreed on.
This step is very important as it outlines all the legal aspects of the deal. That is why the terms and conditions section of your proposal needs to be as clear as possible.

I recommend consulting a lawyer or your legal team when working on this section of the business proposal. If you’re a business veteran and understand the legalities of your business, you can use the same terms and conditions across all your proposals.
10. Receiving the decision
The final step of this whole process. Your client has read your business proposal and they want to buy what you have to offer.
Add a small section at the end of your proposal to get the necessary signatures. This way, you and your client can sign the proposal and the partnership becomes official.
Be sure to also include your contact information in your business proposal template. It acts as a gentle prompt to your client to contact you in case they have any questions. A professional way of doig that would be to include an e-business card with your contact details, email i.d and any other social links you want to share. You can go through this article for the best digital business cards .

A business proposal usually aims to answer the following questions:
- Who you are and what your company does
- The problem your buyer is facing
- The solution your company offers to alleviate the problem
- How your company will implement this solution effectively
- An estimate of resources (time, money, etc) required to implement the solution
You can see how this sample business proposal template covers the above points.

Notice how this proposal template addresses the same project like in one of the previous templates, but uses a completely different design style (more retro, while the previous business proposal template is more modern and minimalistic).
Generally, there are three types of business proposals:
1. Formally solicited
A formally solicited business proposal is made when you respond to an official request to write a business proposal.
In this scenario, you know all the requirements and have more (if not all) information about a prospective buyer. You simply need to write the business proposal for your buyer to evaluate so you can begin the sales process .
2. Informally solicited
Informally solicited business proposals are written when there isn’t an official request for a proposal. A prospective buyer is interested in your services and asks for a proposal so they can evaluate it.
An informally solicited proposal requires a lot more research from your end. These types of proposals are usually created out of informal conversations. They are not based on official requests which often contain more detail.
3. Unsolicited
Think of this as a marketing brochure or a cold email . Unsolicited business proposals will often take a generic, one-size-fits-all approach to business proposals. Unsolicited proposals lack any understanding of the buyer or their requirements.
But with additional market research , personalization and identifying customer pain points , you can propose a customized solution based on your buyer’s needs. This can be a very persuasive approach, such as in this business proposal example:

Now that you know how to write a business proposal, let’s look at how you can optimize your proposal to deliver results!
Below you’ll find some winning business proposal templates and examples to get you started. I’ve also included some design tips to keep in mind when you’re creating your next business proposal:
1. Know your audience
If you have some clarity on who your ideal buyer is — their pain points, their budget, deadlines, among other things — you’ve already won half the battle.
If you are a business that helps clients with everything from running giveaways or helping grow their blog , identify which customers to pitch. This is a sure-shot way to close the deal.
Mapping user personas for your ideal buyer can help bring some clarity. It will also help you position your business proposal correctly. This improves the chance of your buyer moving your business proposal to the “Yes!” pile.
2. Put your brand front and center
If your company follows certain brand guidelines, incorporate them in your business proposal templates. Consider how business proposal examples like the one below highlight brand identity :

From the color palettes to the company logos , everything follows their brand guidelines. The result: a business proposal that’s consistent across the board.
Pro Tip: Switching this template to match your brand assets is actually pretty easy. Venngage’s My Brand Kit feature allows you to import your color palettes, logos as well as font choices. Any Venngage template can now be your template.
You can also consider this sample business proposal template:

App design companies sure do know their design. They did a phenomenal job keeping their brand colors consistent while opting for a black design. This unique color scheme also makes their white logo prominent throughout the proposal.
3. Try less text, more visuals
Have you ever read a proposal and thought to yourself, “Wow, this is all text and has no images, I love it!”? Yeah, me neither.
The free business proposal template below is a perfect example of the “less is more” principle. It does a phenomenal job of communicating what it needs to. By substituting some of the text with icons and visuals, you get a clean business proposal that’s much more scannable.

Want to keep things strictly professional? Instead of icons, you can always add your team’s headshots. This shows your buyer exactly who they’ll be working with.
Check out this formal business proposal format for some inspiration:

4. Switch up your business proposal designs
It doesn’t hurt to go above and beyond once in a while. Jazz up your business proposal template with some extra colors. This helps make your business proposal more engaging. It also helps your buyers retain information faster.

The business proposal example alternates between black, white and grey backgrounds. It still manages to maintain consistency in its branding . Just switching up your backgrounds once in a while can also bring in some variety to an otherwise standard business proposal.
This SEO business proposal sample proves that it’s possible to switch up the colors in every other page. But it still maintains the same color scheme across the entire proposal just like a professionally designed website :

Pro Tip: Not a color expert? Our guide on picking colors can help you pick the right color scheme for your proposals.
FAQ about business proposals
What is the purpose of a business proposal.
A business proposal aims to streamline the B2B sales process (which is often complex ) between you as a seller and a buyer.
It does this by serving the dual purpose of acting as a source of information. The proposal also acts as a sales pitch aimed at convincing your buyer why they should buy what you have to offer.
What are the best practices for business proposal design?
- Do a thorough spell-check. The goal of your business proposal is to convince your buyer why you’re the perfect person for the job. A proposal with typos or grammatical errors communicates the opposite. A thorough spell-check before you send your proposal is a must.
- Keep things clear and readable: Clarity is an important aspect that you have to ensure in your business proposal. If you want your proposal to hit home and make an impact on the buyer, you have to write it in an understandable way. To keep things clear and readable, there are a couple of things that you can do. You can, for one, take care to use easy wording and segmented sentences from the get-go. You can also try paraphrasing the hard parts of your proposal once you are done writing it.
- Let your brand shine. As discussed before, writing a business proposal is all about knowing your ideal buyer and focusing on their pain points. But that doesn’t mean your business proposal template has to be boring. Demonstrate how different you are compared to other companies. You can do this through your brand guidelines , by using more visuals, switching up your proposal design or showing off your personality in your writing .
- Create a business proposal PDF. Downloading your business proposal in PDF format allows you to attach other collaterals with your business proposal. These can include a company explainer video or case studies showcasing the work done with past clients. Also, who doesn’t love saving paper?
How long should your business proposal be?
The length depends on the scope of the work as well as the complexity of the project. Here is a one-page business proposal template:

Can your business proposal template really be one page? Yes, as long as you understand who your buyer is and their pain points. You should also have the ability to communicate everything your ideal buyer needs to know about your business in a succinct manner.
Or if you’re feeling adventurous how about just two pages? Often, clients prefer if you go straight to the point and avoid all the fluff.
For example, this green modern marketing proposal template wastes no time in getting down to brass tacks:

Need more inspiration? Check out this blog on the 5 marketing proposal examples that’ll help elevate your business.
There is no one size fits all approach when it comes to deciding how many pages you should include in your business proposal template. And at the end of the day, “the only rules are the ones you set for yourself”.
At the end of the day, writing winning business proposals that sell is all about you understanding your buyer, their potential pain points and positioning yourself as someone who can alleviate those pain points.
Now that you know how to write compelling business proposals, what are you waiting for?
Take action and start creating your own business proposals to close more deals and grow your business today!
More business communications templates + writing tips you might be interested in…
- 31 Consulting Proposal Templates to Close Deals
- 20+ Professional Business Letterhead Templates + Branding Tips
- How to Write a White Paper [Tips & Templates]
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
How to Write a Business Proposal [Examples + Template]
Published: December 05, 2023
Here's what every new business owner needs: an extra 8 hours in the day, an endless supply of coffee, and, most importantly, a really strong business proposal.

A business proposal can bridge the gap between you and potential clients. Done correctly, and it will outline your value proposition and persuade a company or organization to do business with you.
Here, we'll take a look at the various kinds of business proposals and go over how to write one. We’ll also see some ideas and examples to help guide yours.
Know exactly what you need? Jump to one of the following sections:
What is a business proposal?
Types of business proposals, how to write a business proposal, business proposal templates, business proposal example, tips for writing a business proposal, business proposal ideas.
A business proposal is a formal document that’s created by a company and given to a prospect to secure a business agreement.
It's a common misconception that business proposals and business plans are the same. However, a proposal helps you sell your product or service — not your business itself.
Think of it this way: instead of assisting your search for investors to fund your business, a proposal helps you seek new customers.
Follow Along With HubSpot's Business Proposal Template

Download the Template for Free
There are two types of business proposals: unsolicited and solicited.
- Unsolicited Business Proposals : With unsolicited business proposals, you approach a potential customer with a proposal, even if they don't request one, to gain their business.
- Solicited Business Proposals : Solicited business proposals are requested by prospective clients so that they can decide whether to do business with your company.
In a solicited business proposal, the other organization asks for a request for proposal (RFP). When a company needs a problem solved, they invite other businesses to submit a proposal that details how they'd solve it.

Free Business Proposal Template
Propose your business as the ideal solution using our Free Business Proposal Templates
- Problem summary
- Proposed solution
- Pricing information
- Project timeline
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Fill out the form to get your template.
Whether the proposal is solicited or unsolicited, the steps to create your proposal are similar. Make sure it includes three main points:
- A statement of the organization's problem
- Begin with a title page.
- Explain your why with an executive summary.
- State the problem or need.
- Propose a solution.
- Share your qualifications.
- Include pricing options.
- Summarize with a conclusion.
Before writing your business proposal, it's crucial you understand the company. If they've sent you an RFP, make sure you read it carefully, so you know exactly what they want.
I recommend having an initial call or meeting with any new clients to ensure you fully understand their objectives. Ask open-ended questions to understand not just what they want, but why they want it.
Once you've done your research, it's time to begin writing your business proposal. While there's no one-size-fits-all approach to writing a business proposal, there's several elements most proposals include. (I designed this example business proposal using Canva .)
1. Begin with a title page.
You have to convey some basic information here. Introduce yourself and your business. Be sure to include:
- Your company's name
- The date you submitted the proposal
- The name of the client or individual you're submitting the proposal to
Your title page should reconcile engagement with professionalism. I think of it as your first tone-setter, so you need to make sure yours is sleek, aesthetically appealing, and not too "out there."
Here's an example of what a business proposal template looks like when done right:

The executive summary details exactly why you're sending the proposal and why your solution is the best for the prospective client.
Specificity is key here. Why are you the best choice for them?
Like a value proposition, your executive summary outlines the benefits of your company's products or services and how they can solve your potential client's problem.
After reading your executive summary, the prospect should offer a clear idea of how you can help them, even if they don't read the entire proposal. Here's what one should look like:

3. State the problem or need.
This is where you share a summary of the issue impacting the potential client. This is your opportunity to show them you understand their needs and the problem they need help solving.

In the example above, I included several signals to showcase my expertise – that I've been in the photography biz for 10 years, that I've worked with over 500 clients, and that I've been featured a number of publications.
As you approach this section, focus on presenting yourself as an authority. Consider leveraging tools like:
- Case studies
- Client testimonials
- Relevant awards
- Industry accreditations
6. Include pricing options.
Pricing is where things can get a bit tricky, as you don't want to under or over-price your product.
The pricing section of your proposal could include:
- A detailed pricing breakdown, including packages, tiers, and add-ons or optional services
- How product features and benefits align with pricing choices
- Pricing for different needs and budgets
- How your pricing compares with competitors
- An FAQ section to respond to anticipated objections and explain your pricing strategy
7. Summarize with a conclusion.
After sharing the above information, simplify it all into one final section.
- First, briefly summarize the proposal. Be sure to share your qualifications and why you’d serve as the best choice.
- Then, to prompt further conversation, confirm your availability to go over the next steps.
- At the end of the proposal, the goal is to have the client ready to work with you. So, be sure to offer your contact information for easy follow-up.
In need of some inspiration before you begin writing? Here are example business proposal templates from popular business proposal software companies you can use to help create your proposal.
1. HubSpot's Free Business Plan Templates
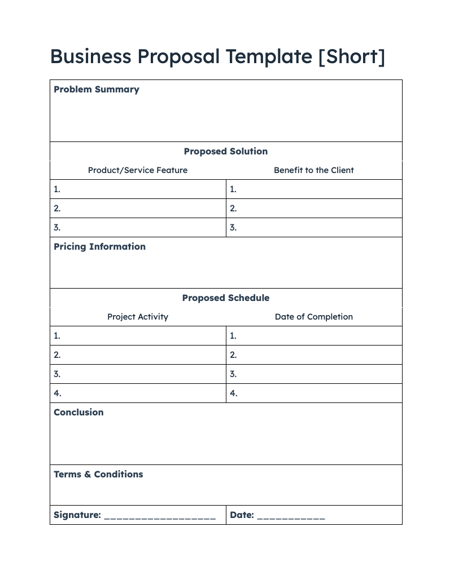
Download these Templates
We know how crucial a great business proposal is to your and your client’s success. That's why we've compiled 2 Free Business Proposal Templates for you to use and customize for any of your projects.
You'll gain access to a concise, one-page template (pictured above), as well as a longer template for you to refine your plan and proposal.
Download the templates now to get started on building your proposal.
What We Like
The one-page template is clear, straightforward, and easy to read — without skipping on the key elements of a business proposal. This format is especially useful for busy clients who appreciate brevity and clarity.
2. Web Design Proposal

With advertising on social networks projected to reach $82.23 billion dollars in 2025 , it's in your business's best interest to have a plan for growing your client's social media presence.
To help you in that effort, the information in this social media marketing proposal includes an executive summary to help introduce your high-level ideas, an assessment of the client’s company to show your diligence, and a breakdown of billing to show how your company charges for posting, content creation, and analytics.
This template includes all the bells and whistles of a social media proposal packaged in a fun yet professional design. It also includes helpful writing instructions under each section.
8. Content Marketing Proposal

Business proposal templates are helpful places to get started, but what should your business proposal look like when it's complete? This template should inspire you.
When pitching your content marketing services to clients, this template can help you organize your ideas. While it walks you through initial objectives and how to communicate your prospected results, one of the most helpful parts of this template is the pricing ideas it gives you when charging for your services.
In the business template example below, Social Portal Consulting (SPC) pitches a marketing proposal to Graphic Bean. At first sight, this proposal appeals to the creative. I recommend going a step forward and designing the layout in your or your client’s brand colors.
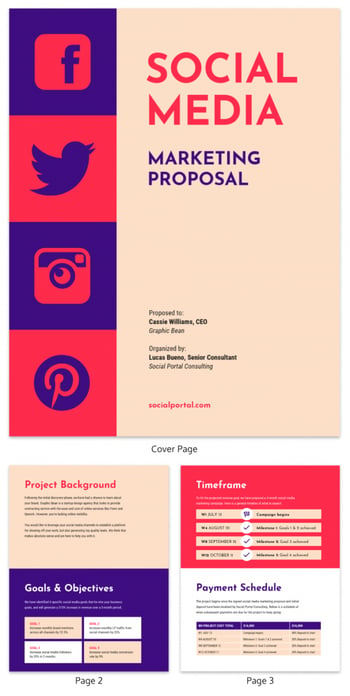
Besides the design, the social media icons quickly tell the prospect what platforms Social Portal is pitching. Because we see Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and Pinterest icons, the client instantly knows that this proposal doesn’t include LinkedIn, YouTube, or other platforms.
While maintaining its design, this example outlines Social Portal Consulting’s plans efficiently. It begins by providing insight into Graphic Bean and its goals before elaborating on how SPC can leverage its expertise to help them achieve them.
This business proposal template includes an easy-to-follow timeframe for goals and objectives while keeping the client abreast of how payment will happen across the project.
Overall, this is an excellent example of how to combine the elements of social media marketing into a creative and concise business proposal. Finally, we'll leave you with some business proposal ideas to get you started on your own.
- Start with an outline.
- Keep it simple.
- Stay on brand.
- Quality control.
- Include data and visuals.
- Add social proof.
- Use a call-to-action.
- Create a sense of urgency.
- Make the decision for them.
- Incorporate video into your proposal.
- Include up-sell and add-on opportunities.
- Clarify your terms and conditions.
- Include a space for signatures to document agreement.
- Create a table of contents.
1. Start with an outline.
If you want to produce a thoughtful, effective business proposal, you need to have some idea of what you're hoping to achieve with it.
Before I dive into writing a proposal, I always outline the major sections of the proposal that I want to include. That way, I can stay focused and make sure my message stays intact as I write.
Use these free business proposal templates to make sure that your outline includes everything you need.
2. Keep it simple.
Ultimately, there's no definitive blueprint for how long a business proposal has to be. Yours should be however long it takes to convey the information you want to get across.
That said, I'm a firm believer in quality over quantity, especially when it comes to business proposals. Keep your sentences short and simple, and avoid including too much business jargon.
You want anyone who picks up your proposal to make sense of it. So, be straightforward and don't get too fancy. Aim for substance over flash.
3. Stay on brand.
Don't be afraid to let your company's personality shine through in your proposal. Stay true to your brand and show the client what sets you apart from your competitors.
4. Quality control.
I've made it a habit to add an editing/QA step in my writing process. During this step, I do a quick spelling and grammar check before hitting send.
So, as you draft your proposal, and after checking for the basics, keep scanning this document until it's just right.
Check to make sure your proposal:
- Meets client needs and expectations
- Highlights your value proposition
- Is well-structured and easy to read or skim
- Complies with legal, ethical, and regulatory requirements
- Looks professional and engaging
5. Include data and visuals.
You want your business proposal to capture your prospect's attention and help set you apart from any other ones they might have received. One of the best ways to do that is to include hard, quantitative data that helps stress the value of your business.
Use relevant, compelling figures that highlight what you have to offer. This can establish authority and make your proposal more convincing. It also helps to include visuals such as charts and graphs to enhance your proposal.
6. Add social proof.
From my experience, you can only be so convincing when you're personally talking up how great your business is — which is why adding social proof is key to establishing credibility.
At the end of the day, prospects are skeptical. They may not take you at your word. But they'll likely trust peers and fellow customers. That's why including elements like customer quotes and testimonials can go a long way.
7. Use a call-to-action.
I've learned that the best proposal in the world can only take you so far if you don't clearly define the next steps. That's why you have to make sure the reader knows what to do after reading your proposal.
A clear call-to-action is the best way to get there.
Define and highlight exactly what they should do to act on the interest your proposal has generated. Without that guidance, you might leave your reader in limbo.
HubSpot customers : Use this CTA builder to create powerful customized CTAs.
8. Create a sense of urgency.
No one wants to feel as if they missed out on a great opportunity. From my experience, prospect tend to drag their feet and put off making a decision if there isn't a sense of urgency.
So, as you create your business proposal, your goal should be to add a degree of urgency. When prospective clients read your business proposal they should feel that the best time to sign up for your service is now .
One way I accomplish this is by stating short and long-term goals for their business. They'll have to wait for the long-term goals, but I make the short-term goals so enticing that they'll be ready to begin a collaboration.
9. Make the decision for them.
Craft your copy in a way that seems like saying "no" to the proposal would be stepping over dollars to pick up pennies. Your offer should go above and beyond their expectations. Do everything in your power to remove friction and objections along the way.
10. Incorporate video into your proposal.
If you're creating an online proposal using document file formats like PDF, add multimedia elements. This will enhance the proposal experience, make your document richer, and keep them engaged.
Try adding a video at the beginning as an intro to your proposal. Or, put a video in the project breakdown to verbally discuss some of the more confusing parts.
Extras like this can make an impression. This tip works especially well with prospects who are visual or auditory communicators.
Pro tip : HubSpot Video makes it easy to record and embed video into a website or email for a big proposal boost.
11. Include up-sell and add-on opportunities.
They say you won't receive unless you ask. And readers won't explore the upper tiers of your solutions if you don't give them the opportunity.
So, share some upsells and add-ons about your business that they can act on. Call out a specific pain point and how this extra can add value.
With this step, balance is important. Show them everything your business has to offer without overwhelming your recipient.
12. Clarify your terms and conditions.
Your business proposal should include details on your project timeline and payment schedule. This summary is basically what you and the client agree to if they accept your proposal.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

A Complete Guide to Successful Brand Positioning

70 Small Business Ideas for Anyone Who Wants to Run Their Own Business
![business plan business proposal How to Start a Business: A Startup Guide for Entrepreneurs [Template]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/How-to-Start-a-Business-Aug-11-2023-10-39-02-4844-PM.jpg)
How to Start a Business: A Startup Guide for Entrepreneurs [Template]

Door-to-Door Sales: The Complete Guide

Amazon Affiliate Program: How to Become an Amazon Associate to Boost Income

Product Differentiation and What it Means for Your Brand

The 25 Best PayPal Alternatives of 2023

The First-Mover Advantage, Explained

Intrapreneurship vs. Entrepreneurship: What's the Difference?

What Are Current Assets? Definition + Examples
Propose your business as the ideal solution using this free template.
Powerful and easy-to-use sales software that drives productivity, enables customer connection, and supports growing sales orgs
Sales | How To
How to Write a Business Proposal (+ Template & Examples)
Published February 27, 2023
Published Feb 27, 2023
REVIEWED BY: Jess Pingrey
WRITTEN BY: Bianca Caballero
This article is part of a larger series on Sales Management .
Free Business Proposal Template
- 1 Determine Sales Proposal Requirements
- 2 Gather Necessary Information
- 3 Design Your Proposed Solution
- 4 Calculate Pricing
- 5 Draft Your Proposal
- 6 Edit Your Proposal Draft
- 7 Send Your Proposal
- 8 Follow Up With Your Recipient
- 9 Best Practices in Writing Sales Proposals
- 10 Bottom Line
A business proposal is a document sent to a prospective client that outlines a firm’s product or service offerings. It also explains how you will provide a solution, the cost, timeline, and qualifying information, such as your background and prior work experience. In this article, we outline eight steps for how to create a business proposal, offer a free proposal template, and provide best practices for writing proposals.
Creating a sales proposal can feel tedious, especially if you’re drafting it from scratch each time. We’ve created a free template that you can use as a resource for your sales proposal.
FILE TO DOWNLOAD OR INTEGRATE
Free Sales Business Proposal Template

Thank you for downloading!
💡 Quick Tip:
Use ClickUp for free to see your entire sales funnel in one place.
- ✓ Free forever, unlimited users
- ✓ Manage all leads, emails and tasks
- ✓ Create presentations, lead forms, and contracts
- ✓ Professional workspace templates
After you’ve downloaded our free template above, you can now customize it according to your business needs as you follow the steps to writing a proposal below:
1. Determine Sales Proposal Requirements
The first step in learning how to write a business proposal is knowing what needs to be included. Government agencies, public universities, and large corporations typically use requests for proposals (RFPs). These are formal solicitation requests for products or services in which the requirements are normally laid out line by line and must be followed precisely.
If you are writing a proposal for a potential customer undergoing your unique sales process , include things a decision-maker would like to see. For instance, pricing, timelines, and the proposed solution regarding quantities and the mode of product or service delivery are critical purchasing factors enclosed in the document.
Pro tip: ClickUp is a free-forever project management tool that helps teams:
- Create professional proposals
- Collaborate with shared tasks and team chat
- Assign tasks to teammates
Visit ClickUp
ClickUp project management board (Source: ClickUp )
2. Gather Necessary Information
Gathering essential information and materials for your proposal can be complex because each potential client may want different details. This could demand other personnel to get involved in pulling the documents and information needed. For instance, some may only request the price and proposed solution, while others will ask for your background story, client reference lists, and work samples to show you’re qualified.
While learning how to write a proposal for business purposes, you may have to dig around your file database for company information, employee biographies, marketing materials, and pricing sheets. Keeping all resources needed for a proposal in one place makes this process easier. Use customer relationship management (CRM) systems to track your proposal progress and acquire what’s needed to draft it in one place.
Pro tip: HubSpot is a popular CRM platform that lets you monitor opportunities using sales pipelines and store documents—all in one system. You can utilize the Sales Documents feature to store, share, and customize templates and materials you’ll need for your proposals.
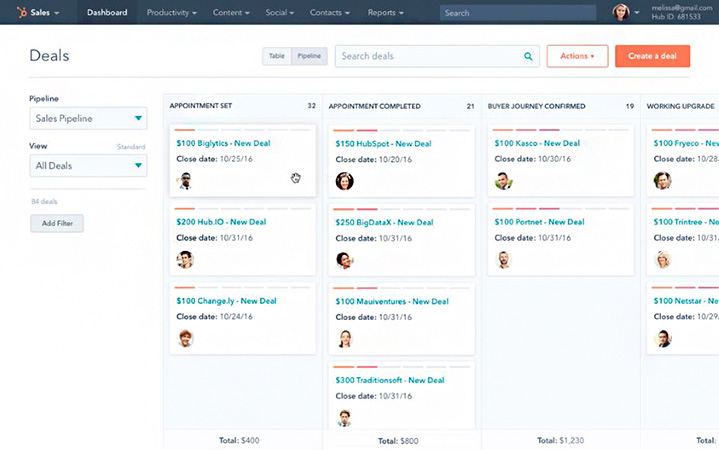
HubSpot’s deals and opportunities pipeline (Source: HubSpot )
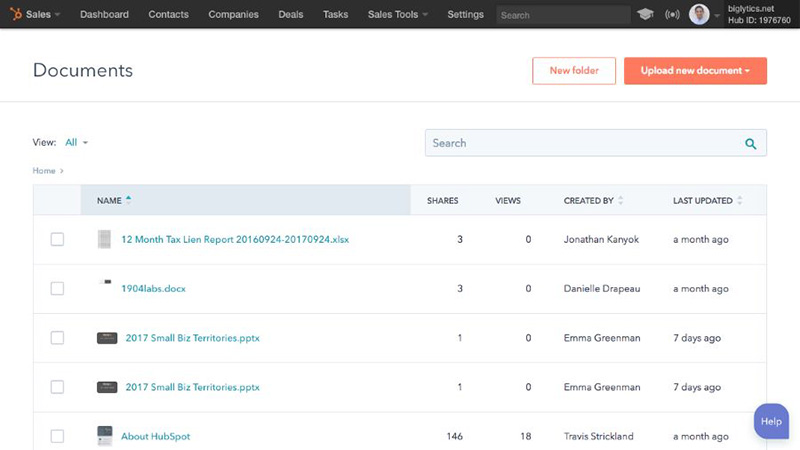
HubSpot’s Sales Documents library (Source: HubSpot )
3. Design Your Proposed Solution
Your proposed solution involves the processes, materials, product quantities, and personnel required to fulfill the offerings or address your customer’s problem statement. Additionally, it should be included in the scope of work section in the proposal. For businesses that only provide a product, such as equipment for a manufacturing plant, this step could be as easy as knowing the quantity and having a logistics plan for delivery and installment.
For more service-based businesses, such as business consultants or content development services, there will likely be more steps and deliverables to complete the work. Regardless of your business, you can use the five W’s and an H methodology to construct a proposed solution that addresses your prospect’s primary pain points:
- Who: Who will be involved, do the work, manage, and be a point of contact for the prospect?
- What: What solutions or products will be delivered, and what resources, processes, or technology will be used?
- Where: Where will work be done or delivered to?
- When: When will the work start and be completed, what are the key milestones throughout the project, and when is each deliverable expected to occur?
- Why: Why did you choose this particular solution for this customer’s needs?
- How: How will work be done, managed, and checked for high quality and customer satisfaction?
For example, a business-to-business (B2B) content writing business might be trying to address a statement of needs issued by a client: “We would like to express thought leadership on the topic of the Zero Trust Cybersecurity Framework.” In this case, the business could use the solution in this business proposal example:
The objective of this business proposal is to demonstrate how ABC Writing Agency can promote the thought leadership of Cybersecurity Corp. for the Zero Trust Security Model. We believe the best course of action is to research and copyright a branded e-book (roughly 4,000 words) regarding Zero Trust Security, the details of the solution, its benefits, and the modern-day security challenges it solves (what) with the final product completed in August 2022. (when) The e-book will use your logo and branding scheme to convey your personal grasp on the subject and thought leadership using a series of direct quotes and statistical callouts. (why)
To ensure high-quality work and client satisfaction, we will begin with an initial call to construct a detailed outline discussing the sections, style guides, tone, and to retrieve direct quotes. Following an initial draft, multiple rounds of edits will take place between Cybersecurity Corp. and ABC Writing Agency to develop a final draft. (how)
The project will be led by our senior editor, Collin Buchanan, and content manager, Jake Cunningham, who comes from the world of cybersecurity. Our team will utilize and manage freelancers experienced in writing e-books on technical topics to research and copyright the asset. (who) All work will be completed by us virtually and delivered via Google Docs. (where)
4. Calculate Pricing
Once you know how you’ll provide your product or service, the next step in writing a proposal is formulating the costs to specify in the document’s pricing section. This is one of the toughest steps because of all the factors that need to be considered, such as product cost and other expenses. That’s why it is critical to accurately communicate your costs to avoid losing a deal for overcharging—or worse—winning a deal with significantly underestimated costs.
As you price everything, you can either do a flat fee, hourly rate, per-unit charge, or some combination of the three. Sometimes, it’s best to work backward by establishing your desired probability first in the form of a percent like 20% profit or a flat dollar amount such as $10,000 above the work cost.
For example, you want to make a 20% profit on the work for an equipment installation job for a manufacturing business, and you’re pricing using a flat fee. You’ve itemized the costs as the following:
- 1 x $80,000 manufacturing equipment = $80,000
- 3 installation/delivery employees x 5 hours x $32 per hour = $480 wages
- $480 employee wages x 7% employer payroll tax = $33.6 payroll tax
- $480 employee wages x 20% benefits and workers’ compensation = $96 benefits and compensation
- $200 for the delivery truck and gas = $200 for delivery costs
When you add all the itemized expenses, the total cost for this installation job will be around $80,809. To get the total, you need to charge this customer to meet your desired profitability, and multiply it by 20% to get $16,162. Add that to your total cost ($80,809 + $16,162), and $96,971 is the flat fee you will charge for the installation job.
Pro tip: Struggling to visualize your pricing process? Try using these seven free estimate templates . Designed for various business types, these templates allow you to outline and itemize the costs of providing work to share with your customers to help win more deals easily.
5. Draft Your Proposal
Now that you know your proposal requirements, have gathered the necessary information, determined the proposed solution, and calculated pricing, you are ready to draft the document. Following along with our free template, your draft will consist of the following elements:
The title page leans more toward showing the professionalism of your business than providing information. There should be a specific title establishing the purpose, such as “ABC Writing Agency Proposal for Cybersecurity Corp. to Promote Thought Leadership on Zero Trust Security.”
Also, be sure to indicate who the proposal was prepared for in terms of the decision-making person and their company name. Add your logo to the front and the contact information for the primary point of contact for your business so they can contact you with further questions.
Table of Contents
Use a table of contents to break down each part of the proposal for business so they can easily navigate through it. Because of the digital age we live in, we recommend linking your table of contents electronically to each associated section. That way, those reading your proposal can go to any part of the document by clicking on the table of contents.
Executive Summary
The executive summary takes everything in your proposal and compresses it into one paragraph. Essentially, if a reader reads this section, they should be able to grasp the general idea of your solution. Here’s a business proposal example using the content writing example above:
With over 10 years of experience in writing high-quality marketing assets, we are eager to assist Cybersecurity Corp in its endeavor to promote thought leadership on Zero Trust Security. We plan to achieve this by writing a comprehensive e-book using engaging copy, stat callouts, and direct quotes from your leaders to help associate the security framework with your brand.
Company Background
Here’s your time to talk about your inception story, mission statement , founding purpose, and company history. You can also provide biographies and professional pictures of your company founders, leaders, and key personnel that might be involved in the work you provide.
This is also the time to express your unique selling proposition . In other words, addressing the question “why choose us” over competitors. Lastly, if you’ve had any recognition or won any company awards, this is the section to highlight those successes.
Scope of Work
This section correlates with creating your proposed solution in step three as you present it in an actionable business plan. Describe the work that will be completed and the tangible deliverables associated with it.
In this small business proposal example, we see how a content writing business might construct a scope of work:
We will provide content writing services to create predetermined marketing assets for Cybersecurity Corp. This includes researching online data for usable information, interviewing subject matter experts (SMEs) for additional insights and quotes, copywriting drafts, inserting callouts, and making edits per revision requests made by Cybersecurity Corp. Deliverables for the scope of work above include:
- 1 x outline developed by ABC Writing Agency and approved by Cybersecurity Corp.
- 1 x drafted e-book (max. 4,000 words) delivered by Google Doc
No matter how long your scope of work is, it’s crucial to avoid industry or technical jargon that the general audience may not understand. Take the time to review the scope of work and translate any statements that may be misunderstood or confusing.
Be sure to indicate how long you expect it to take to complete the entire scope of work. It’s also a good idea to provide estimates for each milestone or individual deliverable you set. Whenever possible, present the information visually to help your reader absorb it better. Below is a sales proposal timeline example for a sales consulting business and its milestones.
Pricing or Price Estimate
For this section, take the price calculation you did in step four and present it to the potential customer. While you should itemize it to show where the price comes from, avoid adding your desired profitability, as that should be private to your business. Make sure it’s clear as to how each item is priced, whether that be hourly, per unit, or a flat fee.
This section should also be used to explain payment expectations, e.g., when invoices must be paid by, how much money is required upfront vs after work is completed, refund policy, and if other billable expenses can be included automatically or require client approval.
Be upfront with your estimate if you don’t know how many units you’ll need or how many hours it will take to accomplish your business offering. Provide an explanation and an estimated range.
Conclusion, Terms & Appendix
The final sections should include additional information that could be useful to your prospective client. A conclusion should express your gratitude for the opportunity and explain the next steps to move forward. Terms (or terms and conditions) can be added in a proposal or in the service agreement to cover legal aspects of a working contract, like contract dispute policies, confidentiality, rules on subcontracting, etc.
The appendix is optional but would utilize visuals or supplemental documents to enrich your proposal. For instance, you might include links to sample work, a client reference list, or a catalog of options for materials or software vendors from which the client can choose.
6. Edit Your Proposal Draft
Once you have completed the first draft of your proposal, run it by multiple departments to ensure it is comprehensive and accurate. Some things to consider as you review it for potential revisions:
- Has strong readability: The proposal uses appropriate style, tone, and structured sentences to create a clean flow of information understood by the specific reader.
- Avoids grammar and technical errors: The proposal avoids punctuation, spelling, or other errors related to proper writing mechanics.
- Addresses requirements: The proposal contains all the information and sections required to meet the reader’s or customer’s needs and objectives.
Use editing tools such as Grammarly to evaluate your business proposal writing for enhanced quality. Grammarly lets users upload text into a system to check for grammar and spelling mistakes as well as for engagement and readability of content. There’s also a plagiarism check feature to evaluate the text to billions of pages online. You can even adjust style preferences when subscribing to Grammarly Business to ensure it meets all your goals.
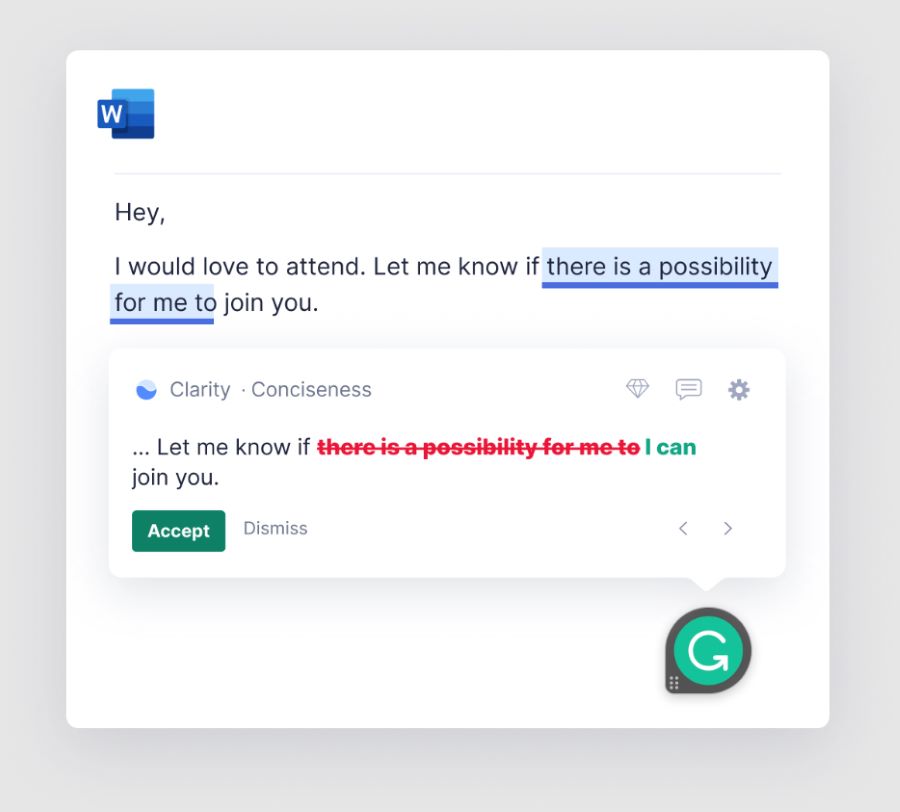
Grammarly Business’ in-line writing suggestion (Source: Grammarly Business )
Pro tip: Use graphic design tools like Canva to give your sales proposal the professional touch it needs. Canva is a user-friendly platform with thousands of free templates for presentations, marketing materials, social media posts, and proposals for business. Users of all design skill levels can easily turn regular copies into visual masterpieces.
Canva’s sales proposal templates (Source: Canva )
7. Send Your Proposal
Now that your proposal is drafted, edited, and has the aesthetics it needs, it’s time to send the document for review. More formal submissions for RFPs may require that you submit them in person, electronically, or both, so review those provisions carefully before sending them in.
Some sales plans incorporate unsolicited proposals to new leads to present problems they didn’t know existed with viable solutions they could offer. In these cases, they use the proposal to get their foot in the door and create sales opportunities.
When taking this course of action, it’s important to add context to the unsolicited proposal. For instance, in a sales email , briefly introduce yourself, your business, and what services you provide. Furthermore, indicate why you wanted to send a proposal to them specifically and let them know they can reach out if they wish to discuss it further.
8. Follow Up With Your Recipient
Even after you send a proposal, the process is not over. Make time to follow up to confirm the contact received the proposal and see if they have any questions. Because of the proposals’ details, there are usually other clarification steps in the procurement process, such as interviews, client meetings , or sales presentations before work begins.
We recommend using a customer relationship management (CRM) system with task management capabilities to ensure sales reps don’t forget to reach out to a prospect after a proposal is initially sent. A CRM like Pipedrive lets you design and assign tasks to team members from within a project. You can also create projects that are linked to open or won deals.
Pipedrive’s project and task management feature (Source: Pipedrive )
Best Practices in Writing Sales Proposals
Now that you know the steps in how to write a business proposal, there are a few tips you can practice and maintain to produce thoughtful and effective proposals.
Keep It Simple
When learning how to make a business proposal, remember to write short, simple sentences. While there is no strict rule on the business proposal format or length, make sure it is straightforward and easy to understand. Avoid loading it with too much business jargon and fancy words. Instead, strike the sweet spot between conveying essential information and ensuring anyone who reads it can understand it.
Outline Major Sections & Pertinent Information
The first thing to do when learning how to do a business proposal is to outline all the major sections of your document. This should also include all the pertinent information that you want to get across. The business proposal outline will help you stay focused on the main points of the document and keep your ideas from drifting away.
Add Data & Visuals
Capture your prospect’s attention by including quantitative data and figures highlighting your offerings and the value of your company. For example, you can show your month-on-month sales trends as proof of your stellar performance. Adding visual elements like charts and graphs can also help make your proposal more engaging.
Increase Credibility With Social Proof
Assert your company’s credibility. Many prospects won’t readily believe your claims about your business and are most likely to trust the word of their own peers and other customers. To help build your credibility and gain their trust, include social proof, such as reviews and testimonials from your own customers.
Use a Call to Action (CTA)
After the prospect reads your proposal, direct them to the next step. Use a call to action with a verb that defines what they should do to act on their interest in your proposal. Examples of CTAs are “Subscribe today” or “Download this guide now.” You can also use a CTA with a no-obligation statement like “Sign up, it’s free” for prospects who perceive risks in taking action.
Another excellent idea when adding CTAs is to create a sense of urgency to make your prospect feel that now is the best time to subscribe to your service. Some people are motivated to do something right away for fear of missing out (FOMO). That said, phrases like “Limited-time offer” and “On sale now for 20% off” can trigger action from prospects.
Stay True to Your Brand
Each company has a different brand voice and personality. Staying true to your business brand is a great way to stand out among your competitors. For instance, if your company sells baby clothes, it is best to use language that parents with babies can relate to, like “cute and cuddly” or “snug and comfy.” Use a more formal tone of voice in your proposal if you are selling office wear.
Bottom Line
Many business owners and sales managers would like to standardize their proposal-writing system. However, it can be tricky to address the unique needs of every solicited and unsolicited opportunity to get the correct information in order and present their proposed solutions. Our how-to sales proposal examples and free template will help you streamline your bidding process to win more deals.
About the Author

Find Bianca On LinkedIn
Bianca Caballero
Bianca Caballero is a subject matter expert at Fit Small Business who covers Sales and Customer service topics. Prior to working at FSB, she was in field sales and territory management. When she launched her career as a writer, she worked with companies from the US, Australia, and China. At present, she uses her 12+ years of writing experience to provide FSB readers with the best answers to their questions.
Join Fit Small Business
Sign up to receive more well-researched small business articles and topics in your inbox, personalized for you. Select the newsletters you’re interested in below.
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Business Proposal in 7 Steps

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
Whether you’re a B2B or a B2C company, you’re in the business of convincing customers to choose to spend their money with your business. For a B2B company that process usually involves a business proposal. In the B2B industry, once you've attracted new customers, which are most likely other businesses, you have to actually make a deal. Unlike B2C companies, who use marketing strategies and then hope their customers respond and purchase their product and service, there's a little more involved in this exchange. That's where your business proposal will come into the picture.
Luckily, even though your process and the exact format for your business proposal can be unique to your company, there is also a general formula you can follow to make things easier, especially the first few times you write a proposal.
In this guide, we'll walk you through the general steps of how to write a business proposal—including how to decide what kind of proposal you're writing, how you should organize it, and what information you should include.

How to write a b usiness proposal: 7 essential steps to follow
With these starting points in mind, let's get down to the process. Whether you’re just learning how to write a business proposal, or want to change up the one you’ve already been using, you’ll want to break down writing into a step-by-step approach. The organization is key when you’re writing a business proposal—structure will not only help you answer the core questions mentioned above, but it’ll also help you create consistent, successful proposals every time you’re pitching new business.
This being said, when writing a business proposal, you can break down the document into these sections:
Introduction
Table of contents
Executive summary
Project details
Deliverables and milestones
Bonus: Appendix (if necessary)
Step 1: Introduction
The introduction to your business proposal should provide your client with a succinct overview of what your company does (similar to the company overview in your business plan). It should also include what sets your company apart from its peers, and why it’s particularly well-suited to be the selected vendor to undertake a job—whether the assignment is a singular arrangement or an ongoing relationship.
The most effective business proposal introductions accomplish more with less: It’s important to be comprehensive without being overly wordy. You'll want to resist the temptation to share every detail about your company’s history and lines of business, and don’t feel the need to outline every detail of your proposal. You'll want to keep the introduction section to one page or shorter.
Step 2: Table of contents
Once you've introduced your business and why you're the right fit for the client you're submitting the proposal to (a quasi-cover letter), you'll want to next create a table of contents. Like any typical table of contents, this section will simply outline what the client can expect to find in the remainder of the proposal. You'll include all of the sections that we'll cover below, simply laid out as we just did above.
If you're sending an electronic proposal, you may want to make the table of contents clickable so the client can easily jump from section to section by clicking the links within the actual table of contents.
Step 3: Executive summary
Next, your business proposal should always include an executive summary that frames out answers to the who, what, where, when, why, and how questions that you’re proposing to the client lead. Here, the client will understand that you understand them.
It's important to note that despite the word "summary," this section shouldn't be a summary of your whole business proposal. Instead, this section should serve as your elevator pitch or value proposition. You'll use the executive summary to make an explicit case for why your company is the best fit for your prospect’s needs. Talk about your strengths, areas of expertise, similar problems you’ve solved, and the advantages you provide over your competitors—all from the lens of how these components could help your would-be client’s business thrive.
Step 4: Project details
When it comes to how to write a business proposal, steps four through six will encompass the main body of your proposal—where your potential client will understand how you’ll address their project and the scope of the work.
Within this body, you'll start by explaining your recommendation, solution, or approach to servicing the client. As you get deeper within your explanation, your main goal will be to convey to the client that you’re bringing something truly custom to the table. Show that you've created this proposal entirely for them based on their needs and any problems they need to solve. At this point, you'll detail your proposed solution, the tactics you’ll undertake to deliver on it, and any other details that relate to your company’s recommended approach.
Step 5: Deliverables and milestones
This section will nest inside the project details section, but it’s an essential step on its own.
Your proposal recipient doesn’t get merely an idea of your plan, of course—they get proposed deliverables. You'll outline your proposed deliverables here with in-depth descriptions of each (that might include quantities or the scope of services, depending on the kind of business you run). You never want to assume a client is on the same page as you with expectations, because if you’re not aligned, they might think you over-promised and under-delivered. Therefore, this is the section where you'll want to go into the most detail.
Along these lines, you can also use this section of the prospective client's proposal to restrict the terms and scope of your services. This can come in handy if you’re concerned that the work you’re outlining could lead to additional projects or responsibilities that you’re not planning to include within your budget.
Moreover, you might also want to consider adding milestones to this section, either alongside deliverables or entirely separately. Milestones can be small, such as delivery dates for a specific package of project components, or when you send over your first draft of a design. Or, you can choose to break out the project into phases. For longer projects, milestones can be a great way to convey your company’s organization and responsibility.
Step 6: Budget
There’s no way around the fact that pricing projects isn’t easy or fun—after all, you need to balance earning what you’re worth and proving value, while also not scaring away a potential client, or getting beaten out by a competitor with a cheaper price. Nevertheless, a budget or pricing section is an integral part of a business proposal, so you'll want to prepare your pricing strategy ahead of time before getting into the weeds of any proposal writing.
This being said, if you fear the fee might seem too high to your potential client, you might decide to break out the individual components of the budget—for example: social media services, $700; web copywriting $1,500—or create a few different tiers of pricing with different services contained in each. The second approach might not work for all types of businesses or proposal requests, but it may be worth considering if you’re worried about your overall fee appearing steep.
With these points in mind, once you've determined how to outline your pricing, you'll list it out (you might even include optional fees or services) and the overall cost for the scope of work you've described.
Step 7: Conclusion
Finally, your conclusion should wrap up your understanding of the project, your proposed solutions, and what kind of work (and costs) are involved. This is your last opportunity to make a compelling case within your business proposal—reiterate what you intend to do, and why it beats your competitors’ ideas.
If you're writing an RFP, again, meaning a potential client has requested this document from you, you might also include a terms and conditions section at this point. This end-on piece would detail the terms of your pricing, schedule, and scope of work that the client would be agreeing to by accepting this proposal.
Bonus step: Appendix (optional)
After the conclusion, you might also decide to include an appendix—where you add any supplemental information that that either doesn’t fit within the main proposal without being disruptive for the reader, or is less than essential to understanding the main components of your proposal. You’ll likely only need an appendix if you have stats, figures, illustrations, or examples of work that you want to share with your potential client. This being said, you might also include contact information, details about your team, and other relevant information in this section.
If you don't have any additional information to include, don't worry—you can end your business proposal with the conclusion section.
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
Business proposal considerations
Before you dive into determining how to write a business proposal that will give you a competitive edge, there are a few important things to keep in mind.
First, you'll want to make sure that you’re accomplishing the right objectives with your proposal. When writing a business proposal, you’re trying to walk a line between both promoting your company and addressing the needs of your would-be client, which can be difficult for any company to do.
This being said, you'll want to remember that a business proposal is different than a business plan, which you likely already wrote for your company when you were starting your business. Your business plan spells out your company's overall growth goals and objectives, but a business proposal speaks directly to a specific could-be client with the purpose of winning their business for your company.
With this in mind, in order to write a business proposal for any potential client, you'll need to establish your internal objectives and how these will contribute to the work you're proposing. To explain, you'll need to consider the following:
What tasks will need to be done for this work?
Who will do each task, and oversee the job at large?
What you’ll charge for the job?
Where will the work be delivered?
When will it be done?
Why are you the best fit for the job the client needs to be accomplished?
How will you achieve results?
Not only are these questions at the heart of clear and concise writing, but you also won't be able to write your business proposal without answers to them. So as you're going through the different pieces of your business proposal, keep in mind the objectives of your business, while also remaining persuasive regarding why the potential client should work with you instead of someone else.
The next important thing you'll need to keep in mind before you start writing a business proposal is what kind of proposal are you writing. Essentially, there are two types of business proposals—solicited proposals where someone requested the proposal from your company—and unsolicited proposals, where you're sending the document to another business unprompted.
In the case of solicited proposals, often called RFPs (short for a request for proposal), it’s likely that this potential client already knows at least a little about your business. With these kinds of business proposals, you'll want to spend less time convincing the client that you're the best small business consultant for the job and more on making your proposal feel custom to their specific brief, project, or problem. On the whole, the less generic your business proposal is, the more likely you are to win the work.
Unsolicited proposals, on the other hand, are much harder to sell.
As you’re writing a business proposal to a company that doesn’t know they may need your services, you’ll want to focus on getting them to understand why your company is specifically unique. You want to show them that you can add significant value to their business that they don’t already have. If there is currently someone performing the function you would like to, the sell will even be more difficult.
Business proposal examples
So, now that we've gone through all of the steps to show you how to write a business proposal, let's discuss some examples. As you go through the writing process, you might find it's helpful to consult external resources to review business proposal samples or templates and see how other businesses have structured these types of documents. Specifically, it might be even more helpful to review business proposal examples that relate to your particular industry—such as marketing, advertising, or finance.
General business proposal sample
If you're looking for a general business proposal example, you might consult BPlan, which offers advice, examples, and templates for the documents that are required to plan and operate a small business. In the BPlan sample, BPlan breaks their example into three overarching parts—a problem statement, a proposed solution, and a pricing estimate. This may be a good place to start if you're writing a business proposal for the first time and need a simple, general example to follow.
For a solicited proposal or RFP, you may want to reference a business proposal example that specifically operates under the assumption that you've been asked for this proposal. In this case, you may check out one of the downloadable RFP templates from Template Lab.
Template Lab offers both Word and PDF versions of their templates—and these business proposal samples will include sections more appropriate for RFPs including terms and conditions, scheduling, and points of contact.
Business proposal template services or software
For the most advanced and plug-and-play type business proposal samples, you may decide to utilize a service like Proposify or PandaDoc. These software services allow you to choose from their library of professionally designed and outlined business proposal examples (which are also usually industry-specific) and customize the template for your business's needs.
It's important to note, however, that although you may be able to sign up for a free trial for these services, most of them will eventually require a paid subscription.
5 best practices for writing a business proposal
Writing a business proposal can seem overwhelming at first, as it requires you to provide information about your company and its services as they relate specifically to what your prospect needs. As you go through the process again and again, however, it will become easier and easier to write a succinct and effective business proposal.
This being said, there are a few best practices you can keep in mind to help you as you get started:
1. Be direct.
Although you might feel the urge to show off your language skills while trying to impress a client, when you’re writing a business proposal, tour best bet to win business is to be clear, concise, and direct. You won't want to use overly flowery language or anything that could possibly be misconstrued.
2. Don’t leave room for ambiguity.
You'll want to make sure your proposal is straightforward and easy to understand, with no room for misinterpretation around what you say you’ll do or deliver.
Therefore, you'll want to avoid overly complicated industry jargon to be sure your client can understand exactly what you're talking about and what it means within the scope of your (and their) business.
3. Write for the right audience.
If you were writing a proposal for a specialty food business, it shouldn't look or sound exactly the same as if you were writing a proposal for an asset management company. You'll always want to keep your audience in mind as your craft and develop your proposal.
Ultimately, your best bet is to be straightforward, clear, and stick to the details, but you also shouldn't be afraid to tailor your writing to your audience so that your client feels that the proposal has truly been created with their business in mind.
This being said, your proposal should show that you not only understand your potential client but that you also respect them professionally.
4. Consider a title page.
Although this may not be necessary for a shorter business proposal, a title page can help with the general organization, flow, and professional feel of your document.
Like a title page for any other type of report, this one-page cover sheet would precede the remainder of your proposal and would likely include your business's name, contact information, and logo, as well as who you're submitting the proposal to.
Depending on your business or the potential client you're submitting the proposal to, you might decide that a title page is unnecessary, however, it's worth keeping in mind that it may be something to visually draw in your reader from the start.
5. Err on the side of brevity.
Finally, within the world of business proposals, shorter is usually better. This isn't to say, of course, that you should leave out details or omit important sections—it simply means that you should try to find the most succinct way to say what you need to say and get your point across to the potential client.

Start Your Dream Business
The bottom line
There's no doubt about it—learning how to write a business proposal is a lot of work. Luckily, however, you can follow our steps so you know what to include in your proposal and how to include it.
Ultimately, selling your services to potential clients is part of running and managing your business and as you do it again and again, it will only become easier.
This being said, as you go through the lifecycle of your business, you'll begin to accumulate a library of business proposals that you can continuously reference and use to develop your pitching strategy and writing process based on proposals that have and have not worked. And, hopefully, by taking the time to invest in this business proposal process, you'll be winning the work you need to grow your business.
This article originally appeared on JustBusiness, a subsidiary of NerdWallet.
On a similar note...

Business Plan and Proposal: Everything You Need to Know
A business plan and proposal are two different documents with two different purposes and functions. 3 min read updated on February 01, 2023
A business plan and proposal are two different documents with two different purposes and functions. A business plan is a document that clearly spells out how a business intends to realize its objectives and goals, while a business proposal is a sales document that a business entity uses to request a contract from a client.
Business Plan vs. Business Proposal
A business plan and a business proposal are different from each other by content, goals, writing style, and structure. The major difference between both is that a business plan is a document that presents facts, while a business proposal is a request for a deal and a quotation of prices.
A Business Plan
You can think of a business plan as the documentation of a company's grand vision. Business plans are naturally tactical. It's like stating where and when you want to start, when you want to get to the next point in view, and how you intend to accomplish that progress. A business plan includes descriptions of how the business is intended to run, the details of financial goals, possible business rivalry, marketing strategy, executive summary, and other factors that affect a company's planned business growth.
A business plan is particularly effective in making potential investors interested in a company (especially a startup company that's yet to make a name in its industry). Additionally, a business plan can provide an idea of what a company requires for professionals such as attorneys, accountants, and potential employees. A business plan distinctly describes the scope of the business, and in so doing, clears your thoughts as a business owner.
The business plan should be honestly made because it's the outline of the company's vision. It indicates whether or not the business goals of the company are realistically achievable. Experts say an effective business plan would take approximately six weeks of thorough research and groundwork to create. In other words, you typically can't create an effective business plan in one day, present it to potential investors the next day, and achieve desired results.
A Business Proposal
A business proposal goes to a prospective client directly from an established business. It's an attempt to sell a business entity's service or product to a client, and not an attempt to sell the business itself. Also, a business proposal isn't an estimate. Though costs and certain other details will be provided in the business proposal, an estimate is a lot more unofficial and simply a provision to skim over the costs. It doesn't present the entire picture.
Basically, business proposals show a particular idea, such as a new, profitable undertaking. The proposal is intended to get investors to support the particular business endeavor being suggested. For instance, a well-known eatery chain may wish to extend its business to a nearby state. Such an eatery would have to compose a business proposal in order to get the financial support of its target investors.
Though the business proposal provides an overview of what the company does (similar to a business plan), its major objective is to provide the details of the suggested business idea, including providing answers in advance for any concerns that could be raised by potential investors.

Components of a Business Plan
Basically, a business plan has three components: business model description, sales tactics, and financial goals. However, more elaborately, it has the following sections of information:
- Executive summary
- Description of products and services
- Industry analysis (analysis of possible business rivalry)
- Marketing strategy
- Operating plan
- Structure of leadership
- Internal analysis
- Built-out plan
- Introduction of management
- Financial goals (deliberations on monetary concerns, and how to address them and achieve expected results).
Solicited vs. Unsolicited Business Proposals
A solicited business proposal, when presented in response to a request for proposal (RFP), should be in the format requested by the client in their RFP. The same format may or may not be used for an unsolicited business proposal. Its purpose is to suggest and develop a business idea. Therefore, it's recommended to use the same format or some other format that's well-known in the field of endeavor.
An unsolicited business proposal offers a business entity the flexibility to choose what structure they deem appropriate. However, the proposal is expected to meet industry standards, no matter what format is used. For instance, it should emphasize major areas of interest, be thoroughly researched, offer a proposition of value, and feature a call to action.
If you need help with a business plan and proposal, you can post your legal need on UpCounsel's marketplace. UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- Business Proposal Ideas
- Comparison Between Business Proposal and Business Plan
- Business Contract Proposal
- Business Proposal Introduction
- How To Write A Business Proposal
- Writing A Contract Proposal
- LLC Business Plan Template
- Sample of a Good Business Plan
- Service Business Plan
- How to Contact Companies for Business

Business Plan vs. Business Proposal
The terms “business plan” and “business proposal” are sometimes used interchangeably, however, they are very different. The main difference between a business plan and a business proposal is that a business plan documents your growth strategy while a business proposal is a specific ask for someone to take an action you desire (e.g., buy your product/service, invest in your company, partner with you, etc.).
In this article, we will define a business plan and a business proposal and give you examples of when each is appropriate for you to use.
What is a Business Plan?

Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here
Business Plan Structure
Typically, the business plan structure contains the following 10 components:
- Executive Summary
- Business Description & Overview
- Market Research & Analysis
- Customer Analysis
- Competitive Analysis
- Marketing Strategy & Plan
- Operations Plan
- Management Team
- Financial Projections & Plan
It is recommended that a business plan is updated annually to adjust for changes in the industry trends and the business itself.
What is a Business Proposal?

In terms of what you are asking from them, it can be anything that involves funds and time on their end including cash investment, product development assistance, and even employees if they have applicable skill sets.
Business Proposal Structure
An invited business proposal is written in response to an RFP. A request for proposal (RFP) is a document that invites potential suppliers to submit business proposals. How to write a business proposal depends on the format requested and the questions included in the RFP.
The following are the components that usually make up a business proposal:
- Brief description of your company’s services/products as the proposed solution to the goals of the RFP
- Reiteration of the scope of the particular project
- Responses to questions asked in the RFP
- Cost of the project, including drafting services, materials, tools, labor, delivery and other expenses
An unsolicited business proposal is essentially the same format, but it will solicit the client’s business while anticipating the clients’ concerns and issues. A business proposal is more of a marketing document than an offer because it attempts to persuade the potential client to do business by demonstrating your value proposition and a call to action.
So, What’s the Difference Between a Business Proposal vs. a Business Plan?
In a business proposal, company representatives typically work with the customer to tailor a business proposition that is attractive to both parties. This usually comes in the form of a written document detailing the services and cost associated with fulfilling an offer or request but can also include electronic contracts.
In contrast, a business plan is a description of your company on the executive and operational levels aimed at investors for raising financial support or other stakeholders in order to facilitate long-term growth. For example, an investor will want to know about how different departments within your business interact with one another, while somebody who will be implementing your product probably only needs more limited information such as design specs because they are not going into production themselves.
A business proposal may provide you with more details of the project, but it does not include information about your company’s operations or future plans.
Examples of Business Plans vs. Business Proposals
- When you give a potential investor your business plan which includes all sorts of information about how we will achieve your goals together as well as the amount of money it’s going to take. The business proposal is for them to write you a check in return for interest/principal payments or a percentage of your company.
- You might be getting partners involved in your business who will help with product development and distribution. You are offering them a business proposal to work together. However, they may request to see your business plan to better understand your goals, potential profitability, and how you plan to reach these goals before deciding to work with you.
- Your existing business has been so successful that you decide to outsource the social media marketing efforts to a freelancer to free up more of your time. The freelancer would provide a business proposal stating their terms and conditions along with the agreed-upon pay arrangement for their services. This change in organizational structure may be noted in your business plan to demonstrate expansion and financial stability to continue growth.
- In your business plan , one of your goals is to grow your client base by 5% each month. You identify potential clients in need of your services or products and send an unsolicited business proposal to demonstrate how your products or services can benefit them in order to develop a new prospective client list.
The business plan is a roadmap for your company’s present and future, while the business proposal has to do with what you are asking someone else for money. Applying this difference into practice can be difficult at times because business plans are often marketed as business proposals. However, it is important to be able to identify the difference between a business plan and business proposal in order to maximize their effectiveness and importance with potential investors or partners.
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

How to Write a Business Proposal [Steps, Tips, & Templates]
You need to send a business proposal, and you want it to close. But how can you improve your chances?
Every year, we analyze the proposals sent with our software to discover what makes closing more likely. We used this research to craft this very guide .
To help you write better business proposals, we’ve curated the essential proposal format, a step-by-step process, plenty of templates to help you get started, and strategies for following up.
From images to esignatures, keep reading for data-backed insights into the most successful proposals.

What’s in this guide:
What is a business proposal?
Basic proposal format, what to prepare before writing a business proposal, how to write a business proposal in 7 steps, 8 business proposal templates, 5 ideas to take your business proposal to the next level, what to do after you send a business proposal, using analytics for business proposal insights.
A business proposal is sent by a salesperson or account manager to a prospective client in order to pitch a product or service. A great proposal should include an executive summary or cover letter, details on the project timelines and deliverables, what makes the company the right choice for the job, and pricing and payment details.
Business proposals are typically sent from one business to another for all sorts of different services, such as enterprise software subscriptions, interior design, accounting, marketing, event catering, etc.
The purpose of a business proposal is to:
Sell your product or service with details, client results, testimonials, etc.
Clarify what is and isn’t included in the proposal to accurately manage expectations
Layout terms and conditions to protect both parties
Lock in the deal right away with esignatures built into the proposal
Large corporations and government agencies will typically send out a request for proposal to competing companies and then choose the best (or cheapest) one.
A business proposal is very different from a business plan, because it is typically written to clarify a paid engagement between two companies. This might be a short project or a long contract. A business plan, on the other hand, is typically an internal document crafted to chart a businesses path forward towards goals, such as market expansion, revenue growth, new product lines, etc.
Types of business proposals
There are many different types of business proposals. They are typically broken down by industry.
Here are some common types of business proposals, by industry :
Real estate and construction
Professional services
Proposals can also be categorized based on the type of offering :
One-off projects
Recurring subscription
Ongoing service
Package options
Later on in this guide, we include a variety of proposal templates. Depending on what you selling, you might find it easier to begin with a template designed for your industry or for the type of offer you’re selling (such as a one-off project). So be sure to peruse through the previews of each proposal so that you can see which template will save you the most time.
Business proposal example
An excellent business proposal addresses the client’s pain points and showcases the proposed solution.
Here’s an example business proposal to inspire you. The accounting proposal kicks things off with an attractive cover page.

All in all, it includes the cover page, an executive summary letter, an about us section, team photos and bios, a project summary, a breakdown of the proposed services, a pricing section, onboarding steps, and a contract with esignatures.
The services breakdown offers a great example of how to categorize your services and provide hourly estimates.

After researching over 1 million proposals, we found that winning proposals are most likely to include all of the following.
Here’s the idea proposal structure :
1. Cover page
The cover page, also called a title page, should be kept simple. It prominently features a photograph or graphic design that is on-brand, you can use graphic design templates as a starting point. It also usually includes the project name, or the client name, as well as your company name. Some companies might include contact information on the cover page, while others will save that for a separate page.
Check out this cover page , which is bright, bold, and on-brand.

2. Executive summary
The executive summary is essentially your pitch.
It’s your shot at capturing the client’s attention and showing them that you have an approach that will exceed their expectations.
It’s typically written in paragraph form (1 to 3 paragraphs) but can also include a bulleted list for a more skimmable style.
Make sure that your executive summary includes:
A quick description of the client’s problem or starting point
How your company will serve the client and why you’re suggesting this unique approach
Why your company is the best choice (average results, unique selling propositions, differentiators, awards, etc.)
This content marketing proposal offers an excellent example of an executive summary. Though in this proposal, the section is instead titled “Focus and Objectives.” What makes it great is that it’s on brand, goal-oriented, personable, and skimmable.

3. Approach or solution
In this section, you write about your process and why you approach things the way you do. For example, a Facebook marketing agency might say that they believe that creative work is essential to advertising success, and that’s why they devote 90% of their time to developing videos, images, and copy.
Some companies will craft a custom approach section for each client, while others will re-use the section again and again. It all comes down to the number of services you offer and how much or how little you customize your work.
In corporate training, it’s essential to clarify your approach so the client knows why your system will be effective. In this training template example , their process shows the essential steps in their proprietary approach.

4. About the company
This is your chance to brag. In your company bio, be sure to mention all of the important things that set your company apart. That might include your management style, the talent you have on your team, your average client retention rate or contract length, and any accolades.
With their location, awards, and team structure, this About Us page is an excellent example of how to sell yourself with authority.

5. Deliverables
Use the deliverables section to summarize exactly what the client will receive from the engagement.
A TikTok ads management firm might include 15 ad creatives per month in their deliverables, for example. While an accounting firm might list the reports that will be sent weekly or monthly, along with the bookkeeping service.
In a construction project, on the other hand, the company might showcase the different milestones that the project will hit, and when these milestones are expected to be completed.
In this proposal , the Deliverables section is titled “Scope of Services,” and it includes a list of all of the services that the prospective client will receive. Deliverables are mentioned within the scope, including a logo, brand colors, business cards, and brand guidelines.

6. Social proof or work samples
No matter what you sell, prospective clients will want to know that you have the right experience for the job.
Social proof can come in the form of written testimonials and case studies, video testimonials and case studies, portfolio photographs, G2 and Capterra badges, and rating averages from Google, Trustpilot, or other review sites.
For an architecture firm, construction company, or website designer, work examples can prove more powerful than testimonials. Prospects want to see what you can do. This architecture proposal showcases the company’s work on a rehabilitation project.

The pricing section is of course the one that your clients will read again and again and deliberate over. That’s why it’s so important to make it clear, simple, and well-formatted.
Tables are a great way to showcase what’s included in the total project cost or to provide package options.
Similar to interior design and construction services, event planning typically includes both hourly costs and hard costs (for products and venues). Here’s an example of an event management proposal that includes a breakdown of the hourly work and the hard costs.
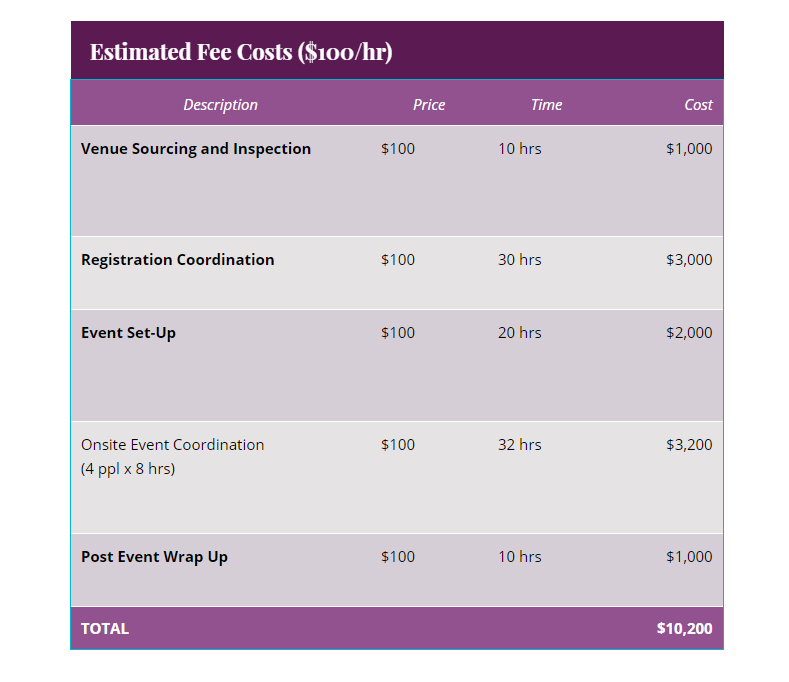
8. Terms and conditions
When you use modern proposal software , you can build a contract right into your proposal, eliminating the need for separate contract software.
Your proposal should include legal jargon that can protect both you and your client. You might have a statement of work and a master service agreement or terms and conditions.
In this website design proposal , there are 6 pages in total for the contract section. The potential client can easily click around to view all of these pages and share the proposal with their legal team if needed.

For proposals that are longer than 8 pages, it’s wise to include a table of contents. If you use Proposify as your proposal software, then every proposal will automatically have the table of contents on the left-hand side, making it easier for the potential client to click around and review important sections multiple times.
A lot goes into writing a proposal. Before you can get to the writing part, you need to prepare.
This means talking with the client to figure out their needs, using your experience to pitch the best project, and talking with colleagues who will be involved in the project to see if they agree on the services you plan to propose.
You might also need to talk with your legal department and ask them for a contract template that you can include at the end of the proposal so that when the client signs off, it's legally binding.
Everything you need to prepare to write a business proposal:
An understanding of the client's needs
Your determination of the best approach
Details that will get the client to say yes
Agreement with internal colleagues
The pricing options you want to offer
Knowledge of who needs to sign off
Legal contract language or templates
To be a good writer , you must be concise, specific, and detailed. It really is that simple. The more examples and details you provide, the better.
That said, it does help to follow a process so that you can be sure you’re providing everything that the decision-makers expect and more.
Here are the 7 essential steps for writing a business proposal:
Step 1. Determine the client’s needs
The first step is to figure out what your client needs.
As mentioned in our section on preparation above, you’ll need to speak with your client. If this is a new client, it might take two to five sales calls to collect all of the information you need. For an existing client, you can probably figure out what to include in their renewal proposal with just one call.
But of course, asking your client what they need isn’t enough. You need to use your expertise to choose the best solution for them, even if it’s not what they want or expect.
Step 2. Kick off your proposal with a template
Once you’ve done your due diligence, the next step is to choose a proposal template so you’ll save time on both writing and designing.
You can use a template that matches your specific business or click around to find one with all the sections and a design style you like. Even if it’s not created for your specific industry, it’ll be easy to update the content to match your service or product.
Check out our full library of proposal templates.

Step 3. Write the evergreen messaging about your company
It’s always smart to tackle writing section by section. This way, you don’t get overwhelmed.
We recommend starting with the sections that are relevant to your business and that can be reused again and again. Your value propositions should guide the content.
Tackle these sections:
The cover page
The approach section
The about us page and team bios
The social proof or portfolio pieces
By starting off with what makes your company special, you’ll break the ice during your writing process and also create your own custom template that you can use for further proposal writing.

Step 4. Craft the meat of the proposal (executive summary, approach, deliverables, etc.)
By now, you should have chosen a template and written your core company messaging.
Now it’s time to write the meat of the proposal.
In this step, you’ll be catering your proposal to the new client. A startup will require a different proposal than a small business, and the same goes for an enterprise.
Here are some of the things you might need to write:
The unique methodology or approach you’ll offer this client (if it changes per client)
The problem statement or executive summary
The client’s goals
The scope of work
The project process and timelines
The deliverables

You can fill in your template’s sections and take a peek at other templates to get inspiration and see if there are any additional sections or details you should add.
Step 5. Add in the project total or pricing options
Next, you should calculate your fees.
Depending on your business, you might add up flat rates, product costs, or hourly estimates to come up with a fixed project total. Or, you might present a price range that the project will likely fall between (making it clear that additional hourly costs could arise. Or perhaps, you’ll offer a pricing table with different options to choose from.

Step 6. Add legal terms and conditions and esignatures
When you use proposal software (instead of just a PDF or Google slides), you can add a contract directly to your proposal.
If you already have approved contract language from your legal department, you can simply add it to the contract section of your proposal in Proposify. If not, you’ll need to chat with your legal team or business lawyer to ensure you’re adding all the right stipulations.
Proposals with esignatures close 35% faster and are 426% more likely to be accepted. So be sure to assign an esignature both to yourself and your client.

Step 7. Finalize the design and review all of the content before sending
Now it’s time to review and finalize your proposal. Check for errors, places in the template you forgot to fill out, and wording that can be improved.
Make sure the graphic design is on point too. Switch out the template with your own brand colors and fonts. You can have a designer on your team handle this, or handle style customization yourself (with no design experience necessary).
The best way to write a business proposal? With a template of course.
We’ve rounded up 10 of the best templates for different types of businesses. And for each, we show you the proposal sections included to help you pick the right one for you.
Keep in mind that with any of these proposals, you can add and remove sections and also customize any page with text, headlines, images, videos, fee tables, and more.
1. Business consulting proposal template

This consulting proposal template can be used by any type of consulting firm.
Proposal sections :
Project Summary
Project Activities
Your Investment
2. Advertising Proposal Template
With this advertising proposal template, you can showcase your digital or traditional advertising services. The template includes TV, web, radio, and magazine, but you can update it to reflect your pitch.
Cover Letter
Who Are We?
Testimonials
Your Advertising Media Mix
3. Branding Proposal Template
Perfect for branding consultants, logo designers, and messaging strategists, this branding proposal template includes the project scope and timeline to help you clarify your process to potential clients.
Overview & Goals
Scope of Services
Sample Case Study
4. Commercial Lease Proposal Template
This commercial lease proposal template can be used for leasing office buildings, manufacturing facilities, warehouses, and event spaces.
Our Process
Meet Our Team
Terms and Conditions
5. Construction Bid Template
Use this construction bid template for new construction projects or renovations. It includes a detailed cost estimate table and a required deposit.
Cost Estimate
6. Catering Proposal Template
This catering proposal template is perfect for corporate projects but can work for weddings or personal events as well. You can use it for conferences, luncheons, retreats, or any other type of event.
Introduction
Event Details
7. Corporate Photography Proposal Template
With a beautifully designed portfolio section and a very detailed pricing table and print options, this is the perfect template for corporate photography . It also includes tips for success, so clients know how to make the most of their photoshoot time.
What We Offer
Photography Packages
Tips for Success
8. Financial Services Proposal Template
You can use this financial services proposal template to pitch financial services like risk management, budgeting, and investment management.
Services and Fees
Looking to kick up your proposals a notch?
Try one of these smart ideas:
1. Make your pricing dynamic
Dynamic pricing means that clients can choose what they want and that will automatically change the project total that they sign off on.
Proposals with options and add-ons have a 35.8% higher closing rate . Try giving package options and including add-ons such as ancillary services or maintenance work.
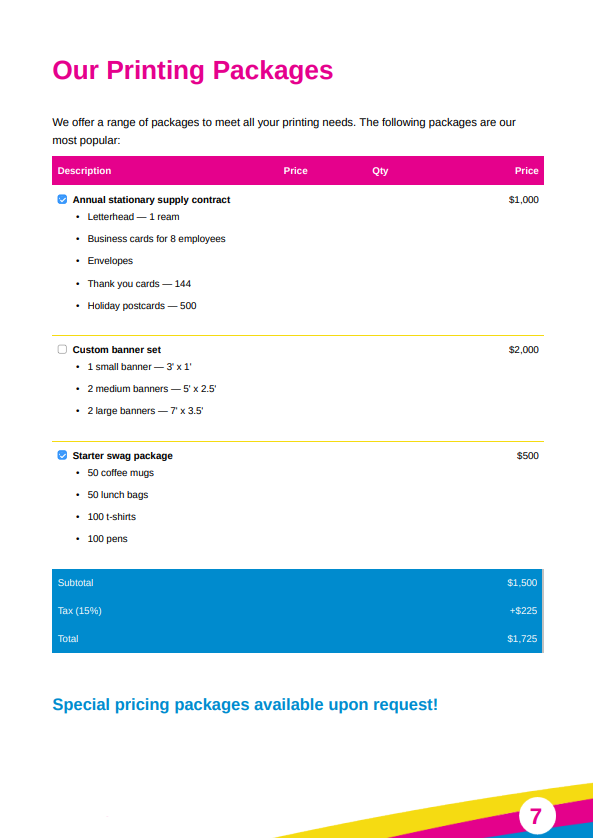
2. Create graphic designs for timelines and processes
Winning business proposals often include informative visuals to help clients understand your process at a glance.
You could create a graphic for project phases, milestones, or big deliverables.

3. Get creative with your social proof
Client testimonials are an easy starting point when it comes to social proof.
But can you do better? Can you get more creative and stand out from other consulting firms?
Here are some ways to improve your social proof game:
Include visuals for your average ratings (for example 4 and a half stars filled in).
Add any badges or graphics available from review sites like G2 and Trustpilot.
Film professional case study videos and embed them in your proposal.
Create a screenshare video where you talk through your digital portfolio samples.
Include an informal video testimonial from your client.
Add a video showing your team at work (ie, on the job site, running a workshop, speaking, etc.)
Write mini case studies with before and after transformations, result data, etc.
4. Have an “excludes” section
Is there something that is definitely not included in your proposal? Do clients often assume it’s included or do they get confused?
If so, try adding a section that describes everything that isn’t included in the proposal. You could mention that you don’t offer these services, or state that they’re available at an additional fee (if you want to upsell them).

5. Include videos for introductions or complex concepts
When you add a video to your proposal, you increase its chances of closing by 41% .
Here are some video ideas to try:
Informal intros filmed with Loom
Professional videos of your team at work
Case study videos
Quick descriptions of complex deliverables, methodologies, etc.

You sent the proposal. Now what?
Here’s what to do next.
Sign it yourself
Make sure you sign the proposal right away (before your client opens it). This offers a more professional presentation and makes it more likely that your new client will add their signature too.

Be prepared to follow up
Project proposals don’t always close all by themselves. As any good salesperson knows, follow-up is essential.
With Proposify, you can set up automated reminders. When we analyzed over 1 million proposals sent with our software, we found that proposals with pre-scheduled reminders have a 35% higher closing rate than those without.
Make adjustments to the proposal to close the deal
It’s okay to make changes. In fact, proposals that get revised are actually more likely to close than ones that don’t. When a client asks for revisions, it means they’re interested.
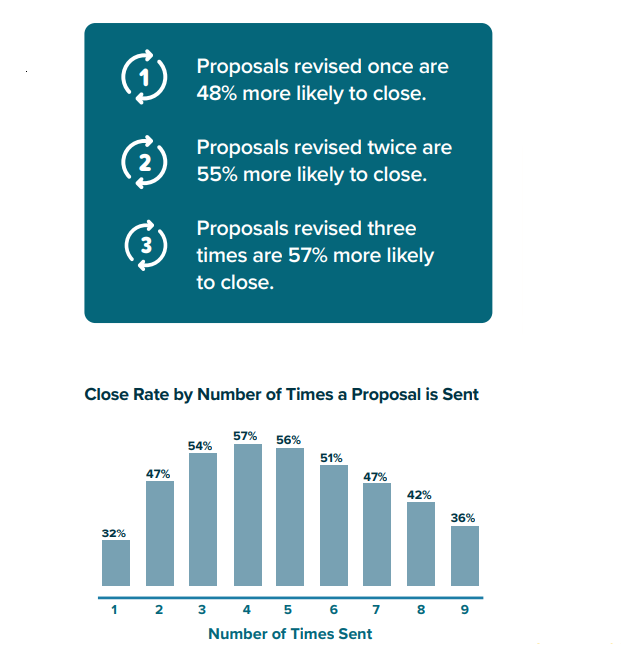
You might need to adjust your proposal document for its scope, deliverables, timeframe, or payment schedules.
Save different proposal templates
After you’ve created one proposal, you should save it as a template and give it a name. You might also want to duplicate it and adjust it to create a new proposal template. For example, if you offer SEO services , you might want to have one proposal for an SEO audit and another one for your monthly SEO retainer.
Create email templates
You can also create and store email templates that will save you time in the long run.
Try creating different templates for sending, reminders, and thank yous. If you offer different types of services, you can craft a unique sending template for each one.

Get feedback from clients on both won and lost proposals
One of the best ways to improve is to take feedback. Whether you win or lose the proposal, find out why.
Here are some tips on how to do this:
Won - When you win a proposal, you might ask the client why they decided to move forward with you on their first strategy call. Or, have their account manager ask the same question and pass the info to you.
Lost - If a client doesn’t sign the proposal after 3 weeks, you can send a quick email with something like, “Just looking for some feedback. Can you let me know why you decided not to move forward? Thanks.”
In today’s digital world, a business proposal should be more than a formal document.
When you use the right tool to create and send your proposal, you should be able to gather important insights and trends.
Viewing metrics for a specific client
With Proposify, you can see the activity for every proposal. Know when clients are opening and viewing proposals so you can follow up in a way that matches their activity.

Average viewing metrics
Proposify also offers average viewing metrics that help you benchmark your views:
Total viewed
Average time to view
Average length of viewing
Average views per proposal
This is great for gauging how a new client compares with past activity.

Average closing metrics
You can also check your average closing rate and track it over time.
Check these closing metrics:
Closing rate
Try setting goals for improving your closing rate and then check your progress each month.
Insights by proposal type
Segment viewing and closing metrics by workspace, client name, or stream. A stream is a custom category that you can use for different service types, client industries, etc.
Growth trends
And lastly, you can check your growth trends to find out how much you’re earning in new contracts and existing contracts. This is great for seeing your past revenue growth and for forecasting.
Trends include:
New won proposals (chart)
Active income (chart)
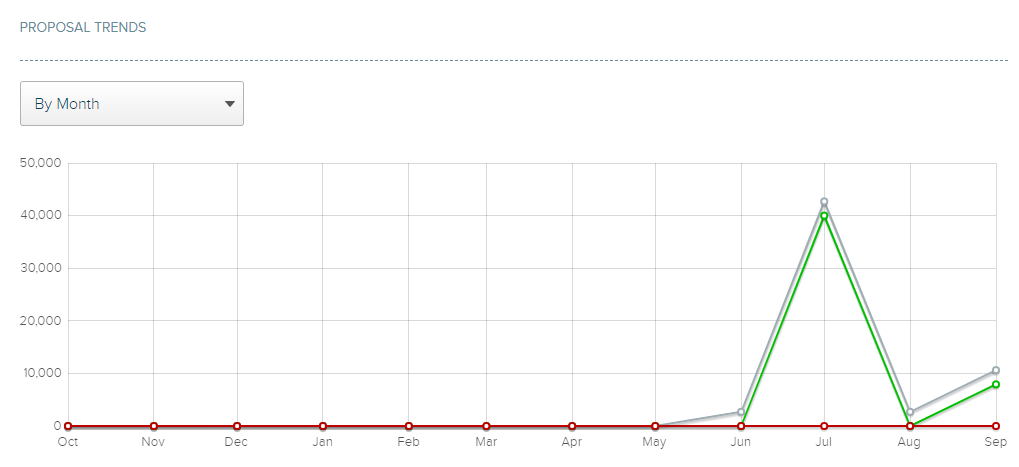
Start with a solid understanding of your client’s goals and needs. Use a template to save time creating messaging and tables that will seal the deal. Then, try advanced techniques like dynamic pricing and videos to improve your closing rates even further.
Sign up for Proposify free for 14 days or get started with one of our templates .

How to Create a Business Proposal That Closes Deals
June 28, 2022

Winning Proposal Structure Tips (What The Research Says)
June 21, 2022

Business Plan vs. Business Proposal: Everything You Need to Know
“Ok, so you sell things.”
Well, honestly, I wasn’t surprised or peeved at the half-baked knowledge of my friend’s father when he made a snap judgment and conveniently labeled my marketing profession as sales.
After all, this wasn’t my first time when someone tagged me as a salesperson. So, I took a deep breath and explained to him how sales are different from marketing.
We, humans, dwell in a herd mentality and hone our word skills from our surroundings. Sometimes, we are simply careless, sometimes oblivious, but most of the time, we actually don’t know that the word has a different meaning.
This can be ignored in a casual conversation, but using the wrong words in a business space can change the implied meaning and lead to miscommunication. For example, cost vs. price , digitization vs. digitalization , warranty vs. guarantee , machine learning vs. artificial intelligence , etc.
“Don’t use words too big for the subject. Don’t say ‘infinitely’ when you mean ‘very’; otherwise you’ll have no word left when you want to talk about something really infinite.” – C. S. Lewis
This Process Street guest post untangles the confusion between two crucial terms – business plan and business proposal. These are used interchangeably in the business world, but their meaning and application are pretty different.
Words are the building blocks of communication. There is a French phrase for using the right word – le mot juste .
Let us strive for le mot juste !
Hop on and be a part of this fantabulous journey.
What is a business plan?
What is a business proposal, business plan vs. business proposal: what are the differences.
- Bonus: How to make ‘wow’ business plans and business proposals?
Winding-up: Key takeaways
Here we go!
A business plan is a formal guide that acts as a blueprint, deciphering every root and branch to make a business successful. It is a written document that provides insights to internal and external stakeholders on business vision, goals, and strategies to achieve those goals.
“Without a plan, even the most brilliant business can get lost. You need to have goals, create milestones and have a strategy in place to set yourself up for success.” – Yogi Berra
A business plan, at its core, is an explanation of the below questions –
- Who are we?
- What are our offerings?
- Who are our customers?
- Who are the competitors?
- What is our competitive advantage?
- What are the business projections?
- What is the roadmap to achieve the goals – marketing, operations, research and development, manufacturing, and financial plans?
- What are the funding/investment requirements?
- What is the return on investment?
Why do you need a business plan?
A business plan is not a bag of puffery statements. It is a document with factual information necessary for the survival of a business. You can create a business plan with the right tools or opt for a good business coach to get you started.
Let’s see what Tim Berry , business plan expert, founder and chairman of Palo Alto Softwar and bplans.com , has to say on business plans.
“What I love most about business plans is the business planning: like walking, it’s constant correction and review and revision. Planning, done right, is steering a business, managing growth, aiming the business towards the right future.” – Tim Berry , Small Business Trends
According to a study done by Palo Alto Software, those who create business plans double their chances to succeed in business .
Let us get down to brass tacks and understand why a business plan is super-duper important.
Record and present business information The primary intent of a business plan is to record and communicate information. It must document the business goals and the methods to attain those goals in a structured manner. It keeps businesses on track with their objectives.
A blueprint for seeking business investment ️ Whether you are a fledgling start-up or an established business seeking expansion or diversification, writing a winning business plan acts as a magnet to attract investors. It builds confidence and trust among investors about the lucrativeness of a business idea.
Lay down the right path ✔️ Not everything discussed verbally at an ideation stage transforms into reality in a pragmatic environment. Jotting down a business plan differentiates achievable from impracticable based on market dynamics, opportunities and threats, and company’s strengths and weaknesses. It sets the right track for business growth.
Establish short-term and long-term goals A business plan sets down short-term and long-term goals and the direction to accomplish them, right from baby steps to giant leaps. It becomes a basis to revisit the goals from time-to-time and make iterations depending on the present scenario.
“Any business plan won’t survive its first encounter with reality. The reality will always be different. It will never be the plan.” – Jeff Bezos, CEO of Amazon
Get clarity on your business A frequent question that pops-up in business discussions is: “Are we doing it right?”
A well-articulated business plan brings insightful knowledge on each aspect of a business – from what it has to offer to how to market the offerings.
Make informed decisions A business plan is a reality check to track what is being fruitful and what is causing hindrance. It paves the way to make a business sustainable.
Predict future financial performance Financial projection is the spotlight of a business plan. It’s the carrot that captivates the eyeballs and tickles investors to fund a new business.
A promising business plan talks about the company’s future financial performance – expenditure, profit, revenue, etc.
Explore new business opportunities A business plan is a flexible document that enables learning on the go. It bolsters research and infuses businesses with new and more feasible business opportunities. It gives organizations a fresh outlook and ushers them to be a howling success.
How to prepare for a business plan
Now that we have answered the ‘what’ and ‘why’ of a business plan, let us move forward to solve the next riddle – how do you prepare it?
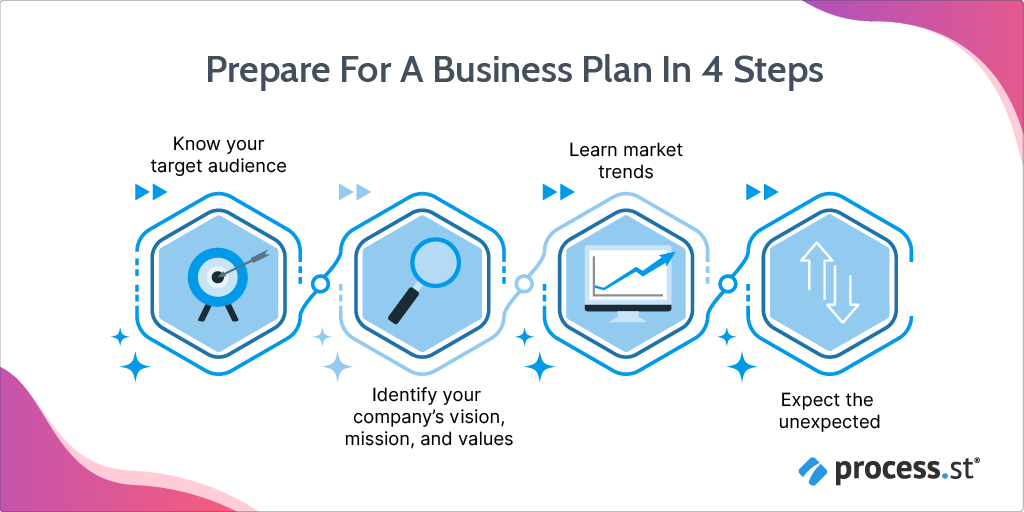
Identify your company’s vision, mission, and values Start by answering and figuring out your business personality:
- What do you desire to be?
- How do you want to be perceived?
- What values put your business in motion?
This is your organization’s compass that acts as a foundation for the succeeding steps.
Know your target audience Dig deep into:
- Whom are you going to cater to?
- What is your target market?
- What is the size and potential of the target market?
- What are the needs of a prospective customer?
- How are the needs addressed presently?
Learn market trends Identifying market trends keeps businesses ahead of the game. Analysis of industry data leads to business growth and profitability in the long run.
Weigh in the impact of unforeseen circumstances From financial turbulence to natural calamities and pandemics – a lot can go wrong in the future and leave a business shaking. Expect the unexpected and gird your loins for these testing times.
How to write a business plan
Creating a winning business plan increases the chances of success and spurs investors to fund your business.
According to a study published in Small Business Economics , entrepreneurs that create a plan are 152% more likely to start their business and appoint a registered agent and 129% more likely to push forward with their business beyond the initial start-up phase and grow it.
Here are the key components of an excellent business plan:
Executive summary First impression is the last impression!
An executive summary is a crucial part of this document. It provides the essence of the whole plan:
- Company details;
- Size and scope of business opportunity;
- A description of your offerings and how it will solve the problem;
- Growth projection;
- Financial requirements.
It should be informative and able to spark readers’ interest to know more about the business plan.
Overview of the business This section lists down information on:
- Your business;
- Your target market;
- Description of your products/services;
- Why and how your offerings are a great fit for prospective customers;
- Your capabilities to handle the demands;
- Your value proposition and competitive advantage.
…and all other related details.
Market analysis and strategies Put forth a strong case built on the solid rock of data analysis and statistics – present data on target market size, industry trends, sales forecasts, and marketing strategy.
Operating plan The operating plan highlights the operational requirements for the smooth functioning of a business. It includes facilities, supply chain management, inventory, manufacturing, shipment, logistics, staff management – everything under the sun that covers capital and expense (CapEx) requirements.
Growth plan This section answers the question: “Where do you see the business going in the next few years?” It provides visibility to investors on the milestones and how you will make money in near future.
Marketing plan Thee marketing plan section describes how to market the offerings to create and fulfill customers’ needs (who are the customers, product positioning, pricing policy, and promotional strategies?)
Management plan This section outlines how your organization is structured and basically how strong you are together. It describes the skills, background, and responsibilities of the management team. It builds conviction that the business is in good hands and has a proficient human capital.
Financial plan and projections This is the part where numbers become the king.
It draws up deets on inflow and outflow of money, sales forecast, profit and loss statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, and budget expense. It discloses and forecasts the company’s financial goals, profitability model, and charts a course for the coming years.
Conclusion and appendix Conclude the business plan by succinctly bringing out the key pointers – the business’s vision, mission, goals, strengths, and growth trajectory. Make it compelling and to-the-point. Add relevant appendices to strengthen your business plan.
Pro tip: Use an all-inclusive ready-made business plan template document and Process Street ‘s business plan workflow to create unbeatable business plans.
Business Plan Workflow
Click here to access the Business Plan Checklist!
Types of business plans
There are varying types of business plans depending on the purpose and usage:
- Business plan for start-ups A winning start-up business plan can be a game-changer to attract funding from investors. It should weave all key components to make it a promising investment – company overview, products/services, estimated costs, market evaluation, competition insights, risk analysis, cash flow projections, marketing strategies, and the management team’s strengths.
- Strategic business plan It lays down the details of a company’s strategies to fulfill its goals. It outlines the company’s vision, mission, strategy, and goals, the driving force for success, and the timelines.
- Internal business plan This plan moves the needle and steers focus on in-house planning and growth. It ensures that everyone grasps the company’s overall plan for growth. It prepares organizations to move forward by identifying and removing any blockages and assess and revise the strategies when required.
- Operations business plan It is an internal plan that maps out the nitty-gritties of a company’s operations plans and activities.
- Development business plan This is a development or an expansion plan of a business. It is used for both internal and external purposes. An external growth plan is written to attract investment from external sources. An internal development plan counts on its own business capabilities, revenue, and resources. It works as a guide to provide the right directions.
- Feasibility business plan A company scouts out a feasibility study when it plans to foray into a new venture, new product, or a new market. It articulates: How well will the product or service perform? Is the business promising? What is the expected return on investment (ROI)?
- What-if business plan At a point where you face unordinary conditions, you need a variation on the existing plan. A what-if business plan arranges to fall back on a contingency plan when things go sideways. For example, an unexpected surge in demand, new competition, drop in market size, etc.
A business proposal is the mantra that draws you closer to win a customer or bag a project.
Generally, it is a formal response to a Request for Proposal (RFP) sent by a prospective client looking for the right solution to their problems. It explains the particulars of a seller’s offerings and convinces the buyer that the proposed solution is the gateway to their business’s success and productivity.
“And, after all, winning business is what writing proposals is all about.” ― Tom Sant, Persuasive Business Proposals: Writing to Win More Customers, Clients, and Contracts
A business proposal comprises of four main points :
- What are the challenges of prospective clients?
- How can our solution solve their problems?
- Why should they choose us over others?
- What are the best pricing options available?
Why do you need a business proposal?
A business proposal is a testimony in itself that asserts, “I am the best you can get.”
Here are the reasons why you should and must make a business proposal :
- Create or leverage a business opportunity The prime motive is to win, win, and win! It is a medium to encash a business opportunity by putting forward an I-can’t-say-no-to-this proposal.
- Stand out from the competition It persuades the prospects that you are way ahead of other rivals in the industry in terms of the value you offer.
How to prepare for a business proposal
The heart of preparedness is research and further research. After all, the devil is in the details.
Talk to prospective customers, visit their website(s), read published articles, and be a know-it-all for your prospective clients.
Sort out the ‘who’ First and foremost, dig every possible information about the client:
- Who is the client (its vision, mission, and goals)?
- What does it produce?
- What are its key markets and target customers?
- What are its business growth plans?
- Which markets is it presently serving?
- Also, figure out the kingpins of a proposal approval process. This will help you to create a comprehensive proposal with all the necessary answers expected by the decision-makers.
Understand the challenges Find what’s bothering them and what is causing hindrance to their business success. Learn about their existing solution and its challenges.
Stitch the glitch and offer the best solution After a thorough review of all the points mentioned above, find the best solution to your prospective client’s problems.
List down key differentiators This will help you to beat the competition in the dust. It draws a comparison chart and puts you in a superior position.
According to Gray Mackenzie, founder of GuavaBox ,
“Prior to submitting a proposal, make sure you have clearly defined all the major points verbally with the potential customer. By discussing the scope, cost, timeline, and details prior to submitting a written proposal, you can uncover objections earlier in the process.” – Gray Mackenzie, 10 Sales Experts Share Their Best Business Proposal Tips
How to write a business proposal
Let’s get down to the fundamental elements that form a business proposal. Learn how to create a business proposal that stands out and close sales.
Title page/Cover page The name says it all.
Pretty easy-peasy thing to understand, right? After all, you have been creating the title pages since school days.
Still, make a note: Always write a gripping title that intrigues prospective clients’ interest and urges them to read on.
Other components that should be included on the title page are:
- Your company name and logo;
- Prospective customer’s name;
- Submission date.
Table of contents (TOC) As the name suggests, a TOC is a well-structured layout of the document. It helps to skim and scan and navigate speedily through different sections of a business proposal.
Executive summary It sets the tone for a proposal and makes the reader inquisitive about reading subsequent sections. It sums up the entire business proposal – the purpose of sharing the proposal and why and how your solution is the right fit for the prospective client. Leave no stone unturned to boast about your offerings in the executive summary.
Details of offerings This is an in-depth description of the products or services your company has to offer.
How will the offerings solve the client’s problems? This explains why your products/services are the right fit to address a prospective client’s needs and why it is a better alternative than the competition.
The methodology/implementation of offerings This section is a blanket explanation of how the promised deliverables will be executed. It provides step-by-step clarity on each action along with timelines. It gives the client peace of mind and builds trust and confidence in the offering.
Pricing, payment, and legal matters Here, you talk about the pricing structure, applicable taxes, payment schedule, cancellation policy, and how you plan to solve the legal matters (if any arise in the future).
Here are some tips for this section:
- Ensure that the pricing details are concise and complete.
- Providing a comparison chart with different pricing options helps to make decisions faster.
- Don’t go overboard with pricing, and also, don’t underrate yourself.
- Always refer to the RFP and verify if every request has been fulfilled.
- Separate out and create a new legal section if your business demands an extensive list of legal requirements.
Details about your company This is an exhaustive overview of your company. Don’t forget to add relevant customer testimonials, case studies, or success stories to build your case among prospective customers.
Signatures and Call to action This is the moment that gets butterflies in your stomach; the closure. This is the concluding part of a business proposal. Here (if all your prayers get answered), you and your client sign the proposal and secure the deal. Hurray!
Pro tip: Once you send the business proposal, don’t sit idle in your cocoon day-dreaming of winning the proposal. Always proactively do follow-ups with the prospective clients and clarify their doubts.
For start-ups or small businesses, drafting a business proposal can be an unnerving experience. They work fingers to the bone to write a perfect business proposal. Spending too much time on it might lead to missing the deadline and eventually losing out on a golden opportunity.
According to a report by Better Proposal , sending a business proposal within 24 hours increases the likelihood of winning the deal by 25%.
Here’s the secret sauce to speedily create flawless business proposals :
First, pick a professionally vetted and ready-to-use business proposal template and draft a business proposal like a cakewalk. Such as the Business Proposal Template included below.
Next, always use Process Street ‘s super-powered business proposal template checklist and ensure no step gets missed in the process.
Business Proposal Template Checklist
It even turns out a blessing for big businesses since they have to draft multiple proposals all the time. Templates and checklists save a lot of time, enhance productivity, and increase the chances of success.
Types of business proposals
Majorly, there are two types of business proposals:
Solicited business proposal Also known as an invited business proposal, it comes into play when a buyer, or a company, outlines its requirements and requests suppliers to present an offer. It can be a response to a public tender issued by big corporations or government agencies.
Alternatively, a solicited business proposal can also be submitted as a response to the RFP shared by a prospective client.
The difference between the two is that while the earlier one is open to all bidders, the latter’s scope is limited as it is shared with shortlisted suppliers.
Pro tip: Do a thorough check before submitting an invited business proposal. Missing out on-minute details can kick you out from their consideration list.
Unsolicited business proposal An uninvited or unsolicited business proposal is a proactive attempt to create a business opportunity. This proposal is sent to prospective clients without being asked.
The good news is, there are slim chances of your rival sending a business proposal simultaneously, so less or no competition.
The bad news is, it might breathe in the customer’s inbox for a few days and then, without being read, depart to the heavenly abode -the trash folder.
But still, like a cold call, it leaves some impression on prospective clients and shoots up the chances to cut a deal in the long run.
Pro tip: An unsolicited business proposal is mostly sent through emails. Make certain to write an attention-grabbing headline and a convincing explanation to draw attention.
Here’s a comparison chart that distinguishes between business plan and business proposal:
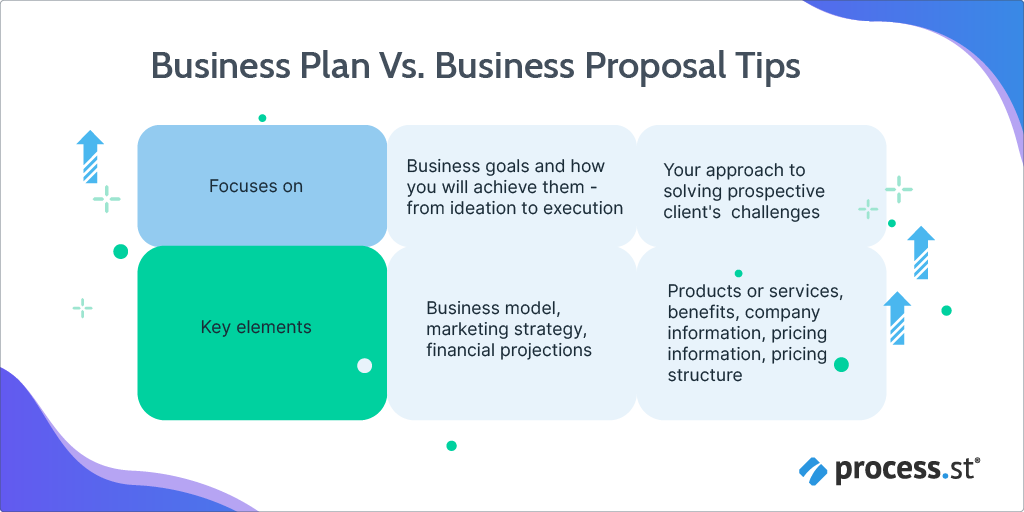
Bonus: How to make ‘wow’ business plans and business proposals
Here are the secret ingredients to make awesome and captivating business plans and proposals:
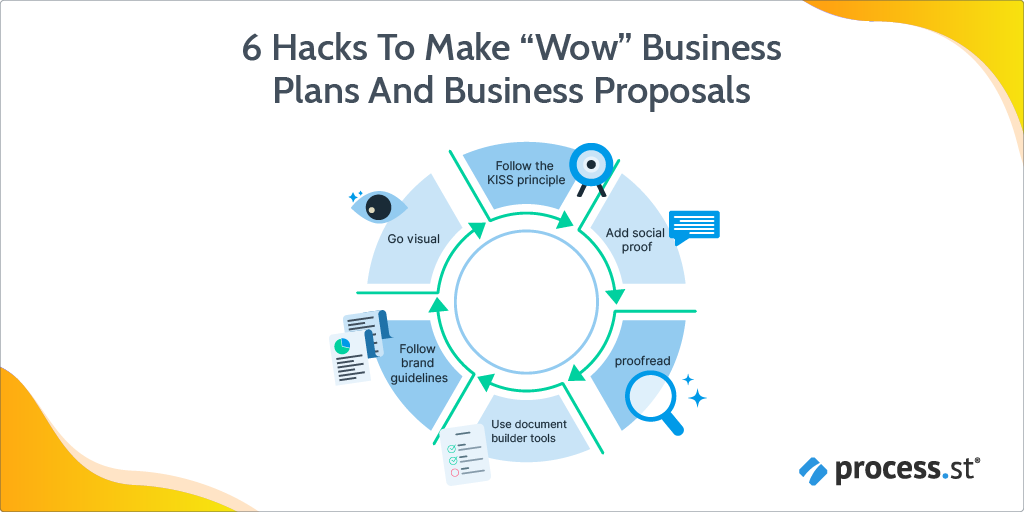
Follow the principle of KISS (Keep it simple, silly)
This is not the right place to brag about your vocabulary skills. You want the prospective customer to focus on reading rather than wasting time looking up for a word.
Always remember! Communication is the key.
So, go simple and ditch those heavy jargons.
Don’t wear-out the pupils of your prospects with long-winded documents. Capitalize on the multisensorial abilities of humans as well.
Visuals increase people’s desire to read content by 80%.
Leverage the power of visuals and make your document easily graspable by adding graphs, infographics, flowcharts, tables, images, and videos.
Add social proof
Do not forget to add positive feedback or customer testimonials. If similar projects have been delivered in the past, do add relevant links and case studies of that work. It helps to build trust and strengthen your case.
“Make sure you have great success stories that you can share with potential clients. At the end of the day, most, if not all, potential clients want to know you will provide value to them and generate positive ROI.” – Mathew Bivens, Podcast and marketing consultant, 10 Sales Experts Share Their Best Business Proposal Tips
Proofread ️
Ensure the document is free from grammar and spelling errors.
Follow brand guidelines
Your document should reflect your brand. Bring consistency in all your documents and design them as per the brand guidelines.
Use document builder tools ️
Time is money!
The likelihood of getting a ‘yes’ on your business plans and business proposals depends on how fast you can create a flawless document.
Empower your organization with a smart and all-in-one document builder tool like Revv – create, communicate, collaborate, and close your documents in no time.
Business plans and business proposals are two different worlds with distinct purposes and goals. But, both play a prime role in increasing the odds of business success.
People often get the wrong end of the stick and ask for a business plan when they mean business proposal or vice-versa.
But, we don’t need to worry about that since we are now clear on what is what.
Cheers to us!
P.S: Don’t forget to subscribe to the Process Street blog to get notified of our upcoming articles. We also have a podcast “Tech Out Loud” featuring content written by respected industry leaders such as Peep Laja , Sujan Patel , Tomasz Tunguz , and more!
What is your take on business plans and business proposals? Have you ever got your wires crossed with these two terminologies? Don’t forget to post your comments below.
Get our posts & product updates earlier by simply subscribing
Molly Stovold
Hey, I'm Molly, Junior Content Writer at Process Street with a First-Class Honors Degree in Development Studies & Spanish. I love writing so much that I also have my own blog where I write about everything that interests me; from traveling solo to mindful living. Check it out at mollystovold.com .
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Take control of your workflows today

550+ Business Plan Examples to Launch Your Business

Need help writing your business plan? Explore over 550 industry-specific business plan examples for inspiration.
Find your business plan example

Accounting, Insurance & Compliance Business Plans
- View All 25

Children & Pets Business Plans
- Children's Education & Recreation
- View All 33

Cleaning, Repairs & Maintenance Business Plans
- Auto Detail & Repair
- Cleaning Products
- View All 39

Clothing & Fashion Brand Business Plans
- Clothing & Fashion Design
- View All 26

Construction, Architecture & Engineering Business Plans
- Architecture
- Construction
- View All 46

Consulting, Advertising & Marketing Business Plans
- Advertising
- View All 54

Education Business Plans
- Education Consulting
- Education Products
Business plan template: There's an easier way to get your business plan done.

Entertainment & Recreation Business Plans
- Entertainment
- Film & Television
- View All 60

Events Business Plans
- Event Planning
- View All 17

Farm & Agriculture Business Plans
- Agri-tourism
- Agriculture Consulting
- View All 16

Finance & Investing Business Plans
- Financial Planning
- View All 10

Fine Art & Crafts Business Plans

Fitness & Beauty Business Plans
- Salon & Spa
- View All 36

Food and Beverage Business Plans
- Bar & Brewery
- View All 77

Hotel & Lodging Business Plans
- Bed and Breakfast
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy

IT, Staffing & Customer Service Business Plans
- Administrative Services
- Customer Service
- View All 22

Manufacturing & Wholesale Business Plans
- Cleaning & Cosmetics Manufacturing
- View All 68

Medical & Health Business Plans
- Dental Practice
- Health Administration
- View All 41

Nonprofit Business Plans
- Co-op Nonprofit
- Food & Housing Nonprofit
- View All 13

Real Estate & Rentals Business Plans
- Equipment Rental

Retail & Ecommerce Business Plans
- Car Dealership
- View All 116

Technology Business Plans
- Apps & Software
- Communication Technology

Transportation, Travel & Logistics Business Plans
- Airline, Taxi & Shuttle
- View All 62
View all sample business plans
Example business plan format
Before you start exploring our library of business plan examples, it's worth taking the time to understand the traditional business plan format . You'll find that the plans in this library and most investor-approved business plans will include the following sections:
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally only one to two pages. You should also plan to write this section last after you've written your full business plan.
Your executive summary should include a summary of the problem you are solving, a description of your product or service, an overview of your target market, a brief description of your team, a summary of your financials, and your funding requirements (if you are raising money).
Products & services
The products & services chapter of your business plan is where the real meat of your plan lives. It includes information about the problem that you're solving, your solution, and any traction that proves that it truly meets the need you identified.
This is your chance to explain why you're in business and that people care about what you offer. It needs to go beyond a simple product or service description and get to the heart of why your business works and benefits your customers.
Market analysis
Conducting a market analysis ensures that you fully understand the market that you're entering and who you'll be selling to. This section is where you will showcase all of the information about your potential customers. You'll cover your target market as well as information about the growth of your market and your industry. Focus on outlining why the market you're entering is viable and creating a realistic persona for your ideal customer base.
Competition
Part of defining your opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage may be. To do this effectively you need to get to know your competitors just as well as your target customers. Every business will have competition, if you don't then you're either in a very young industry or there's a good reason no one is pursuing this specific venture.
To succeed, you want to be sure you know who your competitors are, how they operate, necessary financial benchmarks, and how you're business will be positioned. Start by identifying who your competitors are or will be during your market research. Then leverage competitive analysis tools like the competitive matrix and positioning map to solidify where your business stands in relation to the competition.
Marketing & sales
The marketing and sales plan section of your business plan details how you plan to reach your target market segments. You'll address how you plan on selling to those target markets, what your pricing plan is, and what types of activities and partnerships you need to make your business a success.
The operations section covers the day-to-day workflows for your business to deliver your product or service. What's included here fully depends on the type of business. Typically you can expect to add details on your business location, sourcing and fulfillment, use of technology, and any partnerships or agreements that are in place.
Milestones & metrics
The milestones section is where you lay out strategic milestones to reach your business goals.
A good milestone clearly lays out the parameters of the task at hand and sets expectations for its execution. You'll want to include a description of the task, a proposed due date, who is responsible, and eventually a budget that's attached. You don't need extensive project planning in this section, just key milestones that you want to hit and when you plan to hit them.
You should also discuss key metrics, which are the numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common data points worth tracking include conversion rates, customer acquisition costs, profit, etc.
Company & team
Use this section to describe your current team and who you need to hire. If you intend to pursue funding, you'll need to highlight the relevant experience of your team members. Basically, this is where you prove that this is the right team to successfully start and grow the business. You will also need to provide a quick overview of your legal structure and history if you're already up and running.
Financial projections
Your financial plan should include a sales and revenue forecast, profit and loss statement, cash flow statement, and a balance sheet. You may not have established financials of any kind at this stage. Not to worry, rather than getting all of the details ironed out, focus on making projections and strategic forecasts for your business. You can always update your financial statements as you begin operations and start bringing in actual accounting data.
Now, if you intend to pitch to investors or submit a loan application, you'll also need a "use of funds" report in this section. This outlines how you intend to leverage any funding for your business and how much you're looking to acquire. Like the rest of your financials, this can always be updated later on.
The appendix isn't a required element of your business plan. However, it is a useful place to add any charts, tables, definitions, legal notes, or other critical information that supports your plan. These are often lengthier or out-of-place information that simply didn't work naturally into the structure of your plan. You'll notice that in these business plan examples, the appendix mainly includes extended financial statements.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. To get the most out of your plan, it's best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used for external purposes. Typically this is the type of plan you'll need when applying for funding or pitching to investors. It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or in any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear format in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It's faster to write out and update, and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan . This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business.
By starting with a one-page plan , you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You'll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan.
Growth planning
Growth planning is more than a specific type of business plan. It's a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, forecast, review, and refine based on your performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27 minutes . However, it's even easier to convert into a more detailed plan thanks to how heavily it's tied to your financials. The overall goal of growth planning isn't to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the growth planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and remain stable through times of crisis.
It's faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
Download a free sample business plan template
Ready to start writing your own plan but aren't sure where to start? Download our free business plan template that's been updated for 2024.
This simple, modern, investor-approved business plan template is designed to make planning easy. It's a proven format that has helped over 1 million businesses write business plans for bank loans, funding pitches, business expansion, and even business sales. It includes additional instructions for how to write each section and is formatted to be SBA-lender approved. All you need to do is fill in the blanks.
How to use an example business plan to help you write your own

How do you know what elements need to be included in your business plan, especially if you've never written one before? Looking at examples can help you visualize what a full, traditional plan looks like, so you know what you're aiming for before you get started. Here's how to get the most out of a sample business plan.
Choose a business plan example from a similar type of company
You don't need to find an example business plan that's an exact fit for your business. Your business location, target market, and even your particular product or service may not match up exactly with the plans in our gallery. But, you don't need an exact match for it to be helpful. Instead, look for a plan that's related to the type of business you're starting.
For example, if you want to start a vegetarian restaurant, a plan for a steakhouse can be a great match. While the specifics of your actual startup will differ, the elements you'd want to include in your restaurant's business plan are likely to be very similar.
Use a business plan example as a guide
Every startup and small business is unique, so you'll want to avoid copying an example business plan word for word. It just won't be as helpful, since each business is unique. You want your plan to be a useful tool for starting a business —and getting funding if you need it.
One of the key benefits of writing a business plan is simply going through the process. When you sit down to write, you'll naturally think through important pieces, like your startup costs, your target market , and any market analysis or research you'll need to do to be successful.
You'll also look at where you stand among your competition (and everyone has competition), and lay out your goals and the milestones you'll need to meet. Looking at an example business plan's financials section can be helpful because you can see what should be included, but take them with a grain of salt. Don't assume that financial projections for a sample company will fit your own small business.
If you're looking for more resources to help you get started, our business planning guide is a good place to start. You can also download our free business plan template .
Think of business planning as a process, instead of a document
Think about business planning as something you do often , rather than a document you create once and never look at again. If you take the time to write a plan that really fits your own company, it will be a better, more useful tool to grow your business. It should also make it easier to share your vision and strategy so everyone on your team is on the same page.
Adjust your plan regularly to use it as a business management tool
Keep in mind that businesses that use their plan as a management tool to help run their business grow 30 percent faster than those businesses that don't. For that to be true for your company, you'll think of a part of your business planning process as tracking your actual results against your financial forecast on a regular basis.
If things are going well, your plan will help you think about how you can re-invest in your business. If you find that you're not meeting goals, you might need to adjust your budgets or your sales forecast. Either way, tracking your progress compared to your plan can help you adjust quickly when you identify challenges and opportunities—it's one of the most powerful things you can do to grow your business.
Prepare to pitch your business
If you're planning to pitch your business to investors or seek out any funding, you'll need a pitch deck to accompany your business plan. A pitch deck is designed to inform people about your business. You want your pitch deck to be short and easy to follow, so it's best to keep your presentation under 20 slides.
Your pitch deck and pitch presentation are likely some of the first things that an investor will see to learn more about your company. So, you need to be informative and pique their interest. Luckily we have a round-up of real-world pitch deck examples used by successful startups that you can review and reference as you build your pitch.
For more resources, check out our full Business Pitch Guide .
Ready to get started?
Now that you know how to use an example business plan to help you write a plan for your business, it's time to find the right one.
Use the search bar below to get started and find the right match for your business idea.

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
We earn commissions if you shop through the links below. Read more
Business Plan vs. Business Proposal
Back to Business Plans
Written by: Carolyn Young
Carolyn Young is a business writer who focuses on entrepreneurial concepts and the business formation. She has over 25 years of experience in business roles, and has authored several entrepreneurship textbooks.
Edited by: David Lepeska
David has been writing and learning about business, finance and globalization for a quarter-century, starting with a small New York consulting firm in the 1990s.
Published on February 27, 2023 Updated on December 11, 2023

A business plan and a business proposal are similar documents. In fact, in some cases the terms can be used interchangeably, such as when both aim to attract investment.
But generally speaking, a business proposal tends to have broader scope, and this handy guide lays out precisely how these two common terms differ.
- What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a detailed document laying out how the business will function and develop in its first few years. The key is the “plan” part of the name, as it will specify how you will launch, gain customers, operate, make money, and, with any luck, expand.
Yet what many first-time business owners seem to forget is that a business plan is not a static document. The initial version is based largely on assumptions, supported by research. But as you run your business you’ll learn what works and what does not and make endless tweaks to your plan.
Thus, creating a business plan is not a one-time action – it’s a dynamic and continuous process of crafting and adapting your vision and strategy.
Components of a Business Plan
A business plan is generally much more detailed and broader than a business proposal, and has several elements :
- Executive Summary
- Company Description/Overview
- Products or Services Offered
- Market Analysis
- Marketing and Sales Strategies
- Operations and Management
- Financial Plan
- What is a Business Proposal?
A business proposal is created in connection to a specific business deal being offered by one party to another. As mentioned, when you take a business plan to an investor, you’re proposing a business relationship, so in this case a business plan and a business proposal are much the same.
But a business proposal could also be for others purposes, including:
- Bringing on a partner
- Proposing a management contract to a person you want to hire
- Proposing a business relationship with a potential customer
- Proposing a partnership with another company
- Suggesting a deal to a member of your board of directors
A business proposal may offer specific terms for the potential relationship, or it may be just about the benefits the relationship will bring, with terms to be negotiated later. Essentially, it’s a sales tool to get people or companies to do business with you in some way.
Business proposals can be structured in various ways, but usually, they’ll include a summary of what your company can offer, a scope of the work to be done together, and sometimes, a price quote or a proposed structure of the business relationship.
Clearly, a business plan and a business proposal are similar – and can even be one and the same. At the same time, they can also serve very different purposes. Unlike a business plan, a business proposal can have a variety of aims and thus does not have a “one size fits all” structure.
Whichever one you need, be sure to take your time with the research and writing so your business has the best chance for success.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Featured resources.
Crafting the Perfect Business Plan: A Deep Dive with Upmetrics’ Vinay Kevadiya
Carolyn Young
Published on October 13, 2023
In the first segment of our conversation with Vinay Kevadiya, the visionary behind Upmetrics, we explored the platform’s origins and itsunique ...

LivePlan Software Review
Published on September 15, 2023
When you’re starting a business, a business plan is essential whether you’re going to obtain financing or not. Creating a business plan helpsyou ...

What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix?
Published on September 13, 2023
Launching a business involves countless tasks, and one of the crucial early hurdles is writing a business plan. Many entrepreneurs who aren’tlooki ...
No thanks, I don't want to stay up to date on industry trends and news.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans for May 2024 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How To Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A business proposal is a document designed to outline a business plan to convince potential client, investor or partner to engage in a business agreement with you or your company. It's basically a sales pitch in writing to persuade potential clients to show them benefits of working with you or your company for their business success.
A business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines the overall vision, strategy and goals of your business. In contrast, a business proposal is a targeted pitch to a specific client or ...
Here's an example of what a business proposal template looks like when done right: 2. Explain your "why" with an executive summary. The executive summary details exactly why you're sending the proposal and why your solution is the best for the prospective client. Specificity is key here.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Common items to include are credit histories, resumes, product pictures, letters of reference, licenses, permits, patents, legal documents, and other contracts. Example traditional business plans. Before you write your business plan, read the following example business plans written by fictional business owners.
A business proposal is a document you'd send to a prospective client, outlining the service you're offering, and explaining why you're the best person for the job. It's a pitch by a business or individual to complete a specific job or project, to supply a service, or, in some instances, to be the vendor of a certain product.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
A business proposal is a document that aims to secure a business agreement. Whether printed or digital, a business proposal is written by a business and offered to a prospective customer. In many cases, the prospective customer is also a business that's looking for the best B2B solution. The purpose of a business proposal varies.
Download as Google Doc. After you've downloaded our free template above, you can now customize it according to your business needs as you follow the steps to writing a proposal below: 1. Determine Sales Proposal Requirements. 2. Gather Necessary Information. 3. Design Your Proposed Solution.
Business Proposal vs. Business Plan. The common myth is that business proposals and business plans are interchangeable. The thing is, both tools are important for growing your business. Yet, they play different roles. Business proposals help you pitch your product and service to prospective customers. On the flip side, business plans lay a ...
This template encompasses all essential sections to showcase your offerings, including a summary, project overview, plan, co-branding prospects, benefits, terms and beyond. To get feedback about your proposal from coworkers quickly, you can invite them to your Visme project using Visme's collaborative features.
The template includes data widgets and a detailed list format to present your business services best. The pricing page features a three-tier pricing structure with corresponding services, making it easy to compare options. 3. Mobile Video Game Development Business Proposal Example.
Step 3: Executive summary. Next, your business proposal should always include an executive summary that frames out answers to the who, what, where, when, why, and how questions that you're ...
A business plan and proposal are two different documents with two different purposes and functions. A business plan is a document that clearly spells out how a business intends to realize its objectives and goals, while a business proposal is a sales document that a business entity uses to request a contract from a client.
The terms "business plan" and "business proposal" are sometimes used interchangeably, however, they are very different. The main difference between a business plan and a business proposal is that a business plan documents your growth strategy while a business proposal is a specific ask for someone to take an action you desire (e.g., buy your product/service, invest in your company ...
In this proposal, the Deliverables section is titled "Scope of Services," and it includes a list of all of the services that the prospective client will receive. Deliverables are mentioned within the scope, including a logo, brand colors, business cards, and brand guidelines. 6. Social proof or work samples.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 1. Create a Cover Page. The first thing investors will see is the cover page for your business plan. Make sure it looks professional. A great cover page shows that you think about first impressions. A good business plan should have the following elements on a cover page:
A promising business plan talks about the company's future financial performance - expenditure, profit, revenue, etc. Explore new business opportunities. A business plan is a flexible document that enables learning on the go. It bolsters research and infuses businesses with new and more feasible business opportunities.
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea. The structure ditches a linear format in favor of a cell-based template.
A business plan is a document that helps small business owners determine the viability of their business idea. Combining market research and financial analysis, a professional business plan helps startup CEOs and potential investors determine if the company can compete in the target market. Typically, a good business plan consists of the following:
Business Plan. Business Proposal. Purpose. Outlines a company's mission, vision, and means to achieve its goals. Proposes a specific project or solution to a client or potential partner. Audience. Investors, stakeholders, financial institutions, and internal team. Potential clients, partners, or businesses. Content.
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...