Center for Teaching and Learning
Step 4: develop assessment criteria and rubrics.
Just as we align assessments with the course learning objectives, we also align the grading criteria for each assessment with the goals of that unit of content or practice, especially for assignments than cannot be graded through automation the way that multiple-choice tests can. Grading criteria articulate what is important in each assessment, what knowledge or skills students should be able to demonstrate, and how they can best communicate that to you. When you share grading criteria with students, you help them understand what to focus on and how to demonstrate their learning successfully. From good assessment criteria, you can develop a grading rubric .
Develop Your Assessment Criteria | Decide on a Rating Scale | Create the Rubric

Developing Your Assessment Criteria
Good assessment criteria are
- Clear and easy to understand as a guide for students
- Attainable rather than beyond students’ grasp in the current place in the course
- Significant in terms of the learning students should demonstrate
- Relevant in that they assess student learning toward course objectives related to that one assessment.
To create your grading criteria, consider the following questions:
- What is the most significant content or knowledge students should be able to demonstrate understanding of at this point in the course?
- What specific skills, techniques, or applications should students be able to use to demonstrate using at this point in the course?
- What secondary skills or practices are important for students to demonstrate in this assessment? (for example, critical thinking, public speaking skills, or writing as well as more abstract concepts such as completeness, creativity, precision, or problem-solving abilities)
- Do the criteria align with the objectives for both the assessment and the course?
Once you have developed some ideas about the assessment’s grading criteria, double-check to make sure the criteria are observable, measurable, significant, and distinct from each other.
Assessment Criteria Example Using the questions above, the performance criteria in the example below were designed for an assignment in which students had to create an explainer video about a scientific concept for a specified audience. Each elements can be observed and measured based on both expert instructor and peer feedback, and each is significant because it relates to the course and assignment learning goals.
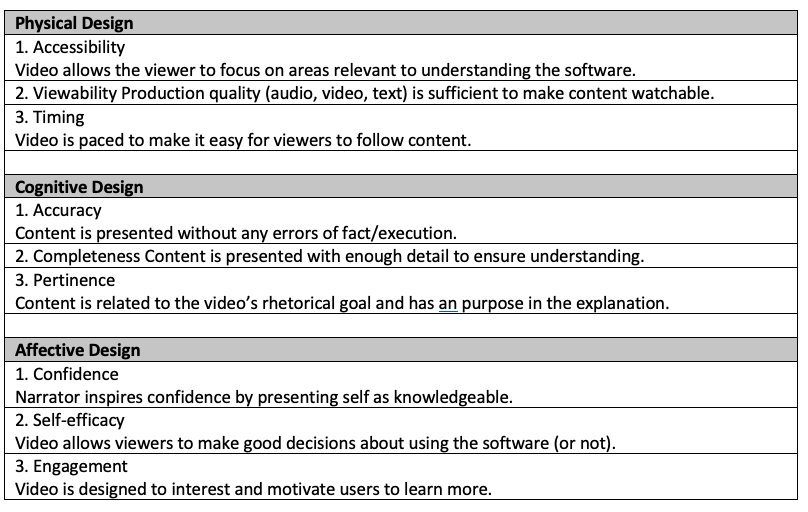
Additional Assessment Criteria Resources Developing Grading Criteria (Vanderbilt University) Creating Grading Criteria (Brown University) Sample Criteria (Brown University) Developing Grading Criteria (Temple University)
Decide on a Rating Scale
Deciding what scale you will use for an assessment depends on the type of learning you want students to demonstrate and the type of feedback you want to give students on this particular assignment or test. For example, for an introductory lab report early in the semester, you might not be as concerned with advanced levels of precision as much as correct displays of data and the tone of the report; therefore, grading heavily on copy editing or advanced analysis would not be appropriate. The criteria would likely more rigorous by the end of the semester, as you build up to the advanced level you want students to reach in the course.
Rating scales turn the grading criteria you have defined into levels of performance expectations for the students that can then be interpreted as a letter, number, or level. Common rating scales include
- A, B, C, etc. (without or without + and -)
- 100 point scale with defined cut-off for a letter grade if desired (ex. a B = 89-80; or a B+ = 89-87, B = 86-83, B- = 82-80)
- Yes or no, present or not present (if the rubric is a checklist of items students must show)
- below expectations, meets expectations, exceeds expectations
- not demonstrated, poor, average, good, excellent
Once you have decided on a scale for the type of assignment and the learning you want students to demonstrate, you can use the scale to clearly articulate what each level of performance looks like, such as defining what A, B, C, etc. level work would look like for each grading criteria. What would distinguish a student who earns a B from one who earns a C? What would distinguish a student who excelled in demonstrating use of a tool from a student who clearly was not familiar with it? Write these distinctions out in descriptive notes or brief paragraphs.
Ethical Implications of Rating Scales There are ethical implications in each of these types of rating skills. On a project worth 100 points, what is the objective difference between earning an 85 or and 87? On an exceeds/meets/does not meet scale, how can those levels be objectively applied? Different understandings of "fairness" can lead to several ways of grading that might disadvantage some students. Learn more about equitable grading practices here.
Create the Rubric
Rubrics Can Make Grading More Effective
- Provide students with more complete and targeted feedback
- Make grading more timely by enabling the provision of feedback soon after assignment is submitted/presented.
- Standardize assessment criteria among those assigning/assessing the same assignment.
- Facilitate peer evaluation of early drafts of assignment.
Rubrics Can Help Student Learning
- Convey your expectations about the assignment through a classroom discussion of the rubric prior to the beginning of the assignment
- Level the playing field by clarifying academic expectations and assignments so that all students understand regardless of their educational backgrounds.(e.g. define what we expect analysis, critical thinking, or even introductions/conclusions should include)
- Promote student independence and motivation by enabling self-assessment
- Prepare students to use detailed feedback.
Rubrics Have Other Uses:
- Track development of student skills over several assignments
- Facilitate communication with others (e.g. TAs, communication center, tutors, other faculty, etc)
- Refine own teaching skills (e.g. by responding to common areas of weaknesses, feedback on how well teaching strategies are working in preparing students for their assignments).
In this video, CTL's Dr. Carol Subino Sullivan discusses the value of the different types of rubrics.
Many non-test-based assessments might seem daunting to grade, but a well-designed rubric can alleviate some of that work. A rubric is a table that usually has these parts:
- a clear description of the learning activity being assessed
- criteria by which the activity will be evaluated
- a rating scale identifying different levels of performance
- descriptions of the level of performance a student must reach to earn that level.
When you define the criteria and pre-define what acceptable performance for each of those criteria looks like ahead of time, you can use the rubric to compare with student work and assign grades or points for each criteria accordingly. Rubrics work very well for projects, papers/reports, and presentations , as well as in peer review, and good rubrics can save instructors and TAs time when grading .
Sample Rubrics This final rubric for the scientific concept explainer video combines the assessment criteria and the holistic rating scale:
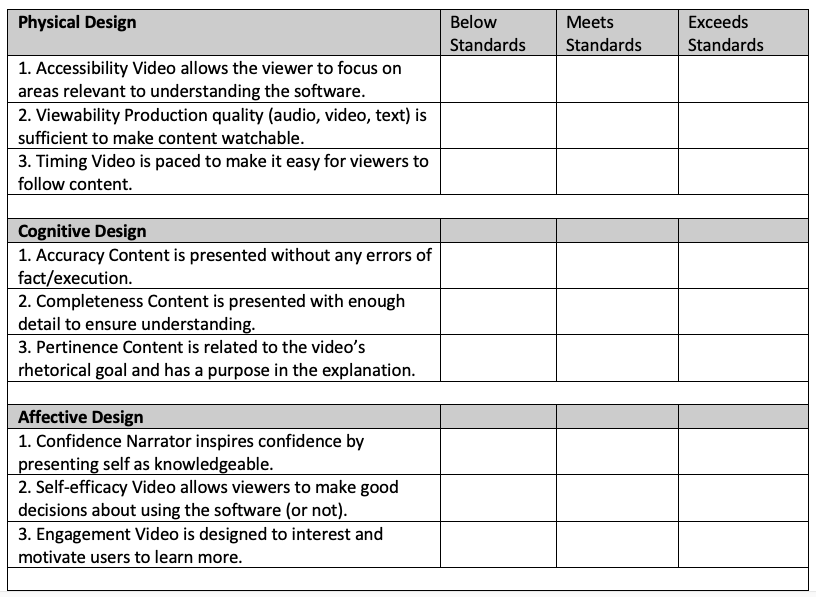
When using this rubric, which can be easily adapted to use a present/not present rating scale or a letter grade scale, you can use a combination of checking items off and adding written (or audio/video) comments in the different boxes to provide the student more detailed feedback.
As a second example, this descriptive rubric was used to ask students to peer assess and self-assess their contributions to a collaborative project. The rating scale is 1 through 4, and each description of performance builds on the previous. ( See the full rubric with scales for both product and process here. This rubric was designed for students working in teams to assess their own contributions to the project as well as their peers.)
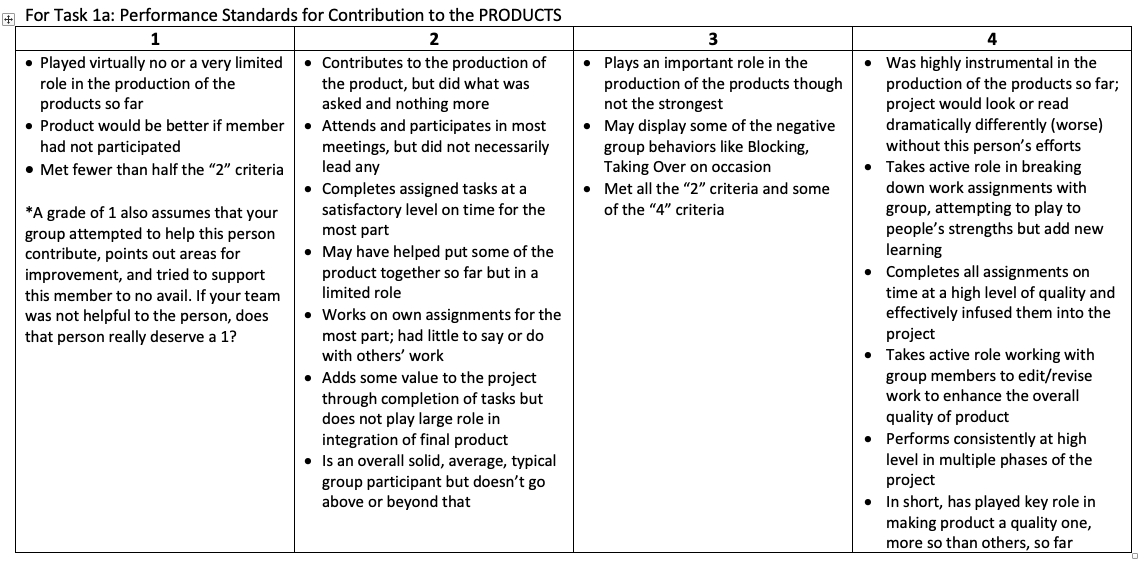
Building a Rubric in Canvas Assignments You can create rubrics for assignments and discussions boards in Canvas. Review these Canvas guides for tips and tricks. Rubrics Overview for Instructors What are rubrics? How do I align a rubric with a learning outcome? How do I add a rubric to an assignment? How do I add a rubric to a quiz? How do I add a rubric to a graded discussion? How do I use a rubric to grade submissions in SpeedGrader? How do I manage rubrics in a course?
Additional Resources for Developing Rubrics Designing Grading Rubrics (Brown University) Step-by-step process for creating an effective, fair, and efficient grading rubric.
Creating and Using Rubrics (Carnegie Mellon University) Explores the basics of rubric design along with multiple examples for grading different types of assignments.
Using Rubrics (Cornell University) Argument for the value of rubrics to support student learning.
Rubrics (University of California Berkeley) Shares "fun facts" about rubrics, and links the rubric guidelines from many higher ed organizations such as the AAC&U.
Creating and Using Rubrics (Yale University) Introduces different styles of rubrics and ways to decide what style to use given your course's learning goals.
Best Practices for Designing Effective Resources (Arizona State University) Comprehensive overview of rubric design principles.
Return to Main Menu | Return to Step 3 | Go to Step 5 Determine Feedback Strategy
Accessibility Information
Download Microsoft Products > Download Adobe Reader >

- Digital Teaching and Learning Tools
- Assessment and Feedback Tools
Assessment Criteria and Rubrics
An introduction.
This guide is an introduction to:
- Writing an assessment brief with clear assessment criteria and rubrics
- Grading tools available in Turnitin enabling the use of criteria and rubrics in marking.
Clear and explicit assessment criteria and rubrics are meant to increase the transparency of the assessment and aim to develop students into ‘novice assessors’ (Gipps, 1994) and facilitating deep learning. Providing well-designed criteria and rubrics, contributes to communicating assessment requirements that can be more inclusive to all (including markers) regardless of previous learning experiences, and or individual differences in language, cultural and educational background. It also facilitates the development of self-judgment skills (Boud & Falchikov, 2007).
- Assessment brief
- Assessment criteria
- Assessment rubric
- Guidance in how to create rubrics and grading forms
- Guidance on how to create a rubric in Handin
Terminology Explored
The terms ‘assessment brief’ , ‘assessment criteria’ and ‘assessment rubrics’ however, are often used interchangeably and that may lead to misunderstandings and impact on the effectiveness of the design and interpretation of the assessment brief. Therefore, it is important to first clarify these terms:
Assessment Brief
An assessment (assignment) brief refers to the instructions provided to communicate the requirements and expectations of assessment tasks, including the assessment criteria and rubrics to students. The brief should clearly outline which module learning outcomes will assessed in the assignment.
NOTE: If you are new to writing learning outcomes, or need a refresher, have a look at Baume’s guide to “Writing and using good learning outcomes”, (2009). See list of references.
When writing an assessment brief, it may be useful to consider the following questions with regards to your assessment brief:
- Have you outlined clearly what type of assessment you require students to complete? For example, instead of “written assessment”, outline clearly what type of written assessment you require from your students; is it a report, a reflective journal, a blog, presentation, etc. It is also recommended to give a breakdown of the individual tasks that make up the full assessment within the brief, to ensure transparency.
- Is the purpose of the assessment immediately clear to your students, i.e. why the student is being asked to do the task? It might seem obvious to you as an academic, but for students new to academia and the subject discipline, it might not be clear. For example, explain why they have to write a reflective report or a journal and indicate which module learning outcomes are to be assessed in this specific assessment task.
- Is all the important task information clearly outlined, such as assessment deadlines, word count, criteria and further support and guidance?
Assessment Criteria
Assessment criteria communicate to students the knowledge, skills and understanding (thus in line with the expected module learning outcomes) the assessors expect from students to evidence in any given assessment task. To write a good set of criteria, the focus should be on the characteristics of the learning outcomes that the assignment will evidence and not only consider the characteristics of the assignment (task), i.e., presentation, written task, etc.
Thus, the criteria outlines what we expect from our students (based on learning outcomes), however it does not in itself make assumptions about the actual quality or level of achievement (Sadler, 1987: 194) and needs to be refined in the assessment rubric.
When writing an assessment brief, it may be useful to consider the following questions with regards to the criteria that will be applied to assess the assignment:
- Are your criteria related and aligned with the module and (or) the course learning outcomes?
- What are the number of criteria you will assess in any particular task? Consider how realistic and achievable this may be.
- Are the criteria clear and have you avoided using any terms not clear to students (academic jargon)?
- Are the criteria and standards (your quality definitions) aligned with the level of the course? For guidance, consider revisiting the Credit Level Descriptors (SEEC, 2016) and the QAA Subject Benchmarks in Framework for the Higher Education Qualifications that are useful starting points to consider.
Assessment Rubric
The assessment rubric, forms part of a set of criteria and refers specifically to the “levels of performance quality on the criteria.” (Brookhart & Chen, 2015, p. 343)
Generally, rubrics are categorised into two categories, holistic and or analytic. A holistic rubric assesses an assignment as a whole and is not broken down into individual assessment criteria. For the purpose of this guidance, the focus will be on an analytic rubric that provides separate performance descriptions for each criterion.
An assessment rubric is therefore a tool used in the process of assessing student work that usually includes essential features namely the:
- Scoring strategy – Can be numerical of qualitative, associated with the levels of mastery (quality definitions). (Shown as SCALE in Turnitin)
- Quality definitions (levels of mastery) – Specify the levels of achievement / performance in each criterion.
(Dawson, 2017).
The figure below, is an example of the features of a complete rubric including the assessment criteria.
| 80% plus | (72, 75, 78) | (62, 65, 68) | (52, 55, 58) | (42, 45, 48) | Below 40% | |
When writing an assessment brief, it may be useful to consider the following questions with regards to firstly, the assessment brief, and secondly, the criteria and associated rubrics.
- Does your scoring strategy clearly define and cover the whole grading range? For example, do you distinguish between the distinctions (70-79%) and 80% and above?
- Are the words and terms used to indicate level of mastery, clearly outlining and enabling students to distinguish between the different judgements? For example, how do you differentiate between work that is outstanding, excellent and good?
- Is the chosen wording in your rubric too explicit? It should be explicit but at the same time not overly specific to avoid students adopting a mechanistic approach to your assignment. For example, instead of stating a minimum number references, consider stating rather effectiveness or quality of the use of literature, and or awareness or critical analysis of supporting literature.
NOTE: For guidance across Coventry University Group on writing criteria and rubrics, follow the links to guidance.
POST GRADUATE Assessment criteria and rubrics (mode R)
UNDER GRADUATE Assessment criteria and rubrics (mode E)
Developing Criteria and Rubrics within Turnitin
Within Turnitin, depending on the type of assessment, you have a choice between four grading tools:
- Qualitative Rubric – A rubric that provides feedback but has no numeric scoring. More descriptive than measurable. This rubric is selected by choosing the ‘0’ symbol at the base of the Rubric.
- Standard Rubric – Used for numeric scoring. Enter scale values for each column (rubric score) and percentages for each criteria row, combined to be equal to 100%. This rubric can calculate and input the overall grade. This rubric is selected by choosing the % symbol at the base of the Rubric window.
- Custom Rubric – Add criteria (row) and descriptive scales (rubric), when marking enter (type) any value directly into each rubric cell. This rubric will calculate and input the overall grade. This rubric is selected by choosing the ‘Pencil’ symbol at the base of the Rubric window.
- Grading form – Can be used with or without numerical score. If used without numerical score, then it is more descriptive feedback. If used with numerical scoring, this can be added together to create an overall grade. Note that grading forms can be used without a ‘paper assignment’ being submitted, for example, they can be used to assess work such as video submission, work of art, computer programme or musical performance.
Guidance on how to Create Rubric and Grading Forms
Guidance by Turnitin:
https://help.turnitin.com/feedback-studio/turnitin-website/instructor/rubric-scorecards-and-grading-forms/creating-a-rubric-or-grading-form-during-assignment-creation.htm
University of Kent – Creating and using rubrics and grading form (written guidance):
https://www.kent.ac.uk/elearning/files/turnitin/turnitin-rubrics.pdf
Some Examples to Explore
It is useful to explore some examples in Higher Education, and the resource developed by UCL of designing generic assessment criteria and rubrics from level 4 to 7, is a good starting point.
Guidance on how to Create Rubric in Handin
Within Handin, depending on the type of assessment, you have a choice between three grading tools, see list below, as well as the choice to use “free-form” grading that allows you to enter anything in the grade field when grading submissions.
- None = qualitative
- Range = quantitative – can choose score from range
- Fixed = quantitative – one score per level
Guide to Handin: Creating ungraded (“free-form”) assignments
https://aula.zendesk.com/hc/en-us/articles/360053926834
Guide to Handin: Creating rubrics https://aula.zendesk.com/hc/en-us/articles/360017154820-How-can-I-use-Rubrics-for-Assignments-in-Aula-
References and Further Reading
Baume, D (2009) Writing and using good learning outcomes. Leeds Metropolitan University. ISBN 978-0-9560099-5-1 Link to Leeds Beckett Repository record: http://eprints.leedsbeckett.ac.uk/id/eprint/2837/1/Learning_Outcomes.pdf
Boud, D & Falchikov, N. (2007) Rethinking Assessment in Higher Education. London: Routledge.
Brookhart, S.M. & Chen, F. (2015) The quality and effectiveness of descriptive rubrics, Educational Review, 67:3, pp.343-368. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00131911.2014.929565
Dawson, P. (2017) Assessment rubrics: Towards clearer and more replicable design, research and practice. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 42(3), pp.347-360. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2015.1111294
Gipps, C.V. (1994) Beyond testing: Towards a theory of educational assessment. Psychology Press.
Sadler, D.R. (1987) Specifying and promulgating achievement standards. Oxford Review of Education, 13(2), pp.191-209.
SEEC (2016) Credit Level Descriptors. Available: http://www.seec.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/SEEC-descriptors-2016.pdf
UK QAA Quality Code (2014) Part A – Setting and Maintaining Academic Standards. Available: https://www.qaa.ac.uk/docs/qaa/quality-code/qualifications-frameworks.pdf

Head of Academic Development. Keen interest in things digital.

IOE - Faculty of Education and Society

Understanding assessment requirements
Learn to understand and meet assessment requirements.
- Titles and instructions
Plan your assignment
Develop a research proposal, titles and instructions .
You may be given essay or assignment titles which you will need to interpret. If you are setting your own title, you still need to make sure the writing matches the title. The title is not simply an invitation to write anything you like about the topic. It will be asking for something specific, and is often closely related to the module content and the module reading.
What should I read for this assignment?
Reading is a very important part of any assignment. Start with the recommended reading lists for the module, and for the session(s) which relate to this title (if relevant). Although you will need to read more widely, do not try to 'start from scratch', or you will risk spending a lot of time searching through unrelated material. Start with your reading list, as the tutors have recommended these articles and books for a reason!
How can I analyse the title?
You can analyse your title using the following questions:
Which theory (or theories) is this question asking for?
Can you think of theories from the module which relate to this question?
What perspective(s) could you use to answer this question? Which perspective seems most suitable for you to use?
For example, a policy perspective, a critical race perspective, the perspective of the children, the perspective of a researcher.
What would you need to add to the question to be able to answer it?
For example, you may need to add the particular perspective you will use, or any definitions of terms.
Which terms would need to be defined for the purposes of your essay?
The "Definitions" section in Argument, voice and structure may help.
What position(s) could you take with relation to this question?
How could you actually answer the question? Is it a question where you could say yes/ no/ to some extent? Is it a question asking for a solution, or is it simply asking whether something is a problem? This is another way of saying what is your main thesis, or your main point.
Which examples could you use to help illustrate, support or explain your claims?
You may decide to use a combination of examples from your reading, examples from real-life experience, or even hypothetical examples. Remember that these examples will have different levels of importance within the essay.
These example title formats may help you to devise your own title. You can also analyse them using the questions above, to help understand what tutors might expect when they set a title.
- "The model of how people make choices presented by Krishnamurthy and Nagpal (2010) is too rational to be useful". Discuss.
- To what extent might marketers be able to affect the decisions which consumers make?
- Is there a solution to the problem of our insufficient understanding of how people make decisions?
- What is the relationship between the order people view products, and their final choice of product? Discuss the possible significance of this relationship.
- With reference to at least TWO studies, compare approaches to the study of how people make decisions.
- To what extent are you convinced by Bruce's (2011) position regarding approaches to decision making?
Back to top
Follow the basic steps below to plan your assignment.
1. Check the assessment criteria
Check the current student handbook (you will need to download the pdf file from the Moodle page for your course). Search for the criteria in the handbook using the 'Search' function. Please look at these criteria before you start writing your assignment.
2. Address the question/assignment/instructions
It is important to address the question(s) or instructions as directly as possible. Follow these three steps:
Analyse the question/title
What type of question, title, or instruction is it? Is it a yes/no question? Is it a why question? Is it an open question? Is it asking you to critically discuss an issue? Are there two sides? (Are there more than two sides?) Is it asking for a comparison? Is it asking for an evaluation of evidence? Is it asking for a discussion of a causal relationship (a relationship of cause and effect/contributing factors)? Is it asking for a critical discussion of an article or book chapter?
Try to look past the details and identify what the simplest form of the question/ instruction is. In simple terms, what might the answer to this question be? What evidence would be needed to support this type of answer? ("Yes, because...")
Generally, assignment instructions are not invitations to discuss an issue in a roundabout way. They are asking for a direct response. Try to identify what type of response is required. You also need to pay attention to what type of information will be required when answering the question. Are there any particular theories which you will need to refer to?
Are there any terms in the title which need to be defined, for the purposes of your discussion? This might include terms which can have different meanings in different circumstances. You can probably find definitions of terms in one of the recommended books, by looking in the introduction or first chapter.
Further reading
- "Titles and instructions" in Understanding assessment requirements
Gather information
Before you can write your answer to the question, you need to gather information. In an academic context, this means information from relevant textbooks, journal articles, or published research reports or government policies. If you have a reading list from the course tutor, look at the recommended books on the reading list, and identify which will be relevant to your question. If you are not provided with a reading list, you should try to identify a textbook which provides an overview of the field, such as an introductory textbook.
Next, search in the content pages and index of the book to identify relevant sections. Read these sections, making notes about anything that might be connected to your question. Do not forget to record page numbers so that you can easily find the information again, and so that you can refer to it correctly in your essay. If you are being asked to review an article or book chapter, you will need to read this thoroughly several times. Unfortunately, there are no shortcuts to reading the text thoroughly. The more times you read it, the more you will be able to say about it.
- "Read confidently" in Academic reading: Reading critically
Generate ideas
Look at the information you have gathered, and work out how this could fit into a direct response to the essay title or an answer to the question. Make sure that you have evidence to support your claims. The evidence needs to be taken from the reading you have done (and do not forget you will report it with references, as described below).
- "Critical reading questions" in Academic reading: Reading critically
"Avoiding plagiarism for beginners" in Referencing and avoiding plagiarism
3. Plan the structure
Plan your organisation/structure.
The overall structure will be as follows: title, introduction, main body, conclusion. You will need an introduction and conclusion, but these do not add much to the content of your essay. Most of your planning needs to be how to organise the ideas in the main body. For the main body, make sure you plan how many sections you need to answer the question or address the title in the way you planned in step three above. You can experiment with planning different ways of organising the information. Choose an organisation that seems logical and that will be easy to read and follow.
What goes in the introduction?
- A brief explanation of why the topic is important, and the perspective you will take.
- If necessary, a definition of any terms from the title for the purposes of this essay.
- An outline of the organisation/structure your essay will follow.
- A brief statement or summary of your response/ your answer to the question (sometimes called your "conclusion" or "thesis statement").
A logical structure for the main body
In the main body, how can I persuade the reader that my structure is logical? Many different structures can work, but if you add linking sections at the beginning or end of your paragraphs, it will help the reader feel like there is a logical flow through the essay. Linking sections can include phrases such as "having discussed these two theories, the following section will provide an evaluation". You can see other examples of linking sections in many pieces of academic writing, and probably in the reports, articles or books you use to inform your own writing.
What goes in the conclusion?
- Re-state your answer to the question (sometimes called your "conclusion" or "thesis statement").
- A summary of your discussion.
- Any implications, consequences, or suggestions for further research.
Editing (important)
When I edit my essay, how can I check that I have persuaded the reader that I have answered the question directly? Read your essay again, and check that each paragraph is either connected to the next through a linking phrase, or that there is some link to the question. As mentioned above, you can see examples of this when you read other academic work or textbooks.
- "Introductions", "Conclusions", "Organise, structure and edit", "Linking and transitions" in Argument, voice, structure
- "Editing tips" in Reviewing, editing and responding to feedback
4. Combine your own ideas with the work of others
This is an important aspect of the essay, but many people find it challenging. The most important aspects are understanding how to include your own judgement in an acceptable way in an academic context, and how to make sure you are referring to information in an acceptable format. The section on avoiding plagiarism shows you some examples of this.
Can I give my own opinion?
In every case, you need to make sure that any claim you make is supported with suitable evidence. Usually, in a straightforward essay, the best evidence comes from published work. This means that when you give your own opinion, it will be based on what another author has said. In an academic context, your opinion usually seems more valid if it is based on published evidence, for example explaining how or why you are convinced (or not convinced) by what someone else has written.
Sometimes people think the advice given above sounds strange, as they want to give their own view, but you need to remember the context in which you are writing. In an academic context, your opinion is much more "interesting" if it is an opinion about another piece of academic work or evidence from research, rather than something completely unsupported. Unfortunately, rather than seeing this as creative thinking, the academic community will be more likely to see it as lacking suitable evidence, examples or support. The safest way to give your own judgement in an academic situation, therefore, is to base your judgement on what someone else has written in a book or journal article, and reference that author.
How do I reference correctly?
Look at the section Referencing and avoiding plagiarism , and make sure you are referencing correctly.
Back to top
The sections below provide guidance on developing a research proposal as part of postgraduate / doctoral studies or when applying for a research grant. Please note that the guidance below is generic and you should follow any additional specific guidance given by your department or funding body.
What is a research proposal?
A research proposal provides a detailed plan of a research project before you undertake the research. A proposal is usually submitted before you undertake research for a final dissertation during postgraduate study, and before or during doctoral studies. A proposal may also be submitted as part of an application for a funding grant.
What to include in a research proposal
A research proposal will usually (but not always) include the following key elements:
- an outline of the background and context of the research topic/issue
- reasons why the specific topic / issue is important (rationale)
- a review of key literature related to the topic/issue
- an outline of the intended research methodology (including consideration of ethical issues)
- a discussion of ethical issues
- how the findings will be disseminated
- a timescale for the research.
Getting started
Start by choosing a topic or issue related to your course. A broader topic / issue will need to be narrowed down to a more specific focus that can be explored or investigated. Recommendations for further research at the end of published papers can be a useful source of ideas.
To help narrow down a topic/issue and plan your research project:
- Start by re-reading some of the research papers which you read as part of your course. Conduct a preliminary review of the literature related to the topic/issue. This can include literature related to theoretical concepts as well as practical research.
- Aim to identify what is currently known and whether there are any 'gaps' in existing knowledge. This will enable you to determine how your own research will contribute to and build on what is already known.
- Identify how research on the topic/issue has previously been conducted in terms of, for example: approach, methods, analysis of data.
- It will also be useful to refer to literature on research methods – check the recommended reading list for your dissertation module / Centre for Doctoral Education guidance.
- For Master’s level research, the contribution to existing knowledge does not necessarily need to be something completely new that has never been explored before. Your research could contribute to existing knowledge by, for example: adopting a less commonly used research approach / research method or focusing on a particular context (such as a school or country) where a limited amount of research has been conducted.
- For doctoral level research, there will usually be a need to demonstrate more originality.
Writing the Proposal
Below is an outline of the sections typically included in a research proposal. Specific guidance on how to structure the research proposal for a dissertation or doctoral research will usually be given by individual departments. If you are applying for doctoral research funding, specific guidelines will be stipulated by the funding body. It is important to follow specific guidance given by your department or funding body when writing your own research proposal for a dissertation or PhD application, but the following can be used as general guidance.
Title / working title of the research
An initial idea of the title should be given - this is likely to be revised as the research progresses and can therefore be a tentative suggestion at the proposal stage.
Introduction
The context and background of the research topic / issue, as well as the rationale for undertaking the research, should be outlined in the introduction section. Reference to key literature should be included to strengthen the rationale for conducting the research. This will enable the reader to understand what the research will be about and why it is important. At the end of the introduction, include an outline (or synopsis) of how the proposal is organised.
Literature review
This should expand on the key literature referred to in the introduction. The review of the literature will need to go further than listing individual studies or theories. You will need to demonstrate an awareness of the current state of knowledge and an understanding of key lines of argument and debates on the topic/issue. The literature will need to be critically analysed and evaluated rather than just described. This means demonstrating how studies, arguments and debates are linked and how the existing body of research links to your own research area/issue.
Research aims and questions
The research aims and research questions should be used to guide your research. The aims of the research relate to the purpose of conducting the research and what you specifically want to achieve. The research questions should be formulated to show how you will achieve the aims of the research and what you want to find out. The research aims and questions can either be stated at the end of the introduction (before the outline of the proposal) or after the literature review – guidance from your department / funding body may specify this.
Methodology
The methodology section of the proposal should outline how the research will be conducted. This should include a description and justification of: sample / participants, methods, data collection and analysis, and ethical considerations. To justify the chosen methodology, you can refer to recommended reading for research methods as well as previous studies conducted on your chosen topic.
Including a detailed discussion of the ethics of your research project can really strengthen the proposal. It forces you to think in very practical and detailed terms about what you are planning to do.
You may be required to include a schedule or plan of how you intend to conduct the research within a specified timeframe. This can be presented in a variety of ways but should generally include specific milestones (e.g. collection of data, analysis of findings) and intended completion dates.
Reference list
The reference list should include all sources cited in the research proposal. Departmental guidelines for referencing should be followed for in-text citations and the reference list.
The word count is a communication about the level of detail required. It would be possible to write a short statement of 80 words, or a thesis of 80 000 words, on the same topic. The word count lets you know information such as how much detail to give, how many main points and sub points to choose, and how detailed the examples should be.
What is included in the word count?
Please refer to your programme and module handbooks for guidance on word counts as requirements may differ slightly.
What does the word count mean?
At IOE, UCL's Faculty of Education and Society, you may be given the word count in one of the following ways:
- 2000 words: this means you need to write 2000 words, plus or minus 10% leeway. This means you need to write a minimum of 1800 words and a maximum of 2200 words. Generally, the more successful students will write more, rather than less, and will end up trying to reduce the word count to meet the limit. This is because they will have discussed the issues in more detail, given more examples and counter-examples, and used a significant amount of referencing and hedging language.
- 1500-2000 words: here, you need to write within the word count stated. There is no 10% extra leeway.
Remember that in academic writing, once you start adding referencing, hedging, and critical commentary, you need many more words to say the same thing. The word count will probably start to seem short by the time you have got used to writing in this way.
Back to top
Assessment Rubrics
A rubric is commonly defined as a tool that articulates the expectations for an assignment by listing criteria, and for each criteria, describing levels of quality (Andrade, 2000; Arter & Chappuis, 2007; Stiggins, 2001). Criteria are used in determining the level at which student work meets expectations. Markers of quality give students a clear idea about what must be done to demonstrate a certain level of mastery, understanding, or proficiency (i.e., "Exceeds Expectations" does xyz, "Meets Expectations" does only xy or yz, "Developing" does only x or y or z). Rubrics can be used for any assignment in a course, or for any way in which students are asked to demonstrate what they've learned. They can also be used to facilitate self and peer-reviews of student work.
Rubrics aren't just for summative evaluation. They can be used as a teaching tool as well. When used as part of a formative assessment, they can help students understand both the holistic nature and/or specific analytics of learning expected, the level of learning expected, and then make decisions about their current level of learning to inform revision and improvement (Reddy & Andrade, 2010).
Why use rubrics?
Rubrics help instructors:
Provide students with feedback that is clear, directed and focused on ways to improve learning.
Demystify assignment expectations so students can focus on the work instead of guessing "what the instructor wants."
Reduce time spent on grading and develop consistency in how you evaluate student learning across students and throughout a class.
Rubrics help students:
Focus their efforts on completing assignments in line with clearly set expectations.
Self and Peer-reflect on their learning, making informed changes to achieve the desired learning level.
Developing a Rubric
During the process of developing a rubric, instructors might:
Select an assignment for your course - ideally one you identify as time intensive to grade, or students report as having unclear expectations.
Decide what you want students to demonstrate about their learning through that assignment. These are your criteria.
Identify the markers of quality on which you feel comfortable evaluating students’ level of learning - often along with a numerical scale (i.e., "Accomplished," "Emerging," "Beginning" for a developmental approach).
Give students the rubric ahead of time. Advise them to use it in guiding their completion of the assignment.
It can be overwhelming to create a rubric for every assignment in a class at once, so start by creating one rubric for one assignment. See how it goes and develop more from there! Also, do not reinvent the wheel. Rubric templates and examples exist all over the Internet, or consider asking colleagues if they have developed rubrics for similar assignments.
Sample Rubrics
Examples of holistic and analytic rubrics : see Tables 2 & 3 in “Rubrics: Tools for Making Learning Goals and Evaluation Criteria Explicit for Both Teachers and Learners” (Allen & Tanner, 2006)
Examples across assessment types : see “Creating and Using Rubrics,” Carnegie Mellon Eberly Center for Teaching Excellence and & Educational Innovation
“VALUE Rubrics” : see the Association of American Colleges and Universities set of free, downloadable rubrics, with foci including creative thinking, problem solving, and information literacy.
Andrade, H. 2000. Using rubrics to promote thinking and learning. Educational Leadership 57, no. 5: 13–18. Arter, J., and J. Chappuis. 2007. Creating and recognizing quality rubrics. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson/Merrill Prentice Hall. Stiggins, R.J. 2001. Student-involved classroom assessment. 3rd ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall. Reddy, Y., & Andrade, H. (2010). A review of rubric use in higher education. Assessment & Evaluation In Higher Education, 35(4), 435-448.
- Help & FAQ
Assigning Projects to Project Managers in a Multiple-Project Management Environment: A Pilot Study of a Decision Support Model
- Black School of Business (Behrend)
Research output : Contribution to conference › Paper › peer-review
Project assignment is considered one of the critical project decisions since it influences the performance of projects, and eventually the performance of the organization. Despite its importance, the literature reveals two major gaps on project assignment criteria and methodology. To close these gaps, this study proposes an additional set of project assignment criteria and a systematic methodology for project assignments, so called, a decision support model for project assignments (DSM). By using the concepts of case study research combined with a literature review, the important potential criteria for project assignments are identified. These criteria are used in conjunction with the concepts of the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) and the integer programming (IP) to develop a DSM for one company. The DSM is executed and validated with the company's information. As a past of this research project, this paper illustrates the results of the pilot study developed for the feasibility study of the DSM development.
| Original language | English (US) |
|---|---|
| Pages | 236-245 |
| Number of pages | 10 |
| State | Published - 2003 |
All Science Journal Classification (ASJC) codes
- General Engineering
- Strategy and Management
Other files and links
- Link to publication in Scopus
- Link to the citations in Scopus
Fingerprint
- Decision Support Model Business & Economics 100%
- Project management Engineering & Materials Science 79%
- Project Manager Business & Economics 70%
- Managers Engineering & Materials Science 64%
- Project Management Business & Economics 62%
- Analytic hierarchy process Engineering & Materials Science 41%
- Integer programming Engineering & Materials Science 40%
- Industry Engineering & Materials Science 32%
T1 - Assigning Projects to Project Managers in a Multiple-Project Management Environment
T2 - A Pilot Study of a Decision Support Model
AU - Patanakul, Peerasit
AU - Milosevic, Dragan
AU - Anderson, Timothy
N2 - Project assignment is considered one of the critical project decisions since it influences the performance of projects, and eventually the performance of the organization. Despite its importance, the literature reveals two major gaps on project assignment criteria and methodology. To close these gaps, this study proposes an additional set of project assignment criteria and a systematic methodology for project assignments, so called, a decision support model for project assignments (DSM). By using the concepts of case study research combined with a literature review, the important potential criteria for project assignments are identified. These criteria are used in conjunction with the concepts of the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) and the integer programming (IP) to develop a DSM for one company. The DSM is executed and validated with the company's information. As a past of this research project, this paper illustrates the results of the pilot study developed for the feasibility study of the DSM development.
AB - Project assignment is considered one of the critical project decisions since it influences the performance of projects, and eventually the performance of the organization. Despite its importance, the literature reveals two major gaps on project assignment criteria and methodology. To close these gaps, this study proposes an additional set of project assignment criteria and a systematic methodology for project assignments, so called, a decision support model for project assignments (DSM). By using the concepts of case study research combined with a literature review, the important potential criteria for project assignments are identified. These criteria are used in conjunction with the concepts of the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) and the integer programming (IP) to develop a DSM for one company. The DSM is executed and validated with the company's information. As a past of this research project, this paper illustrates the results of the pilot study developed for the feasibility study of the DSM development.
UR - http://www.scopus.com/inward/record.url?scp=1442353186&partnerID=8YFLogxK
UR - http://www.scopus.com/inward/citedby.url?scp=1442353186&partnerID=8YFLogxK
AN - SCOPUS:1442353186
| | | | |
| > > > Adding Assignment Criteria to Assignment Rules This topic explains how to add assignment criteria to assignment rules.This task is a step in as well as a step in . Criteria are sets of conditions describing the attributes of objects or candidates, or both, that are evaluated to determine optimal assignment. Criteria are the fundamental building blocks for assignment rules. An assignment rule can contain none, one, or many criteria. Assignment rules use criteria to determine which candidates qualify as potential assignees. Criteria also determine which assignment rule should be evaluated in assigning an object. Assignment rules can be created with no criteria. A rule of this nature functions to make sure that data items of a particular type are assigned, that is, that all objects of the defined type pass. Use such rules carefully, because a rule defined with no criteria can make unnecessary assignments. To add an assignment criterion to an assignment rule Navigate to the Administration - Assignment screen, and then the Assignment Rules List view. In the Assignment Rules list, drill down on the assignment rule for which you want to create an assignment criterion, and then click the Criteria view tab (if not already active). In the Criteria list, click New. In the new criterion record, click in the available fields to enter the relevant information.If you want to query for an assignment criterion, you must use the name of the assignment criterion, not the display name for the assignment criterion object you configured using Siebel Tools. For example, if the name of the Account assignment criteria is ACCOUNT_ID, then you must use this name for your query, although the display name is Account. Similarly, do not use display names when querying seed assignment criteria. shows the predefined fields for assignment criteria. Table 24. Assignment Criteria Predefined Fields | ||
| Field Name | Description | Example Value |
|---|---|---|
Rule Criterion | The criteria evaluated for the assignment rule. | Product Defect Priority |
Comparison Method | Methods used by Assignment Manager to determine how objects and candidates are matched. Choices are: Compare to Object Compare to Person Compare Object to Person Compare to Organization Compare Object to OrganizationFor explanations of each method, see . For assignment criteria that use the Compare to Object, Compare to Person, or Compare to Organization comparison method, each criteria includes one or more values. | Compare to Object |
Inclusion | Methods used by Assignment Manager to determine how criteria values and candidates are matched. Choices are: Include, Include All Matching, Include All, and Exclude. For more information about each inclusion method, see . Depending on the Inclusion method, candidates that meet the criteria value have the criteria value score added to their total score. Criteria values can be defined as constants or can use wildcard characters to include a wider selection of potential matches between assignment rule and object. | Include |
Required | Determines whether the criteria is required. Choices are: Always Never When AvailableFor detailed information about the required field, see . | Always |
Score | Score for this criteria. Candidates that satisfy this criteria have this score added to their total score. For more information about how you can use the criteria score, see . | Not applicable |
Minimum Score | Minimum score required to qualify for this criterion. This field can be left blank. If the total score from all matching criterion values (calculated based on the inclusion method for the rule) is greater than or equal to the minimum score specified for the criterion, then the criterion passes. | Not applicable |
Inherited | If selected, indicates the criterion was inherited from a parent rule. This is a read-only field. If the Inherited flag for a criterion is TRUE in the Administration - Assignment view, the Read Only flag is TRUE in the Administration - Delegated Assignment views. If the Inherited field is not visible, use the Columns Displayed feature to make it visible (right-click, select Inherited, use the arrows to move Inherited from Available Columns to Selected Columns, and then click Save). | Not applicable |
Template | If selected, Assignment Manager excludes the criterion when processing rules. Assignment Manager does not process criteria templates until an inheritor of an assignment rule chooses to apply a template to the inherited rule. For more information about applying criteria templates, see . When a rule with a criterion using a template is inherited, the criterion is not automatically inherited with the other criteria. You must explicitly apply the criterion to the inherited rule. After the criterion is applied to the inherited rule, you can modify the criterion as you would any other criteria. If the Template field is not visible, use the Columns Displayed feature to make it visible (right-click, select Columns Displayed, use the arrows to move Template from Available Columns to Selected Columns, and then click Save). | Not applicable |
DA Read Only | If selected, makes a criterion read-only for delegated administrators. By checking this field, the assignment administrator (AA) makes sure the criterion is read-only to all users who view the rule from the delegated assignment views, including the owner of that child rule group. For example, if the AA creates Rule A in a rule group and that rule is inherited as Rule B in a child rule group, the AA can add a criterion to Rule B and make it read-only. The owner of the child rule group cannot change this setting. Without this flag, the owner of the child rule group could delete that criterion because it was not inherited from the parent rule. If the DA Read Only field for a criterion is TRUE in the Administration - Assignment view, the Read Only flag is TRUE in the Administration - Delegated Assignment view. If the DA Read Only field is not visible, use the Columns Displayed feature to make it visible (right-click, select Columns Displayed, use the arrows to move DA Read Only from Available Columns to Selected Columns, and then click Save). | Not applicable |
Figure 8 shows an example of an assignment criterion using the values from Table 24 . This example shows an always-required Product Defect Priority rule criterion for an assignment rule that is compared to service objects using the Include inclusion method.
| Copyright © 2010, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. | ||
UVP Explore tab
Online assignment criteria and overall platform rules
Online assignment criteria.
UNV screens all submitted assignment descriptions before publishing them. When you submit an assignment, make sure it…
Benefits sustainable human development
Your assignment description should clearly state how the Online Volunteer will contribute to sustainable human development and to the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) .
Only request online support
Your organization’s collaboration with Online Volunteers must take place online, and the final product must be submitted over the internet. Online Volunteers must not be asked to be physically present at any specific location. Online Volunteers must never be requested to make donations in-kind or financial contributions or to solicit donations from third parties. Furthermore, Online Volunteers must not be asked to supervise anyone.
Supports your own organization’s activities
Online Volunteering assignments must not be posted on behalf of another organization. It is important for online volunteers to know that the organizations they support have been properly screened and are in line with the Online Volunteering service eligibility criteria.
Is non-discriminatory
The Online Volunteering service is a global platform. Assignments should be inclusive, and Online Volunteers chosen based on their skills, knowledge, and experience free from any discrimination, defined as any unfair treatment or arbitrary distinction based on a person’s race, sex, religion, nationality, ethnic origin, sexual orientation, disability, age, language, social origin or other protected status.
Is written in English, French, or Spanish
Assignments must be posted in one of the three currently available languages: English, French, and Spanish. Upon prior agreement with UNV, some assignments may also be posted in Portuguese.
Is short-term
Online volunteering assignments are short-term and must be no longer than 12 weeks each. A properly defined task is one that has a clear beginning and end so that the individual managing the Online Volunteer and the Online Volunteers themselves can easily determine when the task is complete.
Is task-based
Online volunteering assignments are task-based, which means each task represents a piece of work that must be done to complete the project. The task must be straightforward and be clearly described in the assignment form. Your organization can request up to a maximum of 25 Online Volunteers for each task.
The UNV is available to guide you in designing “SMART” assignment descriptions that are in line with the above criteria. Together, we make sure that each assignment corresponds to a Specific task that can lead to a Measurable result and contribution to advance sustainable development. We check that the outcome of the online collaboration is Attainable considering task complexity and the number of Online Volunteers required. Explaining the bigger picture and giving due recognition motivates Online Volunteers and makes the assignment Rewarding for them. Finally, only Time-bound assignments allow Online Volunteers to pursue their other professional, academic or personal commitments while volunteering online.
In short, SMART assignments are attractive for Online Volunteers and yield great results for your organization!
Overall Platform Rules
Online Volunteer Legal Status
Please note that Online Volunteers shall not be deemed in any respect as being a UN Volunteer and, as such, shall not benefit from this status. In addition, they shall not be considered in any respect as being the employee, staff or agent of UNV or the United Nations.
Assignment Management
Each assignment represents the collaboration between the Online Volunteer and your organization on one clear task with a clearly described deliverable. Therefore, for each task requested by your organization, a separate assignment must be submitted. This also applies to already completed tasks for which another collaboration is requested. Assignments shall only be re-published in case the first round of applications did not end with a suitable Online Volunteer candidate. In case the collaboration was interrupted early, the assignment may be re-published to receive more applications, or a previous applicant may be contacted.
Assignments may be published for two weeks. However, it is suggested to close assignments after it has attracted a good number of qualified candidates or as soon as a suitable candidate to perform the task has been selected.
Online Volunteer Management
Please be aware that UNV reserves the right to put publishing of further assignments on hold when it determines candidates’ applications have not been adequately taken care of in previously published assignments.
Fundraising related assignments
When you seek help from Online Volunteers related to fundraising activities Online Volunteers must never be asked or requested to solicit donations/funds from third parties.
UNV reserves the right to take any action it deems appropriate should it become aware of any infringements of the assignment criteria or overall platform rules.

Cloud SYlla
Your Agile & Digital Partner
- Mar 2, 2023
Understanding Assignment Rules: A Comprehensive Guide

Assignment rules are an important feature of Salesforce that help businesses automate assigning records to specific users or teams based on predefined criteria. This article will discuss assignment rules, how they work, and the benefits they provide to businesses.
What are Assignment Rules?
Assignment rules are a set of criteria that are defined by businesses to determine how records should be assigned to users or teams within the Salesforce system. These criteria can be based on several factors, such as the record type, location, record status, or the user's role or territory. For example, a company may set up an assignment rule to automatically assign a new lead to the sales rep who covers that particular region or product line.
How do Assignment Rules Work?
When a record is created or updated, the assignment rules evaluate the record based on predefined criteria. The assignment rule automatically assigns the record to the designated user or team if the criteria are met. Once the record is assigned, the user or team can work on the record.
Salesforce provides a simple wizard that enables administrators to set up assignment rules. The wizard allows administrators to define the criteria for the assignment, select the user or team to assign records to, and set up any needed notifications or escalations.
How to Set Up Assignment Rules in Salesforce

Setting up assignment rules in Salesforce is a straightforward process that requires the following steps:
Identify the criteria for record assignment - Before creating an assignment rule, businesses should first identify the criteria used to assign records. It might include the record type, location, user role, or other custom fields.
Create the assignment rule - Once the criteria have been identified, businesses can create the assignment rule in Salesforce. It involves setting up a rule that evaluates the criteria and assigns records to the appropriate user or team.
Test the assignment rule - After the assignment rule has been created, businesses should test it to ensure it is working correctly. It might involve creating test records and verifying that they are assigned to the correct user or team.
Activate the assignment rule - Testing it in Salesforce will allow it to be activated. It allows it to automatically assign records to the appropriate user or team.
Types of Assignment Rules in Salesforce

Salesforce offers two types of assignment rules: standard assignment rules and lead assignment rules.
Standard assignment rules assign records to users or teams based on predefined criteria. They can be set up for various record types, including leads, cases, and opportunities.
Lead assignment rules are specific assignment rules used to assign leads to sales reps. They evaluate the criteria for a lead, such as location or product interest, and assign the lead to the appropriate sales rep based on a round-robin or customized assignment method.
Benefits of Assignment Rules
There are several benefits to using assignment rules in Salesforce, including:
Increased Efficiency
One of the most significant benefits of assignment rules is their increased efficiency. By automating the process of assigning records, sales, and customer support teams can spend less time manually assigning leads and cases to the appropriate users or teams. They can focus on more important tasks, such as following up with leads, resolving customer issues, and closing deals.
With assignment rules, businesses can streamline their processes and reduce the time it takes to respond to customer inquiries, ultimately improving their overall efficiency and productivity.
Improved Customer Satisfaction
Another important benefit of assignment rules is the improved customer satisfaction they can provide. Businesses can automatically assign cases to the appropriate user or team to ensure that customer inquiries are handled promptly and efficiently. Customers receive faster responses to their inquiries, which can help improve their overall satisfaction with the company.
In addition, by assigning cases to users with the appropriate skills and knowledge, businesses can ensure that customer issues are resolved more effectively, further improving customer satisfaction.

Accurate Data
Assignment rules also help businesses maintain accurate data in their CRM system. By automating the process of assigning records, businesses can ensure that data is entered correctly and consistently. It means that reports and analytics generated from the data are more accurate and reliable, which can help businesses make more informed decisions.
In addition, businesses can use assignment rules to enforce data validation rules, which can help prevent incorrect data from being entered into the system.
Consistency
Another benefit of assignment rules is that they help ensure consistency in record assignments. By automating the process of assigning records, businesses can ensure that records are assigned to the appropriate user or team consistently. It reduces the risk of errors or omissions occurring when records are manually assigned.
In addition, by using assignment rules to enforce a standardized process for record assignment, businesses can ensure that records are handled consistently across different teams and regions.
Flexibility
Finally, assignment rules provide businesses with great flexibility in assigning records. Businesses can define complex rules based on various criteria, such as record type, location, or user role. Businesses can customize their assignment rules to fit their specific needs and workflows.
In addition, assignment rules can be updated or modified as needed, allowing businesses to adapt to changes in their business or industry.
Best Practices for Using Assignment Rules in Salesforce
Businesses should follow these best practices to ensure Salesforce assignment rules are working effectively:
Define clear assignment criteria: Before setting up assignment rules, businesses should define clear criteria for record assignments. It will help ensure that records are assigned accurately and consistently.
Test assignment rules before activation: Before activating assignment rules, businesses should test them to ensure that they are working correctly. It will help prevent errors and ensure that records are assigned to the appropriate user or team.
Monitor and adjust assignment rules: It is important to monitor them regularly to ensure they are working properly. Businesses should also be prepared to adjust assignment rules as needed to accommodate changes in their business or industry.
Communicate changes to users: When changes are made to assignment rules, businesses should communicate with them to ensure they are aware of any changes in their workload or responsibilities.
In conclusion, assignment rules are a powerful feature of Salesforce that helps businesses automate assigning records to specific users or teams. The benefits of assignment rules include increased efficiency, improved customer satisfaction, accurate data, and consistency.
By using assignment rules, businesses can streamline their processes, improve their overall effectiveness, and achieve their goals more efficiently.
At Cloud Sylla, our sole focus is on assisting businesses in achieving success through digital transformation. Our goal is to aid customers in making the crucial shift to digital technologies, enabling them to bolster their strategies, multi-channel distribution, and internal operations.
Recent Posts
What is Orchestration Flow in Salesforce? Detailed Guide
What is Record-Triggered Flow in Salesforce? Detailed Guide
How to Get & Reset Security Token in Salesforce? (Detailed Guide)

The Learning Strategies Center
- Meet the Staff
- –Supplemental Course Schedule
- AY Course Offerings
- Anytime Online Modules
- Winter Session Workshop Courses
- –About Tutoring
- –Office Hours and Tutoring Schedule
- –LSC Tutoring Opportunities
- –How to Use Office Hours
- –Campus Resources and Support
- –Student Guide for Studying Together
- –Find Study Partners
- –Productivity Power Hour
- –Effective Study Strategies
- –Concept Mapping
- –Guidelines for Creating a Study Schedule
- –Five-Day Study Plan
- –What To Do With Practice Exams
- –Consider Exam Logistics
- –Online Exam Checklist
- –Open-Book Exams
- –How to Tackle Exam Questions
- –What To Do When You Get Your Graded Test (or Essay) Back
- –The Cornell Note Taking System
- –Learning from Digital Materials
- –3 P’s for Effective Reading
- –Textbook Reading Systems
- –Online Learning Checklist
- –Things to Keep in Mind as you Participate in Online Classes
- –Learning from Online Lectures and Discussions
- –Online Group Work
- –Learning Online Resource Videos
- –Start Strong!
- –Effectively Engage with Classes
- –Plans if you Need to Miss Class
- –Managing Time
- –Managing Stress
- –The Perils of Multitasking
- –Break the Cycle of Procrastination!
- –Finish Strong
- –Neurodiversity at Cornell
- –LSC Scholarship
- –Pre-Collegiate Summer Scholars Program
- –Study Skills Workshops
- –Private Consultations
- –Resources for Advisors and Faculty
- –Presentation Support (aka Practice Your Talk on a Dog)
- –About LSC
- –Meet The Team
- –Contact Us
The Cornell Note Taking System
Why do you take notes? What do you hope to get from your notes? What are Cornell Notes and how do you use the Cornell note-taking system?
There are many ways to take notes. It’s helpful to try out different methods and determine which work best for you in different situations. Whether you are learning online or in person, the physical act of writing can help you remember better than just listening or reading. Research shows that taking notes by hand is more effective than typing on a laptop. This page and our Canvas module will teach you about different note-taking systems and styles and help you determine what will work best for your situation.
In our Cornell Note Taking System module you will:
- Examine your current note taking system
- Explore different note taking strategies (including the Cornell Notes system)
- Assess which strategies work best for you in different situations
The best way to explore your current note-taking strategies and learn about the Cornell note taking system is to go through our Canvas note taking module. The module will interactively guide you through how to use Cornell Notes – click on the link here or the button below. This module is publicly available.

Just want to see a bit more about Cornell Notes? You can view the videos below.
Watch: What are Cornell Notes?
Watch: Learn how students use the Cornell Note Taking System
The Cornell Note-Taking System was originally developed by Cornell education professor, Walter Pauk. Prof. Pauk outlined this effective note-taking method in his book, How to Study in College (1).
- Pauk, Walter; Owens, Ross J. Q. (2010). How to Study in College (10 ed.). Boston, MA: Wadsworth. ISBN 978-1-4390-8446-5 . Chapter 10: “The Cornell System: Take Effective Notes”, pp. 235-277
- Columbia University in the City of New York
- Office of Teaching, Learning, and Innovation
- University Policies
- Columbia Online
- Academic Calendar
- Resources and Technology
- Instructional Technologies
- Teaching in All Modalities
Designing Assignments for Learning
The rapid shift to remote teaching and learning meant that many instructors reimagined their assessment practices. Whether adapting existing assignments or creatively designing new opportunities for their students to learn, instructors focused on helping students make meaning and demonstrate their learning outside of the traditional, face-to-face classroom setting. This resource distills the elements of assignment design that are important to carry forward as we continue to seek better ways of assessing learning and build on our innovative assignment designs.
On this page:
Rethinking traditional tests, quizzes, and exams.
- Examples from the Columbia University Classroom
- Tips for Designing Assignments for Learning
Reflect On Your Assignment Design
Connect with the ctl.
- Resources and References

Cite this resource: Columbia Center for Teaching and Learning (2021). Designing Assignments for Learning. Columbia University. Retrieved [today’s date] from https://ctl.columbia.edu/resources-and-technology/teaching-with-technology/teaching-online/designing-assignments/
Traditional assessments tend to reveal whether students can recognize, recall, or replicate what was learned out of context, and tend to focus on students providing correct responses (Wiggins, 1990). In contrast, authentic assignments, which are course assessments, engage students in higher order thinking, as they grapple with real or simulated challenges that help them prepare for their professional lives, and draw on the course knowledge learned and the skills acquired to create justifiable answers, performances or products (Wiggins, 1990). An authentic assessment provides opportunities for students to practice, consult resources, learn from feedback, and refine their performances and products accordingly (Wiggins 1990, 1998, 2014).
Authentic assignments ask students to “do” the subject with an audience in mind and apply their learning in a new situation. Examples of authentic assignments include asking students to:
- Write for a real audience (e.g., a memo, a policy brief, letter to the editor, a grant proposal, reports, building a website) and/or publication;
- Solve problem sets that have real world application;
- Design projects that address a real world problem;
- Engage in a community-partnered research project;
- Create an exhibit, performance, or conference presentation ;
- Compile and reflect on their work through a portfolio/e-portfolio.
Noteworthy elements of authentic designs are that instructors scaffold the assignment, and play an active role in preparing students for the tasks assigned, while students are intentionally asked to reflect on the process and product of their work thus building their metacognitive skills (Herrington and Oliver, 2000; Ashford-Rowe, Herrington and Brown, 2013; Frey, Schmitt, and Allen, 2012).
It’s worth noting here that authentic assessments can initially be time consuming to design, implement, and grade. They are critiqued for being challenging to use across course contexts and for grading reliability issues (Maclellan, 2004). Despite these challenges, authentic assessments are recognized as beneficial to student learning (Svinicki, 2004) as they are learner-centered (Weimer, 2013), promote academic integrity (McLaughlin, L. and Ricevuto, 2021; Sotiriadou et al., 2019; Schroeder, 2021) and motivate students to learn (Ambrose et al., 2010). The Columbia Center for Teaching and Learning is always available to consult with faculty who are considering authentic assessment designs and to discuss challenges and affordances.
Examples from the Columbia University Classroom
Columbia instructors have experimented with alternative ways of assessing student learning from oral exams to technology-enhanced assignments. Below are a few examples of authentic assignments in various teaching contexts across Columbia University.
- E-portfolios: Statia Cook shares her experiences with an ePorfolio assignment in her co-taught Frontiers of Science course (a submission to the Voices of Hybrid and Online Teaching and Learning initiative); CUIMC use of ePortfolios ;
- Case studies: Columbia instructors have engaged their students in authentic ways through case studies drawing on the Case Consortium at Columbia University. Read and watch a faculty spotlight to learn how Professor Mary Ann Price uses the case method to place pre-med students in real-life scenarios;
- Simulations: students at CUIMC engage in simulations to develop their professional skills in The Mary & Michael Jaharis Simulation Center in the Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons and the Helene Fuld Health Trust Simulation Center in the Columbia School of Nursing;
- Experiential learning: instructors have drawn on New York City as a learning laboratory such as Barnard’s NYC as Lab webpage which highlights courses that engage students in NYC;
- Design projects that address real world problems: Yevgeniy Yesilevskiy on the Engineering design projects completed using lab kits during remote learning. Watch Dr. Yesilevskiy talk about his teaching and read the Columbia News article .
- Writing assignments: Lia Marshall and her teaching associate Aparna Balasundaram reflect on their “non-disposable or renewable assignments” to prepare social work students for their professional lives as they write for a real audience; and Hannah Weaver spoke about a sandbox assignment used in her Core Literature Humanities course at the 2021 Celebration of Teaching and Learning Symposium . Watch Dr. Weaver share her experiences.
Tips for Designing Assignments for Learning
While designing an effective authentic assignment may seem like a daunting task, the following tips can be used as a starting point. See the Resources section for frameworks and tools that may be useful in this effort.
Align the assignment with your course learning objectives
Identify the kind of thinking that is important in your course, the knowledge students will apply, and the skills they will practice using through the assignment. What kind of thinking will students be asked to do for the assignment? What will students learn by completing this assignment? How will the assignment help students achieve the desired course learning outcomes? For more information on course learning objectives, see the CTL’s Course Design Essentials self-paced course and watch the video on Articulating Learning Objectives .
Identify an authentic meaning-making task
For meaning-making to occur, students need to understand the relevance of the assignment to the course and beyond (Ambrose et al., 2010). To Bean (2011) a “meaning-making” or “meaning-constructing” task has two dimensions: 1) it presents students with an authentic disciplinary problem or asks students to formulate their own problems, both of which engage them in active critical thinking, and 2) the problem is placed in “a context that gives students a role or purpose, a targeted audience, and a genre.” (Bean, 2011: 97-98).
An authentic task gives students a realistic challenge to grapple with, a role to take on that allows them to “rehearse for the complex ambiguities” of life, provides resources and supports to draw on, and requires students to justify their work and the process they used to inform their solution (Wiggins, 1990). Note that if students find an assignment interesting or relevant, they will see value in completing it.
Consider the kind of activities in the real world that use the knowledge and skills that are the focus of your course. How is this knowledge and these skills applied to answer real-world questions to solve real-world problems? (Herrington et al., 2010: 22). What do professionals or academics in your discipline do on a regular basis? What does it mean to think like a biologist, statistician, historian, social scientist? How might your assignment ask students to draw on current events, issues, or problems that relate to the course and are of interest to them? How might your assignment tap into student motivation and engage them in the kinds of thinking they can apply to better understand the world around them? (Ambrose et al., 2010).
Determine the evaluation criteria and create a rubric
To ensure equitable and consistent grading of assignments across students, make transparent the criteria you will use to evaluate student work. The criteria should focus on the knowledge and skills that are central to the assignment. Build on the criteria identified, create a rubric that makes explicit the expectations of deliverables and share this rubric with your students so they can use it as they work on the assignment. For more information on rubrics, see the CTL’s resource Incorporating Rubrics into Your Grading and Feedback Practices , and explore the Association of American Colleges & Universities VALUE Rubrics (Valid Assessment of Learning in Undergraduate Education).
Build in metacognition
Ask students to reflect on what and how they learned from the assignment. Help students uncover personal relevance of the assignment, find intrinsic value in their work, and deepen their motivation by asking them to reflect on their process and their assignment deliverable. Sample prompts might include: what did you learn from this assignment? How might you draw on the knowledge and skills you used on this assignment in the future? See Ambrose et al., 2010 for more strategies that support motivation and the CTL’s resource on Metacognition ).
Provide students with opportunities to practice
Design your assignment to be a learning experience and prepare students for success on the assignment. If students can reasonably expect to be successful on an assignment when they put in the required effort ,with the support and guidance of the instructor, they are more likely to engage in the behaviors necessary for learning (Ambrose et al., 2010). Ensure student success by actively teaching the knowledge and skills of the course (e.g., how to problem solve, how to write for a particular audience), modeling the desired thinking, and creating learning activities that build up to a graded assignment. Provide opportunities for students to practice using the knowledge and skills they will need for the assignment, whether through low-stakes in-class activities or homework activities that include opportunities to receive and incorporate formative feedback. For more information on providing feedback, see the CTL resource Feedback for Learning .
Communicate about the assignment
Share the purpose, task, audience, expectations, and criteria for the assignment. Students may have expectations about assessments and how they will be graded that is informed by their prior experiences completing high-stakes assessments, so be transparent. Tell your students why you are asking them to do this assignment, what skills they will be using, how it aligns with the course learning outcomes, and why it is relevant to their learning and their professional lives (i.e., how practitioners / professionals use the knowledge and skills in your course in real world contexts and for what purposes). Finally, verify that students understand what they need to do to complete the assignment. This can be done by asking students to respond to poll questions about different parts of the assignment, a “scavenger hunt” of the assignment instructions–giving students questions to answer about the assignment and having them work in small groups to answer the questions, or by having students share back what they think is expected of them.
Plan to iterate and to keep the focus on learning
Draw on multiple sources of data to help make decisions about what changes are needed to the assignment, the assignment instructions, and/or rubric to ensure that it contributes to student learning. Explore assignment performance data. As Deandra Little reminds us: “a really good assignment, which is a really good assessment, also teaches you something or tells the instructor something. As much as it tells you what students are learning, it’s also telling you what they aren’t learning.” ( Teaching in Higher Ed podcast episode 337 ). Assignment bottlenecks–where students get stuck or struggle–can be good indicators that students need further support or opportunities to practice prior to completing an assignment. This awareness can inform teaching decisions.
Triangulate the performance data by collecting student feedback, and noting your own reflections about what worked well and what did not. Revise the assignment instructions, rubric, and teaching practices accordingly. Consider how you might better align your assignment with your course objectives and/or provide more opportunities for students to practice using the knowledge and skills that they will rely on for the assignment. Additionally, keep in mind societal, disciplinary, and technological changes as you tweak your assignments for future use.
Now is a great time to reflect on your practices and experiences with assignment design and think critically about your approach. Take a closer look at an existing assignment. Questions to consider include: What is this assignment meant to do? What purpose does it serve? Why do you ask students to do this assignment? How are they prepared to complete the assignment? Does the assignment assess the kind of learning that you really want? What would help students learn from this assignment?
Using the tips in the previous section: How can the assignment be tweaked to be more authentic and meaningful to students?
As you plan forward for post-pandemic teaching and reflect on your practices and reimagine your course design, you may find the following CTL resources helpful: Reflecting On Your Experiences with Remote Teaching , Transition to In-Person Teaching , and Course Design Support .
The Columbia Center for Teaching and Learning (CTL) is here to help!
For assistance with assignment design, rubric design, or any other teaching and learning need, please request a consultation by emailing [email protected] .
Transparency in Learning and Teaching (TILT) framework for assignments. The TILT Examples and Resources page ( https://tilthighered.com/tiltexamplesandresources ) includes example assignments from across disciplines, as well as a transparent assignment template and a checklist for designing transparent assignments . Each emphasizes the importance of articulating to students the purpose of the assignment or activity, the what and how of the task, and specifying the criteria that will be used to assess students.
Association of American Colleges & Universities (AAC&U) offers VALUE ADD (Assignment Design and Diagnostic) tools ( https://www.aacu.org/value-add-tools ) to help with the creation of clear and effective assignments that align with the desired learning outcomes and associated VALUE rubrics (Valid Assessment of Learning in Undergraduate Education). VALUE ADD encourages instructors to explicitly state assignment information such as the purpose of the assignment, what skills students will be using, how it aligns with course learning outcomes, the assignment type, the audience and context for the assignment, clear evaluation criteria, desired formatting, and expectations for completion whether individual or in a group.
Villarroel et al. (2017) propose a blueprint for building authentic assessments which includes four steps: 1) consider the workplace context, 2) design the authentic assessment; 3) learn and apply standards for judgement; and 4) give feedback.
References
Ambrose, S. A., Bridges, M. W., & DiPietro, M. (2010). Chapter 3: What Factors Motivate Students to Learn? In How Learning Works: Seven Research-Based Principles for Smart Teaching . Jossey-Bass.
Ashford-Rowe, K., Herrington, J., and Brown, C. (2013). Establishing the critical elements that determine authentic assessment. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education. 39(2), 205-222, http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2013.819566 .
Bean, J.C. (2011). Engaging Ideas: The Professor’s Guide to Integrating Writing, Critical Thinking, and Active Learning in the Classroom . Second Edition. Jossey-Bass.
Frey, B. B, Schmitt, V. L., and Allen, J. P. (2012). Defining Authentic Classroom Assessment. Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation. 17(2). DOI: https://doi.org/10.7275/sxbs-0829
Herrington, J., Reeves, T. C., and Oliver, R. (2010). A Guide to Authentic e-Learning . Routledge.
Herrington, J. and Oliver, R. (2000). An instructional design framework for authentic learning environments. Educational Technology Research and Development, 48(3), 23-48.
Litchfield, B. C. and Dempsey, J. V. (2015). Authentic Assessment of Knowledge, Skills, and Attitudes. New Directions for Teaching and Learning. 142 (Summer 2015), 65-80.
Maclellan, E. (2004). How convincing is alternative assessment for use in higher education. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education. 29(3), June 2004. DOI: 10.1080/0260293042000188267
McLaughlin, L. and Ricevuto, J. (2021). Assessments in a Virtual Environment: You Won’t Need that Lockdown Browser! Faculty Focus. June 2, 2021.
Mueller, J. (2005). The Authentic Assessment Toolbox: Enhancing Student Learning through Online Faculty Development . MERLOT Journal of Online Learning and Teaching. 1(1). July 2005. Mueller’s Authentic Assessment Toolbox is available online.
Schroeder, R. (2021). Vaccinate Against Cheating With Authentic Assessment . Inside Higher Ed. (February 26, 2021).
Sotiriadou, P., Logan, D., Daly, A., and Guest, R. (2019). The role of authentic assessment to preserve academic integrity and promote skills development and employability. Studies in Higher Education. 45(111), 2132-2148. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075079.2019.1582015
Stachowiak, B. (Host). (November 25, 2020). Authentic Assignments with Deandra Little. (Episode 337). In Teaching in Higher Ed . https://teachinginhighered.com/podcast/authentic-assignments/
Svinicki, M. D. (2004). Authentic Assessment: Testing in Reality. New Directions for Teaching and Learning. 100 (Winter 2004): 23-29.
Villarroel, V., Bloxham, S, Bruna, D., Bruna, C., and Herrera-Seda, C. (2017). Authentic assessment: creating a blueprint for course design. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education. 43(5), 840-854. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2017.1412396
Weimer, M. (2013). Learner-Centered Teaching: Five Key Changes to Practice . Second Edition. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Wiggins, G. (2014). Authenticity in assessment, (re-)defined and explained. Retrieved from https://grantwiggins.wordpress.com/2014/01/26/authenticity-in-assessment-re-defined-and-explained/
Wiggins, G. (1998). Teaching to the (Authentic) Test. Educational Leadership . April 1989. 41-47.
Wiggins, Grant (1990). The Case for Authentic Assessment . Practical Assessment, Research & Evaluation , 2(2).
Wondering how AI tools might play a role in your course assignments?
See the CTL’s resource “Considerations for AI Tools in the Classroom.”
This website uses cookies to identify users, improve the user experience and requires cookies to work. By continuing to use this website, you consent to Columbia University's use of cookies and similar technologies, in accordance with the Columbia University Website Cookie Notice .

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Writing Assignments
Kate Derrington; Cristy Bartlett; and Sarah Irvine

Introduction
Assignments are a common method of assessment at university and require careful planning and good quality research. Developing critical thinking and writing skills are also necessary to demonstrate your ability to understand and apply information about your topic. It is not uncommon to be unsure about the processes of writing assignments at university.
- You may be returning to study after a break
- You may have come from an exam based assessment system and never written an assignment before
- Maybe you have written assignments but would like to improve your processes and strategies
This chapter has a collection of resources that will provide you with the skills and strategies to understand assignment requirements and effectively plan, research, write and edit your assignments. It begins with an explanation of how to analyse an assignment task and start putting your ideas together. It continues by breaking down the components of academic writing and exploring the elements you will need to master in your written assignments. This is followed by a discussion of paraphrasing and synthesis, and how you can use these strategies to create a strong, written argument. The chapter concludes with useful checklists for editing and proofreading to help you get the best possible mark for your work.
Task Analysis and Deconstructing an Assignment
It is important that before you begin researching and writing your assignments you spend sufficient time understanding all the requirements. This will help make your research process more efficient and effective. Check your subject information such as task sheets, criteria sheets and any additional information that may be in your subject portal online. Seek clarification from your lecturer or tutor if you are still unsure about how to begin your assignments.
The task sheet typically provides key information about an assessment including the assignment question. It can be helpful to scan this document for topic, task and limiting words to ensure that you fully understand the concepts you are required to research, how to approach the assignment, and the scope of the task you have been set. These words can typically be found in your assignment question and are outlined in more detail in the two tables below (see Table 19.1 and Table 19.2 ).
Table 19.1 Parts of an Assignment Question
| Topic words | These are words and concepts you have to research and write about. |
| Task words | These will tell you how to approach the assignment and structure the information you find in your research (e.g., discuss, analyse). |
| Limiting words | These words define the scope of the assignment, e.g., Australian perspectives, relevant codes or standards or a specific timeframe. |
Make sure you have a clear understanding of what the task word requires you to address.
Table 19.2 Task words
| Give reasons for or explain something has occurred. This task directs you to consider contributing factors to a certain situation or event. You are expected to make a decision about why these occurred, not just describe the events. | the factors that led to the global financial crisis. | |
| Consider the different elements of a concept, statement or situation. Show the different components and show how they connect or relate. Your structure and argument should be logical and methodical. | the political, social and economic impacts of climate change. | |
| Make a judgement on a topic or idea. Consider its reliability, truth and usefulness. In your judgement, consider both the strengths and weaknesses of the opposing arguments to determine your topic’s worth (similar to evaluate). | the efficacy of cogitative behavioural therapy (CBT) for the treatment of depression. | |
| Divide your topic into categories or sub-topics logically (could possibly be part of a more complex task). | the artists studied this semester according to the artistic periods they best represent. Then choose one artist and evaluate their impact on future artists. | |
| State your opinion on an issue or idea. You may explain the issue or idea in more detail. Be objective and support your opinion with reliable evidence. | the government’s proposal to legalise safe injecting rooms. | |
| Show the similarities and differences between two or more ideas, theories, systems, arguments or events. You are expected to provide a balanced response, highlighting similarities and differences. | the efficiency of wind and solar power generation for a construction site. | |
| Point out only the differences between two or more ideas, theories, systems, arguments or events. | virtue ethics and utilitarianism as models for ethical decision making. | |
| (this is often used with another task word, e.g. critically evaluate, critically analyse, critically discuss) | It does not mean to criticise, instead you are required to give a balanced account, highlighting strengths and weaknesses about the topic. Your overall judgment must be supported by reliable evidence and your interpretation of that evidence. | analyse the impacts of mental health on recidivism within youth justice. |
| Provide a precise meaning of a concept. You may need to include the limits or scope of the concept within a given context. | digital disruption as it relates to productivity. | |
| Provide a thorough description, emphasising the most important points. Use words to show appearance, function, process, events or systems. You are not required to make judgements. | the pathophysiology of Asthma. | |
| Highlight the differences between two (possibly confusing) items. | between exothermic and endothermic reactions. | |
| Provide an analysis of a topic. Use evidence to support your argument. Be logical and include different perspectives on the topic (This requires more than a description). | how Brofenbrenner’s ecological system’s theory applies to adolescence. | |
| Review both positive and negative aspects of a topic. You may need to provide an overall judgement regarding the value or usefulness of the topic. Evidence (referencing) must be included to support your writing. | the impact of inclusive early childhood education programs on subsequent high school completion rates for First Nations students. | |
| Describe and clarify the situation or topic. Depending on your discipline area and topic, this may include processes, pathways, cause and effect, impact, or outcomes. | the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the film industry in Australia. | |
| Clarify a point or argument with examples and evidence. | how society’s attitudes to disability have changed from a medical model to a wholistic model of disability. | |
| Give evidence which supports an argument or idea; show why a decision or conclusions were made. Justify may be used with other topic words, such as outline, argue. | Write a report outlining the key issues and implications of a welfare cashless debit card trial and make three recommendations for future improvements. your decision-making process for the recommendations. | |
| A comprehensive description of the situation or topic which provides a critical analysis of the key issues. | Provide a of Australia's asylum policies since the Pacific Solution in 2001. | |
| An overview or brief description of a topic. (This is likely to be part of a larger assessment task.) | the process for calculating the correct load for a plane. |
The criteria sheet , also known as the marking sheet or rubric, is another important document to look at before you begin your assignment. The criteria sheet outlines how your assignment will be marked and should be used as a checklist to make sure you have included all the information required.
The task or criteria sheet will also include the:
- Word limit (or word count)
- Referencing style and research expectations
- Formatting requirements
Task analysis and criteria sheets are also discussed in the chapter Managing Assessments for a more detailed discussion on task analysis, criteria sheets, and marking rubrics.
Preparing your ideas
Brainstorm or concept map: List possible ideas to address each part of the assignment task based on what you already know about the topic from lectures and weekly readings.
Finding appropriate information: Learn how to find scholarly information for your assignments which is
See the chapter Working With Information for a more detailed explanation .
What is academic writing?
Academic writing tone and style.
Many of the assessment pieces you prepare will require an academic writing style. This is sometimes called ‘academic tone’ or ‘academic voice’. This section will help you to identify what is required when you are writing academically (see Table 19.3 ). The best way to understand what academic writing looks like, is to read broadly in your discipline area. Look at how your course readings, or scholarly sources, are written. This will help you identify the language of your discipline field, as well as how other writers structure their work.
Table 19.3 Comparison of academic and non-academic writing
| Is clear, concise and well-structured | Is verbose and may use more words than are needed |
| Is formal. It writes numbers under twenty in full. | Writes numbers under twenty as numerals and uses symbols such as “&” instead of writing it in full |
| Is reasoned and supported (logically developed) | Uses humour (puns, sarcasm) |
| Is authoritative (writes in third person- This essay argues…) | Writes in first person (I think, I found) |
| Utilises the language of the field/industry/subject | Uses colloquial language e.g., mate |
Thesis statements
Essays are a common form of assessment that you will likely encounter during your university studies. You should apply an academic tone and style when writing an essay, just as you would in in your other assessment pieces. One of the most important steps in writing an essay is constructing your thesis statement. A thesis statement tells the reader the purpose, argument or direction you will take to answer your assignment question. A thesis statement may not be relevant for some questions, if you are unsure check with your lecturer. The thesis statement:
- Directly relates to the task . Your thesis statement may even contain some of the key words or synonyms from the task description.
- Does more than restate the question.
- Is specific and uses precise language.
- Let’s your reader know your position or the main argument that you will support with evidence throughout your assignment.
- The subject is the key content area you will be covering.
- The contention is the position you are taking in relation to the chosen content.
Your thesis statement helps you to structure your essay. It plays a part in each key section: introduction, body and conclusion.
Planning your assignment structure

When planning and drafting assignments, it is important to consider the structure of your writing. Academic writing should have clear and logical structure and incorporate academic research to support your ideas. It can be hard to get started and at first you may feel nervous about the size of the task, this is normal. If you break your assignment into smaller pieces, it will seem more manageable as you can approach the task in sections. Refer to your brainstorm or plan. These ideas should guide your research and will also inform what you write in your draft. It is sometimes easier to draft your assignment using the 2-3-1 approach, that is, write the body paragraphs first followed by the conclusion and finally the introduction.
Writing introductions and conclusions
Clear and purposeful introductions and conclusions in assignments are fundamental to effective academic writing. Your introduction should tell the reader what is going to be covered and how you intend to approach this. Your conclusion should summarise your argument or discussion and signal to the reader that you have come to a conclusion with a final statement. These tips below are based on the requirements usually needed for an essay assignment, however, they can be applied to other assignment types.
Writing introductions

Most writing at university will require a strong and logically structured introduction. An effective introduction should provide some background or context for your assignment, clearly state your thesis and include the key points you will cover in the body of the essay in order to prove your thesis.
Usually, your introduction is approximately 10% of your total assignment word count. It is much easier to write your introduction once you have drafted your body paragraphs and conclusion, as you know what your assignment is going to be about. An effective introduction needs to inform your reader by establishing what the paper is about and provide four basic things:
- A brief background or overview of your assignment topic
- A thesis statement (see section above)
- An outline of your essay structure
- An indication of any parameters or scope that will/ will not be covered, e.g. From an Australian perspective.
The below example demonstrates the four different elements of an introductory paragraph.
1) Information technology is having significant effects on the communication of individuals and organisations in different professions. 2) This essay will discuss the impact of information technology on the communication of health professionals. 3) First, the provision of information technology for the educational needs of nurses will be discussed. 4) This will be followed by an explanation of the significant effects that information technology can have on the role of general practitioner in the area of public health. 5) Considerations will then be made regarding the lack of knowledge about the potential of computers among hospital administrators and nursing executives. 6) The final section will explore how information technology assists health professionals in the delivery of services in rural areas . 7) It will be argued that information technology has significant potential to improve health care and medical education, but health professionals are reluctant to use it.
1 Brief background/ overview | 2 Indicates the scope of what will be covered | 3-6 Outline of the main ideas (structure) | 7 The thesis statement
Note : The examples in this document are taken from the University of Canberra and used under a CC-BY-SA-3.0 licence.
Writing conclusions
You should aim to end your assignments with a strong conclusion. Your conclusion should restate your thesis and summarise the key points you have used to prove this thesis. Finish with a key point as a final impactful statement. Similar to your introduction, your conclusion should be approximately 10% of the total assignment word length. If your assessment task asks you to make recommendations, you may need to allocate more words to the conclusion or add a separate recommendations section before the conclusion. Use the checklist below to check your conclusion is doing the right job.
Conclusion checklist
- Have you referred to the assignment question and restated your argument (or thesis statement), as outlined in the introduction?
- Have you pulled together all the threads of your essay into a logical ending and given it a sense of unity?
- Have you presented implications or recommendations in your conclusion? (if required by your task).
- Have you added to the overall quality and impact of your essay? This is your final statement about this topic; thus, a key take-away point can make a great impact on the reader.
- Remember, do not add any new material or direct quotes in your conclusion.
This below example demonstrates the different elements of a concluding paragraph.
1) It is evident, therefore, that not only do employees need to be trained for working in the Australian multicultural workplace, but managers also need to be trained. 2) Managers must ensure that effective in-house training programs are provided for migrant workers, so that they become more familiar with the English language, Australian communication norms and the Australian work culture. 3) In addition, Australian native English speakers need to be made aware of the differing cultural values of their workmates; particularly the different forms of non-verbal communication used by other cultures. 4) Furthermore, all employees must be provided with clear and detailed guidelines about company expectations. 5) Above all, in order to minimise communication problems and to maintain an atmosphere of tolerance, understanding and cooperation in the multicultural workplace, managers need to have an effective knowledge about their employees. This will help employers understand how their employee’s social conditioning affects their beliefs about work. It will develop their communication skills to develop confidence and self-esteem among diverse work groups. 6) The culturally diverse Australian workplace may never be completely free of communication problems, however, further studies to identify potential problems and solutions, as well as better training in cross cultural communication for managers and employees, should result in a much more understanding and cooperative environment.
1 Reference to thesis statement – In this essay the writer has taken the position that training is required for both employees and employers . | 2-5 Structure overview – Here the writer pulls together the main ideas in the essay. | 6 Final summary statement that is based on the evidence.
Note: The examples in this document are taken from the University of Canberra and used under a CC-BY-SA-3.0 licence.
Writing paragraphs
Paragraph writing is a key skill that enables you to incorporate your academic research into your written work. Each paragraph should have its own clearly identified topic sentence or main idea which relates to the argument or point (thesis) you are developing. This idea should then be explained by additional sentences which you have paraphrased from good quality sources and referenced according to the recommended guidelines of your subject (see the chapter Working with Information ). Paragraphs are characterised by increasing specificity; that is, they move from the general to the specific, increasingly refining the reader’s understanding. A common structure for paragraphs in academic writing is as follows.
Topic Sentence
This is the main idea of the paragraph and should relate to the overall issue or purpose of your assignment is addressing. Often it will be expressed as an assertion or claim which supports the overall argument or purpose of your writing.
Explanation/ Elaboration
The main idea must have its meaning explained and elaborated upon. Think critically, do not just describe the idea.
These explanations must include evidence to support your main idea. This information should be paraphrased and referenced according to the appropriate referencing style of your course.
Concluding sentence (critical thinking)
This should explain why the topic of the paragraph is relevant to the assignment question and link to the following paragraph.
Use the checklist below to check your paragraphs are clear and well formed.
Paragraph checklist
- Does your paragraph have a clear main idea?
- Is everything in the paragraph related to this main idea?
- Is the main idea adequately developed and explained?
- Do your sentences run together smoothly?
- Have you included evidence to support your ideas?
- Have you concluded the paragraph by connecting it to your overall topic?
Writing sentences
Make sure all the sentences in your paragraphs make sense. Each sentence must contain a verb to be a complete sentence. Avoid sentence fragments . These are incomplete sentences or ideas that are unfinished and create confusion for your reader. Avoid also run on sentences . This happens when you join two ideas or clauses without using the appropriate punctuation. This also confuses your meaning (See the chapter English Language Foundations for examples and further explanation).
Use transitions (linking words and phrases) to connect your ideas between paragraphs and make your writing flow. The order that you structure the ideas in your assignment should reflect the structure you have outlined in your introduction. Refer to transition words table in the chapter English Language Foundations.
Paraphrasing and Synthesising
Paraphrasing and synthesising are powerful tools that you can use to support the main idea of a paragraph. It is likely that you will regularly use these skills at university to incorporate evidence into explanatory sentences and strengthen your essay. It is important to paraphrase and synthesise because:
- Paraphrasing is regarded more highly at university than direct quoting.
- Paraphrasing can also help you better understand the material.
- Paraphrasing and synthesising demonstrate you have understood what you have read through your ability to summarise and combine arguments from the literature using your own words.
What is paraphrasing?
Paraphrasing is changing the writing of another author into your words while retaining the original meaning. You must acknowledge the original author as the source of the information in your citation. Follow the steps in this table to help you build your skills in paraphrasing (see Table 19.4 ).
Table 19.4 Paraphrasing techniques
| 1 | Make sure you understand what you are reading. Look up keywords to understand their meanings. |
| 2 | Record the details of the source so you will be able to cite it correctly in text and in your reference list. |
| 3 | Identify words that you can change to synonyms (but do not change the key/topic words). |
| 4 | Change the type of word in a sentence (for example change a noun to a verb or vice versa). |
| 5 | Eliminate unnecessary words or phrases from the original that you don’t need in your paraphrase. |
| 6 | Change the sentence structure (for example change a long sentence to several shorter ones or combine shorter sentences to form a longer sentence). |
Example of paraphrasing
Please note that these examples and in text citations are for instructional purposes only.
Original text
Health care professionals assist people often when they are at their most vulnerable . To provide the best care and understand their needs, workers must demonstrate good communication skills . They must develop patient trust and provide empathy to effectively work with patients who are experiencing a variety of situations including those who may be suffering from trauma or violence, physical or mental illness or substance abuse (French & Saunders, 2018).
Poor quality paraphrase example
This is a poor example of paraphrasing. Some synonyms have been used and the order of a few words changed within the sentences however the colours of the sentences indicate that the paragraph follows the same structure as the original text.
Health care sector workers are often responsible for vulnerable patients. To understand patients and deliver good service , they need to be excellent communicators . They must establish patient rapport and show empathy if they are to successfully care for patients from a variety of backgrounds and with different medical, psychological and social needs (French & Saunders, 2018).
A good quality paraphrase example
This example demonstrates a better quality paraphrase. The author has demonstrated more understanding of the overall concept in the text by using the keywords as the basis to reconstruct the paragraph. Note how the blocks of colour have been broken up to see how much the structure has changed from the original text.
Empathetic communication is a vital skill for health care workers. Professionals in these fields are often responsible for patients with complex medical, psychological and social needs. Empathetic communication assists in building rapport and gaining the necessary trust to assist these vulnerable patients by providing appropriate supportive care (French & Saunders, 2018).
The good quality paraphrase example demonstrates understanding of the overall concept in the text by using key words as the basis to reconstruct the paragraph. Note how the blocks of colour have been broken up, which indicates how much the structure has changed from the original text.
What is synthesising?
Synthesising means to bring together more than one source of information to strengthen your argument. Once you have learnt how to paraphrase the ideas of one source at a time, you can consider adding additional sources to support your argument. Synthesis demonstrates your understanding and ability to show connections between multiple pieces of evidence to support your ideas and is a more advanced academic thinking and writing skill.
Follow the steps in this table to improve your synthesis techniques (see Table 19.5 ).
Table 19.5 Synthesising techniques
| 1 | Check your referencing guide to learn how to correctly reference more than one author at a time in your paper. |
| 2 | While taking notes for your research, try organising your notes into themes. This way you can keep similar ideas from different authors together. |
| 3 | Identify similar language and tone used by authors so that you can group similar ideas together. |
| 4 | Synthesis can not only be about grouping ideas together that are similar, but also those that are different. See how you can contrast authors in your writing to also strengthen your argument. |
Example of synthesis
There is a relationship between academic procrastination and mental health outcomes. Procrastination has been found to have a negative effect on students’ well-being (Balkis, & Duru, 2016). Yerdelen, McCaffrey, and Klassens’ (2016) research results suggested that there was a positive association between procrastination and anxiety. This was corroborated by Custer’s (2018) findings which indicated that students with higher levels of procrastination also reported greater levels of the anxiety. Therefore, it could be argued that procrastination is an ineffective learning strategy that leads to increased levels of distress.
Topic sentence | Statements using paraphrased evidence | Critical thinking (student voice) | Concluding statement – linking to topic sentence
This example demonstrates a simple synthesis. The author has developed a paragraph with one central theme and included explanatory sentences complete with in-text citations from multiple sources. Note how the blocks of colour have been used to illustrate the paragraph structure and synthesis (i.e., statements using paraphrased evidence from several sources). A more complex synthesis may include more than one citation per sentence.
Creating an argument
What does this mean.
Throughout your university studies, you may be asked to ‘argue’ a particular point or position in your writing. You may already be familiar with the idea of an argument, which in general terms means to have a disagreement with someone. Similarly, in academic writing, if you are asked to create an argument, this means you are asked to have a position on a particular topic, and then justify your position using evidence.
What skills do you need to create an argument?
In order to create a good and effective argument, you need to be able to:
- Read critically to find evidence
- Plan your argument
- Think and write critically throughout your paper to enhance your argument
For tips on how to read and write critically, refer to the chapter Thinking for more information. A formula for developing a strong argument is presented below.
A formula for a good argument
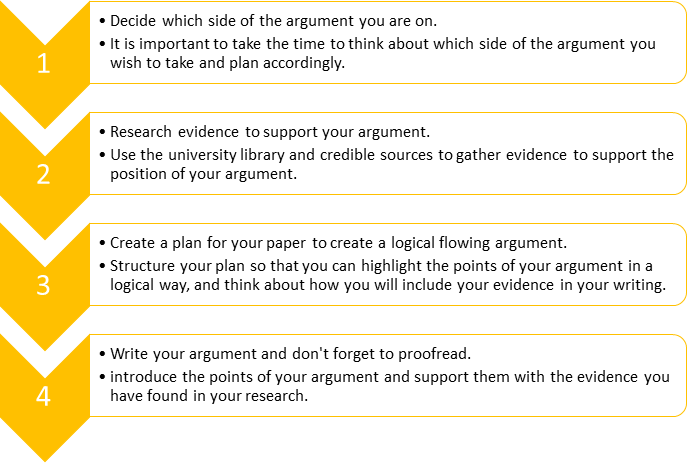
What does an argument look like?
As can be seen from the figure above, including evidence is a key element of a good argument. While this may seem like a straightforward task, it can be difficult to think of wording to express your argument. The table below provides examples of how you can illustrate your argument in academic writing (see Table 19.6 ).
Table 19.6 Argument
| Introducing your argument | • This paper will argue/claim that... • ...is an important factor/concept/idea/ to consider because... • … will be argued/outlined in this paper. |
| Introducing evidence for your argument | • Smith (2014) outlines that.... • This evidence demonstrates that... • According to Smith (2014)… • For example, evidence/research provided by Smith (2014) indicates that... |
| Giving the reason why your point/evidence is important | • Therefore this indicates... • This evidence clearly demonstrates.... • This is important/significant because... • This data highlights... |
| Concluding a point | • Overall, it is clear that... • Therefore, … are reasons which should be considered because... • Consequently, this leads to.... • The research presented therefore indicates... |
Editing and proofreading (reviewing)
Once you have finished writing your first draft it is recommended that you spend time revising your work. Proofreading and editing are two different stages of the revision process.
- Editing considers the overall focus or bigger picture of the assignment
- Proofreading considers the finer details
As can be seen in the figure above there are four main areas that you should review during the editing phase of the revision process. The main things to consider when editing include content, structure, style, and sources. It is important to check that all the content relates to the assignment task, the structure is appropriate for the purposes of the assignment, the writing is academic in style, and that sources have been adequately acknowledged. Use the checklist below when editing your work.
Editing checklist
- Have I answered the question accurately?
- Do I have enough credible, scholarly supporting evidence?
- Is my writing tone objective and formal enough or have I used emotive and informal language?
- Have I written in the third person not the first person?
- Do I have appropriate in-text citations for all my information?
- Have I included the full details for all my in-text citations in my reference list?
There are also several key things to look out for during the proofreading phase of the revision process. In this stage it is important to check your work for word choice, grammar and spelling, punctuation and referencing errors. It can be easy to mis-type words like ‘from’ and ‘form’ or mix up words like ‘trail’ and ‘trial’ when writing about research, apply American rather than Australian spelling, include unnecessary commas or incorrectly format your references list. The checklist below is a useful guide that you can use when proofreading your work.
Proofreading checklist
- Is my spelling and grammar accurate?
- Are they complete?
- Do they all make sense?
- Do they only contain only one idea?
- Do the different elements (subject, verb, nouns, pronouns) within my sentences agree?
- Are my sentences too long and complicated?
- Do they contain only one idea per sentence?
- Is my writing concise? Take out words that do not add meaning to your sentences.
- Have I used appropriate discipline specific language but avoided words I don’t know or understand that could possibly be out of context?
- Have I avoided discriminatory language and colloquial expressions (slang)?
- Is my referencing formatted correctly according to my assignment guidelines? (for more information on referencing refer to the Managing Assessment feedback section).
This chapter has examined the experience of writing assignments. It began by focusing on how to read and break down an assignment question, then highlighted the key components of essays. Next, it examined some techniques for paraphrasing and summarising, and how to build an argument. It concluded with a discussion on planning and structuring your assignment and giving it that essential polish with editing and proof-reading. Combining these skills and practising them, can greatly improve your success with this very common form of assessment.
- Academic writing requires clear and logical structure, critical thinking and the use of credible scholarly sources.
- A thesis statement is important as it tells the reader the position or argument you have adopted in your assignment. Not all assignments will require a thesis statement.
- Spending time analysing your task and planning your structure before you start to write your assignment is time well spent.
- Information you use in your assignment should come from credible scholarly sources such as textbooks and peer reviewed journals. This information needs to be paraphrased and referenced appropriately.
- Paraphrasing means putting something into your own words and synthesising means to bring together several ideas from sources.
- Creating an argument is a four step process and can be applied to all types of academic writing.
- Editing and proofreading are two separate processes.
Academic Skills Centre. (2013). Writing an introduction and conclusion . University of Canberra, accessed 13 August, 2013, http://www.canberra.edu.au/studyskills/writing/conclusions
Balkis, M., & Duru, E. (2016). Procrastination, self-regulation failure, academic life satisfaction, and affective well-being: underregulation or misregulation form. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 31 (3), 439-459.
Custer, N. (2018). Test anxiety and academic procrastination among prelicensure nursing students. Nursing education perspectives, 39 (3), 162-163.
Yerdelen, S., McCaffrey, A., & Klassen, R. M. (2016). Longitudinal examination of procrastination and anxiety, and their relation to self-efficacy for self-regulated learning: Latent growth curve modeling. Educational Sciences: Theory & Practice, 16 (1).
Writing Assignments Copyright © 2021 by Kate Derrington; Cristy Bartlett; and Sarah Irvine is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Become an Online Volunteer
Have you considered dedicating your skills and expertise virtually to advance global peace, development and humanitarian efforts. Through the Online Volunteering service of the United Nations Volunteers (UNV) programme, you can connect with UN entities, governments, public institutions and civil society organizations. Find out how to become an Online Volunteer and help tackle today’s sustainable development challenges – from any device, anywhere in the world .
- Through Online Volunteering, you can contribute your skills and expertise towards achieving sustainable human development efforts of organizations around the world.
- You can get first-hand practical experience with organizations working in the development sector.
- You can also extend your network among different organizations and make invaluable connections.
- You will find Online Volunteer assignments advertised on our Unified Volunteering Platform (UVP) .
- Use the filters to distinguish online from onsite assignments and check the description of assignment for details.
- To sign up on the Unified Volunteering Platform and apply for Online Volunteer assignments, you must be at least 18 years of age.
- There is no particular background required to become an Online Volunteer. Each Online Volunteer assignment is different and has its own requirements, set by the host organization.
- As an Online Volunteer, you can only support organizations remotely in assignments up to 20 hours per week for a maximum of 12 weeks for each assignment.
- Anyone interested in contributing their time and skills to the global sustainable human development efforts can become an Online Volunteer, regardless of your background or location.
- Online Volunteers are not under contract with the UNV programme or the engaging organization and are not affiliated with either of them.
- Furthermore, Online Volunteers do not receive any volunteer living allowances or any other kind of financial compensation or benefits.
- For each Online Volunteering assignment, a maximum of 25 Online Volunteers can be engaged for up to 20 hours per week and for a maximum of 12 weeks.
- Non-profit organizations working for peace and development – UN agencies, governments & public institutions, and civil society organizations – register their organization details.
- UNV reviews and approves the registration of eligible organizations.
- Organizations complete an online form explaining what they need from online volunteers.
- UNV provides guidance and support on how to best organize online collaboration.
- UNV reviews the descriptions of assignments and publishes them if they meet the criteria .
- Volunteers find assignments of their interest and apply.
- Organizations select the volunteers they want to engage.
- Volunteers and organizations collaborate online.
- Volunteers and organizations provide feedback on their collaboration.
- Organizations issue an electronic certificate of appreciation to their volunteers.

- youtube-play
This website benefits from the continuous support of Online Volunteers. UNV is administered by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
UNV Scam Alert
UNV Privacy Policy
UNV Website Terms of Use

Understanding Assignments
What this handout is about.
The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms and practices into meaningful clues to the type of writing your instructor expects. See our short video for more tips.
Basic beginnings
Regardless of the assignment, department, or instructor, adopting these two habits will serve you well :
- Read the assignment carefully as soon as you receive it. Do not put this task off—reading the assignment at the beginning will save you time, stress, and problems later. An assignment can look pretty straightforward at first, particularly if the instructor has provided lots of information. That does not mean it will not take time and effort to complete; you may even have to learn a new skill to complete the assignment.
- Ask the instructor about anything you do not understand. Do not hesitate to approach your instructor. Instructors would prefer to set you straight before you hand the paper in. That’s also when you will find their feedback most useful.
Assignment formats
Many assignments follow a basic format. Assignments often begin with an overview of the topic, include a central verb or verbs that describe the task, and offer some additional suggestions, questions, or prompts to get you started.
An Overview of Some Kind
The instructor might set the stage with some general discussion of the subject of the assignment, introduce the topic, or remind you of something pertinent that you have discussed in class. For example:
“Throughout history, gerbils have played a key role in politics,” or “In the last few weeks of class, we have focused on the evening wear of the housefly …”
The Task of the Assignment
Pay attention; this part tells you what to do when you write the paper. Look for the key verb or verbs in the sentence. Words like analyze, summarize, or compare direct you to think about your topic in a certain way. Also pay attention to words such as how, what, when, where, and why; these words guide your attention toward specific information. (See the section in this handout titled “Key Terms” for more information.)
“Analyze the effect that gerbils had on the Russian Revolution”, or “Suggest an interpretation of housefly undergarments that differs from Darwin’s.”
Additional Material to Think about
Here you will find some questions to use as springboards as you begin to think about the topic. Instructors usually include these questions as suggestions rather than requirements. Do not feel compelled to answer every question unless the instructor asks you to do so. Pay attention to the order of the questions. Sometimes they suggest the thinking process your instructor imagines you will need to follow to begin thinking about the topic.
“You may wish to consider the differing views held by Communist gerbils vs. Monarchist gerbils, or Can there be such a thing as ‘the housefly garment industry’ or is it just a home-based craft?”
These are the instructor’s comments about writing expectations:
“Be concise”, “Write effectively”, or “Argue furiously.”
Technical Details
These instructions usually indicate format rules or guidelines.
“Your paper must be typed in Palatino font on gray paper and must not exceed 600 pages. It is due on the anniversary of Mao Tse-tung’s death.”
The assignment’s parts may not appear in exactly this order, and each part may be very long or really short. Nonetheless, being aware of this standard pattern can help you understand what your instructor wants you to do.
Interpreting the assignment
Ask yourself a few basic questions as you read and jot down the answers on the assignment sheet:
Why did your instructor ask you to do this particular task?
Who is your audience.
- What kind of evidence do you need to support your ideas?
What kind of writing style is acceptable?
- What are the absolute rules of the paper?
Try to look at the question from the point of view of the instructor. Recognize that your instructor has a reason for giving you this assignment and for giving it to you at a particular point in the semester. In every assignment, the instructor has a challenge for you. This challenge could be anything from demonstrating an ability to think clearly to demonstrating an ability to use the library. See the assignment not as a vague suggestion of what to do but as an opportunity to show that you can handle the course material as directed. Paper assignments give you more than a topic to discuss—they ask you to do something with the topic. Keep reminding yourself of that. Be careful to avoid the other extreme as well: do not read more into the assignment than what is there.
Of course, your instructor has given you an assignment so that they will be able to assess your understanding of the course material and give you an appropriate grade. But there is more to it than that. Your instructor has tried to design a learning experience of some kind. Your instructor wants you to think about something in a particular way for a particular reason. If you read the course description at the beginning of your syllabus, review the assigned readings, and consider the assignment itself, you may begin to see the plan, purpose, or approach to the subject matter that your instructor has created for you. If you still aren’t sure of the assignment’s goals, try asking the instructor. For help with this, see our handout on getting feedback .
Given your instructor’s efforts, it helps to answer the question: What is my purpose in completing this assignment? Is it to gather research from a variety of outside sources and present a coherent picture? Is it to take material I have been learning in class and apply it to a new situation? Is it to prove a point one way or another? Key words from the assignment can help you figure this out. Look for key terms in the form of active verbs that tell you what to do.
Key Terms: Finding Those Active Verbs
Here are some common key words and definitions to help you think about assignment terms:
Information words Ask you to demonstrate what you know about the subject, such as who, what, when, where, how, and why.
- define —give the subject’s meaning (according to someone or something). Sometimes you have to give more than one view on the subject’s meaning
- describe —provide details about the subject by answering question words (such as who, what, when, where, how, and why); you might also give details related to the five senses (what you see, hear, feel, taste, and smell)
- explain —give reasons why or examples of how something happened
- illustrate —give descriptive examples of the subject and show how each is connected with the subject
- summarize —briefly list the important ideas you learned about the subject
- trace —outline how something has changed or developed from an earlier time to its current form
- research —gather material from outside sources about the subject, often with the implication or requirement that you will analyze what you have found
Relation words Ask you to demonstrate how things are connected.
- compare —show how two or more things are similar (and, sometimes, different)
- contrast —show how two or more things are dissimilar
- apply—use details that you’ve been given to demonstrate how an idea, theory, or concept works in a particular situation
- cause —show how one event or series of events made something else happen
- relate —show or describe the connections between things
Interpretation words Ask you to defend ideas of your own about the subject. Do not see these words as requesting opinion alone (unless the assignment specifically says so), but as requiring opinion that is supported by concrete evidence. Remember examples, principles, definitions, or concepts from class or research and use them in your interpretation.
- assess —summarize your opinion of the subject and measure it against something
- prove, justify —give reasons or examples to demonstrate how or why something is the truth
- evaluate, respond —state your opinion of the subject as good, bad, or some combination of the two, with examples and reasons
- support —give reasons or evidence for something you believe (be sure to state clearly what it is that you believe)
- synthesize —put two or more things together that have not been put together in class or in your readings before; do not just summarize one and then the other and say that they are similar or different—you must provide a reason for putting them together that runs all the way through the paper
- analyze —determine how individual parts create or relate to the whole, figure out how something works, what it might mean, or why it is important
- argue —take a side and defend it with evidence against the other side
More Clues to Your Purpose As you read the assignment, think about what the teacher does in class:
- What kinds of textbooks or coursepack did your instructor choose for the course—ones that provide background information, explain theories or perspectives, or argue a point of view?
- In lecture, does your instructor ask your opinion, try to prove their point of view, or use keywords that show up again in the assignment?
- What kinds of assignments are typical in this discipline? Social science classes often expect more research. Humanities classes thrive on interpretation and analysis.
- How do the assignments, readings, and lectures work together in the course? Instructors spend time designing courses, sometimes even arguing with their peers about the most effective course materials. Figuring out the overall design to the course will help you understand what each assignment is meant to achieve.
Now, what about your reader? Most undergraduates think of their audience as the instructor. True, your instructor is a good person to keep in mind as you write. But for the purposes of a good paper, think of your audience as someone like your roommate: smart enough to understand a clear, logical argument, but not someone who already knows exactly what is going on in your particular paper. Remember, even if the instructor knows everything there is to know about your paper topic, they still have to read your paper and assess your understanding. In other words, teach the material to your reader.
Aiming a paper at your audience happens in two ways: you make decisions about the tone and the level of information you want to convey.
- Tone means the “voice” of your paper. Should you be chatty, formal, or objective? Usually you will find some happy medium—you do not want to alienate your reader by sounding condescending or superior, but you do not want to, um, like, totally wig on the man, you know? Eschew ostentatious erudition: some students think the way to sound academic is to use big words. Be careful—you can sound ridiculous, especially if you use the wrong big words.
- The level of information you use depends on who you think your audience is. If you imagine your audience as your instructor and they already know everything you have to say, you may find yourself leaving out key information that can cause your argument to be unconvincing and illogical. But you do not have to explain every single word or issue. If you are telling your roommate what happened on your favorite science fiction TV show last night, you do not say, “First a dark-haired white man of average height, wearing a suit and carrying a flashlight, walked into the room. Then a purple alien with fifteen arms and at least three eyes turned around. Then the man smiled slightly. In the background, you could hear a clock ticking. The room was fairly dark and had at least two windows that I saw.” You also do not say, “This guy found some aliens. The end.” Find some balance of useful details that support your main point.
You’ll find a much more detailed discussion of these concepts in our handout on audience .
The Grim Truth
With a few exceptions (including some lab and ethnography reports), you are probably being asked to make an argument. You must convince your audience. It is easy to forget this aim when you are researching and writing; as you become involved in your subject matter, you may become enmeshed in the details and focus on learning or simply telling the information you have found. You need to do more than just repeat what you have read. Your writing should have a point, and you should be able to say it in a sentence. Sometimes instructors call this sentence a “thesis” or a “claim.”
So, if your instructor tells you to write about some aspect of oral hygiene, you do not want to just list: “First, you brush your teeth with a soft brush and some peanut butter. Then, you floss with unwaxed, bologna-flavored string. Finally, gargle with bourbon.” Instead, you could say, “Of all the oral cleaning methods, sandblasting removes the most plaque. Therefore it should be recommended by the American Dental Association.” Or, “From an aesthetic perspective, moldy teeth can be quite charming. However, their joys are short-lived.”
Convincing the reader of your argument is the goal of academic writing. It doesn’t have to say “argument” anywhere in the assignment for you to need one. Look at the assignment and think about what kind of argument you could make about it instead of just seeing it as a checklist of information you have to present. For help with understanding the role of argument in academic writing, see our handout on argument .
What kind of evidence do you need?
There are many kinds of evidence, and what type of evidence will work for your assignment can depend on several factors–the discipline, the parameters of the assignment, and your instructor’s preference. Should you use statistics? Historical examples? Do you need to conduct your own experiment? Can you rely on personal experience? See our handout on evidence for suggestions on how to use evidence appropriately.
Make sure you are clear about this part of the assignment, because your use of evidence will be crucial in writing a successful paper. You are not just learning how to argue; you are learning how to argue with specific types of materials and ideas. Ask your instructor what counts as acceptable evidence. You can also ask a librarian for help. No matter what kind of evidence you use, be sure to cite it correctly—see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial .
You cannot always tell from the assignment just what sort of writing style your instructor expects. The instructor may be really laid back in class but still expect you to sound formal in writing. Or the instructor may be fairly formal in class and ask you to write a reflection paper where you need to use “I” and speak from your own experience.
Try to avoid false associations of a particular field with a style (“art historians like wacky creativity,” or “political scientists are boring and just give facts”) and look instead to the types of readings you have been given in class. No one expects you to write like Plato—just use the readings as a guide for what is standard or preferable to your instructor. When in doubt, ask your instructor about the level of formality they expect.
No matter what field you are writing for or what facts you are including, if you do not write so that your reader can understand your main idea, you have wasted your time. So make clarity your main goal. For specific help with style, see our handout on style .
Technical details about the assignment
The technical information you are given in an assignment always seems like the easy part. This section can actually give you lots of little hints about approaching the task. Find out if elements such as page length and citation format (see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial ) are negotiable. Some professors do not have strong preferences as long as you are consistent and fully answer the assignment. Some professors are very specific and will deduct big points for deviations.
Usually, the page length tells you something important: The instructor thinks the size of the paper is appropriate to the assignment’s parameters. In plain English, your instructor is telling you how many pages it should take for you to answer the question as fully as you are expected to. So if an assignment is two pages long, you cannot pad your paper with examples or reword your main idea several times. Hit your one point early, defend it with the clearest example, and finish quickly. If an assignment is ten pages long, you can be more complex in your main points and examples—and if you can only produce five pages for that assignment, you need to see someone for help—as soon as possible.
Tricks that don’t work
Your instructors are not fooled when you:
- spend more time on the cover page than the essay —graphics, cool binders, and cute titles are no replacement for a well-written paper.
- use huge fonts, wide margins, or extra spacing to pad the page length —these tricks are immediately obvious to the eye. Most instructors use the same word processor you do. They know what’s possible. Such tactics are especially damning when the instructor has a stack of 60 papers to grade and yours is the only one that low-flying airplane pilots could read.
- use a paper from another class that covered “sort of similar” material . Again, the instructor has a particular task for you to fulfill in the assignment that usually relates to course material and lectures. Your other paper may not cover this material, and turning in the same paper for more than one course may constitute an Honor Code violation . Ask the instructor—it can’t hurt.
- get all wacky and “creative” before you answer the question . Showing that you are able to think beyond the boundaries of a simple assignment can be good, but you must do what the assignment calls for first. Again, check with your instructor. A humorous tone can be refreshing for someone grading a stack of papers, but it will not get you a good grade if you have not fulfilled the task.
Critical reading of assignments leads to skills in other types of reading and writing. If you get good at figuring out what the real goals of assignments are, you are going to be better at understanding the goals of all of your classes and fields of study.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Standardize assessment criteria among those assigning/assessing the same assignment. Facilitate peer evaluation of early drafts of assignment. Rubrics Can Help Student Learning. Convey your expectations about the assignment through a classroom discussion of the rubric prior to the beginning of the assignment
Assessment Rubric. The assessment rubric, forms part of a set of criteria and refers specifically to the "levels of performance quality on the criteria." (Brookhart & Chen, 2015, p. 343) Generally, rubrics are categorised into two categories, holistic and or analytic. A holistic rubric assesses an assignment as a whole and is not broken ...
or expected in the assignment/course/program Figure 2: Elements of a learning outcome statement . Guidelines for Writing Effective Assessment Criteria Page 3 October 23, 2017 ... Criteria about theory must describe what aspects of the use of theory are being assessed. You may value any one of the following: the students ability to make an ...
Follow the basic steps below to plan your assignment. 1. Check the assessment criteria. Check the current student handbook (you will need to download the pdf file from the Moodle page for your course). Search for the criteria in the handbook using the 'Search' function. Please look at these criteria before you start writing your assignment.
Assignment criteria are sets of conditions describing the attributes of objects or candidates, or both, that are evaluated to determine optimal assignment. Assignment rules use criteria to determine which candidates qualify as potential assignees. Criteria also determine which assignment rule is evaluated in assigning an object.
ASSIGNMENT CRITERIA After discussing the important attributes of a civil trial judge, we now suggest criteria for assigning those judges to civil case calendars. In general judicial assignment criteria should be objective and transparent to promote effective case management and to curb politicization of the assignment pro-cess as much as possible.
Grading Criteria for Writing Assignments. Generally speaking, these criteria define the categories essential to the success of an essay. Essays are evaluated based on these elements, each of which must fulfill a specific function to support the overall effectiveness of the essay. Depending on the assignment, certain criteria may be weighted ...
project assignment criteria, which can be used later in the development of a methodology for project assignments. These research objectives are supported by the research
This rubric applies to your writing assignments. Criteria values will be determined based on point value. Always review the rubric prior to completing a writing assignment. Criteria Approved with Commendations Acceptable Adequate Inadequate Unacceptable Score Voice, Grammar, and Flow of Thought Commendable attention is given to voice, grammar, and
Assignment criteria attributes make it possible for a single assignment criterion to consist of multiple attributes, known as composite criteria. For composite criteria, all the attributes must have a 1:1 relationship and refer to the same base table record. For example, the Account City-State-Country is a good composite criterion because San ...
Here are a few suggestions: Think It Through: Consider how each written assignment relates to your course goals, not only in terms of the knowledge and skills you want students to acquire, but also in terms of their development as critical thinkers. Don't hesitate to share those goals with students, since they're more likely to be engaged ...
People assignment criteria are constructs that are used in the task model to identify sets of people that can be assigned to an instance-based authorization role. At run time, the people resolution uses the people assignment criteria to retrieve the user IDs and other user information from the people directory, for example, for composing emails.
Assessment Rubrics. A rubric is commonly defined as a tool that articulates the expectations for an assignment by listing criteria, and for each criteria, describing levels of quality (Andrade, 2000; Arter & Chappuis, 2007; Stiggins, 2001). Criteria are used in determining the level at which student work meets expectations.
To close these gaps, this study proposes an additional set of project assignment criteria and a systematic methodology for project assignments, so called, a decision support model for project assignments (DSM). By using the concepts of case study research combined with a literature review, the important potential criteria for project ...
This topic explains how to add assignment criteria to assignment rules. This task is a step in Process of Defining Criteria Values as Skills with Expertise Codes and Weighting Factors as well as a step in Process of Defining Assignment Rules.. Criteria are sets of conditions describing the attributes of objects or candidates, or both, that are evaluated to determine optimal assignment.
the assignment criteria and tends to focus on global issues. What's That Supposed to Mean? 149 WRITING SPACES 4 The form of the feedback indicates what you may need to do with it, but we also need to understand the content of your feedback. Content of Feedback
Online assignment criteria. UNV screens all submitted assignment descriptions before publishing them. When you submit an assignment, make sure it… Benefits sustainable human development. Your assignment description should clearly state how the Online Volunteer will contribute to sustainable human development and to the achievement of the ...
Assignment rules are a set of criteria that are defined by businesses to determine how records should be assigned to users or teams within the Salesforce system. These criteria can be based on several factors, such as the record type, location, record status, or the user's role or territory. For example, a company may set up an assignment rule ...
In our Cornell Note Taking System module you will: The best way to explore your current note-taking strategies and learn about the Cornell note taking system is to go through our Canvas note taking module. The module will interactively guide you through how to use Cornell Notes - click on the link here or the button below.
CONSULTANT ENG. & INSPECTION (Facilities) FOR PROJECT 301-195 DARIEN STA. (This assignment is exempt from recent selection criteria) DESIGN SERVICES FOR PROJECT 94-261 & 94-235 NB GOLDSTAR. 7/21/22 TASK ORDER CONSTRUCTION ENG & INSPECTION (This assignment is exempt from recent selection criteria) 7/8/22. 7/1/22.
VALUE ADD encourages instructors to explicitly state assignment information such as the purpose of the assignment, what skills students will be using, how it aligns with course learning outcomes, the assignment type, the audience and context for the assignment, clear evaluation criteria, desired formatting, and expectations for completion ...
This study had three goals. First, we examined the prevalence of the participant roles of bullying in middle adolescence and possible gender differences therein. Second, we examined the behavioral and status characteristics associated with the participant roles in middle adolescence. Third, we compared two sets of criteria for assigning students to the participant roles of bullying ...
Assignment and Conveyance Agreement As defined in Subsection 6.01. Nomination Criteria means the criteria made up of the Over-Riding Nomination Criteria andthe Specific Nomination Factors, and is also referred to as "this Criteria". Assignment / job means the work to be performed by the Consultant pursuant to the Contract.
10 examples of professional development goals. Here are ten examples of professional development goals to inspire your own: 1. Develop a new skill set. Growing professionally often means expanding the arsenal of things you're able to do. What skill you choose to develop can depend on your industry, job, and personal preferences.
The criteria sheet, also known as the marking sheet or rubric, is another important document to look at before you begin your assignment. The criteria sheet outlines how your assignment will be marked and should be used as a checklist to make sure you have included all the information required. The task or criteria sheet will also include the:
UNV reviews the descriptions of assignments and publishes them if they meet the criteria. Volunteers find assignments of their interest and apply. Organizations select the volunteers they want to engage. Volunteers and organizations collaborate online. Volunteers and organizations provide feedback on their collaboration.
What this handout is about. The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms ...
Hundreds of millions of votes cast, more than six weeks of polling, and billions of dollars spent: India on Tuesday will declare a new leader after a mammoth nationwide election that has become a ...