- Constitution of India
- Indian Penal Code
- Indian Contract Act
- Indian Evidence Act
- Transfer of Property
- Intellectual Property Rights
- Consumer Protection
- Right to Information
- Human Rights
- Voice of Women
- Expert Corner
- Case Summary
- Legal Maxims
- Internships
- General Knowledge
- Submit Post

Assignment of Contract

An agreement enforceable by law becomes a contract. A contract involves both rights and obligations because a contract is an agreement enforceable by law. An agreement involves promises from both sides, and thus, there is the creation of both rights and obligations. For instance, X promises to sell his car to Y, and Y promises to pay Rs. 5,00,000 for his car. This constitutes a valid contract between X and Y. Here, the right on the part of X is to get Rs. 5,00,000 as consideration for selling his car, and the obligation for X is to deliver the car to Y as consideration for Rs. 5,00,000 paid to X by Y for selling his car.
Similarly, the right on the part of Y is to get the car delivered as consideration for Rs. 5,00,000 paid, and the obligation for Y is to pay Rs. 5,00,000 as consideration for the vehicle. If either X or Y fails to discharge their responsibility, there will be a breach of contract. In this way, a contract leads to the creation of both rights and obligations for both parties.
Assignment of contract refers to transferring contractual rights and liabilities under the contract to the third party with or without the other party’s concurrence. For instance, X owes Y Rs. 1,000, and Y owes Z the same amount. In this case, Y is under obligation to pay Rs. One thousand to Z and has the right to receive Rs. 1,000 from Z. In this case if Y asks Z to directly pay Rs. 1,000 to X, and if X accepts the same, there will be an assignment of Y’s right to Z. But, if in a similar situation, instead of transferring his ownership, Y would have transferred any of his obligations, then it would amount to novation. Section 37 of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, enables the parties to dispense the performance by way of the contract’s Assignment. Apart from conforming with the Indian Contract Act, 1872, there are exceptional circumstances where the contract assignment must be duly stamped in conformity with the provisions of the Indian Stamp Act, 1899.
The common law system did give effect to three kinds of transactions, viz., acknowledgment, novation, and power of attorney, which to some extent did work of an assignment. Under the Indian Contract Law, any form of contract can be assigned as long as consent is involved in the Assignment. The consent of the ‘promisee’ is necessary for assigning any obligation under the contract. There are three parties involved in contracts of Assignment, namely, the assignor, assignee, and obligor. The working and application of the contract assignment depend on a multiplicity of factors such as the contract’s language, applicability, availability of the assignment clause in the agreement, etc. There are contracts that contain a clause prohibiting Assignment, while other contracts require the consent of the other party to the Assignment.
But if a contract between two parties relies entirely on the’ promisor’s skill or expertise, then such a contract cannot be assigned under any circumstances. This is because the ‘promisee’ has entered into the contract based on the’ promisor’s skill or expertise. The case of Robinson v Davison is important case law in this regard . In this case, the defendant’s wife promised to play piano on a particular at a concert. She was unable to discharge her liability, that is, to play piano at the concert because of her illness. In this case, it was held that the contract was directly dependent on the good health and the personal skill of the defendant’s wife, and the illness of his wife discharged the contract. It was also stated that the defendant could not be made liable to pay compensation for the non-performance of the contract. As the contract was based on the ‘promisor’s skill in the above case law, the wife could not assign her right/obligation to any third party.
Case Study: Kapilaben & Ors. v Ashok Kumar Jayantilal Seth through POA Gopalbhai Manusudhan Case
Kapilaben & Ors. v Ashok Kumar Jayantilal Seth through POA Gopalbhai Manusudhan is a recent judgment delivered by the Supreme Court of India on November 25, 2019, concerning the Assignment of rights and Interests in a contract. In this judgment, the Supreme Court reaffirmed that a party to a contract could not assign its liabilities or obligations without the consent of the other party.
The facts of the case are: The appeals to the Supreme Court resulted from the Gujrat High Court’s decision that had allowed the appeals of the respondent against the trial court’s decision. The dispute, in this case, is related to a property owned by the appellants (Vendor). The appellant has had formulated an agreement to sell in favor of some of the respondents in 1986 regarding the above-mentioned property. The respondents, who were the original vendees, had paid a part of the consideration part. The Original Vendees, in 1987, assigned the former’s rights in favor of Respondent 1 and executed an agreement in favor of Respondent 1. This led to several disputes, and subsequently, Respondent 1 filed suits against the Original Vendees and the vendor demanding specific performance of the agreement executed in 1987. The Respondent’s suits were dismissed by the trial courts stating that the Original Vendees could not have assigned their outstanding obligation of paying Vendor the remaining money to Respondent 1 without the consent of the Vendor. On the other hand, Gujrat High Court reversed the decision of the trial court and declared the Assignment of rights in favor of Respondent 1 as valid.
The Supreme Court in its judgment reaffirmed the view of the trial courts and stated that: “ It is further relevant to note that under the 1987 agreements, payment of the outstanding consideration amount is to be made to the original vendees, not the Appellants, and possession/ownership of the suit property is to be handed over by the original vendees. The 1987 agreements nowhere provide for the discharge of the original vendees’ pending obligations towards the Appellants by Respondent Nos. 1. Hence, we are inclined to accept the Appellants’ argument that the 1987 agreements were not a case of Assignment but appear to be independent/sovereign agreements for sale which were contingent and dependent on the execution and implementation of the 1986 agreement. Therefore, the only way Respondent Nos. 1 can seek specific performance of the 1986 agreement against the Appellants is by proving the Appellants’ knowledge of and consent to transfer the original vendees’ rights and liabilities Respondent Nos. 1.”
From the above discussion, it is clear that the Assignment of contract refers to transferring contractual rights and liabilities under the contract to the third party with or without the other party’s concurrence. Section 37 of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, thatenables the parties to dispense is the performance by way of Assignment of the contract. Under the Indian Contract Law, any form of contract can be assigned as long as consent is involved in the Assignment. The consent of the ‘promisee’ is necessary for assigning any obligation under the contract. The working and application of the contract assignment depend on a multiplicity of factors such as the contract’s language, applicability, availability of the assignment clause in the agreement, etc. There are contracts that contain a clause prohibiting Assignment, while other contracts require the consent of the other party to the Assignment. The Assignment of obligations/liabilities is not possible in the case of contracts solely relying on the personal skill or expertise of the ‘promisor’.
The recent judgment of the Supreme Court in Kapilaben & Ors. v Ashok Kumar Jayantilal Seth, through POA Gopalbhai Manusudhan Case, also reaffirms that in case of transfer/assigning of outstanding obligations under the contract, the consent of the other party is a necessary condition to make the Assignment valid. Even though this judgment reaffirms the point upheld by law, it still suggests the parties to a contract consider the various complexities of contracts, the intent contract, the availability of the assignability clause in the written agreement, etc., before drafting a commercial contract.
References:
- The Indian Contract Act, 1872, No. 2(h) (Indian).
- Dr. R.K. Bangia, The Indian Contract Act, 2 (12 th Edition, 2005), Allahabad Law Agency, Haryana.
- Krishnendu Kanungo & Pritisha Chakraborty , Assignment Of Rights And Its Practical Relevance In Financial Transactions: A Lender’s Perspective Manupatra, http://docs.manupatra.in/newsline/articles/Upload/E915DA6B-361C-493B-91D1-96D8EB703128.pdf (last accessed Mar. 12, 2021).
- The Indian Contract Act, 1872, No. 37 (Indian)
- Sir Oshley Roy Marshall, The Assignment of Choses in Action (Pitman Publishing 1950).
- Krishnendu, supra note 3, at 1.
- Khared & Co. Ltd. v Ramon & Co. Ltd., AIR 1962 SC 1810.
- Krishnendu, supra note 3, at 2.
- Robinson v Davison, (1871) L.R. Ex. 269.
- BANGIA, supra note 1, at 255.
- Ramesh Vaidyanathan & Aishini Mandal, Assignment Of Contractual Obligations – Is Consent Necessary Advayalegal (Dec. 6, 2019) https://www.advayalegal.com/blog/contractual-rights/ (last accessed Mar. 13, 2021).
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
A detailed analysis of provisions related to coercions under the indian contract law, free consent (section 13 & 14), a detailed analysis of provisions related to compensation for loss or damage caused by breach of contract under the indian contract law, editor picks, popular posts, maneka gandhi vs union of india – case summary, contract of bailment and pledge, adm jabalpur vs shivkant shukla (1976) 2 scc 521 – case..., popular category.
- NEWS UPDATE 1750
- Bare Act PDF 919
- Case Summary 363
- Legal Maxims 269
- Articles 177
- Indian Penal Code 104
- Articles 86
- Voice of Women 72

COMMERCIAL LAW BLOG
Research & Updates
Sub-contracting and Assignment : Resolving the Legal Conundrum

The performance of a contract may require third party involvement towards the fulfilment of obligations under a contract. In certain specific circumstances, the contracting parties may decide to “sub-contract” or “assign” their rights and obligations to a third party depending upon the nature of the contract.
In common parlance, sub-contracting and assignment are used interchangeably, however, a significant difference lies between the two when one examines the terms from a legal stand point. This post aims to discuss the concept of Sub-Contracting and Assignment and explains the key difference between the two concepts.
Sub-contracting
Sub-contracting refers to the delegation of certain duties and obligations by contracting parties to a third party, i.e. a sub-contractor who aids in the performance of the contract. According to the Black’s Law Dictionary, a sub-contract is “where a person has contracted for the performance of certain work and he, in turn, engages a third party to perform the whole or part of that which is included in the original contract, his agreement with such third person is called a subcontract and such person is called a subcontractor .” [1] A subcontractor could be a company, self-employed professionals or an agency undertaking to fulfil obligations under a contract.
Sub-contracting is generally undertaken in complex projects where the contract has a prolonged life cycle or multiple components for completion of a project, for instance, infrastructure contracts, construction contracts, renewable energy contracts or certain information technology-related contracts. However, the rights and duties of the sub-contractor under the sub-contracting agreement are relatively similar to that of the principal contractor in the main agreement.
Furthermore, while drafting a contract, one must ensure to incorporate a clause on sub-contracting which clearly spells out that parties to the contract shall sub-contract the rights and obligations only after seeking prior written consent from the other party. The sub-contracting arrangement maybe two-fold, depending upon the nature of the main contract:
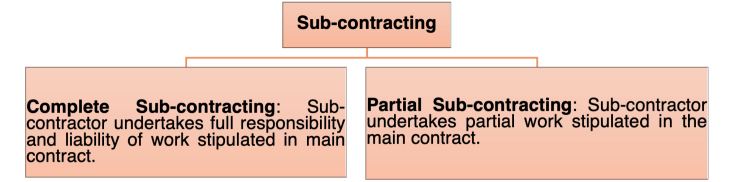
Primarily, the basic idea behind delegation of the obligations to a sub-contractor is to ensure greater flexibility in the performance of the contract. However, it is imperative to enter into a sub-contractor’s agreement that specifies all the details of the work to be performed by the subcontractor, including optimum time required to accomplish the task, payment of charges to the subcontractor, termination of the agreement, etc.
While subcontracting is time-saving and cost efficient, it may result into legal issues between the contracting parties. For instance, issues may arise with respect to the payment conditions where the payment to sub-contractor is contingent upon or linked to the principal contractor receiving its payment from the employer. Further, the courts in India have always upheld the principle of privity of contract between employer and the principal contractor on the one hand and between the principal contractor and sub-contractor(s) on the other. The Supreme Court of India in the case of Zonal General Manager, Ircon International Ltd. v. Vinay Heavy Equipments [2] upheld that in the absence of a back-to-back covenant in the main contract, “ the distinct and sole liability of the middle-contractor is presumed and that the rules in relation to privity of contract will mean that the jural relationship between the employer and the main contractor on the one hand and between the sub-contractor and the main contractor on the other will be quite distinct and separate” . Therefore, in order to avoid ambiguities and future legal squabbles, careful consideration must be given while drafting specific terms and obligation that will pass down the contractual chain.
Assignment of contract refers to an act of transferring contractual rights and liabilities under the contract to a third party with other party’s concurrence. Section 37 of the India Contract Act, 1872 (“ Contract Act ”) enables the contracting parties to dispense with the performance of a contract by way of an assignment. While the principle of assignment is well recognized under Indian law, it derives its origin from the English law.
Assignment of rights is a “complete transfer of rights to receive benefits” accruing to one party under a contract. Performance of a contract may be assigned as long as the contracting parties provide their consent towards the assignment. However, the act of assignment needs to be looked at from the perspective of the contracting parties. Essentially, there are three parties involved, namely, the assignor, assignee and obligor.
An important principle affecting assignments is that the burden or liability under a contract cannot be assigned. Essentially, the moot question that often arises is with respect to assignment of “rights” vis à vis assignment of “obligations”. The Supreme Court in the case of Khardah Company Ltd. v. Raymon & Co. (India) Private Limited [3] categorically distinguished between assignment of “rights” and “obligations”. The court upheld that, “ an assignment of a contract might result by transfer either of the rights or of the obligations thereunder. But there is a well-recognised distinction between these two classes of assignments. As a rule, obligations under a contract cannot be assigned except with the consent of the promisee, and when such consent is given, it is really a novation resulting in substitution of liabilities. On the other hand rights under a contract are assignable unless the contract is personal in its nature (or) the rights are incapable of assignment either under the law or under an agreement between the parties” . Primarily, the court clarified that obtaining prior consent to assign “obligations” under a contract would be considered as novation as it will result into substitution of liabilities and obligations to the assignee. Moreover, introduction of a new party into an existing contract will result into novation of a contract i.e. creation of a new contract between original party and new party. As the courts have interpreted that transfer of obligations can be undertaken through novation, the assignment clause in a contract must clearly deal with novation, if the intention is to transfer obligations.
Furthermore, the Supreme Court, in the case of Gopalbhai Manusudhan [4] , reaffirmed that whenever there is a case of assignment or even the transfer of the obligations, it must be acclaimed that there is the presence of the consent of the parties. Without the consent of the parties, the assignment will be not considered valid. In addition to upholding the legal point, this ruling also indicates that before establishing a commercial contract, the parties must consider the different complications of contracts, such as the objective of the contract and the presence of an assignability clause in the agreement.
Therefore, the judicial trend in India has time and again reiterated and laid down that rights under contract can be assigned unless (a) the contract is personal in nature i.e. requires personal engagement of a specific person or (b) the rights are incapable of assignment either under law or under an agreement between the parties. In the case of Robinson v. Davison [5] , the defendant’s wife pledged to perform piano at a concert on a specific date. Due to “her illness”, she was unable to fulfil her obligation, which was to play the piano at an event. The contract in this instance was ruled to be solely dependent on the defendant’s wife’s good health and personal talent, and the defendant’s wife’s illness led the contract to be void. Further, the court ruled that the defendant could not be held liable for damages as a result of the contract’s non-performance. The wife could not assign her right/obligation to a third party because the contract was founded on the “promisor’s expertise” in the aforesaid case.
While assignment is a boiler plate clause, it requires careful consideration on a case-to-case basis. For instance, in real estate transactions, a buyer would insist on retaining the right to assign the “agreement to sell” in favour of a nominee (a company, affiliate or any other third party), in order to facilitate final conveyance in favour of the intended buyer. Similarly, in lending transactions, a borrower will be prohibited from assigning rights under the contract, however, the lender will retain absolute and free right to assign/sell loan portfolios to other lenders or securitisation company.
The apex court has time and again reiterated that the best policy is to unequivocally state the intent with respect to assignment in the agreement to avoid litigation in the future. The contracting parties must expressly specify the rights and obligations stemming from assignment under a contract. Any agreed limitation on such an assignment must be expressly laid down in the contract to avoid adverse consequences.
For a person drafting a contract, it is important to understand these subtle differences, between sub-contracting and assignment. While “sub-contracting” is delegating or outsourcing the liabilities and obligations, “assignment” is literally transferring the obligations. It will be not fallacious to say that an “assignment” transfers the entire legal obligation to perform to the party assigned the obligation whereas, subcontracting leaves the primary responsibility to perform the obligation with the contracting party.
Archana Balasubramanian (Partner), Vaishnavi Vyas (Associate)
[1] Black’s Law Dictionary 4th ed. (St. Paul: West, 1951).
[2] 2006 SCC OnLine Mad 1107
[3] MANU/SC/0428/1962
[4] Kapilaben & Ors. v Ashok Kumar Jayantilal Seth through POA Gopalbhai Manusudhan 2019 (10) SCJ 269
[5] (1871) LR 6 Ex 269
Share this:
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
Leave a comment Cancel reply
- Agama Announcements
- Arbitration
- Commercial Laws
- Covid-19 Updates
- Criminal Law
- Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain
- Data Protection/Privacy
- Environmental Law
- Family Laws
- In the News
- Intellectual Property Laws
- Labour/Employment
- Labour/Employment – Women
- Real Estate
- Securities Law
- Will & Succession
Follow Blog via Email
Enter your email address to follow this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
Email Address:
This website does not provide any legal advice and is for information purposes only. Any reliance on information or opinion contained herein would be against the advice of the administrators of this website and entirely at risk and cost of the recipient or user of this information. No attorney-client relationship is formed through this website, directly or indirectly. Opinions are of authors and does not necessarily bind the administrators or owners of the website or the law firm.

Create a website or blog at WordPress.com

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar

Assignment of Contract
Jump to section, what is an assignment of contract.
An assignment of contract is a legal term that describes the process that occurs when the original party (assignor) transfers their rights and obligations under their contract to a third party (assignee). When an assignment of contract happens, the original party is relieved of their contractual duties, and their role is replaced by the approved incoming party.
How Does Assignment of Contract Work?
An assignment of contract is simpler than you might think.
The process starts with an existing contract party who wishes to transfer their contractual obligations to a new party.
When this occurs, the existing contract party must first confirm that an assignment of contract is permissible under the legally binding agreement . Some contracts prohibit assignments of contract altogether, and some require the other parties of the agreement to agree to the transfer. However, the general rule is that contracts are freely assignable unless there is an explicit provision that says otherwise.
In other cases, some contracts allow an assignment of contract without any formal notification to other contract parties. If this is the case, once the existing contract party decides to reassign his duties, he must create a “Letter of Assignment ” to notify any other contract signers of the change.
The Letter of Assignment must include details about who is to take over the contractual obligations of the exiting party and when the transfer will take place. If the assignment is valid, the assignor is not required to obtain the consent or signature of the other parties to the original contract for the valid assignment to take place.
Check out this article to learn more about how assigning a contract works.
Contract Assignment Examples
Contract assignments are great tools for contract parties to use when they wish to transfer their commitments to a third party. Here are some examples of contract assignments to help you better understand them:
Anna signs a contract with a local trash company that entitles her to have her trash picked up twice a week. A year later, the trash company transferred her contract to a new trash service provider. This contract assignment effectively makes Anna’s contract now with the new service provider.
Hasina enters a contract with a national phone company for cell phone service. The company goes into bankruptcy and needs to close its doors but decides to transfer all current contracts to another provider who agrees to honor the same rates and level of service. The contract assignment is completed, and Hasina now has a contract with the new phone company as a result.
Here is an article where you can find out more about contract assignments.
Christina M.
Assignment of Contract in Real Estate
Assignment of contract is also used in real estate to make money without going the well-known routes of buying and flipping houses. When real estate LLC investors use an assignment of contract, they can make money off properties without ever actually buying them by instead opting to transfer real estate contracts .
This process is called real estate wholesaling.
Real Estate Wholesaling
Real estate wholesaling consists of locating deals on houses that you don’t plan to buy but instead plan to enter a contract to reassign the house to another buyer and pocket the profit.
The process is simple: real estate wholesalers negotiate purchase contracts with sellers. Then, they present these contracts to buyers who pay them an assignment fee for transferring the contract.
This process works because a real estate purchase agreement does not come with the obligation to buy a property. Instead, it sets forth certain purchasing parameters that must be fulfilled by the buyer of the property. In a nutshell, whoever signs the purchase contract has the right to buy the property, but those rights can usually be transferred by means of an assignment of contract.
This means that as long as the buyer who’s involved in the assignment of contract agrees with the purchasing terms, they can legally take over the contract.
But how do real estate wholesalers find these properties?
It is easier than you might think. Here are a few examples of ways that wholesalers find cheap houses to turn a profit on:
- Direct mailers
- Place newspaper ads
- Make posts in online forums
- Social media posts
The key to finding the perfect home for an assignment of contract is to locate sellers that are looking to get rid of their properties quickly. This might be a family who is looking to relocate for a job opportunity or someone who needs to make repairs on a home but can’t afford it. Either way, the quicker the wholesaler can close the deal, the better.
Once a property is located, wholesalers immediately go to work getting the details ironed out about how the sale will work. Transparency is key when it comes to wholesaling. This means that when a wholesaler intends to use an assignment of contract to transfer the rights to another person, they are always upfront about during the preliminary phases of the sale.
In addition to this practice just being good business, it makes sure the process goes as smoothly as possible later down the line. Wholesalers are clear in their intent and make sure buyers know that the contract could be transferred to another buyer before the closing date arrives.
After their offer is accepted and warranties are determined, wholesalers move to complete a title search . Title searches ensure that sellers have the right to enter into a purchase agreement on the property. They do this by searching for any outstanding tax payments, liens , or other roadblocks that could prevent the sale from going through.
Wholesalers also often work with experienced real estate lawyers who ensure that all of the legal paperwork is forthcoming and will stand up in court. Lawyers can also assist in the contract negotiation process if needed but often don’t come in until the final stages.
If the title search comes back clear and the real estate lawyer gives the green light, the wholesaler will immediately move to locate an entity to transfer the rights to buy.
One of the most attractive advantages of real estate wholesaling is that very little money is needed to get started. The process of finding a seller, negotiating a price, and performing a title search is an extremely cheap process that almost anyone can do.
On the other hand, it is not always a positive experience. It can be hard for wholesalers to find sellers who will agree to sell their homes for less than the market value. Even when they do, there is always a chance that the transferred buyer will back out of the sale, which leaves wholesalers obligated to either purchase the property themselves or scramble to find a new person to complete an assignment of contract with.
Learn more about assignment of contract in real estate by checking out this article .
Who Handles Assignment of Contract?
The best person to handle an assignment of contract is an attorney. Since these are detailed legal documents that deal with thousands of dollars, it is never a bad idea to have a professional on your side. If you need help with an assignment of contract or signing a business contract , post a project on ContractsCounsel. There, you can connect with attorneys who know everything there is to know about assignment of contract amendment and can walk you through the whole process.
ContractsCounsel is not a law firm, and this post should not be considered and does not contain legal advice. To ensure the information and advice in this post are correct, sufficient, and appropriate for your situation, please consult a licensed attorney. Also, using or accessing ContractsCounsel's site does not create an attorney-client relationship between you and ContractsCounsel.
Meet some of our Lawyers
Business-minded, analytical and detail-oriented attorney with broad experience in real estate and corporate law, with an emphasis on retail leasing, sales and acquisitions and real estate finance. Extensive experience in drafting complex commercial contracts, including purchase and sale contracts for businesses in a wide variety of industries. Also experienced in corporate formation and governance, mergers and acquisitions, employment and franchise law. Admitted to practice in Colorado since 2001, Bar No. 33427.
I am a regulatory transactional attorney with 16 years of in-house experience, largely in the gaming/gambling industry. I have negotiated various types and sizes of contracts from janitorial services for a small commercial building to multi-million dollar technology transactions. I also have a strong regulatory background that strengthens my ability to navigate contracts that are subject to stringent regulations.
I was born in Charlotte, NC and primarily raised in Dalton, GA. I graduated from Dalton High School in 1981 where I was in the band and the French club. I also participated in Junior Achievement and was a member of Tri-Hi-Y. New York granted my first license as an attorney in 1990. I then worked as a partner in the firm of Broda and Burnett for almost 10 years and as a solo practitioner for about 2 years. I worked as a general practitioner (primarily doing divorces, child abuse cases, custody matters and other family law matters, bankruptcy, real estate closings, contracts, taxes, etc.) and as a Law Guardian (attorney who represents children). I obtained my license in Tennessee in December 2002 and began working as an associate at Blackburn & McCune from February of 2003 until May of 2005. At Blackburn & McCune I provided telephone legal counsel to Prepaid Legal Services (now known as Legal Shield) members, wrote letters for members, reviewed contracts, attended hearings on traffic ticket matters and represented members with regard to IRS matters. In May of 2005, I went to work for North American Satellite Corporation where I served as Corporate Counsel. I handled a number of taxation issues, reviewed and wrote contracts, counseled the CEO and Board of Directors on avoiding legal problems and resolving disputes, and represented employees on a variety of matters, and also assisted the company for a period of time as its Director of Accounting. In 2010, I volunteered as a law clerk for Judge Robert Adams in Dalton, Georgia until I obtained my license to practice law in Georgia in November, 2010. In Georgia, I have handled a variety of family law matters, drafted wills, advanced health care directives, power of attorney documents, reviewed and drafted contracts, and conducted real estate closings. Currently, I accept cases in the areas of adoption, child support, custody, divorce, legitimation and other family law matters. In addition, I handle name change petitions and draft wills.
Michigan and USPTO licensed attorney with over 20 years of experience on counseling clients in the fields of intellectual property, transactional law, technology involvement, negotiations, and business litigation.
Attorney with over 10+ years' experience and have closed over $1 Billion in real estate, telecommunications, & business transactions
I am an attorney with over 13 years experience licensed in both Illinois and Indiana. I spent the early part of my career as a civil litigation attorney. Eventually, I moved into an in-house role, specifically as general counsel, to help companies avoid the pains of litigation. In doing so, I gained significant experience in executive leadership, corporate governance, risk management and cybersecurity/privacy. I bring this wealth of experience to my client engagements to not only resolve the immediate issue, but help implement lasting improvements in practices to avoid similar problems going forward.
I am a Spanish-fluent corporate and commercial real estate attorney and broker licensed in New York and New Jersey. My pragmatic approach towards conflict resolution allows me to provide valuable advice to clients on avoiding issues of liability through effective risk management and strategic allocation of resources. I counsel businesses, developers, owners and investors on residential/commercial real estate and corporate transactions involving the acquisition, finance, development, leasing and disposition of all asset classes. In addition, I advise on joint venture partnerships and the negotiation, structure and drafting of operating agreements. Throughout my successful practice, I have held in-house counsel positions at large corporations, including JPMorgan Chase and Duane Reade, and had the privilege of working for the Department of Justice where I honed expertise in all aspects of mortgage-backed securities.
Find the best lawyer for your project

Quick, user friendly and one of the better ways I've come across to get ahold of lawyers willing to take new clients.
Need help with a Contract Agreement?
Post Your Project
Get Free Bids to Compare
Hire Your Lawyer
CONTRACT LAWYERS BY TOP CITIES
- Austin Contracts Lawyers
- Boston Contracts Lawyers
- Chicago Contracts Lawyers
- Dallas Contracts Lawyers
- Denver Contracts Lawyers
- Houston Contracts Lawyers
- Los Angeles Contracts Lawyers
- New York Contracts Lawyers
- Phoenix Contracts Lawyers
- San Diego Contracts Lawyers
- Tampa Contracts Lawyers

ASSIGNMENT OF CONTRACT LAWYERS BY CITY
- Austin Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Boston Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Chicago Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Dallas Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Denver Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Houston Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Los Angeles Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- New York Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Phoenix Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- San Diego Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
- Tampa Assignment Of Contract Lawyers
Contracts Counsel was incredibly helpful and easy to use. I submitted a project for a lawyer's help within a day I had received over 6 proposals from qualified lawyers. I submitted a bid that works best for my business and we went forward with the project.
I never knew how difficult it was to obtain representation or a lawyer, and ContractsCounsel was EXACTLY the type of service I was hoping for when I was in a pinch. Working with their service was efficient, effective and made me feel in control. Thank you so much and should I ever need attorney services down the road, I'll certainly be a repeat customer.
I got 5 bids within 24h of posting my project. I choose the person who provided the most detailed and relevant intro letter, highlighting their experience relevant to my project. I am very satisfied with the outcome and quality of the two agreements that were produced, they actually far exceed my expectations.
How It Works
Want to speak to someone.
Get in touch below and we will schedule a time to connect!
Find lawyers and attorneys by city

Kluwer Arbitration Blog
Does the assignment of a contract assign the arbitration agreement: the indian perspective.
Under the Indian Contract Act 1872 (“ ICA ”), an arbitration agreement is a distinct and separate contract. Like all other contracts, it can be transferred by way of assignment to third parties under Section 37 of the ICA. The Supreme Court of India in Khardah Company Ltd vs Raymon & Co. (India) Private Ltd has held that there is a distinction between the assignment of “rights” and “liabilities.” A contract stands novated when assigning rights and liabilities to a third party. This raises a fundamental question – does the arbitration agreement also stand novated when the principal contract is assigned to a third party? If it does, then as held by the Supreme Court in Kapilaben v. Ashok Kumar Jayantilal Sheth the assignment of every obligation, such as the obligation to refer the dispute to arbitration, requires the parties’ fresh consent.
If, on the other hand, the arbitration agreement does not stand novated on assignment of the principal contract, does it mean that the arbitration agreement is automatically transferred along with the principal contract to the third party without the need for fresh consent (“ Automatic Transfer Approach ”)?
The United States courts have always been divided in their approach. Some earlier decisions, such as Hosiery Mfrs’ Corp. v. Goldston and Nissan Motor Acceptance Corp v. Ross , support the Automatic Transfer Approach. On the contrary, decisions like Lachmar v. Trunkline LNG Co . require express consent of the assignee (third party). However, in recent years courts have critically analysed the principal contract than merely choosing sides to ascertain assignment of the arbitration agreement, adopting an approach similar to the highest court of Bulgaria .
In similar vein, the Indian courts have been inconsistent in their decisions on whether the assignment of a contract also amounts to the assignment of the arbitration agreement to a third party.
Requirement of Specific Consent
In Delhi Iron and Steel Co. Ltd. v. U.P. Electricity Board , the Delhi High Court took the view that the assignment of the principal contract does not ipso facto result in the assignment of the arbitration agreement. The principal contract is assignable, but the arbitration agreement is not. Since an arbitration agreement is a distinct and separate agreement, the arbitral intent between the original party and the assignee of the other party must be made manifest. A similar view was adopted in Vishranti CHSL v. Tattva Mittal Corpn. (P) Ltd . holding that in the absence of specific consent to the assignment of the arbitration agreement, the arbitration agreement would not be assigned to the third party, even if the principal contract has been assigned.
The basis for this view can be found in the judgement of the Indian Supreme Court in M.C. Chacko v. State of Travancore which held that a person who is not a party to the contract cannot enforce the terms of the contract. However, it is pertinent to note that even in this judgement, the Supreme Court had recognised the assignment exception. Thus, the requirement of specific consent by the assignee to transfer the arbitration agreement is an approach adopted by Indian courts only in a handful cases.
No Separate Consent Required
The predominant view by Indian courts has been that the doctrine of separability enshrined under Section 16 of the Arbitration and Conciliation Act 1996 (“ Act ”) relates to the right of the arbitral tribunal to rule on its own jurisdiction. The doctrine of separability and its jurisprudence cannot be extended to mean that a separate arbitration agreement is to be executed between the parties at the time of assignment of a contract. Therefore, as held by the Bombay High Court in DLF Power Ltd. v. Mangalore Refinery & Petrochemicals Ltd . (“ DLF ”), a third party, to whom the principal contract is assigned, can enforce the arbitration agreement.
Specifically, if the rights and obligations under the principal contract are assigned to a third party and this third party also performs obligations under the contract, such as making payments, seeking extension of time or approval, joint survey, etc., this third party is entitled to invoke arbitration.
Consensual Theory of Arbitration
Taking a similar approach, the Delhi High Court in Rajesh Gupta v. Mohit Lata Sunda held that if the parties to the principal contract knew of the assignment and were fully aware that a third party ‘had stepped into the shoes’ of another party, the arbitration agreement stood assigned. These views are essentially based on the consensual theory in arbitration stated in Aerens Goldsouk International Co. Ltd. v. Samit Kavdia , which recognises that non-signatories to the arbitration agreement can invoke the arbitration clause and are thus ‘parties’ to the arbitration agreement under Section 2(1)(h) of the Act.
Consequently, the consensual theory aims to infer consent from the parties’ behaviour if an agreement is not self-evident. Agency, assignment, and group of companies doctrine are among such theories. Recently, the Delhi High Court in Tomorrow Sales Agency (P) Ltd. v. SBS Holdings Inc. , held that the non-signatories may either invoke the arbitration agreement, being the beneficiaries of the contract, or otherwise be bound by the same. The Court noted, “ 30. Gary B. Born, has explained that the legal basis for holding that a non-signatory is bound by an arbitration agreement includes “both purely consensual theories (e.g., agency, assumption, assignment) and non-consensual theories ( e.g. , estoppels, alter ego).” However, this decision has been challenged in an appeal which is currently pending. It would be interesting to see how the court deals with the question of third parties invoking arbitration, especially in cases of assignment of the principal contract.
Nonetheless, the Bombay High Court in DLF echoed a similar view and held that the arbitration clause does not take away the right of assignment of a party to a contract if it is otherwise assignable. The High Court noted that there is a clear distinction between the assignment of rights under a contract by a party who has performed its obligations under the contract and the assignment of a claim. The latter is a mere claim which cannot be assigned in law. It further observed that once the other party has accepted the assignment and insisted on compliance with rights, duties and obligations, the assignee steps into the shoes of the assignor and will be entitled to all rights, obligations and benefits, including the arbitration agreement forming part of the said agreement.
Similarly, in Bestech India (P) Ltd. v. MGF Developments Ltd. , the Delhi High Court considered the parties’ conduct post-assignment of the contract and rejected the submissions of the original party that the assignee had no locus standi to file an application for appointment of an arbitrator or that the assignee had no privity of the contract with the original party.
While Indian courts have been inconsistent in following the Automatic Transfer Approach when the principal contract is assigned, the predominant view aligns with international practices. Though the minority view requiring specific consent for assignment of the arbitration agreement may be correct on a strict reading of the requirement of express consent to refer the dispute to arbitration, a more practical and pragmatic approach requires inferring such consent by the assignment.
As explained by the Singapore Court of Appeal in the case of BXH v. BXI , “an arbitration agreement does not have a purpose or life independent of the substantive obligations that it attaches to.” Thus, the requirement of express consent, though sound, defies a more holistic understanding of the purpose of the arbitration agreement, i.e. , to refer disputes arising out of the obligations under the principal contract to arbitration.
While the views discussed above were from different Indian High Courts, the applicability and binding nature of the arbitration agreement to non-signatories through assignment has now been recognised in the recent landmark judgment by the Indian Supreme Court in Cox and Kings Ltd. v. SAP India Pvt. Ltd. and Another which has been discussed on the Blog here . Though the Supreme Court has not explicitly addressed the issue of the requirement of express consent for assignment of the arbitration agreement, the extension of the arbitration agreement to non-signatories implies that specific consent may not be required for assignment of the arbitration agreement when the principal contract is assigned.
The author would like to thank Mr. Ankit Singh, Senior Associate, Mr. Ayush Kumar, Associate, ANR LAW LLP and Ms. Ramya Singh, Final Year Student, Ram Manohar Lohia National Law University, Lucknow for their research assistance.
________________________
To make sure you do not miss out on regular updates from the Kluwer Arbitration Blog, please subscribe here . To submit a proposal for a blog post, please consult our Editorial Guidelines .
References [ + ]

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

Indian Contract Act 1872 Notes [Law of Contracts Notes]
- Contract Act Blogs Subject-wise Law Notes
- Aishwarya Agrawal
- July 27, 2024

This article provides Contracts Law Notes notes with case laws .
Law of Contracts dealing with matters relating to Contracts. A contract is made when an agreement becomes enforceable by law. There is no legal obligation as long as it is a mere agreement. Once the agreement becomes a contract, there is a legal obligation by the parties involved.
Hello Readers!
As a learner, you can consider this Indian Contract Act 1872 notes as a free, online, and self-paced course.
As a competitive exams aspirant, you will find it perfect for Judicial Service Exams, UPSC CSE Law Optional, etc.
As a reader, this Law of Contracts notes is sufficient for you to learn or research on Indian Contract Act, 1872!
Happy Learning!
Note: For books on Law of Contracts, click here .
Introduction to the Law of Contracts
Agreement under indian contract act (section 2 to 9, indian contract act), capacity to contract under indian contract act (sections: 10, 11, 12, 64, 65, 68), free consent (sections 13 to 22, indian contract act), consideration under indian contract act (sections 23 to 25 indian contract act), lawful object in contracts, void agreements: limitations on freedom of contract (s. 24 – 30, indian contract act), quasi – contracts and unjust enrichment (section 68 to 72, indian contract act), discharge of a contract (section 37 to 67, indian contract act), breach of contract (ss. 73, 74 & 75), contract of indemnity, contract of guarantee under indian contract act, bailment under indian contract act, pledge under indian contract act, agency under indian contract act, other concepts.
For notes on other subjects, click here .
For case briefs and analysis, click here .
We hope you found Indian Contract Act notes’ on every topic related to the Law of Contracts .
If you think we missed anything, help us by mentioning the details in this form.
Disclaimer:
We have done our best to provide the right information. However, we don’t claim the content to be genuine. We suggest readers to do check it.
You might like

Income Tax for Freelancers (Legal Consultants)

What is Contract Costing?

Aristotle’s Theory of Justice
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Name *
Email *
Add Comment *
Post Comment
Assignment In Arbitration: Scope And Issues In India
Contributor.

Arbitration is a binding voluntary alternative dispute resolution process by a private forum chosen by the parties. It can broadly be divided into three stages, first being the pre-arbitration stage (prior to the time when the dispute arises), second is during the course of arbitration proceeding and last is following the passing of arbitral award.
The term 'assignment' is defined as the transfer by a party of all its rights to some kind of property, usually intangible property such as rights in a lease, mortgage, agreement of sale or partnership. The arbitration clause/agreement provides the right to arbitrate to the concerned parties of that agreement. Therefore, the question arises as to whether such right can be transferred through assignment to some other party. The authors in this post have discussed the scope of assignment in arbitration and the issues that arise in making such assignment.
Assignment in Arbitration: An Overview
Arbitration is a separate contract by the separability principle as envisaged under section 16(1)(b) of the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996. An assignment of a contract might result from a transfer either of the rights or of the obligations thereunder. As a result, obligations under a contract cannot be assigned except with the consent of the promisee and then it is a novation resulting in substitution of liabilities. On the other hand, rights under a contract are assignable unless a contract is personal in nature or the rights are incapable of being assigned. This view has been upheld in DLF Power Limited v. Mangalore Refinery & Petrochemicals Limited & Ors. , 2016 SCC Online Bom 5069. The Bombay High Court in its judgment stated that the arbitration clause does not take away the right of assignment of a party to a contract if it is otherwise assignable. The Court noted that there is a clear distinction between assignment of rights under a contract by a party who has performed its obligations thereunder and the assignment of a claim. The latter is a mere claim which cannot be assigned in law. It was further held in this case that once the other party has accepted the assignment and had insisted for compliance of rights, duties and obligations, the assignee steps into the shoes of the assignor and will be entitled to all rights, obligations and benefits including the arbitration agreement forming part of the said agreement.
Alternatively, parties may expressly prohibit assignment. The benefits of the contract are not then assignable. In such a case, a purported assignment by one party of the contract is invalid as against the other party, but it is valid and enforceable between the assignor and the assignee. The terms of a contract could be expressed, or may be implied as it is legitimate to take the surrounding circumstances into account.
Taking into consideration the general principles relating to the concept of assignment in arbitration, it is to be considered whether the situation for assignment remains same throughout different stages of arbitration (pre-arbitration, during the course of the arbitral proceedings and following the passing of arbitral award).
Pre-Arbitration
The Calcutta High Court in Hindustan Steel Works Construction Ltd. v. Bharat Spun Pipe Co. , AIR 1975 Cal 8, while deciding the application for setting aside an arbitral award, discussed the scope of assignment and held that the correct position in law seems to be that whether the contract is assignable or not depends upon the nature of the contract. A contract in the nature of a personal covenant cannot be assigned. Secondly, the rights under a contract can be assigned, but the obligations under a contract lawfully cannot be assigned. Thirdly, the intention about assignability would depend upon the terms and the language used in a contract. Lastly, existence of an arbitration clause per se does make neither the contract non-assignable or assignable.
The Delhi High Court in Kotak Mahindra Bank v. S. Nagabhushan & Ors. , 2018 SCC OnLine Del 6832, while deciding the application under section 34 was faced with the question whether there was valid assignment of arbitration agreement or not. The arbitrator decided that since the claimant is not signatory to the arbitration agreement the matter cannot be decided through arbitration. However, the Court held that the loan agreement by its very nature was assignable. The Court viewed that once the rights under the loan agreement are assigned in favour of the petitioner, the rights under the arbitration agreement, being only in the nature of a remedy for enforcement of such rights, are equally assignable and have been duly assigned in favour of the petitioner in the present case by way of the assignment agreement. The Court followed Bestech India Private Ltd. v. MGF Developments Ltd. (2009) 161 DLT 282 and held that if a contract is assignable, an arbitration clause will follow the assignment of the contract.
During the Course of the Arbitral Proceedings
The Bombay High Court in Agri Marketing Co. SARL v. Imperial Exports Ltd. , (2002) 2 Bom CR 646, while deciding the enforcement application of an arbitral award, stated that the right under an arbitration clause is assignable even after arbitration proceedings have commenced and that the assignee may simply take over the assignor's proceedings without the need to start afresh. However, the right was subject to two important qualifications:
- the notice to the arbitrator must be given within a reasonable time;
- in writing.
- with notice to the other party (and the arbitrators).
Following the Passing of Arbitral Award
By virtue of section 36 of the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996, on expiry of the period for an application of setting aside, an arbitral award shall be enforceable in accordance with the provisions of Civil Procedure Code, 1908 in the same manner as a decree of a court. Therefore, the award is assignable according to the provisions of the Civil Procedure Code, 1908 dealing with assignment of decree.
Champerty & Assignment
A claim for damages for breach of contract, after breach, is not an 'actionable claim', within the meaning of section 3 of the Transfer of Property Act, 1882, but a mere right to sue within the meaning of section 6(e) of that Act, and it cannot therefore be assigned. Rights of action arising out of or incidental to rights of property can be assigned with the property transferred. An assignment of a bare right of action may also be upheld if the assignee has a genuine commercial or financial interest in taking the assignment; but a step towards the sale of bare cause of action to a third party who had no genuine commercial interest in the claims will be void as champertous since it involves trafficking in litigation.
The Privy Council has generally held that champertous agreements are void in England as it violates the statute of champerty. However, it also recognized that this principle is inapplicable in India. The courts have looked the champertous agreements with caution as they may violate the public policy of the country. But the Indian courts have not faced any situation where the issue involved the funding arrangement with any party to the arbitration proceedings.
The concept of assignment in arbitration is based on the principles of transfer of contractual rights. Assignment can be undertaken during any of the stages and this is beneficial to the parties involved in arbitration. Assignment may be beneficial in various ways. Prior to the dispute if there is some acquisition which occurs or the party does not want to further invest in the project then it can assign the contractual rights (including right to arbitrate to the other parties). During the proceedings, the stressed companies with no real assets but pending arbitration claims can assign their claim to the party whom the debt is own. However, all of this will depend on the agreement of the concerned parties.
It is to be noted that Indian courts have held that assignment of claim is not allowed. However, assignment has been allowed during the arbitral proceedings. This is contradictory, since the pending arbitration proceeding will be considered as a claim only. The courts or the legislature should address this issue.
Therefore, Indian courts may have taken the view that assignment in arbitration is permissible. However, its scope is not clarified and therefore it should be included in the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996 as well, so that the unaddressed issues can be settled and assignment becomes a right in the hand of a party having a legitimate claim. Such a statutory recognition will introduce certainty in the arbitral regime of the country and will help India in its stride to become a hub for international arbitration.
Originally published by IndiaCorp Law Blog .
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.

Litigation, Mediation & Arbitration
Mondaq uses cookies on this website. By using our website you agree to our use of cookies as set out in our Privacy Policy.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Section 2(h) of the Indian Contract Act, 1872 defines a contract as “an agreement enforceable by law”. It is characterised by an offer and an acceptance along with consideration and is backed by the power of law.
Under the Indian Contract Law, any form of contract can be assigned as long as consent is involved in the Assignment. The consent of the ‘promisee’ is necessary for assigning any obligation under the contract.
Section 37 of the India Contract Act, 1872 (“Contract Act”) enables the contracting parties to dispense with the performance of a contract by way of an assignment. While the principle of assignment is well recognized under Indian law, it derives its origin from the English law.
Assignment of contract refers to an act of transferring contractual rights and liabilities under the contract to a third party with other party's concurrence. Section 37 of the India Contract Act, 1872 (" Contract Act ") enables the contracting parties to dispense with the performance of a contract by way of an assignment.
‘Assignment’ means transfer of contractual rights or liability by a party to the contract to some other person who is not a party. It would not be wrong to say that as a matter of established principle, obligations are not assignable and once assigned it amounts to novation.
An assignment of contract is a legal term that describes the process that occurs when the original party (assignor) transfers their rights and obligations under their contract to a third party (assignee).
The legal documents provided outline the following key principles regarding the assignment of contracts under Indian law: 1. **Assignment of Rights vs. Obligations**: - Assignment of a contract can involve the transfer of either the rights or the obligations under the contract [Indira Devi VS Veena Gupta - Supreme Court, P. Seshareddy (D) Rep ...
Under the Indian Contract Act 1872 (“ICA”), an arbitration agreement is a distinct and separate contract. Like all other contracts, it can be transferred by way of assignment to third parties under Section 37 of the ICA.
This article provides Contracts Law Notes notes with case laws. Law of Contracts dealing with matters relating to Contracts. A contract is made when an agreement becomes enforceable by law. There is no legal obligation as long as it is a mere agreement.
Assignment in Arbitration: An Overview. Arbitration is a separate contract by the separability principle as envisaged under section 16(1)(b) of the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996. An assignment of a contract might result from a transfer either of the rights or of the obligations thereunder.