

How To Write A Strategic Plan In 6 Steps + Examples

Gone are the days of rigid, 5 or 10-year planning cycles that don't leave room for flexibility and innovation. To stay ahead of the curve, you need a dynamic and execution-ready strategic plan that can guide your business through the ever-evolving landscape.
In this article, we'll show you how to write a strategic plan in 6 simple steps . By the end, you'll have a comprehensive, actionable strategic plan that will help you align your organization on the path to success.
💡Pro tip : Use our customizable, free Strategic Planning Template that includes all the key elements of a strategic plan to streamline your strategic planning process.
Follow this guide step-by-step, or skip to the part you're most interested in:
- Pre-Planning Phase: Build The Foundation
- Key Elements of a Strategic Plan
How To Write A Strategic Plan In 6 Simple Steps
Develop an iterative strategic planning process, 3 strategic plan examples to get you started, how to achieve organizational alignment with your strategic plan.
- Quick Overview of Key Steps In Writing A Strategic Plan
Create An Execution-Ready Strategic Plan With Cascade 🚀
Before jumping into the planning phase, it's essential to lay the groundwork.
Pre-Planning Phase: Build The Foundation
Your strategic planning process should start well before you write your strategic plan. The pre-planning phase is crucial for gathering the data and strategic insights necessary to create an effective plan.
1. Conduct Strategic Analysis
Strategic analysis is a crucial step before writing your strategic plan. It's like building a house – you wouldn't start constructing the walls without a strong foundation, and the same goes for strategic planning. It equips you with the knowledge and insights to create a strategic plan that is well-targeted, addresses your actual situation, and positions your organization for success.
Use a strategic framework like GAP analysis , SWOT analysis , Porter's Five Forces , Ansoff matrix , McKinsey 7S model , or GE matrix to structure your analysis sessions. Incorporating a risk matrix can also help align and decide on key strategic priorities.
Additionally, consider running a strategic planning workshop with your team. Co-creating the plan with stakeholders is a significant advantage, as it fosters a sense of ownership and increases the likelihood of successful strategy execution . According to McKinsey , initiatives where employees contribute to development are 3.4 times more likely to succeed .
2. Choose your strategic planning model
Before creating your strategic plan, decide on the structure you will use. There are hundreds of ways to structure a strategic plan. You've likely heard of famous strategic models such as OKRs and the Balanced Scorecard .
But beyond the well-known ones, there's also a myriad of other strategic planning models . However, many models that work well on paper often fail to meet organizational needs in practice.
Common issues with many models include:
- Complexity: People get lost in terminology rather than focusing on execution
- Scalability: They work well for small organizations but fail when extended across multiple teams
- Rigidity: They force unnecessary layers, hindering flexibility
- Lack of measurability: They state outcomes well but fail to help measure success
- Adaptability: They don’t adjust well to changing economic landscapes
Our goal is to provide a simpler, more effective way to write a strategic plan. The Cascade Strategy Model , refined over years of working with +20,000 teams, offers a proven approach to strategic planning that is adaptable, scalable, and effective for organizations of all sizes.
In the following sections, we'll explore the key elements and steps to write a strategic plan based on the Cascade Model.
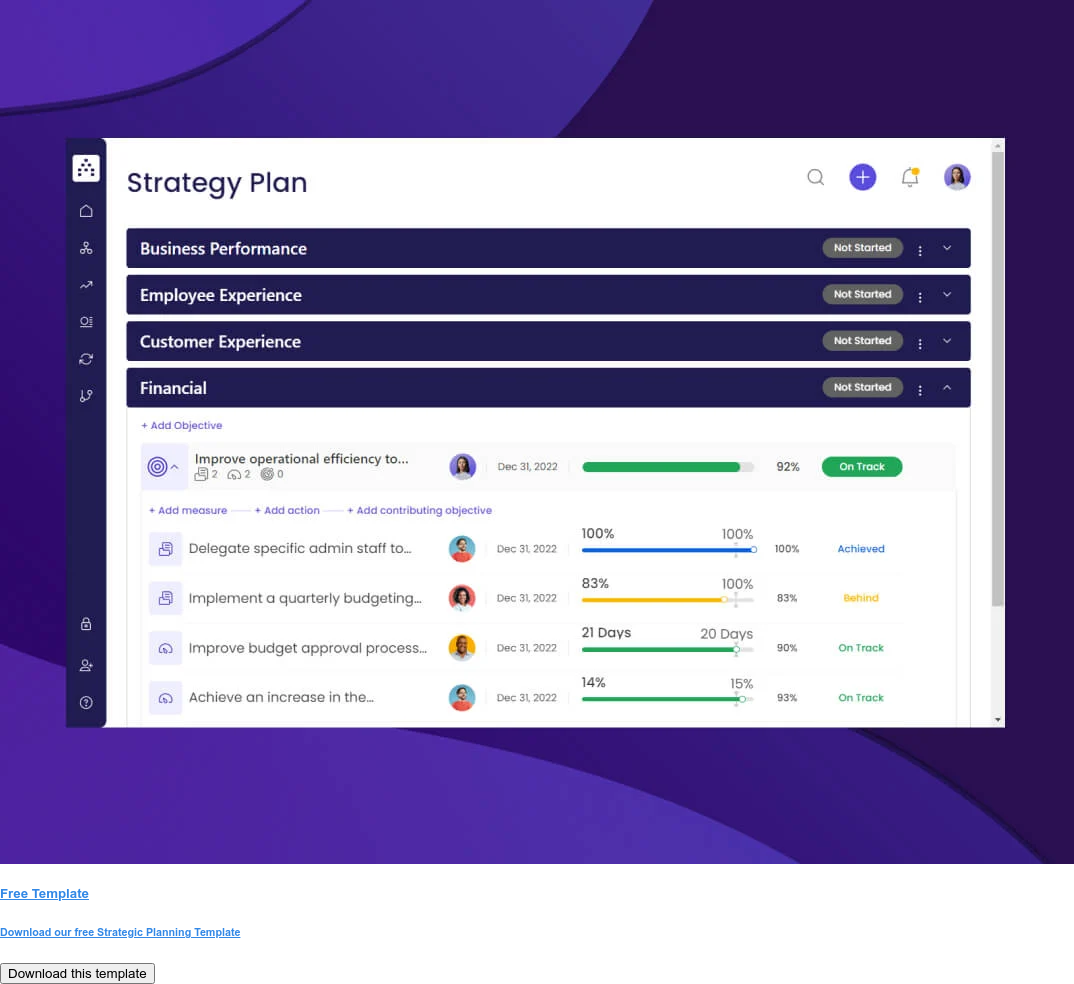
Key Elements Of A Strategic Plan
.jpeg)
The key elements of a strategic plan using the Cascade Model work together to create a clear and actionable roadmap for your organization.
Think of it as a step-by-step guide, where each element builds upon the previous one:
- Vision: Where do you want to get to?
- Values: How will you behave on the journey?
- Focus Areas: What are going to be your strategic priorities?
- Strategic objectives: What do you want to achieve?
- Actions and projects: How are you going to achieve the objectives?
- KPIs: How will you measure success?
These interconnected elements ensure everyone in your organization is aligned on your overall strategy . Above all, the Cascade Model is intended to be execution-ready—in other words, it has been proven to deliver success far beyond strategic planning.
To create a powerful strategic plan, follow this clear, step-by-step process using the Cascade Model.
💡 Pro Tip : If you want to follow along as we cover each step, you can use our Strategic Planning Template spreadsheet (Excel format), or, for the best experience, sign up for instant access to our free Strategic Planning Template in Cascade .
Your vision statement is your organization's anchor - it defines where you want to get to .
A good vision statement can help funnel your strategy towards long-term goals that matter the most to your organization, and everything you write in your plan from this point on will help you get closer to achieving your vision.
Trying to do too much at once is a surefire way to sink your strategic plan. By creating a clear and inspiring vision statement, you can avoid this trap and provide guidance and inspiration for your team.
For example, a bike manufacturing company might have a vision statement like, “To be the premier bike manufacturer in the Pacific Northwest.” This statement clearly articulates the organization's goals and is a powerful motivator for the team.
In short, don't start your strategic plan without a clear vision statement. It will keep your organization focused and help you navigate toward success.
📚 Recommended read: How to Write a Vision Statement (With Examples, Tips, and Formulas)
Alongside your organization’s vision, a well-crafted mission statement is essential. It succinctly defines your purpose, culture, goals, and values, serving as a foundation for your strategic plan. Ensure your mission statement is clear and aligns with your organization’s vision to drive cohesive and effective strategies.
Values are the enablers of your vision statement —they represent how your organization will behave as you work towards your strategic goals.
Make sure to integrate your organization's core values into everyday operations and interactions. In today's highly-competitive world, it's crucial to remain steadfast in your values and cultivate an organizational culture that's transparent and trustworthy.
Companies with the best company cultures consistently outperform competitors and their average market by up to 115.6%, as reported by Glassdoor .
For example, a bike manufacturing company might have core values like:
- Accountability
These values reflect the organization's desire to become the leading bike manufacturer, while still being accountable to employees, customers, and shareholders.
👉 You can create and add your values, mission and vision statements directly in Cascade . This ensures your company's core principles remain top of mind for everyone.
📚When you're ready to start creating some company values, check out our guide, How To Create Company Values .
3. Focus Areas
Your focus areas are the strategic priorities that will keep your team on track and working toward the company's mission statement and vision. They represent the high-level areas that you need to focus on to achieve desired business outcomes.
In fact, companies with clearly defined priorities are more likely to achieve their objectives. According to a case study by the Harvard Business Review , teams that focus on a small number of key strategic initiatives are more likely to succeed than those that try to do too much.
Rather than spreading your resources too thin over multiple focus areas, prioritize three to five.
Following our manufacturing example above, some good focus areas include:
- Aggressive growth
- Producing the nation's best bikes
- Becoming a modern manufacturer
- Becoming a top place to work
Your focus areas should be tighter in scope than your vision statement, but broader than specific goals, time frames, or metrics.
With a clear set of focus areas, your team will be better able to prioritize their work and stay focused on the most important things, which will ultimately lead to better business results.
👉 In Cascade, you can add focus areas while creating or importing an existing strategic plan from a spreadsheet.
With Cascade's Focus Area deep-dive functionality, you will be able to:
- Review the health of your focus areas in one place
- Get a breakdown by plans, budgets, resources, and people behind each strategic priority
- See something at-risk? Drill down into each piece of work regardless of how many plans it's a part of

📚 Recommended read: Strategic Focus Areas: How to create them + Examples
4. Strategic Objectives
Strategic objectives are the specific and measurable outcomes you want to achieve . While they should align with your focus areas, they should be more detailed and have a clear deadline.
According to the 2022 State of High Performing Teams report , there is a strong correlation between goals and success not only at the individual and team level but also at the organizational level. Here's what they found:
- Employees who are unaware of their company's strategic goals are over three times more likely to work at a company experiencing a revenue decline than employees who are aware of the goals
- Companies with shrinking revenues are almost twice as likely to have employees with unclear work expectations.
Jumping straight into actions without defining clear objectives is a common mistake that can lead to missed opportunities or misalignment between strategy and execution.
To avoid this pitfall, we recommend you add between three and six objectives to each focus area .
It's here that we need to start being a bit more specific for the first time in your strategic planning process. Let's take a look at an example of a well-written strategic objective:
- Continue top-line growth that outpaces the industry by 31st Dec 2023.
This is too specific to be a focus area. While it's still very high level, it indicates what the company wants to accomplish and includes a clear deadline. Both these aspects are critical to a good strategic objective.
Your strategic objectives are the heart and soul of your plan, and you need to ensure they are well-crafted. So, take the time to create well-planned objectives that will help you achieve your vision and lead your organization to success.
👉 Adding objectives in Cascade is intuitive, straightforward, and accessible. With one click, you'll open the objective sidebar and fill out the details. These can include a timeline, the objective's owner, collaborators, and how your objective will be measured (success criteria).
📚 Recommended read: What are Strategic Objectives? How to write them + Examples
5. Actions and projects
Once you've defined your strategic objectives, the next step is to identify the specific strategic initiatives or projects that will help you achieve those objectives . They are short-term goals or actionable steps you or your team members will take to accomplish objectives. They should leverage the company's resources and core competencies.
Effective projects and actions in your strategic plan should:
- Be specific
- Contain a deadline
- Have an owner
- Align with at least one of your strategic objectives
- Provide clarity on how you or your team will achieve the strategic objective
Let's take a look at an example of a well-written project continuing with our bike manufacturing company using the strategic objective from above:
Strategic objective: Continue top-line growth that outpaces the industry by 31st Dec 2023.
Project: Expand into the fixed gear market by 31st December 2023.
This is more specific than the objective it links to, and it details what you will do to achieve the objective.
Actions and projects are where the rubber meets the road. They connect the organizational strategic goals with the actual capabilities of your people and the resources at their disposal. Defining projects is a vital reality check every strategic plan needs.
👉You can create actions and projects easily in Cascade! From the Objective sidebar, you can choose to add a project or action under your chosen objective. In the following steps, you can assign an owner and timeline to each action or project.
Plus, in Cascade, you can track the progress of each project or action in four different ways. You can do it manually, via milestones, checklists, or automatically by integrating with Jira and 1000+ other available integrations .
📚 Recommended read: What are Strategic Initiatives? How to Develop & Execute + Examples
6. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Measuring progress towards strategic objectives is essential to effective strategic control and business success. That's where Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) come in.
KPIs are measurable values that track progress toward achieving key business objectives . They help you stay on track and focused on your organization's strategic goals.
To get the most out of your KPIs, make sure you link them to a specific goal or objective. This way, you'll avoid creating KPIs that don't contribute to your objectives and distract you from focusing on what matters.
Ideally, you will add both leading and lagging KPIs to each objective so you can get a more balanced view of how well you're progressing. Leading KPIs can indicate future performance, while lagging KPIs show how well you've done in the past.
Think of KPIs as a form of signpost in your organization. They provide critical insights that inform business leaders of their organization's progress toward key business objectives. Plus, they can help you identify opportunities faster and capitalize on flexibility.
👉 In Cascade , you can add measures while creating your objectives or add them afterward. Open the Objective sidebar and add your chosen measure.
When you create your Measure, you can choose how to track it. Using Cascade, you can track it manually or automatically. You can automate tracking via 1000+ integrations , including Excel spreadsheets and Google Sheets . This way, you can save time and ensure that your team has up-to-date information for faster and more confident decision-making.
📚 Recommended reads:
- 10 Popular KPI Software Tools To Connect & Visualize Your Data (2024 Guide)
- How To Track KPIs To Hit Your Business Goals
Developing an iterative strategic planning process is essential for staying adaptable and responsive to change. This approach involves continuously reviewing and refining your strategies to ensure they remain relevant in a dynamic business environment. Regularly assess your plan's effectiveness, gather stakeholder feedback, analyze performance data, and make necessary adjustments.
This cycle of strategic planning, execution, and evaluation helps identify areas for improvement, fosters innovation, and keeps your organization aligned with its long-term goals. By adopting an iterative strategic planning process, you can navigate challenges more effectively and maintain a competitive edge.
📚 Check out our article Develop An Iterative Strategic Planning Process to dive into this topic
Corporate Strategic Plan
Following the steps outlined above, you should end up with a strategic plan that looks something like this:

This is a preview of a corporate strategic plan template that is pre-filled with examples. Here, you can use the template for free and begin filling it out to align with your organization's needs. Plus, it's suitable for organizations of all sizes and any industry.
Once you fill in the template, you can also switch to the timeline view. You'll get a complete overview of how the different parts of your plan are distributed across the roadmap in a Gantt chart view.

This template will help you create a structured approach to the strategic planning process, focus on key strategic priorities, and drive accountability to achieve necessary business outcomes.
👉 Get your free corporate strategic plan template here.
Coca-Cola Strategic Plan
Need a bit of extra inspiration with your plan? Check out this strategic plan example, inspired by Coca-Cola's business plan:

This strategic planning template is pre-filled with Coca-Cola's examples so you can inspire your strategic success on one of the most iconic brands on the planet.
👉 Grab your free example of a Coca-Cola strategic plan here.
The Ramsay Health Care expansion strategy
Ramsay Health Care is a multinational healthcare provider with a strong presence in Australia, Europe, and Asia.
Almost all of its growth was organic and strategic. The company founded its headquarters in Sydney, Australia, but in the 21st century, it decided to expand globally through a primary strategy of making brownfield investments and acquisitions in key locations.
Ramsay's strategy was simple yet clever. By becoming a majority shareholder of the biggest local players, the company expanded organically in each region by leveraging and expanding their expertise.
Over the last two decades, Ramsay's global network has grown to 460 locations across 10 countries with over $13 billion in annual revenue.
📚 Recommended read: Strategy study: The Ramsay Health Care Growth Study
✨ Bonus resource: We've created a list of the most popular and free strategic plan templates in our library that will help you build a strategic plan based on the Cascade model explained in this article. You can use these templates to create a plan on a corporate, business unit, or team level.
We highlighted before that other strategic models often fail to scale strategic plans and goals across multiple teams and organizational levels.
In an ideal world, you want to have a maximum of two layers of detail underneath each of your focus areas. This means you'll have a focus area, followed by a layer of objectives. Underneath the objectives, you'll have a layer of actions, projects (or strategic initiatives), and KPIs.

If you have a single team that's responsible for the strategy execution, this works well. However, how do you implement a strategy across multiple and cross-functional teams? And why is it important?
According to LSA research of 410 companies across 8 industries, highly aligned companies grow revenue 58% faster and are 72% more profitable. And this is what Cascade can help you achieve.
To achieve achieve organization-wide alignment with your strategic plan and impact the bottom line, there are two ways to approach it in Casade: through contributing objectives or shared objectives .
1. Contributing objectives
This approach involves adding contributing objectives that link to your main strategic objectives, like this:

For each contributing objective, you simply repeat the Objective → Action/Project → KPI structure as follows:

Here's how you can create contributing objectives in Cascade:
Option A: Create contributing objectives within the same plan
This means creating multiple contributing objectives within the same strategic plan that contribute to the main objective.
However, be aware that if you have a lot of layers, your strategic plan can become cluttered, and people might have difficulty understanding how their daily efforts contribute to the strategic plan at the top level.
For example, the people responsible for managing contributing objectives at the bottom of the plan ( functional / operational level ) will lose visibility on how are their objectives linked to the main focus areas and objectives (at a corporate / business level ).
This approach is best suited to smaller organizations that only need to add a few layers of objectives to their plan.
Option B: Create contributing objectives from multiple strategic plans linking to the main objective
This approach creates a network of aligned strategic plans within your organization. Each plan contains a set of focus areas and one single layer of objectives, each with its own set of projects, actions, and KPIs. This concept looks like this:

This example illustrates an objective that is a main objective in the IT strategic plan , but also contributes to the main strategic plan's objective.
For example, let's say that your main business objective is to improve customer satisfaction by reducing product delivery time by 25% in the next quarter. This objective requires multiple operational teams within your organization to work together to achieve a shared objective.
Each team will create its own objective in its plan to contribute to the main objective:
- Logistics team: Reduce the shipment preparation time by 30%
- IT team: Implement new technology to reduce manual handling in the warehouse
- Production team: Increase production output by hour for 5%
Here's how this example would look like within the Cascade platform:

Although each contributing objective was originally created in its own plan, you can see how each contributing objective relates to the main strategic objective and its status in real-time.
2. Shared objectives
In Cascade, shared objectives are the same objectives shared across different strategic plans.
For example, you can have an objective that is “Achieve sustainable operations” . This objective can be part of the Corporate Strategy Plan, but also part of the Operations Plan , Supply Chain Plan , Production Plan, etc. In short, this objective becomes a shared objective between multiple teams and strategic plans.
This approach helps you to:
- Cascade your business strategy as deep as you want across a near-infinite number of people while maintaining strategic alignment throughout your organization .
- Create transparency and a much higher level of engagement in the strategy throughout your organization since objective owners are able to identify how their shared efforts contribute to the success of the main business objectives.
The more shared objectives you have across your organization, the more your teams will be aligned with the overarching business strategy. This is what we call " alignment health ”.
Here's how you can see the shared objectives in the alignment map and analyze alignment health within Cascade:

You get a snapshot of how your corporate strategic plan is aligned with sub-plans from different business units or departments and the status of shared objectives. This helps you quickly identify misaligned strategic initiatives and act before it's too late. Plus, cross-functional teams have better visibility of how their efforts contribute to shared objectives.
So whether you choose contributing objectives or shared objectives, Cascade has the tools and features to help you achieve organization-wide alignment and boost your bottom line.
Quick Overview Of Key Steps In Writing A Strategic Plan
Here's a quick infographic to help you remember how everything connects and why each element is critical to effective strategic planning:

This simple answer to how to write a strategic plan avoids confusing jargon and has elements that the whole organization can both get behind and understand.
💡Tip: Save this image or bookmark this article for your next strategic planning session.
If you're struggling to write an execution-ready strategic plan, the Cascade Strategy Model is the solution you've been looking for. With its clear, easy-to-understand terminology, and simple linkages between objectives, projects, and KPIs, you can create a plan that's both scalable and flexible.
But why is a flexible and execution-ready strategic plan so important? It's simple: without a clear and actionable plan, you'll never be able to achieve your business objectives. By using the Cascade Strategic Planning Model, you'll be able to create a plan that's both tangible and measurable, with KPIs that help you track progress towards your goals.
However, the real value of the Cascade framework lies in its flexibility . By creating links between main business objectives and your teams' objectives, you can easily scale your plan without losing focus. Plus, the model's structure of linked layers means that you can always adjust your strategy in response to new challenges to easily develop an iterative strategic planning process.
So if you want to achieve results with your strategic plan, start using Cascade today. With its unique combination of flexibility and focus, it's the perfect tool for any organization looking to master strategy execution and succeed in today's fast-paced business world.
Want to see Cascade in action? Get started for free or book a 1:1 demo with Cascade's in-house strategy expert.

This article is part one of our mini-series "How to Create a Strategy". This first article will give you a solid strategy model for your plan and get the strategic thinking going.
Think of it as the foundation for your new strategy. Subsequent parts of the series will show you how to create the content for your strategic plan.
Articles in our "How To Create a Strategy" series
- How To Write A Strategic Plan In 6 Steps + Examples (This article)
- How to Write a Good Vision Statement
- How To Create Company Values
- Creating Strategic Focus Areas
- How To Write Strategic Objectives
- How To Create Effective Projects
- How To Write KPIs + Ultimate Guide To Strategic Planning
More resources on strategic planning and strategy execution:
- 6 Steps to Successful Strategy Execution
- 4-Step Strategy Reporting Process (With Template)
- Annual Planning: Plan Like a Pro In 5 Steps (+ Template)
- 18 Free Strategic Plan Templates (Excel & Cascade) 2024
- The Right Way To Set Team Goals
- 23 Best Strategy Tools For Your Organization in 2024
Popular articles
.png)
Strategic Analysis Complete Guide: Definition, Tools & Examples

Annual Planning: 5 Easy Steps To Plan Next Year (+Template)
.png)
11 Best Strategic Frameworks For Your Organization + Free eBook

6 Steps To Successful Strategy Execution & Best Practices
Your toolkit for strategy success.

Essential Guide to the Strategic Planning Process
By Joe Weller | April 3, 2019 (updated March 26, 2024)
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, you’ll learn the basics of the strategic planning process and how a strategic plan guides you to achieving your organizational goals. Plus, find expert insight on getting the most out of your strategic planning.
Included on this page, you'll discover the importance of strategic planning , the steps of the strategic planning process , and the basic sections to include in your strategic plan .
What Is Strategic Planning?
Strategic planning is an organizational activity that aims to achieve a group’s goals. The process helps define a company’s objectives and investigates both internal and external happenings that might influence the organizational path. Strategic planning also helps identify adjustments that you might need to make to reach your goal. Strategic planning became popular in the 1960s because it helped companies set priorities and goals, strengthen operations, and establish agreement among managers about outcomes and results.
Strategic planning can occur over multiple years, and the process can vary in length, as can the final plan itself. Ideally, strategic planning should result in a document, a presentation, or a report that sets out a blueprint for the company’s progress.
By setting priorities, companies help ensure employees are working toward common and defined goals. It also aids in defining the direction an enterprise is heading, efficiently using resources to achieve the organization’s goals and objectives. Based on the plan, managers can make decisions or allocate the resources necessary to pursue the strategy and minimize risks.
Strategic planning strengthens operations by getting input from people with differing opinions and building a consensus about the company’s direction. Along with focusing energy and resources, the strategic planning process allows people to develop a sense of ownership in the product they create.

“Strategic planning is not really one thing. It is really a set of concepts, procedures, tools, techniques, and practices that have to be adapted to specific contexts and purposes,” says Professor John M. Bryson, McKnight Presidential Professor of Planning and Public Affairs at the Hubert H. Humphrey School of Public Affairs, University of Minnesota and author of Strategic Planning for Public and Nonprofit Organizations: A Guide to Strengthening and Sustaining Organizational Achievement . “Strategic planning is a prompt to foster strategic thinking, acting, and learning, and they all matter and they are all connected.”
What Strategic Planning Is Not
Strategic planning is not a to-do list for the short or long term — it is the basis of a business, its direction, and how it will get there.
“You have to think very strategically about strategic planning. It is more than just following steps,” Bryson explains. “You have to understand strategic planning is not some kind of magic solution to fixing issues. Don’t have unrealistic expectations.”
Strategic planning is also different from a business plan that focuses on a specific product, service, or program and short-term goals. Rather, strategic planning means looking at the big picture.
While they are related, it is important not to confuse strategic planning with strategic thinking, which is more about imagining and innovating in a way that helps a company. In contrast, strategic planning supports those thoughts and helps you figure out how to make them a reality.
Another part of strategic planning is tactical planning , which involves looking at short-term efforts to achieve longer-term goals.
Lastly, marketing plans are not the same as strategic plans. A marketing plan is more about introducing and delivering a service or product to the public instead of how to grow a business. For more about marketing plans and processes, read this article .
Strategic plans include information about finances, but they are different from financial planning , which involves different processes and people. Financial planning templates can help with that process.
Why Is Strategic Planning Important?
In today’s technological age, strategic plans provide businesses with a path forward. Strategic plans help companies thrive, not just survive — they provide a clear focus, which makes an organization more efficient and effective, thereby increasing productivity.

“You are not going to go very far if you don’t have a strategic plan. You need to be able to show where you are going,” says Stefan Hofmeyer, an experienced strategist and co-founder of Global PMI Partners . He lives in the startup-rich environment of northern California and says he often sees startups fail to get seed money because they do not have a strong plan for what they want to do and how they want to do it.
Getting team members on the same page (in both creating a strategic plan and executing the plan itself) can be beneficial for a company. Planners can find satisfaction in the process and unite around a common vision. In addition, you can build strong teams and bridge gaps between staff and management.
“You have to reach agreement about good ideas,” Bryson says. “A really good strategy has to meet a lot of criteria. It has to be technically workable, administratively feasible, politically acceptable, and legally, morally, and ethically defensible, and that is a pretty tough list.”
By discussing a company’s issues during the planning process, individuals can voice their opinions and provide information necessary to move the organization ahead — a form of problem solving as a group.
Strategic plans also provide a mechanism to measure success and progress toward goals, which keeps employees on the same page and helps them focus on the tasks at hand.
When Is the Time to Do Strategic Planning?
There is no perfect time to perform strategic planning. It depends entirely on the organization and the external environment that surrounds it. However, here are some suggestions about when to plan:
If your industry is changing rapidly
When an organization is launching
At the start of a new year or funding period
In preparation for a major new initiative
If regulations and laws in your industry are or will be changing
“It’s not like you do all of the thinking and planning, and then implement,” Bryson says. “A mistake people make is [believing] the thinking has to precede the acting and the learning.”
Even if you do not re-create the entire planning process often, it is important to periodically check your plan and make sure it is still working. If not, update it.
What Is the Strategic Planning Process?
Strategic planning is a process, and not an easy one. A key is to make sure you allow enough time to complete the process without rushing, but not take so much time that you lose momentum and focus. The process itself can be more important than the final document due to the information that comes out of the discussions with management, as well as lower-level workers.

“There is not one favorite or perfect planning process,” says Jim Stockmal, president of the Association for Strategic Planning (ASP). He explains that new techniques come out constantly, and consultants and experienced planners have their favorites. In an effort to standardize the practice and terms used in strategic planning, ASP has created two certification programs .
Level 1 is the Strategic Planning Professional (SPP) certification. It is designed for early- or mid-career planners who work in strategic planning. Level 2, the Strategic Management Professional (SMP) certification, is geared toward seasoned professionals or those who train others. Stockmal explains that ASP designed the certification programs to add structure to the otherwise amorphous profession.
The strategic planning process varies by the size of the organization and can be formal or informal, but there are constraints. For example, teams of all sizes and goals should build in many points along the way for feedback from key leaders — this helps the process stay on track.
Some elements of the process might have specific start and end points, while others are continuous. For example, there might not be one “aha” moment that suddenly makes things clear. Instead, a series of small moves could slowly shift the organization in the right direction.
“Don’t make it overly complex. Bring all of the stakeholders together for input and feedback,” Stockmal advises. “Always be doing a continuous environmental scan, and don’t be afraid to engage with stakeholders.”
Additionally, knowing your company culture is important. “You need to make it work for your organization,” he says.
There are many different ways to approach the strategic planning process. Below are three popular approaches:
Goals-Based Planning: This approach begins by looking at an organization’s mission and goals. From there, you work toward that mission, implement strategies necessary to achieve those goals, and assign roles and deadlines for reaching certain milestones.
Issues-Based Planning: In this approach, start by looking at issues the company is facing, then decide how to address them and what actions to take.
Organic Planning: This approach is more fluid and begins with defining mission and values, then outlining plans to achieve that vision while sticking to the values.
“The approach to strategic planning needs to be contingent upon the organization, its history, what it’s capable of doing, etc.,” Bryson explains. “There’s such a mistake to think there’s one approach.”
For more information on strategic planning, read about how to write a strategic plan and the different types of models you can use.
Who Participates in the Strategic Planning Process?
For work as crucial as strategic planning, it is necessary to get the right team together and include them from the beginning of the process. Try to include as many stakeholders as you can.
Below are suggestions on who to include:
Senior leadership
Strategic planners
Strategists
People who will be responsible for implementing the plan
People to identify gaps in the plan
Members of the board of directors
“There can be magic to strategic planning, but it’s not in any specific framework or anybody’s 10-step process,” Bryson explains. “The magic is getting key people together, getting them to focus on what’s important, and [getting] them to do something about it. That’s where the magic is.”
Hofmeyer recommends finding people within an organization who are not necessarily current leaders, but may be in the future. “Sometimes they just become obvious. Usually they show themselves to you, you don’t need to look for them. They’re motivated to participate,” he says. These future leaders are the ones who speak up at meetings or on other occasions, who put themselves out there even though it is not part of their job description.
At the beginning of the process, establish guidelines about who will be involved and what will be expected of them. Everyone involved must be willing to cooperate and collaborate. If there is a question about whether or not to include anyone, it is usually better to bring on extra people than to leave someone out, only to discover later they should have been a part of the process all along. Not everyone will be involved the entire time; people will come and go during different phases.
Often, an outside facilitator or consultant can be an asset to a strategic planning committee. It is sometimes difficult for managers and other employees to sit back and discuss what they need to accomplish as a company and how they need to do it without considering other factors. As objective observers, outside help can often offer insight that may escape insiders.
Hofmeyer says sometimes bosses have blinders on that keep them from seeing what is happening around them, which allows them to ignore potential conflicts. “People often have their own agendas of where they want to go, and if they are not aligned, it is difficult to build a strategic plan. An outsider perspective can really take you out of your bubble and tell you things you don’t necessarily want to hear [but should]. We get into a rhythm, and it’s really hard to step out of that, so bringing in outside people can help bring in new views and aspects of your business.”
An outside consultant can also help naysayers take the process more seriously because they know the company is investing money in the efforts, Hofmeyer adds.
No matter who is involved in the planning process, make sure at least one person serves as an administrator and documents all planning committee actions.
What Is in a Strategic Plan?
A strategic plan communicates goals and what it takes to achieve them. The plan sometimes begins with a high-level view, then becomes more specific. Since strategic plans are more guidebooks than rulebooks, they don’t have to be bureaucratic and rigid. There is no perfect plan; however, it needs to be realistic.
There are many sections in a strategic plan, and the length of the final document or presentation will vary. The names people use for the sections differ, but the general ideas behind them are similar: Simply make sure you and your team agree on the terms you will use and what each means.
One-Page Strategic Planning Template
“I’m a big fan of getting a strategy onto one sheet of paper. It’s a strategic plan in a nutshell, and it provides a clear line of sight,” Stockmal advises.
You can use the template below to consolidate all your strategic ideas into a succinct, one-page strategic plan. Doing so provides you with a high-level overview of your strategic initiatives that you can place on your website, distribute to stakeholders, and refer to internally. More extensive details about implementation, capacity, and other concerns can go into an expanded document.
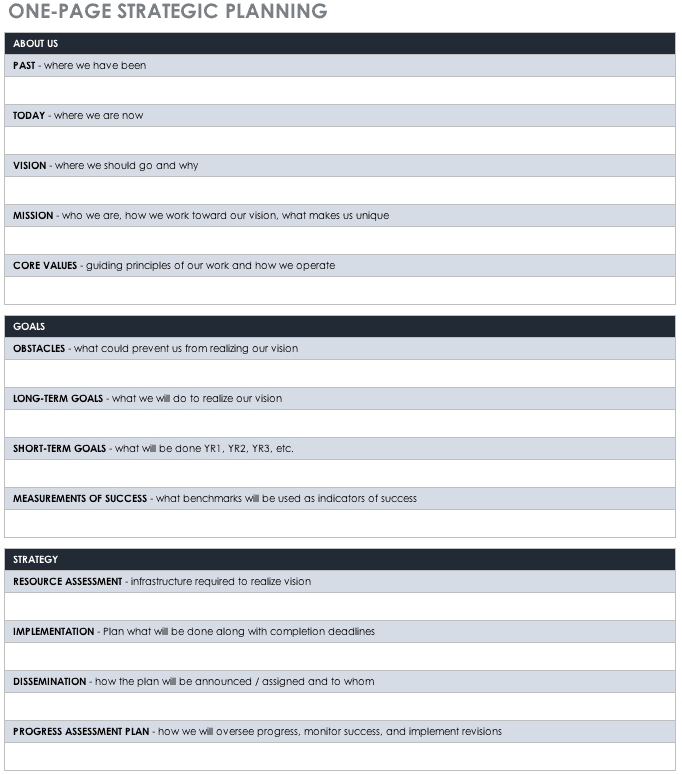
Download One-Page Strategic Planning Template Excel | Word | Smartsheet
The most important part of the strategic plan is the executive summary, which contains the highlights of the plan. Although it appears at the beginning of the plan, it should be written last, after you have done all your research.
Of writing the executive summary, Stockmal says, “I find it much easier to extract and cut and edit than to do it first.”
For help with creating executive summaries, see these templates .
Other parts of a strategic plan can include the following:
Description: A description of the company or organization.
Vision Statement: A bold or inspirational statement about where you want your company to be in the future.
Mission Statement: In this section, describe what you do today, your audience, and your approach as you work toward your vision.
Core Values: In this section, list the beliefs and behaviors that will enable you to achieve your mission and, eventually, your vision.
Goals: Provide a few statements of how you will achieve your vision over the long term.
Objectives: Each long-term goal should have a few one-year objectives that advance the plan. Make objectives SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, and time-based) to get the most out of them.
Budget and Operating Plans: Highlight resources you will need and how you will implement them.
Monitoring and Evaluation: In this section, describe how you will check your progress and determine when you achieve your goals.
One of the first steps in creating a strategic plan is to perform both an internal and external analysis of the company’s environment. Internally, look at your company’s strengths and weaknesses, as well as the personal values of those who will implement your plan (managers, executives, board members). Externally, examine threats and opportunities within the industry and any broad societal expectations that might exist.
You can perform a SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) analysis to sum up where you are currently and what you should focus on to help you achieve your future goals. Strengths shows you what you do well, weaknesses point out obstacles that could keep you from achieving your objectives, opportunities highlight where you can grow, and threats pinpoint external factors that could be obstacles in your way.
You can find more information about performing a SWOT analysis and free templates in this article . Another analysis technique, STEEPLE (social, technological, economic, environmental, political, legal, and ethical), often accompanies a SWOT analysis.
Basics of Strategic Planning
How you navigate the strategic planning process will vary. Several tools and techniques are available, and your choice depends on your company’s leadership, culture, environment, and size, as well as the expertise of the planners.
All include similar sections in the final plan, but the ways of driving those results differ. Some tools are goals-based, while others are issues- or scenario-based. Some rely on a more organic or rigid process.
Hofmeyer summarizes what goes into strategic planning:
Understand the stakeholders and involve them from the beginning.
Agree on a vision.
Hold successful meetings and sessions.
Summarize and present the plan to stakeholders.
Identify and check metrics.
Make periodic adjustments.
Items That Go into Strategic Planning
Strategic planning contains inputs, activities, outputs, and outcomes. Inputs and activities are elements that are internal to the company, while outputs and outcomes are external.
Remember, there are many different names for the sections of strategic plans. The key is to agree what terms you will use and define them for everyone involved.
Inputs are important because it is impossible to know where you are going until you know what is around you where you are now.
Companies need to gather data from a variety of sources to get a clear look at the competitive environment and the opportunities and risks within that environment. You can think of it like a competitive intelligence program.
Data should come from the following sources:
Interviews with executives
A review of documents about the competition or market that are publicly available
Primary research by visiting or observing competitors
Studies of your industry
The values of key stakeholders
This information often goes into writing an organization’s vision and mission statements.
Activities are the meetings and other communications that need to happen during the strategic planning process to help everyone understand the competition that surrounds the organization.
It is important both to understand the competitive environment and your company’s response to it. This is where everyone looks at and responds to the data gathered from the inputs.
The strategic planning process produces outputs. Outputs can be as basic as the strategic planning document itself. The documentation and communications that describe your organization’s strategy, as well as financial statements and budgets, can also be outputs.
The implementation of the strategic plan produces outcomes (distinct from outputs). The outcomes determine the success or failure of the strategic plan by measuring how close they are to the goals and vision you outline in your plan.
It is important to understand there will be unplanned and unintended outcomes, too. How you learn from and adapt to these changes influence the success of the strategic plan.
During the planning process, decide how you will measure both the successes and failures of different parts of the strategic plan.
Sharing, Evaluating, and Monitoring the Progress of a Strategic Plan
After companies go through a lengthy strategic planning process, it is important that the plan does not sit and collect dust. Share, evaluate, and monitor the plan to assess how you are doing and make any necessary updates.
“[Some] leaders think that once they have their strategy, it’s up to someone else to execute it. That’s a mistake I see,” Stockmal says.
The process begins with distributing and communicating the plan. Decide who will get a copy of the plan and how those people will tell others about it. Will you have a meeting to kick off the implementation? How will you specify who will do what and when? Clearly communicate the roles people will have.
“Before you communicate the plan [to everyone], you need to have the commitment of stakeholders,” Hofmeyer recommends. Have the stakeholders be a part of announcing the plan to everyone — this keeps them accountable because workers will associate them with the strategy. “That applies pressure to the stakeholders to actually do the work.”
Once the team begins implementation, it’s necessary to have benchmarks to help measure your successes against the plan’s objectives. Sometimes, having smaller action plans within the larger plan can help keep the work on track.
During the planning process, you should have decided how you will measure success. Now, figure out how and when you will document progress. Keep an eye out for gaps between the vision and its implementation — a big gap could be a sign that you are deviating from the plan.
Tools are available to assist with tracking performance of strategic plans, including several types of software. “For some organizations, a spreadsheet is enough, but you are going to manually enter the data, so someone needs to be responsible for that,” Stockmal recommends.
Remember: strategic plans are not written in stone. Some deviation will be necessary, and when it happens, it’s important to understand why it occurred and how the change might impact the company's vision and goals.
Deviation from the plan does not mean failure, reminds Hofmeyer. Instead, understanding what transpired is the key. “Things happen, [and] you should always be on the lookout for that. I’m a firm believer in continuous improvement,” he says. Explain to stakeholders why a change is taking place. “There’s always a sense of re-evaluation, but do it methodically.”
Build in a schedule to review and amend the plan as necessary; this can help keep companies on track.
What Is Strategic Management?
Strategic planning is part of strategic management, and it involves the activities that make the strategic plan a reality. Essentially, strategic management is getting from the starting point to the goal effectively and efficiently using the ongoing activities and processes that a company takes on in order to keep in line with its mission, vision, and strategic plan.
“[Strategic management] closes the gap between the plan and executing the strategy,” Stockmal of ASP says. Strategic management is part of a larger planning process that includes budgeting, forecasting, capital allocation, and more.
There is no right or wrong way to do strategic management — only guidelines. The basic phases are preparing for strategic planning, creating the strategic plan, and implementing that plan.
No matter how you manage your plan, it’s key to allow the strategic plan to evolve and grow as necessary, due to both the internal and external factors.
“We get caught up in all of the day-to-day issues,” Stockmal explains, adding that people do not often leave enough time for implementing the plan and making progress. That’s what strategic management implores: doing things that are in the plan and not letting the plan sit on a shelf.
Improve Strategic Planning with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
- Gartner client? Log in for personalized search results.
Essential Guide to Strategic Planning
Strategic planning maps the initiatives and investments required to achieve long‑term strategic objectives. Here’s how to do it well.

Download Your Guide to Strategic Planning Success
By clicking the "Continue" button, you are agreeing to the Gartner Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.
Contact Information
All fields are required.
Company/Organization Information
Please provide the consent below
I have read, understood and accepted Gartner Separate Consent Letter , whereby I agree (1) to provide Gartner with my personal information, and understand that information will be transferred outside of mainland China and processed by Gartner group companies and other legitimate processing parties and (2) to be contacted by Gartner group companies via internet, mobile/telephone and email, for the purposes of sales, marketing and research.
By clicking the "Submit" button, you are agreeing to the Gartner Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.
By clicking the "Begin Download" button, you are agreeing to the Gartner Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.
Strategic planning that works — even in volatile times
Just 29% of strategists say their organizations change plans fast enough to respond to disruption. What’s the problem? Most often, unclear objectives, poor strategic planning processes and disengaged business leaders.
Use this guide to:
Turn your strategy into action faster
Combat 7 mistakes common to strategic planning
Capture and communicate your plans with an exclusive one-page template
4 critical things to know about strategic planning
Especially in times of disruption, it’s key to understand what strategic planning is and does, what assumptions you need and how to leverage the value of adaptive strategy and scenario planning.
- What Is Strategic Planning?
- Strategic Assumptions
- Scenario Planning
- Adaptive Strategy
Strategy and strategic plans: How they are different and why it matters
Strategy creates a common understanding of what an organization wants to achieve and what it needs to do to meet its goals. Strategic plans bridge the gap from overall direction to specific projects and day-to-day actions that ultimately execute the strategy. Job No. 1 is to know the difference between strategy and strategic plans — and why it matters.
Strategy defines the long-term direction of the enterprise. It articulates what the enterprise will do to compete and succeed in its chosen markets or, for the public sector, what the agency will do to achieve its mission.
Strategic planning defines how the enterprise will realize its strategic ambitions in the midterm. Too often, strategic plans are created and then forgotten until the next planning cycle begins. A well-done strategic plan turns an enterprise strategy into a clear roadmap of initiatives, actions and investments required to execute the strategy and meet business goals.
Functional strategic plans document the choices and actions needed for the function to move from the current state to the desired end state, and contribute effectively to the enterprise business model and goals.
Business unit strategic plans define and finalize business unit goals, objectives and initiatives, while cognizant of enterprise priorities and external trends.
Operational plans deal with the short-term execution of specific projects and changes, as well as any operational tasks not contained in the strategic plan.

If you’re responsible for functional strategy, such as IT , create strategic frameworks focused only on what’s material — critical assumptions, relevant metrics and the key initiatives your function needs to contribute effectively to organizational goals, even as those goals shift.
Look out for key trends and disruptions, and test strategic assumptions
It’s critical to scan and respond to trends and disruptions that could impact your strategy and strategic plans — and change your strategic assumptions. Strategic planning cycles should incorporate some mechanism to vet assumptions for relevance (also see “Scenario Planning”).
Ignoring or devaluing trends and disruptions can leave critical gaps in both your strategic assumptions and your strategic planning process, because you may be overlooking both threats and opportunities for your value proposition and competitive positioning.
One Gartner survey found that only 38% of organizations have a formal process for this type of trendspotting. Gartner scopes the seven key areas of disruptive change as a “TPESTRE” of interconnected trend areas (see figure).
Executives across functions and teams can use the TPESTRE construct to identify key trends at any time — from augmented human experience to purpose-driven organizations and digitally enabled sustainability — and analyze their impact. From there, they can build strategic assumptions around the trends as they begin to map what actions might be needed in terms of business models, people/capabilities, IT systems and resources.
After sudden humanitarian or geopolitical disruptions like the COVID-19 pandemic or Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, a framework like TPESTRE can help you identify and monitor a range of risks that may affect your enterprise or function and that you may need to include in scenario planning.

Scenario planning as a strategic planning tool for functions
Scenario planning enables executives and their teams to explore and evaluate plausible alternative futures to make strategic plans more robust and resilient. Pandemic-related disruption and volatility showed the importance of leveraging a range of scenarios to reset business strategy and strategic plans.
Commonly used by strategists at the organizational level, scenario planning at the functional level is just as valuable. Many functional leaders have little experience with strategic scenario planning, even though they may regularly work with their CFO to build budget and forecast scenarios. Those who can learn and apply scenario planning in strategic planning can help their organization navigate volatile and dynamic conditions more effectively, especially in areas like supply chain , where disruption remains high.
Exploring scenarios enables you to determine suitable action plans or strategies for different possible futures. It reveals how to react to a specific future and which set of actions would make sense no matter what conditions ultimately unfold.
For leaders of functional teams, developing scenarios and their underlying assumptions is in itself a useful exercise to corroborate or challenge strategies and keep them current.
The objective of scenario planning is to secure the best immediate outcome while preparing suitable alternative action plans, depending on how a situation unfolds. Proactively agreeing on both near-term operational decisions and long-term strategic plans will reduce the time it takes you to respond to emerging risks and opportunities. This can help your function preempt, rather than reactively control for, the negative effects of a major event or disruption.

Additional resources:
Guide to Scenario Planning for Functional Leaders
Scenario Planning for Supply Chain Leaders
Scenario Planning Ignition Guide for Marketing
Strengthen Your R&D Portfolio With Scenario Planning
Use adaptive strategic planning to enable a dynamic response
In an increasingly volatile and uncertain world, strategy can rapidly become out-of-date. To address this challenge, strategic planning must be adaptive. The faster the rate of change in operating conditions and the more disruptions you need to integrate into long-term strategy, the more adaptive your strategy models must be.
An adaptive strategy approach is what ensures your organization can spot new opportunities earlier and respond more quickly than your competitors, making you most likely to succeed in a dynamic digital world.
A truly adaptive strategy approach is consistent with four core practices (see figure) designed to move the enterprise from a rigid, top-down, calendar-based process to a more event-driven strategy approach. Functional strategy can incorporate the same principles. While a truly adaptive approach will be based on all four core practices, functional leaders can initially focus on the practices that address their immediate strategy challenges.
Rather than requiring perfect or complete information to execute, adaptive strategy uses available information to identify immediate actions required for an enterprise or function to be successful. These actions may range from focusing on high-priority areas to making foundational investments or conducting experiments to test ideas. You can use insights from these actions, along with any new information and analysis, to identify your next set of actions.
Adaptive strategy requires you to review strategy whenever new (and relevant) information becomes available, so it’s important to continually scan the business context to identify changes and review — and, where necessary, adjust — strategy in response to changes. (Also see “Strategic Assumptions.”)

Check out more strategic planning essentials for your function
Audit Compliance Finance Human Resources Information Technology Legal
Marketing Research & Development Risk Sales Service & Support Supply Chain
Experience Gartner Conferences
Join your peers for the unveiling of the latest insights at Gartner conferences.

Frequently asked questions
What is strategic planning.
Strategic planning is the process through which enterprises, functions and business units identify the roadmap of initiatives and portfolio of investments that will be required in the medium term to achieve long-term strategic objectives.
What are the four types of strategic planning and the three levels of strategic planning?
Strategic planning starts with setting strategy at the enterprise level, but that strategy must then be turned into action. The three levels of strategic planning typically refer to corporate versus business unit and functional. The four types of plans are typically strategic, operational, tactical and contingency.
What steps are involved in the strategic planning process?
To build a successful strategic plan with a consistent and sequential process, functional leaders should:
Ensure consistent usage of terms to minimize confusion in strategic planning and set a baseline for collaboration
Build a strong foundation for more detailed planning by setting or pressure-testing mission, vision and goal statements first
Streamline stakeholder input by limiting mission, vision and goal setting to senior leadership, and leaving objective, action plan, and measure and metric development to managers with execution expertise
What are the key elements of strategic planning?
The key elements of a successful strategic plan include:
Mission and vision. The organization’s mission articulates its reasons for being, and the vision lays out where the organization hopes to be. The strategic plan, which links the two, must be adaptive enough to respond if the context changes during execution.
Strategic assumptions. To build a successful strategic plan, leadership should scope for trends and disruptions, and assess their potential impact on enterprise goals.
Strategic plan design. A rigorous strategic planning design effectively translates the strategy into plans that can and will be executed. Poor plans lead to poor execution.
What are the key terms in strategic planning?
Mission: Organization’s purpose
Vision: Desired future state
Objective: How to reach goals
Action plan: What’s needed to achieve objectives
Measures and metrics: To track progress toward goals
How do we design a strategic planning system?
Strategic planning “systems” refer to the tools used to document strategic plans. Gartner urges organizations not to focus on strategy in terms of the document they’re creating, but instead focus on turning strategy into an easily communicated action plan.
What is a strategic action plan?
The strategic action plan is a formal document that serves as the primary source of information for how objectives will be executed, monitored, controlled and closed. Many organizations also deploy an associated but separate “action plan” for achieving the operating model.
What are strategic measures and metrics?
Measures are observable outcomes that allow organizations to evaluate the efficacy of their action plans. Metrics quantify those observed changes to enable an organization to concretely quantify its progress and stay aligned to its chosen measures.
What are the 7 key success factors involved in strategic planning?
These seven success factors are key to producing high-quality strategic plans that will be successfully executed yet responsive to change:
Focus on designing a minimally viable strategy.
Customize planning efforts to meet participants where they are.
Sketch out initiative design before prioritizing strategic actions.
Be clear about who owns what.
Cascade plans side to side, not just top-down.
Focus performance measures on key assumptions.
Pressure-test plans against a narrow set of future scenarios.
Drive stronger performance on your mission-critical priorities.
Looking for AI in local government? See our newest product, Madison AI.
More Like this
What is the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan.
It is not uncommon that the terms ‘strategic plan’ and ‘business plan’ get confused in the business world. While a strategic plan is a type of business plan, there are several important distinctions between the two types that are worth noting. Before beginning your strategic planning process or strategy implementation, look at the article below to learn the key difference between a business vs strategic plan and how each are important to your organization.
Definition of a business plan vs. a strategic plan
A strategic plan is essential for already established organizations looking for a way to manage and implement their strategic direction and future growth. Strategic planning is future-focused and serves as a roadmap to outline where the organization is going over the next 3-5 years (or more) and the steps it will take to get there.
Get the Free Guide for Setting OKRs that Work (with 100 examples!)
A strategic plan serves 6 functions for an organization that is striving to reach the next level of their growth:.
- Defines the purpose of the organization.
- Builds on an organization’s competitive advantages.
- Communicates the strategy to the staff.
- Prioritizes the financial needs of the organization.
- Directs the team to move from plan to action.
- Creates long-term sustainability and growth impact
Alternatively, a business plan is used by new businesses or organizations trying to get off the ground. The fundamentals of a business plan focus on setting the foundation for the business or organization. While it looks towards the future, the focus is set more on the immediate future (>1 year). Some of the functions of a business plan may overlap with a strategic plan. However, the focus and intentions diverge in a few key areas.
A business plan for new businesses, projects, or organizations serves these 5 functions:
- Simplifies or explains the objectives and goals of your organization.
- Coordinates human resource management and determines operational requirements.
- Secures funding for your organization.
- Evaluates potential business prospects.
- Creates a framework for conceptualizing ideas.
In other words, a strategic plan is utilized to direct the momentum and growth of an established company or organization. In contrast, a business plan is meant to set the foundation of a newly (or not quite) developed company by setting up its operational teams, strategizing ways to enter a new market, and obtaining funding.
A strategic plan focuses on long-term growth and the organization’s impact on the market and its customers. Meanwhile, a business plan must focus more on the short-term, day-to-day operational functions. Often, new businesses don’t have the capacity or resources to create a strategic plan, though developing a business plan with strategy elements is never a bad idea.
Business and strategic plans ultimately differ in several key areas–timeframe, target audience, focus, resource allocation, nature, and scalability.
While both a strategic and business plan is forward-facing and focused on future success, a business plan is focused on the more immediate future. A business plan normally looks ahead no further than one year. A business plan is set up to measure success within a 3- to 12-month timeframe and determines what steps a business owner needs to take now to succeed.
A strategic plan generally covers the organizational plan over 3 to 5+ years. It is set with future expansion and development in mind and sets up roadmaps for how the organization will reach its desired future state.
Pro Tip: While a vision statement could benefit a business plan, it is essential to a strategic plan.
Target Audience
A strategic plan is for established companies, businesses, organizations, and owners serious about growing their organizations. A strategic plan communicates the organization’s direction to the staff and stakeholders. The strategic plan is communicated to the essential change makers in the organization who will have a hand in making the progress happen.
A business plan could be for new businesses and entrepreneurs who are start-ups. The target audience for the business plan could also be stakeholders, partners, or investors. However, a business plan generally presents the entrepreneur’s ideas to a bank. It is meant to get the necessary people onboard to obtain the funding needed for the project.
A strategic plan provides focus, direction, and action to move the organization from where they are now to where they want to go. A strategic plan may consist of several months of studies, analyses, and other processes to gauge an organization’s current state. The strategy officers may conduct an internal and external analysis, determine competitive advantages, and create a strategy roadmap. They may take the time to redefine their mission, vision, and values statements.
Alternatively, a business plan provides a structure for ideas to define the business initially. It maps out the more tactical beginning stages of the plan.
Pro Tip: A mission statement is useful for business and strategic plans as it helps further define the enterprise’s value and purpose. If an organization never set its mission statement at the beginning stages of its business plan, it can create one for its strategic plan.
A strategic plan is critical to prioritizing resources (time, money, and people) to grow the revenue and increase the return on investment. The strategic plan may start with reallocating current financial resources already being utilized more strategically.
A business plan will focus on the resources the business still needs to obtain, such as vendors, investors, staff, and funding. A business plan is critical if new companies seek funding from banks or investors. It will add accountability and transparency for the organization and tell the funding channels how they plan to grow their business operations and ROI in the first year of the business.
The scalability of a business plan vs. strategic plan
Another way to grasp the difference is by understanding the difference in ‘scale’ between strategic and business plans. Larger organizations with multiple business units and a wide variety of products frequently start their annual planning process with a corporate-driven strategic plan. It is often followed by departmental and marketing plans that work from the Strategic Plan.
Smaller and start-up companies typically use only a business plan to develop all aspects of operations of the business on paper, obtain funding and then start the business.
Why understanding the differences between a business plan vs a strategic plan matters
It is important to know the key differences between the two terms, despite often being used interchangeably. But here’s a simple final explanation:
A business plan explains how a new business will get off the ground. A strategic plan answers where an established organization is going in the future and how they intend to reach that future state.
A strategic plan also focuses on building a sustainable competitive advantage and is futuristic. A business plan is used to assess the viability of a business opportunity and is more tactical.
10 Comments
I agree with your analysis about small companies, but they should do a strategic plan. Just check out how many of the INC 500 companies have an active strategic planning process and they started small. Its about 78%,
Strategic management is a key role of any organization even if belong to small business. it help in growth and also to steam line your values. im agree with kristin.
I agree with what you said, without strategic planning no organization can survive whether it is big or small. Without a clear strategic plan, it is like walking in the darkness.. Best Regards..
Vision, Mission in Business Plan VS Strategic Plan ?
you made a good analysis on strategic plan and Business plan the difference is quite clear now. But on the other hand, it seems that strategic plan and strategic management are similar which I think not correct. Please can you tell us the difference between these two?. Thanks
Thank you. I get points to work on it
super answer Thanking you
Hi. I went through all the discussions, comments and replies. Thanks! I got a very preliminary idea about functions and necessity of Strategic Planning in Business. But currently I am looking for a brief nice, flowery, juicy definition of “Business Strategic Planning” as a whole, which will give anyone a fun and interesting way to understand. Can anyone help me out please? Awaiting replies…… 🙂
that was easy to understand,
Developing a strategic plan either big or small company or organization mostly can’t achieve its goal. A strategic plan or formulation is the first stage of the strategic management plan, therefore, we should be encouraged to develop a strategic management plan. We can develop the best strategic plan but without a clear plan of implementation and evaluation, it will be difficult to achieve goals.
Comments Cancel
Join 60,000 other leaders engaged in transforming their organizations., subscribe to get the latest agile strategy best practices, free guides, case studies, and videos in your inbox every week..

Leading strategy? Join our FREE community.
Become a member of the chief strategy officer collaborative..
Free monthly sessions and exclusive content.
Do you want to 2x your impact.
- Product overview
- All features
- Latest feature release
- App integrations
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- asana-intelligence icon Asana AI
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Capacity planning
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- Permissions
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Project intake
- Resource planning
- Product launches
- View all uses arrow-right icon

- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Business strategy |
- 7 strategic planning models, plus 8 fra ...
7 strategic planning models, plus 8 frameworks to help you get started
Strategic planning is vital in defining where your business is going in the next three to five years. With the right strategic planning models and frameworks, you can uncover opportunities, identify risks, and create a strategic plan to fuel your organization’s success. We list the most popular models and frameworks and explain how you can combine them to create a strategic plan that fits your business.
A strategic plan is a great tool to help you hit your business goals . But sometimes, this tool needs to be updated to reflect new business priorities or changing market conditions. If you decide to use a model that already exists, you can benefit from a roadmap that’s already created. The model you choose can improve your knowledge of what works best in your organization, uncover unknown strengths and weaknesses, or help you find out how you can outpace your competitors.
In this article, we cover the most common strategic planning models and frameworks and explain when to use which one. Plus, get tips on how to apply them and which models and frameworks work well together.
Strategic planning models vs. frameworks
First off: This is not a one-or-nothing scenario. You can use as many or as few strategic planning models and frameworks as you like.
When your organization undergoes a strategic planning phase, you should first pick a model or two that you want to apply. This will provide you with a basic outline of the steps to take during the strategic planning process.
![business plan in strategic management [Inline illustration] Strategic planning models vs. frameworks (Infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/89236d14-1abf-4f49-8b91-4187147f1c63/inline-business-strategy-strategic-planning-models-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
During that process, think of strategic planning frameworks as the tools in your toolbox. Many models suggest starting with a SWOT analysis or defining your vision and mission statements first. Depending on your goals, though, you may want to apply several different frameworks throughout the strategic planning process.
For example, if you’re applying a scenario-based strategic plan, you could start with a SWOT and PEST(LE) analysis to get a better overview of your current standing. If one of the weaknesses you identify has to do with your manufacturing process, you could apply the theory of constraints to improve bottlenecks and mitigate risks.
Now that you know the difference between the two, learn more about the seven strategic planning models, as well as the eight most commonly used frameworks that go along with them.
![business plan in strategic management [Inline illustration] The seven strategic planning models (Infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/23048ae4-8a18-4b9b-ad9e-33b0fc5d04ee/inline-business-strategy-strategic-planning-models-2-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
1. Basic model
The basic strategic planning model is ideal for establishing your company’s vision, mission, business objectives, and values. This model helps you outline the specific steps you need to take to reach your goals, monitor progress to keep everyone on target, and address issues as they arise.
If it’s your first strategic planning session, the basic model is the way to go. Later on, you can embellish it with other models to adjust or rewrite your business strategy as needed. Let’s take a look at what kinds of businesses can benefit from this strategic planning model and how to apply it.
Small businesses or organizations
Companies with little to no strategic planning experience
Organizations with few resources
Write your mission statement. Gather your planning team and have a brainstorming session. The more ideas you can collect early in this step, the more fun and rewarding the analysis phase will feel.
Identify your organization’s goals . Setting clear business goals will increase your team’s performance and positively impact their motivation.
Outline strategies that will help you reach your goals. Ask yourself what steps you have to take in order to reach these goals and break them down into long-term, mid-term, and short-term goals .
Create action plans to implement each of the strategies above. Action plans will keep teams motivated and your organization on target.
Monitor and revise the plan as you go . As with any strategic plan, it’s important to closely monitor if your company is implementing it successfully and how you can adjust it for a better outcome.
2. Issue-based model
Also called goal-based planning model, this is essentially an extension of the basic strategic planning model. It’s a bit more dynamic and very popular for companies that want to create a more comprehensive plan.
Organizations with basic strategic planning experience
Businesses that are looking for a more comprehensive plan
Conduct a SWOT analysis . Assess your organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats with a SWOT analysis to get a better overview of what your strategic plan should focus on. We’ll give into how to conduct a SWOT analysis when we get into the strategic planning frameworks below.
Identify and prioritize major issues and/or goals. Based on your SWOT analysis, identify and prioritize what your strategic plan should focus on this time around.
Develop your main strategies that address these issues and/or goals. Aim to develop one overarching strategy that addresses your highest-priority goal and/or issue to keep this process as simple as possible.
Update or create a mission and vision statement . Make sure that your business’s statements align with your new or updated strategy. If you haven’t already, this is also a chance for you to define your organization’s values.
Create action plans. These will help you address your organization’s goals, resource needs, roles, and responsibilities.
Develop a yearly operational plan document. This model works best if your business repeats the strategic plan implementation process on an annual basis, so use a yearly operational plan to capture your goals, progress, and opportunities for next time.
Allocate resources for your year-one operational plan. Whether you need funding or dedicated team members to implement your first strategic plan, now is the time to allocate all the resources you’ll need.
Monitor and revise the strategic plan. Record your lessons learned in the operational plan so you can revisit and improve it for the next strategic planning phase.
The issue-based plan can repeat on an annual basis (or less often once you resolve the issues). It’s important to update the plan every time it’s in action to ensure it’s still doing the best it can for your organization.
You don’t have to repeat the full process every year—rather, focus on what’s a priority during this run.
3. Alignment model
This model is also called strategic alignment model (SAM) and is one of the most popular strategic planning models. It helps you align your business and IT strategies with your organization’s strategic goals.
You’ll have to consider four equally important, yet different perspectives when applying the alignment strategic planning model:
Strategy execution: The business strategy driving the model
Technology potential: The IT strategy supporting the business strategy
Competitive potential: Emerging IT capabilities that can create new products and services
Service level: Team members dedicated to creating the best IT system in the organization
Ideally, your strategy will check off all the criteria above—however, it’s more likely you’ll have to find a compromise.
Here’s how to create a strategic plan using the alignment model and what kinds of companies can benefit from it.
Organizations that need to fine-tune their strategies
Businesses that want to uncover issues that prevent them from aligning with their mission
Companies that want to reassess objectives or correct problem areas that prevent them from growing
Outline your organization’s mission, programs, resources, and where support is needed. Before you can improve your statements and approaches, you need to define what exactly they are.
Identify what internal processes are working and which ones aren’t. Pinpoint which processes are causing problems, creating bottlenecks , or could otherwise use improving. Then prioritize which internal processes will have the biggest positive impact on your business.
Identify solutions. Work with the respective teams when you’re creating a new strategy to benefit from their experience and perspective on the current situation.
Update your strategic plan with the solutions. Update your strategic plan and monitor if implementing it is setting your business up for improvement or growth. If not, you may have to return to the drawing board and update your strategic plan with new solutions.
4. Scenario model
The scenario model works great if you combine it with other models like the basic or issue-based model. This model is particularly helpful if you need to consider external factors as well. These can be government regulations, technical, or demographic changes that may impact your business.
Organizations trying to identify strategic issues and goals caused by external factors
Identify external factors that influence your organization. For example, you should consider demographic, regulation, or environmental factors.
Review the worst case scenario the above factors could have on your organization. If you know what the worst case scenario for your business looks like, it’ll be much easier to prepare for it. Besides, it’ll take some of the pressure and surprise out of the mix, should a scenario similar to the one you create actually occur.
Identify and discuss two additional hypothetical organizational scenarios. On top of your worst case scenario, you’ll also want to define the best case and average case scenarios. Keep in mind that the worst case scenario from the previous step can often provoke strong motivation to change your organization for the better. However, discussing the other two will allow you to focus on the positive—the opportunities your business may have ahead.
Identify and suggest potential strategies or solutions. Everyone on the team should now brainstorm different ways your business could potentially respond to each of the three scenarios. Discuss the proposed strategies as a team afterward.
Uncover common considerations or strategies for your organization. There’s a good chance that your teammates come up with similar solutions. Decide which ones you like best as a team or create a new one together.
Identify the most likely scenario and the most reasonable strategy. Finally, examine which of the three scenarios is most likely to occur in the next three to five years and how your business should respond to potential changes.
5. Self-organizing model
Also called the organic planning model, the self-organizing model is a bit different from the linear approaches of the other models. You’ll have to be very patient with this method.
This strategic planning model is all about focusing on the learning and growing process rather than achieving a specific goal. Since the organic model concentrates on continuous improvement , the process is never really over.
Large organizations that can afford to take their time
Businesses that prefer a more naturalistic, organic planning approach that revolves around common values, communication, and shared reflection
Companies that have a clear understanding of their vision
Define and communicate your organization’s cultural values . Your team can only think clearly and with solutions in mind when they have a clear understanding of your organization's values.
Communicate the planning group’s vision for the organization. Define and communicate the vision with everyone involved in the strategic planning process. This will align everyone’s ideas with your company’s vision.
Discuss what processes will help realize the organization’s vision on a regular basis. Meet every quarter to discuss strategies or tactics that will move your organization closer to realizing your vision.
6. Real-time model
This fluid model can help organizations that deal with rapid changes to their work environment. There are three levels of success in the real-time model:
Organizational: At the organizational level, you’re forming strategies in response to opportunities or trends.
Programmatic: At the programmatic level, you have to decide how to respond to specific outcomes or environmental changes.
Operational: On the operational level, you will study internal systems, policies, and people to develop a strategy for your company.
Figuring out your competitive advantage can be difficult, but this is absolutely crucial to ensure success. Whether it’s a unique asset or strength your organization has or an outstanding execution of services or programs—it’s important that you can set yourself apart from others in the industry to succeed.
Companies that need to react quickly to changing environments
Businesses that are seeking new tools to help them align with their organizational strategy
Define your mission and vision statement. If you ever feel stuck formulating your company’s mission or vision statement, take a look at those of others. Maybe Asana’s vision statement sparks some inspiration.
Research, understand, and learn from competitor strategy and market trends. Pick a handful of competitors in your industry and find out how they’ve created success for themselves. How did they handle setbacks or challenges? What kinds of challenges did they even encounter? Are these common scenarios in the market? Learn from your competitors by finding out as much as you can about them.
Study external environments. At this point, you can combine the real-time model with the scenario model to find solutions to threats and opportunities outside of your control.
Conduct a SWOT analysis of your internal processes, systems, and resources. Besides the external factors your team has to consider, it’s also important to look at your company’s internal environment and how well you’re prepared for different scenarios.
Develop a strategy. Discuss the results of your SWOT analysis to develop a business strategy that builds toward organizational, programmatic, and operational success.
Rinse and repeat. Monitor how well the new strategy is working for your organization and repeat the planning process as needed to ensure you’re on top or, perhaps, ahead of the game.
7. Inspirational model
This last strategic planning model is perfect to inspire and energize your team as they work toward your organization’s goals. It’s also a great way to introduce or reconnect your employees to your business strategy after a merger or acquisition.
Businesses with a dynamic and inspired start-up culture
Organizations looking for inspiration to reinvigorate the creative process
Companies looking for quick solutions and strategy shifts
Gather your team to discuss an inspirational vision for your organization. The more people you can gather for this process, the more input you will receive.
Brainstorm big, hairy audacious goals and ideas. Encouraging your team not to hold back with ideas that may seem ridiculous will do two things: for one, it will mitigate the fear of contributing bad ideas. But more importantly, it may lead to a genius idea or suggestion that your team wouldn’t have thought of if they felt like they had to think inside of the box.
Assess your organization’s resources. Find out if your company has the resources to implement your new ideas. If they don’t, you’ll have to either adjust your strategy or allocate more resources.
Develop a strategy balancing your resources and brainstorming ideas. Far-fetched ideas can grow into amazing opportunities but they can also bear great risk. Make sure to balance ideas with your strategic direction.
Now, let’s dive into the most commonly used strategic frameworks.
8. SWOT analysis framework
One of the most popular strategic planning frameworks is the SWOT analysis . A SWOT analysis is a great first step in identifying areas of opportunity and risk—which can help you create a strategic plan that accounts for growth and prepares for threats.
SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Here’s an example:
![business plan in strategic management [Inline illustration] SWOT analysis (Example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/cfab4ed2-46d1-4636-b801-14b3d86c8367/inline-project-management-SWOT-analysis-4-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
9. OKRs framework
A big part of strategic planning is setting goals for your company. That’s where OKRs come into play.
OKRs stand for objective and key results—this goal-setting framework helps your organization set and achieve goals. It provides a somewhat holistic approach that you can use to connect your team’s work to your organization’s big-picture goals. When team members understand how their individual work contributes to the organization’s success, they tend to be more motivated and produce better results
10. Balanced scorecard (BSC) framework
The balanced scorecard is a popular strategic framework for businesses that want to take a more holistic approach rather than just focus on their financial performance. It was designed by David Norton and Robert Kaplan in the 1990s, it’s used by companies around the globe to:
Communicate goals
Align their team’s daily work with their company’s strategy
Prioritize products, services, and projects
Monitor their progress toward their strategic goals
Your balanced scorecard will outline four main business perspectives:
Customers or clients , meaning their value, satisfaction, and/or retention
Financial , meaning your effectiveness in using resources and your financial performance
Internal process , meaning your business’s quality and efficiency
Organizational capacity , meaning your organizational culture, infrastructure and technology, and human resources
With the help of a strategy map, you can visualize and communicate how your company is creating value. A strategy map is a simple graphic that shows cause-and-effect connections between strategic objectives.
The balanced scorecard framework is an amazing tool to use from outlining your mission, vision, and values all the way to implementing your strategic plan .
You can use an integration like Lucidchart to create strategy maps for your business in Asana.
11. Porter’s Five Forces framework
If you’re using the real-time strategic planning model, Porter’s Five Forces are a great framework to apply. You can use it to find out what your product’s or service’s competitive advantage is before entering the market.
Developed by Michael E. Porter , the framework outlines five forces you have to be aware of and monitor:
![business plan in strategic management [Inline illustration] Porter’s Five Forces framework (Infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/d63265bc-23e2-4ce6-9b91-b3da5a756619/inline-business-strategy-strategic-planning-models-3-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Threat of new industry entrants: Any new entry into the market results in increased pressure on prices and costs.
Competition in the industry: The more competitors that exist, the more difficult it will be for you to create value in the market with your product or service.
Bargaining power of suppliers: Suppliers can wield more power if there are less alternatives for buyers or it’s expensive, time consuming, or difficult to switch to a different supplier.
Bargaining power of buyers: Buyers can wield more power if the same product or service is available elsewhere with little to no difference in quality.
Threat of substitutes: If another company already covers the market’s needs, you’ll have to create a better product or service or make it available for a lower price at the same quality in order to compete.
Remember, industry structures aren’t static. The more dynamic your strategic plan is, the better you’ll be able to compete in a market.
12. VRIO framework
The VRIO framework is another strategic planning tool designed to help you evaluate your competitive advantage. VRIO stands for value, rarity, imitability, and organization.
It’s a resource-based theory developed by Jay Barney. With this framework, you can study your firmed resources and find out whether or not your company can transform them into sustained competitive advantages.
Firmed resources can be tangible (e.g., cash, tools, inventory, etc.) or intangible (e.g., copyrights, trademarks, organizational culture, etc.). Whether these resources will actually help your business once you enter the market depends on four qualities:
Valuable : Will this resource either increase your revenue or decrease your costs and thereby create value for your business?
Rare : Are the resources you’re using rare or can others use your resources as well and therefore easily provide the same product or service?
Inimitable : Are your resources either inimitable or non-substitutable? In other words, how unique and complex are your resources?
Organizational: Are you organized enough to use your resources in a way that captures their value, rarity, and inimitability?
It’s important that your resources check all the boxes above so you can ensure that you have sustained competitive advantage over others in the industry.
13. Theory of Constraints (TOC) framework
If the reason you’re currently in a strategic planning process is because you’re trying to mitigate risks or uncover issues that could hurt your business—this framework should be in your toolkit.
The theory of constraints (TOC) is a problem-solving framework that can help you identify limiting factors or bottlenecks preventing your organization from hitting OKRs or KPIs .
Whether it’s a policy, market, or recourse constraint—you can apply the theory of constraints to solve potential problems, respond to issues, and empower your team to improve their work with the resources they have.
14. PEST/PESTLE analysis framework
The idea of the PEST analysis is similar to that of the SWOT analysis except that you’re focusing on external factors and solutions. It’s a great framework to combine with the scenario-based strategic planning model as it helps you define external factors connected to your business’s success.
PEST stands for political, economic, sociological, and technological factors. Depending on your business model, you may want to expand this framework to include legal and environmental factors as well (PESTLE). These are the most common factors you can include in a PESTLE analysis:
Political: Taxes, trade tariffs, conflicts
Economic: Interest and inflation rate, economic growth patterns, unemployment rate
Social: Demographics, education, media, health
Technological: Communication, information technology, research and development, patents
Legal: Regulatory bodies, environmental regulations, consumer protection
Environmental: Climate, geographical location, environmental offsets
15. Hoshin Kanri framework
Hoshin Kanri is a great tool to communicate and implement strategic goals. It’s a planning system that involves the entire organization in the strategic planning process. The term is Japanese and stands for “compass management” and is also known as policy management.
This strategic planning framework is a top-down approach that starts with your leadership team defining long-term goals which are then aligned and communicated with every team member in the company.
You should hold regular meetings to monitor progress and update the timeline to ensure that every teammate’s contributions are aligned with the overarching company goals.
Stick to your strategic goals
Whether you’re a small business just starting out or a nonprofit organization with decades of experience, strategic planning is a crucial step in your journey to success.
If you’re looking for a tool that can help you and your team define, organize, and implement your strategic goals, Asana is here to help. Our goal-setting software allows you to connect all of your team members in one place, visualize progress, and stay on target.
Related resources

Everything you need to know about requirements management
How to streamline compliance management software with Asana

15 creative elevator pitch examples for every scenario

How Asana streamlines strategic planning with work management
How to improve strategic planning
In conference rooms everywhere, corporate planners are in the midst of the annual strategic-planning process. For the better part of a year, they collect financial and operational data, make forecasts, and prepare lengthy presentations with the CEO and other senior managers about the future direction of the business. But at the end of this expensive and time-consuming process, many participants say they are frustrated by its lack of impact on either their own actions or the strategic direction of the company.
This sense of disappointment was captured in a recent McKinsey Quarterly survey of nearly 800 executives: just 45 percent of the respondents said they were satisfied with the strategic-planning process. 1 1. “ Improving strategic planning: A McKinsey Survey ,” The McKinsey Quarterly , Web exclusive, September 2006. The survey, conducted in late July and early August 2006, received 796 responses from a panel of executives from around the world. All panelists have mostly financial or strategic responsibilities and work in a wide range of industries for organizations with revenues of at least $500 million. Moreover, only 23 percent indicated that major strategic decisions were made within its confines. Given these results, managers might well be tempted to jettison the planning process altogether.
But for those working in the overwhelming majority of corporations, the annual planning process plays an essential role. In addition to formulating at least some elements of a company’s strategy, the process results in a budget, which establishes the resource allocation map for the coming 12 to 18 months; sets financial and operating targets, often used to determine compensation metrics and to provide guidance for financial markets; and aligns the management team on its strategic priorities. The operative question for chief executives is how to make the planning process more effective—not whether it is the sole mechanism used to design strategy. CEOs know that strategy is often formulated through ad hoc meetings or brand reviews, or as a result of decisions about mergers and acquisitions.
Our research shows that formal strategic-planning processes play an important role in improving overall satisfaction with strategy development. That role can be seen in the responses of the 79 percent of managers who claimed that the formal planning process played a significant role in developing strategies and were satisfied with the approach of their companies, compared with only 21 percent of the respondents who felt that the process did not play a significant role. Looked at another way, 51 percent of the respondents whose companies had no formal process were dissatisfied with their approach to the development of strategy, against only 20 percent of those at companies with a formal process.
So what can managers do to improve the process? There are many ways to conduct strategic planning, but determining the ideal method goes beyond the scope of this article. Instead we offer, from our research, five emergent ideas that executives can employ immediately to make existing processes run better. The changes we discuss here (such as a focus on important strategic issues or a connection to core-management processes) are the elements most linked with the satisfaction of employees and their perceptions of the significance of the process. These steps cannot guarantee that the right strategic decisions will be made or that strategy will be better executed, but by enhancing the planning process—and thus increasing satisfaction with the development of strategy—they will improve the odds for success.
Start with the issues
Ask CEOs what they think strategic planning should involve and they will talk about anticipating big challenges and spotting important trends. At many companies, however, this noble purpose has taken a backseat to rigid, data-driven processes dominated by the production of budgets and financial forecasts. If the calendar-based process is to play a more valuable role in a company’s overall strategy efforts, it must complement budgeting with a focus on strategic issues. In our experience, the first liberating change managers can make to improve the quality of the planning process is to begin it by deliberately and thoughtfully identifying and discussing the strategic issues that will have the greatest impact on future business performance.
Granted, an approach based on issues will not necessarily yield better strategic results. The music business, for instance, has discussed the threat posed by digital-file sharing for years without finding an effective way of dealing with the problem. But as a first step, identifying the key issues will ensure that management does not waste time and energy on less important topics.
We found a variety of practical ways in which companies can impose a fresh strategic perspective. For instance, the CEO of one large health care company asks the leaders of each business unit to imagine how a set of specific economic, social, and business trends will affect their businesses, as well as ways to capture the opportunities—or counter the threats—that these trends pose. Only after such an analysis and discussion do the leaders settle into the more typical planning exercises of financial forecasting and identifying strategic initiatives.
One consumer goods organization takes a more directed approach. The CEO, supported by the corporate-strategy function, compiles a list of three to six priorities for the coming year. Distributed to the managers responsible for functions, geographies, and brands, the list then becomes the basis for an offsite strategy-alignment meeting, where managers debate the implications of the priorities for their particular organizations. The corporate-strategy function summarizes the results, adds appropriate corporate targets, and shares them with the organization in the form of a strategy memo, which serves as the basis for more detailed strategic planning at the division and business-unit levels.
A packaged-goods company offers an even more tailored example. Every December the corporate senior-management team produces a list of ten strategic questions tailored to each of the three business units. The leaders of these businesses have six months to explore and debate the questions internally and to come up with answers. In June each unit convenes with the senior-management team in a one-day meeting to discuss proposed actions and reach decisions.
Some companies prefer to use a bottom-up rather than top-down process. We recently worked with a sales company to design a strategic-planning process that begins with in-depth interviews (involving all of the senior managers and selected corporate and business executives) to generate a list of the most important strategic issues facing the company. The senior-management team prioritizes the list and assigns managers to explore each issue and report back in four to six weeks. Such an approach can be especially valuable in companies where internal consensus building is an imperative.
Bring together the right people
An issues-based approach won’t do much good unless the most relevant people are involved in the debate. We found that survey respondents who were satisfied with the strategic-planning process rated it highly on dimensions such as including the most knowledgeable and influential participants, stimulating and challenging the participants’ thinking, and having honest, open discussions about difficult issues. In contrast, 27 percent of the dissatisfied respondents reported that their company’s strategic planning had not a single one of these virtues. Such results suggest that too many companies focus on the data-gathering and packaging elements of strategic planning and neglect the crucial interactive components.
Strategic conversations will have little impact if they involve only strategic planners from both the business unit and the corporate levels. One of our core beliefs is that those who carry out strategy should also develop it. The key strategy conversation should take place among corporate decision makers, business unit leaders, and people with expertise essential to the discussion. In addition to leading the corporate review, the CEO, aided by members of the executive team, should as a rule lead the strategy review for business units as well. The head of a business unit, supported by four to six people, should direct the discussion from its side of the table (see sidebar, "Things to ask in any business unit review").
Things to ask in any business unit review
Are major trends and changes in your business unit’s environment affecting your strategic plan? Specifically, what potential developments in customer demand, technology, or the regulatory environment could have enough impact on the industry to change the entire plan?
How and why is this plan different from last year’s?
What were your forecasts for market growth, sales, and profitability last year, two years ago, and three years ago? How right or wrong were they? What did the business unit learn from those experiences?
What would it take to double your business unit’s growth rate and profits? Where will growth come from: expansion or gains in market share?
If your business unit plans to take market share from competitors, how will it do so, and how will they respond? Are you counting on a strategic advantage or superior execution?
What are your business unit’s distinctive competitive strengths, and how does the plan build on them?
How different is the strategy from those of competitors, and why? Is that a good or a bad thing?
Beyond the immediate planning cycle, what are the key issues, risks, and opportunities that we should discuss today?
What would a private-equity owner do with this business?
How will the business unit monitor the execution of this strategy?
One pharmaceutical company invites business unit leaders to take part in the strategy reviews of their peers in other units. This approach can help build a better understanding of the entire company and, especially, of the issues that span business units. The risk is that such interactions might constrain the honesty and vigor of the dialogue and put executives at the focus of the discussion on the defensive.
Corporate senior-management teams can dedicate only a few hours or at most a few days to a business unit under review. So team members should spend this time in challenging yet collaborative discussions with business unit leaders rather than trying to absorb many facts during the review itself. To provide some context for the discussion, best-practice companies disseminate important operational and financial information to the corporate review team well in advance of such sessions. This reading material should also tee up the most important issues facing the business and outline the proposed strategy, ensuring that the review team is prepared with well-thought-out questions. In our experience, the right 10 pages provide ample fuel to fire a vigorous discussion, but more than 25 pages will likely douse the level of energy or engagement in the room.
Adapt planning cycles to the needs of each business
Managers are justifiably concerned about the resources and time required to implement an issues-based strategic-planning approach. One easy—yet rarely adopted—solution is to free business units from the need to conduct this rigorous process every single year. In all but the most volatile, high-velocity industries, it is hard to imagine that a major strategic redirection will be necessary every planning cycle. In fact, forcing businesses to undertake this exercise annually is distracting and may even be detrimental. Managers need to focus on executing the last plan’s major initiatives, many of which can take 18 to 36 months to implement fully.
Some companies alternate the business units that undergo the complete strategic-planning process (as opposed to abbreviated annual updates of the existing plan). One media company, for example, requires individual business units to undertake strategic planning only every two or three years. This cadence enables the corporate senior-management team and its strategy group to devote more energy to the business units that are “at bat.” More important, it frees the corporate-strategy group to work directly with the senior team on critical issues that affect the entire company—issues such as developing an integrated digitization strategy and addressing unforeseen changes in the fast-moving digital-media landscape.
Other companies use trigger mechanisms to decide which business units will undergo a full strategic-planning exercise in a given year. One industrial company assigns each business unit a color-coded grade—green, yellow, or red—based on the unit’s success in executing the existing strategic plan. “Code red,” for example, would slate a business unit for a strategy review. Although many of the metrics that determine the grade are financial, some may be operational to provide a more complete assessment of the unit’s performance.
Freeing business units from participating in the strategic-planning process every year raises a caveat, however. When important changes in the external environment occur, senior managers must be able to engage with business units that are not under review and make major strategic decisions on an ad hoc basis. For instance, a major merger in any industry would prompt competitors in it to revisit their strategies. Indeed, one advantage of a tailored planning cycle is that it builds slack into the strategic-review system, enabling management to address unforeseen but pressing strategic issues as they arise.
Implement a strategic-performance-management system
In the end, many companies fail to execute the chosen strategy. More than a quarter of our survey respondents said that their companies had plans but no execution path. Forty-five percent reported that planning processes failed to track the execution of strategic initiatives. All this suggests that putting in place a system to measure and monitor their progress can greatly enhance the impact of the planning process.
Most companies believe that their existing control systems and performance-management processes (including budgets and operating reviews) are the sole way to monitor progress on strategy. As a result, managers attempt to translate the decisions made during the planning process into budget targets or other financial goals. Although this practice is sensible and necessary, it is not enough. We estimate that a significant portion of the strategic decisions we recommend to companies can’t be tracked solely through financial targets. A company undertaking a major strategic initiative to enhance its innovation and product-development capabilities, for example, should measure a variety of input metrics, such as the quality of available talent and the number of ideas and projects at each stage in development, in addition to pure output metrics such as revenues from new-product sales. One information technology company, for instance, carefully tracks the number and skill levels of people posted to important strategic projects.
Strategic-performance-management systems, which should assign accountability for initiatives and make their progress more transparent, can take many forms. One industrial corporation tracks major strategic initiatives that will have the greatest impact, across a portfolio of a dozen businesses, on its financial and strategic goals. Transparency is achieved through regular reviews and the use of financial as well as nonfinancial metrics. The corporate-strategy team assumes responsibility for reviews (chaired by the CEO and involving the relevant business-unit leaders) that use an array of milestones and metrics to assess the top ten initiatives. One to expand operations in China and India, for example, would entail regular reviews of interim metrics such as the quality and number of local employees recruited and the pace at which alliances are formed with channel partners or suppliers. Each business unit, in turn, is accountable for adopting the same performance-management approach for its own, lower-tier top-ten list of initiatives.
When designed well, strategic-performance-management systems can give an early warning of problems with strategic initiatives, whereas financial targets alone at best provide lagging indicators. An effective system enables management to step in and correct, redirect, or even abandon an initiative that is failing to perform as expected. The strategy of a pharmaceutical company that embarked on a major expansion of its sales force to drive revenue growth, for example, presupposed that rapid growth in the number of sales representatives would lead to a corresponding increase in revenues. The company also recognized, however, that expansion was in turn contingent on several factors, including the ability to recruit and train the right people. It therefore put in place a regular review of the key strategic metrics against its actual performance to alert managers to any emerging problems.
Integrate human-resources systems into the strategic plan
Simply monitoring the execution of strategic initiatives is not sufficient: their successful implementation also depends on how managers are evaluated and compensated. Yet only 36 percent of the executives we surveyed said that their companies’ strategic-planning processes were integrated with HR processes. One way to create a more valuable strategic-planning process would be to tie the evaluation and compensation of managers to the progress of new initiatives.
Although the development of strategy is ostensibly a long-term endeavor, companies traditionally emphasize short-term, purely financial targets—such as annual revenue growth or improved margins—as the sole metrics to gauge the performance of managers and employees. This approach is gradually changing. Deferred-compensation models for boards, CEOs, and some senior managers are now widely used. What’s more, several companies have added longer-term performance targets to complement the short-term ones. A major pharmaceutical company, for example, recently revamped its managerial-compensation structure to include a basket of short-term financial and operating targets as well as longer-term, innovation-based growth targets.
Although these changes help persuade managers to adopt both short- and long-term approaches to the development of strategy, they don’t address the need to link evaluation and compensation to specific strategic initiatives. One way of doing so is to craft a mix of performance targets that more appropriately reflect a company’s strategy. For example, one North American services business that launched strategic initiatives to improve its customer retention and increase sales also adjusted the evaluation and compensation targets for its managers. Rather than measuring senior managers only by revenue and margin targets, as it had done before, it tied 20 percent of their compensation to achieving its retention and cross-selling goals. By introducing metrics for these specific initiatives and linking their success closely to bonus packages, the company motivated managers to make the strategy succeed.
An advantage of this approach is that it motivates managers to flag any problems early in the implementation of a strategic initiative (which determines the size of bonuses) so that the company can solve them. Otherwise, managers all too often sweep the debris of a failing strategy under the operating rug until the spring-cleaning ritual of next year’s annual planning process.
Some business leaders have found ways to give strategic planning a more valuable role in the formulation as well as the execution of strategy. Companies that emulate their methods might find satisfaction instead of frustration at the end of the annual process.
Renée Dye is a consultant in McKinsey’s Atlanta office, and Olivier Sibony is a director in the Paris office.
This article was first published in the Autumn 2007 issue of McKinsey on Finance . Visit McKinsey’s corporate finance site to view the full issue.

Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Distortions and deceptions in strategic decisions
Tired of strategic planning.
Strategic Planning
The art of formulating business strategies, implementing them, and evaluating their impact based on organizational objectives
What is Strategic Planning?
Strategic planning is the art of creating specific business strategies, implementing them, and evaluating the results of executing the plan, in regard to a company’s overall long-term goals or desires. It is a concept that focuses on integrating various departments (such as accounting and finance, marketing, and human resources) within a company to accomplish its strategic goals. The term strategic planning is essentially synonymous with strategic management.

The concept of strategic planning originally became popular in the 1950s and 1960s, and enjoyed favor in the corporate world up until the 1980s, when it somewhat fell out of favor. However, enthusiasm for strategic business planning was revived in the 1990s and strategic planning remains relevant in modern business.
CFI’s Course on Corporate & Business Strategy is an elective course for the FMVA Program.
Strategic Planning Process
The strategic planning process requires considerable thought and planning on the part of a company’s upper-level management. Before settling on a plan of action and then determining how to strategically implement it, executives may consider many possible options. In the end, a company’s management will, hopefully, settle on a strategy that is most likely to produce positive results (usually defined as improving the company’s bottom line) and that can be executed in a cost-efficient manner with a high likelihood of success, while avoiding undue financial risk.
The development and execution of strategic planning are typically viewed as consisting of being performed in three critical steps:
1. Strategy Formulation
In the process of formulating a strategy, a company will first assess its current situation by performing an internal and external audit. The purpose of this is to help identify the organization’s strengths and weaknesses, as well as opportunities and threats ( SWOT Analysis ). As a result of the analysis, managers decide on which plans or markets they should focus on or abandon, how to best allocate the company’s resources, and whether to take actions such as expanding operations through a joint venture or merger.
Business strategies have long-term effects on organizational success. Only upper management executives are usually authorized to assign the resources necessary for their implementation.
2. Strategy Implementation
After a strategy is formulated, the company needs to establish specific targets or goals related to putting the strategy into action, and allocate resources for the strategy’s execution. The success of the implementation stage is often determined by how good a job upper management does in regard to clearly communicating the chosen strategy throughout the company and getting all of its employees to “buy into” the desire to put the strategy into action.
Effective strategy implementation involves developing a solid structure, or framework, for implementing the strategy, maximizing the utilization of relevant resources, and redirecting marketing efforts in line with the strategy’s goals and objectives.
3. Strategy Evaluation
Any savvy business person knows that success today does not guarantee success tomorrow. As such, it is important for managers to evaluate the performance of a chosen strategy after the implementation phase.
Strategy evaluation involves three crucial activities: reviewing the internal and external factors affecting the implementation of the strategy, measuring performance, and taking corrective steps to make the strategy more effective. For example, after implementing a strategy to improve customer service, a company may discover that it needs to adopt a new customer relationship management (CRM) software program in order to attain the desired improvements in customer relations.
All three steps in strategic planning occur within three hierarchical levels: upper management, middle management, and operational levels. Thus, it is imperative to foster communication and interaction among employees and managers at all levels, so as to help the firm to operate as a more functional and effective team.
Benefits of Strategic Planning
The volatility of the business environment causes many firms to adopt reactive strategies rather than proactive ones. However, reactive strategies are typically only viable for the short-term, even though they may require spending a significant amount of resources and time to execute. Strategic planning helps firms prepare proactively and address issues with a more long-term view. They enable a company to initiate influence instead of just responding to situations.
Among the primary benefits derived from strategic planning are the following:
1. Helps formulate better strategies using a logical, systematic approach
This is often the most important benefit. Some studies show that the strategic planning process itself makes a significant contribution to improving a company’s overall performance, regardless of the success of a specific strategy.
2. Enhanced communication between employers and employees
Communication is crucial to the success of the strategic planning process. It is initiated through participation and dialogue among the managers and employees, which shows their commitment to achieving organizational goals.
Strategic planning also helps managers and employees show commitment to the organization’s goals. This is because they know what the company is doing and the reasons behind it. Strategic planning makes organizational goals and objectives real, and employees can more readily understand the relationship between their performance, the company’s success, and compensation. As a result, both employees and managers tend to become more innovative and creative, which fosters further growth of the company.
3. Empowers individuals working in the organization
The increased dialogue and communication across all stages of the process strengthens employees’ sense of effectiveness and importance in the company’s overall success. For this reason, it is important for companies to decentralize the strategic planning process by involving lower-level managers and employees throughout the organization. A good example is that of the Walt Disney Co., which dissolved its separate strategic planning department, in favor of assigning the planning roles to individual Disney business divisions.
An increasing number of companies use strategic planning to formulate and implement effective decisions. While planning requires a significant amount of time, effort, and money, a well-thought-out strategic plan efficiently fosters company growth, goal achievement, and employee satisfaction.
Additional Resources
Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to Strategic Planning. To keep learning and advancing your career, the additional CFI resources below will be useful:
- Broad Factors Analysis
- Scalability
- Systems Thinking
- See all management & strategy resources
- Share this article

Create a free account to unlock this Template
Access and download collection of free Templates to help power your productivity and performance.
Already have an account? Log in
Supercharge your skills with Premium Templates
Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates.
Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs.
Already have a Self-Study or Full-Immersion membership? Log in
Access Exclusive Templates
Gain unlimited access to more than 250 productivity Templates, CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs, hundreds of resources, expert reviews and support, the chance to work with real-world finance and research tools, and more.
Already have a Full-Immersion membership? Log in
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Creating Brand Value
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
What Is Business Strategy & Why Is It Important?

- 20 Oct 2022
Every business leader wants their organization to succeed. Turning a profit and satisfying stakeholders are worthy objectives but aren’t feasible without an effective business strategy.
To attain success, leaders must hone their skills and set clear business goals by crafting a strategy that creates value for the firm, customers, suppliers, and employees. Here's an overview of business strategy and why it's essential to your company’s success.
Access your free e-book today.
What’s a Business Strategy?
Business strategy is the strategic initiatives a company pursues to create value for the organization and its stakeholders and gain a competitive advantage in the market. This strategy is crucial to a company's success and is needed before any goods or services are produced or delivered.
According to Harvard Business School Online's Business Strategy course, an effective strategy is built around three key questions:
- How can my business create value for customers?
- How can my business create value for employees?
- How can my business create value by collaborating with suppliers?
Many promising business initiatives don’t come to fruition because the company failed to build its strategy around value creation. Creativity is important in business , but a company won't last without prioritizing value.
The Importance of Business Strategy
A business strategy is foundational to a company's success. It helps leaders set organizational goals and gives companies a competitive edge. It determines various business factors, including:
- Price: How to price goods and services based on customer satisfaction and cost of raw materials
- Suppliers: Whether to source materials sustainably and from which suppliers
- Employee recruitment: How to attract and maintain talent
- Resource allocation: How to allocate resources effectively
Without a clear business strategy, a company can't create value and is unlikely to succeed.
Creating Value
To craft a successful business strategy, it's necessary to obtain a thorough understanding of value creation. In the online course Business Strategy , Harvard Business School Professor Felix Oberholzer-Gee explains that, at its core, value represents a difference. For example, the difference between a customer's willingness to pay for a good or service and its price represents the value the business has created for the customer. This difference can be visualized with a tool known as the value stick.
The value stick has four components, representing the value a strategy can bring different stakeholders.

- Willingness to pay (WTP) : The maximum amount a customer is willing to pay for a company's goods or services
- Price : The actual price of the goods or services
- Cost : The cost of the raw materials required to produce the goods or services
- Willingness to sell (WTS) : The lowest amount suppliers are willing to receive for raw materials, or the minimum employees are willing to earn for their work
The difference between each component represents the value created for each stakeholder. A business strategy seeks to widen these gaps, increasing the value created by the firm’s endeavors.
Increasing Customer Delight
The difference between a customer's WTP and the price is known as customer delight . An effective business strategy creates value for customers by raising their WTP or decreasing the price of the company’s goods or services. The larger the difference between the two, the more value is created for customers.
A company might focus on increasing WTP with its marketing strategy. Effective market research can help a company set its pricing strategy by determining target customers' WTP and finding ways to increase it. For example, a business might differentiate itself and increase customer loyalty by incorporating sustainability into its business strategy. By aligning its values with its target audiences', an organization can effectively raise consumers' WTP.
Increasing Firm Margin
The value created for the firm is the difference between the price of an item and its cost to produce. This difference is known as the firm’s margin and represents the strategy's financial success. One metric used to quantify this margin is return on invested capital (ROIC) . This metric compares a business's operating income with the capital necessary to generate it. The formula for ROIC is:
Return on Invested Capital = Net Operating Cost After Tax (NOCAT) / Invested Capital (IC)
ROIC tells investors how successful a company is at turning its investments into profit. By raising WTP, a company can risk increasing prices, thereby increasing firm margin. Business leaders can also increase this metric by decreasing their costs. For example, sustainability initiatives—in addition to raising WTP—can lower production costs by using fewer or more sustainable resources. By focusing on the triple bottom line , a firm can simultaneously increase customer delight and margin.
Increasing Supplier Surplus & Employee Satisfaction
By decreasing suppliers' WTS, or increasing costs, a company can create value for suppliers—or supplier surplus . Since increasing costs isn't sustainable, an effective business strategy seeks to create value for suppliers by decreasing WTS. How a company accomplishes this varies. For example, a brick-and-mortar company might partner with vendors to showcase its products in exchange for a discount. Suppliers may also be willing to offer a discount in exchange for a long-term contract.
In addition to supplier WTS, companies are also responsible for creating value for another key stakeholder: its employees. The difference between employee compensation and the minimum they're willing to receive is employee satisfaction . There are several ways companies can increase this difference, including:
- Increasing compensation: While most companies hesitate to raise salaries, some have found success in doing so. For example, Dan Price, CEO of Gravity Payments, increased his company's minimum wage to $80,000 per year and enjoyed substantial growth and publicity as a result.
- Increasing benefits: Companies can also decrease WTS by making working conditions more desirable to prospective employees. Some offer remote or hybrid working opportunities to give employees more flexibility. Several have also started offering four-day work weeks , often experiencing increased productivity as a result.
There are several ways to increase supplier surplus and employee satisfaction without hurting the company's bottom line. Unfortunately, most managers only devote seven percent of their time to developing employees and engaging stakeholders. Yet, a successful strategy creates value for every stakeholder—both internal and external.

Strategy Implementation
Crafting a business strategy is just the first step in the process. Implementation takes a strategy from formulation to execution . Successful implementation includes the following steps :
- Establish clear goals and key performance indicators (KPIs)
- Set expectations and ensure employees are aware of their roles and responsibilities
- Delegate work and allocate resources effectively
- Put the plan into action and continuously monitor its progress
- Adjust your plan as necessary
- Ensure your team has what they need to succeed and agrees on the desired outcome
- Evaluate the results of the plan
Throughout the process, it's important to remember to adjust your plan throughout its execution but to avoid second-guessing your decisions. Striking this balance is challenging, but crucial to a business strategy's success.

Learn More About Creating a Successful Business Strategy
Business strategy constantly evolves with changing consumer expectations and market conditions. For this reason, business leaders should continuously educate themselves on creating and executing an effective strategy.
One of the best ways to stay up-to-date on best practices is to take an online course, such as HBS Online's Business Strategy program. The course will provide guidance on creating a value-driven strategy for your business.
Do you want to learn how to craft an effective business strategy and create value for your company's stakeholders? Explore our online course Business Strategy , or other strategy courses , to develop your strategic planning skills. To determine which strategy course is right for you, download our free flowchart .

About the Author
What is the strategic management process + how to get started

Every day in every department of your organization, people are making decisions.
It’s important that all of those decisions are aligned with the same goals — goals that give your business a competitive edge.
But how do you determine your company’s strategy? How can you be sure you’re headed in the right direction?
The answer lies in the strategic management process. The strategic management process guides you through planning, implementing, and maintaining the strategies that lead to the best business performance.
This article introduces the strategic management process and gives you tips on how to do it right.
- What is the strategic management process?
Strategic management is the process of defining and implementing an organization’s strategy. It involves analyzing current circumstances, developing a plan to reach important goals, and executing that plan.
All businesses can benefit from strategic management to help them meet long-term objectives. The process is especially important when the organization is going through big changes or facing aggressive competition. For example, a start-up moving into the scale-up phase can implement strategic management to guide growth.
- Why is strategic management important?
Strategic management ensures that the actions of everyone in your organization are aligned with your major goals. It helps departments and business leaders make better, faster decisions.
Strategic management keeps departments on the same page.
Instead of every department head making their own choices about what the company needs, a strategic plan provides a framework for prioritizing projects.
It helps your organization find new opportunities and anticipate new challenges.
Strategic management involves an in-depth analysis of your current circumstances, the market, and the competitive landscape. This helps you discover new opportunities for success.
Strategic management allows for more efficient organizational performance.
Having a strategy helps people in your organization make tactical decisions more quickly, and it keeps you from wasting time on projects that don’t align with the company’s mission.
This streamlines your processes and creates greater operational efficiency.
- What are the 5 steps of the strategic management process?
Now you know why strategic management is so important, let’s take a look at the 5 essential steps in the strategic management process:
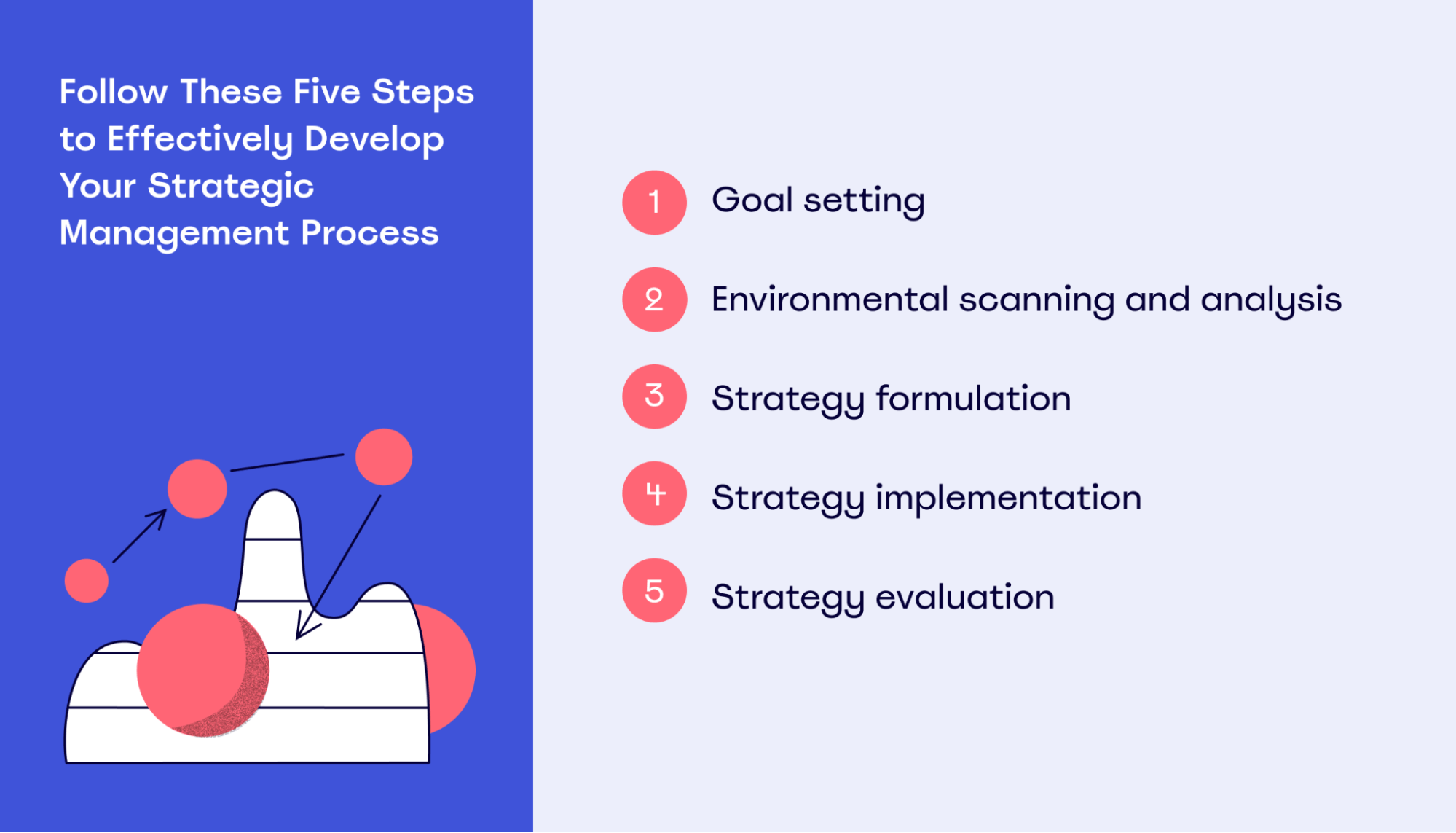
1. Goal setting
The strategic management process is all about creating a roadmap to help you achieve your vision. So before you go any further, you need to clarify what your company wants to achieve.
Many companies kick off the strategic management process by writing a vision statement. A vision statement communicates where you want to be in the future. It’s different from your mission statement — which describes why your company exists — but both statements should inform your strategic plan.
Once you’ve created or reviewed your vision statement, it’s time to pick some broad areas of focus. You don’t need to have specific, measurable goals yet, but you should go into the planning process with an idea of what you want to work on.
For example, growing revenue or improving customer service could be goals at this point.
2. Environmental scanning and analysis
The next part of the process is analysis. Before you can define strategies and tactics, you need to know where you stand currently. That includes internal factors, like your location, structure, and talent, as well as external factors like your competition and market forces.
The more information you have, the stronger the foundation of your strategic plan. Here are some tips for conducting an analysis.
1. Solicit feedback.
Talk to team leaders to get a better understanding of internal operations. Employee surveys, interviews, and discussion groups can be used to learn about the perspectives of everyone in the company.
2. Learn about your customers.
You can survey your existing customers or email list to learn more about how your customers and prospects feel. For example, if they’re generally frustrated with your customer service team’s response time, then improving that can be a strategic objective. Or maybe you’ll learn about new product features they want, and you can plan to develop them.
3. Research the competitive environment.
Researching your competitors can help you find your weak spots and learn where you stand out from the crowd.
You can use Miro’s competitor analysis template to analyze and evaluate the competitive landscape for products, services, and companies.
4. Consider your resources.
When you’re setting your goals, you’ll have to know if you have the people and resources to accomplish them. Having a clear idea of your resources from the start will help you set realistic objectives.
5. Conduct a SWOT analysis.
SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. You can organize your SWOT analysis visually by using Miro’s SWOT Analysis template .
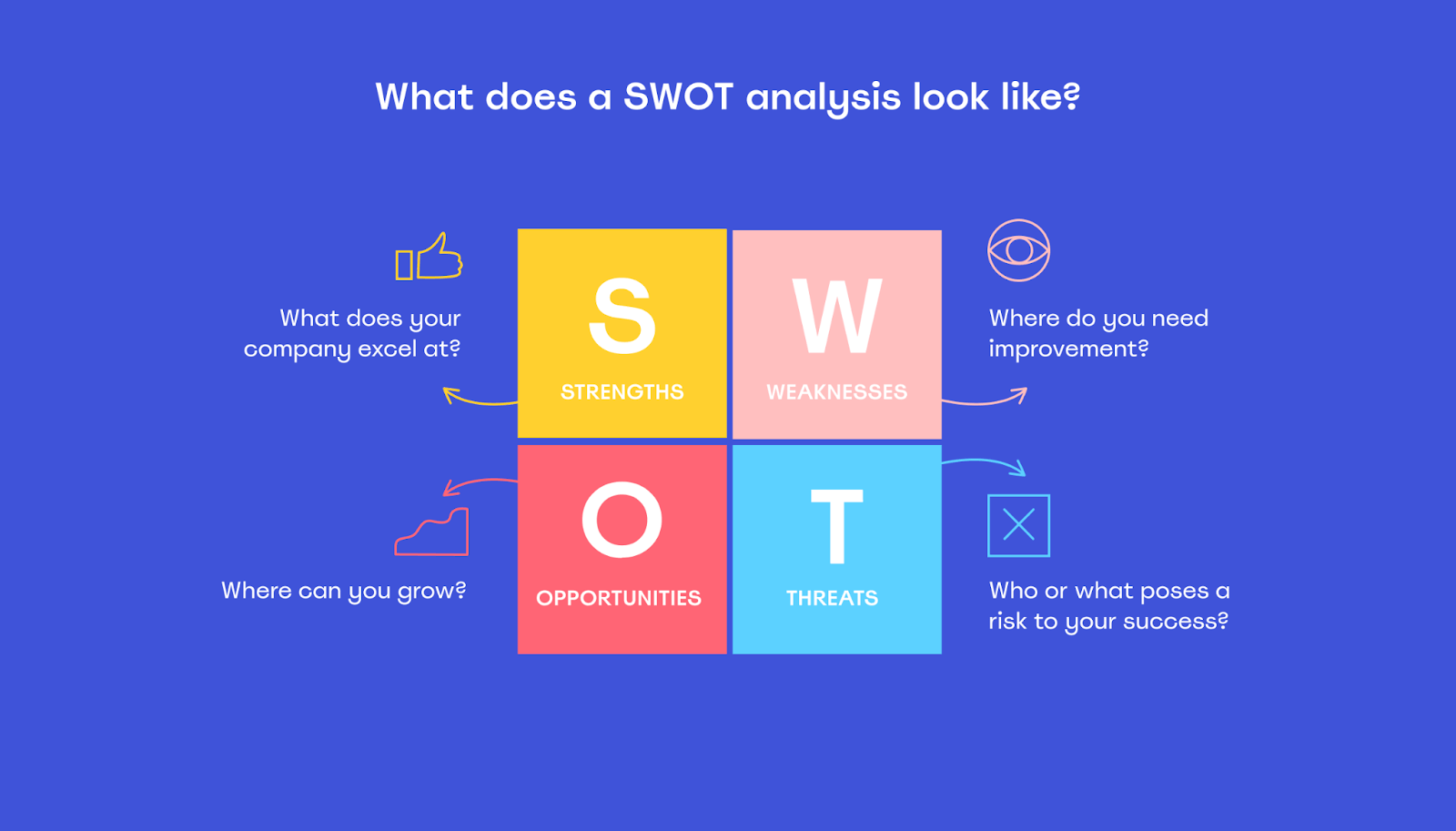
3. Strategy formulation
It’s finally time to write your strategic plan. In addition to your mission and vision statement, a strategic plan has a few key components.
Strategic objectives
Strategic objectives are high-level goals that help you accomplish your mission. Some examples of strategic objectives include:
- Grow earnings per share by 10% per year
- Launch two new products per year
- Increase NPS to 50 by 2024
For each strategic objective, use tactics that tell you specific actions to achieve the goal. For example, if your strategic objective is to increase awareness of your brand, a tactic could be to create profiles on the major social media sites.
Part of the strategic planning process is determining how you’re going to measure your progress toward your objectives. Choose a metric for each goal and make sure you have the ability to track it.
What about projects?
Your strategic plan doesn’t need to go into the projects that each department will undertake. Projects are related to strategic planning as the vehicle for accomplishing a strategic objective. However, projects can be planned by individual departments once the plan is complete.
For example, if your strategy is to improve customer loyalty and your tactic is to implement a rewards program, the marketing or customer experience teams will be put in charge of managing the creation of the program.
4. Strategy implementation
You’ve determined your organization’s strategy, but the work has just begun. Now you need to make a plan for implementing your strategic objectives.
Secure any resources you need.
Make sure you have the resources, budget, and approvals necessary to execute your plan.
Delegate the work.
Roles should be clearly defined at this point. Who’s in charge of communicating the plan to teams? Who will report on plan progress? Which departments will be responsible for which tactics?
Launch the plan.
Communicate the details of the plan to the company.
Depending on your organization, you may also need a plan to communicate your strategy with the board, key customers, investors, or the public.
Communication is a two-way street. Give people a way to ask questions or submit concerns about the plan.
Offer training.
If business decisions are going to be based on your company strategy, decision-makers need to know what that strategy is.
For people who require a deep understanding of your strategic plan, like department leaders, offer educational sessions to get them up to speed.
Make a plan to share your progress.
The whole company is working toward common goals — make sure you keep everyone updated on how they’re doing. Regular communication about how the strategic plan is going will increase buy-in.
5. Strategy evaluation
Most strategic plans cover the next three to five years. But that doesn’t mean you can’t adjust your strategies along the way.
Part of your implementation plan should be a schedule for continually reviewing your strategic plan, including its relevance to your current circumstances, its practicality, and how much progress you’ve made so far.
If any of your strategic objectives or tactics haven’t been implemented on time, ask yourself:
- Are we still making progress toward this goal?
- Do we have the resources to achieve the goal?
- Can the goal be accomplished if the deadline is extended?
- Is the goal still relevant to our current circumstances?
- Can the goal be changed slightly to accomplish something similar?
Some strategies may need to be removed from the plan or updated.
- Strategic management process secrets for success
The strategic management process has many points of possible failure. Some organizations never agree on a plan, while others have great ideas that fall apart in the implementation process.
Following these best practices will give you the best chance of strategic management success.

Start with a core team that owns the process.
Brainstorming and collaboration are easiest if you start with a small group of stakeholders. This shouldn’t just be a few executives. Bring in a diverse group of thinkers from around the organization.
These people will help make and implement the plan. Their buy-in will also be important in making sure that every department is enthusiastic about the company’s new direction.
Make your goals optimistic but realistic.
Setting your strategy for the next several years is exciting — you get to decide the direction your company is headed and what you intend to accomplish. It’s okay to be optimistic about your vision.
But don’t get too carried away. If your objectives aren’t realistic, the plan will fall by the wayside quickly.
Agree on due dates.
To make sure your plan is carried out, everything should be on a schedule. That includes your strategic objectives (like “increase revenue 30% by the end of 2023 ) as well as elements of the strategic management process, such as holding the planning meeting, communicating the plan to your company, and reporting on your progress.
Have a plan for communication.
Part of the strategic planning process is letting everyone in the company know about the plan — and inspiring them to be enthusiastic about it.
Consider having a company-wide strategic plan kickoff event. When you introduce the plan, you can also let employees know about any rewards that will be given to teams or individuals that exceed the plan’s goals.
Use tools that make collaboration easy.
The strategic management process involves the entire organization, so collaboration is key. But group work can be disorganized and unproductive if you don’t have methods to stay on track and share ideas.
The right tools can help you keep planning sessions organized, share ideas, make collaborative decisions, and convey your ideas to others.
Miro’s visual workspace is a full-featured digital space that makes it easy to plan, share, discuss, and review information in real-time. Try brainstorming ideas, add comments and questions using sticky notes , and vote on potential courses of action using our plugin .

The strategic management process sets the long-term direction for your organization, so it’s important to get it right. That means bringing teams together to share ideas and work toward a common goal.
Miro can aid and enhance collaboration on your strategic management process. Get started with one of the fully-customizable templates from our strategic planning suite. Try it for free .
Miro is your team's visual platform to connect, collaborate, and create — together.
Join millions of users that collaborate from all over the planet using Miro.
Keep reading
Pert chart: how to build better plans in project management.
How to use the Ansoff Matrix for strategic planning (with examples)
How to hold a strategic planning meeting: A simple, step-by-step guide for facilitators
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Strategic Planning Should Be a Strategic Exercise
- Graham Kenny
Don’t create a plan. Create a system.
Many managers complain that strategy-making often reduces to an operational action plan that resembles the last one. To prevent that from happening they need to remember that strategy is about creating a system whereby a company’s stakeholders interact to create a sustainable advantage for the company. Strategic planning is how the company designs that system, which is very different from an operational action plan in that it is never a static to-do list but constantly evolves as strategy makers acquire more insights into how their system of stakeholders can create value.
Over the years I’ve facilitated many strategic planning workshops for business, government, and not-for-profit organizations. We reflect on recent changes and future trends and consider how to engage with them for corporate success.
- Graham Kenny is the CEO of Strategic Factors and author of Strategy Discovery . He is a recognized expert in strategy and performance measurement who helps managers, executives, and boards create successful organizations in the private, public, and not-for-profit sectors. He has been a professor of management in universities in the U.S. and Canada.
Partner Center
- Contact sales
Start free trial
Strategic Planning in Business

Table of Contents
What is business strategic planning, the strategic planning process in 3 steps, what is a business strategic plan, key components of a business strategic plan, business strategic plan example, strategic plan vs. business plan.
Strategic planning is key for success in business. By planning strategically for the future, a business can achieve its goals. It’s easier said than done, but the more you know about strategic planning, the better chance you have at succeeding.
Business strategic planning is the process of creating a business strategy and an accompanying business strategic plan to implement a company’s vision and achieve its goals over time. The main goal of strategic planning is to take a company from its current state to its desired state through a series of business actions.
The business strategic planning process usually consists of defining business goals, doing a SWOT analysis to assess the company’s business environment and developing a business strategy. The leadership team is in charge of business strategic planning, as it has a very important impact on the overall direction of a company.
Get your free
Strategic Plan Template
Use this free Strategic Plan Template for Word to manage your projects better.
Strategic Planning is one of the three levels of organizational planning, which is the process that allows organizations to define its objectives for the future and make action plans to guide the efforts of each of its departments, employees and management levels .
The other two levels of organizational planning are tactical and operational planning. Let’s see how these three types of organizational planning differ from each other.
Strategic Planning vs. Tactical Planning
While a strategic plan is created by the top management team and defines the high-level strategic goals of an entire organization, a tactical plan has a narrower scope. A tactical plan is created by the middle management level of a business and describes the specific goals, initiatives, challenges and resources for each department and how its efforts contribute to the completion of the larger strategic plan of the business.
Strategic Planning vs. Operational Planning
An operational plan allows you to establish guidelines, procedures and best practices for the daily operations of your business. The main objective of operational planning is to ensure that your business operations contribute to the accomplishment of the strategic objectives defined in the strategic plan.
Strategic planning is very important, but it doesn’t need to be overly complex. Let’s simplify this process by breaking it down into three simple steps.
1. Set Business Goals
A business goal is simply an accomplishment that a company wants to achieve in the short, medium or long term. Business goals can take many forms such as increasing sales, revenue, customer satisfaction levels and brand positioning, among many other things.
2. Conduct a SWOT Analysis
The goal of a business strategy is to leverage the strengths of a business and minimize the impact of its weaknesses. Those two things are internal factors. The strengths of a company can become competitive advantages that can lead to business growth. There are many types of business strengths and weaknesses such as scale, speed, or R&D, just to name a few.
Threats and opportunities refer to external factors such as competitors or an untapped market. A successful business strategy considers all of these factors to define how a product or service will be created, marketed and sold, and a SWOT analysis is a great starting point.
3. Develop a Business Strategy & Strategic Plan
Once you’ve completed your SWOT analysis, you can create a business strategy that’s designed to help position your company in the market. Your business strategy guides how you produce, market and sell your product or service based on internal and external analysis. In addition to this, it’s advisable to use a scenario planning matrix to estimate how successful your business strategy would be in different scenarios.
Then, you’ll need a strategic plan to explain how you plan to execute that business strategy. To oversee the execution of a business strategic plan, managers need to manage time, costs and tasks. ProjectManager is a project planning tool that allows managers to plan, schedule and manage their team’s work. Plan your work with professional tools such as Gantt charts, kanban boards, task lists and calendars. Then track your progress in real time to stick to your strategic plan. Get started for free.
A business strategic plan is an implementation plan that’s meant to turn a business strategy into action items that can be executed over time. Business strategic plans are usually executed over the course of 3-5 years.
How to Develop a Strategic Plan
To develop a strategic plan, you should ask yourself the following three questions.
- Where Is the Business Now? Gather as much information on your business as possible including internal operations and what drives its profitability. Compare the business to competitors and note the similarities and differences in detail. This isn’t a day-to-day operational study, but a broader look at the business in context to itself and its environment. But don’t go crazy; stay realistic in terms of your business goals. Be detached and critical in your analysis.
- Where Do You Want to Go? Now it’s time to decide what your top-level objectives are for the future. Start with a vision statement , objectives, values, techniques and goals. Look forward to five years or more to forecast where you want the business to be at that time. This means figuring out what the focus of the business will be in the future. Will that focus differ from what it is now, and what competitive advantages do have you in the marketplace? This is where you build the foundation and initiate changes.
- How Can You Get There? Once you know where you are and where you want to go, it’s time to plan. What are the changes to the structure, financing, etc., necessary for the business to get there? Decide on the best way to implement those changes, the timeframe with deadlines and how to finance it. Remember, this is looking at the business at large, so consider major endeavors such as diversification, existing growth, acquisition and other functional matters. A gap analysis can be a big help here.
Once you’ve answered the above questions and have a way to achieve the long-term goals laid out in the strategic plan, the next step is making sure you have the right person to manage all of its moving parts. They must be analytical, a creative thinker and able to grasp operational detail.
That doesn’t mean the strategic plan is led by one person. It’s best to not do it alone; seek other opinions. The people in your organization, from bottom to top, are all great resources to offer perspectives from their standpoints. Don’t forget to take in the advice of stakeholders, including customers, clients, advisors and consultants.
To create a strong strategic plan, one must first have a strong understanding of the business that is to expand. How does the business work? Where does the business stand in relation to competitors in the marketplace? A strategic plan is built on the bones of the following foundational elements:
- Mission Statement: The mission statement describes what your company does.
- Vision Statement: The vision statement explains where your company expects to be in the future.
- Core Values: Guiding principles that shape your company’s organizational culture.
- Business Objectives: Consider using the SMART goal-setting technique . This simply means setting up specific, measurable, attainable, relevant and time-bound objectives that your company wants to achieve.
- SWOT Analysis: External and internal factors that make up your company’s business competitive environment.
- Action Plan: A plan outlining steps that will be taken to achieve the business objectives of your organization.
- Financials: A section that shows the financial performance expectations, the budget and the resources that will be required to implement the action plan.
- Performance Measurements: Performance indicators that will be used to measure the effectiveness of the action plan.
Never forget to check your strategic plan against reality. In addition to being achievable, it must be practical for your business environment, resources and marketplace.
Now let’s look at a simple business strategic plan example. This is a strategic plan for a small construction company.
1. Mission, Vision & Core Values
- Mission Statement: To build residential spaces that provide wellbeing for our clients.
- Vision Statement: To offer the best construction experience for our clients and expand our brand throughout the globe.
- Core Values: Sustainable innovation and respect for the environment.
2. Business Objectives
- Business Objective 1: Grow operating margin from 15% to 20% over the next year.
- Business Objective 2: Reduce operating costs by 5% over the next quarter
- Business Objective 3: Increase the number of new contracts generated by 10% over the next year
3. SWOT Analysis
- Strengths: Available financing, brand visibility and know-how.
- Weaknesses: Lack of PPE, human capital and expertise in construction areas such as plumbing, electrical work and masonry, which requires subcontractors.
- Opportunities: Lack of environmentally-friendly construction companies in the market.
- Threats: Larger construction companies compete for contracts in the area.
4. Action Plan
- Business Objective 1: To grow operating margin, new employees with plumbing, electrical work and masonry experience will be hired to cut down subcontractor costs. This must be done by the end of the first quarter.
- Business Objective 2: To reduce operating costs, the company will acquire property, plant and equipment. By doing this, the company will no longer rent equipment from third parties, which will reduce operating costs significantly in the medium and long term.
- Business Objective 3: To increase the number of new contracts generated, the leadership team will invest more in the PR, marketing and advertising departments. The company will also invest in key positions for the construction bidding process such as contract estimators.
- Financials: This section will explain in detail what are the costs associated with the work items in the action plan as well as the expected financial benefits for the company.
Our free strategic plan template helps leadership teams gather important information about their business strategy, which makes it the perfect tool to start shaping a strategic plan for your business or project.
More Free Strategic Planning Templates
Here are some free strategic planning templates for Word and Excel that will help you with key aspects of the strategic planning process. Use them individually or add them to your strategic plan template for Word so you don’t miss any detail about your organizational strategy.
Strategic Roadmap Template
This strategic roadmap template allows you to map the activities, strategic projects and initiatives that each business department will execute to accomplish the objectives defined in the strategic plan of an organization.
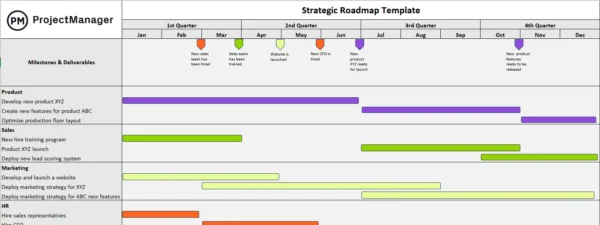
Strategic Map Template
This strategic map template it’s a strategic planning tool that allows you to visualize all the strategic objectives of your organization and understand how they’re interrelated.
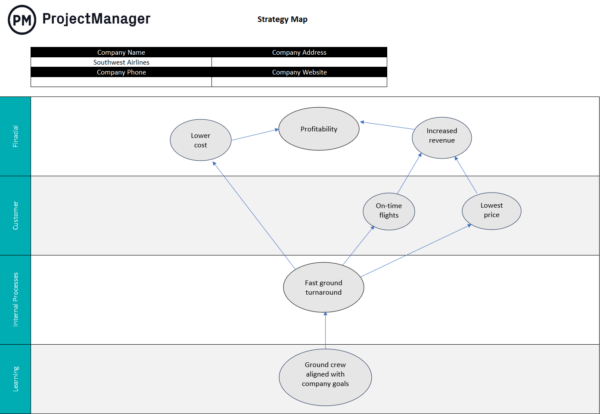
Balanced Scorecard Template
A balanced scorecard is a chart that allows you to set strategic objectives that will benefit your business in one of four key areas, its finances, internal processes, customer satisfaction and organizational learning.
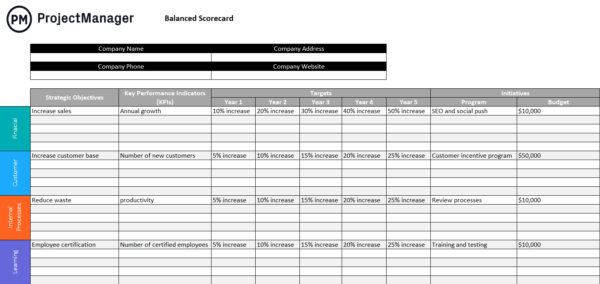
Vision Statement Template
The vision statement is one of the most important aspects of the organizational strategy of a business. It’s a short but powerful statement that describes the overall direction of a company and what it intends to achieve in the future. This free vision statement template will help you focus on what matters most and define the vision of your business.
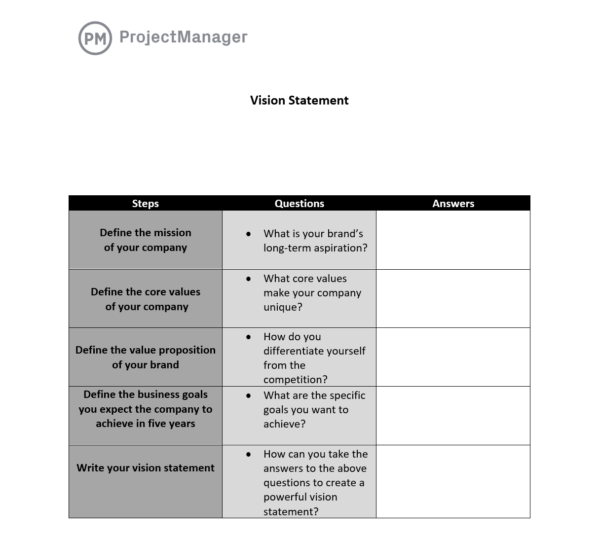
A strategic plan is a type of business plan, but there are distinctions between the two. Whereas a strategic plan is for implementing and managing the strategic direction of a business, a business plan is more often the document that starts a business.
A business plan is used primarily to get funding for the venture or direct the operation, and the two plans target different timeframes in business history. A strategic plan is used to investigate a future period, usually between three-to-five years. A business plan is more routinely a year out.
A Different Intent
A strategic plan offers a business focus, direction and action to help the business grow from the point it presently resides to a greater market share in the future. A business plan, on the other hand, is more focused on offering a structure to capture and implement ideas that initially define a business.
With a strategic plan, existing resources are prioritized to increase revenue and return on investment. The business plan is different in that it’s seeking funding for a venture that doesn’t yet exist. Where a strategic plan is building a sustainable competitive advantage in the future, a business plan is designed to take advantage of a current business opportunity.
So, a strategic plan is communicating direction to teams and stakeholders in order to achieve future goals. A business plan isn’t talking to staff, which is likely nonexistent or minimal at this point. It’s speaking to banks and other financial supporters.
Related Strategic Planning Content
- Strategic Project Management: Planning Strategic Projects
- Strategic Planning Models: An Introduction to 5 Popular Models
- A Quick Guide to Strategic Initiatives
- How to Create a Strategic Roadmap for Your Organization
- Project Alignment: Aligning Your Project to Business Strategy
Strategic planning, like any planning, requires keeping a lot of balls in the air. That means having the right tool to plan, monitor and report on all the various tasks and resources. ProjectManager is online project management software that gives you control over every aspect of creating and implementing a strategic plan. Try it today with this free 30-day trial.

Deliver your projects on time and on budget
Start planning your projects.
- Back to All Programs /
Business Strategy: Evaluating and Executing the Strategic Plan
Explore the concepts and tools of strategic business management.
All Start Dates
11:00 AM – 2:30 PM ET
2 consecutive Tuesdays & Thursdays
$2,750 Programs fill quickly — free cancellation up to 14 days prior
Registration Deadline
September 30, 2024
2 consecutive Tuesdays and Thursdays
$2,850 Programs fill quickly — free cancellation up to 14 days prior
February 10, 2025
2 consecutive Tuesdays & Thursdays
July 14, 2025
What You'll Learn
Understanding how your role is linked to your company’s strategy will help you determine the key issues and priorities needed to focus and align your work with your company’s strategic goals and objectives.
In this online program, you will learn how to identify your organization’s strengths, weaknesses, resources, capabilities, and core competencies, and use strategic tools to evaluate competitive forces, industry attractiveness, and environmental threats and opportunities.
In addition, you will learn to sharpen your vision, critical thinking, and decision-making skills by analyzing various companies’ strategies, as well as assessing the strategy of the company you work for, including how your department can help the company strengthen its strategic position, and build a sustainable competitive advantage.
The online program offering is highly interactive and consists of business cases, interactive discussions, presentations, and group exercises.
Program Benefits
- Perform external and internal analyses for companies and evaluate the dynamics of competition
- Build strategies using appropriate frameworks and tools
- Understand your own company’s strategy
- Align your role with your company’s strategic goals and objectives
- Develop recommendations to strengthen your company’s strategic position and competitive advantage
- Understand the basics of strategy implementation and control
- Earn a digital Certificate of Completion from the Harvard Division of Continuing Education
Topics Covered
- The process of crafting and executing a strategic plan
- Frameworks and tools to conduct external and internal analyses
- Evaluating the competitive conditions and industry attractiveness
- Assessing a company’s resources, capabilities, competencies, and competitive advantage
- Different types of business strategies
- Strategic moves companies make to strengthen their competitive position in the market (i.e., blue ocean and disruptive innovation strategies, amongst other strategies).
- Effective strategy implementation and the strategic change process
Who Should Enroll
This online program is designed for:
- Professionals and managers at all levels of the organization who have limited exposure to strategy
- Managers with some strategy experience who are looking to refresh their business strategy knowledge and skills
- Business owners and employers from any industry who are interested in developing the skills needed to analyze and execute strategies.
Considering this program?
Send yourself the details.
Related Programs
- Advanced Business Strategy Training: Gaining a Competitive Edge
- Leading Your Organization’s Digital Transformation — 4-Day Training
- Strategic Project Management
October Schedule
Week 1, Day 1
- Explore how core competencies drive competitive advantage.
- Understand the process of strategy-making and execution.
- Examine various generic business strategies.
Week 1, Day 2
- Evaluate macro and micro environments to uncover critical strategic issues.
- Assess competitive conditions and industry attractiveness to seize opportunities.
- Analyze current resources and capabilities to identify core competencies.
Week 2, Day 1
- Discover what constitutes a winning strategy.
- Learn the cornerstones of effective strategy execution.
- Study the moves organizations use to strengthen their competitive positions.
Week 2, Day 2
- Develop strategic actions and contribute effectively to organizational goals.
- Master essential skills for strategic leadership.
- Apply what you have learned to your organization and showcase your insights.
February Schedule
July schedule, areen shahbari.
On the first day of the program, [the instructor] presented a slide with a list of key attributes that one needs to become a better strategic thinker. The sliding scales allowed us to evaluate ourselves on these attributes. This exercise really stood out. In fact, I have used it with my team.
Program Manager Cloud Integration, Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas
Certificates of Leadership Excellence
The Certificates of Leadership Excellence (CLE) are designed for leaders with the desire to enhance their business acumen, challenge current thinking, and expand their leadership skills.
This program is one of several CLE qualifying programs. Register today and get started earning your certificate.
Harvard Division of Continuing Education
The Division of Continuing Education (DCE) at Harvard University is dedicated to bringing rigorous academics and innovative teaching capabilities to those seeking to improve their lives through education. We make Harvard education accessible to lifelong learners from high school to retirement.

- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is Strategic Management?
Management styles, strategic management steps, the bottom line.
- Business Essentials
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/wk_headshot_aug_2018_02__william_kenton-5bfc261446e0fb005118afc9.jpg)
Yarilet Perez is an experienced multimedia journalist and fact-checker with a Master of Science in Journalism. She has worked in multiple cities covering breaking news, politics, education, and more. Her expertise is in personal finance and investing, and real estate.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/YariletPerez-d2289cb01c3c4f2aabf79ce6057e5078.jpg)
Investopedia / Alex Dos Diaz
Strategic management strategies help companies restructure, set new goals, implement revised approaches, and determine results.
Strategic management evaluates and may reorganize company resources to achieve new goals and objectives. Strategic management looks at the competitive environment and internal organization, evaluates strategies, and ensures that management rolls out new approaches across the company .
Key Takeaways
- Companies, universities, nonprofits, and other organizations can use strategic management to set goals and meet objectives.
- Flexible companies can more easily restructure than inflexible organizations.
- A strategic manager may oversee strategic management plans and devise ways for organizations to meet their benchmark goals.
Organizational leaders commonly focus on learning from past strategies and examining the current environment. Strategic management may include an analytic process, where all threats and opportunities are accounted for, or merely applying new guiding principles.
The skills and competencies of employees, business culture , and organizational structure influence how an organization can achieve its objectives. Inflexible companies may find it difficult to succeed in a changing business environment. Creating a barrier between strategies and their implementation can make it difficult for managers to determine whether objectives have been efficiently met.
While an organization’s upper management is ultimately responsible for its strategy , the strategies are often sparked by actions and ideas from lower-level managers and employees. An organization may have several employees devoted to strategy, rather than relying solely on the chief executive officer ( CEO ) for guidance.
Participative leadership occurs when management includes team members in the strategic decision-making process.
Strategic management helps organizations turn visions into action to reach business goals and objectives. A prescriptive approach outlines how strategies are developed, while a descriptive approach focuses on how they are implemented. Most organizations generally follow a series of steps that include:
- Goal Setting: An organization must establish clear, realistic goals to articulate its vision and long- and short-term goals. A company can then identify the objectives, or how the goals will be reached.
- Strategic Analysis: Organizations examine, understand, and codify what internal and external forces affect their business and goals, as well as what they need to remain competitive. Analytical tools, such as SWOT analysis , are helpful during this phase.
- Formulation: A company develops its strategy, outlining how it will achieve its goals. In this phase, an organization may identify the people, technology, and other resources it needs, how resources will be allocated to fulfill tasks, and what performance metrics will measure success. It is also critical to gain buy-in from stakeholders and business leaders.
- Execution: Once the strategies are defined, it is time for execution. The strategy moves from planning to implementation. The allocated resources are placed into action based on their roles and responsibilities.
- Determine Success: The final stage of strategic management is to evaluate the effectiveness of implemented strategies using defined metrics . The company will determine whether ineffective methods should be replaced with more viable ones. The organization will monitor the business landscape, and internal operations, and maintain effective strategies.
Examples of Strategic Management
Consider a large company that wants to achieve more ambitious online sales rates. To meet this goal, the company will develop a strategy, communicate the plan, apply it across various units and departments, integrate it with employee goals, and execute it accordingly. If an effective strategy is created, it will help the company achieve its targets through a single, coordinated process.
Suppose a for-profit technical college wishes to increase new student enrollment and enrolled student graduation rates over the next three years. The purpose is to make the college known as the best buy for a student's money and increase revenue. The school may evaluate its financials to create high-tech classrooms and hire the most qualified instructors. The college may also devote resources to marketing and recruitment.
Why Is Strategic Management Important?
Strategic management allows a company to analyze areas for operational improvement. It may follow an analytical process—identifying specific threats and specific opportunities—unique to the company. A company may choose general strategic management guidelines that apply to any company.
What Are the Key Elements of Strategic Management?
Strategic management is not a one-size-fits-all strategy. However, there are key elements that are found to be critical. These include goal setting, industry and organizational analyses, strategy formation, strategy implementation; and the measurement, monitoring, and controlling of strategies.
What Internal Changes May Be Implemented in Strategic Management?
Some action steps that companies may take to execute their strategic management plans include realigning financial and personnel resources or changing the methods to create, sell, and deploy products and services.
Strategic management is the assembling and management of resources to achieve a company's goals and objectives. Companies create and adapt a strategic management process that works best for the firm. Strategic management does not end with implementation but is commonly reevaluated well into the organization's future.
Harvard University. " Strategic Leadership ."
Strategic Planet. " The Strategic Management Process ."
Harvard University. " A Manager's Guide to Successful Strategy Implementation ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/knowrisk-56fd587a5f9b586195c69845.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
More From Forbes
Planning and budgeting for a more volatile world.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
More agile planning and budgeting supports strategy with speed and flexibility
With the start of school and the cooling temperatures of autumn in the northern hemisphere comes another milestone: the commencement of annual business planning and budgeting.
This year, rather than double down on fortunetelling, some companies are starting to consider a different approach. Even as companies deploy generative artificial intelligence tools to improve forecasting , the world remains uncertain, and assumptions about the next 12 to 15 months are likely to require updating, if not summary revision.
At the height of the pandemic, when only a clairvoyant could have made an accurate 12-month business plan, my Bain & Company colleagues Darrell Rigby, Joost Spits, and Steve Berez wrote an article for Harvard Business Review offering a more agile approach. While we are no longer in the grips of a global health crisis, long-established processes feel increasingly outdated, cumbersome, and ill-suited to the more dynamic environment around us. In a world in flux, agility feels more needed today than ever.
Companies can fundamentally reimagine and improve their planning and budgeting processes by doing three things:
1. Change the purpose of the planning and budgeting exercise.
Rather than try to more perfectly smooth earnings—something Bain research finds has relatively little impact on shareholder returns—companies should plan for better performance.
They can do this in three ways. First, by defining success as improving outcomes for customers, employees, investors, and communities—not just hitting budgets. Then, by focusing on learning, adapting, and growing rather than trying to predict the unpredictable. And, finally, by telling the truth about forecasts and exposing honest uncertainties as opposed to pretending they are unthinkable.
Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Of 2024
Best 5% interest savings accounts of 2024.
Consider the shift in planning launched this year by a major consumer products company. Instead of the usual present-forward thinking that traditionally went into its annual and three-year planning processes, the company now asks a much more challenging question: “What could be the full potential of our business in 2030 or 2040, even?” This encourages the team to raise its ambition, to think future-back, and to focus on performance, including how to better serve customers, drive breakthrough innovation, and stay ahead of the competition. The purpose of their regular planning and budgeting exercise is now much different.
2. Shift the focus away from financial precision and toward strategic success.
This turns the targeted outcomes developed in step one into strategic portfolio guidelines for determining budgets and adaptation.
These guidelines force discussions that ground the allocation of resources in strategy, rather than individual projects. Questions this process might raise include: Which outcomes will be most important for strategic success? And, in light of those priorities, where should resources go? By properly aligning resources with strategic priorities, companies can more clearly see the tough tradeoffs that should be made.
Amazon has famously reinvented its budget process to make it more strategic by putting customer priorities at its center . The company allocates funding to activities, not business units, with each activity evaluated on how it affects customers. The owner of each new activity creates a six-page planning document that contains a future press release describing the benefits to customers. Unlike traditional management reviews that focus on financial metrics, Amazon’s focus on real-time customer metrics.
3. Plan faster and more frequently.
Japanese companies are particularly well-known for their rigid and detailed three-year plans, but they are not alone. In today’s rapidly changing world, such plans can quickly become out-of-date, no matter your country.
When you can adjust a long-term forecast every quarter, or every month, it becomes more accurate in less time and with less effort. By setting bold, challenging objectives, and then adjusting plans to incorporate valuable lessons learned along the way, companies can more quickly pivot when business conditions change. There’s an art and science to balancing the need for long-term strategic investment with the flexibility to adjust along the way.
In my own industry of professional services, there is a certain degree of volatility built into the business model. Project-based work can be up and down. At the same time, recruiting and other decisions about investing in people usually must be made before we can have full visibility into customer demand. In such situations, it’s helpful to think about swim lanes. In the Olympics, swimmers must stay in their lane. There is only so much latitude to move right or left. Similarly, if short- to medium-term business momentum argues for dialing up or dialing down capacity, there is some room for adjustment, but only within the parameters designed to keep the business true to its multi-year strategy and objectives. This discipline reduces the risk of reacting too aggressively by going out of the established strategic swim lanes and introducing longer-term problems for the business.
For most companies, traditional planning and budgeting has a comfortable certainty that can be hard to give up, but there is a better way. Companies like Toyota and Maersk are taking the leap, embracing alternatives to traditional annual budgeting that build more dynamic financial plans . The flexibility of these plans helps companies focus on what truly creates value, and that’s key to changing an annual ritual into something that works in today’s world of environmental, geopolitical, supply chain, and technological challenges.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.
- Business units
- News & events
- Directories
Governance and engagement
UDPATED 16 SEPTEMBER 2024
Digital and Services Strategy Board (DSSB)
The Digital and Services Strategy Board (DSSB), established in March 2022, is a strategic committee overseeing the governance of the ANU Digital Plan and implementation of the Service Performance Framework. A whole-of-University resource, the DSSB ensures the effective delivery and benefits realisation of the ANU Digital and Services portfolio of programs, and alignment with the ANU Strategic Plan and Corporate Plan. The Board provides strategic direction, risk insights, progress monitoring, and overall success assurance.
| Professor Lachlan Blackhall | Deputy Vice-Chancellor (Research & Innovation) | Office of the Deputy Vice-Chancellor (Research & Innovation) |
| Professor Tony Connolly | Chair, Academic Board & Dean | College of Law |
| Jonathan Churchill | Chief Operating Officer | Office of the Chief Operating Officer |
| Professor Helen Sulivan | Dean | College of Asia & the Pacific |
| Professor Grady Venville | Deputy Vice-Chancellor (Academic) | Office of the Deputy Vice-Chancellor (Academic) |
Secretariat:
| Service Solutions |
Technical Design Authority (TDA)
The Technical Design Authority (TDA) serves as the key arbitrator for significant information and technical changes at ANU. The TDA ensures that proposed solutions are thoroughly considered, adhere to design guidelines, and align with our future state digital environment objectives.
Executive Sponsor: Chief Information Officer, Information Technology Services (ITS)
| Garry Whatley (Interim Chair) | Director, Digital | ITS |
| Helen Duke | Associate Director, Infrastructure Services | ITS |
| Megan Easton | Senior Data Governance Officer | Scholarly Information Services |
| Professor Sigi Goode | Professor, Information Systems | College of Business & Economics |
| Leone Nurbasari | Associate Director, Business Intelligence & Analytics | Planning & Service Performance (PSP) |
| Adam Reed | Architecture Chapter Lead | ITS |
| Trent Schultheis | Associate Director, Enterprise Services | ITS |
External industry and senior technical ITS representatives to be confirmed.
| Marina Stojkoski | Business Analyst, Project Delivery & Engagement | ITS |
Digital Plan User Group
| Tanya Ali | Senior Manager, Students & Experience | College of Business & Economics (CBE) |
| Richard Andrew | Student Administration Manager | College of Arts & Social Sciences |
| Associate Professor Rebecca Colvin | Associate Professor, Environment, Resources & Development | College of Asia & the Pacific |
| Dr Stephen Dann | Senior Lecturer | CBE |
| Lizzie Gordon | Deputy Manager, Student Central | Division of Student Administration & Academic Services (DSAS) |
| Leeanne Kelly | Senior Manager, Student Safety & Wellbeing | University Experience |
| Hayden Merrell | Deputy Manager, Student Communications, Student Central | DSAS |
| Kus Pandey | Research Funding & Development Manager | Office of Research & Innovation Services |
| Associate Professor Alex Richardson | Associate Professor, Business Information Systems & Deputy Director (Education) | CBE |
| Cameron Roles | Senior Lecturer | College of Law |
| Associate Professor Benjamin Schwessinger | Associate Professor, Research School of Biology | College of Science |
| Vikas Sharma | Engagement Coordinator | College of Engineering. Computing & Cybernetics |
| Ann Smith | Lecturer in Business Management | CBE |
| Zoe Karouzos | College Student Experience Administrator | College of Law |
| Peline Tan | Associate Director, Future Students | International Strategy & Future Students |
| Dr Matt Thompson | Postdoctoral Fellow | College of Science |
| Sarah Walker | Senior Manager, Student Life | Office of the Deputy Vice-Chancellor (Academic) |
| James Watson | Head of Communications | Advancement |
| Associate Professor Alexandra Webb | Associate Professor & Associate Director (Education), Medicine | College of Health & Medicine |
| Donna Webster | School Manager | CBE |
| Professor Marvin Wee | Professor, Research School of Accounting | CBE |
| Renee Weir | Office Manager | Office of the Vice-Chancellor |
| Office of the COO |
Stream governance
Each Digital Plan Stream is governed by a group responsible for ensuring work is planned and prioritised in alignment with clear strategic objectives and that outcomes are tracked and measured. Each of these groups is led by an Executive Sponsor who is ultimately accountable for the successful delivery of the stream’s strategic roadmap. Stream governance groups provide strategic guidance, monitor progress against plans, timelines and budgets, as well as oversee stakeholder engagement, issue management and mitigation to support stream success.
Executive Sponsor & Chair: Professor Lachlan Blackhall, Deputy Vice-Chancellor Research & Innovation
| Chief Information Officer | ITS | |
| Professor Ann Evans | Pro Vice-Chancellor (Graduate Research) | Office of the Pro Vice-Chancellor (Graduate Research) |
| Sophie Holloway | Chief, Research Systems & Innovation | Office of Research & Innovation Services |
| Professor Adrienne Nicotra | Associate Dean (Research) | College of Science |
| Professor Ute Roessner | Pro Vice-Chancellor | Research Initiatives & Infrastructure |
| Professor Emma Schultz | Associate Dean (Research) | College of Business & Economics |
Key contact:
| Jackie Atkin | Stream Lead, Research | ITS |
Learning & Teaching
Executive Sponsor & Chair: Associate Professor Geoff Hinchcliffe, Interim Pro Vice-Chancellor (Learning & Teaching)
| Lucy Arthur | Director | Centre for Learning & Teaching |
| Elizabeth Bailey | Associate Director, Careers & Employability | Office of the Pro Vice-Chancellor (Education & Digital) |
| Chief Information Officer | ITS | |
| Paul Hargreaves | Stream Lead, Learning & Teaching and Student Experience | ITS |
| Paul Hargreaves | Stream Lead, Learning & Teaching and Student Experience | ITS |
Student Experience
| Suzie Alcorn | Head, Academic Standards & Quality Office | Division of Student Administration & Academic Services (DSAS) |
| Chief Information Officer | ITS | |
| Brendon Colquhoun | Head, Examinations, Graduations, Academic Progression & Prizes | DSAS |
| Paul Hargreaves | Stream Lead, Learning & Teaching and Student Experience | ITS |
| Richelle Hilton | Director, Digital Business Transformation | Planning & Service Performance Division |
Core IT Infrastructure
Executive Sponsor & Chair: Chief Information Officer, ITS
| Helen Duke | Associate Director, Infrastructure Services | ITS |
| Associate Professor Steven McEachern | Director, Australian Data Archive | College of Arts & Social Sciences (CASS) |
| Chief Information Security Officer | Information Security Office | |
| Professor Adrian Sheppard | Chair, Informatics Committee | College of Science |
| Professor Sean Smith | Director | National Computational Infrastructure |
| Matthew Talbot | General Manager | CASS |
| Professor Jochen Trumpf | Professor, School of Engineering | College of Engineering. Computing & Cybernetics |
| Sajid Hassan | Program Director, Digital Infrastructure & Cloud Enablement | ITS |
University Services
Executive Sponsor & Chair: Dr Sian Hicks, Director, Division of Shared Services
| Chief Information Officer | ITS | |
| Matt Cousins | General Manager | College of Engineering, Computing & Cybernetics |
| Richelle Hilton | Director | Planning & Service Performance |
| Jeremy Matthew | Director | Facilities & Services Division |
| Ian Willis | Stream Lead, University Services | ITS |
| Ian Willis | Stream Lead, University Services | ITS |
Get involved
Are you an ANU staff member or student and are interested in hearing about future opportunities for co-design and testing, or Digital Plan news and updates?
» We want to hear from you
- ANU Digital Plan
About the Digital Plan
Featured initiatives
Learning and Teaching
Uplifting our IT service delivery
Transforming Data at ANU
Related links
- ANU Strategic Plan 2021-2025
- ANU Corporate Plan 2023-2026
- Service Performance Framework
Page Owner: Information Technology Services

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Overcoming Challenges and Pitfalls. Challenge of consensus over clarity. Challenge of who provides input versus who decides. Preparing a long, ambitious, 5 year plan that sits on a shelf. Finding a balance between process and a final product. Communicating and executing the plan. Lack of alignment between mission, action, and finances.
3. Create Value for Customers. With an understanding of the market and your company's purpose, you can determine how your organization provides unique or greater value and strategize ways to improve. On the value stick, the value captured by customers is called "customer delight.".
Your strategic planning process should start well before you write your strategic plan. The pre-planning phase is crucial for gathering the data and strategic insights necessary to create an effective plan. 1. Conduct Strategic Analysis. Strategic analysis is a crucial step before writing your strategic plan.
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include. 1. Create an executive summary. Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
Step 1: Assess your current business strategy and business environment. Before you can define where you're going, you first need to define where you are. Understanding the external environment, including market trends and competitive landscape, is crucial in the initial assessment phase of strategic planning.
Essentially, strategic management is getting from the starting point to the goal effectively and efficiently using the ongoing activities and processes that a company takes on in order to keep in line with its mission, vision, and strategic plan. "[Strategic management] closes the gap between the plan and executing the strategy," Stockmal ...
Strategic plans bridge the gap from overall direction to specific projects and day-to-day actions that ultimately execute the strategy. Job No. 1 is to know the difference between strategy and strategic plans — and why it matters. Strategy defines the long-term direction of the enterprise. It articulates what the enterprise will do to compete ...
Strategic planning is a critical business practice for positioning an organization for success, aligning leaders to a common plan, and guiding management decisions. Most companies conduct some ...
A strategic plan answers where an established organization is going in the future and how they intend to reach that future state. A strategic plan also focuses on building a sustainable competitive advantage and is futuristic. A business plan is used to assess the viability of a business opportunity and is more tactical.
1. Basic model. The basic strategic planning model is ideal for establishing your company's vision, mission, business objectives, and values. This model helps you outline the specific steps you need to take to reach your goals, monitor progress to keep everyone on target, and address issues as they arise.
Each business unit, in turn, is accountable for adopting the same performance-management approach for its own, lower-tier top-ten list of initiatives. When designed well, strategic-performance-management systems can give an early warning of problems with strategic initiatives, whereas financial targets alone at best provide lagging indicators.
Richard Steele. In most companies, strategic planning isn't about making decisions. It's about documenting choices that have already been made, often haphazardly. Leading firms are rethinking ...
The term strategic planning is essentially synonymous with strategic management. The concept of strategic planning originally became popular in the 1950s and 1960s, and enjoyed favor in the corporate world up until the 1980s, when it somewhat fell out of favor. However, enthusiasm for strategic business planning was revived in the 1990s and ...
An annual strategic business plan should include 8 key sections. Follow these steps to write an effective annual strategic business plan: State information that defines the company. Perform a SWOT analysis. Identify business goals. Identify key performance indicators. Perform and summarize market research. Outline the business marketing plan.
Business strategy is the strategic initiatives a company pursues to create value for the organization and its stakeholders and gain a competitive advantage in the market. This strategy is crucial to a company's success and is needed before any goods or services are produced or delivered. According to Harvard Business School Online's Business ...
Strategic management is the process of defining and implementing an organization's strategy. It involves analyzing current circumstances, developing a plan to reach important goals, and executing that plan. All businesses can benefit from strategic management to help them meet long-term objectives.
What is a strategic plan? In contrast to a business plan, a strategic plan sets out a company's goals and defines the actions it takes to get there. The audience is your own team. Its key purpose is to build alignment and decision-making capacity to ready your company for the future. For example, if a company's business model is ...
Strategic planning is how the company designs that system, which is very different from an operational action plan in that it is never a static to-do list but constantly evolves as strategy makers ...
The biggest difference between a strategic plan vs. a business plan is its purpose. Existing companies use the strategic plan to grow their business, while entrepreneurs use business plans to start a company. There is also a different timeframe for each plan. Generally, a strategic plan is conducted over several years while a business plan ...
To oversee the execution of a business strategic plan, managers need to manage time, costs and tasks. ProjectManager is a project planning tool that allows managers to plan, schedule and manage their team's work. Plan your work with professional tools such as Gantt charts, kanban boards, task lists and calendars.
Different types of business strategies; Strategic moves companies make to strengthen their competitive position in the market (i.e., blue ocean and disruptive innovation strategies, amongst other strategies). Effective strategy implementation and the strategic change process; Who Should Enroll. This online program is designed for:
The Bottom Line. Strategic management is the assembling and management of resources to achieve a company's goals and objectives. Strategic management helps companies set goals, gain a competitive ...
2. Shift the focus away from financial precision and toward strategic success. This turns the targeted outcomes developed in step one into strategic portfolio guidelines for determining budgets ...
UDPATED 16 SEPTEMBER 2024Digital and Services Strategy Board (DSSB)The Digital and Services Strategy Board (DSSB), established in March 2022, is a strategic committee overseeing the governance of the ANU Digital Plan and implementation of the Service Performance Framework. A whole-of-University resource, the DSSB ensures the effective delivery and benefits realisation of the ANU Digital and ...