How to Craft an Outstanding Case Study for Your UX Portfolio
Writing case studies for your UX portfolio can feel opaque and overwhelming. There are so many examples out there, and often the ones that make the rounds are the stunning portfolios of top visual designers. It can be inspiring to see the most beautiful work, but don’t let that distract you from the straightforward format of a good UX case study.
At the core, a UX case study relies on excellent storytelling with a clear, understandable structure . This article breaks down the anatomy of a UX case study to help you tell a simple and effective story that shows off your skills. We’ll start with some general guidelines and structure, then break it down one piece at a time:

UX portfolio overview
What is a ux case study, general guidelines, how to structure a case study, how to fill in the details, defining the problem, understanding your users, early or alternate ideation, final design solution, next steps and learnings.
- Final thoughts
1. Before we get started
Before we dive into all the art and science of the case study, here’s a quick refresher on what a job-winning UX portfolio looks like. In this video, pro designer Dee analyses various design portfolios to pick out what works—and what doesn’t:
Simply put, a case study is the story of a design project you’ve worked on. The goal, of course, is to showcase the skills you used on the project and help potential employers envision how you’d use those skills if you worked for them.
A case study is typically written like a highly visual article, with text walking readers through a curated set of images. Curated is an important word here, because it should be short and sweet. It’s a chance to share what you want potential employers to know about your work on this project.
With that in mind, case studies are really a UX designer’s secret weapon in two ways. First, they get you in the door by showing more about your work than a resume and a top UX cover letter ever could. Another benefit is that they’re really handy in job interviews. If someone asks about a past project, you can walk them through the case study you’ve already created (this is sometimes a requirement anyway).
I mentioned that UX case studies are about storytelling. I’d actually say they’re about stories-telling, since they need to tell two intertwined stories .
The first is the story of your project. This answers questions like what problem you solved, who your users were, what solutions you explored, and what impact they had.
The second story is about you as a designer and your process. This is more about which methods you chose to use and why, how you worked within constraints, and how you worked as a member of a team (or without one).
So what are the steps for an effective case study? Well, like most things in design (and life), it depends. Every case study will be different, depending on what stories you’re telling. The six-part outline below, though, should guide you through an effective format for any UX project story. Here’s the outline (we’ll dive into each component in just a minute):
- Defining the Problem
- Understanding your Users
- Final solution
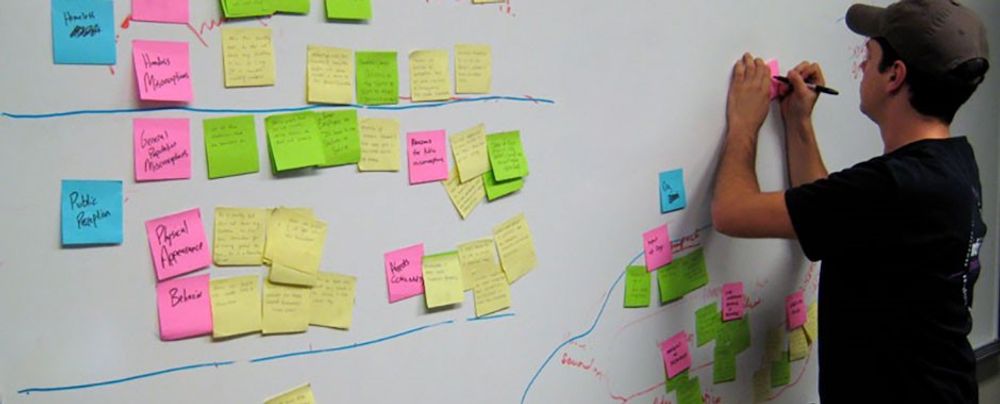
It’s worth it to add a few general notes before we dive into each of the list items above. For each section, include 1-2 short paragraphs and an image of a deliverable that visually tells the story your paragraphs explain. A reader should be able to either just read or just look at the images and roughly get what this moment in the story is communicating.
When choosing images to include, focus on quality over quantity. Choose your best deliverables for each stage and briefly relate them back to the larger narrative. It can be tempting to overload the page with everything you created along the way, but these extra details should stay in your back pocket for interviews.
Lastly, make sure your case study is scannable . In the best of circumstances, people don’t read word for word on the web. Make sure your text is reasonably concise, use headers and strong visual hierarchy, and use bullet points and lists when possible. If you need a refresher on how to achieve this, check out our guide to the principles of visual hierarchy .
Ok, let’s take a look at each step in a bit more detail.
2. Anatomy of a UX case study
Like any story, the introduction sets the stage and gives much of the necessary context readers will need to understand your project. This is one section where people actually might take some extra time to read carefully as they try to discern what this case study is about. Make sure they have all the details they need.
Some key questions to answer are:
- What is your company and/or product?
- What user problem did you try to solve?
- What was your role?
- What tools and methods did you use?
- What are the major insights, impacts, or metrics related to the project
After introducing the project, dive more deeply into the problem you tackled. You touched upon this in the introduction, but this section is an opportunity to make a strong case for why this project exists. Did a competitor analysis or market research demand a new product? Was there past user research in your company that suggests a needed redesign of the product?
Remember that you’ll want to create a through line in the narrative, so try to lay out the problem in a way that frames your design work as a solution.
Deliverables that work really well for this section would be:
- Analytics or usage data
- Market research of internal business metrics
- Survey results or interview highlights
After explaining the problem, show how it impacts your users and their interaction with your product. If you did original user research or you’re seeking user research-oriented jobs, sharing interview scripts, affinity maps , and spreadsheets can be useful in showing your process.
However, this section shouldn’t be only about your process. A key goal of this section is articulating who your users are and what their needs are. These findings should set up your design work that follows, so try to set up that connection.
A few types of the deliverables you might share here are:
- User personas
- Mental models
- Journey maps or customer experience maps
Keep in mind you want to communicate users’ key motivations and challenges, as well as any more specific user groups you identified.
This section can really scale up or down depending on what you have to show. Research shows that hiring managers don’t just want the final product , so it’s clear that showing some of your process is helpful. Especially for students or designers without a fully built product to show, this can be a moment for you to shine.
Don’t worry about the low fidelity of these documents, but the rougher they are, the more you’ll need to guide readers through them. Everything you show here should teach the reader something new about your process and/or your users.
Artifacts you might include are:
- Pen and paper or low fidelity digital wireframes
If you did early testing or faced constraints that determined your future design work, be sure to include them here, too.
This section should include the most final work you did on the project (e.g. wireframe flows or color mockups) and any final product it led to (if you have it). Be clear, though, about which work is yours and which isn’t.
Explain any key decisions or constraints that changed the design from the earlier stages. If you incorporated findings from usability testing, that’s great. If not, try to call out some best practices to help you explain your decisions. Referring to Material Design, WCAG, or Human Interface Guidelines can show the why behind your design.
If you’re able to show the impact of your work, this can take a good case study and make it outstanding. If your project has already been built and made available to users, have a look at any analytics, satisfaction data, or other metrics. See what you could highlight in your case study to show how your design improved the user experience or achieved business goals. Ideally, you can refer back to your original problem statement and business goals from the introduction.
If you don’t have any way of showing the impact of your project, lay out how you would measure the impact. Showing you know how to measure success demonstrates you could do this on future projects.
Lastly, conclude your case study by sharing either your next design steps and/or some key insights you learned from the project. This isn’t just fluff! No project is perfect or final. Showing next steps is a great way to demonstrate your thinking iterative approach (without having to do the work!).
Also, many companies do (or should do) retrospectives after each project to identify challenges and improve future processes. Use this process and the insights you gain from it to inform your case study. Letting employers know you’re capable of reflection shows humility, self-awareness, and the value you can bring to a team.
3. Final thoughts
Since each case study is a unique story you’re telling about your project, it’s a little art and a little science. But starting with the structure laid out in this article will show who you are as a designer and how you solved a problem. And those are two stories companies want to hear!
If you’d like to learn more about how to craft a great UX portfolio, check out these articles:
- 5 Golden rules to build a job-winning UX portfolio
- The best UX design portfolio examples from around the web
- The best free UX/UI portfolio websites to use
- Salary negotiation for UX designers
The Complete Guide to UX Case Studies
Updated: July 18, 2024
Published: August 21, 2023
Writing a UX case study can be overwhelming with the proper guidance. Designing for the user experience and writing about it in a case study is much more than writing content for a webpage. You may ask, “If my design speaks for itself, should I include a UX case study in my portfolio?”

Yes, you should include UX case studies in your portfolio. And here’s why.

You need to make your portfolio stand out among the crowd. A UX case study is a great way to do that. Let’s take a minute to define what a UX case study is and look at some examples.
Table of Contents
What is a UX case study?
The benefits of ux case studies, examples of ux case studies, tips for creating a ux case study.
UX portfolios are essential to showcasing UX designer skills and abilities. Every UX designer knows better designs bring better results. Sometimes, it’s easy to let the design speak for itself — after all, it is meant to engage the audience.
But, in doing that, you, as the designer, leave many things unsaid. For example, the initial problem, the need for the design in the first place, and your process for arriving at the design you created.
This is why you need to include UX case studies in your portfolio.
UX case studies tell a curated story or journey of your design. It explains the “who, what, when, where, and how” of your design. The text should be short and sweet but also walk the reader through the thinking behind the design and the outcome of it.
[Video: Creating a UX Case Study: Right and Wrong Way to Approach It]
There are many benefits to including UX case studies in your portfolio. Think of your UX portfolio as a well-decorated cake. The designs are the cake, and UX case studies are the icing on the cake— they will catch your audience's eye and seal the deal.
Take a look at the benefits of adding UX case studies to your portfolio.
Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![how to make a ux case study How to Become a UX Designer, a Step-By-Step Guide for 2024 [+Expert Tips]](https://knowledge.hubspot.com/hubfs/become-a-ux-designer-1-20240731-321437.webp)
How to Become a UX Designer, a Step-By-Step Guide for 2024 [+Expert Tips]

11 Top UX Research Methods and the Perfect Times to Use Them

I Found 18 Excellent UX Tools. Here's How They Can Enhance User Experience.

Competitor Analysis UX Research: How I Stay Ahead of My Competitors
![how to make a ux case study Website Navigation: The Ultimate Guide [Types & Top Examples]](https://knowledge.hubspot.com/hubfs/ft-nav-bar.webp)
Website Navigation: The Ultimate Guide [Types & Top Examples]
![how to make a ux case study What Is End-User Experience Monitoring? [+Tips For Implementing It]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/end-user-experience-monitoring.png)
What Is End-User Experience Monitoring? [+Tips For Implementing It]

What Is GUI? Graphical User Interfaces, Explained

Horizontal Scrolling in Web Design: How to Do It Well

UX Accessibility: Everything You Need to Know

Your Guide to Creating UX Problem Statements
3 templates for conducting user tests, summarizing UX research, and presenting findings.
CMS Hub is flexible for marketers, powerful for developers, and gives customers a personalized, secure experience
InVisionApp, Inc.
Inside Design
How to write a UX case study
Sarah doody, • jul 19, 2019.
H ave you ever been told your UX portfolio lacks depth, or what you did is unclear, or that it doesn’t seem like you have enough experience, even though you know you do?
Or maybe you landed an in-person interview, it didn’t go very well because you stumbled through presenting and answering questions about your projects.
These are all symptoms of an underlying problem: your UX case studies are not written well enough.
After doing at least 100 hours of my own research through talking to UX candidates one-on-one, reviewing portfolios, and analyzing survey data, one thing became clear: UX professionals put too much emphasis on learning how to make deliverables, and not enough on articulating their design decisions.
When you can’t articulate your design decisions, it will make your day to day role harder, because you won’t know how to deal with pushback. And it will also limit your career options because your ability to write a strong case study is the foundation for creating a strong portfolio and doing well in interviews.
We’re going to go into:
- The role of case studies in your portfolio
- The anatomy of a case study
- The steps to writing a thorough, readable case study
Case studies are the UX application differentiator
It’s no longer enough to just show your work. According to the Center Centre , the job growth of UX designers is expected to rise 22% over the next 10 years. UX is a hot field, and there’s a lot of competition.
Your portfolio, therefore, can’t simply be a curation of sexy-looking deliverables. Recruiters and hiring managers need you to articulate your process and design decisions. A key skill for UX professionals is the ability to communicate; in any UX role, you’ll find yourself not just doing UX, but explaining it over and over.
If you don’t have well-written UX case studies, then how can recruiters and hiring managers trust that you’ll be able to communicate what you did and why you did it if they hire you?
Writing is a skill that we know is important, but as designers rarely practice or study enough. When it comes to UX case studies, though, the quality of your writing is one of the most important variables in the success of your portfolio.
Let’s be real, writing about your UX projects is not an easy task. However, the good news is that by following the steps that follow, you will clearly understand how to write more clearly.
Anatomy of a UX case study
When approaching your UX portfolio and case studies, my advice is to think like a lawyer. Because how do lawyers win legal cases? With strong communication, and even stronger evidence.
The projects inside your portfolio are like evidence in a legal case. And that’s why you must choose the projects for your portfolio very carefully.
Here’s what I recommend including in your UX case study:
- Problem statement
- Users and audience
- Roles and responsibilities
- Scope and constraints
- Process and what you did
- Outcomes and lessons
Want to download a copy of this template? Sign up for Sarah Doody’s newletter and get a free download.
How to write your ux case study.
As you write your case studies, don’t worry about length. Once you get it all on paper you can decide what to put into your portfolio. As you transition your written case studies to something more visual, you will edit them down and also consider how some of the text can be communicated visually.
Step 1. Give your project a title
The big mistake that people make is not giving the project title enough detail when a strong title can give context for the project.
Good: Home Depot user research for mobile app checkout
So-so: Home Depot user research
Bad: Home Depot
Step 2. Write an outline
Lay out your thoughts before you start giving up the details. An outline’s purpose is to help you understand the “big picture” of your project, so you can decide how to structure your case study or if the project is big enough to merit more than one case study.
Start your outline with the seven sections listed above, and start filling in bullet points under each section. Don’t worry about sentence structure; just write and get it out of your head. If you’ve been documenting your projects as you work on them , then you may have some of this already written.
Step 3. Fill in the details
Now that you have an outline and you see the big picture, you can start filling in details.
Give the “Process and what you did” section the bulk of your effort. This is where you’ll document the steps you took, just like documenting science experiments in high school.
You should be answering these questions:
- What did you do? For example, what research method did you use?
- Why did you do it? For example, why did you choose that research method?
- What was the result? For example, did you achieve your research goals?
- What did you learn? For example, what would you do differently next time?
Continuing with our (completely fictional) Home Depot example:
BAD: “ We did usability testing on the checkout of the Home Depot mobile app.”
Why is this weak? Because it only tells the reader what you did. It doesn’t address why you did it, what happened, and what you learned.
GOOD: To evaluate the new checkout on the Home Depot mobile app, we relied on usage metrics in conjunction with 8 usability tests. This allowed us to gain deeper understanding through combining both qualitative and quantitative information. Although users were able to get through the checkout more quickly, they continued to struggle with the shipping section. Discussions with users discussion revealed that often times, products in one order have different shipping addresses, which was possible, but difficult in the current checkout.
This version is much stronger because it goes beyond just talking about what was done. Providing this depth is what will set you apart; articulating your design decisions and process will help position you as a more mature and thoughtful professional.
Step 4. Write headlines
At this point, you’re probably thinking something like “Who would ever read this novel?” Which is a good point. That’s why the next step will help you start to distill everything down so that you are focusing on the key highlights of the story.
The best way to do this is to pretend that you have to write your case study only in tweets. It sounds crazy, but it works.
For each section of the outline we’re working with, write a single headline or sentence—except for the Process section, where you’ll be focusing your energies. For the Process section, you’ll want to have a headline for each step. Using our previous fictitious Home Depot user research example, some of the headlines for the Process section might be:
- Step: What type of research you did and why you did it. Example: Analytics revealed customers struggled, and sometimes abandoned, checkout at the shipping section. To understand why, we conducted eight usability tests.
- Step: Findings from the research. Usability tests revealed that business customers, versus residential, had different shipping needs, which were not being addressed in the current checkout experience.
- Step: Impact of research on product development. We prototyped two new versions of the checkout, allowing customers to choose shipping address on a per-product basis.
By sticking to a 140 character limit, you’ll force yourself to identify the most important points of the case study—which will then become headlines when you create your actual portfolio.
A good way to test whether or not you have strong headlines is to ask yourself if someone would understand the main points of your project by skimming the headlines. If not, then re-write your headlines—because if you want the users of your UX portfolio to quickly understand your project, those are the most important points.
Step 5. Distill the text from your case study into your actual portfolio
Regardless of the format you choose for your portfolio , your writing needs to be clear and succinct.
It won’t happen in one edit! Let’s say you’re working in Keynote with slides, your process will look like this:
- Take the headlines you wrote and place one headline per slide in Keynote.
- Consider that you might merge some bits of information into one slide. For example, you might combine your overview and problem statement. It’s subjective, so you decide!
- Now, you need to go back and start to pull the most important and relevant details from your case study and put them on each slide, as supporting details or evidence.
Examples in action
Simon Pan’s UX portfolio website went viral because he had awesome case studies. Yes, he’s also a visual designer so it looks beautiful. But what you need to focus on is the content. His Uber case study is an excellent example, let’s take a look at why it works:
- Clear problem and framing of the project. Simon’s case study clearly states the problem and frames the project. So even if I’d never heard of Uber before, I’d have enough context to understand the project.
- Explanation of the process. Simon does this with a story. It’s easy to read and keeps my attention. It feels like a cool article that’s well thought out … not to mention the visual design helps draw key points out. In the screenshot below, he is explaining part of the Discovery process. It sounds like I’m reading an article, therefore it keeps my attention. And the use of a user research quote helps bring the story to life even more.
- Thoughtful conclusions and reflection. At the end, Simon concludes the case study with some results, reflections, and insights. People don’t just want to know what you did, they want to know the impact of what you did.
What comes next?
If you follow all these steps, you will have a longform case study edited down into something that’s more readable and scannable for the user of your UX portfolio.
And remember, the UX case studies you write serve many purposes. Of course, they are the foundation of your portfolio, but they also can feed into your resume, LinkedIn, cover letters, and what you say in an interview.
Want to read more by Sarah Doody?
- Seriously, you need to start documenting your UX work
- 4 steps for choosing the right projects for your UX portfolio
- How to create a UX portfolio without UX experience
by Sarah Doody
Sarah Doody is a User Experience Designer, Entrepreneur, and Educator. She is the founder of The UX Portfolio Formula, a UX career accelerator that helps UX professionals learn how to articulate their work so they can create an awesome portfolio. In 2011, she created the curriculum for and taught General Assembly’s first 12-week UX immersive, the genesis of their popular UX programs which are now taught worldwide.
Collaborate in real time on a digital whiteboard Try Freehand
Get awesome design content in your inbox each week, give it a try—it only takes a click to unsubscribe., thanks for signing up, you should have a thank you gift in your inbox now-and you’ll hear from us again soon, get started designing better. faster. together. and free forever., give it a try. nothing’s holding you back..
10x sales on your landing page with Crazy Conversions
Inspiration
How to Write a UX Case Study: A Simple Step-by-Step Guide
Learn the step-by-step process of writing a compelling UX case study that will elevate your online portfolio

Craig Barber
Senior Product Designer

As a digital product designer, one of the most effective ways to showcase your skills and expertise is by creating a compelling UX case study for your online portfolio.
A well-crafted case study not only demonstrates your design process but also highlights your problem-solving abilities and the value you bring to the table.
In this blog post, we'll briefly touch on what a UX case study is, we'll then walk you through the essential steps how to write a UX case study that will impress potential clients and employers.
Let's get started!
What is a UX case study?

A UX case study is like a story that designers tell to explain how they solved a design problem.
It's a way to show others how they researched , planned, and created a digital product or experience that is user-friendly and effective.
It includes details about the project's goals , the people they designed for, the steps they took, and the final design they came up with.
A UX case study helps designers demonstrate their skills and expertise in making things easy to use and enjoyable for users.
It's a friendly and simple way for them to share their design journey and showcase their problem-solving abilities.
Video on how to write a UX case study:
8 Simple steps to creating a UX case study:
1. choose the right project:.

Selecting the right project for your case study is crucial. Aim for a project that best represents your skills and aligns with the type of work you want to attract. It should be a project where you had a significant impact and can showcase your problem-solving abilities and design thinking process effectively.
2. Define the Problem:

Start your case study by clearly defining the problem you were trying to solve. Explain the context, the pain points, and the goals of the project. Highlight the challenges you faced, as well as any research or data that supported your problem identification process.
3. Describe the Research and Discovery Phase:

In this section, describe your research methodologies, including user interviews, surveys , and competitive analysis. Share insights you gained from your research and how they influenced your design decisions. This demonstrates your ability to empathize with users and make informed design choices based on their needs.
4. Outline the Design Process:
Present your design process in a structured and coherent manner. Include wireframes , prototypes, and iterations that show the evolution of your design. Explain the rationale behind your design decisions and how they addressed the identified problem. Be sure to highlight any user testing or feedback loops that helped refine your solution.
5. Showcase the Visual Design:

This section is an opportunity to showcase your visual design skills. Include high-fidelity mockups or screenshots that highlight the aesthetics, typography, color schemes, and overall visual appeal of your design. Explain the reasoning behind your design choices and how they enhance the user experience .
6. Present the Final Solution:

Describe the final solution you arrived at and how it effectively addresses the initial problem. Include metrics or key performance indicators (KPIs) to demonstrate the success of your solution. Whenever possible, provide real-world results , such as increased user engagement, improved conversion rates , or positive user feedback.
7. Reflect and Share Learnings:
Take a moment to reflect on the project and share any lessons or insights gained during the design process . Discuss what worked well, what challenges you encountered, and how you overcame them. This demonstrates your ability to learn and grow as a designer.
8. Present the Case Study Effectively:

Pay attention to the presentation and formatting of your case study. Use clear headings, subheadings, and bullet points to make it easy to read and skim. Include relevant visuals, such as images , diagrams , and charts, to enhance the visual appeal. Make sure your case study is concise, engaging, and aligned with your personal brand.
Frequently asked questions on how to write a UX case study:

Why are UX case studies important?
UX case studies are important for several reasons. They provide insights into the design process , showcase a designer's skills and abilities, and demonstrate how user-centered design principles were applied to solve a specific problem. They are also useful for sharing knowledge, building credibility, and securing job opportunities.
How long should a UX case study be?
The length of a UX case study can vary depending on the complexity of the project and the information you want to convey. However, it's generally recommended to keep it concise and focused, aiming for a length of 800 to 1,500 words. Including visual elements like images , diagrams, or prototypes is also encouraged to enhance understanding and engagement.
What are some tips for creating an effective UX case study?
Here are a few tips to create an effective UX case study:
Clearly define the problem: Start by clearly articulating the problem statement and why it is important to address.
Show the design process: Walk through the design process, highlighting key decisions, iterations, and insights gained along the way.
Include visuals: Incorporate visual elements like wireframes , prototypes, and user interface designs to provide a visual context and make the case study more engaging.
Share the impact: Demonstrate the impact of your design solution by including user feedback, success metrics, or before-and-after comparisons.
Be concise and organized: Keep the case study concise and well-structured, making it easy for the reader to follow your thought process and understand the project's evolution.
Tailor it to the audience: Adapt your case study to the audience you're targeting, focusing on aspects that are most relevant and impactful to them.
Can I include confidential or proprietary information in a UX case study?
It's generally advised to avoid including confidential or proprietary information in a public UX case study. If you need to showcase sensitive information, consider anonymizing or obfuscating the data to protect the privacy and confidentiality of the individuals or organizations involved. Always respect any non-disclosure agreements or intellectual property rights you may have signed.
Should I include negative feedback or challenges faced in a UX case study?
Yes, it's important to be transparent about the challenges and obstacles encountered during a UX project. Including negative feedback or hurdles you faced demonstrates your ability to navigate difficulties and adapt your approach. Highlighting how you addressed and overcame challenges can also provide valuable insights into your problem-solving skills and resilience as a designer .
Can I use visuals created by others in my UX case study?
If you use visuals created by others, such as stock photos , icons , or illustrations , make sure you have the necessary permissions and licenses to use them in your case study. It's important to respect copyright laws and intellectual property rights. When in doubt, it's best to create your own visuals or use resources that are explicitly licensed for free or commercial use.
How should I present my UX case study?
UX case studies can be presented in various formats, depending on the context and requirements. Common formats include a written document, a slide deck presentation, or a web page . Consider the needs of your audience and the platform where you plan to showcase your case study. Ensure it is well-organized, visually appealing, and easy to navigate , allowing the viewer to understand your design process and the outcomes clearly.
Writing a compelling UX case study is an essential skill for any digital product designer.
It allows you to showcase your problem-solving abilities, design process, and the impact you have made on real-world projects.
By carefully selecting the right project, highlighting your research and design decisions, and presenting your case study effectively, you can create a captivating narrative that will impress potential clients and employers.
Remember, a well-crafted case study is not just a reflection of your design skills, but also an opportunity to tell a compelling story about your expertise and approach to UX design.
Showcase your work with a stunning portfolio template
Looking to update your design portfolio? Check out the amazing portfolio templates for Framer at FolioPharmacy.
Get my portfolio template!
You may also like

3 Guaranteed Ways to Make Your Digital Product a Market Leader

How To Use Inversion to Create Winning Digital Products

3 Incredible Things Joe Rogan Taught Me About Addictive Behavior

Product designers
Get inspiration, resources and knowledge sent to your inbox.
One email per week
Easy unsubscribe
Inspiration, resources and knowledge for digital product designers
Bookmark CursorUp: ⌘ + D
Folio Pharmacy
Crazy Conversions
Suggest a site
Suggest a resource
Suggest inspiring site
7 Steps to Creating a Spectacular UX Case Study
UX Design Paula Borowska • March 11, 2020 • 7 minutes READ
In this tutorial, I’m going to walk you through how to create an impactful UX case study. It’s perfect advice for designers who are about to embark on a new job hunt. And, it’s going to be especially helpful for junior designers who are new to creating case studies.
Included are seven steps:
- Problem and the goal
- Target audience
- Deliverables and the outcome
- Lessons learned
Each is going to help you identify how to tell the story of past projects effectively. Once you’ve completed all seven, you will have an excellent case study!
- Include visuals and documentation along the way, not just in the final deliverable sections to tell your stories better.
- Respect the NDAs you’ve signed as you’re generating the case study.
- Don’t forget to treat the case study and the job application process like any other UX design challenge.
Step 1: Case Study Overview
Two major components make up the case study overview. The first is a summary of the project. Keep it around three or four sentences. It might be helpful to wait until you finish writing the entire case study to summarize what you just wrote.
17 Must-Read Books for Product and UX Designers
- How Changing the UX 180 Degrees Made Grew Sales By 180%
- Essential Skills To Become A Great UI/UX Designer
The second major component is your role within this project. What services did you provide? What responsibilities did you have? Give potential employers a better picture of your involvement in the projects. Otherwise, they will have to assume, and that’s not good.
With Postcards Email Builder you can create and edit email templates online without any coding skills! Includes more than 100 components to help you create custom emails templates faster than ever before.
Case study overview in practice
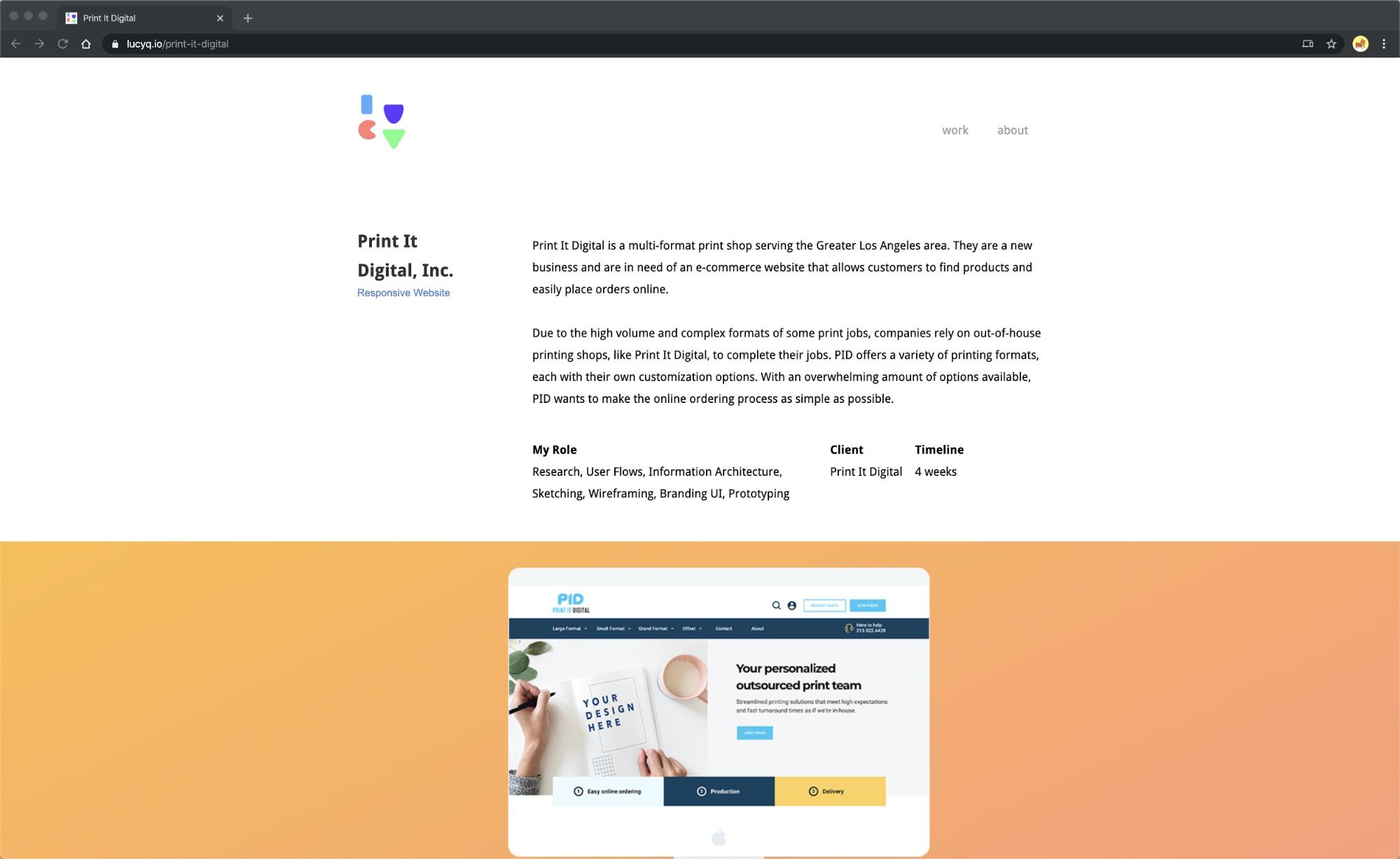
Lucy Qi’s Print It Digital case study offers a detailed overview of the project in addition to identifying her role, the client’s name, and the project timeline.
Step 2: Define the Problem and Goal
Articulating the problem well will help in telling the story of the case study. State the problem concisely.
Next, identify the project’s goal. What did the project aim to achieve? Be as detailed as you can. For example, was it to:
- Gain 10,000 new email subscribers?
- Increase user retention by 10%?
- Improve MoM revenue by 30%?
- Decrease withdrawals by 50%?
- Advance over NPS scores in the next six months?
Defining the problem and goals in practice
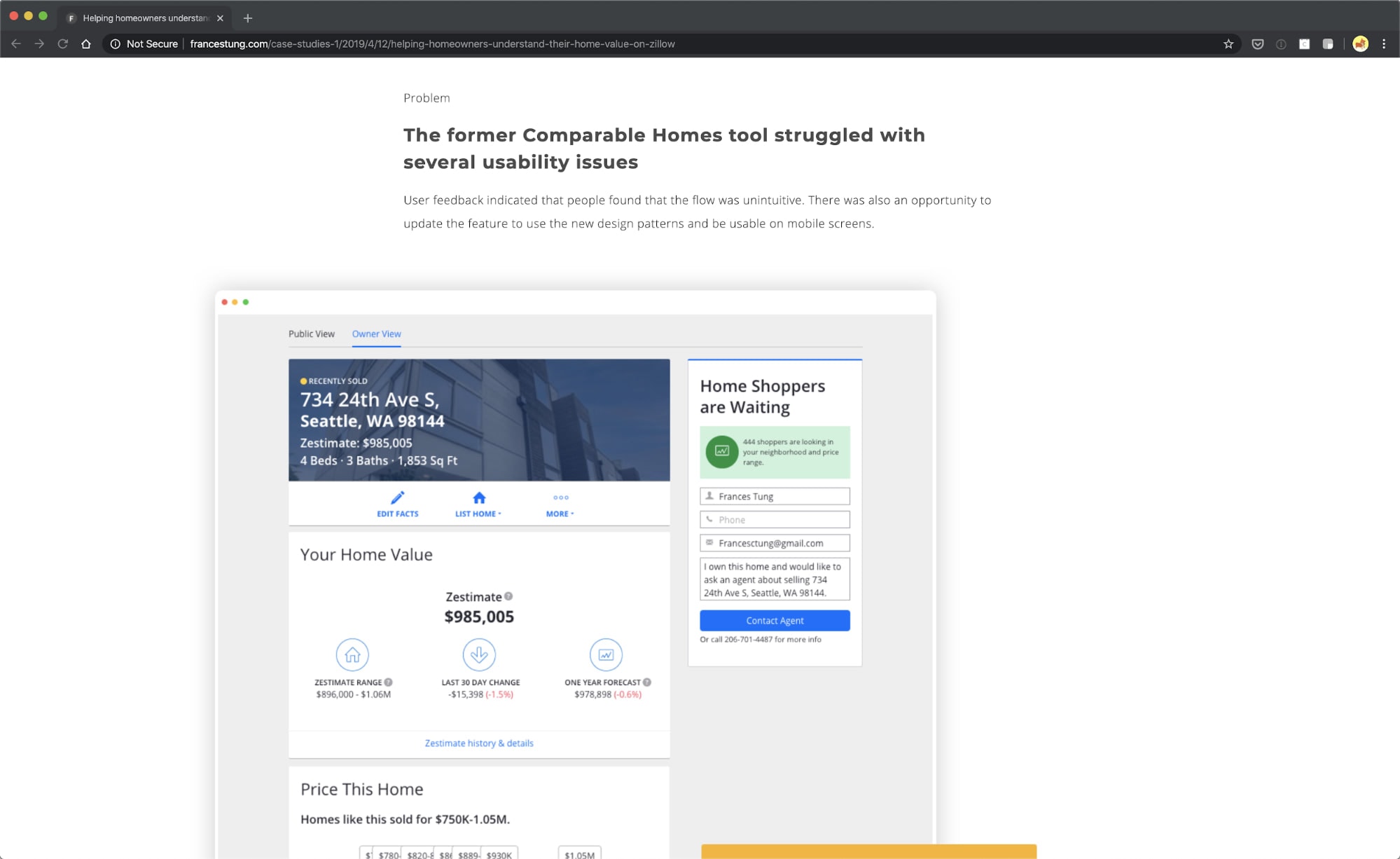
France Sung’s Zillow case study succinctly identified the problem.
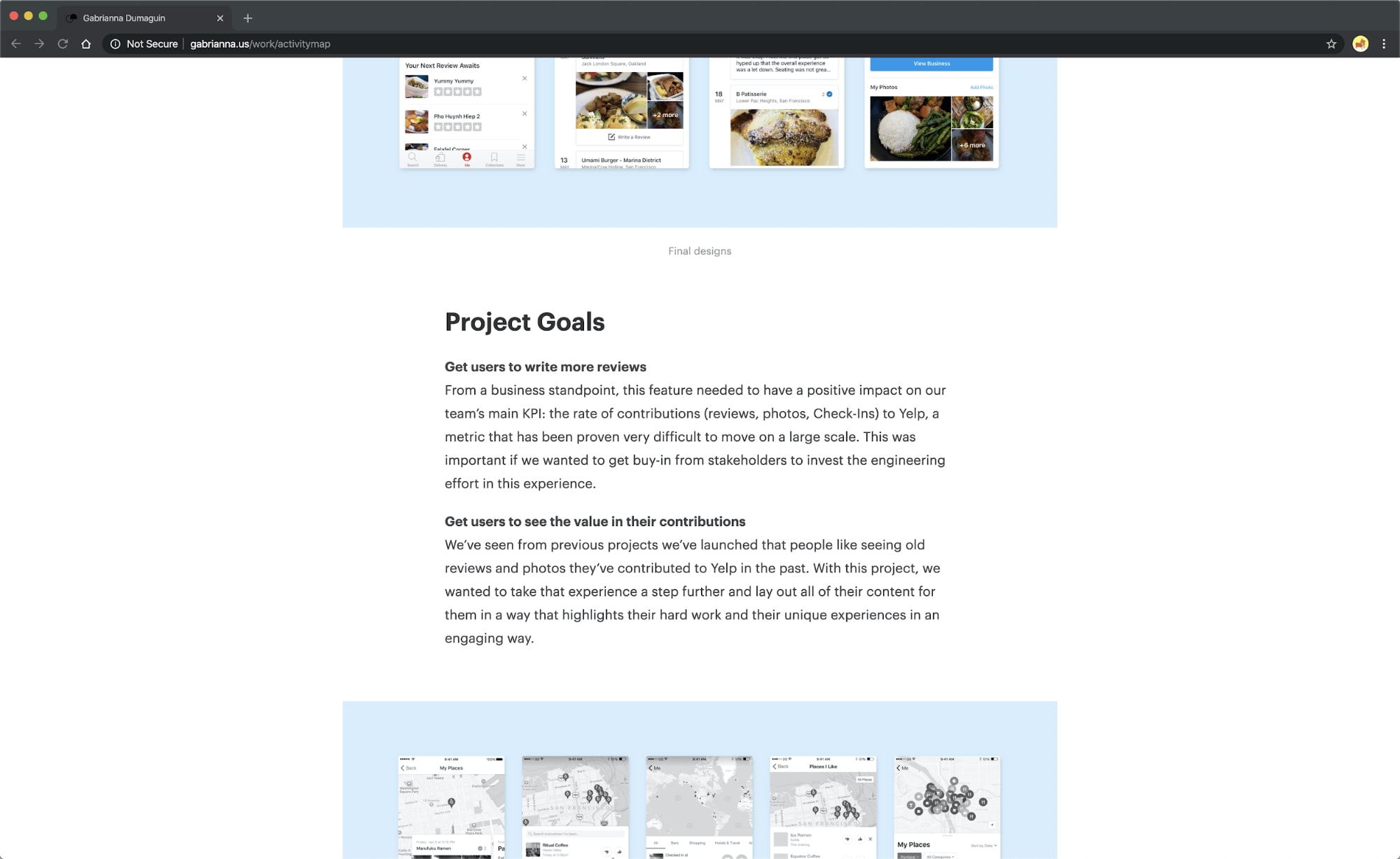
Then there is Gabrianna Dumaguin, who identifies two major goals for the project and how her team plans on measuring them in her Yelp case study .
Step 3: Scope
Stating the project’s scope helps in comprehending the case study further. Say, the overall project scope was large, and you only played a small role in the project; that’s perfectly fine. In this case, identify your scope of the whole project. To further distinguish the project’s boundaries, state anything that was outside of the project’s scope .
If applicable, you use this section as an opportunity to show your project management skills. Talk about how you handled staying on budget, staying on time, or scope creep for this project.
The project scope in practice
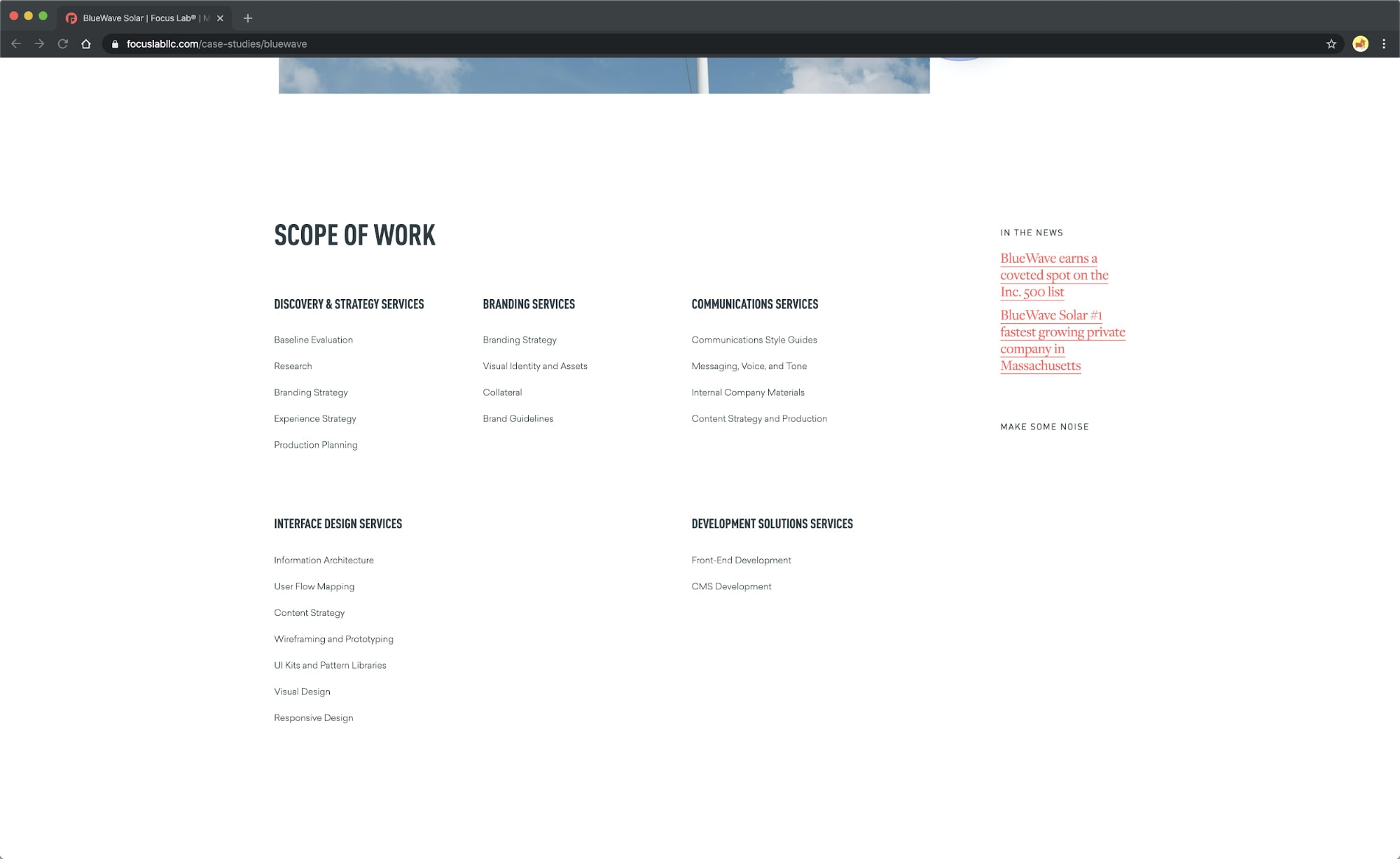
Focus Lab’s BlueWave case study shows off bullet lists of exactly the services the company provided for their client.
With Startup App and Slides App you can build unlimited websites using the online website editor which includes ready-made designed and coded elements, templates and themes.
Step 4: Target Audience
When it comes to identifying the target audience within your case study, start by answering the following questions:
- Who are they?
- How does the problem affect them?
- What key insights do you have about them?
There might be a lot of information to cover to give someone an overview of the target audience. That’s fine. Be concise.
You can treat the audience section in one of two ways. Share everything you know about them upfront, including what you knew going on versus what you learned along the way. Or, you can address what you learned within your process section. It’s up to you where you define this information as long as you do. After all, discovering and handling new information is a big part of being a UX designer.
For added insight into your design process, mention what questions you needed to investigate regarding the audience to solve the problem. Mention the details about user research or user testing in the design process section in the fifth step.
The target audience in practice
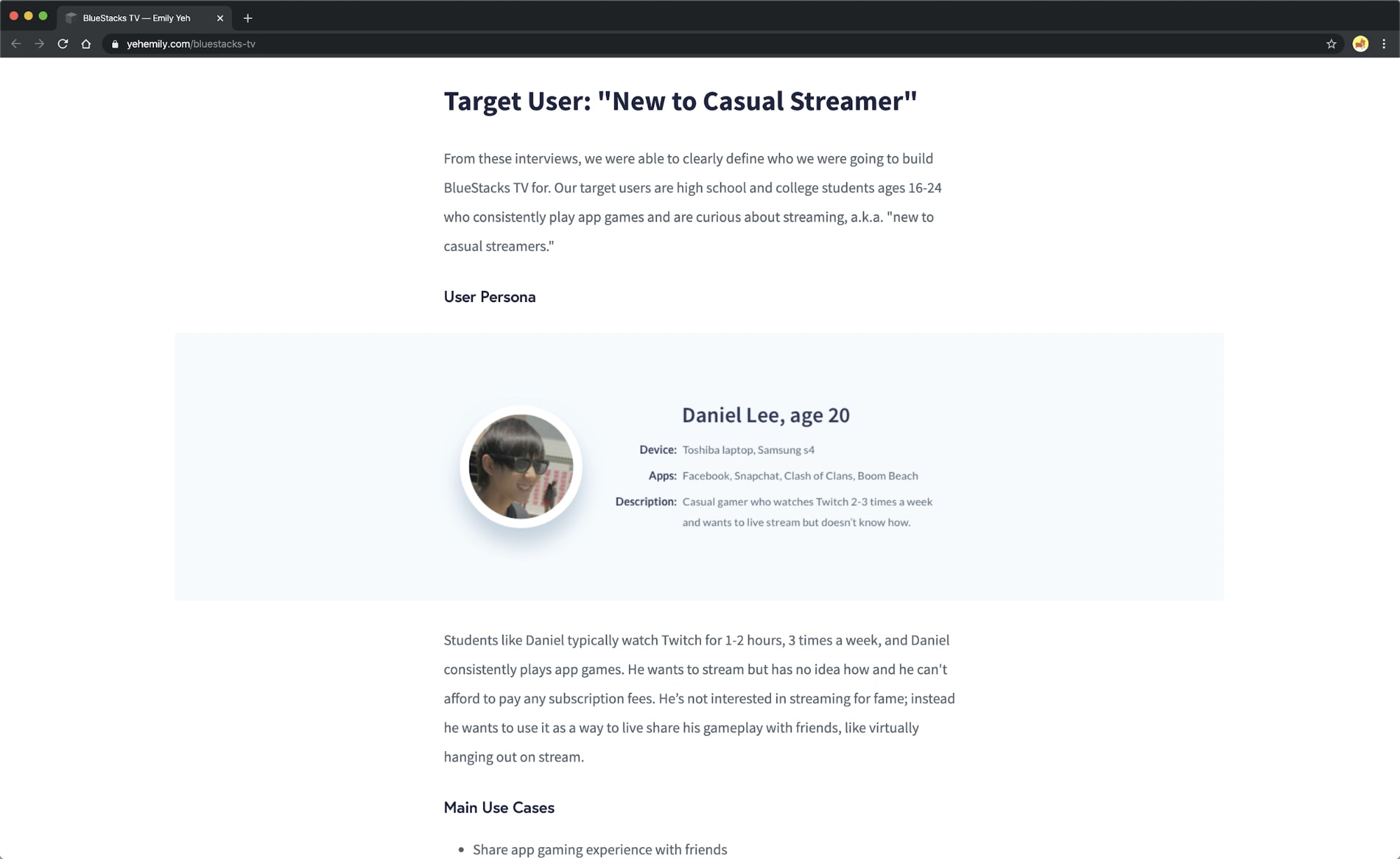
Emily Yeh’s BlueStack TV case study has an extensive break down of the target audience, including a persona, list of main use cases, and a feature list.
On the other hand, Vax Liu’s Battery Saver case study identifies common user pain points addressed by the project.
Step 5: Process
Now, we’ve gotten to the meat and potatoes portion of the case study!
Here is where you will identify the different steps you took in the project, why you did them, and the value of those actions’ outcomes to the project. Show off those fantastic UX skills ! The goal is to share your specific approach and contributions. Additionally, share some of the decisions you’ve made, trade-offs, or ideas that didn’t make the cut.
Each project is different, of course. Describe the process you took as best as you can. Some of the things you can include are:
- User research
- User journey mapping
- User testing
- Accessibility testing
Let’s take wireframes, for example. Explain why you choose to wireframe , how you went about wireframing and what value did it add to the project. How did user research findings influence the wireframes? What was the take away from the wireframes? This is the time to share how you work , how you think, and how you make decisions.
The process section is a great place to mention any collaborations you may have done as well. Showing you can collaborate with other teams is important for many hiring managers. Maybe someone else was responsible for user research? How did the two of you collaborate on it? Perhaps you have to work with a copywriter? Again, how did you collaborate? How did you handle the handoff to developers or cross-browser QA testing with the dev team?
The UX process in practice
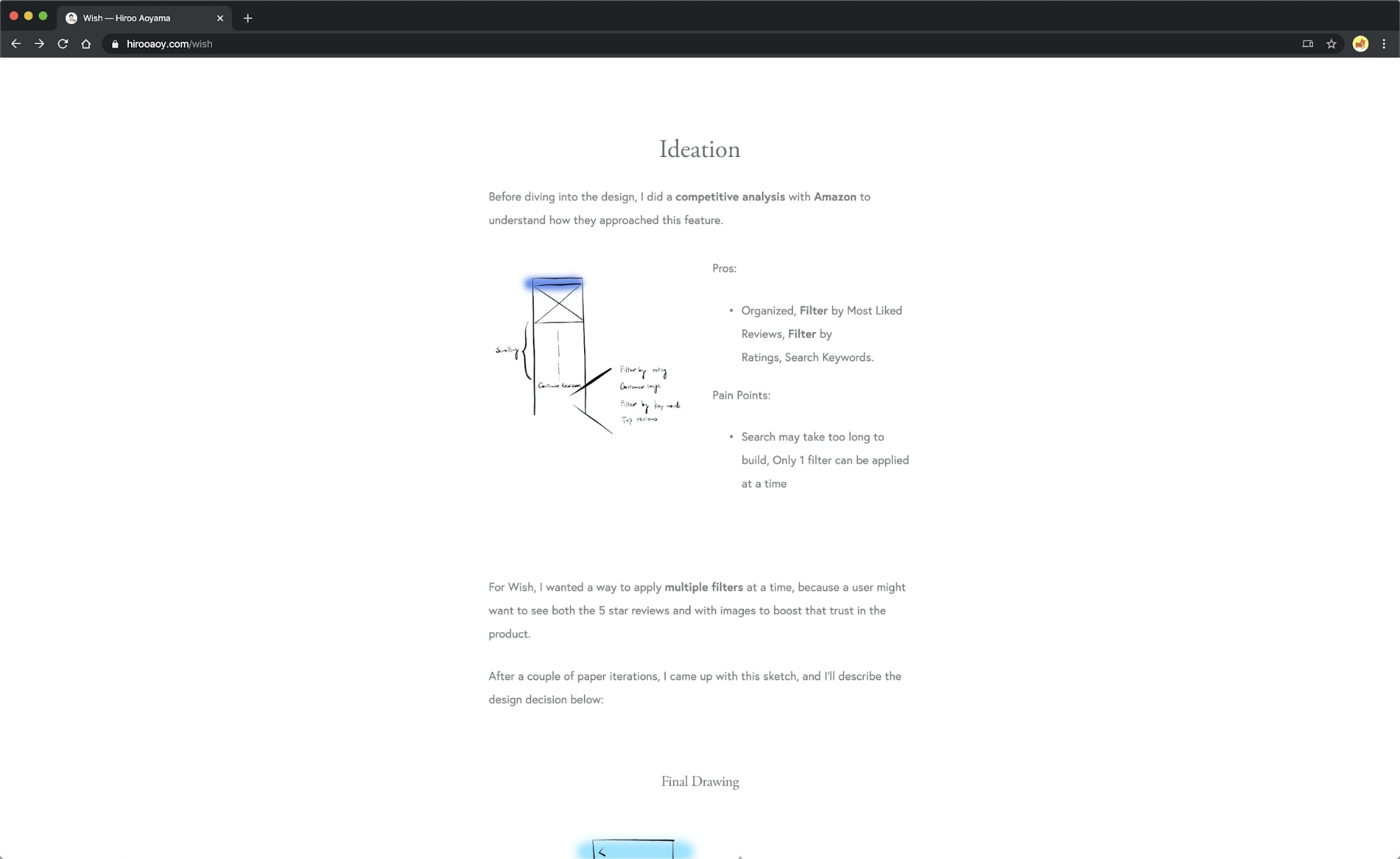
Hiroo Aoyama gives an in-depth walkthrough on conducting research, ideation, and making design decisions in his Wish case study .
Yi Tang’s Play-Later case study does the same thing in explaining different processes, including user journey, user flows, and wireframes.
- Wireframing, Prototyping, Mockuping – What’s the Difference?
Make These Changes to Meet Web Design Accessibility Standards
- A Beginner’s Guide to Voice UX Prototyping
Step 6: Deliverables and Outcome
Now, we’re wrapping up the case study. Do so by showing off a final deliverable. If it’s a new mobile app, provide some screenshots or recordings. You can go a step further and include a bullet list of additional assets or documents you created too. A voice and tone style guides would be one such example.
Most notably, identify whether or not you hit your desired goal and how did you measure success for the project . Basically, show what you’ve made and tell us the effect it had on the business .
- Did you hit, miss, or surpass the goal set?
- What outcome did this project have?
- Can you share other business results?
- Did you decrease withdrawal rates by 15% or customer service complaints by 30%?
- Did your landing page get fantastic conversion rates?
- Did you improve the lifetime value of customers or the NPS scores?
Deliverables and outcomes in practice
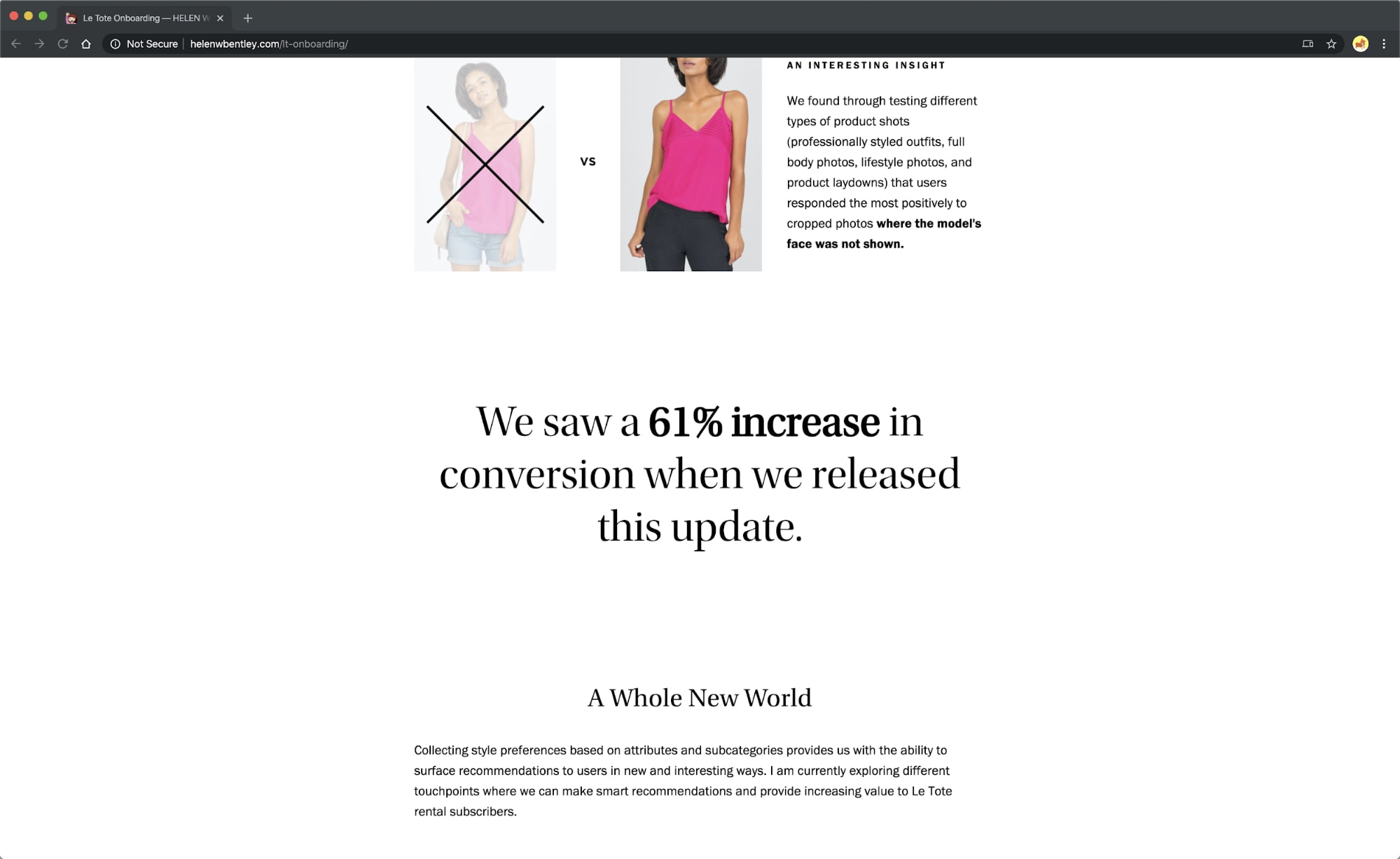
Helen W. Bentley, in her Le Tote case study , proudly exclaims that her work “saw a 61% increase in conversion.”
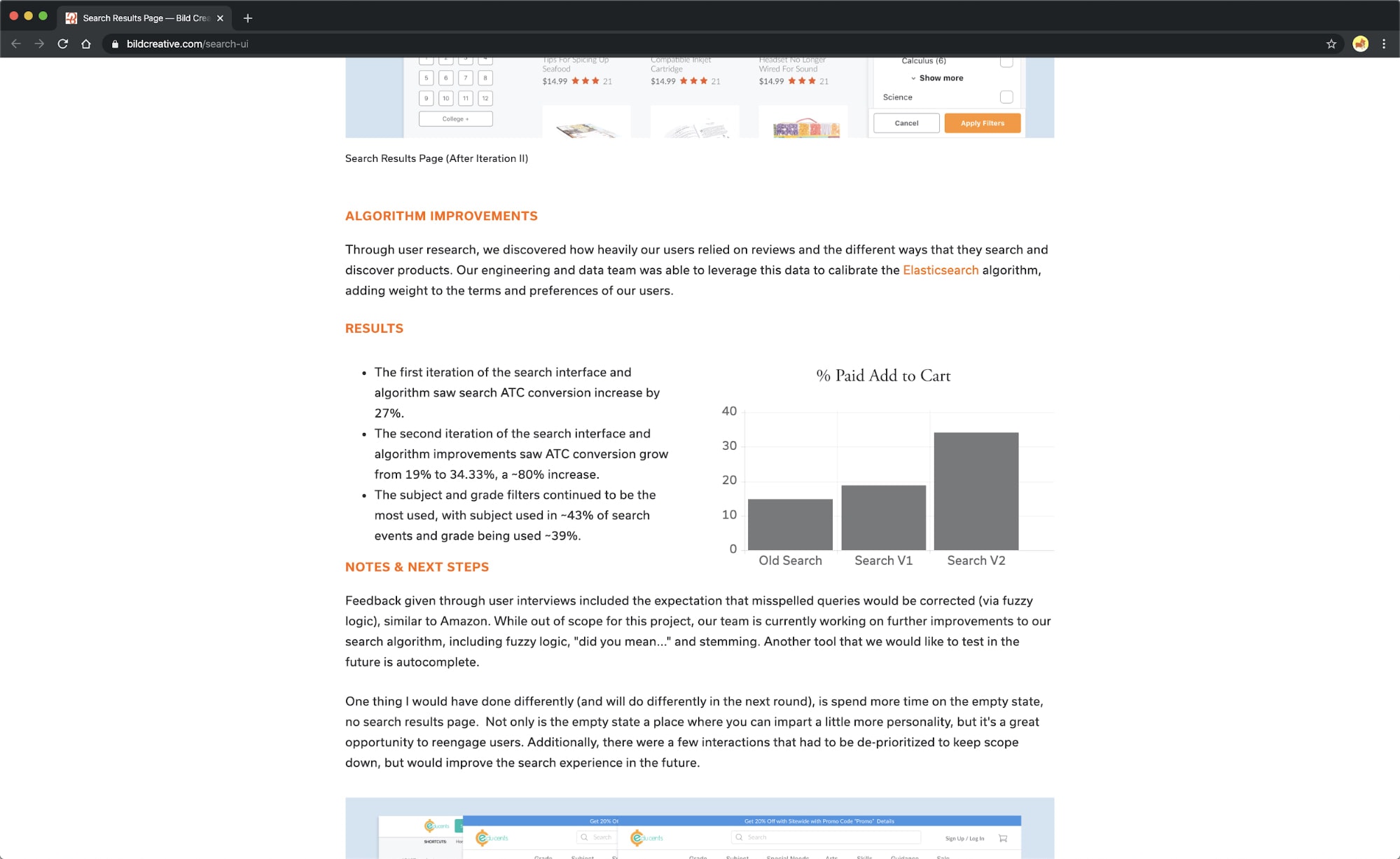
It doesn’t get much better than the detailed results Morgan Gore shares in her Educents case study!
- 5 UX KPIs You Need To Track
- The Design Side Of Conversion Rate Optimization
- How to Improve Customer Loyalty through User Experience
Step 7: Lessons Learned
Tell potential employers what this project taught you. If something went wrong or not according to plan, explain how you handled it.
- What insights have you gathered along the way?
- Especially knowing what you do now, what would you change?
- Did you learn a new method or practice?
- Maybe you figured out a better way to conduct user testing, communicate with project managers ?
- How did you handle scope creep or miscommunication between teams?
Share how you are better at your job because of this project.
Lessons learned in practice
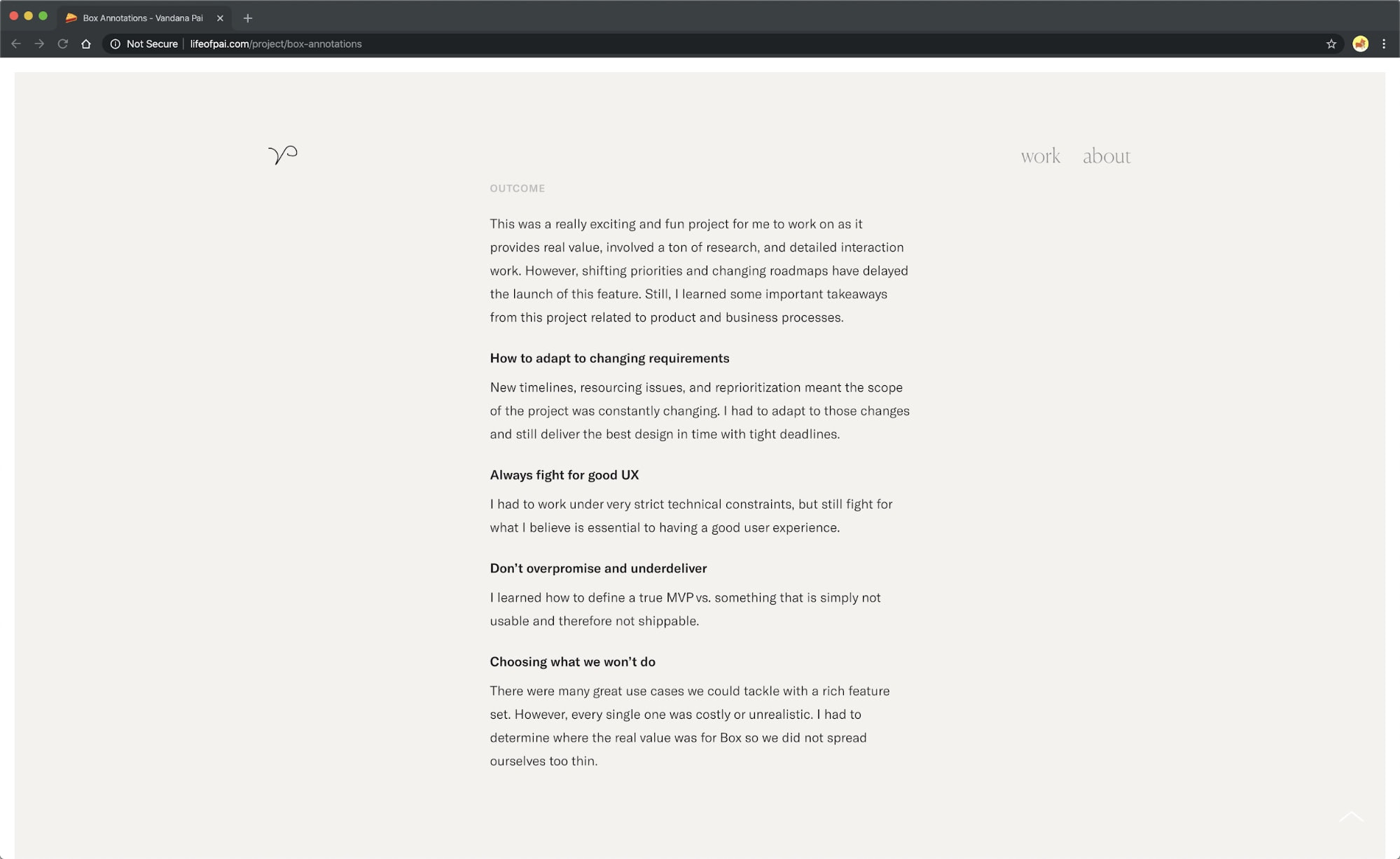
At the end of her Box case study, Vandana Pai shares her four takeaways from working on this project.
Bonus step 8: Visually Design the Case Study
So far, I’ve helped you figure out how to explain the project you’ve worked on and what information to convey. Now, it’s time to put it together in a lovely design. Below are examples of visually captivating case studies to get your inspiration going.
- Moment Brew
- Eleven James
- Space Design System
When putting together a UX case study, you’re telling a story about your work to potential employers. If you follow these steps, you’re going to showcase your UX design skills in a fantastic light. A well-written case study is a compelling case study. You’re bound to be hired in no time with a handful of these case studies.
Like what you're reading? Subscribe to our top stories.
Paula Borowska
Paula Borowska is an innovative and insightful Senior UX Designer at CVS Health, known for her relentless pursuit of designing the best user experiences. As an expert in design systems, user testing, accessibility, and cross-team collaboration, Paula is dedicated to enhancing digital experiences for all users.

11 Ways to Improve Website UX/UI (Using IP Geolocation & Other Tactics)

Using 6 Google Analytics Features to Improve User Experience and Website Metrics

How to Create Effective User Flows in Sketch (3 Simple Steps)

Use Color Accessibility Tools to Improve Your Website Design

Improving the UX with Userstack API
UX Best Practices for Using Search on Your Website
- Postcards: Email Builder
- Slides: Website Generator
- Startup: Bootstrap Builder
- Static Pages
- Affiliate Program
- Help Articles
- Perks (Partners Deals)
- Gmail Email Templates
- Outlook Email Templates
- Mailchimp Email Templates
- HubSpot Email Templates
- Klaviyo Email Templates
- Email Marketing Templates
- Email Newsletter Templates
- Designmodo Experts
- Email Templates
- Website Templates
- Bootstrap Templates
- Siter.io: No-Code Website Builder
- Pulsetic: Website Uptime Monitor
- Static.app: Static Website Hosting
Designmodo Inc. 50 N 1st St, Brooklyn, NY 11249, United States
Copyright © 2010-2024
- Your cart is empty 🙀
- Website Design
- Email Design
- Website Examples
- Email Marketing
- Website Tools
- Email Tools
- View All Articles
- Become an Affiliate
- Lost Password?
- Chat with us
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions
How to Write Great Case Studies for Your UX Design Portfolio
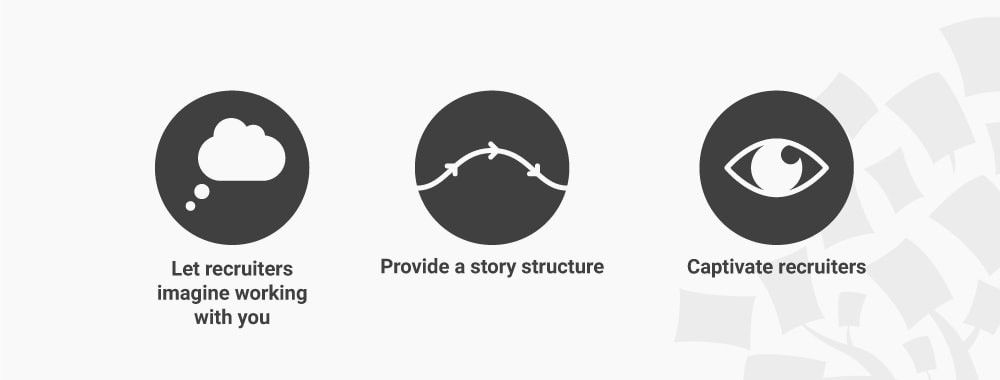
Well, the answer is really simple: write your UX case studies like stories. You see, when you present your case study as a story, you’ll find it far easier to give it a satisfying structure and captivate your reader. What’s more, you’ll make it easy for recruiters to imagine what it’s like to work with you, as they get to understand how you work. This makes your case study powerful and increases your chances of getting your first interview. Let’s take a closer look at what makes story-based case studies so impactful.
Since your case studies first and foremost serve to help you get an interview in your job application, they should answer the following questions (grouped into three categories, based on you as a person, your skill set and the way you do things):
Who are you? What drives you and what’s your background?
What UX skills do you possess?
How do you approach and solve a problem? How do you work with others?
As it turns out, when you tell a narrative through your case studies, you answer these questions effectively. Here are the 3 main reasons why you should write your UX case studies like stories and how this helps you stand out from other applicants.
Because Stories Allow Recruiters to Imagine What it’s Like to Work with You
“Narrative imagining—story—is the fundamental instrument of thought. Rational capacities depend upon it. It is our chief means of looking into the future, of predicting, of planning, and of explaining.” —Mark Turner, cognitive scientist and author
When a recruiter reads your case study, they want to find out if you’ll be a great addition to their team. They want to know not only if you have the right skills and attitude, but also whether they’d enjoy working with you.
When you tell a story, you make it intuitive for a recruiter to imagine what it’s like to work with you . That’s because we use stories to learn and imagine all the time—in fact, people have since the dawn of human history. Therefore, recruiters will find it easier to look into the future and predict if they’d like to work with you when they read a story-based case study. They’ll find it easier to understand who you are and how you solve a problem.

Since the dawn of human history, we have used stories to imagine and learn about our world. Help recruiters understand you by telling a story about your design process .
© Mike Erskine, Fair Use
This sentiment is echoed by Sarah Bellrichard, Senior Vice President of Wholesale Internet Solutions & UX at the American bank Wells Fargo. She shared her tip on case studies and interviews:
“My tip would be, tell stories. When designers present a flat portfolio it doesn’t tell me about how they approach the work they do and how they deal with the ebbs and flows of design. Tell me how you navigate from start to end of a project.” —Sarah Bellrichard, SVP of Wholesale Internet Solutions & UX, Wells Fargo
Because Stories Give Your Case Studies Structure
“Sometimes reality is too complex. Stories give it form.” —Jean Luc Godard, French-Swiss film director
If you’ve worked on a design project before, then you’re painfully aware of just how messy life can be. Deadlines change, project goals shift, and new findings can fundamentally alter design specifications .
Stories will give your past experiences form and make your case studies better organized . You can re-arrange your experience into a meaningful sequence of events—i.e., progress—towards your results. Otherwise, your case study will likely seem chaotic.
The arc of a story—introduction, middle, conclusion—is the perfect order to tell your messy progress towards a project’s final results. Let’s illustrate:
In the introduction :
You set up the context of your project, for instance through a design brief .
You introduce your team’s main goals and some of the main obstacles you faced
In a classic story, this is where we meet the heroes and learn about the venture/goal they’re reaching for and why they’re not satisfied with their current lives.
In the middle :
You illustrate your approach to solving the problem.
You bring your reader through your journey of how you used industry standard practices to tackle the problem. It’s important that you describe what you did and what your team members did, so the recruiter knows what skills and knowledge you possess.
In a classic story, this is where we follow our heroes struggling to conquer the beasts, villains and problems as they strive to reach their goals.
Finally, in the conclusion :
You showcase the final product and the results you and your team achieved.
You reflect upon what you’ve learnt and recount any follow-up tweaks you’ve made to the product.
In a classic story, this is where the heroes reach their goals―they experience personal growth , reap the rewards of their hard work and live happily ever after.
See how nicely it all fits into a story arc?

When you arrange your case study in a story arc, your journey becomes more ordered and meaningful.
© Teo Yu Siang and the Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-NC-SA 3.0.
There’s more! You’ll also find it easier to write your case study when you arrange it like a story. You see, the introduction-middle-conclusion structure of a story forms a skeleton for you to fill in the “meat” of your journey. On top of that, recruiters who read your case study will also find the familiar arc of a story satisfying. Talk about a win-win situation!
Because Stories Captivate
“Tell me the facts and I’ll learn. Tell me the truth and I’ll believe. But tell me a story and it will live in my heart forever.” —Native American proverb
Okay, your case study will most likely not live in your recruiter’s heart forever, but your story-based case study will definitely stand out from other purely fact-based case studies, as your story will engage and captivate your recruiter. You see, a narrative is more engaging and provides a better reading experience than a dry, factual account ever could. It naturally makes the reader feel involved in the story and weaves a common thread throughout the case study.
UX recruiters are incredibly busy. They’ll typically spend only 5 minutes scanning your case studies because they have so many applicants to process. Given that, you have a much better chance if you can capture your reader’s attention for the whole 5 minutes.
And there’s no better way to captivate someone than through a story.
Let’s demonstrate that in an ultra-brief case study―yours should be more detailed and in-depth. Below, you’ll find the same journey told in two ways: first in a factual manner, then in a narrative fashion. See which version you find more engaging.
Factual : User interviews were conducted with 12 people to evaluate the effectiveness of the prototype . The main finding was that the assumption that users shopped based on their weekly nutritional needs was invalid. This finding was used to create a new iteration of the product, which was tested and found to be 50% more successful than the previous version.
Narrative : We conducted interviews with 12 people to evaluate if our prototype was effective. Our finding threw a giant spanner in the works. We realized our assumption—that users shopped based on their weekly nutritional needs—was dead wrong. Undefeated, we scrambled to create a new iteration, and ran another round of tests. This time, it worked—the success rate shot up by a whopping 50%!
You probably find the narrative version way more interesting—and so will your recruiters.
Notice in the factual version how flat and lifeless the account is? Sure, the figures are there, but it looks as if you’re reporting on what someone else did. This tells a recruiter that you’re distant and non-engaged—that you didn’t take ownership in what you’re talking about.
So, embrace the liberating and captivating format of a story. Go ahead and describe how your finding proved you dead wrong and how you scrambled upon meeting a temporary setback.
Best practice:
Convey your emotions and write in an active, engaging tone of voice .
Include the team’s frustrations, problems you faced and new insights you learnt.
Include people: write “we”, “I” and “our team”.
This way, you’ll give your case studies flavor . Furthermore, you’ll reveal who you are and how you work―and your recruiters will come back for more.

Stories naturally captivate us—use that power to captivate your recruiters, too.
© Prasanna Kumar, Fair Use
Turn Your Case Studies into Stories
Of course , we’re not saying that you should write a novel to explain what happened in your project. Your case studies should still be short and sweet, but they also should be punchy and engaging.
In fact, when we sat down with Stephen Gay, Design Lead at Google’s AdWords, to ask him about the importance of a portfolio, he explained that he sees UX case studies as stories about the applicants.
- Transcript loading…
To a recruiter like Stephen Gay, case studies are stories that tell him about the applicants. Author / copyright holder: The Interaction Design Foundation. Copyright terms and license: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0.
As Stephen astutely pointed out, we UX designers regularly use the power of stories in our work. So, use this same storytelling approach in your case studies, too!
The Take Away
The best way to write a case study is to tell it like a story. This way, your case studies become a vessel through which recruiters can imagine a future working with you, since they get to experience and understand exactly how you solve a design problem. Your recruiters will also enjoy the familiarity and structure of a story arc, and they’ll find the reading experience much more engaging. So, go ahead—inject humanity, color and passion into your case studies. Be a storyteller.
References and Where to Learn More
You can find Sarah Bellrichard’s tip on case studies in this article by Justinmind, which gathers tips and insights on how to do well in interviews.
Hero image: © Rawpixel, Fair Use.
Build a Standout UX/UI Portfolio: Land Your Dream Job

Get Weekly Design Tips
Topics in this article, what you should read next, test your prototypes: how to gather feedback and maximize learning.

- 1.1k shares
- 11 mths ago
How to write the conclusion of your case study

- 6 years ago

How to create the perfect structure for a UX case study

The persuasion triad — Aristotle Still Teaches

- 8 years ago
How to Create a PDF UX Design Portfolio
- 4 years ago
Methods to Help You Define Synthesise and Make Sense in Your Research
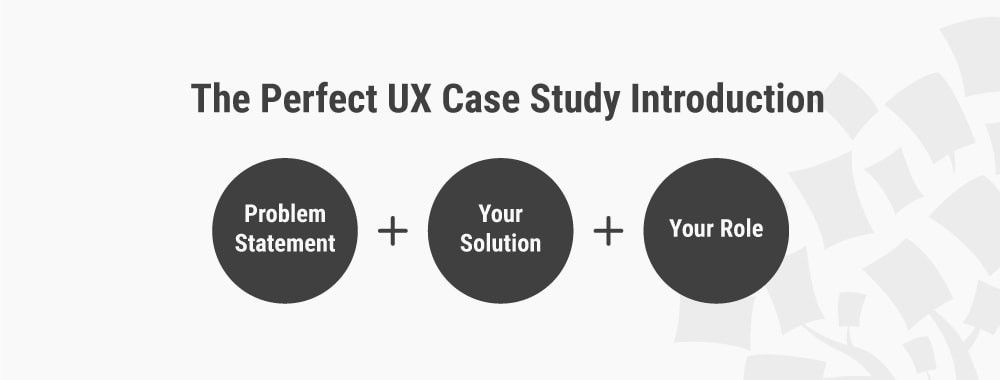
How to Write the Perfect Introduction to Your UX Case Study
- 3 years ago
The Power of Stories in Building Empathy

- 2 years ago
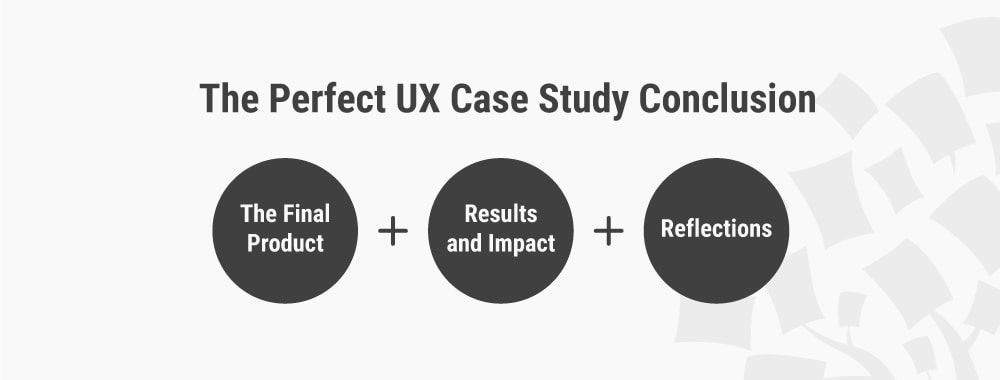
How to Write the Perfect Conclusion to Your UX Case Study
How to Create Effective UX Case Studies with Aristotle’s 7 Elements of Storytelling

Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this article , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share Knowledge, Get Respect!
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this article.
New to UX Design? We’re giving you a free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!
How To Write a UX Case Study in 5 Steps

The first day I sat down to write a UX case study, I had no idea what I was doing. I remember that I wanted to write about an app that I was using constantly, called MyFitnessPal. I had done a bit of research, but when I sat down, my mind went blank and I ended up writing a 900-word diatribe about the social aspects of the app.
To this day, I can’t believe I had the audacity to show anyone this case study. When I showed my friend, he just laughed at it.
“This is a Medium article,” he said, “not a case study.”
When you’re starting out as a UX designer , you know that you need case studies for your portfolio. However, there’s not a lot of concrete information out there on exactly what should be in a case study. People have different expectations for UX case studies, but I’ll give you the 5 basic elements they should all include.
{Resource}
A quick note—case study styles are like Thanksgiving turkey recipes: everyone has one and they all come out a little different, but in the end it won’t ruin the holiday meal. As long as your case study is all meat and bone with no wasted space, it’ll be fine.
Step 1: Define the Scope
Ideally, the first paragraph should tell the reader what you’re planning to talk about. You may want to highlight a problem, show off a stunning design, or highlight a change.
Step 2: Define the problem
Readers of your case study want to see the problem clearly defined. An issue that new UX designers have often is identifying that there is a problem but not identifying the problem itself. A common bad statement might be something like “this app is frustrating for users and they have a high bounce / uninstall rate.” A better statement is something like “users have trouble accessing and understanding their account overview, and navigation to and away from this page is buried in menus.” This outlines the problem clearly and sets you up to solve it concisely over the next few paragraphs. If you’re designing an app from scratch, this section should talk about what problem you are hoping to solve, and why your solution is the cleanest and most effective one.
Step 3: Define the Audience
Not every app is for everyone. An easy example is something like Blind, which is a forum app designed for tech professionals, particularly engineers, to discuss work life at their jobs. Being designed for tech professionals means that it doesn’t have to necessarily be awe-inspiringly beautiful with jaw-dropping animations. It can be austere, and even a bit spartan since the people using it are working in a heavily analytical industry. Even the job posting section of their website is just an Airtable.
Understanding your target audience for a product will make analyzing the success of that product much simpler, as design, copy, and architecture should all work together cohesively.
Step 4: Solve the problem
There are several ways to do this in a single section, but generally, this should be a paragraph or two outlining A) what your solution for the problem is, and B) how you arrived at the solution to this problem. Both are vital to include. An easy way to start is to write something like “I decided to solve this problem by taking these actions,” before outlining the actions you recommend.
Step 5: Show your work
I’m an ignoramus, so algebra never came easy to me. I especially hated when I would arrive at the right answer and be asked to show my work. What does it matter how I got there? I got the correct answer, didn’t I? Let me be the Algebra II Top Gun of this school and leave me alone.
Unfortunately, in design case studies showing your work is necessary, and this is where you get a chance to show your UX design process . How did you arrive at this solution? What steps did you take to ensure that you were being circumspect in your reasoning? You can’t be the Diogenes of UX, hanging out in the middle of the agora shouting dichotomies and hoping someone listens. You have to walk the reader through each step of your thought process.
This is where you get to show off your screens, your prototyped animations, your Tableau repositories, your Typeform and Google Sheets research, your pivot tables, Miro flowcharts, Hotjar heat maps, and beautifully animated PyViz scatter charts. This is where you get to blow your reader’s mind.
Take a look at the case study example in Derrick's profile , one of the Verified Designers on Uxcel.
A quick tip: Head over to Coolors or Adobe Color and pick out a nice cohesive palette to put all your research in. This is an easy way to ensure that it doesn’t confuse the reader (wait, red is good now?) and looks clean and consistent.
Writing a UX case study is incredibly important to your career path, especially when first starting out. However, by ensuring that you have every necessary step in your case studies, you can create beautiful qualitative and quantitative research and design that blows your readers’ minds and lands you your dream job. Happy hunting!
Frequently Asked Questions
Become a UX Design professional with our interactive, self-paced career path and break into a booming industry.
Upskill your design team effectively
Equip your design team with the best-in-class design training that sticks.
Do you know your design team skill level? Send them this quick test & see where their skills stand among 300K+ designers worldwide.
Level up your design career
Get step-by-step guide how to build or advance your UX design career.
Do you know your design skills level? Take a quick test & see where you stand among 300K+ designers worldwide.
Continue reading
12 best ux portfolio websites & builders to use in 2024, 8 tips for onboarding your new ux designer, 11 inspiring ux design portfolio examples & why they work, cookie settings 🍪.
- Interactive UX learning for all levels
- 20+ UX courses and career paths
- Personalized learning & practice
Design-first companies are training their design teams. Are you?
- Measure & identify team skill gaps
- Tailor learning for your team’s needs
- Unlock extensive learning library
- Visualize team growth over time
- Retain your designers

UX Design Mastery
Get started with a career in UX Design

UX Case Study Example #1 plus free template
In my last article , I shared the free UX Portfolio Case Study template that I developed based on over 60 portfolios of successful design hires from Facebook, Amazon, Uber, Twitter, Apple, Google, LinkedIn, Dropbox and the insights of top design recruiters.
We explored what recruiters look for in UX job applications/portfolios and then dived into successfully structuring any UX case study, even conceptual projects .
What you are going to learn
Today I wanted to go a step further and walk you through how to fill in the UX Portfolio Case Study template from scratch and I will use an example UX case study from my portfolio.

The core idea is to try to break down your case study creation process into a writing component and designing component so that you can tackle each one without getting stuck or overwhelmed.
The template ensures that your case study has a good narrative and understandable structure.
This also allows you to plan more effectively what design artifacts you will need in your case study. It’s a system by which you can then rapidly roll out multiple case studies without forgetting anything that’s relevant to a recruiter or client.
The UX Portfolio Case Study template has 8 critical sections that recruiters are looking for.
UX Portfolio Case Study template sections
- Project Title & Subtitle (A headline and subtitle that indicates the name and goal of the project)
- Client/Company/Project type
- Project date (When did you work on the project)
- Your role (What you were responsible for on the project)
- Project Summary/About this Project (An overview that summarizes the project, goal and results)
- The challenge (What specific problem, user needs, business requirements and/or pain points that the project solves. Were there any technical constraints or business KPIs you had to keep in mind? Who are you users and what are their specific needs)
- Solution (What method/process were used to solve specific problem, user needs, business requirements and/or pain points? How did features address the objectives?)
- Results (Project success metrics, awards, reflections, project next steps and/or lessons learnt)
Let’s begin.
The project
The UX portfolio project I will use is one I did as a Senior Designer at a digital marketing agency. The brief was to create a responsive website/microsite for an annual financial publication for an Asset Management company.
Now let’s walk through each section of the UX Portfolio Case Study template and fill it in.
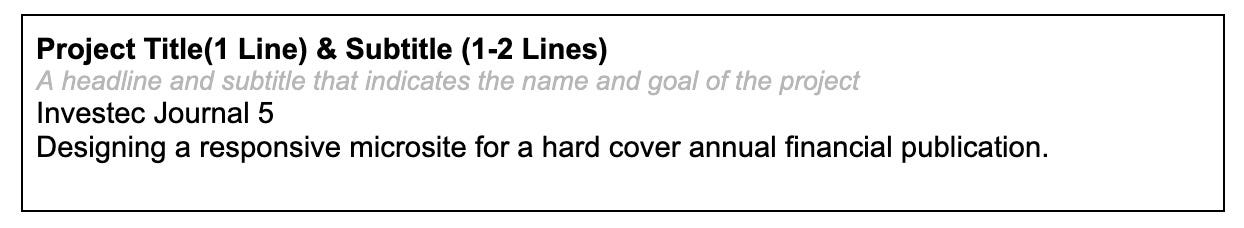
1. Project Title & Subtitle
Length: Project Title (1 line) & Subtitle (1–2 lines)
This one is pretty simple. I used the name we had for the project at the agency. It’s brief enough to fit any case study cover but does show the brand name, and the nature of the product, a journal. I added a sub-title to further explain what the heading means, and give more context around the project title.
2. Client/Company/Project type
Length:1 line
Unless stated in the title, this helps build more background to who the project was for. This was a commercial project for a client so I wrote the name of the client’s brand.

3. Project date/duration
When or how long the project was helps the recruiter establish whether this is your most recent work and most importantly, to gauge where your skill level is. Always try to put up work that is recent because it’s an accurate reflection of your skills. This one was a bit of an old one that I had not drafted a case study for.

4. Your role
Length:1–2 lines
This is a section to state everything you did and were responsible for. Recruiters are looking to accurately assess your skills in the context of the entire project’s execution. I state that I was the Senior UX Designer on the project then note down all the activities I did on a high level, for the project over the course of several months.

5. Project Summary
Length: 1–2 paragraphs
This is a critical section for any reader who does not have a lot of time to read through the entire case study but wants a brief summary of the project, goals, and results. They may be going through a stack of applications and only have a few minutes to scan over one or two projects in your portfolio.
I have kept my summary to three long sentences. The first is the context of the brand. The second touches on the challenge and problem we were attempting to solve. And the last sentence addresses how we would know we had done a good job.

6. The Challenge/Problem
Length: 2–3 paragraphs
This section specifically looks at the problems the project is trying to address. While keeping this paragraph concise I dive into the details of the problem that the client and their user were experiencing.

7. The Solution
Length: As long as needed
This is the longest and more time consuming section to fill in depending on how long ago the project was and how fresh in your mind it still is. For this section I outlined the design process steps and methods followed during the project. I wrote down the high level project steps but at this point I am already thinking of the the relevant design artifacts recruiters might want to see. Everything that I produced from sketches to visual mockups to prototypes.

Length: 1 paragraph
The critical last section concludes the case study by outlining any project success metrics that were achieved. I was fortunate that we wanted to report back to the client how well the site had performed so this information was dug up from the Google Analytics tracking. In most cases clients are happy with just a launch and its really up to you to follow up and get the project impact.

Okay, now that we have filled in our UX Portfolio Case Study template we can move on to getting our design artifacts together. I am happy with the content I put down and importantly, I have not missed any section.

Putting it together
This part is really up to you and how you tackle it, is going to depend on where you are going to host your UX case study. If you have a portfolio site you can use the template content on a site page and fill in the gaps with images and project artifacts.
I have a Behance account where I house my projects and merely need to upload images and write the text in, then publish the portfolio. Taking it a step further I integrate the text and imagery in Sketch/Photoshop then just upload the images.
How to enhance your UX Case Study
Key things that I always like to include in my case studies to make them more interactive and engaging:
- A video or gif of the final product
- A prototype
- Brand imagery to create immersive narrative
UX Case Study Folder structure
I like to create a folder structure for housing everything I will need as follows.
- RAW ( I collate screenshots of the final project, UI designs and wireframe exports in here)
- Images (Relevant visual imagery that can be interlaced between project sections)
- Videos (Optional. In most cases there won’t be one)
- Behance submission (Final design exports for Behance upload)
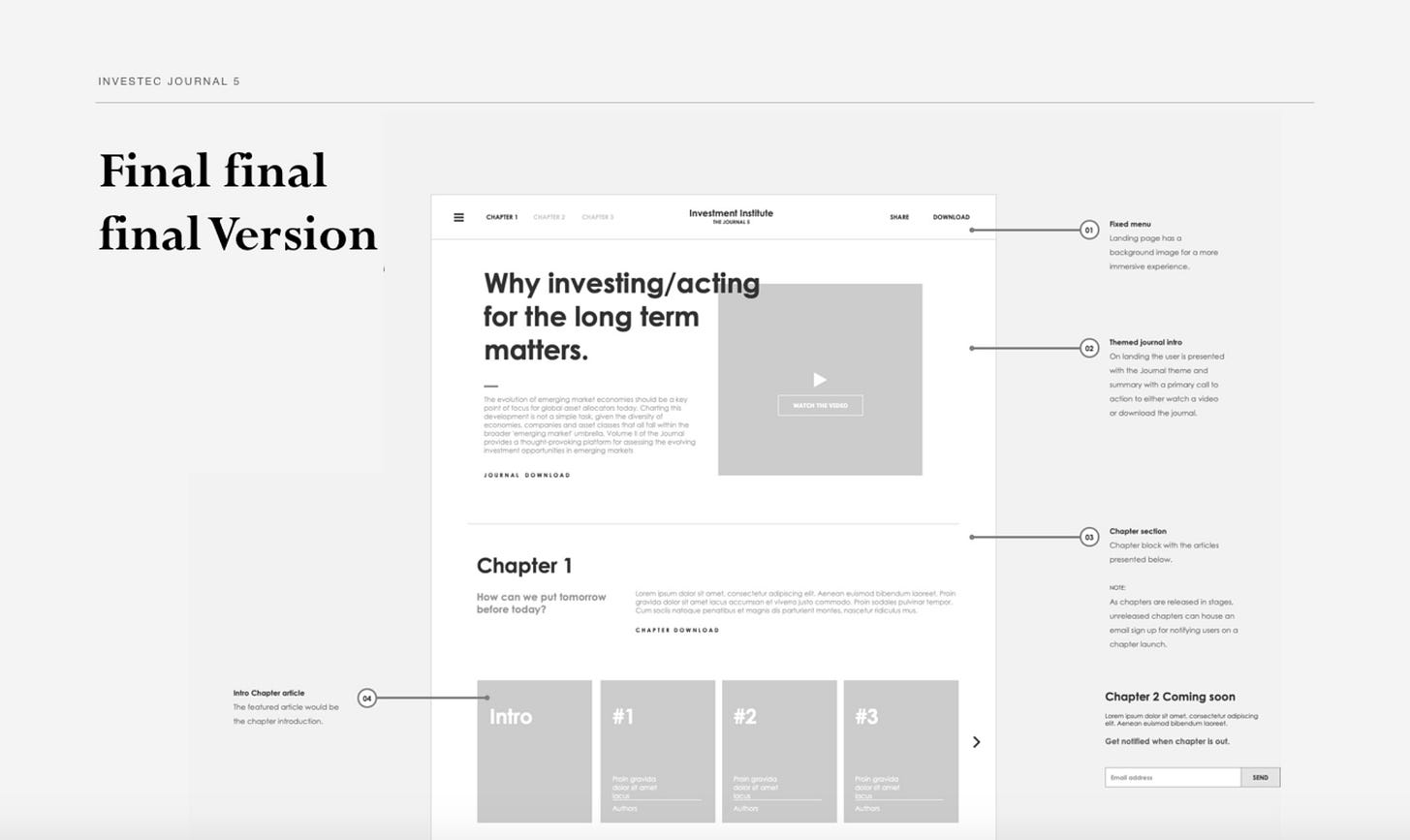
Here are some of the final design screens with the text we filled out in the UX Portfolio Case Study template. Go to this link to view the full case study .
The intro has most of our UX case study sections covered in one go. Super important for recruiters without a lot of time.

The About and challenge sections come directly after that.

Then we can dive into the work. Here is a tiny bit of the Solution section showcasing a wireframe and UI design.
And lastly the results to round off the case study.

Here is the link to my portfolio and other UX case studies.
Calvin Pedzai on Behance I conduct website and mobile app usability audits, heuristic evaluations, user journeys, competitor analysis, user… www.behance.net
If you would like to get down to work, download my UX Portfolio Case Study template for free . Its included with the Design Portfolio Layout Guide , which including 20 online case studies and example scripts for each case study section.

DOWNLOAD GUIDE
What to read next:
Calvin Pedzai
Analytical problem solver who enjoys crafting experiences and currently is the Senior UX designer at an awarding winning agency.
Related Articles

UX Case Study Example #2 plus free template
In Getting started

Axure vs Sketch: What’s the best prototyping tool for a UX Designer

Is Axure RP the best prototyping tool for a UX Designer?

Hi, I’m Sarah Doody, founder of Career Strategy Lab.
Want to advance your career in 2024? Our career coaching clients have been hired at Blue Origin, Capital One, IBM, Wells Fargo, and more.
Apply to our UX career coaching program →
No fee to apply, we have 5 spots open:

How to Write a UX Case Study to Showcase Your Skills, Experience, & Process
14 min read
By: Sarah Doody on May 22, 2023

UX case studies are the foundation of an excellent UX portfolio and have a direct impact on how well you’ll do in job interviews.
To demonstrate your skills to recruiters and hiring managers, user experience (UX) professionals of all types – whether UX writers, content strategists, product strategists, product managers, UX researchers, or any other roles in product development – should create case studies for various projects they’ve worked on. The purpose of UX case studies is to articulate what you did, how you did it (your process and thinking), and what happened (the results and impact).
A well-written UX case study tells the story of each project and represents how well you can communicate not just what you did, but why you did it.
How would your UX career change if you could write UX case studies you’re actually proud of? What would happen if you had a clear and powerful story to tell about each project in your UX portfolio? You’d likely …
- Apply for more roles.
- Get more interviews.
- Make it further in the interview process.
- Be far more confident presenting your projects.
- Stand out as an effective communicator.
- Get more offers.
- Reach your next role faster
But, how exactly do you write more effective UX case studies? Even if you don’t think you’re a good writer, it is possible. You just have to know what questions the recruiters and hiring managers need you to answer in the UX case studies. UX recruiters and hiring managers want your case studies and portfolio to share the details and your process for each project, but not have it be an essay or read like a white paper.
In this article, you will learn:
How to structure a UX case study
- The 5 steps to write a UX case study
- How to actually tell a story of your process
At the end of the article, you’ll find some examples of effective UX case studies. A wordf of caution though, I know you’re tempted to go look at example case studies and copy them. But don’t forget, copying other people’s UX case studies won’t do you any good. You’ll get enamored with the “design” of these case studies and not actually consider the content and the story that each case study tells. Do yourself a huge favor and read the steps below to structure and write your UX case studies. Let’s go! And by the way, this free resource will be tremendously helpful for you:
Featured Resource
Get a UX case study template. It’s a Google Doc so you’ll be able to make a copy and then start writing your own case studies.
Why UX case studies matter
According to Center Centre , the job growth of UX designers is expected to rise 22% over the next 10 years. UX is a hot field, and there’s a lot of competition.
This is why your UX portfolio can’t simply be a curation of sexy-looking deliverables. Recruiters and hiring managers need to see your process. It’s your job to articulate not just what you did, but why you did it.
Communication is a crucial skill for UX professionals. In most UX roles, you’ll find yourself not just doing the actual work, but explaining it over and over as stakeholders challenge your decisions and colleagues who may not be versed in design need a bit of help understanding the process. So ask yourself this …
If you don’t have well-written UX case studies, then how can recruiters and hiring managers trust that you’ll be able to communicate what you did and why you did it if they hire you? Your UX case studies are a reflection of how you think and communication and they’re a preview of how you’ll think and communicate in a role once you are hired.
There are two parts to being an effective communicator, your writing skills and ability to verbally discuss what you did. If you struggle with verbally presenting your projects, chances are it’s because you did not invest time in writing about your projects first.
By literally writing out your UX case studies in a Google Doc first, you’ll become much clearer on what you might say as you get further down the UX job interview process. How you perform in the interviews is what will likely get you hired, but to get in the door for an interview, you need a solid portfolio. The quality of the writing for your case studies is one of the most important variables in the success of your portfolio.
When approaching your UX portfolio and case studies, my advice is: think like a lawyer. Because how do lawyers win legal cases? With strong communication, and even stronger evidence. The projects inside your portfolio are like evidence in a legal case. That’s why you must choose the projects for your portfolio very carefully.
When you write a UX case study, there are 7 main sections that you should cover. It’s important to note this structure does not mean that you will literally have a page in your PDF or section on your website for each of these. Furthermore, not all of these sections will apply for each project. For example, if a project didn’t have many constraints, don’t feel like you must invent or stretch some constraints, just to include it. Use your best judgment, this structure for your UX case study is a guideline, not the gospel.
Here is the high level structure of an effective UX case study:
- Problem statement
- Users and audience
- Roles and responsibilities
- Scope and constraints
- Process and what you did
- Outcomes and lessons

Get this UX case study template. It’s a Google Doc so you’ll be able to make a copy and then start writing your own case studies.
5 steps to write a UX case study for your portfolio
A UX case study is not just about having something for your UX portfolio, but it also equips you for interviews and provides you with content you can also use on your resume and LinkedIn profile.
As you write your case studies, don’t worry about length. If your case study ends up being 2,000 words in a Google Doc, it’s not as though you are going to take all that text and cram it into your portfolio. That would be insane.
There will be a process of editing as you decide which bits of the story in the Google Doc are what hiring managers and recruiters want to hear about. As you take the content in your Google Doc and move it into a more visual format, you’ll pair down what you wrote and come up with a more compact version of the story that you want to share in your UX portfolio.
1: Outline your UX case study
An outline’s purpose is to help you understand the big picture of your project, so you can decide how to structure your case study. It may also help you realize that the project already feels like it’s too big, in which case you should consider breaking it up into multiple smaller projects so that you don’t overwhelm the user of your UX portfolio.
Start your outline with the seven sections listed above ( use this Google Doc template ), and start filling in bullet points under each section. Don’t worry about sentence structure; just write and get it out of your head. If you’ve been documenting your projects as you work on them , then you may have some of this already written.
2: Write the details of your process
Now that you have an outline and you see the big-picture story of the project, you can start filling in details. The bulk of what you write will be for the “Process and what you did” section. This is where you’ll document the steps you took during the project, just like documenting science experiments in high school.
The Process section of your UX case study should address these questions:
- What did you do? For example, what research method did you use?
- Why did you do it? For example, why did you choose that research method?
- What was the result? For example, did you achieve your research goals?
- What did you learn? Anything unique happen? What would you do differently next time?
To continue learning by example, let’s refer back to our fictional example of the Home Depot project that focused on user research for the mobile app checkout. Below are examples of content that could be for the Process section of the project. Imagine this part of the case study is meant to address the research step of the process.
- Poor explanation of the research step: “We did usability testing on the checkout of the Home Depot mobile app.”
Why is this weak? Because it only tells the reader what you did. It doesn’t address why you did it, what happened, and what you learned. It’s too vague and provides no insight into what actually happened. Instead, consider this more descriptive explanation of the user research step of the process:
- Good explanation of the research step: “To evaluate the new checkout on the Home Depot mobile app, we relied on usage metrics in conjunction with 8 usability tests. This allowed us to gain a deeper understanding by combining both qualitative and quantitative information. Although users were able to get through the checkout more quickly, they continued to struggle with the shipping section. Discussions with users discussion revealed that oftentimes , products in one order have different shipping addresses, which was possible, but difficult in the current checkout.”
Why is this good? This version is much stronger because it goes beyond just talking about what was done. Providing this depth is what will set you apart; articulating your design decisions and the process will help position you as a more mature and thoughtful professional.

3: Write headlines to summarize
At this point, you’re likely freaking out and worried your UX case study is too long. You’re right, it probably is. But remember, what you wrote in your Google Doc is not going to all make its way to your actual UX portfolio
Imagine that your Google Doc is a movie and now it’s time to make the 60-second trailer! This next step will help you start to distill everything down so that you are focusing on the key highlights of the story in your case study.
The best way to do this is to pretend that you have to write your case study only in tweets. It sounds crazy, but it works. For each section of the case study outline, write a single headline or sentence, except for the Process section. For the Process section, you’ll want to have a headline for each step. Continuing with our Home Depot user research example, some of the headlines for the Process section might be:
- Step: What type of research you did and why you did it Headline: “Analytics revealed customers struggled and sometimes abandoned, checkout at the shipping section. To understand why we conducted eight usability tests.”
- Step: Findings from the research Headline : “Usability tests revealed that business customers, versus residential, had different shipping needs, which were not being addressed in the current checkout experience.”
- Step: Impact of research on product development Headline: “We prototyped two new versions of the checkout, allowing customers to choose shipping address on a per-product basis.”
By sticking to a tweet-length character limit, you’ll force yourself to identify the most important points of the case study—which will then become headlines when you create your actual portfolio.
A good way to test whether or not you have strong headlines is to ask yourself if someone would understand the main points of your project by skimming the headlines. If not, then re-write your headlines—because if you want the users of your UX portfolio to quickly understand your project, those are the most important points.
4. Create a compelling title
The big mistake that people make is not giving the project title enough detail when a strong title can give context for the project. As an example, imagine you worked on a user research project related to the checkout process on Home Depot’s mobile app. Consider each of these project titles:
- Poor Title: Home Depot
- So-so Title: Home Depot user research
- Good Title: Home Depot user research for mobile app checkout
Let’s break this down … a title with just the company name, such as “Home Depot” tells the reader absolutely nothing about what you did. It could have been visual design or app development. But the user of your UX portfolio has no idea because the project title was not clear.
A title such as “Home Depot User Research” is a bit better. But it still is vague. Yes, it tells the reader that the project was about user research. But it doesn’t reveal the specific area of focus within the product. Something more specific provides a lot more clarity of your experience such as, “ Home Depot User Research For Mobile App Checkout” .
This is the purpose and strategy of an effective case study project title. It’s much clearer, can you see the difference?
5: Edit & move into portfolio slides
Regardless of the format you choose for your portfolio, your writing needs to be clear and succinct. It won’t happen in one edit! Let’s say you’re making your UX portfolio in Keynote or PowerPoint. Your process will look like this:
- Take the headlines you wrote and place one headline per slide in Keynote.
- Consider that you might merge some bits of information into one slide. For example, you might combine your overview and problem statement. It’s subjective, so you decide!
- Now, you need to go back and start to pull the most important and relevant details from your case study and put them on each slide, as supporting details or evidence.
Examples of UX case studies
To help you see what makes a good UX case study, let’s break down a few good ones. Simon Pan’s Uber case study definitely has reached “viral” status … have you read it? A quick word of caution, yes, it looks good. Simon’s a visual designer. But the reason it went viral goes way beyond the visuals. So don’t let that spin you into Imposter Syndrome.
Simon understands how to write a solid story about the problem, people, product, process, and solution. Here’s what Simon’s Uber case study does well:
- Simon’s case study clearly states the problem and frames the project. Even if I’d never heard of Uber before, I’d have enough context to understand the project.
- Next, Simon explains his process. And he does so as a story. It does not read like a white paper. It’s easy to read and keeps my attention.
- At the end, Simon concludes the case study with some results, reflections, and insights. People don’t just want to know what you did, they want to know the impact of what you did.
- Simon creates a scannable and skimmable experience for the user of his case study. Obviously, Simon is a visual designer and was able to nail the visual presentation of this.
In the video below, I do a quick 5-minute teardown of Simon’s Uber case study.
A well-written case study can serve you for years to come in your UX career
If you follow all these steps, you will have a long-form case study and you’ll have edited it down into something that’s more readable and scannable for the user of your UX portfolio. And remember, the UX case studies you write serve many purposes. Of course, they are the foundation of your portfolio, but they also can feed into:
- Bullet points for your resume and LinkedIn problem
- What you include in cover letters
- How you present a project in a UX job interview
- Articles you publish in the future
- Talks you may give at local UX meetups
Learning to write effective UX case studies will also equip you with crucial written communication skills. This will help you in your day-to-day role as a UX professional as you not only do the work but also educate others and advocate for UX.
Get the Career Strategy Lab Newsletter
Join 40,000+ subscribers who get our weekly actionable tips to help you advance your career & get paid what you're worth.
Read These Next

How to Choose the Best Projects to Include in Your UX Portfolio

13 min read
How to Develop Your Professional Network Throughout Your UX Career

Why You Aren’t Getting Hired After a UX Bootcamp: A 3-Step Job Search Pivot Plan

10 min read
The 3 Users of Your UX Portfolio: Who They Are & What They Look For

How Long Should a UX Case Study or Portfolio Be so it Stands Out to Recruiters?

12 min read
How to ask someone to review your UX portfolio and what you can do to get helpful feedback
Most popular, 4 job search tips from hiring managers who’ve worked at meta, shopify, & ibm, 3 tips to announce you’re ‘open to work’ on linkedin so you can stand out, how to write a ux resume to stand out and get more interviews, get more ux job interviews: 3 principles to product manage your job search.

We stand with Ukraine and our team members from Ukraine. Here are ways you can help

A Community Of Over 800,000
How to Craft an Outstanding Case Study for Your UX Portfoliosit
- December 7, 2020

Writing case studies for your UX portfolio can feel opaque and overwhelming. This article breaks down the anatomy of a UX case study to help you tell a simple and effective story that shows off your skills.
Writing case studies for your UX portfolio can feel opaque and overwhelming. There are so many examples out there, and often the ones that make the rounds are the stunning portfolios of top visual designers. It can be inspiring to see the most beautiful work, but don’t let that distract you from the straightforward format of a good UX case study.
At the core, a UX case study relies on excellent storytelling with a clear, understandable structure . This article breaks down the anatomy of a UX case study to help you tell a simple and effective story that shows off your skills. We’ll start with some general guidelines and structure, then break it down one piece at a time:
1. Before we get started
UX portfolio overview
Before we dive into all the art and science of the case study, here’s a quick refresher on some general guidelines to help you create a job-winning UX portfolio. See what CareerFoundry UX design mentor Tobias has to say about it:
What is a UX case study?
Simply put, a case study is the story of a design project you’ve worked on. The goal, of course, is to showcase the skills you used on the project and help potential employers envision how you’d use those skills if you worked for them.
A case study is typically written like a highly visual article, with text walking readers through a curated set of images. Curated is an important word here, because it should be short and sweet. It’s a chance to share what you want potential employers to know about your work on this project.
With that in mind, case studies are really a UX designer’s secret weapon in two ways. First, they get you in the door by showing more about your work than a resume and a cover letter ever could. Another benefit is that they’re really handy in job interviews. If someone asks about a past project, you can walk them through the case study you’ve already created (this is sometimes a requirement anyway).
General guidelines
I mentioned that UX case studies are about storytelling. I’d actually say they’re about stories-telling, since they need to tell two intertwined stories .
The first is the story of your project. This answers questions like what problem you solved, who your users were, what solutions you explored, and what impact they had.
The second story is about you as a designer and your process. This is more about which methods you chose to use and why, how you worked within constraints, and how you worked as a member of a team (or without one).
How to structure a case study
So what are the steps for an effective case study? Well, like most things in design (and life), it depends. Every case study will be different, depending on what stories you’re telling. The six-part outline below, though, should guide you through an effective format for any UX project story. Here’s the outline (we’ll dive into each component in just a minute):
- Defining the Problem
- Understanding your Users
Early or alternate ideation
- Final solution
Next steps and learnings
How to fill in the details

It’s worth it to add a few general notes before we dive into each of the list items above. For each section, include 1-2 short paragraphs and an image of a deliverable that visually tells the story your paragraphs explain. A reader should be able to either just read or just look at the images and roughly get what this moment in the story is communicating.
When choosing images to include, focus on quality over quantity. Choose your best deliverables for each stage and briefly relate them back to the larger narrative. It can be tempting to overload the page with everything you created along the way, but these extra details should stay in your back pocket for interviews.
Lastly, make sure your case study is scannable . In the best of circumstances, people don’t read word for word on the web. Make sure your text is reasonably concise, use headers and strong visual hierarchy, and use bullet points and lists when possible.
Ok, let’s take a look at each step in a bit more detail.
2. Anatomy of a UX case study
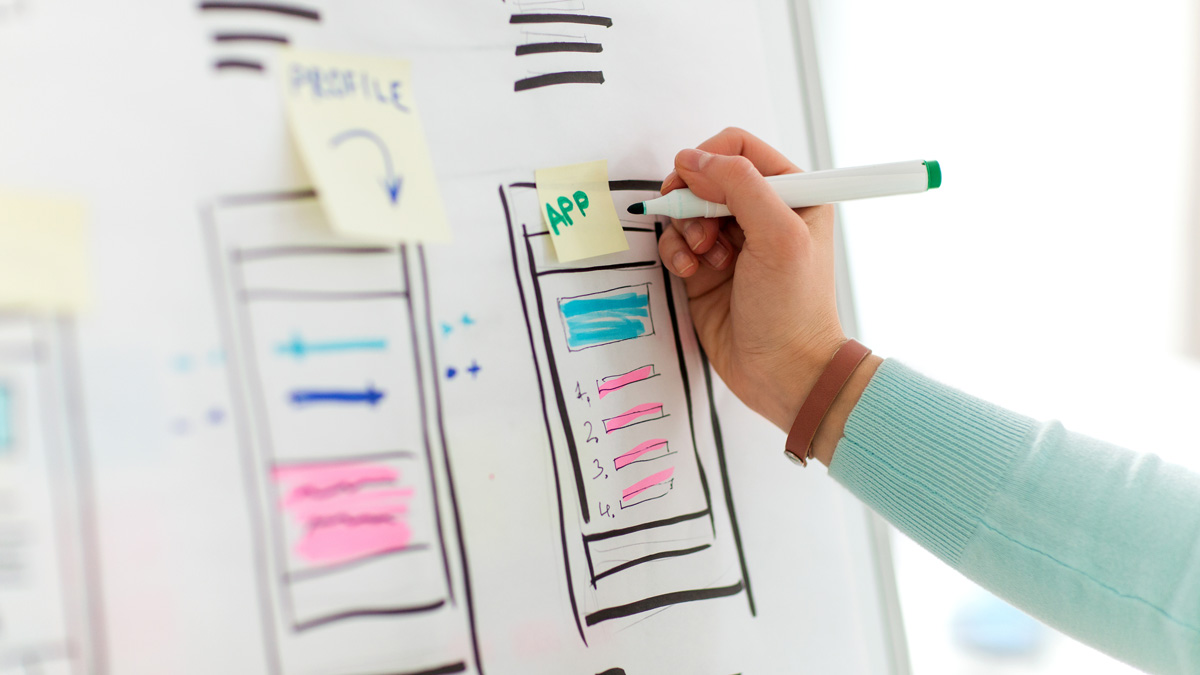

Like any story, the introduction sets the stage and gives much of the necessary context readers will need to understand your project. This is one section where people actually might take some extra time to read carefully as they try to discern what this case study is about. Make sure they have all the details they need.
Some key questions to answer are:
- What is your company and/or product?
- What user problem did you try to solve?
- What was your role?
- What tools and methods did you use?
- What are the major insights, impacts, or metrics related to the project
Defining the problem
After introducing the project, dive more deeply into the problem you tackled. You touched upon this in the introduction, but this section is an opportunity to make a strong case for why this project exists. Did a competitor analysis or market research demand a new product? Was there past user research in your company that suggests a needed redesign of the product?
Remember that you’ll want to create a through-line in the narrative, so try to lay out the problem in a way that frames your design work as a solution.
Deliverables that work really well for this section would be:
- Analytics or usage data
- Market research of internal business metrics
- Survey results or interview highlights
Understanding your users
After explaining the problem, show how it impacts your users and their interaction with your product. If you did original user research or you’re seeking user research-oriented jobs, sharing interview scripts, affinity maps, and spreadsheets can be useful in showing your process.
However, this section shouldn’t be only about your process. A key goal of this section is articulating who your users are and what their needs are. These findings should set up your design work that follows, so try to set up that connection.
A few types of deliverables you might share here are:
- User personas
- Mental models
- Journey maps or customer experience maps
Keep in mind you want to communicate users’ key motivations and challenges, as well as any more specific user groups you identified.
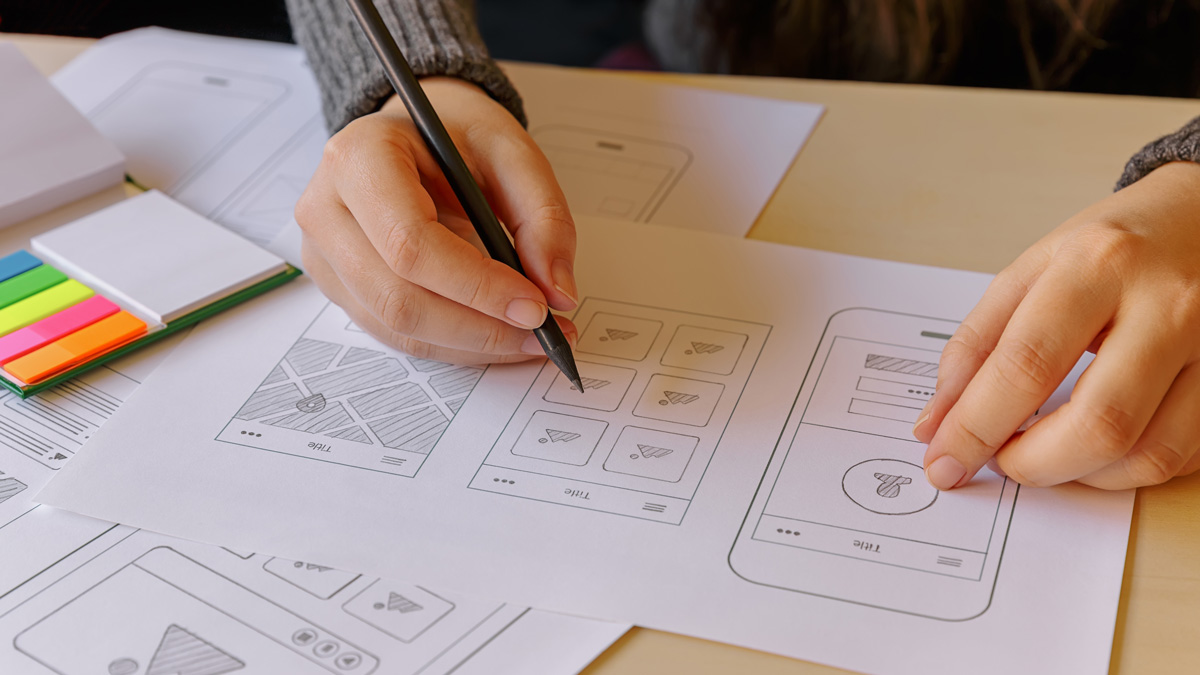

This section can really scale up or down depending on what you have to show. Research shows that hiring managers don’t just want the final product , so it’s clear that showing some of your processes are helpful. Especially for students or designers without a fully built product to show, this can be a moment for you to shine.
Don’t worry about the low fidelity of these documents, but the rougher they are, the more you’ll need to guide readers through them. Everything you show here should teach the reader something new about your process and/or your users.
Artifacts you might include are:
- Pen and paper or low fidelity digital wireframes
If you did early testing or faced constraints that determined your future design work, be sure to include them here, too.
Final design solution
This section should include the most final work you did on the project (e.g. wireframe flows or color mockups) and any final product it led to (if you have it). Be clear, though, about which work is yours and which isn’t.
Explain any key decisions or constraints that changed the design from the earlier stages. If you incorporated findings from usability testing, that’s great. If not, try to call out some best practices to help you explain your decisions. Referring to Material Design, WCAG, or Human Interface Guidelines can show the why behind your design.
If you’re able to show the impact of your work, this can take a good case study and make it outstanding. If your project has already been built and made available to users, have a look at any analytics, satisfaction data, or other metrics. See what you could highlight in your case study to show how your design improved the user experience or achieved business goals. Ideally, you can refer back to your original problem statement and business goals from the introduction.
If you don’t have any way of showing the impact of your project, layout how you would measure the impact. Showing you know how to measure success demonstrates you could do this on future projects.
Lastly, conclude your case study by sharing either your next design steps and/or some key insights you learned from the project. This isn’t just fluff! No project is perfect or final. Showing the next steps is a great way to demonstrate your thinking iterative approach (without having to do the work!).
Also, many companies do (or should do) retrospectives after each project to identify challenges and improve future processes. Use this process and the insights you gain from it to inform your case study. Letting employers know you’re capable of reflection shows humility, self-awareness, and the value you can bring to a team.
3. Final thoughts
Since each case study is a unique story you’re telling about your project, it’s a little art and a little science. But starting with the structure laid out in this article will show who you are as a designer and how you solved a problem. And those are two stories companies want to hear!

- Business UX Leaders , The rise of design , The UX of cars , Things UX People Like , UX Business News , UX Education

I'm a user experience designer with a strong research background. I'm very methodical and research-driven in my approach, but flexible in finding the right method for each project. I design products and services, and I lead in research and design strategy. I've also been teaching design thinking and UX methods at CareerFoundry since February 2017. I've led dozens of students through end-to-end research and design of native mobile apps. I'm a contributing writer to CareerFoundry's blog. My UX work with CareerFoundry helps me work communicate about UX effectively with clients and team members who aren't designers. Learn more about me and see my projects at jonnygrass.com
Related Articles
Ux approach to marketing design: lessons from ikea.
- Design , Design Theory , Design Tools and Software , Marketing and Brand , The rise of design , UX Education , UX Magazine
- The article delves into how integrating UX principles into marketing design can enhance customer engagement and drive business success, using IKEA’s approach as a case study.
Share this link
- June 25, 2024

Tell us about you. Enroll in the course.
First name *
Last name *
Role/title *
Company email address *
Linkedin profile *
Interest in this course: What do you hope to get out of it
If applicable, what AI projects are you working on? describe the initiatives and their objectives and your role in the initiatives
If applicable, what challenges are you faced with in these initiatives?
Describe a future state: If successful, this course will have helped you to ___________
Anything else you'd like us to know about your work or your interest in this course?
Please leave this field empty.
Join 740,000 designers, thinkers, and doers.
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. check our privacy policy and.
How to Make a UX Portfolio That Lands Your Dream Job

Laura Walters

Creating a compelling UX portfolio can be your ticket to standing out in the competitive design industry. However, because of how much impact it can have, it's easy to feel overwhelmed about where to start and what to include.
But don’t worry - you’re not alone, and you don’t have to figure all this out by yourself.
In this guide, I’ll help you build a UX portfolio that communicates who you are, showcases your skills, and emphasizes the value you can bring to a role.
I’ll also cover the most important elements that are designed to help you catch the eye of hiring managers and recruiters, making a strong impression that can lead to exciting opportunities. So that by the end of this guide, you’ll be ready to craft a portfolio that kick-starts your design career.
Ready to get started? Let’s dive in!
Sidenote: Be sure to check out Dan Schifano’s complete career toolkit course if you want to go into even more detail. It covers portfolio design and branding from start to finish.
You can also check out his guide here for some additional examples of great portfolio design .
With that out of the way, let’s get into what you need to include, and more, to make a kick-ass portfolio.
The 7 most important things to include in your UX portfolio
Building an effective UX portfolio involves more than just displaying your work. Your portfolio should be a well-rounded reflection of your skills, experience, and personal design philosophy.
Here’s a breakdown of what to include and how to present it effectively.
#1. Tell people who you are
Always start by introducing yourself, right there on the home page.
This isn't just about listing your qualifications—it's your chance to tell your story.
People want to work with people - not just with skills. So make sure to highlight your background, what drives you as a designer, and what you're passionate about in your work. This introduction should set the tone for your portfolio, giving visitors a sense of who you are right from the start.
Place this introduction at the top of your homepage, where it’s easily visible. Make sure it’s concise yet impactful, and if you have more to share, consider adding an 'About' page that delves deeper into your journey and design philosophy.
#2. Share your project case studies
Your case studies are the heart of your portfolio. They not only show what you’ve done but also provide insight into how you approach problems and deliver solutions, as well as frame the area of your focus.
However, there's a fine line here of how much you should share.
You'll see this in the tips below, but ideally, you want to try to not give too much away in your case studies.
In reality the goal is for the portfolio to be good enough for clients/hiring managers to want to talk to you further. The common next step is a portfolio presentation interview where you are asked to present 1 or 2 projects so it doesn't look good if you can't add more value in the interview.
This is why I recommend adding specific elements to get them interested.
Which case studies should I add?
You need to be selective and avoid turning your portfolio into a repository of old projects that no longer reflect your abilities. Instead, focus on those that align with your career goals and clearly demonstrate your strengths.
How many should I use?
Choose 3-5 projects that best represent your skills and the type of work you want to do in the future.

Go into detail
You don’t just want images. You need to break it all down, so the reader can see what's happening, and what they can expect to get if they hire you.
So, for each case study:
- Start with a brief overview of the project
- Explain the client or the context, the goals of the project, and the specific problem you were solving
- Detail your role in the project—whether you led the effort, collaborated with a team, or worked independently
- And make sure it’s clear what you were responsible for
Throughout, keep in mind the roles you’re aiming for and tailor your explanations to highlight the skills and experiences most relevant to that position.
Integrate story and add emotion
As you walk through your design process inside each case study, be sure to add a narrative story to each.
This helps the reader resonate with the goal, and the impact more.
- Think about the story you’re telling
- Talk about the steps you took, from user research and persona creation to wireframing, prototyping, and user testing
- And be specific about the tools and techniques you used, and explain why you made certain design decisions

Share the results of your work
The impact of your work is crucial, so emphasize the results - what difference did your design make?

If you have metrics like improved user satisfaction or increased conversion rates, include them. If specific metrics aren’t available, share what you learned from the project and how it contributed to your growth as a designer.
Don’t forget to add high-quality visuals!
Visuals play a key role in your case studies, so be sure to use high-quality images, wireframes, mockups, and screenshots to illustrate your process.

Don’t just show the homepage page. Go into detail and share behind the scenes!
You can also annotate these visuals to explain key decisions, and where possible, include links to interactive prototypes so viewers can explore your work in more detail.

Just like before with the story, ensure that these visuals are well-integrated into the narrative of your case study, enhancing rather than overwhelming the story you're telling.
Make them easy to access!
You would be amazed how often people make this mistake, but make sure your case studies are easily accessible from your homepage.
The design should be clean and professional, showcasing your work without distracting from it, and your visitors should be able to navigate your portfolio effortlessly, finding each case study with minimal clicks.
#3. Showcase your skills and tools
Now that you’ve shown your work and possibly hinted at skills, give them a list of what you can actually do (and be sure to update it). This helps to provide a quick reference for hiring managers.
However, rather than just listing each of the tools , think about how you can creatively present this information. (Hiring managers see these all the time, so any chance to stand out is always good).
For example, you might integrate icons or a visual layout that makes it easy to scan.

#4. Share any relevant educational credentials
Although tech cares more about skills and proof (i.e. your case studies), if you have any relevant educational credentials or certifications, then it doesn’t hurt to add those also in your resume or about page.
It’s also a good way to show that you follow the continuous education and improvement path .
#5. Add any personal and side projects
If you have personal or side projects that showcase your creativity and initiative, include them in your portfolio also.

These projects can be just as telling as professional work , especially when they demonstrate your ability to think outside the box or tackle problems independently. So make sure to treat these projects with the same level of detail as your professional case studies!
Just like before:
- Describe the problem
- Outline your process, and
- Highlight the outcomes
You can also take this further by including adjacent work, such as writing a blog , speaking at events, or contributing to podcasts.

This shows that you’re engaged with the broader design community, which can make you stand out as a proactive and passionate candidate.
However, just like before, be smart about which ones you choose to include!
When framing these projects, consider how they fit into your overall career narrative:
- Are they aligned with the type of work you want to pursue?
- Do they showcase a particular skill or interest that complements your professional projects?
Use these personal projects to round out your portfolio, demonstrating your versatility and commitment to continuous learning - while also showing where your passions lie.
#6. Help people trust you with testimonials
Positive feedback and testimonials from clients, colleagues, or mentors can easily add a layer of credibility to your portfolio.

They help vouch for your skills and professionalism, reinforcing the impression you’ve made with your case studies.
However, rather than have a separate page for these, I recommend placing these testimonials strategically throughout your portfolio, perhaps following relevant case studies or in a dedicated section.

Then, as your career progresses, consider adding company logos alongside testimonials to provide a snapshot of the breadth of your experience. (These always look great on the front page under your intro section).

This helps to build trust with potential employers or clients, showing them that others have valued your work and contributions.
#7. Make it easy to contact you!
Make it easy for potential employers or clients to reach out to you. Include your contact details, such as email address, LinkedIn profile, and any other relevant information, right where it’s easy to find.

The goal is to make it as simple as possible for someone to get in touch with you after being impressed by your portfolio.
Offering a downloadable resume is also a good idea, as it allows hiring managers to quickly access your full professional history.
Ready to make your own portfolio?
Creating a UX portfolio is a crucial step in building a successful career in design. It’s your opportunity to showcase your skills, highlight your design process, and demonstrate your ability to solve real-world problems.
Just remember that your portfolio is a living document that should evolve with your career. So be sure to regularly update it with new projects and insights, and always strive to improve it as your skills grow.
So what are you waiting for? Start building your UX portfolio today, and take the first step towards showcasing your unique design talent to the world. You've got this!
Don’t forget if you want to check out a deep dive on how to not only layout and design a professional portfolio- but also how to build it- then check out Dan Schifano's complete career and branding toolkit course.
Better still? If you join the Zero To Mastery Academy as an ongoing member, you’ll have access to the entire course library - covering Figma , Mobile Design , and much more .
Not only that, but you also get access to a private Discord community of designers and developers. So you can ask questions from teachers, and get feedback from other students and working design professionals!
Check them out today, and fast-track your design career!

The Complete Career Toolkit: Personal Branding, Resume Building + more
Let's get serious about reaching your career goals. We'll help you set yourself apart from everyone else by building your personal brand + a professional resume, cover letter & portfolio website that make you STAND OUT.

Motion Design with Figma: Animations, Motion Graphics, UX/UI
Learn motion design using Figma from a design industry pro. This projects-based course will teach you how to use motion to take your designs (and portfolio) to the next level.

Complete Web & Mobile Designer in 2024: UI/UX, Figma + more
Go from complete beginner to getting hired as a Designer in 2024! This is the only design bootcamp you need to learn and master web design, mobile design, Figma, UI & UX, and HTML + CSS.
More from Zero To Mastery

After 10+ years as a Designer, I've made the mistakes so you don't have to. I'll teach you the 4 steps to make your design handoff run as smooth as water!

Want to learn Figma but not sure where to start? In this guide, I break down the basics of Figma, so you can understand what everything does + how to use it!

There are 7 essential questions that will be asked at almost every web design interview. Learn the answers they want to hear and lock down that new job!

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Make sure your text is reasonably concise, use headers and strong visual hierarchy, and use bullet points and lists when possible. If you need a refresher on how to achieve this, check out our guide to the principles of visual hierarchy. Ok, let's take a look at each step in a bit more detail. 2. Anatomy of a UX case study.
You can use a UX case study to engage your readers in your thought process through each design stage. As a result, your readers will gain a solid understanding of the "how" of your UX designs and hopefully understand how working with you or your company benefits them. 3. Highlight (solved) user issues.
In this article, we'll guide you through the process of creating an effective UX/UI case study that leaves a lasting impression. 1. Choose a Project. The first step in creating a compelling UX/UI case study is to select the right project. Choose a project that not only showcases your design skills but also aligns with your interests and passions.
The structure is very simple: The idea story begins by raising a question; it ends when the question is answered.". Idea stories have a structure of discovery, so the question is naturally a "why", "how" or "what if", exactly the type of thing that UX professionals ask themselves daily.
Finally, highlight the results of your design, including metrics, feedback from users, and the overall impact on the business or users. Another important aspect of writing a compelling UX case study is to make it visually appealing and easy to read. Use images, diagrams, and other visual aids to help illustrate your design process and results.
Most UX case studies follow this similar formula, with a walkthrough of your design process, and can be broken down into 5 sections: Overview. Define the scope. Give your audience a high-level project overview and context of the project. The first paragraph should tell the reader what you're planning to talk about.
10 Steps to Create a UX/UI Case Study. Step 1. Introduction. Your introduction sets the stage for your case study, providing readers with a clear understanding of the project's background and your involvement. Here's how to craft a compelling introduction:
A UX case study is a detailed analysis and narrative of a user experience (UX) design project. It illustrates a designer's process and solution to a specific UX challenge. A UX case study encompasses an explanation of the challenge, the designer's research, design decisions and the impact of their work. UX designers include these case studies ...
Create your case study. Choose a platform. You can host your case studies anywhere that allows you to create a webpage with text and images, but I recommend hosting them here on Medium or directly on your portfolio website. Outline your case study. Outline the things you want to include in the sections listed above.
Bad: Home Depot. Step 2. Write an outline. Lay out your thoughts before you start giving up the details. An outline's purpose is to help you understand the "big picture" of your project, so you can decide how to structure your case study or if the project is big enough to merit more than one case study.
As far as UX case studies go, this one provides practical insight into an existing, widely used e-commerce feature, and offers practical solutions. 7. New York Times App. Using a creative illustration website, the designers proposed a landing page feature "Timely" that could counter the problems faced by the NYT app.
2. Define the Problem: Start your case study by clearly defining the problem you were trying to solve. Explain the context, the pain points, and the goals of the project. Highlight the challenges you faced, as well as any research or data that supported your problem identification process. 3.
Step 1: Case Study Overview. Two major components make up the case study overview. The first is a summary of the project. Keep it around three or four sentences. It might be helpful to wait until you finish writing the entire case study to summarize what you just wrote. 17 Must-Read Books for Product and UX Designers
The best way to write a case study is to tell it like a story. This way, your case studies become a vessel through which recruiters can imagine a future working with you, since they get to experience and understand exactly how you solve a design problem. Your recruiters will also enjoy the familiarity and structure of a story arc, and they'll ...
Contents. Step 1: Define the Scope. Step 2: Define the problem. Step 3: Define the Audience. Step 4: Solve the problem. Step 5: Show your work. SHARE this article. The first day I sat down to write a UX case study, I had no idea what I was doing. I remember that I wanted to write about an app that I was using constantly, called MyFitnessPal.
A case study should reflect a meaningful, learning or growth design experience where you worked with real stakeholders and created something of value for the customers. If you are creating case studies solely for the purpose of populating your portfolio, I guarantee those won't be competitive enough. So please don't think of a case study as ...
It always helps if you can create a video explaining your case study. Make sure not to explain the solution for more than 5 minutes, as the recruiters and managers don't have that much time. The preferred time for the explainer video is 3 minutes. 8. Uploading to Portfolio
How to enhance your UX Case Study. Key things that I always like to include in my case studies to make them more interactive and engaging: A video or gif of the final product; A prototype; Brand imagery to create immersive narrative; UX Case Study Folder structure. I like to create a folder structure for housing everything I will need as follows.
Make the stories as simple as possible: like most good stories, there should be one key point. This matters because your reader may be too busy to really understand the detail of the work. You can ...
UX Case Study Template. Description: The Comprehensive Case Study Template is a thoughtfully designed Figma file created to help you showcase your projects and share your design process with the Figma community. This template is perfect for designers, researchers, and UX professionals who want to present their work in a clear and engaging manner.
The 5 steps to write a UX case study; How to actually tell a story of your process; At the end of the article, you'll find some examples of effective UX case studies. A wordf of caution though, I know you're tempted to go look at example case studies and copy them. But don't forget, copying other people's UX case studies won't do you ...
In the best of circumstances, people don't read word for word on the web. Make sure your text is reasonably concise, use headers and strong visual hierarchy, and use bullet points and lists when possible. Ok, let's take a look at each step in a bit more detail. 2. Anatomy of a UX case study. Background.
Place this introduction at the top of your homepage, where it's easily visible. Make sure it's concise yet impactful, and if you have more to share, consider adding an 'About' page that delves deeper into your journey and design philosophy. #2. Share your project case studies. Your case studies are the heart of your portfolio.
Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT). Image by retently When to Use CSAT. Form with the satisfaction score can be triggered in two cases—either a specific interaction with a product (for example, immediately after a customer purchases a product or used a particular feature) or on an ongoing basis (as a part of collecting customer feedback over time).
Employees expressed concern about how their leave could impact their colleagues.; Leave conflicts arise when multiple team members request time off on the same days, leading to staffing shortages and disrupted workflows.; Work planning and leave planning often occurred in separate systems, causing unexpected disruptions, misleading deadlines, and poor resource management.