
Small Business Trends
How to create a farm business plan.

It’s something you nurture, revise, and expand as circumstances dictate and as your farm business matures. Feeling pressure to perfect your business plan from the outset could be paralyzing. Instead, we suggest you view this document as a foundation that can be continuously built upon.
Therefore, your farm business plan should not only anticipate these challenges but also prescribe adaptive measures to navigate through them. It’s this inherent adaptability that transforms a good farm business plan into a great one.
Writing a Farm Business Plan Template: 15+ Things Entrepreneurs Should Include
Creating a robust business plan is of paramount importance, whether you’re kickstarting a farm venture or acquiring an existing one. Our farm business plan template starts off with an executive summary.
Executive Summary
Goals and objectives, introduction, mission statement and values of your farming business plan.
This section enables you to express the core values that led you to the farming business, whether it’s an urban farming venture or a homemade product-based farm. Your mission statement should reflect these values. Sustainable practices and conservation are often key motivations that draw people to farming, so don’t be shy to share your commitment to such principles.
Industry History
Company background and history, competitor analysis, target market.
Clearly define your target market. This can include area groceries, farmers’ markets, or online customers. If you’ll be relying on online sales, ensure your website is professionally designed, keyword optimized, and easily discoverable.
Products and Services
Organization, human resources, and management plans, swot analysis, growth strategy.
A comprehensive growth strategy should outline your plans for debt reduction, savings, and business expansion. Keeping detailed farm production records is key to evaluating the effectiveness of your growth strategy.
Financial Plan
Marketing strategy, establishing a farming business entity, detailed description of farm operations, risk management strategies.
Address potential risks and challenges your farm might face, such as natural disasters, market fluctuations, or pest infestations. Discuss the strategies you plan to implement to mitigate these risks, like insurance coverage, diversification, and emergency response plans.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Community involvement and social responsibility, supply chain and vendor relationships, technology and innovation.
Discuss the role of technology and innovation in your farm business. This could include the use of precision agriculture, innovative irrigation systems, or the adoption of farm management software to enhance efficiency and productivity.
Training and Development Plans
Expansion and diversification, exit strategy.
Wrap up your business plan with a conclusion that reiterates your farm’s core mission and vision, and express your enthusiasm and commitment to making your farm business a success.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do I Need a Business Plan for My Farm?
One of the many advantages of constructing your business plan is the opportunity it affords to involve others. Employees, family members, even your loyal farm dog might have innovative small farm business ideas that could significantly enhance your farm’s productivity and marketability. A different perspective can often yield solutions for issues you might not have even been aware of. Therefore, encourage an open exchange of thoughts and ideas. Who knows, the next great idea could be lying right under your hay bale!
How Do I Write a Small Farm Business Plan?
Don’t sit down to write the whole thing. Chip away, one section at a time. Keep in mind that the plan doesn’t have to be the definitive last word. You can make adaptations.
How do you start a farm business plan?
How much do farm owners make a year, how much does it cost to start a small farm, what is the most profitable farming business.
Poultry farming is currently the most profitable – and common – farm business in the world. It includes chicken, turkey, quail, ducks and goose, that are being raised for meat or eggs.
Starting a Small Farm: A Complete Beginner’s Guide
Starting a small farm can be a challenging and rewarding experience. As someone who has started their own small farm, I can tell you it takes a lot of hard work and dedication.
Whether you’re looking to start a small farm for personal consumption or to sell your products at local markets, there are a few key steps you’ll need to take to get started.
Once you’ve identified your niche, you’ll need to find suitable land to start your farm.
This can be challenging, especially if you’re on a tight budget. Still, various resources are available to help you find affordable land.
Once you’ve secured your land, you’ll need to develop a business plan and figure out how you’ll finance your farm. This may involve applying for grants or loans or finding investors interested in supporting your vision.
Assessing Your Goals and Resources
Defining your goals.
Before starting a small farm, it is essential to define your goals. Ask yourself what you want to achieve by starting a farm. Do you want to grow crops, raise animals, or both?
Are you looking to make a profit or just have a self-sustaining homestead? Do you want to sell your products locally or nationally?
Assessing Your Resources
Assessing your resources is also an important step in starting a small farm. You need to determine what resources you have available to you, such as land, water, equipment, and capital.
Start by evaluating your land. Do you own land or will you need to lease or purchase it? Is the land suitable for farming, or will you need to make improvements? Consider the soil quality, drainage, and access to water.
Finally, assess your financial resources. Starting a small farm can be expensive, so it is important to determine how much capital you have available and how you will finance your farm.
Consider applying for grants or loans from organizations like the USDA or local banks.
READ ALSO: How Farmers Can Earn Money From YouTube (Complete Guide)
Choosing a Farming Method
Conventional farming.
When it comes to conventional farming, the focus is on maximizing yield and minimizing costs. This method relies heavily on synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides to control pests and maximize crop yields.
Conventional farmers also use genetically modified seeds engineered to resist pests and diseases.
Organic Farming
Organic farming is a method that relies on natural processes to cultivate crops and raise livestock. This method avoids the use of synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides and instead focuses on building healthy soil through the use of compost and other organic matter.
Organic farmers also avoid using genetically modified seeds and instead rely on natural methods to control pests and diseases.
Permaculture
Permaculture is a method of farming that focuses on designing sustainable ecosystems that mimic natural systems.
This method involves using a variety of plants and animals that work together to create a self-sustaining ecosystem.
This method can be highly effective in creating a sustainable and resilient farm ecosystem. When choosing a farming method, it’s essential to consider your goals and values as a farmer.
Conventional farming may be a good choice if you’re looking to maximize yields and minimize costs, but it can negatively impact the environment and human health.
Permaculture may be the best choice if you’re looking to create a self-sustaining ecosystem that mimics natural systems.
Ultimately, the choice of farming method will depend on your goals, values, and resources as a farmer.
Selecting Your Farm Site
When starting a small farm, choosing the right location is crucial to success. Here are some factors to consider when selecting your farm site:
Climate and Soil
The climate and soil of your farm site will determine which crops and livestock you can raise. Research the average temperature, rainfall, and growing season length of your area.
Water Resources
Access to water is essential for any farm. Look for a site with a reliable water source, such as a well or a nearby stream.
You should also consider the quality of the water, as it can affect the health of your crops and livestock. If you plan to irrigate your crops, make sure your site has the necessary infrastructure in place.
Access to Markets and Customers
You should also research the demand for your products in your area to ensure a viable market for your farm.
By taking these factors into account, you can select a farm site that will set you up for success in the long run.
Planning Your Farm
Developing a business plan.
To start a small farm, it’s crucial to have a clear idea of what you want to achieve and how you plan to achieve it. Developing a business plan is an essential step in this process.
When developing a business plan, consider the following questions: What crops or livestock will you produce?
Who is your target market? How will you market your products? What are your start-up costs and ongoing expenses? What are your projected revenues and profits?
Creating a Farm Layout
It can help you optimize your use of space, improve efficiency, and reduce costs. When creating a farm layout, consider the following factors: What is the size and shape of your land? What is the topography and soil type?
What are the climate and weather patterns in your region? What is the water source and availability? What are the zoning and land use regulations in your area?
Choosing Crops and Livestock
Here are some tips to help you choose the right crops and livestock for your farm:
READ NEXT: The Key to Safe Towing: Understanding Trailer Tongue Weight
Financing Your Farm
Finding funding sources.
The USDA offers various programs and services to help farmers get started or grow their operations, including farm loans, crop insurance, conservation programs, and disaster assistance.
Additionally, there are private lenders, grants, and crowdfunding platforms that you can explore. When researching funding sources, it’s essential to consider the eligibility requirements, interest rates, repayment terms, and any other fees associated with the loan or grant.
Applying for Loans and Grants
Once you’ve identified potential funding sources, it’s time to start the application process. Applying for loans and grants can be a time-consuming and challenging process, but it’s essential to be thorough and accurate in your application to increase your chances of approval.
When applying for loans, you’ll need to provide financial statements, tax returns, and other documentation to demonstrate your ability to repay the loan.
When applying for grants, you’ll need to provide detailed information about your farm and explain how the grant will help you achieve your goals.
You may also need to provide financial statements, tax returns, and other documentation to demonstrate your eligibility for the grant.
By researching your options and being thorough in your application, you can increase your chances of securing the funding you need to start or grow your farm.
Managing Your Farm
One of the most important aspects of running a successful farm is managing it effectively. This involves managing your finances, marketing your products, and managing your land and livestock. In this section, I will discuss each of these areas in more detail.
Managing Your Finances
This can be done using financial software or by hiring an accountant.
It is also important to have a solid business plan in place. This will help you stay on track and make informed decisions about your farm. Your business plan should include your goals, marketing strategy, and financial projections.
Marketing Your Products
This can include advertising, social media, and attending farmers’ markets and other local events.
You should also consider offering CSA (Community Supported Agriculture) shares. This is a great way to build a loyal customer base and secure a steady source of income.
Managing Your Land and Livestock
This involves regular maintenance and upkeep of your farm, including fertilizing, planting, and harvesting. You should also have a plan in place for managing pests and diseases.
When it comes to livestock, it is important to provide them with proper nutrition, shelter, and medical care. You should also have a breeding plan in place to ensure the sustainability of your herd or flock.
Machinery, engines, and farming have always been a passion of his since he was a young boy. Growing up on a small farm in rural America, he learned the value of hard work and dedication from an early age.
After completing his degree in Engineering, he decided to follow his dream and became a farmer in 2009.
Related Posts
Square baler vs. round baler (quick read), are tractors bad for the environment (uh-oh), kubota vs. massey ferguson (most popular tractors comparison), can my kid ride in a tractor (good idea).
- Business plans
Farm Business Plan
Used 5,069 times
Farm Business Plan gives an overview of the company, including corporation history, owner backgrounds, creations and more. Use this template to quickly develop your farm company plan.
e-Sign with PandaDoc
Farm Business Plan Template

Prepared by:
[Sender.FirstName] [Sender.LastName]
[Sender.Title]
[Sender.Phone]
[Sender.Email]
Executive Summary
[Sender.Company] is owned and operated by [Sender.FirstName] [Sender.LastName] .
[Sender.Company] produces and sells (product types, e.g., produce, pastured animals, herbs, etc.), and we also provide on-farm services including (service types, e.g., apple picking, events, produce stand, etc.).
The target audience for [Sender.Company] 's product will be local consumers and businesses whom we will target directly. To market to this audience, we plan to take advantage of public picking events, farmers' markets, and a roadside farm stand.
Future of the Farm
[Sender.Company] plans to turn our XX acres of farmland into a sustainable source of crops, pastured animals, and pollinators. We plan to use regenerative farming practices as much as possible and understand what management techniques work best for our acreage.
Additionally, we will have a large greenhouse and use season extension techniques to get more value out of our farmland.
To build a locally well-known brand and eventually expand our presence across the state.
To sell enough of our product to generate a positive cash flow, support the farm owners and staff, and pay back capital plus 15% interest to our investors.
To preserve and enhance our farmland so that it remains sustainable and we can continue to share the fruits of the land with others.
Follow a thorough 3-year business plan and reassess every year to ensure we remain on track.
Seek funding from our network of contacts and outside funders for start-up costs.
Execute a creative marketing plan that introduces our brand to our target market.
Company Description
Business address and contact.
[Sender.StreetAddress] , [Sender.City] , [Sender.State] [Sender.PostalCode]
[Sender.FirstName] [Sender.LastName] : [Sender.Phone] , [Sender.Email]
Principal Members
(Owner.FirstName) (Owner.LastName)
Qualifications/Experience
(number) years of experience as a farm hand at (farm name), plus an additional 5 years of experience as the farm manager
(Education)
(Operator.FirstName) (Operator.LastName)
(Experience)
Legal Structure
[Sender.Company] is a sole proprietorship.
Company Details
Our property is zoned for farm use, and we plan to use the land as follows:
X acres for pastured animals
X acres for produce
X acres for agritourism activities and events
Farm Assets
Greenhouse and propagation supplies
Farm stand (planned for 20XX)
Market Research
The demand for locally raised animals and grown produce is climbing at a rate of XX% per year and is expected to reach a total value of $XX billion by 20XX.
Consumer demand for free-range, pasture-raised animals is evidenced by farms like (name competitors) which have grown into valuations of (approximate company values) , respectively.
Regulations
[Sender.Company] is a licensed business in the State of [Sender.State] as of the year 20XX. We are in the process of applying for all of the necessary permits for constructing the farm stand, expanding the barn, and hosting on-site visitors to the farm.
Service Line
Product/service.
Services Include:
Pasture-raised animals
Produce cultivation
Public apple picking
Public hay maze
Special event packages
Marketing & Sales
Customer communications.
[Sender.Company] will communicate with its customers by:
Interacting with customers in-person via farmers markets, the farm stand, and through the leveraging of networking events.
Building an active social media presence on Instagram and TikTok.
Advertising agritourism activities like apple picking, hay mazes, farm trails, and other events.
Creating SEO-friendly blog posts on the company website to increase online presence.
Establishing listings with the local tourism board and activity guides.
Sales Strategy
[Sender.Company] 's product will be sold primarily in the (region) . The farm is located on a road with extensive car traffic, so we plan to build a farm stand on the property to capture attention and drive sales.
We also plan to build a social media presence and leverage local advertising to drive awareness of our brand. We will also attend farmers' markets within the region to meet customers face-to-face and build relationships.
Five-year plan
Year One: 20XX
Create a legal business entity
Apply for necessary licenses and permits.
Finalize farm layout.
Procure additional equipment.
Establish social media profiles.
Build a small farm stand.
Attend farmer's markets.
Year Two: 20XX
(List goals for year two)
Year Three: 20XX
Year Four: 20XX
Year Five: 20XX
[Recipient.FirstName] [Recipient.LastName]
Care to rate this template?
Your rating will help others.
Thanks for your rate!
Useful resources
- Featured templates
- Sales proposals
Farm Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Business Plan Outline
- Farm Business Plan Home
- 1. Executive Summary
- 2. Company Overview
- 3. Industry Analysis
- 4. Customer Analysis
- 5. Competitive Analysis
- 6. Marketing Plan
- 7. Operations Plan
- 8. Management Team
- 9. Financial Plan
Farm Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to create your farm business plan.
We have helped over 5,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans and many have used them to start or grow their farms.
Below are links to each section of a small farm business plan template. It can be used to create a vegetable farm business plan, fruit farm business plan, agriculture farm business plans or many other types of rural businesses.
Sample Business Plan For Farms & Agricultural Businesses
- Executive Summary – The Executive Summary is the most important part of your business plan. It is a brief description of your farm, its products and services, potential market opportunity, and competitive advantage.
- Company Overview – Also called the Company Analysis, here, you will provide a detailed description of your agriculture business history, its products and other services, and business structure.
- Industry Analysis – In the Industry Analysis, you will provide an in-depth analysis of the industry in which your farm operates including industry trends, market size and growth, and government regulations.
- Customer Analysis – In the Customer Analysis, you will identify your target market and provide insights into their purchasing habits. You will also create customer segments and discuss your marketing strategy for reaching them.
- Competitive Analysis – In the Competitive Analysis, you will identify your direct competition and provide insights into their strengths and weaknesses. You will also discuss your competitive advantage and how you plan to stay ahead of the competition.
- Marketing Plan – The Marketing Plan includes a discussion of your marketing strategy and tactics along with your pricing strategy. You will also provide a budget for your marketing activities including attending farmers’ markets or advertising a farm stand.
- Operations Plan – In the Operations Plan, you will discuss your farm’s day-to-day operations. You will also provide your business goals that you plan to achieve and a budget for your operating expenses.
- Management Team – In this section, you will provide a brief overview of the farm owners and farm management team, their experience in the agricultural industry, and the organizational chart.
- Financial Plan – In this section, you will provide three-year financial statements for your farm. This will include your income statements, projected balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
Next Section: Executive Summary >
Farm Business Plan FAQs
What is a farm business plan.
A farm business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your farm business. Among other things, a good agriculture farm business plan outlines your business concept, identifies your target audience , presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
You can easily complete your farm business plan using our Farm Business Plan Template here .
What Are the Main Types of Farms?
There are many types of farms. Some have commercial farms that produce crops and agricultural products for sale. Others have cooperative farms owned by people who pool their resources together and share profits among themselves. There are also vegetable farms, dairy, micro, organic, poultry, subsistence, or urban farms.
What Are the Main Sources of Revenues and Expenses for a Farm?
The primary source of revenue for a farm is the sale of its farmed goods such as rice, corn, milk, beef, chicken, depending on the kind of farm a business is.
Some key expenses for a farm are labor expenses, production costs like irrigation, fertilizer, water, and machinery maintenance.
How Do You Get Funding for Your Agriculture Business?
Farm business plans often receive funding from bank loans. Financing is also typically available from grants offered by local and state governments. Personal savings, credit card financing and angel investors are other funding options. This is true for starting any agricultural business.
What are the Steps To Start a Farm Business?
Starting a farming business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
- Develop An Agricultural Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed agriculture business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast. It should also include your business goals and mission statement. You can quickly complete your farm business plan using our Farm Business Plan Template here .
- Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your farm business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your farm business is in compliance with local laws.
- Register Your Agriculture Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your farm business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
- Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your farm business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
- Choose a Business Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
- Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
- Acquire Necessary Farm Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your agricultural business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
- Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your farm business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.
Learn more about how to start a successful farm business and agribusiness planning:
- How to Start a Farm Business
Where Can I Get a Farm Business Plan PDF?
You can download our free farm business plan template PDF here . This is a good farm business plan template you can use in PDF format.
Free Agriculture Sample Business Plan PDF + How to Write
Elon Glucklich
6 min. read
Updated February 7, 2024

Free Download: Agriculture Business Plan Template
As a farmer, you’re in the business of putting food on the table. Agriculture is one of the world’s oldest professions.
Today it accounts for over 5% of U.S. Gross Domestic Product, and 1 in 10 American workers are in agriculture, food, and related industries.
But starting a new agriculture business requires intensive planning and upfront preparation. If you’re looking for a free, downloadable agriculture sample business plan PDF to help you create a business plan of your own, look no further.
Keep in mind that you don’t need to find a sample business plan that exactly matches your farm. Whether you’re launching a larger agricultural business outside a bustling city or a smaller organic operation, the details will be different, but the foundation of the plan will be the same.
Are you writing a business plan for your farm because you’re seeking a loan? Is your primary concern outlining a clear path for sales growth? Either way, you’re going to want to edit and customize it so it fits your particular farm.
No two agriculture farming businesses are alike.
For example, your strategy will be very different if you’re a dairy operation instead of a soybean farm. So take the time to create your own financial forecasts and do enough market research for your specific type of agriculture so you have a solid plan for success.
- What should you include in an agriculture farm business plan?
Your agriculture business plan doesn’t need to be hundreds of pages—keep it as short and focused as you can. You’ll probably want to include each of these sections:
1. Executive summary
An overview of your agriculture business, with a brief description of your products or services, your legal structure, and a snapshot of your future plans. While it’s the first part of the plan, it’s often easier to write your executive summary last.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
2. Business summary and funding needs
Details about your farming operation, including how much capital you will need and the types of funding you’re considering. Include your business history, your current state, and your future projections. It should also cover your business location, the equipment and facilities needed, and the kinds of crops or livestock you plan to raise.
3. Products and services
Provide details on the types of crops, farming methods, and any value-added products you plan to offer, such as finished goods or even agritourism offerings .
4. Marketing plan
Compile your market research findings, including the demand for your products or services, your target customers , and your competitors. It should also outline your marketing strategy—how you plan to attract and retain customers.
5. Financial plan
Your revenue projections, cost estimates, and break-even analysis. Your financial plan and forecasts should demonstrate that your business has a path to profitability.
- Building on your farm business plan sample
With a free agriculture business plan template as your starting point, you can start chipping away at the unique elements of your business plan.
As the business owner, only you can speak to aspects of your agriculture operation like your mission and core values.
You’re putting in the long hours to start a thriving farm business, so aspects of your mission – like a commitment to sustainable farming practices – will be best explained in your own words. Authenticity will help you connect with a growing market of consumers who value transparency and environmental stewardship in their food sources.
As for more conventional aspects of business planning , you will want to take on things like your marketing and financial plans one at a time. Here are a few specific areas to focus on when writing your business plan.
Invest time in market research
Starting an agriculture operation requires significant startup costs. When you throw in the unique land use considerations involved, it’s crucial to conduct thorough market research before investing hundreds of thousands – or even millions – of dollars into a farm business.
Start by researching the types of farms operating in your locality and wider region, and the specific crops or livestock they specialize in. You will need to understand seasonal trends, including crop yields and livestock productivity.
Note the demographics of the local community to understand their buying habits and preference for local produce. Also, be aware of the competitive landscape and how your farm can differentiate itself from others. All of this information will inform your service, pricing, marketing, and partnership strategy.
From there, you can outline how you plan to reach your target market and promote your farm’s offerings.
Craft your agriculture go-to-market strategy
One of the things that makes an agriculture farm business plan different from some service-based business plans is that you might decide to work only with one or two businesses that purchase your goods.
You may offer different tiers of products to different types of buyers, such as produce for an organic farmers market, and corn for another farm’s animal feed. If that’s the case, make sure you include ideas like setting aside land for organic growth and maintenance.
Discuss your advertising and promotional strategies, emphasizing channels relevant to your target market. Also, consider how partnerships with local businesses, farmers’ markets, and other industry stakeholders can enhance your visibility.
Include your pricing strategy and any special promotions or loyalty programs. Also, consider public relations and media outreach efforts that can raise awareness about your farm and its sustainable practices.
Prepare for unique farming challenges
Running an agricultural business comes with its own set of challenges, including weather-related disruptions and market volatility. Your business plan should identify these potential risks and present contingency plans to address them.
Include a plan to mitigate weather-related risks, such as crop diversification, employing weather-resistant farming practices, investing in appropriate infrastructure like greenhouses or drainage systems, or taking out insurance to cover weather-related losses.
Detail the operational aspects of your business , including land ownership, employee status, farm maintenance, and safety requirements. Also, illustrate your strategies for managing crop production, livestock care, land stewardship, and regulatory compliance.
Plan for the future
Contingency planning is important in all businesses.
But the unique challenges in agriculture of changing market dynamics, regulatory changes, and climate impacts make it especially necessary to plan for the future. Detail how you’ll measure success, and how you will be prepared to adapt your offerings if you need to change the focus of the business due to factors outside your control.
Also, be ready to discuss opportunities for scaling your business over time, such as introducing new crops, expanding farm operations, or opening additional locations.
- Get started with your farm business plan sample
There are obviously plenty of reasons farm owners can benefit from writing a business plan — for example, you’ll need one if you’re seeking a loan or investment. Even if you’re not seeking funding, the process of thinking through every aspect of your business will help you make sure you’re not overlooking anything critical as you grow.
Download this agriculture farm sample business plan PDF for free right now, or visit Bplans’ gallery of more than 550 sample business plans if you’re looking for more options.
Elon is a marketing specialist at Palo Alto Software, working with consultants, accountants, business instructors and others who use LivePlan at scale. He has a bachelor's degree in journalism and an MBA from the University of Oregon.

Table of Contents
Related Articles

11 Min. Read
How to Write a Business Plan for a SaaS Startup

7 Min. Read
How to Write a Dog Grooming Business Plan + Free Sample Plan PDF

6 Min. Read
How to Write a Fix-and-Flip Business Plan + Free Template PDF

How to Write a Bakery Business Plan + Sample
The LivePlan Newsletter
Become a smarter, more strategic entrepreneur.
Your first monthly newsetter will be delivered soon..
Unsubscribe anytime. Privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

[Pdf Sample] Business Plan For Small Vegetable Farming Docx
Starting a small vegetable farm can be an exciting and rewarding venture. It allows you to grow fresh, organic produce while contributing to sustainable agriculture practices. However, like any business, a well-thought-out plan is essential for success. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide to help you develop a small vegetable farm business plan.
[Pdf Sample] Small Vegetable Farm Business Plan Proposal Docx
Table of Contents
Executive Summary
Read Also: [Pdf Sample] Business Plan For Chili Pepper Farming Docx

Market Research and Analysis
Conducting thorough market research is crucial to understand the demand and competition in the local market. Identify your target audience, analyze consumer preferences, and explore market trends. This information will help you make informed decisions about the crops to grow and pricing strategies.
Farm Goals and Objectives
Define your farm’s long-term goals and objectives. Are you aiming to become a leading supplier of organic vegetables in your region? Do you plan to expand your operations over time? Setting clear goals will provide direction and motivation for your business.
Products and Services
Read Also: How To Preserve Vegetables For Long Time Storage
Target Market
Marketing and sales strategy.
Read Also: 15 Common Diseases of Vegetables Farm And How To Treat
Farm Operations
Equipment and resources.
Outline the necessary equipment, tools, and resources needed to run your farm effectively. Consider factors such as irrigation systems, tractors, greenhouse structures, and storage facilities. Explore options for sourcing equipment, including buying, leasing, or borrowing.
Financial Projections
Watch The Below Video On Guide On How To Write A Business Plan For Small Vegetable Farm
Risk Management
Sustainability and environmental practices.
Here Is The Download Link ToSmall Vegetable Farm Business Plan Proposal By Agrolearner.com
How much land do I need to start a small vegetable farm?
Are there any government grants or funding options available for small vegetable farms, what certifications are important for organic vegetable farming.
Organic certification ensures that your produce meets specific standards. Look into certifications such as USDA Organic or Certified Naturally Grown.
How can I differentiate my farm in a competitive market?
How do i determine the pricing for my vegetables.
In conclusion, starting a small vegetable farm requires careful planning and execution. By developing a comprehensive business plan, conducting thorough market research, and implementing sustainable practices, you can increase the likelihood of success. Remember, flexibility and adaptability are key in the ever-evolving agricultural industry.
Share this:
Author: adewebs, you may also like:, [pdf sample] business plan for pig farming docx, starting a poultry farm with limited resources in ghana: a comprehensive guide for new farmers, how to register agribusiness company in kenya (see full guide), starting a poultry farm with limited resources in nigeria: guide for new farmers, leave a reply cancel reply.

Farm Business Plan Template [Updated 2024]
Farm Business Plan
If you want to start a successful farm or expand your current farming business, you need a business plan.
Fortunately, you’re in the right place. Our team has helped develop over 100,000 business plans over the past 20 years, including thousands of farm business plans.
The following farm business plan template and example gives you the key elements you must include in your plan. In our experience speaking with lenders and investors, the template is organized in the precise format they want.
You can download our Farm Business Plan Template (including a full, customizable financial model) to your computer here.
Example Business Plan For Farm Businesses
I. executive summary, business overview.
[Company Name], located at [insert location here] is a new, 500 acre organic dairy, beef, and wheat farm providing food products to regional distributors. [Company Name] is headed by [Founder’s Name], an experienced farm manager.
[Company Name]will sell high-quality beef cuts, wheat by the bushel, and whole milk. The products will be certified organic as growth hormones, fertilizers and pesticides will not be used in production.
Customer Focus
[Company Name] will primarily serve regional distributors of dairy, beef, and wheat products. Some products may be sold directly to manufacturers in the local area for the production of other products from these ingredients.
These businesses typically gross $5 million to $50 million in annual revenues and source their supplies from farms within a 100 mile radius of their facilities.
Distributors and manufacturers of food products in the region see growth in interest in organic products and are in need of organic ingredients for suppliers. Consumers show increased demand for these organic products at stores.
Management Team
[Company Name]’s most valuable asset is the expertise and experience of its founder, [Founder’s Name]. [First name] has been a farm operations manager for the past 15 years. He has spent much of his career working with Blue Ridge Farms, where he oversaw dairy, meat, and grain production.
[Company name] will also employ an experienced salesmanager to sell to distributors and manufacturers. This will be a skilled salesperson trained in farm sales by [Founder’s Name]. An assistant manager will manage day-to-day operations of the farm.
Success Factors
[Company Name] is uniquely qualified to succeed due to the following reasons:
- [Company Name] will fill a specific market niche in organic foods. In addition, we have surveyed the regional distributors and received extremely positive feedback saying that they explicitly want to buy our products when launched.
- Our location is within 100 miles of numerous potential distributors and contains hundreds of acres of arable land.
- The management team has a track record of success in the farming business.
Financial Highlights
[Company Name] is seeking a total funding of $683,200 of debt capital to open its farm. The capital will be used for funding capital expenditures and location build-out, hiring initial employees, marketing expenses and working capital.
Specifically, these funds will be used as follows:
| Financial Summary | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue | $298,947 | $332,212 | $368,689 | $405,491 | $445,762 |
| Total Expenses | $282,316 | $274,810 | $295,944 | $308,335 | $320,390 |
| EBITDA | $16,631 | $57,402 | $72,745 | $97,156 | $125,372 |
| Depreciation | $41,000 | $41,000 | $41,000 | $41,000 | $41,000 |
| EBIT | ($24,369) | $16,402 | $31,745 | $56,156 | $84,372 |
| Interest | $27,328 | $23,912 | $20,496 | $17,080 | $13,664 |
| PreTax Income | ($51,697) | ($7,510) | $11,249 | $39,076 | $70,708 |
| Income Tax Expense | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $21,639 |
| Net Income | ($51,697) | ($7,510) | $11,249 | $39,076 | $49,069 |
| Net Profit Margin | - | - | 3% | 10% | 11% |
II. Company Overview
You can download our Farm Business Plan Template (including a full, customizable financial model) to your computer here.
Who is [Company Name]?
[Company Name], located at [insert location here] is a new 500 acredairy, beef, and wheat farm providing food products to regional distributors. [Company Name] is headed by [Founder’s Name], an experienced farm manager. 300 acres of its land will be devoted to growing wheat and the remainder will be for dairy, beef, and office facilities.
While [Founder’s Name] has been in the farming business for some time, it was in [month, year] that he decided to launch [Company Name]. Specifically, during this time, [Founder] met with a former friend and fellow independent organic farm owner in South Dakota who has had tremendous success. After discussing the business at length, [Founder’s Name] clearly understood that a similar farm would enjoy significant success in his hometown.
Specifically, the customer demographics and competitive situations in the South Dakota area of his friend and in his hometown were so similar that he knew the business would work. After surveying the local market, [Founder’s name] went ahead and founded [Company Name].
[Company Name]’s History
Upon returning from South Dakota, surveying the local customer base, and finding potential land to start the farm, [Founder’s Name] incorporated [Company Name] as an S-Corporation on [date of incorporation].
The business is currently being run out of [Founder’s Name] home office, but once the land is purchased and [Company Name]’s facilities are finalized, all operations will be run from there.
Since incorporation, the Company has achieved the following milestones:
- Found land and negotiated rate
- Developed the company’s name, logo and website located at [website]
- Determined building, equipment and fixture requirements
- Begun recruiting key employees
[Company Name]’s Products
[Founder’s Name] will be able to provide customers with the following products:
- High-quality organic beef cuts
- Organically-grown wheat by the bushel
- Organic whole milk
III. Industry Analysis
The American commercial farming industry continues to be subsidized by the government to bolster low food prices. This is a volatile and difficult industry in the United States, with small and medium-sized farms increasingly being bought by large farms or struggling to survive on their own.
However, for organic foods, trends are positive. Organic foods sales are projected to increase 18% per year over the next three years and were estimated at $23 billion last year, according to the Organic Trade Association Market Survey. This sector is said to represent 3% of overall food and beverage sales. Global demand for organic foods increases by over $5 billion per year.
The farming industry includes multiple segments including poultry meat, beef, dairy, grain crops, vegetables, fruits, and more. Many businesses focus on only one specific segment, while some produce multiple types of crops in order to hedge against price changes in any one segment.
Recently, Horizon, the largest US organic food brand, dropped the term “organic” from its dairy products choosing instead to use the term “natural”. Critics noted that the term “natural” has no regulatory meaning and shows Horizon’s attempt to lower the cost of production by not meeting the requirements for the organic label. This shows a concern in the market about the meaning behind labels and highlights the importance of regulation to create common definitions.
Organic.org published the following list of reasons to support organic foods and beverages:
- Reduce the toxic load: Keep chemicals out of the air, water, soil and our bodies
- Reduce if not eliminate farm pollution
- Protect future generations
- Build healthy soil
- Taste better and truer flavor
- Assist family farmers of all sizes
- Avoid hasty and poor science in your food
- Eating with a sense of place
- Promote biodiversity
- Celebrate the culture of agriculture
Trends in the industry include the following:
- Meat and fish that are organically produced are becoming more popular
- Organic dairy, bread, and grain are becoming more popular
- Organic-only supermarkets are becoming more popular
- Traditional supermarkets are increasing organic purchases to keep up with these competitors.
IV. Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
[Company Name]will primarily serve regional distributors of dairy, beef, and wheat products. Some products may be sold directly to manufacturers in the local area for the production of other products from these ingredients.
These businesses typically gross from $5 million to $50 million in annual revenues and source their supplies from within a 100 mile radius of their facilities.
Customer Segmentation
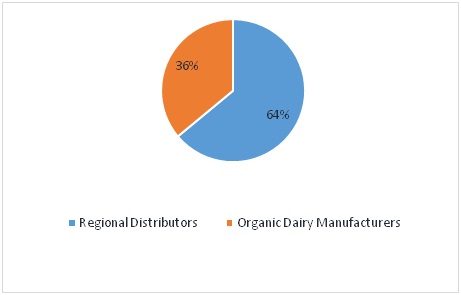
The Company will primarily target the following two customer segments:
- Regional Organic Distributors: Organic food distributors source organic meat, dairy, and grains from medium and large farms, and sell them to food manufacturers who process, package and sell the products.
- Organic Dairy Manufacturers: Small manufacturers that process organic dairy products, such as butter, cream, and cheese work directly with local farms to keep costs low whenever possible.
V.Competitive Analysis
Direct & indirect competitors.
The following twoorganic farms operate within a 100 mileradius of [Company Name]. These, and other smaller organic farms like them, are the direct competitors of the business. Indirect competitors include non-organic dairy, beef, and grain farms.
Nature’s Bounty Farm
Nature’s Bounty Farm is a five-year old farm which produces vegetables and grains for organic distributors. They operate a 1000 acre farm, producing a high volume of goods.
However, Nature’s Bounty Farm does not offer organic dairy and meat, which are up-and-coming products.
Thompson Organics
Thompson Organics is a small, 300 acre, ten-year old farm which produces organic grains and bakes organic breads. They sell all of their products at farmer’s markets and directly at retail stores. This distribution strategy requires Thompson to have skilled customer service and sales employees, as well as facilities for baking and packaging.
Because Thompson avoids selling through to distributors, its brand is known directly by consumers who look for organic foods and it can command a premium. However, they, like Nature’s Bounty Farm, do not offer organic dairy and meat. They also have a high cost structure because of their small scale and operations.
Competitive Advantage
[Company Name] enjoys several advantages over its competitors. These advantages include:
- Client-oriented service: [Company Name] will have a full-time sales manager to keep in contact with customers and answer their everyday questions. [Founder’s Name] realizes the importance of accessibility to customers and will instruct the sales manager to proactively solicit feedback from customers.
- Management: [Founder’s Name] has been extremely successful working in the farming business and will be able to use his previous experience to assure clients of the care that [Company Name] will take to create the best organic products. His unique qualifications will serve customers in a much more sophisticated manner than [Company Name’s] competitors.
- Transparency: To continue to assure customers and the government of the organic quality of [Company Name]’s products, operations can be inspected by customers at a moments notice, and a guide to the operations will be created to detail all of the steps in the production process for each crop.
- Product Line: By offering wheat, dairy, and meat, [Company Name] will seek to hedge against price volatility in any one of these commodities.
VI. Marketing Plan
[Company Name] will use several strategies to promote its name and develop its brand. By using an integrated marketing strategy, [Company Name] will win customers and develop consistent revenue streams.
The [Company Name] Brand
The [Company name] brand will focus on the Company’s unique value proposition:
- High-quality, organic milk, beef, and grains
- Service built on long-term relationships
- Transparency of operations to achieve customer assurance of organic quality
Promotions Strategy
Targeted Cold Calls
[Company Name] will initially invest significant time and energy into contacting potential customers via telephone and then by visiting their facilities. In order to improve the effectiveness of this phase of the marketing strategy, a highly-focused call list will be used; targeting distributors and manufacturers with an expressed interest in organic products. As this is a very time-consuming process, it will primarily be used during the startup phase to build an initial customer base.
Industry Events
By attending regional farming conferences, association meetings, and symposia, [Company Name] will network with industry leaders, and seek referrals to potential customers. [Founder’s Name] will often attend with the company sales manager, but both may attend separately in the future as they gain experience in this networking.
[Company Name] will invest resources in two forms of geographically-focused internet promotion—organic search engine optimization and pay-per-click advertising. The Company will develop its website in such a manner as to direct as much traffic from search engines as possible. Additionally, it will use highly-focused, specific keywords to draw traffic to its website, where potential clients will find a content-rich site that presents [Company Name] as the trustworthy, high quality producer of organic foods that it is.
Pricing Strategy
[Company Name]’s pricing will be competitive compared with Nature’s Bounty Farm. Pricing will be about 50% lower than retail prices to allow for wholesalers and retailers to earn their margins.
VII. Operations
[Company Name] will carry out its sales operations through phone calls and visits to customer offices. The sales manager will increasingly direct sales activities, although [Founder’s Name] will be heavily involved at first.
The assistant manager will run the day-to-day operations of the farm, including scheduling and assigning the work of farm hands, sourcing and purchasing supplies and basic equipment, keeping the company’s books, maintaining legal licenses, handling insurance and insuring that the company meets government regulations. He will contact specialists for equipment repairs when needed and veterinarians to care for the cows when they require medical attention.
Field work by the farm hands will be from sunrise to sunset, with indoor work during the hottest parts of the day and after dark. Field work will include preparing fields for planting, the planting process, tending to planted fields, harvesting, and packaging grain into bushels. Work with the cows will include feeding, taking them in and out of the pasture, and running the milking equipment. It will also include slaughtering and dressing the cows for beef when directed.
[Company Name]’s long term goal is to become the highest quality farmer in the [city] area. We seek to do this by ensuring customer satisfaction and developing a loyal and successful clientele.
The following are a series of steps that will lead to this long-term success. [Company Name] expects to achieve the following milestones in the following [xyz] months:
| Date | Milestone |
|---|---|
| [Date 1] | Close on purchase of land |
| [Date 2] | Design and build out [Company Name] farm buildings |
| [Date 3] | Hire and train initial staff |
| [Date 4] | Kickoff of promotional campaign with targeted cold calls |
| [Date 5] | Produce first harvest |
| [Date 6] | Reach break-even |
VIII. Management Team
[First name] is intimately familiar with the operations requirements for a farm producing the same products as [Company Name]. He has received organic training certification to become an organic food producer.
[Company name] will also employ an assistant manager to manage operations. This will be an experienced operations manager who will be trained in farm operations by [Founder’s Name]. Furthermore, a sales manager will be hired to focus on marketing, sales, and customer service to distributors as manufacturers for [Company Name] products. These two individualswill either have undergraduate business degrees or years of relevant operations or sales experience.
Hiring Plan
In order to launch the business we will also hire the following additional employee:
- Farm Hand: (1 full-time to start) Additional farm hands will be hired if capacity increases or if another farm is started.
The hiring process will be managed by the assistant manager who will be directly responsible for the farm hand, with oversight and approval by [Founder’s Name]. This individual must be in top physical condition, have experience in physical labor, and have great mechanical facility and care for the quality of his work and products.
The assistant manager and [Founder’s Name] will provide back-up support for the farm hand in the busiest times and when he is out sick or on vacation.
IX. Financial Plan
Revenue & pricing.
[Company Name]’s revenues will come primarily fromsale in three product areas.
| Revenue Stream | Current Price | % of Revenue |
|---|---|---|
| Milk | $2 / gallon | 68% |
| Beef | $1 / pound | 8% |
| Grain | $6 / bushel | 24% |
The price of beef is only an average per cow, and individual cuts are sold at market rates depending on the quality of the cut of meat.
Prices are expected to fluctuate with market volatility on the rise, although they are expected to rise consistently, on average.
Key Cost Drivers
As with most services, labor expenses are the key cost drivers. The staff of four will earn competitive salaries allowing [Company Name] to hireexperienced workers. Furthermore, the costs of the mortgage and its interest for the land will be significant.
The major cost drivers for the company’s operation will consist of:
- Marketing expenses (associations, events, internet marketing).
Capital Requirements and Use of Funds
- Build-out of farm and equipment purchases: $273,200
- Initial marketing expenditure: $10,000
- Property down payment: $100,000
- Working capital: $300,000 to pay for marketing, salaries, and lease costs until [Company Name] reaches break-even
Key Assumptions & Forecasts
The following table reflects the key revenue and cost assumptions made in the financial model.
| Acreage for Crops | 300 |
|---|---|
| Number of customers per month | |
| FY1 | 50 |
| FY2 | 75 |
| FY3 | 100 |
| FY4 | 125 |
| FY5 | 150 |
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenues | ||||||
| Product/Service A | $151,200 | $333,396 | $367,569 | $405,245 | $446,783 | |
| Product/Service B | $100,800 | $222,264 | $245,046 | $270,163 | $297,855 | |
| Total Revenues | $252,000 | $555,660 | $612,615 | $675,408 | $744,638 | |
| Expenses & Costs | ||||||
| Cost of goods sold | $57,960 | $122,245 | $122,523 | $128,328 | $134,035 | |
| Lease | $60,000 | $61,500 | $63,038 | $64,613 | $66,229 | |
| Marketing | $20,000 | $25,000 | $25,000 | $25,000 | $25,000 | |
| Salaries | $133,890 | $204,030 | $224,943 | $236,190 | $248,000 | |
| Other Expenses | $3,500 | $4,000 | $4,500 | $5,000 | $5,500 | |
| Total Expenses & Costs | $271,850 | $412,775 | $435,504 | $454,131 | $473,263 | |
| EBITDA | ($19,850) | $142,885 | $177,112 | $221,277 | $271,374 | |
| Depreciation | $36,960 | $36,960 | $36,960 | $36,960 | $36,960 | |
| EBIT | ($56,810) | $105,925 | $140,152 | $184,317 | $234,414 | |
| Interest | $23,621 | $20,668 | $17,716 | $14,763 | $11,810 | |
| PRETAX INCOME | ($80,431) | $85,257 | $122,436 | $169,554 | $222,604 | |
| Net Operating Loss | ($80,431) | ($80,431) | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Income Tax Expense | $0 | $1,689 | $42,853 | $59,344 | $77,911 | |
| NET INCOME | ($80,431) | $83,568 | $79,583 | $110,210 | $144,693 | |
| Net Profit Margin (%) | - | 15.00% | 13.00% | 16.30% | 19.40% |
5 Year Annual Balance Sheet
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASSETS | ||||||
| Cash | $16,710 | $90,188 | $158,957 | $258,570 | $392,389 | |
| Accounts receivable | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Inventory | $21,000 | $23,153 | $25,526 | $28,142 | $31,027 | |
| Total Current Assets | $37,710 | $113,340 | $184,482 | $286,712 | $423,416 | |
| Fixed assets | $246,450 | $246,450 | $246,450 | $246,450 | $246,450 | |
| Depreciation | $36,960 | $73,920 | $110,880 | $147,840 | $184,800 | |
| Net fixed assets | $209,490 | $172,530 | $135,570 | $98,610 | $61,650 | |
| TOTAL ASSETS | $247,200 | $285,870 | $320,052 | $385,322 | $485,066 | |
| LIABILITIES & EQUITY | ||||||
| Debt | $317,971 | $272,546 | $227,122 | $181,698 | $136,273 | |
| Accounts payable | $9,660 | $10,187 | $10,210 | $10,694 | $11,170 | |
| Total Liabilities | $327,631 | $282,733 | $237,332 | $192,391 | $147,443 | |
| Share Capital | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Retained earnings | ($80,431) | $3,137 | $82,720 | $192,930 | $337,623 | |
| Total Equity | ($80,431) | $3,137 | $82,720 | $192,930 | $337,623 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES & EQUITY | $247,200 | $285,870 | $320,052 | $385,322 | $485,066 |
5 Year Annual Cash Flow Statement
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CASH FLOW FROM OPERATIONS | |||||
| Net Income (Loss) | ($80,431) | $83,568 | $79,583 | $110,210 | $144,693 |
| Change in working capital | ($11,340) | ($1,625) | ($2,350) | ($2,133) | ($2,409) |
| Depreciation | $36,960 | $36,960 | $36,960 | $36,960 | $36,960 |
| Net Cash Flow from Operations | ($54,811) | $118,902 | $114,193 | $145,037 | $179,244 |
| CASH FLOW FROM INVESTMENTS | |||||
| Investment | ($246,450) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Net Cash Flow from Investments | ($246,450) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| CASH FLOW FROM FINANCING | |||||
| Cash from equity | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Cash from debt | $317,971 | ($45,424) | ($45,424) | ($45,424) | ($45,424) |
| Net Cash Flow from Financing | $317,971 | ($45,424) | ($45,424) | ($45,424) | ($45,424) |
| SUMMARY | |||||
| Net Cash Flow | $16,710 | $73,478 | $68,769 | $99,613 | $133,819 |
| Cash at Beginning of Period | $0 | $16,710 | $90,188 | $158,957 | $258,570 |
| Cash at End of Period | $16,710 | $90,188 | $158,957 | $258,570 | $392,389 |
Comments are closed.

- Sample Business Plans
- Retail, Consumers & E-commerce
Farming Business Plan
Agriculture is the one industry that consistently does well, irrespective matter the economic conditions of the world. So, for a stable income and career farming business is a great option.
Are you looking to start writing a business plan for your farming business? Creating a business plan is essential to starting, growing, and securing funding for your business. We have prepared a farming business plan template for you to help in start writing yours.

Free Business Plan Template
Download our Free Farming Business Plan Template now and pave the way to success. Let’s turn your vision into an actionable strategy!
- Fill in the blanks – Outline
- Financial Tables
How to Write a Farming Business Plan?
Writing a farming business plan is a crucial step toward the success of your business. Here are the key steps to consider when writing a business plan:
1. Executive Summary
An executive summary is the first section of the business plan intended to provide an overview of the whole business plan. Generally, it is written after the entire business plan is ready. Here are some components to add to your summary:
- Start with a brief introduction: Start your executive summary by introducing your idea behind starting a farming business and explaining what it does. Give a brief overview of the idea that how will your farming business will be different.
- Market opportunity: Describe the target market in brief, and explain the demographics, geographic location, and psychographic attributes of your customer. Explain how your agriculture business meets its needs. Clearly describe the market that your business will serve.
- Mention your services: Describe in detail the products and crops your agriculture farm produces. Also, incorporate all the details about the tools and equipment you will use keeping quality in mind.
- Management team: Name all the key members of your management team with their duties, responsibilities, and qualifications.
- Financial highlights: Provide a summary of your financial projections for the company’s initial years of operation. Include any capital or investment requirements, startup costs, projected revenues, and profits.
- Call to action: After giving a brief about your business plan, end your summary with a call to action, for example; inviting potential investors or readers to the next meeting if they are interested in your business.
Ensure you keep your executive summary concise and clear, use simple language, and avoid jargon.
Say goodbye to boring templates
Build your business plan faster and easier with AI
Plans starting from $7/month

2. Business Overview
Depending on what details of your business are important, you’ll need different elements in your business overview. Still, there are some foundational elements like business name, legal structure, location, history, and mission statement that every business overview should include:
- The name of your farming business and the type of business you are running or will run: organic farming, agricultural farming, dairy farming, commercial farming, or something else.
- Company structure of your farming business whether it is a proprietorship, LLC, partnership firm, or some other.
- Location of your farm and the reason why you selected that place.
- Mission statement: Add a mission statement that sums up your farming business’s objectives and core principles. This statement needs to be memorable, clear, and brief.
- Business history: Include an outline of the farming business history and how it came to be in its current position. If you can, add some personality and intriguing details, especially if you got any achievements or recognitions till now for your incredible services.
- Future goals: It’s crucial to convey your aspirations and your vision. Include the vision of where you see your agriculture in the near future.
This section should provide an in-depth understanding of your farming business. Also, the business overview section should be engaging and precise.
3. Market Analysis
Market analysis provides a clear understanding of the market in which your farming business will run along with the target market, competitors, and growth opportunities. Your market analysis should contain the following essential components:
- Target market: Identify your target market and define your ideal customer. Know more about your customers and which products they prefer: meat, crops, vegetables, or some other products.
- Market size and growth potential: Provide an overview of the agriculture industry. It will include market size, trends, growth potential, and regulatory considerations.
- Competitive analysis: Identify and analyze all other agricultural farms nearby, including direct and indirect competitors. Evaluate their strengths and weaknesses, and explain how your farm can offer qualitative products.
- Market trends: Analyze current and emerging trends in your industry, such as changes in technology, fertilizers, or customer preference. Explain how your farming business will cope with all the trends.
- Regulatory environment: Describe any regulations or licensing requirements that affect the agricultural farm, such as safety codes, or hiring any agricultural engineer or food safety employee.
Some additional tips for writing the market analysis section of your business plan:
- Use a variety of sources to gather data, including industry reports, market research studies, and surveys.
- Be specific and provide detailed information wherever possible.
- Include charts and graphs to help illustrate your key points.
- Keep your target audience in mind while writing the business plan
4. Products And Services
The product and services section of an agriculture business plan should describe the specific services and products that will be offered to customers. To write this section should include the following:
- List the products you will produce or sell, such as crops, fruits, flowers, livestock, or value-added products like cheese or jams.
- Describe each product: Explain the features of your products, such as their quality, variety, and uniqueness. Also, discuss how your products will be packaged and marketed.
- Emphasize safety and quality: In all descriptions of services and products, emphasize the importance of safety and quality. Explain how your farming business will ensure that all services and products are delivered with the highest standards of safety and efficacy.
Overall, the product and services section of a business plan should be detailed, informative, and customer-focused. By providing a clear and compelling description of your offerings, you can help potential investors and readers understand the value of your business.
5. Operations Plan
When writing the operations plan section, it’s important to consider the various aspects of your business operations. Here are the components to include in an operations plan:
- Operational process: Explain the steps taken to produce your crops or raise your livestock. This can involve planting, fertilizing, watering, harvesting, looking after animals, and other activities.
- Technologies: Make a list of the tools and equipment you’ll need to run your farm, including tractors, harvesters, greenhouses, barns, and processing machinery. Describe your plans for purchasing and maintaining your farming business.
By including these key elements in your operations plan section, you can create a comprehensive plan that outlines how you will run your farming business.
6. Management Team
The management team section provides an overview of the individuals responsible for running the farming business. This section should provide a detailed description of the experience and qualifications of each manager, as well as their responsibilities and roles.
- Key managers: Describe the key members of your management team, their roles, and their responsibilities. It should include the owners, senior management, and any other farm manager, soil and plant scientist, agricultural salesperson, or someone else.
- Organizational structure: Describe the organizational structure of the management team, including reporting lines and how decisions will be made.
- Compensation plan: Describe your compensation plan for the management team and staff, including salaries, bonuses, and other benefits.
- Board of advisors: If you have a board of advisors for your business, then mention them along with their roles and experience.
Describe your company’s key personnel and highlight why your business has the fittest team.
7. Financial Plan
When writing the financial plan section of a business plan, it’s important to provide a comprehensive overview of your financial projections for the first few years of your business.
- Profit & loss statement: Create a projected profit & loss statement that describes the expected revenue, cost of products sold, and operational costs. Your farm’s anticipated net profit or loss should be computed and included.
- Cash flow statement: Estimate your cash inflows and outflows for the first few years of operation. It should include cash receipts from clients, payments to vendors, loan payments, and any other cash inflows and outflows.
- Balance sheet: Prepare a projected balance sheet, which shows the business’s assets, liabilities, and equity.
- Break-even point: Determine the point at which your farming business will break even, or generate enough revenue to cover its operating costs. This will help you understand how much revenue you need to generate to make a profit.
- Financing needs: Estimate how much financing you will need to start and operate your farming business. It should include both short-term and long-term financing needs, such as loans or investment capital.
Remember to be realistic with your financial projections, and to provide supporting evidence for all of your estimates.
8. Appendix
When writing the appendix section, you should include any additional information that supports the main content of your plan. This may include financial statements, market research data, legal documents, and other relevant information.
- Include a table of contents for the appendix section to make it easy for readers to find specific information.
- Include financial statements such as income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. These should be up-to-date and show your financial projections for at least the first three years of your business.
- Provide market research data, such as statistics on the size of the agriculture industry, consumer demographics, and trends in the industry.
- Include any legal documents such as permits, licenses, and contracts.
- Provide any additional documentation related to your business plans, such as marketing materials, product brochures, and operational procedures.
- Use clear headings and labels for each section of the appendix so that readers can easily find the information they need.
Remember, the appendix section of your farming business should only include relevant and important information that supports the main content of your plan.
The Quickest Way to turn a Business Idea into a Business Plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
This farming business plan sample will provide an idea for writing a successful farming business plan, including all the essential components of your business.
After this, if you are still confused about how to write an investment-ready agriculture business plan to impress your audience, then download our farming business plan pdf .
Related Posts
Farmers Market Business Plan
Organic Farm Business Plan
Small Farming Business Plan
400+ Business Plan Template Example
How to make Business Plan Cover Page
Best Business Planning Tools
Frequently asked questions, why do you need a farming business plan.
A business plan is an essential tool for anyone looking to start or run a successful farming business. It helps to get clarity in your business, secures funding, and identifies potential challenges while starting and growing your farming business.
Overall, a well-written plan can help you make informed decisions, which can contribute to the long-term success of your farming business.
How to get funding for your farming business?
There are several ways to get funding for your agriculture business, but one of the most efficient and speedy funding options is self-funding. Other options for funding are!
- Bank loan – You may apply for a loan in government or private banks.
- Small Business Administration (SBA) loan – SBA loans and schemes are available at affordable interest rates, so check the eligibility criteria before applying for it.
- Crowdfunding – The process of supporting a project or business by getting many people to invest in your farming business, usually online.
- Angel investors – Getting funds from angel investors is one of the most sought options for startups.
- Venture capital – Venture capitalists will invest in your business in exchange for a percentage of shares, so this funding option is also viable.
Apart from all these options, there are small business grants available, check for the same in your location and you can apply for it.
Where to find business plan writers for your farming business?
There are many business plan writers available, but no one knows your business and idea better than you, so we recommend you write your farming business plan and outline your vision as you have in your mind.
What is the easiest way to write your agriculture business plan?
A lot of research is necessary for writing a business plan, but you can write your plan most efficiently with the help of any farming business plan example and edit it as per your need. You can also quickly finish your plan in just a few hours or less with the help of our business plan software.
About the Author

Vinay Kevadiya
Vinay Kevadiya is the founder and CEO of Upmetrics, the #1 business planning software. His ultimate goal with Upmetrics is to revolutionize how entrepreneurs create, manage, and execute their business plans. He enjoys sharing his insights on business planning and other relevant topics through his articles and blog posts. Read more
Plan your business in the shortest time possible
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee

Create a great Business Plan with great price.
- 400+ Business plan templates & examples
- AI Assistance & step by step guidance
- 4.8 Star rating on Trustpilot
Streamline your business planning process with Upmetrics .


Apply MyCAS
- In the News
- Upcoming Events
- Online Classes
- Agricultural Tourism
- Beginning Farmers
- Dry Farming
- Olive Research for Oregon
- Whole Farm Management
- Start Your Business Plan
- Refine Your Business Plan
- Business Planning Resources
Sample Business Plans
- Berries & Grapes
- Biodiversity & Pest Management
- Harvest & Handling
- Herbs & Flowers
- Nursery Crops & Greenhouses
- Tree Fruits & Nuts
- Winter Farming
- Disaster Relief and Resiliency Programs
- Dry Farming Research
- Community Support Agriculture
- Farmers' Markets
- Marketing Your Farm
- Meat & Eggs
- Raw Agricultural Products
- Value Added
- Organic Fertilizer and Cover Crop Calculators
- Hay Production
- Irrigation & Fencing
- Mud & Manure Management
- Nutrient Management
- Pasture and Grazing Management
- Weeds, Poisonous Plants, & Other Pests
- Soil Testing
- Soil Surveys
- Improving Soil Quality & Cover Crops
- Agricultural Composting and Water Quality
- Water & Irrigation
- Business Planning

Below are examples of different farm business plans and a loan application:
Oregon Flower Farm Business Plan Example
Interval Farm Business Plan Sample
Peach Farm Business Plan Sample
USDA FSA Sample Microloan Application
How to Start a Small Farm Business
- Swarthmore College
Treehugger / Lexie Doehner
- Urban Farms
- Planting Guides
- Indoor Gardening
If you want to start a small farm business, you may be wondering what step to take first. You might not even have land yet, but you are still thinking and planning for the time when you will make your move. And finding farmland is one important step in farming - one that you'll want to take after considering some other factors.
Learn About Farming
You can't go wrong starting with this step. If you're new to farming, learn everything you can about it within the time you have. But be reasonable, too. You can't know everything there is to know. Some learning will have to be on the job, and trial and error is messy, time-consuming and sometimes costly. Yet it's inevitable with farming, so embrace the process. But learn some, too. Balance.
If you can find a mentor - someone you can learn from directly, perhaps in your community now or where you hope to farm - it can be extremely helpful. If you haven't already, work on a farm. Volunteer. Gain experience before you begin.
Design and Plan Your Farm
An important part of starting your farm business is defining what it will be. Do you want to have a micro-scale vegetable farm? Do you plan to grow acres of hay for other farmers? Maybe you want to have a diversified farm - a small-scale operation that grows a variety of animals and crops. You might even be wondering how to start an ecotourism farm, where people will come to stay to see the workings of your farm and perhaps even participate in farm chores.
Write a Business Plan
You may wonder if you need a business plan . The short answer: if you want to start a business, you will need a business plan. In the writing of the business plan, you will consider markets, supply and demand, as well as anything and everything that pertains to your farm operations, management structure, financial analysis, products, and price points. You may cycle between this step and the previous one, designing and planning because they are interconnected. But a business plan is a significant enough part of starting a business to take up an entire step. It's where you take your dreams and brainstorms and make them a reality.
Find Grants and Loans
You might not have all the capital you need to start farming on the scale that you'd like. You can start small, dip a toe in the water and see how you enjoy farming on a micro scale, using whatever you can glean from your monthly household budget to invest in the farm. But it might take a long time to get anywhere using this method, as you may not be able to invest a significant amount, enough to bring product to market. Grants and loans aimed at young and beginning farmers are out there! Help is available for established farmers, too. Programs offer subsidized equipment like high tunnels, assistance in certifying organic, and more.
Get Business Licenses and Permits
Your local and state law may vary when it comes to the requirements for establishing a small farm business. But the basics are the same: you will probably need to register your business name, purchase a business license, get an employer identification number, and carry product liability insurance.
Set Up Finances
You will also need to decide on your business structure. Will this be a sole proprietorship, an LLC or something else? Contact an accountant to get information specific to your situation. Financial planning should be in your business plan. It's very important to set up a system for bookkeeping and accounting from the start of your small farm business.
“ First Steps .” U.S. Department of Agriculture.
“ Growing Opportunity: A Guide to USDA Sustainable Farming Programs .” U.S. Department of Agriculture.
- Details of a Small Farm Business Plan
- How to Start a Small Farm
- How to Start a Hobby Farm
- Starting Your Small Farm from Scratch
- How to Buy Goats for Your Small Farm
- How to Raise Goats on a Small Farm
- Small Farm Grants and Financial Assistance
- What Is a Hobby Farm?
- How to Keep Farm Records
- Should You Raise Turkeys?
- How to Raise Dairy Goats for Milk
- How to Sell Farm Products to Food Distributors
- How to Raise Goat Breeding Stock
- How to Buy Land for a Homestead or Small Farm
- Tips for Starting Your Hobby Farm
- How to Feed and Tend Goats on Small Farms

Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Economics, Business, and Trade
Small Farm Funding Guide

This guide contains information about issues to consider before starting a farming operation.
Find links to full-text guides on how to start a small farm business and develop business and marketing plans. Identify information about funding programs for beginning and experienced farmers, technical assistance contacts, disaster assistance, and organizations with available resources.
Farm Business Planning
- Agribusiness Planning: Providing Direction for Agricultural Firms [extension.psu.edu] Jeffrey Hyde, Sarah Roch. University Park: Penn State University Cooperative Extension. Updated 2017
- Business Development AgMRC
- Business Guide U.S. Small Business Administration
- Guide to Farming: Business Plans Cornell University. Small Farms Program
- Organic Transition: A Business Planner for Farmers, Ranchers and Food Entrepreneurs Sustainable Agriculture Research and Education (SARE)
- Urban Farm Business Plan Handbook U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
- Your Farm’s Business Plan USDA . Farmers.gov
- Farm Sector Income and Finances (publications) . Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service.
- Exploring the Small Farm Dream . Belchertown, MA: New England Small Farm Institute.
- Family Farming in the United States. James MacDonald. Amber Waves. Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service, March 4, 2014.
- National Farmers Markets Directory Search. Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Marketing Service. Updated 2022.
- Financing Small-Scale and Part-Time Farms. Gregory D. Hanson, Jayson K. Harper, George L. Greaser. University Park: Penn State University Cooperative Extension, 2004.
- Small Farm Handbook. 2nd Edition. University of California Agriculture and Natural Resources. 2011.
- Starting or Diversifying an Agricultural Business. Lynne F. Kime, Sarah A. Cornelisse, Jayson K. Harper. University Park: Penn State Small-scale and Part-time Farming Project. Updated 2018. [2005 online; download 2018 edition.]
- Business Structure for Small Farms: A Quick Guide. [wsu.edu] Issued by Washington State University Extension and the U.S. Department of Agriculture. 2015. [PDF 1.75 MB]
- Resources by Topic for New Farmers. [smallfarm.org] B elchertown, MA: Growing New Farmers Consortium.
Contacts for Technical Assistance: Both SBA and USDA provide small business planning technical assistance and USDA also provides technical farming specifics through the extensive network of USDA, Cooperative Extension Service (CES) specialists.
- Cooperative Research and Extension Services
- Small Business Development Centers (SBDC)
- Disaster Resource Center
- Risk Management Agency
- Animal Welfare: Disaster Planning NAL. Animal Welfare Information Center
- Disaster Assistance Food and Nutrition Service
- Protection and Recovery
- Disaster Assistance Discover Tool
Disaster Assistance for Agricultural Producers ATTRA - National Sustainable Agriculture Information Service
Farm Aid 1-800-FARM AID
- Small and Family Farms USDA. National Institute of Food and Agriculture
- Contact the Alternative Farming Systems Information Center [nal.usda.gov] for assistance with your research.
Funding and Program Assistance
State Programs
You may want to start your financial assistance search with your state Department of Agriculture to see if your state has a Beginning Farmer Loan Program or other type of grants or loans for farming and ranching.
- National Association of State Departments of Agriculture (NASDA) is comprised of the departments of agriculture in all fifty states and the territories of American Samoa, Guam, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands.
- Types of state agricultural finance programs may be identified through your Council of State Agricultural Finance Programs. Check with your state agriculture department for programs, like Aggie Bonds.
Agricultural Lenders
Information on Farm Financial Management & Performance can be located on the USDA's Economic Research Service web site.
- Farm Economy [usda.gov]
- Rural Economy & Population [usda.gov]
The nation's farm banks (defined by the Federal Reserve Board as banks that have above average proportions of farm real estate and production loans in their loan portfolios) offer a variety of loans to small and large farms and agribusiness firms; they also handle many of the loans made under USDA's guaranteed farm loan programs.
- American Bankers Association: Agriculture Banking (ABA). [aba.com] ABA has a "special section dedicated to providing advocacy, information, training, education, and public relations for banks that make and service agricultural loans or provide credit and other financial services to those living and working in rural America for nearly 100 years."
Farm Credit : Farm Credit is a nationwide network of 70 customer-owned financial institutions across all 50 states and Puerto Rico and provides loans and related financial services to U.S. farmers and ranchers, farmer-owned cooperatives and other agribusinesses, rural homebuyers and rural infrastructure providers.
- Farm Credit System Lenders in your state
- USDA Veterans [usda.gov] USDA opportunities in and programs for education, employment and entrepreneurship.
- Veteran Affairs, Farm Loans: Home Loans for Rural Residents [va.gov] . 2018 [PDF 415 KB]
- Farmer Veteran Coalition
- Veteran Farmers Project from the Center for Rural Affairs
- Veterans to Farmers
- Farm Loan Program Information
- Beginning Farmers and Ranchers Loans
- Minority and Women Farmers and Ranchers
- Microloan Programs
- Locate Farm/Ranch Properties for Sale by the USDA RD and FSA
- Locate Farm Service Agency Offices by State
- Financial Assistance Programs
- Locate Natural Resources Conservation Service Offices by State
- Renewable Energy for America Program, Renewable Enery Systems, and Energy Efficiency Improvement Guaranteed Loans & Grants Program
- Value-Added Producer Grants
- Socially-Disadvantaged Groups Grant
- Locate Rural Development Offices by State
- Search for a Funding Opportunity in Agriculture
- Small and Family Farms
- Contact the Alternative Farming Systems Information Center for assist with your research.
- Farmers Market Promotion Program
- Specialty Crop Block Grant Program
- Agriculture Center
- National Agriculture Compliance Center 1-888-663-2155
Information and Contacts
- ABA Agricultural Banking Washington, DC: American Bankers Association.
- Alternative Farming Systems Information Center USDA . National Agricultural Library.
- ATTRA, National Sustainable Agriculture Information Service , 1-800-346-9140 Fayetteville, AR.
- Begin Farming Ohio Ecological Food and Farm Association , Columbus, OH: Public-Private Collaborative.
- Beginning Farmers East Lansing: Michigan State University.
- Center for Farm Financial Management 1-800-234-1111 St. Paul: University of Minnesota.
- Farm Answers 1-800-234-1111 St. Paul, Minnesota: The Center for Farm Financial Management (CFFM) at the University of Minnesota.
- Farm Credit Greenwood Village, CO.
- Growing Small Farms North Carolina Cooperative Extension.
- Hawai'i Guide for New Farmers Manoa: University of Hawaii.
- National Ag Risk and Farm Management Library St. Paul: University of Minnesota.
- National Association of State Departments of Agriculture Washington, DC.
- New England Small Farm Institute Belchertown, MA.
- Beginning Farmers and Rancher U.S. Department of Agriculture.
- Cornell Small Farms Program Ithaca, NY: Cornell University, Small Farm Program, Cooperative Extension Service.
- Small Farms Program Corvallis: Oregon State University Extension Service.
- Small Farm Research and Extension Davis: University of California.
- Women's Agricultural Network Burlington: University of Vermont.
Featured Resources

Page Content Curated By
Vineyard Wind allowed to resume limited offshore turbine installation
- Medium Text

- GE Vernova Inc Follow
- Avangrid Inc Follow
Sign up here.
Reporting by Nichola Groom in Altadena, California, and Brijesh Patel and Rahul Paswan in Bengaluru; Editing by Tomasz Janowski, Jonathan Oatis and Marguerita Choy
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. , opens new tab

California pot farmers feel the heat from low pricing, wildfires
Small-scale cannabis farmers in California are calling it quits, crushed by crop damage from devastating wildfires and sliding prices, and industry experts expect the exodus to continue near-term in the largest pot market in the United States.


IMAGES
COMMENTS
The Farm Business Plan Balance Sheet can help gather information for the financial and operational aspects of your plan. Form FSA-2037 is a template that gathers information on your assets and liabilities like farm equipment, vehicles and existing loans. FSA-2037 - Farm Business Plan - Balance Sheet. FSA-2037 Instructions.
Here are a few tips for writing the market analysis section of your small farming business plan: Conduct market research, industry reports, and surveys to gather data. Provide specific and detailed information whenever possible. Illustrate your points with charts and graphs. Write your business plan keeping your target audience in mind. 4.
Down in the Dirt Farm is a small-scale, diversified vegetable and livestock farm owned and operated by Phoebe and Taylor Dirt. They have operated the farm on leased land in central Vermont for the past three years. This business plan will serve as an operating guide for Down in the Dirt Farm as they purchase a new farm and grow their farm business.
Building a Business Plan for Your Farm: Important First Steps is a 20 page farm business planning publication that discusses the initial steps to help you move toward writing a formal business plan. The Center for Agroecology has a Small Farm Business Planning publication that goes over many of the basics in a step by step format.
A business plan is a roadmap for your small farm. It is both process and product. During the writing of a farm business plan, you'll develop an overall vision and mission for your business. You ...
These might be local consumers, restaurants, farmers' markets, or even online customers. Key Strategies: Highlight the strategies you plan to implement to run and grow your business. This could cover marketing techniques, sustainability practices, or partnerships. Mission and Vision: Briefly outline the mission and vision of your farm business.
Developing a Business Plan. To start a small farm, it's crucial to have a clear idea of what you want to achieve and how you plan to achieve it. Developing a business plan is an essential step in this process. A business plan is a written document that outlines your goals, strategies, and financial projections for your farm.
Five-year plan. Year One: 20XX. Create a legal business entity. Apply for necessary licenses and permits. Finalize farm layout. Procure additional equipment. Establish social media profiles. Build a small farm stand. Attend farmer's markets.
Sample Business Plan For Farms & Agricultural Businesses. Executive Summary - The Executive Summary is the most important part of your business plan. It is a brief description of your farm, its products and services, potential market opportunity, and competitive advantage. Company Overview - Also called the Company Analysis, here, you will ...
Your agriculture business plan doesn't need to be hundreds of pages—keep it as short and focused as you can. You'll probably want to include each of these sections: 1. Executive summary. An overview of your agriculture business, with a brief description of your products or services, your legal structure, and a snapshot of your future plans.
Cornell Small Farms Program Online Course BF 202: Business Planning. The Cornell Small Farms Program offers 20+ online courses every year on many topics related to the production and business sides of farming. Most are taught by Cornell Cooperative Extension educators. BF 202 is a 6-week course that will guide you through the process of writing ...
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan. For example, give a brief overview of the farm business industry. Discuss the type of farm business you are operating. Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target customers. Provide a snapshot of your marketing plan.
In conclusion, starting a small vegetable farm requires careful planning and execution. By developing a comprehensive business plan, conducting thorough market research, and implementing sustainable practices, you can increase the likelihood of success. Remember, flexibility and adaptability are key in the ever-evolving agricultural industry.
Use this free farm business plan template to quickly & easily create a great business plan to start, grow or raise funding for your agriculture business. ... Thompson Organics is a small, 300 acre, ten-year old farm which produces organic grains and bakes organic breads. They sell all of their products at farmer's markets and directly at ...
Writing a farming business plan is a crucial step toward the success of your business. Here are the key steps to consider when writing a business plan: 1. Executive Summary. An executive summary is the first section of the business plan intended to provide an overview of the whole business plan. Generally, it is written after the entire ...
Why create a business plan? For many beginning farmers, writing a business plan can seem like a chore, a necessary evil, or at worse, an insurmountable challenge that always falls to the bottom of the to-do list. ... Sample Business Plans - Examples of real farm business plans. Small Farms Program Oregon State University Send E-mail Phone: 541 ...
Business Planning for Your Farm. Small Farm Funding Guide Find links to full-text guides on how to start a small farm business and develop business and marketing plans. Learn more about funding programs for beginning and experienced farmers, technical assistance contacts, disaster assistance and organizations with available resources.
Below are examples of different farm business plans and a loan application: ... Peach Farm Business Plan Sample. USDA FSA Sample Microloan Application. Small Farms Program Oregon State University Send E-mail Phone: 541-713-5009. OSU College of Agricultural Sciences 430 Strand Agriculture Hall Corvallis, Oregon 97331. Contact Us ©2022 Oregon ...
The short answer: if you want to start a business, you will need a business plan. In the writing of the business plan, you will consider markets, supply and demand, as well as anything and ...
A business plan is like a road map to farm success, and is essential for anyone who wants to build a profitable farm business. Business plans can also be essential for securing the necessary financing to fund farmland, farm infrastructure, and machinery costs. Lenders often ask to see a business plan before even considering a loan application. 2.
ision is and how you will make it happen. The goal of this Business Farm Plan Workbook is to provide a s. raightforward approach to writing a plan. If more in-depth planning is desired, there are many other resources available. The focus of this workbook is to help you think through your vision and goals and get detail.
USDA offers dedicated help to beginning farmers and ranchers. USDA considers anyone who has operated a farm or ranch for less than ten years to be a beginning farmer or rancher. USDA can help you get started or grow your operation through a variety of programs and services, from farm loans to crop insurance, and conservation programs to ...
Small Farm Funding Guide. This guide contains information about issues to consider before starting a farming operation. Find links to full-text guides on how to start a small farm business and develop business and marketing plans. Identify information about funding programs for beginning and experienced farmers, technical assistance contacts ...
Starting a farm, no matter how small, is an exciting venture. Whether you're raising a few cows or planning a diverse small-scale operation, a well-thought-out farm plan is crucial. Not only is it often required by lenders, but it also serves as a roadmap for your agricultural journey. Let's break down how to create a simple yet effective farm plan.
Planning is essential to any business, no matter how large or small its inventory, payroll, and bank account. To be successful, farm operators must know their current position and future plans. Thinking about your plans is not enough! Taking time to formulate ideas, evaluate your business, devise a strategy, and anticipate possible problems will help your business be successful.
Vineyard Wind and GE Vernova on Tuesday said U.S. safety officials have allowed them to resume limited construction on an offshore wind farm off the Massachusetts coast where a turbine blade ...