

Getting Started
Why do makefiles exist, what alternatives are there to make, the versions and types of make, running the examples, makefile syntax, the essence of make, more quick examples, the all target, multiple targets, automatic variables and wildcards, automatic variables, fancy rules, implicit rules, static pattern rules, static pattern rules and filter, pattern rules, double-colon rules, commands and execution, command echoing/silencing, command execution, default shell, double dollar sign.
- Error handling with -k, -i, and -
Interrupting or killing make
Recursive use of make, export, environments, and recursive make, arguments to make, variables pt. 2, flavors and modification, command line arguments and override, list of commands and define, target-specific variables, pattern-specific variables, conditional part of makefiles, conditional if/else, check if a variable is empty, check if a variable is defined, $(makeflags), first functions, string substitution, the foreach function, the if function, the call function, the shell function, the filter function, other features, include makefiles, the vpath directive, .delete_on_error, makefile cookbook.
I built this guide because I could never quite wrap my head around Makefiles. They seemed awash with hidden rules and esoteric symbols, and asking simple questions didn’t yield simple answers. To solve this, I sat down for several weekends and read everything I could about Makefiles. I've condensed the most critical knowledge into this guide. Each topic has a brief description and a self contained example that you can run yourself.
If you mostly understand Make, consider checking out the Makefile Cookbook , which has a template for medium sized projects with ample comments about what each part of the Makefile is doing.
Good luck, and I hope you are able to slay the confusing world of Makefiles!
Makefiles are used to help decide which parts of a large program need to be recompiled. In the vast majority of cases, C or C++ files are compiled. Other languages typically have their own tools that serve a similar purpose as Make. Make can also be used beyond compilation too, when you need a series of instructions to run depending on what files have changed. This tutorial will focus on the C/C++ compilation use case.
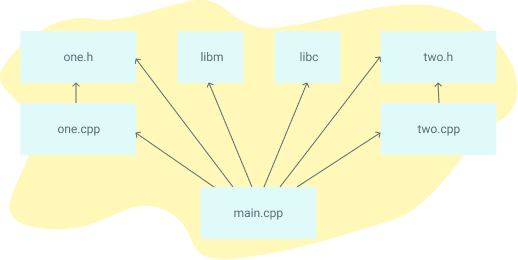
Here's an example dependency graph that you might build with Make. If any file's dependencies changes, then the file will get recompiled:
Popular C/C++ alternative build systems are SCons , CMake , Bazel , and Ninja . Some code editors like Microsoft Visual Studio have their own built in build tools. For Java, there's Ant , Maven , and Gradle . Other languages like Go, Rust, and TypeScript have their own build tools.
Interpreted languages like Python, Ruby, and raw Javascript don't require an analogue to Makefiles. The goal of Makefiles is to compile whatever files need to be compiled, based on what files have changed. But when files in interpreted languages change, nothing needs to get recompiled. When the program runs, the most recent version of the file is used.
There are a variety of implementations of Make, but most of this guide will work on whatever version you're using. However, it's specifically written for GNU Make, which is the standard implementation on Linux and MacOS. All the examples work for Make versions 3 and 4, which are nearly equivalent other than some esoteric differences.
To run these examples, you'll need a terminal and "make" installed. For each example, put the contents in a file called Makefile , and in that directory run the command make . Let's start with the simplest of Makefiles:
Note: Makefiles must be indented using TABs and not spaces or make will fail.
Here is the output of running the above example:
That's it! If you're a bit confused, here's a video that goes through these steps, along with describing the basic structure of Makefiles.
A Makefile consists of a set of rules . A rule generally looks like this:
- The targets are file names, separated by spaces. Typically, there is only one per rule.
- The commands are a series of steps typically used to make the target(s). These need to start with a tab character , not spaces.
- The prerequisites are also file names, separated by spaces. These files need to exist before the commands for the target are run. These are also called dependencies
Let's start with a hello world example:
There's already a lot to take in here. Let's break it down:
- We have one target called hello
- This target has two commands
- This target has no prerequisites
We'll then run make hello . As long as the hello file does not exist, the commands will run. If hello does exist, no commands will run.
It's important to realize that I'm talking about hello as both a target and a file . That's because the two are directly tied together. Typically, when a target is run (aka when the commands of a target are run), the commands will create a file with the same name as the target. In this case, the hello target does not create the hello file .
Let's create a more typical Makefile - one that compiles a single C file. But before we do, make a file called blah.c that has the following contents:
Then create the Makefile (called Makefile , as always):
This time, try simply running make . Since there's no target supplied as an argument to the make command, the first target is run. In this case, there's only one target ( blah ). The first time you run this, blah will be created. The second time, you'll see make: 'blah' is up to date . That's because the blah file already exists. But there's a problem: if we modify blah.c and then run make , nothing gets recompiled.
We solve this by adding a prerequisite:
When we run make again, the following set of steps happens:
- The first target is selected, because the first target is the default target
- This has a prerequisite of blah.c
- Make decides if it should run the blah target. It will only run if blah doesn't exist, or blah.c is newer than blah
This last step is critical, and is the essence of make . What it's attempting to do is decide if the prerequisites of blah have changed since blah was last compiled. That is, if blah.c is modified, running make should recompile the file. And conversely, if blah.c has not changed, then it should not be recompiled.
To make this happen, it uses the filesystem timestamps as a proxy to determine if something has changed. This is a reasonable heuristic, because file timestamps typically will only change if the files are modified. But it's important to realize that this isn't always the case. You could, for example, modify a file, and then change the modified timestamp of that file to something old. If you did, Make would incorrectly guess that the file hadn't changed and thus could be ignored.
Whew, what a mouthful. Make sure that you understand this. It's the crux of Makefiles, and might take you a few minutes to properly understand . Play around with the above examples or watch the video above if things are still confusing.
The following Makefile ultimately runs all three targets. When you run make in the terminal, it will build a program called blah in a series of steps:
- Make selects the target blah , because the first target is the default target
- blah requires blah.o , so make searches for the blah.o target
- blah.o requires blah.c , so make searches for the blah.c target
- blah.c has no dependencies, so the echo command is run
- The cc -c command is then run, because all of the blah.o dependencies are finished
- The top cc command is run, because all the blah dependencies are finished
- That's it: blah is a compiled c program
If you delete blah.c , all three targets will be rerun. If you edit it (and thus change the timestamp to newer than blah.o ), the first two targets will run. If you run touch blah.o (and thus change the timestamp to newer than blah ), then only the first target will run. If you change nothing, none of the targets will run. Try it out!
This next example doesn't do anything new, but is nontheless a good additional example. It will always run both targets, because some_file depends on other_file , which is never created.
clean is often used as a target that removes the output of other targets, but it is not a special word in Make. You can run make and make clean on this to create and delete some_file .
Note that clean is doing two new things here:
- It's a target that is not first (the default), and not a prerequisite. That means it'll never run unless you explicitly call make clean
- It's not intended to be a filename. If you happen to have a file named clean , this target won't run, which is not what we want. See .PHONY later in this tutorial on how to fix this
Variables can only be strings. You'll typically want to use := , but = also works. See Variables Pt 2 .
Here's an example of using variables:
Single or double quotes have no meaning to Make. They are simply characters that are assigned to the variable. Quotes are useful to shell/bash, though, and you need them in commands like printf . In this example, the two commands behave the same:
Reference variables using either ${} or $()
Making multiple targets and you want all of them to run? Make an all target. Since this is the first rule listed, it will run by default if make is called without specifying a target.
When there are multiple targets for a rule, the commands will be run for each target. $@ is an automatic variable that contains the target name.
Both * and % are called wildcards in Make, but they mean entirely different things. * searches your filesystem for matching filenames. I suggest that you always wrap it in the wildcard function, because otherwise you may fall into a common pitfall described below.
* may be used in the target, prerequisites, or in the wildcard function.
Danger: * may not be directly used in a variable definitions
Danger: When * matches no files, it is left as it is (unless run in the wildcard function)
% is really useful, but is somewhat confusing because of the variety of situations it can be used in.
- When used in "matching" mode, it matches one or more characters in a string. This match is called the stem.
- When used in "replacing" mode, it takes the stem that was matched and replaces that in a string.
- % is most often used in rule definitions and in some specific functions.
See these sections on examples of it being used:
There are many automatic variables , but often only a few show up:
Make loves c compilation. And every time it expresses its love, things get confusing. Perhaps the most confusing part of Make is the magic/automatic rules that are made. Make calls these "implicit" rules. I don't personally agree with this design decision, and I don't recommend using them, but they're often used and are thus useful to know. Here's a list of implicit rules:
- Compiling a C program: n.o is made automatically from n.c with a command of the form $(CC) -c $(CPPFLAGS) $(CFLAGS) $^ -o $@
- Compiling a C++ program: n.o is made automatically from n.cc or n.cpp with a command of the form $(CXX) -c $(CPPFLAGS) $(CXXFLAGS) $^ -o $@
- Linking a single object file: n is made automatically from n.o by running the command $(CC) $(LDFLAGS) $^ $(LOADLIBES) $(LDLIBS) -o $@
The important variables used by implicit rules are:
- CC : Program for compiling C programs; default cc
- CXX : Program for compiling C++ programs; default g++
- CFLAGS : Extra flags to give to the C compiler
- CXXFLAGS : Extra flags to give to the C++ compiler
- CPPFLAGS : Extra flags to give to the C preprocessor
- LDFLAGS : Extra flags to give to compilers when they are supposed to invoke the linker
Let's see how we can now build a C program without ever explicitly telling Make how to do the compilation:
Static pattern rules are another way to write less in a Makefile. Here's their syntax:
The essence is that the given target is matched by the target-pattern (via a % wildcard). Whatever was matched is called the stem . The stem is then substituted into the prereq-pattern , to generate the target's prereqs.
A typical use case is to compile .c files into .o files. Here's the manual way :
Here's the more efficient way , using a static pattern rule:
While I introduce the filter function later on, it's common to use in static pattern rules, so I'll mention that here. The filter function can be used in Static pattern rules to match the correct files. In this example, I made up the .raw and .result extensions.
Pattern rules are often used but quite confusing. You can look at them as two ways:
- A way to define your own implicit rules
- A simpler form of static pattern rules
Let's start with an example first:
Pattern rules contain a '%' in the target. This '%' matches any nonempty string, and the other characters match themselves. ‘%’ in a prerequisite of a pattern rule stands for the same stem that was matched by the ‘%’ in the target.
Here's another example:
Double-Colon Rules are rarely used, but allow multiple rules to be defined for the same target. If these were single colons, a warning would be printed and only the second set of commands would run.
Add an @ before a command to stop it from being printed You can also run make with -s to add an @ before each line
Each command is run in a new shell (or at least the effect is as such)
The default shell is /bin/sh . You can change this by changing the variable SHELL:
If you want a string to have a dollar sign, you can use $$ . This is how to use a shell variable in bash or sh .
Note the differences between Makefile variables and Shell variables in this next example.
Error handling with -k , -i , and -
Add -k when running make to continue running even in the face of errors. Helpful if you want to see all the errors of Make at once. Add a - before a command to suppress the error Add -i to make to have this happen for every command.
Note only: If you ctrl+c make, it will delete the newer targets it just made.
To recursively call a makefile, use the special $(MAKE) instead of make because it will pass the make flags for you and won't itself be affected by them.
When Make starts, it automatically creates Make variables out of all the environment variables that are set when it's executed.
The export directive takes a variable and sets it the environment for all shell commands in all the recipes:
As such, when you run the make command inside of make, you can use the export directive to make it accessible to sub-make commands. In this example, cooly is exported such that the makefile in subdir can use it.
You need to export variables to have them run in the shell as well.
.EXPORT_ALL_VARIABLES exports all variables for you.
There's a nice list of options that can be run from make. Check out --dry-run , --touch , --old-file .
You can have multiple targets to make, i.e. make clean run test runs the clean goal, then run , and then test .
There are two flavors of variables:
- recursive (use = ) - only looks for the variables when the command is used , not when it's defined .
- simply expanded (use := ) - like normal imperative programming -- only those defined so far get expanded
Simply expanded (using := ) allows you to append to a variable. Recursive definitions will give an infinite loop error.
?= only sets variables if they have not yet been set
Spaces at the end of a line are not stripped, but those at the start are. To make a variable with a single space, use $(nullstring)
An undefined variable is actually an empty string!
Use += to append
String Substitution is also a really common and useful way to modify variables. Also check out Text Functions and Filename Functions .
You can override variables that come from the command line by using override . Here we ran make with make option_one=hi
The define directive is not a function, though it may look that way. I've seen it used so infrequently that I won't go into details, but it's mainly used for defining canned recipes and also pairs well with the eval function .
define / endef simply creates a variable that is set to a list of commands. Note here that it's a bit different than having a semi-colon between commands, because each is run in a separate shell, as expected.
Variables can be set for specific targets
You can set variables for specific target patterns
ifdef does not expand variable references; it just sees if something is defined at all
This example shows you how to test make flags with findstring and MAKEFLAGS . Run this example with make -i to see it print out the echo statement.
Functions are mainly just for text processing. Call functions with $(fn, arguments) or ${fn, arguments} . Make has a decent amount of builtin functions .
If you want to replace spaces or commas, use variables
Do NOT include spaces in the arguments after the first. That will be seen as part of the string.
$(patsubst pattern,replacement,text) does the following:
"Finds whitespace-separated words in text that match pattern and replaces them with replacement. Here pattern may contain a ‘%’ which acts as a wildcard, matching any number of any characters within a word. If replacement also contains a ‘%’, the ‘%’ is replaced by the text that matched the ‘%’ in pattern. Only the first ‘%’ in the pattern and replacement is treated this way; any subsequent ‘%’ is unchanged." ( GNU docs )
The substitution reference $(text:pattern=replacement) is a shorthand for this.
There's another shorthand that replaces only suffixes: $(text:suffix=replacement) . No % wildcard is used here.
Note: don't add extra spaces for this shorthand. It will be seen as a search or replacement term.
The foreach function looks like this: $(foreach var,list,text) . It converts one list of words (separated by spaces) to another. var is set to each word in list, and text is expanded for each word. This appends an exclamation after each word:
if checks if the first argument is nonempty. If so, runs the second argument, otherwise runs the third.
Make supports creating basic functions. You "define" the function just by creating a variable, but use the parameters $(0) , $(1) , etc. You then call the function with the special call builtin function. The syntax is $(call variable,param,param) . $(0) is the variable, while $(1) , $(2) , etc. are the params.
shell - This calls the shell, but it replaces newlines with spaces!
The filter function is used to select certain elements from a list that match a specific pattern. For example, this will select all elements in obj_files that end with .o .
Filter can also be used in more complex ways:
Filtering multiple patterns : You can filter multiple patterns at once. For example, $(filter %.c %.h, $(files)) will select all .c and .h files from the files list.
Negation : If you want to select all elements that do not match a pattern, you can use filter-out . For example, $(filter-out %.h, $(files)) will select all files that are not .h files.
Nested filter : You can nest filter functions to apply multiple filters. For example, $(filter %.o, $(filter-out test%, $(objects))) will select all object files that end with .o but don't start with test .
The include directive tells make to read one or more other makefiles. It's a line in the makefile that looks like this:
This is particularly useful when you use compiler flags like -M that create Makefiles based on the source. For example, if some c files includes a header, that header will be added to a Makefile that's written by gcc. I talk about this more in the Makefile Cookbook
Use vpath to specify where some set of prerequisites exist. The format is vpath <pattern> <directories, space/colon separated> <pattern> can have a % , which matches any zero or more characters. You can also do this globallyish with the variable VPATH
The backslash ("\") character gives us the ability to use multiple lines when the commands are too long
Adding .PHONY to a target will prevent Make from confusing the phony target with a file name. In this example, if the file clean is created, make clean will still be run. Technically, I should have used it in every example with all or clean , but I wanted to keep the examples clean. Additionally, "phony" targets typically have names that are rarely file names, and in practice many people skip this.
The make tool will stop running a rule (and will propogate back to prerequisites) if a command returns a nonzero exit status. DELETE_ON_ERROR will delete the target of a rule if the rule fails in this manner. This will happen for all targets, not just the one it is before like PHONY. It's a good idea to always use this, even though make does not for historical reasons.
Let's go through a really juicy Make example that works well for medium sized projects.
The neat thing about this makefile is it automatically determines dependencies for you. All you have to do is put your C/C++ files in the src/ folder.
Next: Conditionals , Previous: Recipes , Up: Top [ Contents ][ Index ]
6 How to Use Variables
A variable is a name defined in a makefile to represent a string of text, called the variable’s value . These values are substituted by explicit request into targets, prerequisites, recipes, and other parts of the makefile. (In some other versions of make , variables are called macros .)
Variables and functions in all parts of a makefile are expanded when read, except for in recipes, the right-hand sides of variable definitions using ‘ = ’, and the bodies of variable definitions using the define directive.
Variables can represent lists of file names, options to pass to compilers, programs to run, directories to look in for source files, directories to write output in, or anything else you can imagine.
A variable name may be any sequence of characters not containing ‘ : ’, ‘ # ’, ‘ = ’, or whitespace. However, variable names containing characters other than letters, numbers, and underscores should be considered carefully, as in some shells they cannot be passed through the environment to a sub- make (see Communicating Variables to a Sub- make ). Variable names beginning with ‘ . ’ and an uppercase letter may be given special meaning in future versions of make .
Variable names are case-sensitive. The names ‘ foo ’, ‘ FOO ’, and ‘ Foo ’ all refer to different variables.
It is traditional to use upper case letters in variable names, but we recommend using lower case letters for variable names that serve internal purposes in the makefile, and reserving upper case for parameters that control implicit rules or for parameters that the user should override with command options (see Overriding Variables ).
A few variables have names that are a single punctuation character or just a few characters. These are the automatic variables , and they have particular specialized uses. See Automatic Variables .
Next: Flavors , Previous: Using Variables , Up: Using Variables [ Contents ][ Index ]
6.1 Basics of Variable References
To substitute a variable’s value, write a dollar sign followed by the name of the variable in parentheses or braces: either ‘ $(foo) ’ or ‘ ${foo} ’ is a valid reference to the variable foo . This special significance of ‘ $ ’ is why you must write ‘ $$ ’ to have the effect of a single dollar sign in a file name or recipe.
Variable references can be used in any context: targets, prerequisites, recipes, most directives, and new variable values. Here is an example of a common case, where a variable holds the names of all the object files in a program:
Variable references work by strict textual substitution. Thus, the rule
could be used to compile a C program prog.c . Since spaces before the variable value are ignored in variable assignments, the value of foo is precisely ‘ c ’. (Don’t actually write your makefiles this way!)
A dollar sign followed by a character other than a dollar sign, open-parenthesis or open-brace treats that single character as the variable name. Thus, you could reference the variable x with ‘ $x ’. However, this practice can lead to confusion (e.g., ‘ $foo ’ refers to the variable f followed by the string oo ) so we recommend using parentheses or braces around all variables, even single-letter variables, unless omitting them gives significant readability improvements. One place where readability is often improved is automatic variables (see Automatic Variables ).
Next: Advanced , Previous: Reference , Up: Using Variables [ Contents ][ Index ]
6.2 The Two Flavors of Variables
There are two ways that a variable in GNU make can have a value; we call them the two flavors of variables. The two flavors are distinguished in how they are defined and in what they do when expanded.
The first flavor of variable is a recursively expanded variable. Variables of this sort are defined by lines using ‘ = ’ (see Setting Variables ) or by the define directive (see Defining Multi-Line Variables ). The value you specify is installed verbatim; if it contains references to other variables, these references are expanded whenever this variable is substituted (in the course of expanding some other string). When this happens, it is called recursive expansion .
For example,
will echo ‘ Huh? ’: ‘ $(foo) ’ expands to ‘ $(bar) ’ which expands to ‘ $(ugh) ’ which finally expands to ‘ Huh? ’.
This flavor of variable is the only sort supported by most other versions of make . It has its advantages and its disadvantages. An advantage (most would say) is that:
will do what was intended: when ‘ CFLAGS ’ is expanded in a recipe, it will expand to ‘ -Ifoo -Ibar -O ’. A major disadvantage is that you cannot append something on the end of a variable, as in
because it will cause an infinite loop in the variable expansion. (Actually make detects the infinite loop and reports an error.)
Another disadvantage is that any functions (see Functions for Transforming Text ) referenced in the definition will be executed every time the variable is expanded. This makes make run slower; worse, it causes the wildcard and shell functions to give unpredictable results because you cannot easily control when they are called, or even how many times.
To avoid all the problems and inconveniences of recursively expanded variables, there is another flavor: simply expanded variables.
Simply expanded variables are defined by lines using ‘ := ’ or ‘ ::= ’ (see Setting Variables ). Both forms are equivalent in GNU make ; however only the ‘ ::= ’ form is described by the POSIX standard (support for ‘ ::= ’ was added to the POSIX standard in 2012, so older versions of make won’t accept this form either).
The value of a simply expanded variable is scanned once and for all, expanding any references to other variables and functions, when the variable is defined. The actual value of the simply expanded variable is the result of expanding the text that you write. It does not contain any references to other variables; it contains their values as of the time this variable was defined . Therefore,
is equivalent to
When a simply expanded variable is referenced, its value is substituted verbatim.
Here is a somewhat more complicated example, illustrating the use of ‘ := ’ in conjunction with the shell function. (See The shell Function .) This example also shows use of the variable MAKELEVEL , which is changed when it is passed down from level to level. (See Communicating Variables to a Sub- make , for information about MAKELEVEL .)
An advantage of this use of ‘ := ’ is that a typical ‘descend into a directory’ recipe then looks like this:
Simply expanded variables generally make complicated makefile programming more predictable because they work like variables in most programming languages. They allow you to redefine a variable using its own value (or its value processed in some way by one of the expansion functions) and to use the expansion functions much more efficiently (see Functions for Transforming Text ).
You can also use them to introduce controlled leading whitespace into variable values. Leading whitespace characters are discarded from your input before substitution of variable references and function calls; this means you can include leading spaces in a variable value by protecting them with variable references, like this:
Here the value of the variable space is precisely one space. The comment ‘ # end of the line ’ is included here just for clarity. Since trailing space characters are not stripped from variable values, just a space at the end of the line would have the same effect (but be rather hard to read). If you put whitespace at the end of a variable value, it is a good idea to put a comment like that at the end of the line to make your intent clear. Conversely, if you do not want any whitespace characters at the end of your variable value, you must remember not to put a random comment on the end of the line after some whitespace, such as this:
Here the value of the variable dir is ‘ /foo/bar ’ (with four trailing spaces), which was probably not the intention. (Imagine something like ‘ $(dir)/file ’ with this definition!)
There is another assignment operator for variables, ‘ ?= ’. This is called a conditional variable assignment operator, because it only has an effect if the variable is not yet defined. This statement:
is exactly equivalent to this (see The origin Function ):
Note that a variable set to an empty value is still defined, so ‘ ?= ’ will not set that variable.
Next: Values , Previous: Flavors , Up: Using Variables [ Contents ][ Index ]
6.3 Advanced Features for Reference to Variables
This section describes some advanced features you can use to reference variables in more flexible ways.
Next: Computed Names , Previous: Advanced , Up: Advanced [ Contents ][ Index ]
6.3.1 Substitution References
A substitution reference substitutes the value of a variable with alterations that you specify. It has the form ‘ $( var : a = b ) ’ (or ‘ ${ var : a = b } ’) and its meaning is to take the value of the variable var , replace every a at the end of a word with b in that value, and substitute the resulting string.
When we say “at the end of a word”, we mean that a must appear either followed by whitespace or at the end of the value in order to be replaced; other occurrences of a in the value are unaltered. For example:
sets ‘ bar ’ to ‘ a.c b.c l.a c.c ’. See Setting Variables .
A substitution reference is shorthand for the patsubst expansion function (see Functions for String Substitution and Analysis ): ‘ $( var : a = b ) ’ is equivalent to ‘ $(patsubst % a ,% b , var ) ’. We provide substitution references as well as patsubst for compatibility with other implementations of make .
Another type of substitution reference lets you use the full power of the patsubst function. It has the same form ‘ $( var : a = b ) ’ described above, except that now a must contain a single ‘ % ’ character. This case is equivalent to ‘ $(patsubst a , b ,$( var )) ’. See Functions for String Substitution and Analysis , for a description of the patsubst function.
sets ‘ bar ’ to ‘ a.c b.c l.a c.c ’.
Previous: Substitution Refs , Up: Advanced [ Contents ][ Index ]
6.3.2 Computed Variable Names
Computed variable names are a complicated concept needed only for sophisticated makefile programming. For most purposes you need not consider them, except to know that making a variable with a dollar sign in its name might have strange results. However, if you are the type that wants to understand everything, or you are actually interested in what they do, read on.
Variables may be referenced inside the name of a variable. This is called a computed variable name or a nested variable reference . For example,
defines a as ‘ z ’: the ‘ $(x) ’ inside ‘ $($(x)) ’ expands to ‘ y ’, so ‘ $($(x)) ’ expands to ‘ $(y) ’ which in turn expands to ‘ z ’. Here the name of the variable to reference is not stated explicitly; it is computed by expansion of ‘ $(x) ’. The reference ‘ $(x) ’ here is nested within the outer variable reference.
The previous example shows two levels of nesting, but any number of levels is possible. For example, here are three levels:
Here the innermost ‘ $(x) ’ expands to ‘ y ’, so ‘ $($(x)) ’ expands to ‘ $(y) ’ which in turn expands to ‘ z ’; now we have ‘ $(z) ’, which becomes ‘ u ’.
References to recursively-expanded variables within a variable name are re-expanded in the usual fashion. For example:
defines a as ‘ Hello ’: ‘ $($(x)) ’ becomes ‘ $($(y)) ’ which becomes ‘ $(z) ’ which becomes ‘ Hello ’.
Nested variable references can also contain modified references and function invocations (see Functions for Transforming Text ), just like any other reference. For example, using the subst function (see Functions for String Substitution and Analysis ):
eventually defines a as ‘ Hello ’. It is doubtful that anyone would ever want to write a nested reference as convoluted as this one, but it works: ‘ $($($(z))) ’ expands to ‘ $($(y)) ’ which becomes ‘ $($(subst 1,2,$(x))) ’. This gets the value ‘ variable1 ’ from x and changes it by substitution to ‘ variable2 ’, so that the entire string becomes ‘ $(variable2) ’, a simple variable reference whose value is ‘ Hello ’.
A computed variable name need not consist entirely of a single variable reference. It can contain several variable references, as well as some invariant text. For example,
will give dirs the same value as a_dirs , 1_dirs , a_files or 1_files depending on the settings of use_a and use_dirs .
Computed variable names can also be used in substitution references:
defines sources as either ‘ a.c b.c c.c ’ or ‘ 1.c 2.c 3.c ’, depending on the value of a1 .
The only restriction on this sort of use of nested variable references is that they cannot specify part of the name of a function to be called. This is because the test for a recognized function name is done before the expansion of nested references. For example,
attempts to give ‘ foo ’ the value of the variable ‘ sort a d b g q c ’ or ‘ strip a d b g q c ’, rather than giving ‘ a d b g q c ’ as the argument to either the sort or the strip function. This restriction could be removed in the future if that change is shown to be a good idea.
You can also use computed variable names in the left-hand side of a variable assignment, or in a define directive, as in:
This example defines the variables ‘ dir ’, ‘ foo_sources ’, and ‘ foo_print ’.
Note that nested variable references are quite different from recursively expanded variables (see The Two Flavors of Variables ), though both are used together in complex ways when doing makefile programming.
Next: Setting , Previous: Advanced , Up: Using Variables [ Contents ][ Index ]
6.4 How Variables Get Their Values
Variables can get values in several different ways:
- You can specify an overriding value when you run make . See Overriding Variables .
- You can specify a value in the makefile, either with an assignment (see Setting Variables ) or with a verbatim definition (see Defining Multi-Line Variables ).
- Variables in the environment become make variables. See Variables from the Environment .
- Several automatic variables are given new values for each rule. Each of these has a single conventional use. See Automatic Variables .
- Several variables have constant initial values. See Variables Used by Implicit Rules .
Next: Appending , Previous: Values , Up: Using Variables [ Contents ][ Index ]

6.5 Setting Variables
To set a variable from the makefile, write a line starting with the variable name followed by ‘ = ’, ‘ := ’, or ‘ ::= ’. Whatever follows the ‘ = ’, ‘ := ’, or ‘ ::= ’ on the line becomes the value. For example,
defines a variable named objects . Whitespace around the variable name and immediately after the ‘ = ’ is ignored.
Variables defined with ‘ = ’ are recursively expanded variables. Variables defined with ‘ := ’ or ‘ ::= ’ are simply expanded variables; these definitions can contain variable references which will be expanded before the definition is made. See The Two Flavors of Variables .
The variable name may contain function and variable references, which are expanded when the line is read to find the actual variable name to use.
There is no limit on the length of the value of a variable except the amount of memory on the computer. You can split the value of a variable into multiple physical lines for readability (see Splitting Long Lines ).
Most variable names are considered to have the empty string as a value if you have never set them. Several variables have built-in initial values that are not empty, but you can set them in the usual ways (see Variables Used by Implicit Rules ). Several special variables are set automatically to a new value for each rule; these are called the automatic variables (see Automatic Variables ).
If you’d like a variable to be set to a value only if it’s not already set, then you can use the shorthand operator ‘ ?= ’ instead of ‘ = ’. These two settings of the variable ‘ FOO ’ are identical (see The origin Function ):
The shell assignment operator ‘ != ’ can be used to execute a shell script and set a variable to its output. This operator first evaluates the right-hand side, then passes that result to the shell for execution. If the result of the execution ends in a newline, that one newline is removed; all other newlines are replaced by spaces. The resulting string is then placed into the named recursively-expanded variable. For example:
If the result of the execution could produce a $ , and you don’t intend what follows that to be interpreted as a make variable or function reference, then you must replace every $ with $$ as part of the execution. Alternatively, you can set a simply expanded variable to the result of running a program using the shell function call. See The shell Function . For example:
As with the shell function, the exit status of the just-invoked shell script is stored in the .SHELLSTATUS variable.
Next: Override Directive , Previous: Setting , Up: Using Variables [ Contents ][ Index ]
6.6 Appending More Text to Variables
Often it is useful to add more text to the value of a variable already defined. You do this with a line containing ‘ += ’, like this:
This takes the value of the variable objects , and adds the text ‘ another.o ’ to it (preceded by a single space, if it has a value already). Thus:
sets objects to ‘ main.o foo.o bar.o utils.o another.o ’.
Using ‘ += ’ is similar to:
but differs in ways that become important when you use more complex values.
When the variable in question has not been defined before, ‘ += ’ acts just like normal ‘ = ’: it defines a recursively-expanded variable. However, when there is a previous definition, exactly what ‘ += ’ does depends on what flavor of variable you defined originally. See The Two Flavors of Variables , for an explanation of the two flavors of variables.
When you add to a variable’s value with ‘ += ’, make acts essentially as if you had included the extra text in the initial definition of the variable. If you defined it first with ‘ := ’ or ‘ ::= ’, making it a simply-expanded variable, ‘ += ’ adds to that simply-expanded definition, and expands the new text before appending it to the old value just as ‘ := ’ does (see Setting Variables , for a full explanation of ‘ := ’ or ‘ ::= ’). In fact,
is exactly equivalent to:
On the other hand, when you use ‘ += ’ with a variable that you defined first to be recursively-expanded using plain ‘ = ’, make does something a bit different. Recall that when you define a recursively-expanded variable, make does not expand the value you set for variable and function references immediately. Instead it stores the text verbatim, and saves these variable and function references to be expanded later, when you refer to the new variable (see The Two Flavors of Variables ). When you use ‘ += ’ on a recursively-expanded variable, it is this unexpanded text to which make appends the new text you specify.
is roughly equivalent to:
except that of course it never defines a variable called temp . The importance of this comes when the variable’s old value contains variable references. Take this common example:
The first line defines the CFLAGS variable with a reference to another variable, includes . ( CFLAGS is used by the rules for C compilation; see Catalogue of Built-In Rules .) Using ‘ = ’ for the definition makes CFLAGS a recursively-expanded variable, meaning ‘ $(includes) -O ’ is not expanded when make processes the definition of CFLAGS . Thus, includes need not be defined yet for its value to take effect. It only has to be defined before any reference to CFLAGS . If we tried to append to the value of CFLAGS without using ‘ += ’, we might do it like this:
This is pretty close, but not quite what we want. Using ‘ := ’ redefines CFLAGS as a simply-expanded variable; this means make expands the text ‘ $(CFLAGS) -pg ’ before setting the variable. If includes is not yet defined, we get ‘ -O -pg ’ , and a later definition of includes will have no effect. Conversely, by using ‘ += ’ we set CFLAGS to the unexpanded value ‘ $(includes) -O -pg ’ . Thus we preserve the reference to includes , so if that variable gets defined at any later point, a reference like ‘ $(CFLAGS) ’ still uses its value.
Next: Multi-Line , Previous: Appending , Up: Using Variables [ Contents ][ Index ]
6.7 The override Directive
If a variable has been set with a command argument (see Overriding Variables ), then ordinary assignments in the makefile are ignored. If you want to set the variable in the makefile even though it was set with a command argument, you can use an override directive, which is a line that looks like this:
To append more text to a variable defined on the command line, use:
See Appending More Text to Variables .
Variable assignments marked with the override flag have a higher priority than all other assignments, except another override . Subsequent assignments or appends to this variable which are not marked override will be ignored.
The override directive was not invented for escalation in the war between makefiles and command arguments. It was invented so you can alter and add to values that the user specifies with command arguments.
For example, suppose you always want the ‘ -g ’ switch when you run the C compiler, but you would like to allow the user to specify the other switches with a command argument just as usual. You could use this override directive:
You can also use override directives with define directives. This is done as you might expect:
See Defining Multi-Line Variables .
Next: Undefine Directive , Previous: Override Directive , Up: Using Variables [ Contents ][ Index ]
6.8 Defining Multi-Line Variables
Another way to set the value of a variable is to use the define directive. This directive has an unusual syntax which allows newline characters to be included in the value, which is convenient for defining both canned sequences of commands (see Defining Canned Recipes ), and also sections of makefile syntax to use with eval (see Eval Function ).
The define directive is followed on the same line by the name of the variable being defined and an (optional) assignment operator, and nothing more. The value to give the variable appears on the following lines. The end of the value is marked by a line containing just the word endef .
Aside from this difference in syntax, define works just like any other variable definition. The variable name may contain function and variable references, which are expanded when the directive is read to find the actual variable name to use.
The final newline before the endef is not included in the value; if you want your value to contain a trailing newline you must include a blank line. For example in order to define a variable that contains a newline character you must use two empty lines, not one:
You may omit the variable assignment operator if you prefer. If omitted, make assumes it to be ‘ = ’ and creates a recursively-expanded variable (see The Two Flavors of Variables ). When using a ‘ += ’ operator, the value is appended to the previous value as with any other append operation: with a single space separating the old and new values.
You may nest define directives: make will keep track of nested directives and report an error if they are not all properly closed with endef . Note that lines beginning with the recipe prefix character are considered part of a recipe, so any define or endef strings appearing on such a line will not be considered make directives.
When used in a recipe, the previous example is functionally equivalent to this:
since two commands separated by semicolon behave much like two separate shell commands. However, note that using two separate lines means make will invoke the shell twice, running an independent sub-shell for each line. See Recipe Execution .
If you want variable definitions made with define to take precedence over command-line variable definitions, you can use the override directive together with define :
See The override Directive .
Next: Environment , Previous: Multi-Line , Up: Using Variables [ Contents ][ Index ]
6.9 Undefining Variables
If you want to clear a variable, setting its value to empty is usually sufficient. Expanding such a variable will yield the same result (empty string) regardless of whether it was set or not. However, if you are using the flavor (see Flavor Function ) and origin (see Origin Function ) functions, there is a difference between a variable that was never set and a variable with an empty value. In such situations you may want to use the undefine directive to make a variable appear as if it was never set. For example:
This example will print “undefined” for both variables.
If you want to undefine a command-line variable definition, you can use the override directive together with undefine , similar to how this is done for variable definitions:
Next: Target-specific , Previous: Undefine Directive , Up: Using Variables [ Contents ][ Index ]
6.10 Variables from the Environment
Variables in make can come from the environment in which make is run. Every environment variable that make sees when it starts up is transformed into a make variable with the same name and value. However, an explicit assignment in the makefile, or with a command argument, overrides the environment. (If the ‘ -e ’ flag is specified, then values from the environment override assignments in the makefile. See Summary of Options . But this is not recommended practice.)
Thus, by setting the variable CFLAGS in your environment, you can cause all C compilations in most makefiles to use the compiler switches you prefer. This is safe for variables with standard or conventional meanings because you know that no makefile will use them for other things. (Note this is not totally reliable; some makefiles set CFLAGS explicitly and therefore are not affected by the value in the environment.)
When make runs a recipe, variables defined in the makefile are placed into the environment of each shell. This allows you to pass values to sub- make invocations (see Recursive Use of make ). By default, only variables that came from the environment or the command line are passed to recursive invocations. You can use the export directive to pass other variables. See Communicating Variables to a Sub- make , for full details.
Other use of variables from the environment is not recommended. It is not wise for makefiles to depend for their functioning on environment variables set up outside their control, since this would cause different users to get different results from the same makefile. This is against the whole purpose of most makefiles.
Such problems would be especially likely with the variable SHELL , which is normally present in the environment to specify the user’s choice of interactive shell. It would be very undesirable for this choice to affect make ; so, make handles the SHELL environment variable in a special way; see Choosing the Shell .
Next: Pattern-specific , Previous: Environment , Up: Using Variables [ Contents ][ Index ]
6.11 Target-specific Variable Values
Variable values in make are usually global; that is, they are the same regardless of where they are evaluated (unless they’re reset, of course). One exception to that is automatic variables (see Automatic Variables ).
The other exception is target-specific variable values . This feature allows you to define different values for the same variable, based on the target that make is currently building. As with automatic variables, these values are only available within the context of a target’s recipe (and in other target-specific assignments).
Set a target-specific variable value like this:
Target-specific variable assignments can be prefixed with any or all of the special keywords export , override , or private ; these apply their normal behavior to this instance of the variable only.
Multiple target values create a target-specific variable value for each member of the target list individually.
The variable-assignment can be any valid form of assignment; recursive (‘ = ’), simple (‘ := ’ or ‘ ::= ’), appending (‘ += ’), or conditional (‘ ?= ’). All variables that appear within the variable-assignment are evaluated within the context of the target: thus, any previously-defined target-specific variable values will be in effect. Note that this variable is actually distinct from any “global” value: the two variables do not have to have the same flavor (recursive vs. simple).
Target-specific variables have the same priority as any other makefile variable. Variables provided on the command line (and in the environment if the ‘ -e ’ option is in force) will take precedence. Specifying the override directive will allow the target-specific variable value to be preferred.
There is one more special feature of target-specific variables: when you define a target-specific variable that variable value is also in effect for all prerequisites of this target, and all their prerequisites, etc. (unless those prerequisites override that variable with their own target-specific variable value). So, for example, a statement like this:
will set CFLAGS to ‘ -g ’ in the recipe for prog , but it will also set CFLAGS to ‘ -g ’ in the recipes that create prog.o , foo.o , and bar.o , and any recipes which create their prerequisites.
Be aware that a given prerequisite will only be built once per invocation of make, at most. If the same file is a prerequisite of multiple targets, and each of those targets has a different value for the same target-specific variable, then the first target to be built will cause that prerequisite to be built and the prerequisite will inherit the target-specific value from the first target. It will ignore the target-specific values from any other targets.
Next: Suppressing Inheritance , Previous: Target-specific , Up: Using Variables [ Contents ][ Index ]
6.12 Pattern-specific Variable Values
In addition to target-specific variable values (see Target-specific Variable Values ), GNU make supports pattern-specific variable values. In this form, the variable is defined for any target that matches the pattern specified.
Set a pattern-specific variable value like this:
where pattern is a %-pattern. As with target-specific variable values, multiple pattern values create a pattern-specific variable value for each pattern individually. The variable-assignment can be any valid form of assignment. Any command line variable setting will take precedence, unless override is specified.
For example:
will assign CFLAGS the value of ‘ -O ’ for all targets matching the pattern %.o .
If a target matches more than one pattern, the matching pattern-specific variables with longer stems are interpreted first. This results in more specific variables taking precedence over the more generic ones, for example:
In this example the first definition of the CFLAGS variable will be used to update lib/bar.o even though the second one also applies to this target. Pattern-specific variables which result in the same stem length are considered in the order in which they were defined in the makefile.
Pattern-specific variables are searched after any target-specific variables defined explicitly for that target, and before target-specific variables defined for the parent target.
Next: Special Variables , Previous: Pattern-specific , Up: Using Variables [ Contents ][ Index ]
6.13 Suppressing Inheritance
As described in previous sections, make variables are inherited by prerequisites. This capability allows you to modify the behavior of a prerequisite based on which targets caused it to be rebuilt. For example, you might set a target-specific variable on a debug target, then running ‘ make debug ’ will cause that variable to be inherited by all prerequisites of debug , while just running ‘ make all ’ (for example) would not have that assignment.
Sometimes, however, you may not want a variable to be inherited. For these situations, make provides the private modifier. Although this modifier can be used with any variable assignment, it makes the most sense with target- and pattern-specific variables. Any variable marked private will be visible to its local target but will not be inherited by prerequisites of that target. A global variable marked private will be visible in the global scope but will not be inherited by any target, and hence will not be visible in any recipe.
As an example, consider this makefile:
Due to the private modifier, a.o and b.o will not inherit the EXTRA_CFLAGS variable assignment from the prog target.
Previous: Suppressing Inheritance , Up: Using Variables [ Contents ][ Index ]
6.14 Other Special Variables
GNU make supports some variables that have special properties.
Contains the name of each makefile that is parsed by make , in the order in which it was parsed. The name is appended just before make begins to parse the makefile. Thus, if the first thing a makefile does is examine the last word in this variable, it will be the name of the current makefile. Once the current makefile has used include , however, the last word will be the just-included makefile.
If a makefile named Makefile has this content:
then you would expect to see this output:
Sets the default goal to be used if no targets were specified on the command line (see Arguments to Specify the Goals ). The .DEFAULT_GOAL variable allows you to discover the current default goal, restart the default goal selection algorithm by clearing its value, or to explicitly set the default goal. The following example illustrates these cases:
This makefile prints:
Note that assigning more than one target name to .DEFAULT_GOAL is invalid and will result in an error.
This variable is set only if this instance of make has restarted (see How Makefiles Are Remade ): it will contain the number of times this instance has restarted. Note this is not the same as recursion (counted by the MAKELEVEL variable). You should not set, modify, or export this variable.
When make starts it will check whether stdout and stderr will show their output on a terminal. If so, it will set MAKE_TERMOUT and MAKE_TERMERR , respectively, to the name of the terminal device (or true if this cannot be determined). If set these variables will be marked for export. These variables will not be changed by make and they will not be modified if already set.
These values can be used (particularly in combination with output synchronization (see Output During Parallel Execution ) to determine whether make itself is writing to a terminal; they can be tested to decide whether to force recipe commands to generate colorized output for example.
If you invoke a sub- make and redirect its stdout or stderr it is your responsibility to reset or unexport these variables as well, if your makefiles rely on them.
The first character of the value of this variable is used as the character make assumes is introducing a recipe line. If the variable is empty (as it is by default) that character is the standard tab character. For example, this is a valid makefile:
The value of .RECIPEPREFIX can be changed multiple times; once set it stays in effect for all rules parsed until it is modified.
Expands to a list of the names of all global variables defined so far. This includes variables which have empty values, as well as built-in variables (see Variables Used by Implicit Rules ), but does not include any variables which are only defined in a target-specific context. Note that any value you assign to this variable will be ignored; it will always return its special value.
Expands to a list of special features supported by this version of make . Possible values include, but are not limited to:
Supports ar (archive) files using special file name syntax. See Using make to Update Archive Files .
Supports the -L ( --check-symlink-times ) flag. See Summary of Options .
Supports “else if” non-nested conditionals. See Syntax of Conditionals .
Supports “job server” enhanced parallel builds. See Parallel Execution .
Supports the .ONESHELL special target. See Using One Shell .
Supports order-only prerequisites. See Types of Prerequisites .
Supports secondary expansion of prerequisite lists.
Uses the “shortest stem” method of choosing which pattern, of multiple applicable options, will be used. See How Patterns Match .
Supports target-specific and pattern-specific variable assignments. See Target-specific Variable Values .
Supports the undefine directive. See Undefine Directive .
Has GNU Guile available as an embedded extension language. See GNU Guile Integration .
Supports dynamically loadable objects for creating custom extensions. See Loading Dynamic Objects .
Expands to a list of directories that make searches for included makefiles (see Including Other Makefiles ).
Each word in this variable is a new prerequisite which is added to targets for which it is set. These prerequisites differ from normal prerequisites in that they do not appear in any of the automatic variables (see Automatic Variables ). This allows prerequisites to be defined which do not impact the recipe.
Consider a rule to link a program:
Now suppose you want to enhance this makefile to ensure that updates to the compiler cause the program to be re-linked. You can add the compiler as a prerequisite, but you must ensure that it’s not passed as an argument to link command. You’ll need something like this:
Then consider having multiple extra prerequisites: they would all have to be filtered out. Using .EXTRA_PREREQS and target-specific variables provides a simpler solution:
This feature can also be useful if you want to add prerequisites to a makefile you cannot easily modify: you can create a new file such as extra.mk :
then invoke make -f extra.mk -f Makefile .
Setting .EXTRA_PREREQS globally will cause those prerequisites to be added to all targets (which did not themselves override it with a target-specific value). Note make is smart enough not to add a prerequisite listed in .EXTRA_PREREQS as a prerequisite to itself.
Next: Conditional Parts of Makefiles , Previous: Writing Recipes in Rules , Up: GNU make [ Contents ][ Index ]
6 How to Use Variables
A variable is a name defined in a makefile to represent a string of text, called the variable’s value . These values are substituted by explicit request into targets, prerequisites, recipes, and other parts of the makefile. (In some other versions of make , variables are called macros .)
Variables and functions in all parts of a makefile are expanded when read, except for in recipes, the right-hand sides of variable definitions using ‘ = ’, and the bodies of variable definitions using the define directive. The value a variable expands to is that of its most recent definition at the time of expansion. In other words, variables are dynamically scoped.
Variables can represent lists of file names, options to pass to compilers, programs to run, directories to look in for source files, directories to write output in, or anything else you can imagine.
A variable name may be any sequence of characters not containing ‘ : ’, ‘ # ’, ‘ = ’, or whitespace. However, variable names containing characters other than letters, numbers, and underscores should be considered carefully, as in some shells they cannot be passed through the environment to a sub- make (see Communicating Variables to a Sub- make ). Variable names beginning with ‘ . ’ and an uppercase letter may be given special meaning in future versions of make .
Variable names are case-sensitive. The names ‘ foo ’, ‘ FOO ’, and ‘ Foo ’ all refer to different variables.
It is traditional to use upper case letters in variable names, but we recommend using lower case letters for variable names that serve internal purposes in the makefile, and reserving upper case for parameters that control implicit rules or for parameters that the user should override with command options (see Overriding Variables ).
A few variables have names that are a single punctuation character or just a few characters. These are the automatic variables , and they have particular specialized uses. See Automatic Variables .
- Basics of Variable References
- The Two Flavors of Variables
- Advanced Features for Reference to Variables
- How Variables Get Their Values
- Setting Variables
- Appending More Text to Variables
- The override Directive
- Defining Multi-Line Variables
- Undefining Variables
- Variables from the Environment
- Target-specific Variable Values
- Pattern-specific Variable Values
- Suppressing Inheritance
- Other Special Variables

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Makefiles are used to help decide which parts of a large program need to be recompiled. In the vast majority of cases, C or C++ files are compiled. Other languages typically have their own tools that serve a similar purpose as Make.
To set a variable from the makefile, write a line starting with the variable name followed by one of the assignment operators ‘=’, ‘:=’, ‘::=’, or ‘:::=’. Whatever follows the operator and any initial …
The shell assignment operator ‘!=’ can be used to execute a shell script and set a >variable to its output. This operator first evaluates the right-hand side, then passes >that result to the shell for …
You can specify a value in the makefile, either with an assignment (see Setting Variables) or with a verbatim definition (see Defining Multi-Line Variables). Variables in the environment become …
This appendix summarizes the directives, text manipulation functions, and special variables which GNU make understands. See Special Built-in Target Names, Catalogue of Built-In Rules, and …
A variable is a name defined in a makefile to represent a string of text, called the variable’s value. These values are substituted by explicit request into targets, prerequisites, recipes, and other …